Abstract
Toxin-antitoxin (TA) modules are bacterial regulatory switches that facilitate conflicting outcomes for cells by promoting a pro-survival phenotypic adaptation and/or by directly mediating cell death, all through the toxin activity upon degradation of antitoxin. Intensive study has revealed specific details of TA module functions, but significant gaps remain about the molecular details of activation via antitoxin degradation used by different bacteria and in different environments. This review summarizes the current state of knowledge about the interaction of antitoxins with cellular proteases Lon and ClpP to mediate TA module activation. An understanding of these processes can answer long-standing questions regarding stochastic versus specific activation of TA modules and provide insight into the potential for manipulation of TA modules to alter bacterial growth.
1. Introduction
Bacteria undergo complex adaptive metabolic changes to promote survival under stressful or harsh conditions. Toxin-antitoxin (TA) modules play crucial roles in bacterial immunity and in adaptation to the environment [1,2,3]. There is a growing interest in co-opting TA modules to control bacterial growth, but significant questions remain concerning the mechanisms of antitoxin degradation, which is required to promote adaptive changes [4,5,6]. Current estimates put the occurrence of TA modules at greater than 10,000 loci, a testament to the widespread nature of these genetic units [7,8,9]. There is also a striking overlap between the pathways inhibited by the toxin components and many essential cellular functions that comprise current antibiotic targets [9,10,11,12,13].
TA modules have been the topic of several excellent recent reviews, and these provide a historical background for the discovery and functions of TA modules, as well as highlighting the potential involvement of TA modules in bacterial persistence and chronic infections [5,14,15,16,17]. The review by Page et al. summarizes the mechanism used for control of TA module transcription called conditional cooperativity, as was previously elaborated by Loris et al. and others [15,18]. In this mechanism, altering the relative stoichiometry of toxin to antitoxin molecules dictates the level of transcriptional repression mediated by the antitoxin, as demonstrated for the TA families Doc/PhD, CcdAB, ParDE, RelBE, Kid/Kis, VapBC [15]. The review by Chan et al. details the DNA-binding activity of antitoxins used for transcriptional repression, and different DNA-binding motifs within the same TA family serve to further sub-divide the system classifications [14]. Finally, the review by Woods outlined the known signaling pathways leading to TA module activation and current efforts to combat the resulting phenotypic persistence in E. coli [5]. The current review will build from these recent publications and focus on the limited knowledge for specific molecular details of degradation of the antitoxin component by cellular proteases, resulting in TA module activation.
2. Activation and Phenotypic Outcomes of TA Modules
Canonical TA modules encode a bacterial poison (toxin) and a more labile antidote (antitoxin); cellular homeostasis is maintained only with replenishing supplies of antitoxin. The antitoxins from Type II TA modules are proteins that are degraded by cytoplasmic proteases, particularly the Lon protease [6,8,19]. In TA modules, the antitoxin typically mediates transcriptional self-repression by binding to an operator in the promoter region of its own operon. Degradation of the antitoxin relieves this transcriptional repression and results in increasing the production of the dicistronic transcript for antitoxin and toxin. Depletion of antitoxin, which is only known to occur by proteolytic degradation, lowers the ratio of antitoxin to toxin thereby altering the stoichiometry of TA complexes and resulting in conditional cooperativity [15,18]. Therefore, the degradation of antitoxin is the determining factor for TA module effects on the cell.
The toxin proteins, which can be classified by their shared cellular targets, affect many different and physiologically essential pathways. Some toxins, such as the RelE and VapC families, inhibit translation by degrading RNA, while other families target cellular replication or membrane integrity [1,20]. Among the most paradoxical aspects of TA modules is the broad conservation of structure despite disparate sequences and without correlation to the targeted cellular pathways [21]. This is exemplified by high structural similarity between the ParE gyrase-inhibiting toxins and the RelE mRNA-degrading toxins [22,23,24,25]. Additional modularity exists between toxin families and antitoxin families, resulting in frequent interchange of module components [1,24].
TA pairs are frequently found on pathogenicity islands or on exogenous plasmids harboring multi-drug resistance cassettes [26,27,28]. While plasmid-borne TA modules were initially discovered due to their activity in mediating post-segregational killing, chromosomal TA modules appear to be highly redundant and implicated in physiological adaptation responses [29,30]. The outcomes of TA module activation are varied, even within the same toxin family, with reports of some modules promoting bacterial cell death [31,32,33], particularly in a plasmid segregation model [34,35,36,37,38,39,40], and others strongly implicated in promoting survival through the formation of biofilms and persister populations, which are highly resistant to antibiotics [41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49]. Thus, the roles of TA modules within infectious etiology can be positive, resulting in death of the bacterial cell or loss of genetic material, or negative by resulting in increased resistance to therapeutics [50,51].
The formation of antibiotic tolerant cells, including dormant or persister cells, has a dependence on TA modules presumably due to their ability to mediate reduced metabolic turnover [13,41,52,53,54,55,56]. The resulting dormant state is a heterogeneous population of phenotypically resistant cells [5,15,57,58]. Ectopic over-expression of RNA-degrading toxins, including RelE and MazF, can directly trigger the phenotypic changes resulting in persister cell formation [12,30,50,54,59,60,61]. It is still debated if a specific switch exists to activate given TA modules, or if the emergence of sub-populations results from stochastic selection of a pre-existing population with activated TA modules, or even if these models are conserved for all TA modules or are mutually exclusive (Figure 1) [30,41,45,46,47,62,63,64,65].

Figure 1.
TA (Toxin-antitoxin) modules have been implicated in multiple models of bacterial physiology. Some pathways result in pro-survival changes, such as persister formation, or by selection of a stochastic population. Other changes result in cell death, consistent with the role of TA modules in the retention of genetic material. The toxin dose, or length of exposure, may also contribute to observed physiological changes.
Populations of bacterial persisters have been characterized and recent work has found a direct link between the SOS and stringent response pathway leading to an up-regulation of polyphosphates through the Obg GTPase, and resulting in activation of TA modules in a protease-dependent manner [62,66,67]. In general, dormant persister populations present major impediments to the current antibiotic arsenal [36,68,69], and efforts are being made to re-awaken persisters with extrinsic signaling molecules [5,70] or to prevent their formation by blocking extracellular communication [71].
Because degradation of the antitoxin relieves transcriptional repression by shifting the ratio of antitoxin to toxin (Figure 2), activation of TA modules can be measured by monitoring mRNA levels. This effect can be mimicked by inhibition of protein translation, which would prevent replenishment of antitoxin in response to basal turnover levels. Further, a decrease in mRNA level indicates a shift in the ratio of antitoxin to toxin (Figure 2). Any regulation of antitoxin degradation remains unknown, but one possible mechanism is by up-regulation of protease levels, such as noted for Lon during heat stress [72,73,74,75]. Several studies have demonstrated the up-regulation of TA modules under antibiotic or starvation conditions [76,77,78,79]. To analyze the expression levels of TA genes and the proteases Lon and ClpP under various antibiotic and stress conditions, RNA-Seq data files were downloaded from the NCBI database and analyzed according to published protocols, with results shown in Table 1 [80].

