Fumonisin Intake from Consumption of Wheat- and Corn-Based Products in Hungary
Abstract
1. Introduction
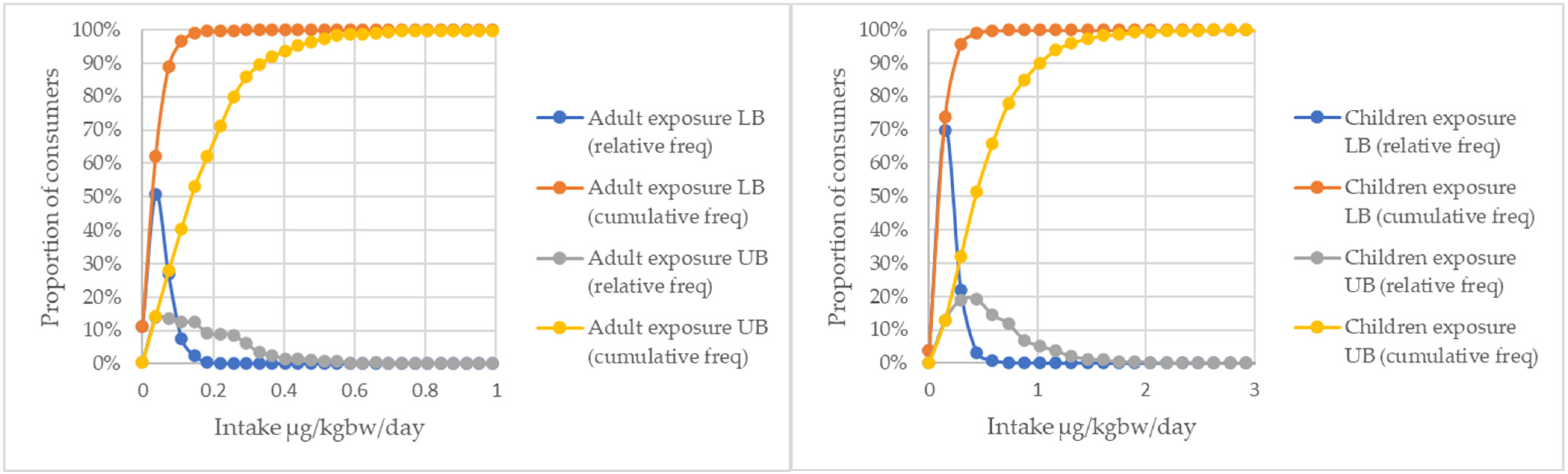
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Collection of Food Samples and Measurement of Mycotoxin Contamination
5.2. Food Consumption Data Collection
5.3. Estimation of Fumonisin Exposure
5.4. Estimation of Food Category Contributions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BW | body weight |
| DON | deoxynivalenol |
| EDI | estimated daily intake |
| EFS | European Food Safety Authority |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| ESI | electrospray ionisation |
| FB1 | fumonisin B1 |
| FB2 | fumonisin B2 |
| FUM | fumonisins |
| LB | lower bound |
| LC-MS | liquid chromatography mass spectrometry |
| LOD | limit of detection |
| LOQ | limit of quantification |
| MB | middle bound |
| NÉBIH | National Food Chain Safety Office of Hungary |
| TDI | tolerable daily intake |
| UB | upper bound |
| ZEN | zearalenone |
Appendix A
| Food Category | n | FB1 < LOD | LOD < FB1 <LOQ | LOQ < FB1 | FB1 Mean (mg/kg) | FB1 Median (mg/kg) | FB1 Max (mg/kg) | FB2 < LOD | LOD < FB2 <LOQ | LOQ < FB2 | FB2 Mean (mg/kg) | FB2 Median (mg/kg) | FB2 Max (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| corn flour | 124 | 26 | 48 | 50 | 0.270 | 0.181 | 1.463 | 84 | 24 | 7 | 0.359 | 0.342 | 0.731 |
| cornmeal | 122 | 60 | 33 | 29 | 0.308 | 0.152 | 1.959 | 90 | 8 | 6 | 0.300 | 0.263 | 0.577 |
| cornflakes | 124 | 80 | 32 | 12 | 0.127 | 0.106 | 0.460 | 100 | 2 | 1 | 0.027 | 0.027 | 0.027 |
| Canned corn | 78 | 74 | 3 | 1 | 0.197 | 0.197 | 0.197 | 73 | 2 | 0 | - | - | - |
| other corn-based products | 158 | 94 | 33 | 31 | 0.258 | 0.161 | 1.100 | 110 | 15 | 3 | 0.181 | 0.172 | 0.200 |
| brown rice | 70 | 67 | 2 | 1 | 0.388 | 0.388 | 0.388 | 69 | 1 | 0 | - | - | - |
| white rice | 76 | 73 | 2 | 1 | 0.557 | 0.557 | 0.557 | 75 | 0 | 1 | 0.275 | 0.275 | 0.275 |
| rice-based products | 67 | 61 | 5 | 1 | 0.144 | 0.144 | 0.144 | 66 | 1 | 0 | - | - | - |
| wheat-based products | 59 | 50 | 2 | 7 | 0.257 | 0.251 | 0.587 | 53 | 5 | 1 | 0.160 | 0.160 | 0.160 |
| fine wheat flour | 65 | 65 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | 65 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - |
| whole wheat flour | 61 | 60 | 1 | 0 | - | - | - | 61 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - |
| Food Category | LB Mean | LB Median | LB P95 | LB Min | LB Max | MB Mean | MB Median | MB P95 | MB Min | MB Max | UB Mean | UB Median | UB P95 | UB Min | UB Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| corn flour | 0.052 | 0 | 0.275 | 0 | 0.395 | 0.115 | 0.072 | 0.352 | 0.041 | 0.395 | 0.178 | 0.144 | 0.398 | 0.082 | 0.439 |
| cornmeal | 0.026 | 0 | 0.102 | 0 | 0.775 | 0.074 | 0.041 | 0.132 | 0.041 | 0.775 | 0.122 | 0.082 | 0.243 | 0.082 | 0.775 |
