Co-Occurrence of Toxic Bloom-Forming Cyanobacteria Planktothrix, Cyanophage, and Symbiotic Bacteria in Ohio Water Treatment Waste: Implications for Harmful Algal Bloom Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
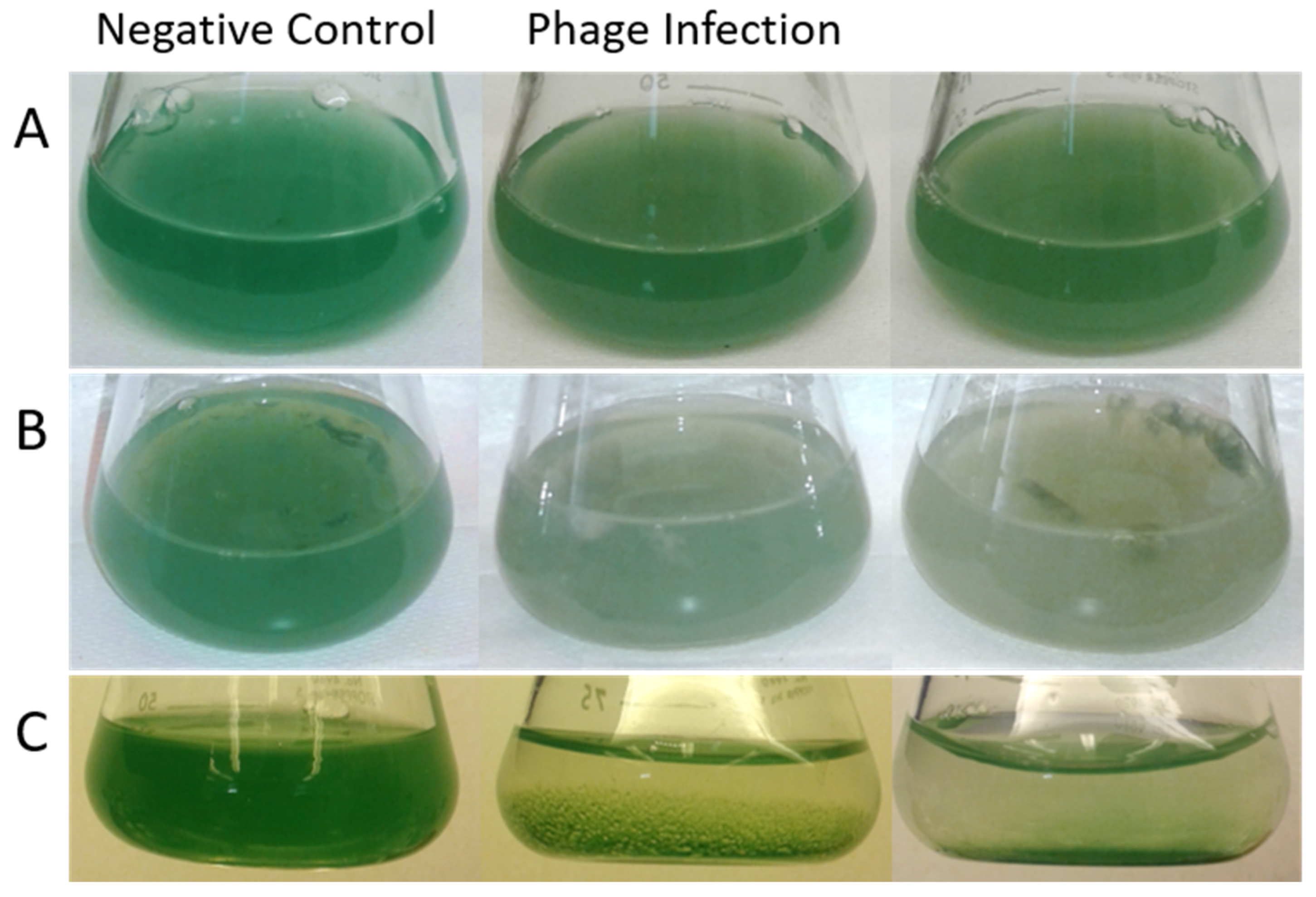
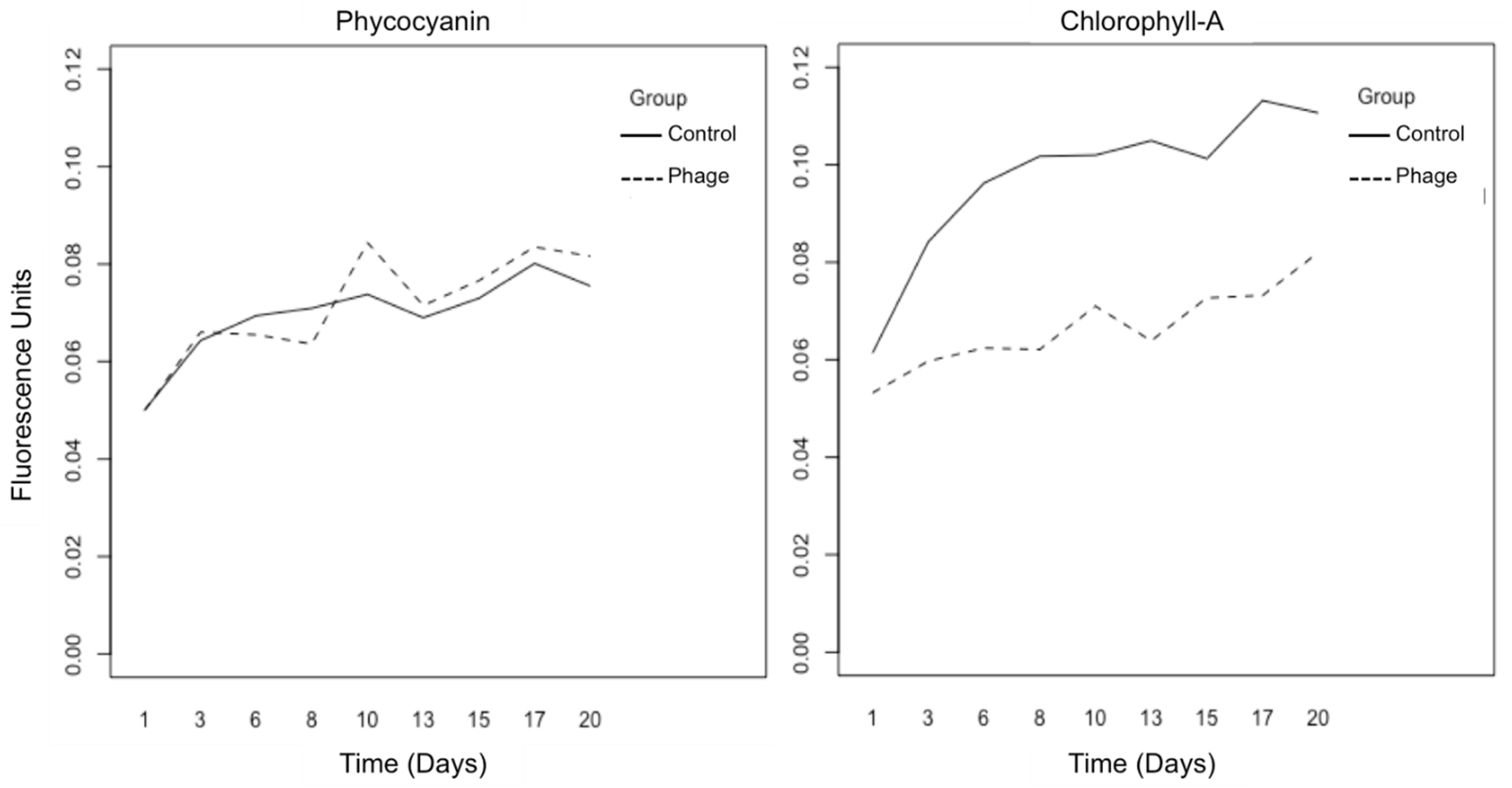
2.1. Optical Observation and Fluorometry
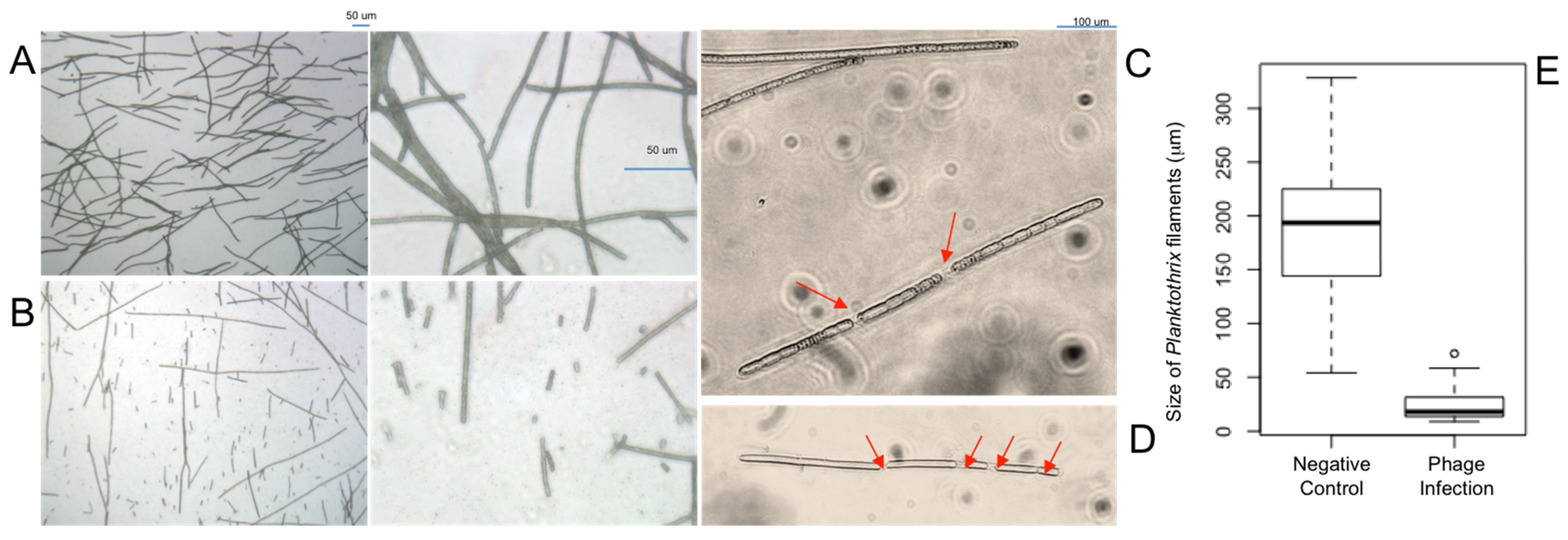
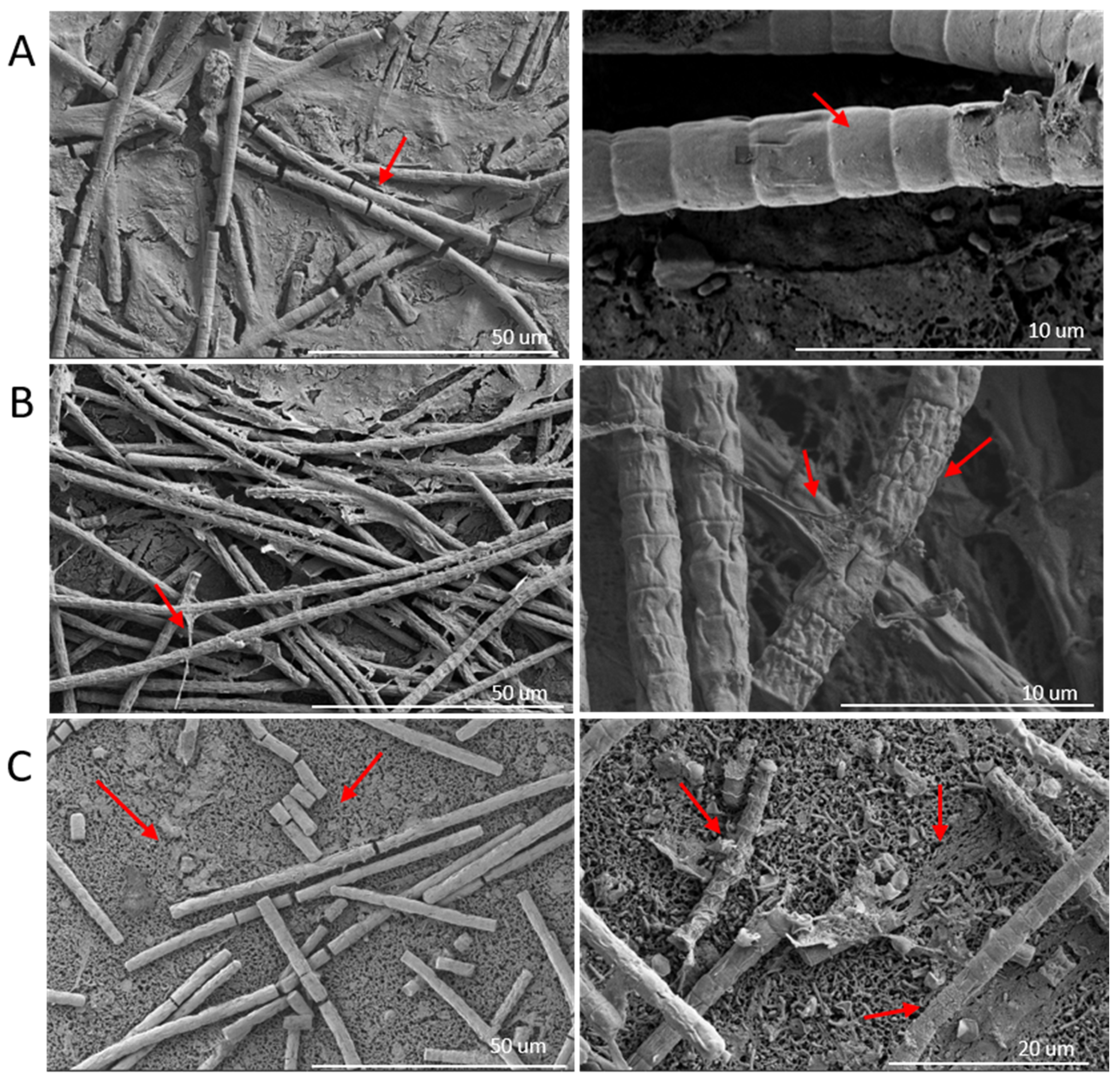
2.2. Optical and Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.3. Next Generation Sequencing
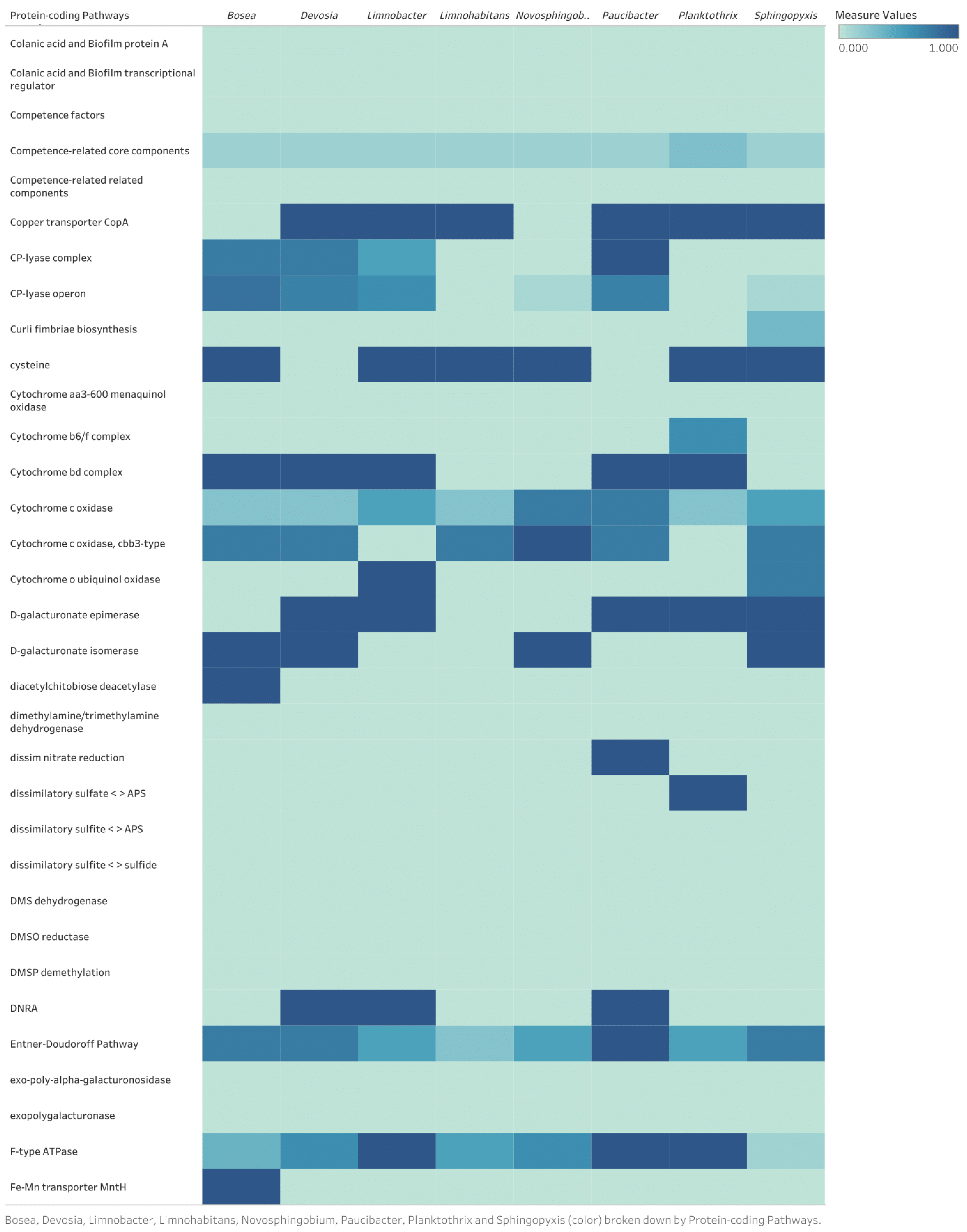