Figure 2.
Activation of TA modules requires removal of antitoxin (red, magenta) from toxin (blue, green) by cellular proteases, and the stoichiometry of these two components control transcriptional repression through conditional cooperativity. (A) Normal cell growth typically has an excess of antitoxin modules, wherein transcription of the TA operon is repressed; (B) a TA module is activated both for transcription and for toxin activity in the cell by degradation of the antitoxin, shifting the stoichiometry to an excess of toxin molecules. It is not clear if degradation of TA complexes takes place directly from the DNA bound state, within the cytosol, or both. (Inset) The protease must be able to access the antitoxin, generally from the C-terminus, thereby removing it by overcoming typically very strong interactions with toxin.

Table 1.
Transcript levels of TA (Toxin-antitoxin) modules in E. coli are altered in response to different treatment conditions.
Within these data sets (Table 1), the rnlBA module was highly up-regulated in starvation conditions, as was yafO-yafN, mqsAR, hicBA and the yafQ and cbtA toxins. The up-regulation of a toxin gene without a similar up-regulation in antitoxin is surprising, and was also observed for the mazF, yafQ and yoeB toxins during heat shock treatment, while the antitoxin rnlB was highly increased relative to its toxin. In Enterococcus species, an increase in transcript levels of toxin mRNA levels (relB, mazF, and higB) during heat stress was noted while antitoxin transcripts remained constant [83], as also found for mazF and relE during heat shock conditions for strains of E. coli [84]. We surmise that these mRNAs may be enriched in sequences that are targeted for degradation, perhaps by up-regulated RNase toxins. In general, yafO-yafN, yafQ-dinJ and yhaV-prlF were the most up-regulated across these treatment conditions, wherein heat stress triggered an increase in RNA degrading toxins (mazF, relE, yafQ, yafO, yoeB, refer to Table 1). The only TA module transcripts observed to decrease in amounts were the chpBS and fic-yhfG during starvation and heat shock treatments. Other TA modules exhibited modest changes in transcript level, particularly during the ampicillin- and tetracycline-adapted treatments. Interestingly, the hipBA locus was not identified as up-regulated in any of these treatments.
The rifampicin treatment produced the largest responses of TA modules of any examined, which is contradictory as the treatment inhibits RNA polymerase. However, we note that the treatment was minimal, lasting only for 30 s prior to extraction. Further, strong upregulation of the lon protease gene was observed in these cells, and when translated to a protein product this could mediate efficient degradation of antitoxins. It is noteworthy that in this condition, up-regulation of lon levels was not sufficient to mediate degradation of antitoxins from the cbtA-cbeA, fic-yhfG, higBA, hipBA, and mazEF modules. Other than the rifampicin treatment, the increases in TA module transcripts arise due to degradation of the antitoxin without an increase in lon or clpP protease levels. Instead, it is more likely that the proteases have an increased enzymatic activity or a specific factor such as an adaptor is produced, as discussed below.
3. Proteases Shape the TA Module Proteome
TA modules affect cellular physiology following degradation of the antitoxin partner, thus freeing the active toxin component to interact with cellular pathways. Antitoxins are known to have very short half-lives of typically less than 15–20 min, while in E. coli, ~75% of the proteome has a half-life of 25 h [85,86]. The controlled half-life is mediated by cellular protease networks that recognize loosely structured C-terminal domains of the antitoxins [14,15,18]. This is an interesting paradigm in antitoxin activity, as the C-terminal domain interacts with the toxin partner frequently with a picomolar affinity, yet intrinsically disordered C-terminal free ends apparently can still be accessed for degradation (Figure 2) [87].
ATP-dependent proteases have been identified as mediators of this degradation in many situations, including the Lon (La) protease and the caseinolytic or caspase-3 like protease ClpP (see Table 2 and reviewed in [6,8,19,88,89,90]). Within the cellular environment, these ATP-dependent proteases act as regulators of protein quality control and can re-shape the proteome to mediate general adaptation responses [90,91,92], to DNA damage and metal exposure [93], to temperature changes [85,94] and for degradation of misfolded or aggregated proteins to promote optimal survival chances [95].

Table 2.
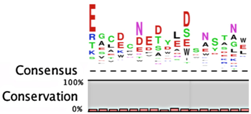
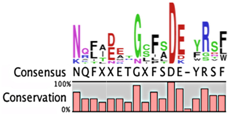
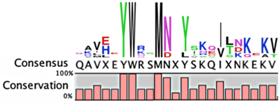
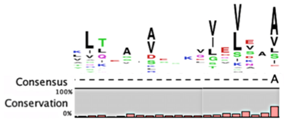
Prevalence of different antitoxin families, proteases identified as mediating degradation, and C-terminal sequence conservation of antitoxin families.
The Lon protease is found in all domains of life and has been described as having a “pivotal role in physiology” [85], although it is lacking in some Gram-positive bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus [96,97]. When present, Lon carries out the housekeeping functions in bacterial cells [88], with estimates of it carrying out ~50% of E. coli protein energy-dependent protein degradation [85]. Other studies with ClpP and its associated ATPase domain ClpX indicate the degradation up to 25% of the stress-induced SOS proteome, used as a means to turn off the SOS response [95].