| cornflakes | 0.005 | 0 | 0.045 | 0 | 0.096 | 0.052 | 0.041 | 0.072 | 0.041 | 0.173 | 0.099 | 0.082 | 0.144 | 0.082 | 0.250 |
| canned corn | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.043 | 0.041 | 0.070 | 0.041 | 0.124 | 0.087 | 0.082 | 0.141 | 0.082 | 0.247 |
| other corn-based products | 0.040 | 0 | 0.219 | 0 | 0.731 | 0.091 | 0.041 | 0.296 | 0.041 | 0.731 | 0.141 | 0.082 | 0.373 | 0.082 | 0.731 |
| brown rice | 0.006 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.388 | 0.049 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.465 | 0.091 | 0.082 | 0.082 | 0.082 | 0.542 |
| white rice | 0.014 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.832 | 0.054 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.832 | 0.095 | 0.082 | 0.082 | 0.082 | 0.832 |
| rice-based products | 0.002 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.144 | 0.047 | 0.041 | 0.072 | 0.041 | 0.170 | 0.091 | 0.082 | 0.144 | 0.082 | 0.195 |
| wheat-based products | 0.033 | 0 | 0.268 | 0 | 0.747 | 0.077 | 0.041 | 0.345 | 0.041 | 0.747 | 0.122 | 0.082 | 0.422 | 0.082 | 0.747 |
| fine wheat flour | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.082 | 0.082 | 0.082 | 0.082 | 0.082 |
| whole wheat flour | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.042 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.072 | 0.083 | 0.082 | 0.082 | 0.082 | 0.144 |
| Food Category | LB Mean | LB Median | LB P95 | LB Min | LB Max | MB Mean | MB Median | MB P95 | MB Min | MB Max | UB Mean | UB Median | UB P95 | UB Min | UB Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| corn flour | 0.129 | 0 | 0.477 | 0 | 2.194 | 0.182 | 0.072 | 0.539 | 0.0155 | 2.194 | 0.236 | 0.144 | 0.616 | 0.031 | 2.194 |
| cornmeal | 0.088 | 0 | 0.598 | 0 | 2.371 | 0.132 | 0.0465 | 0.610 | 0.0155 | 2.371 | 0.176 | 0.093 | 0.621 | 0.031 | 2.371 |
| cornflakes | 0.012 | 0 | 0.108 | 0 | 0.460 | 0.056 | 0.041 | 0.142 | 0.0155 | 0.537 | 0.100 | 0.082 | 0.168 | 0.031 | 0.614 |
| canned corn | 0.003 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.197 | 0.045 | 0.041 | 0.072 | 0.0155 | 0.274 | 0.087 | 0.082 | 0.144 | 0.031 | 0.351 |
| other corn-based products | 0.054 | 0 | 0.364 | 0 | 1.100 | 0.098 | 0.041 | 0.439 | 0.0155 | 1.177 | 0.142 | 0.082 | 0.490 | 0.031 | 1.254 |
| brown rice | 0.006 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.388 | 0.048 | 0.041 | 0.055 | 0.041 | 0.465 | 0.090 | 0.082 | 0.110 | 0.082 | 0.542 |
| white rice | 0.011 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.832 | 0.052 | 0.041 | 0.046 | 0.041 | 0.832 | 0.094 | 0.082 | 0.091 | 0.082 | 0.832 |
| rice-based products | 0.002 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.144 | 0.046 | 0.041 | 0.072 | 0.041 | 0.170 | 0.090 | 0.082 | 0.144 | 0.082 | 0.195 |