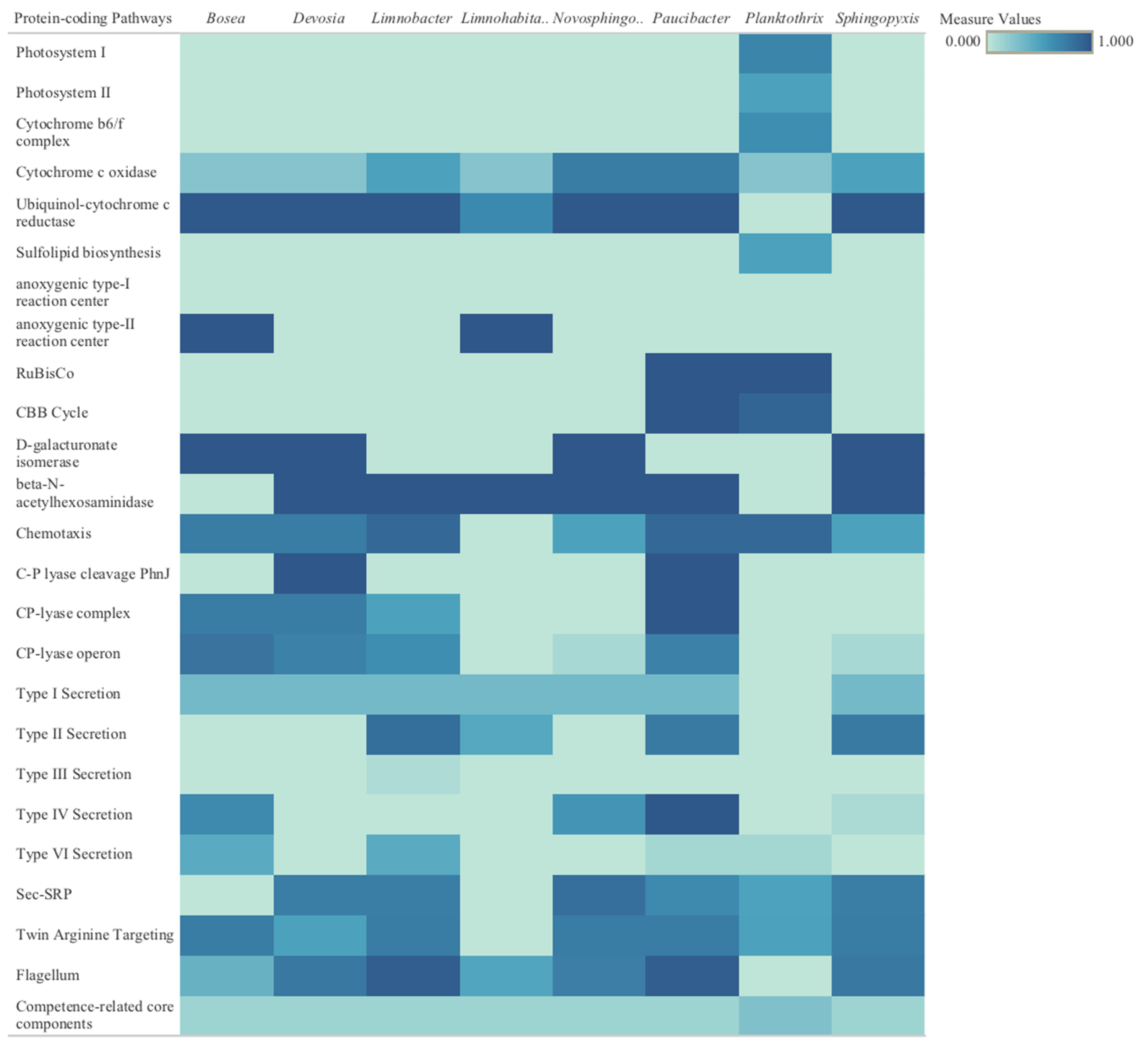
2.3.1. Metagenome-Assembled Genomes
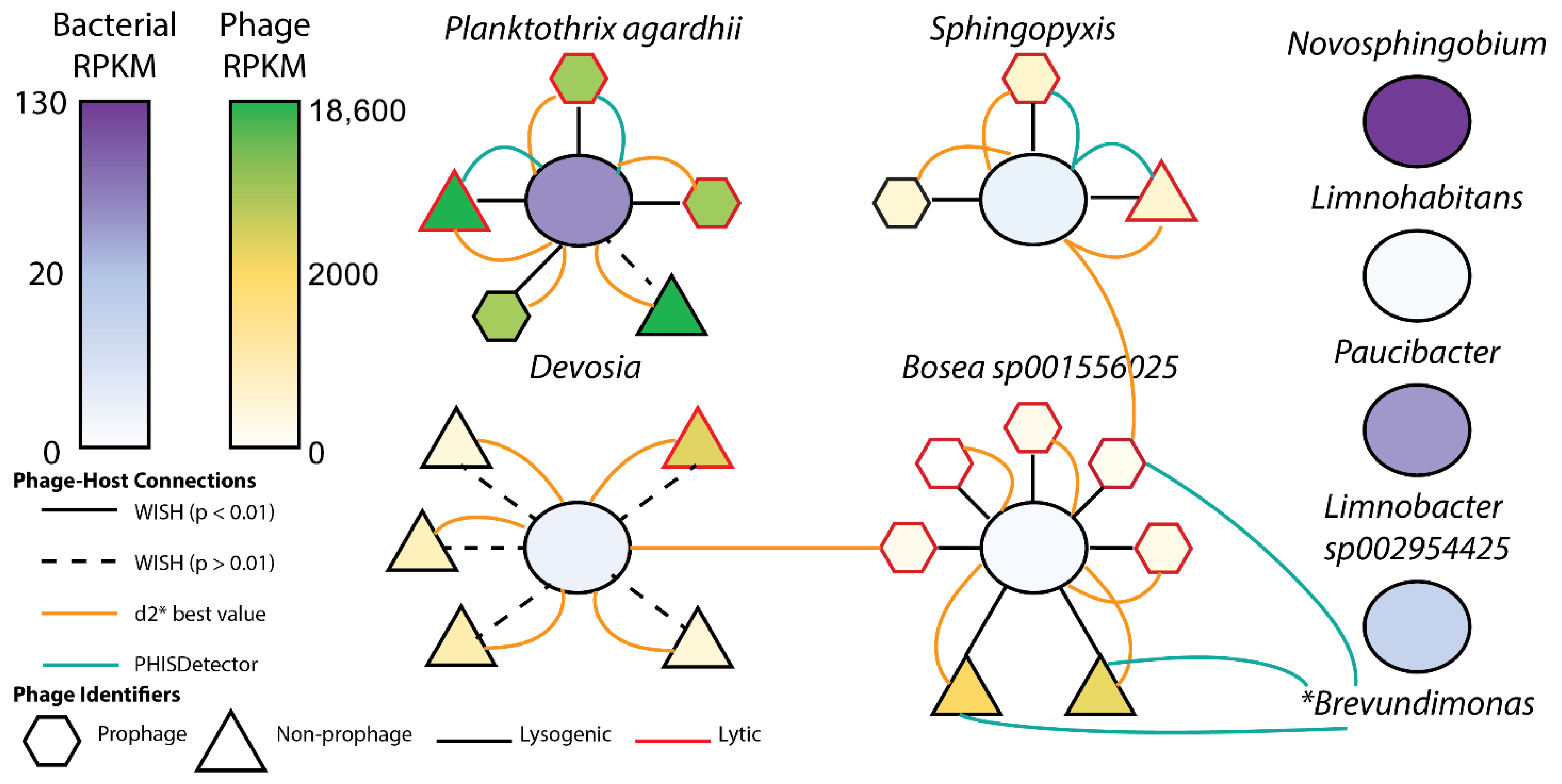
2.3.2. Viral Genomic Fragments and Phage–Host Associations
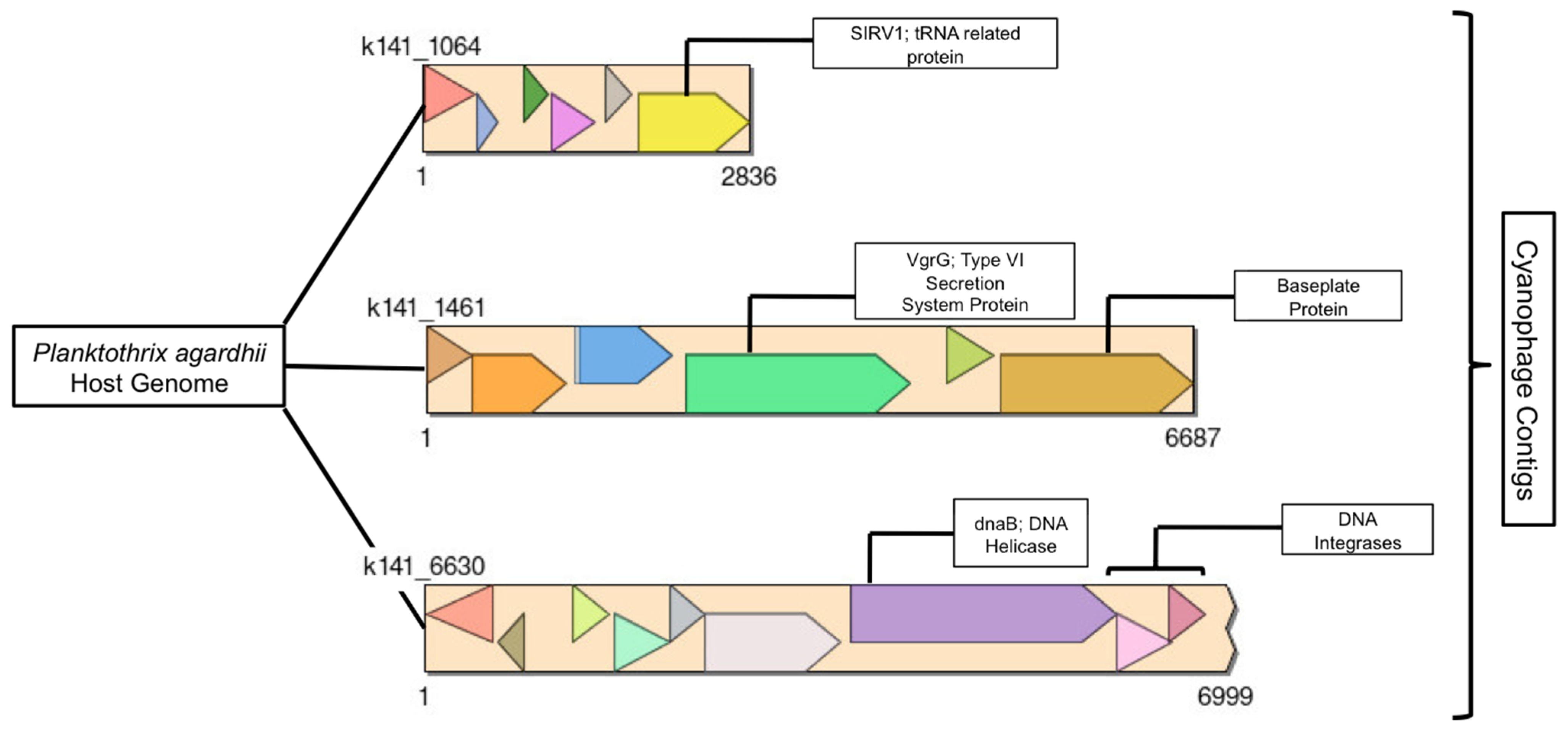
2.3.3. Phage Genetic Analysis
3. Discussion
3.1. Optical Observation and Fluorometry
3.2. Optical and Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.3. Next Generation Sequencing
3.3.1. Metagenome-Assembled Genomes
3.3.2. Viral Genomic Fragments and Phage–Host Associations
3.3.3. Phage Genetic Analysis
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Cyanobacteria Host Maintenance and Monitoring
5.2. Cyanophage Extraction and Elution from WTR Samples
5.3. Cyanophage Inoculation and Screening
5.4. Cyanophage Collection and Concentration
5.5. Cyanophage–Host Interactions In Vitro
5.6. Optical Light Microscopy
5.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy
5.8. DNA Preparation for Whole Genome Sequencing
5.9. Bioinformatics Analysis
5.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| WTRs | Water treatment residuals |
| DWTP | Drinking water treatment plant |
| HAB | Harmful algal bloom |
| MCs | Microcystins |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| MAGs | Metagenome-assembled-genomes |
| VGFs | Viral genomic fragments |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
Appendix A




Appendix B
Discussion of Identified Metabolic Pathways for Eight Bacterial Genomes
Appendix C

Appendix D
Discussion of Identified Proteins in Three Phage Contigs
References
- U.S. EPA. Cyanobacterial Harmful Algal Blooms (CyanoHABs) in Water Bodies. 2018. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/cyanohabs (accessed on 23 May 2019).
