Statistical Inferences Applying Non-Parametric Data on Cyanobacterial Investigations: Contributions to Water Quality and New Trends under Global Changes on Portuguese Freshwater Ecosystems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Air Temperature
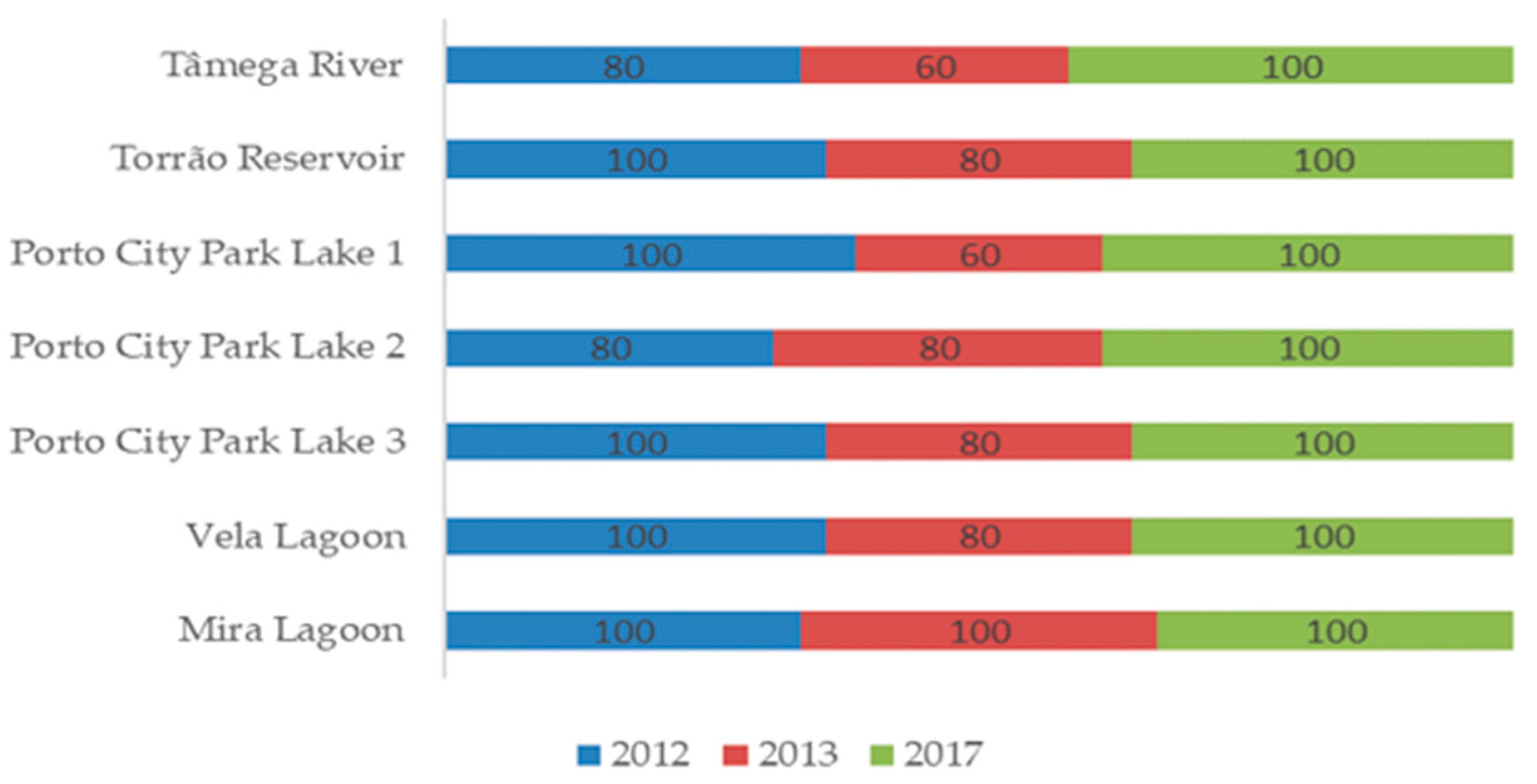
2.2. Bloom Occurrence
2.3. Isolation
2.4. M. aeruginosa
2.5. R. raciborskii
2.6. P. agardhii
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Sampling
5.2. Sample Processing
5.3. Isolation and Culturing
5.4. DNA Extraction
5.5. PCR Amplification
5.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bekker, A.; Holland, H.D.; Wang, P.-L.; Rumble, D.; Stein, H.J.; Hannah, J.L.; Coetzee, L.L.; Beukes, N.J. Dating the rise of atmospheric oxygen. Nature 2004, 427, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirrmeister, B.E.; de Vos, J.M.; Antonelli, A.; Bagheri, H.C. Evolution of multicellularity coincided with increased diversification of cyanobacteria and the Great Oxidation Event. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 1791–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Herfindal, L.; Jokela, J.; Shishido, T.; Wahlsten, M.; Døskeland, S.; Sivonen, K. Cyanobacteria from Terrestrial and Marine Sources Contain Apoptogens Able to Overcome Chemoresistance in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 2036–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falconer, I.R.; Humpage, A.R. Health risk assessment of cyanobacterial (blue-green algal) toxins in drinking water. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2005, 2, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, W.W. Health Effects of Toxin-Producing Cyanobacteria: “The CyanoHABs”. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. An Int. J. 2001, 7, 1393–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, P.A.; Banack, S.A.; Murch, S.J.; Rasmussen, U.; Tien, G.; Bidigare, R.R.; Metcalf, J.S.; Morrison, L.F.; Codd, G.A.; Bergman, B. Diverse taxa of cyanobacteria produce -N-methylamino-L-alanine, a neurotoxic amino acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 5074–5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmann, E.; Wiegand, C. Cyanobacterial toxins—Occurrence, biosynthesis and impact on human affairs. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2006, 50, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochimsen, E.M.; Carmichael, W.W.; An, J.; Cardo, D.M.; Cookson, S.T.; Holmes, C.E.M.; Antunes, M.B.; de Melo Filho, D.A.; Lyra, T.M.; Barreto, V.S.T.; et al. Liver Failure and Death after Exposure to Microcystins at a Hemodialysis Center in Brazil. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, P.R.; Runnegar, M.T.C.; Jackson, A.R.B.; Falconer, I.R. Severe hepatotoxicity caused by the tropical cyanobacterium (blue-green alga) Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Woloszynska) Seenaya and Subba Raju isolated from a domestic water supply reservoir. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1985, 50, 1292–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagos, N.; Onodera, H.; Zagatto, P.A.; Andrinolo, D.; Azevedo, S.M.F.Q.; Oshima, Y. The first evidence of paralytic shellfish toxins in the freshwater cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii, isolated from Brazil. Toxicon 1999, 37, 1359–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmann, E.; Neilan, B.A.; Borner, T. Molecular biology of peptide and polyketide biosynthesis in cyanobacteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 57, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bonilla, S.; Aubriot, L.; Soares, M.C.S.; González-Piana, M.; Fabre, A.; Huszar, V.L.M.; Lürling, M.; Antoniades, D.; Padisák, J.; Kruk, C. What drives the distribution of the bloom-forming cyanobacteria Planktothrix agardhii and Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii? FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 79, 594–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, K.M.; Schembri, M.A.; Baker, P.D.; Saint, C.P. Molecular Characterization of the Toxic Cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii and Design of a Species-Specific PCR. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, Y.; Kasai, F.; Watanabe, M.M. Multilocus sequence typing (MLST) reveals high genetic diversity and clonal population structure of the toxic cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Microbiology 2007, 153, 3695–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Churro, C.; Pereira, P.; Vasconcelos, V.; Valério, E. Species-specific real-time PCR cell number quantification of the bloom-forming cyanobacterium Planktothrix agardhii. Arch. Microbiol. 2012, 194, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, V. Cyanobacteria toxins: Diversity and Ecological Effects. Limnetica 2001, 20, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano, S. Toxicity Risks Linked to Cyanobacteria Blooms in Southern Portugal Reservoirs. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Algarve, Faro, Portugal, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, J.P.; Gibbs, P.D.L.; Schmale, M.C.; Saker, M.L. Toxicity of cylindrospermopsin, and other apparent metabolites from Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii and Aphanizomenon ovalisporum, to the zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryo. Toxicon 2009, 53, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churro, C.; Azevedo, J.; Vasconcelos, V.; Silva, A. Detection of a Planktothrix agardhii Bloom in Portuguese Marine Coastal Waters. Toxins 2017, 9, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, C.; Vasconcelos, V.; Antunes, A. Genetic characterization of Microcystis aeruginosa isolates from Portuguese freshwater systems. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 32, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gremberghe, I.; Leliaert, F.; Mergeay, J.; Vanormelingen, P.; Van der Gucht, K.; Debeer, A.-E.; Lacerot, G.; De Meester, L.; Vyverman, W. Lack of Phylogeographic Structure in the Freshwater Cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa Suggests Global Dispersal. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, C.; Mendes, R.; Azevedo, J.; Vasconcelos, V.; Antunes, A. First occurrence of cylindrospermopsin in Portugal: A contribution to its continuous global dispersal. Toxicon 2017, 130, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padisák, J. Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Woloszynska) Seenayya et Subba Raju, an expanding, highly adaptive cyanobacterium: Worldwide distribution and review of its ecology. Arch. Hydrobiol. Suppl. Monogr. Beitr. 1997, 107, 563–593. [Google Scholar]