| wheat-based products | 0.033 | 0 | 0.268 | 0 | 0.747 | 0.077 | 0.041 | 0.345 | 0.041 | 0.747 | 0.122 | 0.082 | 0.422 | 0.082 | 0.747 |
| fine wheat flour | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.082 | 0.082 | 0.082 | 0.082 | 0.082 |
| whole wheat flour | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.042 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.072 | 0.083 | 0.082 | 0.082 | 0.082 | 0.144 |
| LB (Adults) | MB (Adults) | UB (Adults) | LB (Children) | MB (Children) | UB (Children) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mean | 0.035 | 0.101 | 0.168 | 0.111 | 0.313 | 0.516 |
| median | 0.027 | 0.083 | 0.137 | 0.086 | 0.256 | 0.421 |
| standard deviation | 0.035 | 0.088 | 0.142 | 0.099 | 0.248 | 0.403 |
| P90 | 0.075 | 0.203 | 0.336 | 0.224 | 0.611 | 1.016 |
| P95 | 0.096 | 0.262 | 0.437 | 0.293 | 0.756 | 1.230 |
| P99 | 0.149 | 0.383 | 0.647 | 0.454 | 1.117 | 1.793 |
| maximum | 0.332 | 0.747 | 1.173 | 1.433 | 3.564 | 5.695 |
References
- Han, Z.; Nie, D.; Ediage, E.N.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, B.; Li, S.; On, S.L.W.; De Saeger, S.; Wu, A. Cumulative Health Risk Assessment of Co-Occurring Mycotoxins of Deoxynivalenol and Its Acetyl Derivatives in Wheat and Maize: Case Study, Shanghai, China. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 74, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battilani, P.; Rossi, V.; Giorni, P.; Pietri, A.; Gualla, A.; van der Fels-Klerx, H.J.; Booij, C.J.H.; Moretti, A.; Logrieco, A.; Miglietta, F.; et al. Modelling, Predicting and Mapping the Emergence of Aflatoxins in Cereals in the EU Due to Climate Change. EFSA Support. Publ. 2012, 9, 223E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kos, J.; Anić, M.; Radić, B.; Zadravec, M.; Janić Hajnal, E.; Pleadin, J. Climate Change—A Global Threat Resulting in Increasing Mycotoxin Occurrence. Foods 2023, 12, 2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Fels-Klerx, H.J. Evaluation of Performance of Predictive Models for Deoxynivalenol in Wheat. Risk Anal. 2014, 34, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-Sancho, G.; Sanchis, V.; Ramos, A.J.; Marín, S. Effect of Food Processing on Exposure Assessment Studies with Mycotoxins. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2013, 30, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meca, G.; Zhou, T.; Li, X.-Z.; Mañes, J. Beauvericin Degradation during Bread and Beer Making. Food Control 2013, 34, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tittlemier, S.A.; Roscoe, M.; Trelka, R.; Patrick, S.K.; Bamforth, J.M.; Gräfenhan, T.; Schlichting, L.; Fu, B.X. Fate of Moniliformin during Milling of Canadian Durum Wheat, Processing, and Cooking of Spaghetti. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2014, 94, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, A.; Marín, S.; Morales, H.; Ramos, A.J.; Sanchis, V. The Fate of Deoxynivalenol and Ochratoxin A during the Breadmaking Process, Effects of Sourdough Use and Bran Content. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 68, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R. Mycotoxins in Food: Occurrence, Health Implications, and Control Strategies-A Comprehensive Review. Toxicon 2024, 248, 108038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Anwar, F.; Ghazali, F.M. A Comprehensive Review of Mycotoxins: Toxicology, Detection, and Effective Mitigation Approaches. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabó, A.; Péter, M.; Balogh, G.; Török, Z.; Kóta, Z.; Vígh, L.; Ali, O.; Timár, B.; Kövér, G.; Nagy, T.; et al. Liver Lipidomics, Histology, Transcriptomics, and Clinical Chemistry of Rats Intraperitoneally Treated with Fumonisin B1 for 5 Days. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 24975–24996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Mycotoxins. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/mycotoxins (accessed on 10 August 2025).
- Habschied, K.; Kanižai Šarić, G.; Krstanović, V.; Mastanjević, K. Mycotoxins—Biomonitoring and Human Exposure. Toxins 2021, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anumudu, C.K.; Ekwueme, C.T.; Uhegwu, C.C.; Ejileugha, C.; Augustine, J.; Okolo, C.A.; Onyeaka, H. A Review of the Mycotoxin Family of Fumonisins, Their Biosynthesis, Metabolism, Methods of Detection and Effects on Humans and Animals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DSM-Firmenich. Dsm-Firmenich World Mycotoxin Survey 2024. Available online: https://www.dsm-firmenich.com/anh/products-and-services/tools/mycotoxin-contamination/mycotoxin-survey/mycotoxin-survey-report-q4-2024.html (accessed on 11 August 2025).
- DSM-Firmenich. Dsm-Firmenich World Mycotoxin Survey January to June 2025. Available online: https://www.dsm-firmenich.com/anh/news/downloads/whitepapers-and-reports/dsm-firmenich-world-mycotoxin-survey-january-to-june-2025.html (accessed on 11 August 2025).
- Agriopoulou, S.; Stamatelopoulou, E.; Varzakas, T. Advances in Occurrence, Importance, and Mycotoxin Control Strategies: Prevention and Detoxification in Foods. Foods 2020, 9, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brera, C.; Debegnach, F.; De Santis, B.; Di Ianni, S.; Gregori, E.; Neuhold, S.; Valitutti, F. Exposure Assessment to Mycotoxins in Gluten-Free Diet for Celiac Patients. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 69, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. Safety Evaluation of Certain Food Additives and Contaminants: Prepared by the Seventy Fourth Meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012; ISBN 978-92-4-166065-5.