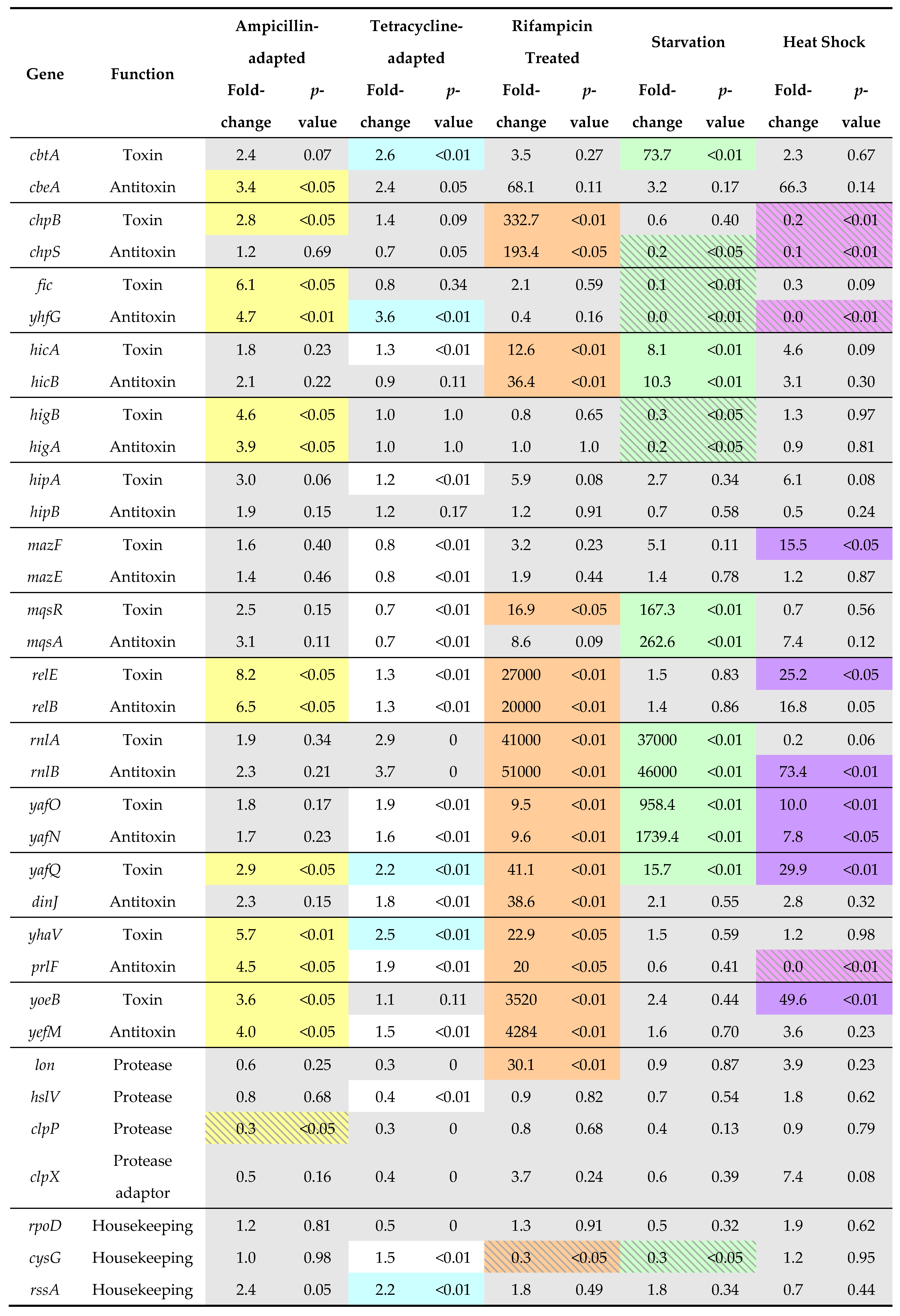
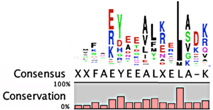
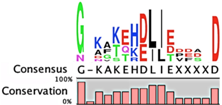
The degradation signals for antitoxins or substrate specificities for proteases remain largely undefined. Advances in proteomic approaches have highlighted, in general, the context sensitivity and broad overlap of protease pathways [92]. In the simplest form, and seemingly the most likely to be used for antitoxins, are the preference of Lon for exposed hydrophobic patches [85,98,99] and for ClpXP, two C-terminal alanine residues [100]. Antitoxin sequences from the Toxin-Antitoxin DataBase (TADB) [101] were aligned and assessed in efforts to identify conserved potential protease “degrons” (Table 2). While the analysis was limited to the C-terminal portion, overall no significant consensus was observed outside of a series of small hydrophobic residues for the HicB antitoxin. The PhD antitoxin family has some conservation of hydrophobic residues in this region, which is interspersed with acidic residues. Similarly, the YefM antitoxin is enriched in acidic residues at its C-termini. The lack of conservation in sequences, even in patterns of hydrophobicity, is striking, particularly for families with many members, such as the RelB/DinJ antitoxins. The Epsilon antitoxin was degraded ~20 amino acids upstream of the C-terminus [102], which for most antitoxins would overlap with their toxin binding sites. It would seem that toxin binding would then hinder protease-mediated degradation, as was noted for the CcdA antitoxin [103].
Both Lon and Clp ATPases can recognize overlapping sequences present at the either termini of a client protein but with a commonality of being relatively unstructured, as is the case for at least some antitoxin proteins [15,18,125]. Further, recent studies have validated protease substrate “queuing”, where multiple client proteins can compete for degradation by Lon or ClpP, and the efficiency of degradation is then dictated by both relative affinity and concentrations [126]. The Lon and ClpP proteases have a common domain structure, with a typical ring-shaped oligomer contributing the protease domain and an additional ATPase domain in Lon or an associated protein with ClpP. For ClpP, this permits a modular function by pairing different Clp ATPase rings with the ClpP protease [127,128]. Both Lon and Clp systems undergo conformational changes that move loops found at the opening of the central pore in response to ATP hydrolysis and ADP release. These loops are typically lined with hydrophobic and especially aromatic ring-containing residues that result in a “pumping” action to unfold the client protein substrate and feed it into the associated protease chamber [127,128]. It is not clear if antitoxins are unfolded as part of their degradation, and this unfolded state would require the removal of the tightly bound toxin molecule.
The oligomeric state of the proteases affects its ability to degrade small or partially folded protein domains. Lon has been identified to form a concentration-dependent dodecamer (a dimer of hexamers) with a large central chamber that could accommodate small clients with residual secondary structure [129,130], such as perhaps an antitoxin molecule. Similarly, the central pore of ClpP is opened significantly when it associates with an ATPase oligomer [131]. Acyldepsipeptides (ADEPs), produced by Streptomyces species, can induce an opening of the central pore without an ATPase partner, resulting in constitutive activation and allowing the protease activity to access partially folded protein domains [132,133,134]. It is possible that ADEP’s are able to effectively eradicate persister cells [132,135], in part, by non-specific degradation of antitoxin molecules.
Of note, many antitoxins are no longer degraded when the gene for E. coli Lon or ClpP protease or S. aureus ClpP protease is deleted from the genome (Table 2). Antitoxins that have been identified as Lon substrates under different experimental conditions include PenI and PasA from low copy number plasmids and chromosomal E. coli RelB, ChpB, HicB and MazE during amino acid starvation (Table 2) [111,118,136,137,138]. The direct recognition and active unfolding of antitoxin molecules has not been demonstrated in vivo, and it remains unknown if the antitoxin can be degraded in the absence of unfolding. It is also unclear if the protease used for basal turnover during the “inactivated” state is the same as the one used for activation upon stress induction. Further, studies using in vivo protease deletion strains frequently result in reduction but not complete loss of antitoxin degradation, and in vitro assays with purified components are inherently slower (Table 2 and references therein). These data imply that the degradation pathway is more complex than simple association with Lon protease, and current models cannot capture the specificity measured for antitoxin activation under different adaptation conditions (for example, see Table 1).
What is clear is that not all TA modules are activated at the same time (for example, see Table 1). A stochastic mechanism would still require interaction of antitoxin with protease, but in an unregulated or “stochastic” way. This could give rise to specific TA module activation by selection during a stress, presumably based upon a positive effect mediated by the freed toxin. Another model is that sub-sets of antitoxins are specifically targeted in response to a stress, requiring controlled mechanisms for the protease and antitoxin interaction. Regardless of the activation model, it is feasible that the specificity of interactions between antitoxins and protease(s) are influenced by specific cellular conditions, including stressors [139], cell density [140], and protease concentration, particularly as induced by a heat shock condition [72,85,88,105,141,142]. Unfolded proteins allosterically activate the Mg2+ dependent Lon protease, during heat stress [99,131]. Its activity is also modulated by DNA binding and through interaction with polyphosphates, as produced during stringent response to amino acid starvation [143,144,145,146]. However, other studies have found no role for polyphosphates in Lon activation or in leading to a persistent phenotype in response to aminoglycosides [5,147,148]. Additionally, the antitoxin prlF was noted to have an activating effect on Lon via unknown mechanisms [149,150].