- Bridgeman, T.B.; Chaffin, J.D.; Filbrun, J.E. A novel method for tracking western Lake Erie Microcystis blooms, 2002–2011. J. Great Lakes Res. 2013, 39, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brittain, S.M.; Wang, J.; Babcock-Jackson, L.; Carmichael, W.W.; Rinehart, K.L.; Culver, D.A. Isolation and Characterization of Microcystins, Cyclic Heptapeptide Hepatotoxins from a Lake Erie Strain of Microcystis aeruginosa. J. Great Lakes Res. 2000, 26, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinta-Kanto, J.M.; Ouellette, A.J.A.; Boyer, G.L.; Twiss, M.R.; Bridgeman, T.B.; Wilhelm, S.W. Quantification of Toxic Microcystis spp. during the 2003 and 2004 Blooms in Western Lake Erie using Quantitative Real-Time PCR. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 4198–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, R.K.; Qin, X.; McKay, R.L.; Miner, J.; Czajkowski, K.; Savino, J.; Bridgeman, T. Phycocyanin detection from LANDSAT TM data for mapping cyanobacterial blooms in Lake Erie. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 89, 381–392. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, T.W.; Bullerjahn, G.S.; Tuttle, T.; McKay, R.M.; Watson, S.B. Effects of Increasing Nitrogen and Phosphorus Concentrations on Phytoplankton Community Growth and Toxicity During Planktothrix Blooms in Sandusky Bay, Lake Erie. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 7197–7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millie, D.F.; Fahnenstiel, G.L.; Bressie, J.D.; Pigg, R.J.; Rediske, R.R.; Klarer, D.M.; Tester, P.A.; Litaker, R.W. Late-summer phytoplankton in western Lake Erie (Laurentian Great Lakes): Bloom distributions, toxicity, and environmental influences. Aquat. Ecol. 2009, 43, 915–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, W.W. The Cyanotoxins. In Advances in Botanical Research; Callow, J.A., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1997; Volume 27, pp. 211–256. Available online: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0065229608602827 (accessed on 17 December 2019).
- Imanishi, S.; Kato, H.; Mizuno, M.; Tsuji, K.; Harada, K.-I. Bacterial Degradation of Microcystins and Nodularin. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2005, 18, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamp, L.; Church, J.L.; Carpino, J.; Faltin-Mara, E.; Rubio, F. The effects of water sample treatment, preparation, and storage prior to cyanotoxin analysis for cylindrospermopsin, microcystin and saxitoxin. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 246, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, D.; Hoeger, S. Guidance values for microcystins in water and cyanobacterial supplement products (blue-green algal supplements): A reasonable or misguided approach? Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 203, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, W.J.; Hitzfeld, B.C.; Tencalla, F.; Eriksson, J.E.; Mikhailov, A.; Dietrich, D.R. Microcystin-LR Toxicodynamics, Induced Pathology, and Immunohistochemical Localization in Livers of Blue-Green Algae Exposed Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Toxicol. Sci. 2000, 54, 365–373. [Google Scholar]
- Gorham, P.R.; Carmichael, W.W. Hazards of freshwater blue-green algae (cyanobacteria). In Algae and Human Affairs; Lembi, C., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Runnegar, M.; Berndt, N.; Kong, S.M.; Lee, E.Y.C.; Zhang, L.F. In Vivo and in Vitro Binding of Microcystin to Protein Phosphatase 1 and 2A. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 216, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Apeldoorn, M.E.; van Egmond, H.P.; Speijers, G.J.A.; Bakker, G.J.I. Toxins of cyanobacteria. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 7–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Bureau of Economic Analysis. Gross Domestic Product by State: Fourth Quarter and Annual 2016; U.S. Department of Commerce: Washington, DC, USA, 2017.
- U.S. EPA. Facts and Figures about the Great Lakes. 2015. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/greatlakes/great-lakes-facts-and-figures (accessed on 2 September 2025).
- American Society of Civil Engineers; American Water Works Association. Management of Water Treatment Plant Residuals: Technology Transfer Handbook; ASCE Publications: Reston, VA, USA, 1996; p. 324. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, M.L. Water and Wastewater Engineering; McGraw-Hill Professional Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2010; p. 524. Available online: http://ebookcentral.proquest.com/lib/ohiostate-ebooks/detail.action?docID=4658082 (accessed on 18 March 2020).
- Ippolito, J.A.; Barbarick, K.A.; Elliott, H.A. Drinking Water Treatment Residuals: A Review of Recent Uses. J. Environ. Qual. 2011, 40, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, M.E.; Lake, C.B.; Gagnon, G.A. Strategic pathways for the sustainable management of water treatment plant residuals. J. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2008, 7, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Lee, S.; Lee, J. Drinking water treatment residuals from cyanobacteria bloom-affected areas: Investigation of potential impact on agricultural land application. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 135756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clokie, M.R.; Millard, A.D.; Letarov, A.V.; Heaphy, S. Phages in nature. Bacteriophage 2011, 1, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gons, H.J.; Ebert, J.; Hoogveld, H.L.; van den Hove, L.; Pel, R.; Takkenberg, W.; Woldringh, C.J. Observations on cyanobacterial population collapse in eutrophic lake water. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 2002, 81, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatfull, G.F.; Hendrix, R.W. Bacteriophages and their Genomes. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2011, 1, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suttle, C.A. Marine viruses—Major players in the global ecosystem. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H. Nutrient and other environmental controls of harmful cyanobacterial blooms along the freshwater–marine continuum. In Cyanobacterial Harmful Algal Blooms: State of the Science and Research Needs; Hudnell, H.K., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 217–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safferman, R.S.; Morris, M.E. Control of Algae with Viruses. J. AWWA 1964, 56, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Hayes, P.K. Evidence for cyanophages active against bloom-forming freshwater cyanobacteria. Freshw. Biol. 2008, 53, 1240–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Li, D.; Sun, Z.; Tong, Y.; Yan, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Pei, G. A novel freshwater cyanophage vB_MelS-Me-ZS1 infecting bloom-forming cyanobacterium Microcystis elabens. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 7979–7989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, H.; Li, T.; Deng, F.; Hu, Z. Freshwater cyanophages. Virol. Sin. 2013, 28, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Jin, H.; Wang, X.-Q.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.-T.; Cui, N.; Jiang, Y.-L.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Q.-F.; Zhou, C.-Z.; et al. Genomic Analysis of Mic1 Reveals a Novel Freshwater Long-Tailed Cyanophage. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; You, F.; He, Y.; Te, S.H.; Gin, K.Y.H. Isolation and Characterization of the First Freshwater Cyanophage Infecting Pseudanabaena. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00682-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, E.; Yuan, X.; Li, R.; Zhang, Q. Isolation of a novel cyanophage infectious to the filamentous cyanobacterium Planktothrix agardhii (Cyanophyceae) from Lake Donghu, China. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2009, 54, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKindles, K.M.; Manes, M.A.; DeMarco, J.R.; McClure, A.; McKay, R.M.; Davis, T.W.; Bullerjahn, G.S.; Schaffner, D.W. Dissolved Microcystin Release Coincident with Lysis of a Bloom Dominated by Microcystis spp. in Western Lake Erie Attributed to a Novel Cyanophage. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e01397-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKindles, K.M.; Manes, M.; Neudeck, M.; McKay, R.M.; Bullerjahn, G.S. Multi-year molecular quantification and ‘omics analysis of Planktothrix-specific cyanophage sequences from Sandusky Bay, Lake Erie. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1199641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, D.; Tominaga, K.; Nishimura, Y.; Yoshida, N.; Kimura, S.; Sako, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Schaffner, D.W. Cooccurrence of Broad- and Narrow-Host-Range Viruses Infecting the Bloom-Forming Toxic Cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e01170-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, S.; Pollard, P. Identification of Cyanophage Ma-LBP and Infection of the Cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa from an Australian Subtropical Lake by the Virus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Takashima, Y.; Tomaru, Y.; Shirai, Y.; Takao, Y.; Hiroishi, S.; Nagasaki, K. Isolation and Characterization of a Cyanophage Infecting the Toxic Cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolduc, B.; Youens-Clark, K.; Roux, S.; Hurwitz, B.L.; Sullivan, M.B. iVirus: Facilitating new insights in viral ecology with software and community data sets imbedded in a cyberinfrastructure. ISME J. 2017, 11, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohiuddin, M.; Schellhorn, H.E. Spatial and temporal dynamics of virus occurrence in two freshwater lakes captured through metagenomic analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Berg, K.; Lyra, C.; Sivonen, K.; Paulin, L.; Suomalainen, S.; Tuomi, P.; Rapala, J. High diversity of cultivable heterotrophic bacteria in association with cyanobacterial water blooms. ISME J. 2009, 3, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Lin, F.; Yang, C.; Wang, J.; Lin, Y.; Shen, M.; Park, M.S.; Li, T.; Zhao, J. A Large-Scale Comparative Metagenomic Study Reveals the Functional Interactions in Six Bloom-Forming Microcystis-Epibiont Communities. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijsbertsen-Abrahamse, A.J.; Schmidt, W.; Chorus, I.; Heijman, S.G.J. Removal of cyanotoxins by ultrafiltration and nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 276, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, S.; Adriaenssens, E.M.; E Dutilh, B.; Koonin, E.V.; Kropinski, A.M.; Krupovic, M.; Kuhn, J.H.; Lavigne, R.; Brister, J.R.; Varsani, A.; et al. Minimum information about an uncultivated virus genome (MIUViG). Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Halstvedt, C.; Rohrlack, T.; Andersen, T.; Skulberg, O.; Edvardsen, B. Seasonal dynamics and depth distribution of Planktothrix spp. in Lake Steinsfjorden (Norway) related to environmental factors. J. Plankton Res. 2007, 29, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohio Sea Grant. Harmful Algal Blooms in Ohio Waters. 2010. Available online: https://cees.indianapolis.iu.edu/doc/2010osgfact-habsv1a.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2019).
- Ohio Sea Grant. Ohio Sea Grant College Program. What Triggers Algal Blooms in Sandusky Bay? 2014. Available online: https://ohioseagrant.osu.edu/news/2014/t8zho/what-triggers-algal-blooms-in-sandusky-bay (accessed on 18 May 2020).
- Whitton, B.A.; Potts, M. (Eds.) The Ecology of Cyanobacteria: Their Diversity in Time and Space; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000; Available online: https://www.springer.com/gp/book/9780792347354 (accessed on 10 December 2019).
- Gorham, T.; Jia, Y.; Shum, C.K.; Lee, J. Ten-year survey of cyanobacterial blooms in Ohio’s waterbodies using satellite remote sensing. Harmful Algae 2017, 66, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, E.B.; Gui, J.F.; Zhang, Q.Y. A Novel Cyanophage with a Cyanobacterial Nonbleaching Protein A Gene in the Genome. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, C.E.W.; Hartmann, H.M. Planktonic bloom-forming Cyanobacteria and the eutrophication of lakes and rivers. Freshw. Biol. 1988, 20, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsby, A.E. Gas vesicles. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1994, 58, 94–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, K.R.; Kropinski, A.M.; Clokie, M.R. Bacteriophage behavioral ecology. Bacteriophage 2014, 4, e29866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, F.; De Philippis, R. Role of Cyanobacterial Exopolysaccharides in Phototrophic Biofilms and in Complex Microbial Mats. Life 2015, 5, 1218–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marion, J.W.; Lee, J.; Wilkins, J.R.; Lemeshow, S.; Lee, C.; Waletzko, E.J.; Buckley, T.J. In Vivo Phycocyanin Flourometry as a Potential Rapid Screening Tool for Predicting Elevated Microcystin Concentrations at Eutrophic Lakes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 4523–4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Chapter 8: Algae and cyanobacteria in fresh water. In Guidelines for Safe Recreational Water Environments; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003; Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/42591/9241545801.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 4 November 2019).
- Kasalický, V.; Jezbera, J.; Šimek, K.; Hahn, M.W. Limnohabitans planktonicus sp. nov., and Limnohabitans parvus sp. nov., two novel planktonic Betaproteobacteria isolated from a freshwater reservoir. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 2710–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.D. Devosia subaequoris sp. nov., isolated from beach sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 2212–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notomista, E.; Pennacchio, F.; Cafaro, V.; Smaldone, G.; Izzo, V.; Troncone, L.; Varcamonti, M.; Di Donato, A. The Marine Isolate Novosphingobium sp. PP1Y Shows Specific Adaptation to Use the Aromatic Fraction of Fuels as the Sole Carbon and Energy Source. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 61, 582–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spring, S.; Kämpfer, P.; Schleifer, K.H. Limnobacter thiooxidans gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel thiosulfate-oxidizing bacterium isolated from freshwater lake sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2001, 51, 1463–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, V.; Casson, N.; Greub, G. New Afipia and Bosea strains isolated from various water sources by amoebal co-culture. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 30, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedler, E.; Heinaru, E.; Jutkina, J.; Viggor, S.; Koressaar, T.; Remm, M.; Heinaru, A. Limnobacter spp. as newly detected phenol-degraders among Baltic Sea surface water bacteria characterised by comparative analysis of catabolic genes. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 36, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.X.; Hong, Q.; Han, P.; Dong, X.J.; Shen, Y.J.; Li, S.P. Isolation and characterization of a carbofuran-degrading strain Novosphingobium sp. FND-3. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 271, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.H.; Kang, S.J.; Park, S.; Oh, T.K. Devosia insulae sp. nov., isolated from soil, and emended description of the genus Devosia. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 1310–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, D.J.; Chen, X.G.; Xiang, H.Y.; Ouyang, L.; Yang, B. Isolation, identification and characterization of a microcystin-degrading bacterium Paucibacter sp. strain CH. Huan Jing Ke Xue Huanjing Kexue 2014, 35, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pheng, S.; Lee, J.J.; Eom, M.K.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, S.G. Paucibacter oligotrophus sp. nov., isolated from fresh water, and emended description of the genus Paucibacter. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 2231–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapala, J.; Berg, K.A.; Lyra, C.; Niemi, R.M.; Manz, W.; Suomalainen, S.; Paulin, L.; Lahti, K. Paucibacter toxinivorans gen. nov., sp. nov., a bacterium that degrades cyclic cyanobacterial hepatotoxins microcystins and nodularin. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 1563–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Maseda, H.; Okano, K.; Kurashima, T.; Kawauchi, Y.; Xue, Q.; Utsumi, M.; Zhang, Z.; Sugiura, N. Enzymatic pathway for biodegrading microcystin LR in Sphingopyxis sp. C-1. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2012, 114, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Pan, G.; Yan, H. Microbial biodegradation of microcystin-RR by bacterium Sphingopyxis sp. USTB-05. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziga, D.; Wasylewski, M.; Wladyka, B.; Nybom, S.; Meriluoto, J. Microbial Degradation of Microcystins. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2013, 26, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, M.M.; Li, Z.; Effler, T.C.; Hauser, L.J.; Boyer, G.L.; Wilhelm, S.W.; Bertilsson, S. Comparative Metagenomics of Toxic Freshwater Cyanobacteria Bloom Communities on Two Continents. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mell, J.C.; Redfield, R.J. Natural Competence and the Evolution of DNA Uptake Specificity. J. Bacteriol. 2014, 196, 1471–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, R.K.; Jobling, M.G. Genetics. In Medical Microbiology, 4th ed.; Baron, S., Ed.; University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston: Galveston, TX, USA, 1996. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK7908/ (accessed on 14 May 2020).