- Van Egmond, H.P.; Schothorst, R.C.; Jonker, M.A. Regulations Relating to Mycotoxins in Food. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 389, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, F.; Peng, S.; Ou, Y.; He, B.; Li, Y.; Lin, Q. Effects of Artemisia Argyi Powder on Egg Quality, Antioxidant Capacity, and Intestinal Development of Roman Laying Hens. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 902568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheik Abdul, N.; Marnewick, J.L. Fumonisin B1-Induced Mitochondrial Toxicity and Hepatoprotective Potential of Rooibos: An Update. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2020, 40, 1602–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marnewick, J.L.; Rautenbach, F.; Venter, I.; Neethling, H.; Blackhurst, D.M.; Wolmarans, P.; Macharia, M. Effects of Rooibos (Aspalathus linearis) on Oxidative Stress and Biochemical Parameters in Adults at Risk for Cardiovascular Disease. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 133, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority; Knutsen, H.-K.; Barregård, L.; Bignami, M.; Brüschweiler, B.; Ceccatelli, S.; Cottrill, B.; Dinovi, M.; Edler, L.; Grasl-Kraupp, B.; et al. Appropriateness to Set a Group Health-Based Guidance Value for Fumonisins and Their Modified Forms. EFSA J. 2018, 16, e05172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brera, C.; de Santis, B.; Debegnach, F.; Miano, B.; Moretti, G.; Lanzone, A.; Del Sordo, G.; Buonsenso, D.; Chiaretti, A.; Hardie, L.; et al. Experimental Study of Deoxynivalenol Biomarkers in Urine. EFSA Support. Publ. 2015, 12, 818E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. Overview of the Procedures Currently Used at EFSA for the Assessment of Dietary Exposure to Different Chemical Substances. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. Scientific Opinion on the Risks for Public Health Related to the Presence of Zearalenone in Food. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. Risks to Human and Animal Health Related to the Presence of Deoxynivalenol and Its Acetylated and Modified Forms in Food and Feed|EFSA. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/pub/4718 (accessed on 11 August 2025).
- Zentai, A.; Szeitzné-Szabó, M.; Mihucz, G.; Szeli, N.; Szabó, A.; Kovács, M. Occurrence and Risk Assessment of Fumonisin B1 and B2 Mycotoxins in Maize-Based Food Products in Hungary. Toxins 2019, 11, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission Regulation—2023/915—EN—EUR-Lex. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2023/915/oj/eng (accessed on 11 August 2025).
- Li, Y.; He, X.; Sun, B.; Hu, N.; Li, J.; You, R.; Tao, F.; Fang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhai, Q. Combined Exposure of Beta-Cypermethrin and Emamectin Benzoate Interferes with the HPO Axis through Oxidative Stress, Causing an Imbalance of Hormone Homeostasis in Female Rats. Reprod. Toxicol. 2024, 123, 108502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Gao, B.; Li, J.; Xiang, Y.; Cao, L.; Zhao, M. Clinical Features, Diagnosis, and Management of COVID-19 Vaccine-Associated Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada Disease. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2023, 19, 2220630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, M.P.; Braun, H.-J. (Eds.) Wheat Improvement: Food Security in a Changing Climate; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; ISBN 978-3-030-90672-6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Jiang, D.; Zheng, F.; Chen, J.; Li, W. Fumonisins B1, B2 and B3 in Corn Products, Wheat Flour and Corn Oil Marketed in Shandong Province of China. Food Addit. Contam. Part B 2015, 8, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanković, S.; Lević, J.; Ivanović, D.; Krnjaja, V.; Stanković, G.; Tančić, S. Fumonisin B1 and Its Co-Occurrence with Other Fusariotoxins in Naturally-Contaminated Wheat Grain. Food Control 2012, 23, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DSM-Firmenich. 2021 Dsm-Firmenich World Mycotoxin Survey Report. Available online: https://www.dsm-firmenich.com/anh/news/downloads/whitepapers-and-reports/2021-dsm-world-mycotoxin-survey-report.html (accessed on 11 August 2025).
- DSM-Firmenich. Dsm-Firmenich World Mycotoxin Survey 2022 Report PDF. Available online: https://www.dsm-firmenich.com/anh/news/downloads/whitepapers-and-reports/dsm-world-mycotoxin-survey-2022-report.html (accessed on 11 August 2025).
- Vita Trace Nutrition. DSM-Firmenich “World Mycotoxin Survey 2023”. Available online: https://www.vitatrace.com/post/dsm-firmenich-world-mycotoxin-survey-2023 (accessed on 10 August 2025).