The degradation potential of antitoxins may also be impacted by the availability of adaptor proteins. The adaptor TrfA functions in the Gram-positive bacterium, S. aureus, which lacks a Lon protease, to deliver each of the three antitoxins (Axe1, Axe2 and a MazE) to the ClpCP complex [96,97]. Similarly, in Caulobacter crescentus the antitoxin SocA acts as an adaptor required for proteolytic degradation of toxin SocB [151]. This creates an inverted mechanism for the TA module and imparts a requirement of both the antitoxin and the ClpXP protease for growth of the organism. A related variation is a tripartite toxin-antitoxin-chaperone (TAC) module identified in Mycobacterium tuberculosis and encoding a SecB-like protein at the start of a HigBA operon. The SecB chaperone was demonstrated to protect the antitoxin HigA from aggregation and in so doing to facilitate its interaction with the HigB toxin [152,153]. While no adaptors have been identified for the Lon protease, there is no a priori reason to expect there are none [142]. A newly identified TA module, named GraTA, is degraded by a unique yet unidentified ATP-independent protease, and this module has also recently been demonstrated to target ribosome biogenesis in a unique mechanism [154,155]. This was the first report of antitoxin degradation independent of Lon or ClpP.
Within protease systems it is clear that one protein client can be a substrate for multiple proteases [100,156]. For example, in E. coli the MazE antitoxin is degraded by ClpAP in normal growth conditions [111] but becomes a substrate for Lon during amino acid starvation [142,157]. Similarly, the antitoxin DinJ is stabilized in E. coli by the absence of either Lon or ClpXP [108]. While ectopic expression of the Lon protease identifies its ability to degrade many antitoxins, caution is warranted because the cellular context is not retained in these experiments [92]. However, overexpression of Lon protease in E. coli did not result in RelB or MazE antitoxin degradation, despite RelB being a known target for Lon protease [107], while the YefM antitoxin was very efficiently degraded [106,142]. Later studies found that YefM was efficiently degraded by heat shock treatment, and the stress factor rpoH played a role in sustained activation [105]. The stoichiometry of the toxin-antitoxin complex can further complicate this type of degradation kinetics, as the complex may alter the protease-antitoxin interaction. Given the cooperative control in TA modules, the availability of antitoxin for degradation is another important factor in the activation pathway.
4. Conclusions
There is a strong connection linking TA module activation to reports of protease involvement in the paradoxical survival of cells upon treatment with antibiotics, such as DNA damaging quinolones in E. coli and P. aeruginosa [158,159]. Treatment with this class of antibiotics is known to induce an SOS response which up-regulates Lon expression, potentially permitting survival with the aid of TA module activation. An important question for future studies is: does the disordered structure, or specific sequences in the antitoxin, determine the course of degradation, or, does the cell control this by changing expression or allosteric activation of proteases? Based on information in Table 1, only some TA modules are activated under a given stress while in Table 2, it seems that given antitoxin classes do not possess an intrinsic identification sequence or degron. The activation of TA modules has been proposed as a promising new method to control bacterial growth [3,4,6,10,43,77,160,161,162]. Advances in antibacterial developments by taking advantage of these potential weak points in bacterial physiology can be realized as this antitoxin-protease networked response is delineated.
Acknowledgments
The Bourne lab is supported by an Institutional Development Award (IDeA) from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health, grant number P20GM10364, and the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Oklahoma. We are grateful to Peter Klein and Fares Najar for assistance with RNAseq data analysis.
Author Contributions
M.M., J.C.W. and C.R.B. conceived the paper; M.M. performed data analysis; and M.M., J.C.W. and C.R.B. prepared the figures and tables, and wrote the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Makarova, K.S.; Wolf, Y.I.; Koonin, E.V. Comparative genomics of defense systems in archaea and bacteria. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 4360–4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Melderen, L.; Saavedra de Bast, M. Bacterial toxin-antitoxin systems: More than selfish entities? PLoS Genet. 2009, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Park, J.H.; Inouye, M. Toxin-antitoxin systems in bacteria and archaea. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2011, 45, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, W.T.; Balsa, D.; Espinosa, M. One cannot rule them all: Are bacterial toxins-antitoxins druggable? FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 39, 522–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, T.K. Combatting bacterial persister cells. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2016, 113, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, F.; Kedzierska, B. Regulating toxin-antitoxin expression: Controlled detonation of intracellular molecular timebombs. Toxins 2014, 6, 337–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unterholzner, S.J.; Poppenberger, B.; Rozhon, W. Toxin-antitoxin systems: Biology, identification, and application. Mob. Genet. Elem. 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brzozowska, I.; Zielenkiewicz, U. Regulation of toxin-antitoxin systems by proteolysis. Plasmid 2013, 70, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, D.P.; Gerdes, K. Toxin-antitoxin loci are highly abundant in free-living but lost from host-associated prokaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 966–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buts, L.; Lah, J.; Dao-Thi, M.H.; Wyns, L.; Loris, R. Toxin-antitoxin modules as bacterial metabolic stress managers. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2005, 30, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerdes, K.; Christensen, S.K.; Lobner-Olesen, A. Prokaryotic toxin-antitoxin stress response loci. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wood, T.K. Toxin-antitoxin systems influence biofilm and persister cell formation and the general stress response. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 5577–5583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerdes, K.; Maisonneuve, E. Bacterial persistence and toxin-antitoxin loci. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 66, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, W.T.; Espinosa, M.; Yeo, C.C. Keeping the wolves at bay: Antitoxins of prokaryotic type II toxin-antitoxin systems. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2016, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, R.; Peti, W. Toxin-antitoxin systems in bacterial growth arrest and persistence. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocker, A.; Meinhart, A. Type II toxin: Antitoxin systems. More than small selfish entities? Curr. Genet. 2016, 62, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, C.F.; Bertram, R. Toxin-antitoxin systems of Staphylococcus aureus. Toxins 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loris, R.; Garcia-Pino, A. Disorder- and dynamics-based regulatory mechanisms in toxin-antitoxin modules. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 6933–6947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerdes, K. Toxin-antitoxin modules may regulate synthesis of macromolecules during nutritional stress. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarova, K.S.; Wolf, Y.I.; Koonin, E.V. Comprehensive comparative-genomic analysis of type 2 toxin-antitoxin systems and related mobile stress response systems in prokaryotes. Biol. Direct 2009, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasari, V.; Mets, T.; Tenson, T.; Kaldalu, N. Transcriptional cross-activation between toxin-antitoxin systems of Escherichia coli. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boggild, A.; Sofos, N.; Andersen, K.R.; Feddersen, A.; Easter, A.D.; Passmore, L.A.; Brodersen, D.E. The crystal structure of the intact E. coli RelBE toxin-antitoxin complex provides the structural basis for conditional cooperativity. Structure 2012, 20, 1641–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, K.M.; Crosson, S. A conserved mode of protein recognition and binding in a ParD-ParE toxin-antitoxin complex. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 2205–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.J.; Son, W.S.; Lee, B.J. Structural overview of toxin-antitoxin systems in infectious bacteria: A target for developing antimicrobial agents. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1834, 1155–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurley, J.M.; Cruz, J.W.; Ouyang, M.; Woychik, N.A. Bacterial toxin RelE mediates frequent codon-independent mrna cleavage from the 5′ end of coding regions in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 14770–14778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, M.; Austin, S. Prevalence and significance of plasmid maintenance functions in the virulence plasmids of pathogenic bacteria. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 2502–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grady, R.; Hayes, F. Axe-Txe, a broad-spectrum proteic toxin-antitoxin system specified by a multidrug-resistant, clinical isolate of Enterococcus faecium. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 47, 1419–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamada, K.; Hanaoka, F. Conformational change in the catalytic site of the ribonuclease YoeB toxin by YefM antitoxin. Mol. Cell 2005, 19, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertram, R.; Schuster, C.F. Post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression in bacterial pathogens by toxin-antitoxin systems. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2014, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maisonneuve, E.; Shakespeare, L.J.; Jorgensen, M.G.; Gerdes, K. Bacterial persistence by RNA endonucleases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 13206–13211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelberg-Kulka, H.; Amitai, S.; Kolodkin-Gal, I.; Hazan, R. Bacterial programmed cell death and multicellular behavior in bacteria. PLoS Genet. 2006, 2, 1518–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erental, A.; Kalderon, Z.; Saada, A.; Smith, Y.; Engelberg-Kulka, H. Apoptosis-like death, an extreme SOS response in Escherichia coli. mBio 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erental, A.; Sharon, I.; Engelberg-Kulka, H. Two programmed cell death systems in Escherichia coli: An apoptotic-like death is inhibited by the mazEF-mediated death pathway. PLoS Biol. 2012, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, P.; Couturier, M. Cell killing by the F plasmid CcdB protein involves poisoning of DNA-topoisomerase II complexes. J. Mol. Biol. 1992, 226, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, R.B.; Grohmann, E.; Schwab, H.; Diaz-Orejas, R.; Gerdes, K. Comparison of ccd of F, parDE of RP4, and parD of R1 using a novel conditional replication control system of plasmid R1. Mol. Microbiol. 1995, 17, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolodkin-Gal, I.; Verdiger, R.; Shlosberg-Fedida, A.; Engelberg-Kulka, H. A differential effect of E. coli toxin-antitoxin systems on cell death in liquid media and biofilm formation. PLoS ONE 2009, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehnherr, H.; Yarmolinsky, M.B. Addiction protein Phd of plasmid prophage P1 is a substrate of the ClpXP serine protease of Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 3274–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, R.C.; Strom, A.R.; Helinski, D.R. The parDE operon of the broad-host-range plasmid RK2 specifies growth inhibition associated with plasmid loss. J. Mol. Biol. 1994, 237, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.S.; Rawlings, D.E. The poison-antidote stability system of the broad-host-range Thiobacillus ferrooxidans plasmid Ptf-Fc2. Mol. Microbiol. 1997, 26, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Yamaichi, Y.; Waldor, M.K. The three Vibrio cholerae chromosome II-encoded ParE toxins degrade chromosome I following loss of chromosome II. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holden, D.W. Microbiology. Persisters unmasked. Science 2015, 347, 30–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, S.; Benedik, M.J.; Wood, T.K. Orphan toxin OrtT (YdcX) of Escherichia coli reduces growth during the stringent response. Toxins 2015, 7, 299–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keren, I.; Mulcahy, L.R.; Lewis, K. Persister eradication: Lessons from the world of natural products. Methods Enzymol. 2012, 517, 387–406. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.S.; Grigoriu, S.; Page, R.; Peti, W.; Wood, T.K. Escherichia coli toxin/antitoxin pair MqsR/MqsA regulate toxin CspD. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 1105–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maisonneuve, E.; Castro-Camargo, M.; Gerdes, K. (p)ppGpp controls bacterial persistence by stochastic induction of toxin-antitoxin activity. Cell 2013, 154, 1140–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaban, N.Q. Persistence: Mechanisms for triggering and enhancing phenotypic variability. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2011, 21, 768–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaban, N.Q.; Merrin, J.; Chait, R.; Kowalik, L.; Leibler, S. Bacterial persistence as a phenotypic switch. Science 2004, 305, 1622–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasani, R.A.; Savageau, M.A. Molecular mechanisms of multiple toxin-antitoxin systems are coordinated to govern the persister phenotype. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E2528–E2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheverton, A.M.; Gollan, B.; Przydacz, M.; Wong, C.T.; Mylona, A.; Hare, S.A.; Helaine, S. A salmonella toxin promotes persister formation through acetylation of tRNA. Mol. Cell 2016, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Allison, K.R.; Brynildsen, M.P.; Collins, J.J. Heterogeneous bacterial persisters and engineering approaches to eliminate them. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2011, 14, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel, B.; Nair, R.; Bermejo-Rodriguez, C.; Preston, M.A.; Agu, C.A.; Wang, X.; Bernal, J.A.; Sherratt, D.J.; de la Cueva-Mendez, G. Toxin Kid uncouples DNA replication and cell division to enforce retention of plasmid R1 in Escherichia coli cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 2734–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, M.J.; Jakob, U. Oxidative stress protection by polyphosphate-new roles for an old player. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2015, 24C, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kint, C.I.; Verstraeten, N.; Fauvart, M.; Michiels, J. New-found fundamentals of bacterial persistence. Trends Microbiol. 2012, 20, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, K. Persister cells. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 64, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, T.K.; Knabel, S.J.; Kwan, B.W. Bacterial persister cell formation and dormancy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 7116–7121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gefen, O.; Gabay, C.; Mumcuoglu, M.; Engel, G.; Balaban, N.Q. Single-cell protein induction dynamics reveals a period of vulnerability to antibiotics in persister bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6145–6149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogwill, T.; Comfort, A.C.; Furio, V.; MaClean, R.C. Persistence and resistance as complementary bacterial adaptations to antibiotics. J. Evol. Biol. 2016, 29, 1223–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofsteenge, N.; van Nimwegen, E.; Silander, O.K. Quantitative analysis of persister fractions suggests different mechanisms of formation among environmental isolates of E. coli. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keren, I.; Kaldalu, N.; Spoering, A.; Wang, Y.; Lewis, K. Persister cells and tolerance to antimicrobials. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 230, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Laslop, N.; Lee, H.; Neyfakh, A.A. Increased persistence in Escherichia coli caused by controlled expression of toxins or other unrelated proteins. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 3494–3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, B.W.; Valenta, J.A.; Benedik, M.J.; Wood, T.K. Arrested protein synthesis increases persister-like cell formation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 1468–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerdes, K.; Maisonneuve, E. Remarkable functional convergence: Alarmone ppGpp mediates persistence by activating type I and II toxin-antitoxins. Mol. Cell 2015, 59, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meredith, H.R.; Srimani, J.K.; Lee, A.J.; Lopatkin, A.J.; You, L. Collective antibiotic tolerance: Mechanisms, dynamics and intervention. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 11, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasani, R.A.; Savageau, M.A. Unrelated toxin-antitoxin systems cooperate to induce persistence. J. R. Soc. Interface 2015, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotem, E.; Loinger, A.; Ronin, I.; Levin-Reisman, I.; Gabay, C.; Shoresh, N.; Biham, O.; Balaban, N.Q. Regulation of phenotypic variability by a threshold-based mechanism underlies bacterial persistence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 12541–12546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verstraeten, N.; Knapen, W.J.; Kint, C.I.; Liebens, V.; van den Bergh, B.; Dewachter, L.; Michiels, J.E.; Fu, Q.; David, C.C.; Fierro, A.C.; et al. Obg and membrane depolarization are part of a microbial bet-hedging strategy that leads to antibiotic tolerance. Mol. Cell 2015, 59, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrigan, R.M.; Bellows, L.E.; Wood, A.; Grundling, A. ppGpp negatively impacts ribosome assembly affecting growth and antimicrobial tolerance in gram-positive bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E1710–E1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armalyte, J.; Jurenaite, M.; Beinoraviciute, G.; Teiserskas, J.; Suziedeliene, E. Characterization of Escherichia coli DinJ-YafQ toxin-antitoxin system using insights from mutagenesis data. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, J.J.; Wade, W.D.; Akierman, S.; Vacchi-Suzzi, C.; Stremick, C.A.; Turner, R.J.; Ceri, H. The chromosomal toxin gene YafQ is a determinant of multidrug tolerance for Escherichia coli growing in a biofilm. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 2253–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, C.N.; Morozov, A.; Planzos, P.; Zelaya, H.M. The fatty acid signaling molecule cis-2-decenoic acid increases metabolic activity and reverts persister cells to an antimicrobial-susceptible state. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 6976–6991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Bahar, A.A.; Syed, H.; Ren, D. Reverting antibiotic tolerance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 persister cells by (z)-4-bromo-5-(bromomethylene)-3-methylfuran-2(5h)-one. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, T.A.; VanBogelen, R.A.; Neidhardt, F.C. Lon gene product of Escherichia coli is a heat-shock protein. J. Bacteriol. 1984, 159, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Breidenstein, E.B.; Hancock, R.E. Armand-frappier outstanding student award—Role of ATP-dependent proteases in antibiotic resistance and virulence. Can. J. Microbiol. 2013, 59, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonas, K.; Liu, J.; Chien, P.; Laub, M.T. Proteotoxic stress induces a cell-cycle arrest by stimulating Lon to degrade the replication initiator dnaA. Cell 2013, 154, 623–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdez-Cruz, N.A.; Ramirez, O.T.; Trujillo-Roldan, M.A. Molecular responses of Escherichia coli caused by heat stress and recombinant protein production during temperature induction. Bioeng. Bugs 2011, 2, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes, T.; Schubert, O.T.; Rose, G.; Arnvig, K.B.; Comas, I.; Aebersold, R.; Young, D.B. Genome-wide mapping of transcriptional start sites defines an extensive leaderless transcriptome in mycobacterium tuberculosis. Cell Rep. 2013, 5, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelberg-Kulka, H.; Sat, B.; Reches, M.; Amitai, S.; Hazan, R. Bacterial programmed cell death systems as targets for antibiotics. Trends microbiol. 2004, 12, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korch, S.B.; Hill, T.M. Ectopic overexpression of wild-type and mutant Hipa genes in Escherichia coli: Effects on macromolecular synthesis and persister formation. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 3826–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, D.; Zhang, Z.; Khodursky, A.; Kaldalu, N.; Kurg, K.; Lewis, K. Persisters: A distinct physiological state of E. coli. BMC Microbiol. 2006, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anders, S.; McCarthy, D.J.; Chen, Y.; Okoniewski, M.; Smyth, G.K.; Huber, W.; Robinson, M.D. Count-based differential expression analysis of RNA sequencing data using R and bioconductor. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1765–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. Edger: A bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soheili, S.; Ghafourian, S.; Sekawi, Z.; Neela, V.K.; Sadeghifard, N.; Taherikalani, M.; Khosravi, A.; Ramli, R.; Hamat, R.A. The MazEF toxin-antitoxin system as an attractive target in clinical isolates of Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 2553–2561. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; Jiang, X. Expression of stress and virulence genes in Escherichia coli O157:H7 heat shocked in fresh dairy compost. J. Food Prot. 2015, 78, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Melderen, L.; Aertsen, A. Regulation and quality control by Lon-dependent proteolysis. Res. Microbiol. 2009, 160, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goeders, N.; Van Melderen, L. Toxin-antitoxin systems as multilevel interaction systems. Toxins 2014, 6, 304–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drobnak, I.; De Jonge, N.; Haesaerts, S.; Vesnaver, G.; Loris, R.; Lah, J. Energetic basis of uncoupling folding from binding for an intrinsically disordered protein. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 1288–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottesman, S. Proteases and their tagets in Escherichia coli. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1996, 30, 465–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narberhaus, F.; Obrist, M.; Fuhrer, F.; Langklotz, S. Degradation of cytoplasmic substrates by FtsH, a membrane-anchored protease with many talents. Res. Microbiol. 2009, 160, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivares, A.O.; Baker, T.A.; Sauer, R.T. Mechanistic insights into bacterial AAA+ proteases and protein-remodelling machines. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauer, R.T.; Baker, T.A. AAA+ proteases: ATP-fueled machines of protein destruction. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2011, 80, 587–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schilling, O.; Overall, C.M. Proteomic discovery of protease substrates. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2007, 11, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruteanu, M.; Baker, T.A. Proteolysis in the SOS response and metal homeostasis in Escherichia coli. Res. Microbiol. 