- Gugger, M.; Molica, R.; Le Berre, B.; Dufour, P.; Bernard, C.; Humbert, J.-F. Genetic Diversity of Cylindrospermopsis Strains (Cyanobacteria) Isolated from Four Continents. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 1097–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais, J. Avaliação do Risco de Ocorrência de Cianobactérias Tóxicas nos Lagos do Parque da Cidade do Porto. Master’s Thesis, University of Porto, Porto, Portugal, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kokociński, M.; Stefaniak, K.; Mankiewicz-Boczek, J.; Izydorczyk, K.; Soininen, J. The ecology of the invasive cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Nostocales, Cyanophyta) in two hypereutrophic lakes dominated by Planktothrix agardhii (Oscillatoriales, Cyanophyta). Eur. J. Phycol. 2010, 45, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellappa, N.; Borba, J.; Rocha, O. Phytoplankton community and physical-chemical characteristics of water in the public reservoir of Cruzeta, RN, Brazil. Braz. J. Biol. 2008, 68, 477–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotai, J. Instructions for preparation of modified nutrient solution Z8 for algae. Nor. Inst. Water Res. Oslo 1972, 11, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Neilan, B.A.; Jacobs, D.; Therese, D.D.; Blackall, L.L.; Hawkins, P.R.; Cox, P.T.; Goodman, A.E. rRNA Sequences and Evolutionary Relationships among Toxic and Nontoxic Cyanobacteria of the Genus Microcystis. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1997, 47, 693–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungblut, A.-D.; Hawes, I.; Mountfort, D.; Hitzfeld, B.; Dietrich, D.R.; Burns, B.P.; Neilan, B.A. Diversity within cyanobacterial mat communities in variable salinity meltwater ponds of McMurdo Ice Shelf, Antarctica. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisbergues, M.; Christiansen, G.; Rouhiainen, L.; Sivonen, K.; Börner, T. PCR-based identification of microcystin-producing genotypes of different cyanobacterial genera. Arch. Microbiol. 2003, 180, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Analysis of Deviance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. aeruginosa | Factor | χ2 | df | p |
| Year | 12.38 | 2 | <0.01 | |
| Region | 3.58 | 1 | 0.059 | |
| Rescaled model coefficients for Year: Intercept (2012) = 0.97; 2013 = 0.30; 2017 = 1 | ||||
| R. raciborskii | Year | 21.55 | 2 | <0.001 |
| Region | 0.81 | 1 | 0.37 | |
| Rescaled model coefficients for Year: Intercept (2012) = 0.54; 2013 = 0.033; 2017 = 0.38 | ||||
| P. agardhii | Year | 0.16 | 2 | 0.92 |
| Region | 1.83 | 1 | 0.18 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moreira, C.; Matos, A.; Barreiro, A.; Gomes, C.; Vasconcelos, V.; Antunes, A. Statistical Inferences Applying Non-Parametric Data on Cyanobacterial Investigations: Contributions to Water Quality and New Trends under Global Changes on Portuguese Freshwater Ecosystems. Toxins 2022, 14, 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14090638
Moreira C, Matos A, Barreiro A, Gomes C, Vasconcelos V, Antunes A. Statistical Inferences Applying Non-Parametric Data on Cyanobacterial Investigations: Contributions to Water Quality and New Trends under Global Changes on Portuguese Freshwater Ecosystems. Toxins. 2022; 14(9):638. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14090638
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoreira, Cristiana, Ana Matos, Aldo Barreiro, Cidália Gomes, Vitor Vasconcelos, and Agostinho Antunes. 2022. "Statistical Inferences Applying Non-Parametric Data on Cyanobacterial Investigations: Contributions to Water Quality and New Trends under Global Changes on Portuguese Freshwater Ecosystems" Toxins 14, no. 9: 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14090638
APA StyleMoreira, C., Matos, A., Barreiro, A., Gomes, C., Vasconcelos, V., & Antunes, A. (2022). Statistical Inferences Applying Non-Parametric Data on Cyanobacterial Investigations: Contributions to Water Quality and New Trends under Global Changes on Portuguese Freshwater Ecosystems. Toxins, 14(9), 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14090638