- Szabó-Fodor, J.; Szeitzné-Szabó, M.; Bóta, B.; Schieszl, T.; Angeli, C.; Gambacorta, L.; Solfrizzo, M.; Szabó, A.; Kovács, M. Assessment of Human Mycotoxin Exposure in Hungary by Urinary Biomarker Determination and the Uncertainties of the Exposure Calculation: A Case Study. Foods 2022, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblanc, J.-C.; Tard, A.; Volatier, J.-L.; Verger, P. Estimated Dietary Exposure to Principal Food Mycotoxins from The First French Total Diet Study. Food Addit. Contam. 2005, 22, 652–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirot, V.; Fremy, J.-M.; Leblanc, J.-C. Dietary Exposure to Mycotoxins and Health Risk Assessment in the Second French Total Diet Study. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 52, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprong, R.C.; de Wit-Bos, L.; Te Biesebeek, J.D.; Alewijn, M.; Lopez, P.; Mengelers, M.J.B. A Mycotoxin-Dedicated Total Diet Study in the Netherlands in 2013: Part III—Exposure and Risk Assessment. World Mycotoxin J. 2016, 9, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis, B.; Debegnach, F.; Toscano, P.; Crisci, A.; Battilani, P.; Brera, C. Overall Exposure of European Adult Population to Mycotoxins by Statistically Modelled Biomonitoring Data. Toxins 2021, 13, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerding, J.; Ali, N.; Schwartzbord, J.; Cramer, B.; Brown, D.L.; Degen, G.H.; Humpf, H.-U. A Comparative Study of the Human Urinary Mycotoxin Excretion Patterns in Bangladesh, Germany, and Haiti Using a Rapid and Sensitive LC-MS/MS Approach. Mycotoxin Res. 2015, 31, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuanny Franco, L.; Mousavi Khaneghah, A.; In Lee, S.H.; Fernandes Oliveira, C.A. Biomonitoring of Mycotoxin Exposure Using Urinary Biomarker Approaches: A Review. Toxin Rev. 2021, 40, 383–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deressa, T.; Adugna, G.; Suresh, L.M.; Bekeko, Z.; Opoku, J.; Vaughan, M.; Proctor, R.H.; Busman, M.; Burgueño, J.; Prasanna, B.M. Biophysical Factors and Agronomic Practices Associated with Fusarium Ear Rot and Fumonisin Contamination of Maize in Multiple Agroecosystems in Ethiopia. Crop Sci. 2024, 64, 827–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, M.; Cavero, J.; Franco-Luesma, S.; Álvaro-Fuentes, J.; Ariño, A.; Lorán, S. Mycotoxins and Crop Yield in Maize as Affected by Irrigation Management and Tillage Practices. Agronomy 2023, 13, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Xue, K.S.; Su, X.; Qu, H.; Duan, X.; Jiang, Y. The Occurrence and Management of Fumonisin Contamination across the Food Production and Supply Chains. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 60, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeters, G.; Rosa, L.; Kolossa, M.; Barouki, R.; Tarroja, E.; Uhl, M.; Klanova, J.; Melymuk, L.; Horvat, M.; Bocca, B.; et al. HBM4EU—Scoping Documents for 2021 for the First and Second Round HBM4EU Priority Substances; Deliverable Report D4.9; German Environment Agency (UBA): Dessau-Roßlau, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Alvito, P.; Assunção, R.M.; Bajard, L.; Martins, C.; Mengelers, M.J.B.; Mol, H.; Namorado, S.; van den Brand, A.D.; Vasco, E.; Viegas, S.; et al. Current Advances, Research Needs and Gaps in Mycotoxins Biomonitoring under the HBM4EU—Lessons Learned and Future Trends. Toxins 2022, 14, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Food Category | n | FB1 < LOD | LOD < FB1 < LOQ | LOQ < FB1 | FB1 Mean (mg/kg) | FB1 Median (mg/kg) | FB1 Max (mg/kg) | FB2 < LOD | LOD < FB2 < LOQ | LOQ < FB2 | FB2 Mean (mg/kg) | FB2 Median (mg/kg) | FB2 Max (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| corn flour | 60 | 14 | 29 | 17 | 0.175 | 0.162 | 0.285 | 45 | 14 | 1 | 0.128 | 0.128 | 0.128 |