2009, 160, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, C.; Rasouly, A.; Gur, E.; Shenhar, Y.; Biran, D.; Ron, E.Z. Temperature-dependent proteolysis as a control element in Escherichia coli metabolism. Res. Microbiol. 2009, 160, 684–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neher, S.B.; Villen, J.; Oakes, E.C.; Bakalarski, C.E.; Sauer, R.T.; Gygi, S.P.; Baker, T.A. Proteomic profiling of ClpXP substrates after DNA damage reveals extensive instability within SOS regulon. Mol. Cell 2006, 22, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donegan, N.P.; Thompson, E.T.; Fu, Z.; Cheung, A.L. Proteolytic regulation of toxin-antitoxin systems by ClpCP in staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 1416–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donegan, N.P.; Marvin, J.S.; Cheung, A.L. Role of adaptor Trfa and ClpPC in controlling levels of SsrA-tagged proteins and antitoxins in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 2014, 196, 4140–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, M.; Frank, E.G.; Levine, A.S.; Woodgate, R. Lon-mediated proteolysis of the Escherichia coli UmuD mutagenesis protein: In vitro degradation and identification of residues required for proteolysis. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 3889–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gur, E. The Lon AAA+ protease. Subcell Biochem. 2013, 66, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Flynn, J.M.; Neher, S.B.; Kim, Y.I.; Sauer, R.T.; Baker, T.A. Proteomic discovery of cellular substrates of the ClpXP protease reveals five classes of ClpX-recognition signals. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 671–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Harrison, E.M.; Bi, D.; Tai, C.; He, X.; Ou, H.Y.; Rajakumar, K.; Deng, Z. Tadb: A web-based resource for Type 2 toxin-antitoxin loci in bacteria and archaea. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D606–D611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brzozowska, I.; Zielenkiewicz, U. The ClpXP protease is responsible for the degradation of the epsilon antidote to the zeta toxin of the streptococcal pSM19035 plasmid. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 7514–7523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Melderen, L.; Thi, M.H.; Lecchi, P.; Gottesman, S.; Couturier, M.; Maurizi, M.R. ATP-dependent degradation of CcdA by Lon protease. Effects of secondary structure and heterologous subunit interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 27730–27738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, S.K.; Gerdes, K. Delayed-relaxed response explained by hyperactivation of rele. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 53, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, B.D.; Garza-Sanchez, F.; Hayes, C.S. YoeB toxin is activated during thermal stress. Microbiologyopen 2015, 4, 682–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, S.K.; Maenhaut-Michel, G.; Mine, N.; Gottesman, S.; Gerdes, K.; Van Melderen, L. Overproduction of the Lon protease triggers inhibition of translation in Escherichia coli: Involvement of the YefM-YoeB toxin-antitoxin system. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 51, 1705–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overgaard, M.; Borch, J.; Gerdes, K. RelB and RelEof Escherichia coli form a tight complex that represses transcription via the ribbon-helix-helix motif in RelB. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 394, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prysak, M.H.; Mozdzierz, C.J.; Cook, A.M.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Inouye, M.; Woychik, N.A. Bacterial toxin YafQ is an endoribonuclease that associates with the ribosome and blocks translation elongation through sequence-specific and frame-dependent mRNA cleavage. Mol. Microbiol. 2009, 71, 1071–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.S.; Rawlings, D.E. Efficiency of the pTF-Fc2 pas poison-antidote stability system in Escherichia coli is affected by the host strain, and antidote degradation requires the Lon protease. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 5458–5462. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Winther, K.S.; Gerdes, K. Regulation of enteric VapBC transcription: Induction by VapC toxin dimer-breaking. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 4347–4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aizenman, E.; Engelberg-Kulka, H.; Glaser, G. An Escherichia coli chromosomal “addiction module” regulated by guanosine [corrected] 3′,5′-bispyrophosphate: A model for programmed bacterial cell death. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 6059–6063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, S.K.; Gerdes, K. RelE toxins from bacteria and archaea cleave mRNAs on translating ribosomes, which are rescued by tmRNA. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 48, 1389–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diago-Navarro, E.; Hernandez-Arriaga, A.M.; Kubik, S.; Konieczny, I.; Diaz-Orejas, R. Cleavage of the antitoxin of the ParD toxin-antitoxin system is determined by the ClpAP protease and is modulated by the relative ratio of the toxin and the antitoxin. Plasmid 2013, 70, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen-Dalsgaard, M.; Jorgensen, M.G.; Gerdes, K. Three new RelE-homologous mRNA interferases of Escherichia coli differentially induced by environmental stresses. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 75, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, S.; Vulic, M.; Min, J.; Yen, T.J.; Schumacher, M.A.; Brennan, R.G.; Lewis, K. Regulation of the Escherichia coli HipBA toxin-antitoxin system by proteolysis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Melderen, L.; Bernard, P.; Couturier, M. Lon-dependent proteolysis of CcdA is the key control for activation of CcdB in plasmid-free segregant bacteria. Mol. Microbiol. 1994, 11, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Lord, D.M.; Hong, S.H.; Peti, W.; Benedik, M.J.; Page, R.; Wood, T.K. Type II toxin/antitoxin MqsR/MqsA controls Type V toxin/antitoxin GhoT/GhoS. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 1734–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, M.G.; Pandey, D.P.; Jaskolska, M.; Gerdes, K. HicA of Escherichia coli defines a novel family of translation-independent mRNA interferases in bacteria and archaea. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leplae, R.; Geeraerts, D.; Hallez, R.; Guglielmini, J.; Dreze, P.; Van Melderen, L. Diversity of bacterial Type II toxin-antitoxin systems: A comprehensive search and functional analysis of novel families. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 5513–5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbing, M.A.; Handelman, S.K.; Kuzin, A.P.; Verdon, G.; Wang, C.; Su, M.; Rothenbacher, F.P.; Abashidze, M.; Liu, M.; Hurley, J.M.; et al. Crystal structures of Phd-Doc, HigA, and YeeU establish multiple evolutionary links between microbial growth-regulating toxin-antitoxin systems. Structure 2010, 18, 996–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, R.D.; Coggill, P.; Eberhardt, R.Y.; Eddy, S.R.; Mistry, J.; Mitchell, A.L.; Potter, S.C.; Punta, M.; Qureshi, M.; Sangrador-Vegas, A.; et al. The pFam protein families database: Towards a more sustainable future. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D279–D285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, L.C.; Garrido, S.S.; Marchetto, R. Btoxdb: A comprehensive database of protein structural data on toxin-antitoxin systems. Comput. Biol. Med. 2015, 58, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crooks, G.E.; Hon, G.; Chandonia, J.M.; Brenner, S.E. Weblogo: A sequence logo generator. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1188–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- QIAGEN. Available online: https://www.qiagenbioinformatics.com/ (accessed on 7 July 2016).