- Briand, E.; Gugger, M.; François, J.C.; Bernard, C.; Humbert, J.F.; Quiblier, C. Temporal Variations in the Dynamics of Potentially Microcystin-Producing Strains in a Bloom-Forming Planktothrix agardhii (Cyanobacterium) Population. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 3839–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briand, E.; Yéprémian, C.; Humbert, J.F.; Quiblier, C. Competition between microcystin-and non-microcystin-producing Planktothrix agardhii (cyanobacteria) strains under different environmental conditions. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 3337–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, G.; Fastner, J.; Erhard, M.; Börner, T.; Dittmann, E. Microcystin Biosynthesis in Planktothrix: Genes, Evolution, and Manipulation. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyman, P.; Abedon, S.T. Chapter 7—Bacteriophage Host Range and Bacterial Resistance. In Advances in Applied Microbiology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010; Volume 70, pp. 217–248. Available online: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0065216410700071 (accessed on 1 June 2020).
- Martins, P.D.; Danczak, R.E.; Roux, S.; Frank, J.; Borton, M.A.; Wolfe, R.A.; Burris, M.N.; Wilkins, M.J. Viral and metabolic controls on high rates of microbial sulfur and carbon cycling in wetland ecosystems. Microbiome 2018, 6, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, D.L.; Lynch, K.H.; Stothard, P.; Dennis, J.J. The isolation and characterization of two Stenotrophomonas maltophilia bacteriophages capable of cross-taxonomic order infectivity. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, J.; Wijffels, R.H.; Smidt, H.; Sipkema, D. The effect of the algal microbiome on industrial production of microalgae. Microb. Biotechnol. 2018, 11, 806–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomon, P.S.; Janson, S.; Granéli, E. Molecular identification of bacteria associated with filaments of Nodularia spumigena and their effect on the cyanobacterial growth. Harmful Algae 2003, 2, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedouelle, H. Tyrosyl-tRNA Synthetases. Madame Curie Bioscience Database [Internet]. In Landes Bioscience; National Institutes of Health: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2013. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK6553/ (accessed on 17 May 2020).
- Learn, B.A.; Um, S.J.; Huang, L.; McMacken, R. Cryptic single-stranded-DNA binding activities of the phage λ P and Escherichia coli DnaC replication initiation proteins facilitate the transfer of E. coli DnaB helicase onto DNA. PNAS 1997, 94, 1154–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullerjahn, G.S.; McKay, R.M.; Davis, T.W.; Baker, D.B.; Boyer, G.L.; D’Anglada, L.V.; Doucette, G.J.; Ho, J.C.; Irwin, E.G.; Kling, C.L.; et al. Global solutions to regional problems: Collecting global expertise to address the problem of harmful cyanobacterial blooms. A Lake Erie case study. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, M.M.; Davis, T.W.; McKay, R.M.; Bullerjahn, G.S.; Krausfeldt, L.E.; Stough, J.M.; Neitzey, M.L.; Gilbert, N.E.; Boyer, G.L.; Johengen, T.H.; et al. Ecophysiological Examination of the Lake Erie Microcystis Bloom in 2014: Linkages between Biology and the Water Supply Shutdown of Toledo, OH. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6745–6755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda, Y.N.; Bhatt, P.; Ates, N.; Engel, B.A.; Simsek, H. Cyanophage-cyanobacterial interactions for sustainable aquatic environment. Environ. Res. 2023, 229, 115728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, C.R.; Pokrzywinski, K.L.; Waechter, C.; Rycroft, T.; Zhang, Y.; Aligata, A.; Kramer, M.; Lamsal, A. A Review of Cyanophage–Host Relationships: Highlighting Cyanophages as a Potential Cyanobacteria Control Strategy. Toxins 2022, 14, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jassim, S.A.A.; Limoges, R.G. Bacteriophage Biocontrol: Deployment in Aquatic Ecosystems. In Bacteriophages: Practical Applications for Nature’s Biocontrol; Jassim, S.A.A., Limoges, R.G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2017; pp. 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Ha, C.; Lee, S.; Kwon, J.; Cho, H.; Gorham, T.; Lee, J. Characterization of Cyanophages in Lake Erie: Interaction Mechanisms and Structural Damage of Toxic Cyanobacteria. Toxins 2019, 11, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.H.; Ha, K.; Lucas, M.C.; Joo, G.J.; Takamura, N. Changes in microcystin production by Microcystis aeruginosa exposed to phytoplanktivorous and omnivorous fish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2004, 68, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J. Planktothrix agardhii from Western Lake Erie, Ohio. Unpublished Data, 2016.
- Wommack, K.E.; Williamson, K.E.; Helton, R.R.; Bench, S.R.; Winget, D.M. Methods for the Isolation of Viruses from Environmental Samples. In Bacteriophages: Methods and Protocols; Clokie, M.R.J., Kropinski, A.M., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2009; Volume 1, pp. 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, S.W.; Carberry, M.J.; Eldridge, M.L.; Poorvin, L.; Saxton, M.A.; Doblin, M.A. Marine and Freshwater Cyanophages in a Laurentian Great Lake: Evidence from Infectivity Assays and Molecular Analyses of g20 Genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 4957–4963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haramoto, E.; Katayama, H.; Oguma, K.; Ohgaki, S. Application of Cation-Coated Filter Method to Detection of Noroviruses, Enteroviruses, Adenoviruses, and Torque Teno Viruses in the Tamagawa River in Japan. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 2403–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OSU Methods > Basic SEM Protocol|Campus Microscopy & Imaging Facility (CMIF) [Internet]. 2020. Available online: https://www.cmif.osu.edu/instruments-and-services/sem-sample-preparation (accessed on 5 May 2019).