| cornmeal | 60 | 42 | 15 | 3 | 0.405 | 0.517 | 0.59 | 57 | 1 | 2 | 0.175 | 0.175 | 0.185 |
| cornflakes | 60 | 43 | 13 | 4 | 0.063 | 0.056 | 0.096 | 58 | 1 | 1 | 0.027 | 0.027 | 0.027 |
| canned corn | 60 | 57 | 3 | 0 | - | - | - | 59 | 1 | 0 | - | - | - |
| other corn-based products | 73 | 46 | 13 | 14 | 0.197 | 0.148 | 0.531 | 62 | 10 | 1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| brown rice | 60 | 58 | 1 | 1 | 0.388 | 0.388 | 0.388 | 59 | 1 | 0 | - | - | - |
| white rice | 60 | 59 | 0 | 1 | 0.557 | 0.557 | 0.557 | 59 | 0 | 1 | 0.275 | 0.275 | 0.275 |
| rice-based products | 60 | 54 | 5 | 1 | 0.144 | 0.144 | 0.144 | 59 | 1 | 0 | - | - | - |
| wheat-based products | 59 | 50 | 2 | 7 | 0.257 | 0.251 | 0.587 | 53 | 5 | 1 | 0.160 | 0.160 | 0.160 |
| fine wheat flour | 65 | 65 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | 65 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - |
| whole wheat flour | 60 | 59 | 1 | 0 | - | - | - | 60 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - |
| Food Category | LB Mean | LB Max | MB Mean | MB Max | UB Mean | UB Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| corn flour | 0.052 | 0.395 | 0.115 | 0.395 | 0.178 | 0.439 |
| cornmeal | 0.026 | 0.775 | 0.074 | 0.775 | 0.122 | 0.775 |
| cornflakes | 0.005 | 0.096 | 0.052 | 0.173 | 0.099 | 0.250 |
| canned corn | 0 | 0 | 0.043 | 0.124 | 0.087 | 0.247 |
| other corn-based products | 0.040 | 0.731 | 0.091 | 0.731 | 0.141 | 0.731 |
| brown rice | 0.006 | 0.388 | 0.049 | 0.465 | 0.091 | 0.542 |
| white rice | 0.014 | 0.832 | 0.054 | 0.832 | 0.095 | 0.832 |
| rice-based products | 0.002 | 0.144 | 0.047 | 0.170 | 0.091 | 0.195 |
| wheat-based products | 0.033 | 0.747 | 0.077 | 0.747 | 0.122 | 0.747 |
| fine wheat flour | 0 | 0 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.082 | 0.082 |
| whole wheat flour | 0 | 0 | 0.042 | 0.072 | 0.083 | 0.144 |
| LB (Adults) | MB (Adults) | UB (Adults) | LB (Children) | MB (Children) | UB (Children) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mean | 0.035 | 0.101 | 0.168 | 0.109 | 0.313 | 0.516 |
| median | 0.028 | 0.083 | 0.137 | 0.086 | 0.256 | 0.422 |
| standard deviation | 0.034 | 0.087 | 0.142 | 0.095 | 0.247 | 0.403 |
| P90 | 0.075 | 0.204 | 0.336 | 0.219 | 0.614 | 1.017 |
| P95 | 0.096 | 0.258 | 0.433 | 0.280 | 0.744 | 1.230 |
| P99 | 0.144 | 0.381 | 0.634 | 0.444 | 1.112 | 1.793 |
| maximum | 0.321 | 0.747 | 1.173 | 1.425 | 3.560 | 5.694 |
| Food Category | P50 (Adults) | P90 (Adults) | P95 (Adults) | P99 (Adults) | P50 (Children) | P90 (Children) | P95 (Children) | P99 (Children) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| corn flour | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| cornmeal | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 |
| cornflakes | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.6 |
| canned corn | 1.3 | 2.1 | 2.8 | 2.9 | 1.4 | 2.5 | 2.7 | 3.0 |