- Smith, C.K.; Baker, T.A.; Sauer, R.T. Lon and Clp family proteases and chaperones share homologous substrate-recognition domains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 6678–6682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogle, C.T.; Mather, W.H. Proteolytic crosstalk in multi-protease networks. Phys. Biol. 2016, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iosefson, O.; Nager, A.R.; Baker, T.A.; Sauer, R.T. Coordinated gripping of substrate by subunits of a AAA+ proteolytic machine. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 11, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.C.; Su, S.C.; Su, M.Y.; Liang, P.H.; Feng, C.C.; Wu, S.H.; Chang, C.I. Structural insights into the allosteric operation of the Lon AAA+ protease. Structure 2016, 24, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohlever, M.L.; Baker, T.A.; Sauer, R.T. A mutation in the N domain of Escherichia coli Lon stabilizes dodecamers and selectively alters degradation of model substrates. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 5622–5628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieux, E.F.; Wohlever, M.L.; Chen, J.Z.; Sauer, R.T.; Baker, T.A. Distinct quaternary structures of the AAA+ lon protease control substrate degradation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E2002–E2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.C.; Lin, C.C.; Tai, H.C.; Chang, M.Y.; Ho, M.R.; Babu, C.S.; Liao, J.H.; Wu, S.H.; Chang, Y.C.; Lim, C.; et al. Structural basis for the magnesium-dependent activation and hexamerization of the Lon AAA+ protease. Structure 2016, 24, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerdes, K.; Ingmer, H. Antibiotics: Killing the survivors. Nature 2013, 503, 347–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conlon, B.P.; Nakayasu, E.S.; Fleck, L.E.; LaFleur, M.D.; Isabella, V.M.; Coleman, K.; Leonard, S.N.; Smith, R.D.; Adkins, J.N.; Lewis, K. Activated ClpP kills persisters and eradicates a chronic biofilm infection. Nature 2013, 503, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.H.; Chung, Y.S.; Gloyd, M.; Joseph, E.; Ghirlando, R.; Wright, G.D.; Cheng, Y.Q.; Maurizi, M.R.; Guarne, A.; Ortega, J. Acyldepsipeptide antibiotics induce the formation of a structured axial channel in ClpP: A model for the ClpX/ClpA-bound state of ClpP. Chem. Biol. 2010, 17, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, W.; Ngan, G.J.; Low, J.L.; Poulsen, A.; Chia, B.C.; Ang, M.J.; Yap, A.; Fulwood, J.; Lakshmanan, U.; Lim, J.; et al. Target mechanism-based whole-cell screening identifies bortezomib as an inhibitor of caseinolytic protease in mycobacteria. mBio 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazan, R.; Engelberg-Kulka, H. Escherichia coli MazEF-mediated cell death as a defense mechanism that inhibits the spread of phage P1. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2004, 272, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sat, B.; Hazan, R.; Fisher, T.; Khaner, H.; Glaser, G.; Engelberg-Kulka, H. Programmed cell death in Escherichia coli: Some antibiotics can trigger MazEF lethality. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 2041–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, S.K.; Mikkelsen, M.; Pedersen, K.; Gerdes, K. RelE, a global inhibitor of translation, is activated during nutritional stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 14328–14333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micevski, D.; Dougan, D.A. Proteolytic regulation of stress response pathways in Escherichia coli. Subcell Biochem. 2013, 66, 105–128. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, N.; Lan, L. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Lon and ClpXP proteases: Roles in linking carbon catabolite repression system with quorum-sensing system. Curr. Genet. 2016, 62, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goff, S.A.; Goldberg, A.L. Production of abnormal proteins in E. coli stimulates transcription of Lon and other heat shock genes. Cell 1985, 41, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsilibaris, V.; Maenhaut-Michel, G.; van Melderen, L. Biological roles of the Lon ATP-dependent protease. Res. Microbiol. 2006, 157, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.; Suzuki, C.K. Functional mechanics of the ATP-dependent Lon protease—Lessons from endogenous protein and synthetic peptide substrates. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1784, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazir, A.; Harinarayanan, R. Inactivation of cell division protein FtsZ by SulA makes Lon indispensable for the viability of a ppGpp0 strain of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 2015, 198, 688–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroda, A.; Nomura, K.; Ohtomo, R.; Kato, J.; Ikeda, T.; Takiguchi, N.; Ohtake, H.; Kornberg, A. Role of inorganic polyphosphate in promoting ribosomal protein degradation by the Lon protease in E. coli. Science 2001, 293, 705–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.Y.; Chen, Y.D.; Chang, Y.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Chang, C.F.; Huang, S.J.; Wu, S.H.; Hsu, C.H. Structural basis for DNA-mediated allosteric regulation facilitated by the AAA+ module of Lon protease. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2014, 70, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osbourne, D.O.; Soo, V.W.; Konieczny, I.; Wood, T.K. Polyphosphate, cyclic AMP, guanosine tetraphosphate, and c-di-GMP reduce in vitro Lon activity. Bioengineered 2014, 5, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, Y.; Lazinski, D.; Rowe, S.; Camilli, A.; Lewis, K. Genetic basis of persister tolerance to aminoglycosides in Escherichia coli. mBio 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, O.; Schuenemann, V.J.; Hand, N.J.; Silhavy, T.J.; Martin, J.; Lupas, A.N.; Djuranovic, S. PrlF and YhaV encode a new toxin-antitoxin system in Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 372, 894–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, W.B.; Silhavy, T.J. Enhanced export of beta-galactosidase fusion proteins in PrlF mutants is Lon dependent. J. Bacteriol. 1992, 174, 5661–5668. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aakre, C.D.; Phung, T.N.; Huang, D.; Laub, M.T. A bacterial toxin inhibits DNA replication elongation through a direct interaction with the beta sliding clamp. Mol. Cell 2013, 52, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordes, P.; Cirinesi, A.M.; Ummels, R.; Sala, A.; Sakr, S.; Bitter, W.; Genevaux, P. SecB-like chaperone controls a toxin-antitoxin stress-responsive system in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8438–8443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sala, A.; Calderon, V.; Bordes, P.; Genevaux, P. Tac from Mycobacterium tuberculosis: A paradigm for stress-responsive toxin-antitoxin systems controlled by SecB-like chaperones. Cell Stress Chaperones 2013, 18, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ainelo, A.; Tamman, H.; Leppik, M.; Remme, J.; Horak, R. The toxin GraT inhibits ribosome biogenesis. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 100, 719–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamman, H.; Ainelo, A.; Tagel, M.; Horak, R. Stability of the GraA antitoxin depends on the growth phase, ATP level and global regulator MexT. J. Bacteriol. 2015, 198, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.F.; Zhou, Y.; Gottesman, S. Redundant in vivo proteolytic activities of Escherichia coli Lon and the ClpyQ (HslUV) protease. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 3681–3687. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Christensen, S.K.; Pedersen, K.; Hansen, F.G.; Gerdes, K. Toxin-antitoxin loci as stress-response-elements: ChpAK/MazF and ChpBK cleave translated RNAs and are counteracted by tmRNA. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 332, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.; Capecci, J.; Drlica, K. Lon protease is essential for paradoxical survival of Escherichia coli exposed to high concentrations of quinolone. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 3103–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breidenstein, E.B.; Bains, M.; Hancock, R.E. Involvement of the Lon protease in the SOS response triggered by ciprofloxacin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 2879–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.J.; Hergenrother, P.J. Artificial activation of toxin-antitoxin systems as an antibacterial strategy. Trends Microbiol. 2012, 20, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanouchi, Y.; Lee, A.J.; Meredith, H.; You, L. Programmed cell death in bacteria and implications for antibiotic therapy. Trends Microbiol. 2013, 21, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, C.F.; Bertram, R. Toxin-antitoxin systems are ubiquitous and versatile modulators of prokaryotic cell fate. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2013, 340, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).