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.M.; Luo, R.; Sadakane, K.; Lam, T.W. MEGAHIT: An ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de Bruijn graph. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieft, K.; Zhou, Z.; Anantharaman, K. VIBRANT: Automated recovery, annotation and curation of microbial viruses, and evaluation of virome function from genomic sequences. bioRxiv 2019, 855387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.D.; Li, F.; Kirton, E.; Thomas, A.; Egan, R.; An, H.; Wang, Z. MetaBAT 2: An adaptive binning algorithm for robust and efficient genome reconstruction from metagenome assemblies. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alneberg, J.; Bjarnason, B.S.; de Bruijn, I.; Schirmer, M.; Quick, J.; Ijaz, U.Z.; Lahti, L.; Loman, N.J.; Andersson, A.F.; Quince, C. Binning metagenomic contigs by coverage and composition. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 1144–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uritskiy, G.V.; DiRuggiero, J.; Taylor, J. MetaWRAP—A flexible pipeline for genome-resolved metagenomic data analysis. Microbiome 2018, 6, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, D.H.; Imelfort, M.; Skennerton, C.T.; Hugenholtz, P.; Tyson, G.W. CheckM: Assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaumeil, P.A.; Mussig, A.J.; Hugenholtz, P.; Parks, D.H. GTDB-Tk: A toolkit to classify genomes with the Genome Taxonomy Database. Bioinformatics 2019, 36, 1925–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyatt, D.; Chen, G.L.; LoCascio, P.F.; Land, M.L.; Larimer, F.W.; Hauser, L.J. Prodigal: Prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aramaki, T.; Blanc-Mathieu, R.; Endo, H.; Ohkubo, K.; Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S.; Ogata, H. KofamKOALA: KEGG Ortholog assignment based on profile HMM and adaptive score threshold. Bioinformatics 2019, 36, 2251–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, E.D.; Heidelberg, J.F.; Tully, B.J. Potential for primary productivity in a globally-distributed bacterial phototroph. ISME J. 2018, 12, 1861–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlgren, N.A.; Ren, J.; Lu, Y.Y.; Fuhrman, J.A.; Sun, F. Alignment-free |d∗2| oligonucleotide frequency dissimilarity measure improves prediction of hosts from metagenomically-derived viral sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 45, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiez, C.; Siebert, M.; Enault, F.; Vincent, J.; Söding, J. WIsH: Who is the host? Predicting prokaryotic hosts from metagenomic phage contigs. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3113–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhou, F.; Gan, R.; Ren, C.; Jia, Y.; Yu, L.; Huang, Z. PHISDetector: A web tool to detect diverse in silico phage-host interaction signals. bioRxiv 2019, 661074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veltri, D.; Wight, M.M.; Crouch, J.A. SimpleSynteny: A web-based tool for visualization of microsynteny across multiple species. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W41–W45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassambara, A. rstatix: Pipe-Friendly Framework for Basic Statistical Tests. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=rstatix (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Kassambara, A. ggpubr: “ggplot2” Based Publication Ready Plots. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=ggpubr (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Available online: https://ggplot2.tidyverse.org (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Wickham, H. tidyverse: Easily Install and Load the “Tidyverse”. 2017. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=tidyverse (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Passalacqua, K.D.; Charbonneau, M.-E.; O’rIordan, M.X.; Kudva, I.T.; Cornick, N.A. Bacterial Metabolism Shapes the Host–Pathogen Interface. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 15–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhams, G.H.; Armitage, J.P. Making sense of it all: Bacterial chemotaxis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 1024–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayton, E.A.; Basta, N.T. Characterization of Drinking Water Treatment Residuals for Use as a Soil Substitute. Water Environ. Res. 2001, 73, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nriagu, J.O.; Kemp, A.L.W.; Wong, H.K.T.; Harper, N. Sedimentary record of heavy metal pollution in Lake Erie. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1979, 43, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoostal, M.J.; Bidart-Bouzat, M.G.; Bouzat, J.L. Local adaptation of microbial communities to heavy metal stress in polluted sediments of Lake Erie. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2008, 65, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benning, C.; Garavito, R.M.; Shimojima, M. Sulfolipid Biosynthesis and Function in Plants. In Sulfur Metabolism in Phototrophic Organisms; Hell, R., Dahl, C., Knaff, D., Leustek, T., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grotjohann, I.; Fromme, P. Structure of cyanobacterial Photosystem I. Photosynth. Res. 2005, 85, 51–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, E.R.; Mecsas, J. Bacterial Secretion Systems: An Overview. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, C.F.; Lima, S.; Tamagnini, P.; Oliveira, P. Chapter 18—Cyanobacterial Secretion Systems: Understanding Fundamental Mechanisms Toward Technological Applications. In Cyanobacteria; Mishra, A.K., Tiwari, D.N., Rai, A.N., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 359–381. Available online: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128146675000180 (accessed on 14 May 2020).
- Yao, M.; Henny, C.; Maresca, J.A. Freshwater Bacteria Release Methane as a By-Product of Phosphorus Acquisition. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 6994–7003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, D.B.; Confesor, R.; Ewing, D.E.; Johnson, L.T.; Kramer, J.W.; Merryfield, B.J. Phosphorus loading to Lake Erie from the Maumee, Sandusky and Cuyahoga rivers: The importance of bioavailability. J. Great Lakes Res. 2014, 40, 502–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kling, G.; Hayhoe, K.; Johnson, L.; Magnuson, J.; Polassky, S.; Robinson, S.K.; Shuter, B.J.; Wander, M.M.; Wuebbles, D.J.; Zak, D.R. Confronting Climate Change in the Great Lakes Region: Impacts on Our Communities and Ecosystems; Union of Concerned Scientists: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hýsková, V. Different Roles of β-N-Acetylhexosaminidase in Metabolism. Biochem. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Richlen, M.L.; Sehein, T.R.; Kulis, D.M.; Anderson, D.M.; Cai, Z. Microbial Community Structure and Associations During a Marine Dinoflagellate Bloom. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedl, J.; De Rosa, D.; Rowlings, D.W.; Grace, P.R.; Müller, C.; Scheer, C. Dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium (DNRA), not denitrification dominates nitrate reduction in subtropical pasture soils upon rewetting. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 125, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacin-Lizarbe, C.; Camarero, L.; Hallin, S.; Jones, C.M.; Cáliz, J.; Casamayor, E.O.; Catalan, J. The DNRA-Denitrification Dichotomy Differentiates Nitrogen Transformation Pathways in Mountain Lake Benthic Habitats. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Koç, C.; Kühner, P.; Stierhof, Y.-D.; Krismer, B.; Enright, M.C.; Penadés, J.R.; Wolz, C.; Stehle, T.; Cambillau, C.; et al. An essential role for the baseplate protein Gp45 in phage adsorption to Staphylococcus aureus. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.S.; Logger, L.; Spinelli, S.; Legrand, P.; Pham, T.T.H.; Trinh, T.T.N.; Cherrak, Y.; Zoued, A.; Desmyter, A.; Durand, E.; et al. Type VI secretion TssK baseplate protein exhibits structural similarity with phage receptor-binding proteins and evolved to bind the membrane complex. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 17103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.C.-H.; Krucinski, J.; Miercke, L.J.W.; Finer-Moore, J.S.; Tang, A.H.; Leavitt, A.D.; Stroud, R.M. Crystal structure of the HIV-1 integrase catalytic core and C-terminal domains: A model for viral DNA binding. PNAS 2000, 97, 8233–8238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Davis, A.B.; Evans, M.; McKindles, K.; Lee, J. Co-Occurrence of Toxic Bloom-Forming Cyanobacteria Planktothrix, Cyanophage, and Symbiotic Bacteria in Ohio Water Treatment Waste: Implications for Harmful Algal Bloom Management. Toxins 2025, 17, 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090450
Davis AB, Evans M, McKindles K, Lee J. Co-Occurrence of Toxic Bloom-Forming Cyanobacteria Planktothrix, Cyanophage, and Symbiotic Bacteria in Ohio Water Treatment Waste: Implications for Harmful Algal Bloom Management. Toxins. 2025; 17(9):450. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090450
Chicago/Turabian StyleDavis, Angela Brooke, Morgan Evans, Katelyn McKindles, and Jiyoung Lee. 2025. "Co-Occurrence of Toxic Bloom-Forming Cyanobacteria Planktothrix, Cyanophage, and Symbiotic Bacteria in Ohio Water Treatment Waste: Implications for Harmful Algal Bloom Management" Toxins 17, no. 9: 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090450
APA StyleDavis, A. B., Evans, M., McKindles, K., & Lee, J. (2025). Co-Occurrence of Toxic Bloom-Forming Cyanobacteria Planktothrix, Cyanophage, and Symbiotic Bacteria in Ohio Water Treatment Waste: Implications for Harmful Algal Bloom Management. Toxins, 17(9), 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090450