| other corn-based products | 1.2 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 4.5 | 4.8 | 5.5 | 5.7 |
| brown rice | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| white rice | 17.3 | 15.7 | 15.1 | 14.7 | 13.4 | 14.7 | 14.8 | 14.6 |
| rice-based products | 0.7 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 1.0 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| wheat-based products | 56.2 | 64.2 | 64.9 | 65.4 | 62.7 | 63.3 | 62.7 | 62.8 |
| fine wheat flour | 21.5 | 15.0 | 14.4 | 13.8 | 16.1 | 12.7 | 12.2 | 11.8 |
| whole wheat flour | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Food Category in the Present Study | Food Consumption Data Obtained from the Survey |
|---|---|
| corn flour | “corn flour” |
| cornmeal | “cornmeal” |
| cornflakes | “cornflakes” |
| canned corn | “corn, fresh”, “corn, frozen”, “corn, canned” |
| other corn-based products | “corn chips”, “starch, corn starch”, “corn, for popping”, “corn, popped, without oil”, “corn, popped, with oil”, “corn, popped, cheese flavoured”, “corn, flakes, extruded, natural”, “oil, corn oil”, “puffy, extruded corn flakes, salty”, “nachos tortilla chips” |
| brown rice | “rice, brown rice” |
| white rice | “rice, polished”, “rice, unpolished”, “rice, semi-polished”, “flour, rice flour” |
| rice-based products | “rice chips”, “baby biscuits, organic mini rice cakes”, “cereal porridge, organic natural rice flakes”, “rice, puffed”, “rice, puffed, with paprika”, “rice, puffed, enriched with vitamins and minerals” |
| wheat-based products | “bread roll”, “bread roll, with grain, rye”, “bread roll, with sesame seeds”, “crescent roll”, “dry pasta”, “dry pasta, gluten-free”, “flat dough”, “puff pastry”, “breadcrumbs”, “yeast dough”, “sweet bread”, “muesli, organic baby muesli”, “muesli, fruit muesli”, “muesli, raspberry-strawberry flavour with banana”, “muesli, organic fruit muesli dessert”, “muesli bar, with chocolate”, “muesli bar, fruity”, “muesli bar, fruity, enriched with calcium”, “salty breadstick”, “choux pastry”, “shortcrust pastry”, “bulgur”, “wheat, germ”, “wheat, semolina”, “wheat, bran”, “seitan”, “hamlet, wheat”, “tortilla, wheat” |
| fine wheat flour | “flour, wheat flour bl 55”, “flour, wheat flour bl 65”, “flour, durum flour”, “flour, spelt flour” |
| whole wheat flour | “flour, wheat, whole grain”, “flour, Graham flour bl 96” |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schieszl, T.; Jozwiak, Á.; Süth, M.; Nemes, I.; Kovács, M.; Zentai, A. Fumonisin Intake from Consumption of Wheat- and Corn-Based Products in Hungary. Toxins 2025, 17, 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17120566
Schieszl T, Jozwiak Á, Süth M, Nemes I, Kovács M, Zentai A. Fumonisin Intake from Consumption of Wheat- and Corn-Based Products in Hungary. Toxins. 2025; 17(12):566. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17120566
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchieszl, Tamás, Ákos Jozwiak, Miklós Süth, Imre Nemes, Melinda Kovács, and Andrea Zentai. 2025. "Fumonisin Intake from Consumption of Wheat- and Corn-Based Products in Hungary" Toxins 17, no. 12: 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17120566
APA StyleSchieszl, T., Jozwiak, Á., Süth, M., Nemes, I., Kovács, M., & Zentai, A. (2025). Fumonisin Intake from Consumption of Wheat- and Corn-Based Products in Hungary. Toxins, 17(12), 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17120566





