Clinical Studies of Bee Venom Acupuncture for Lower Back Pain in the Korean Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
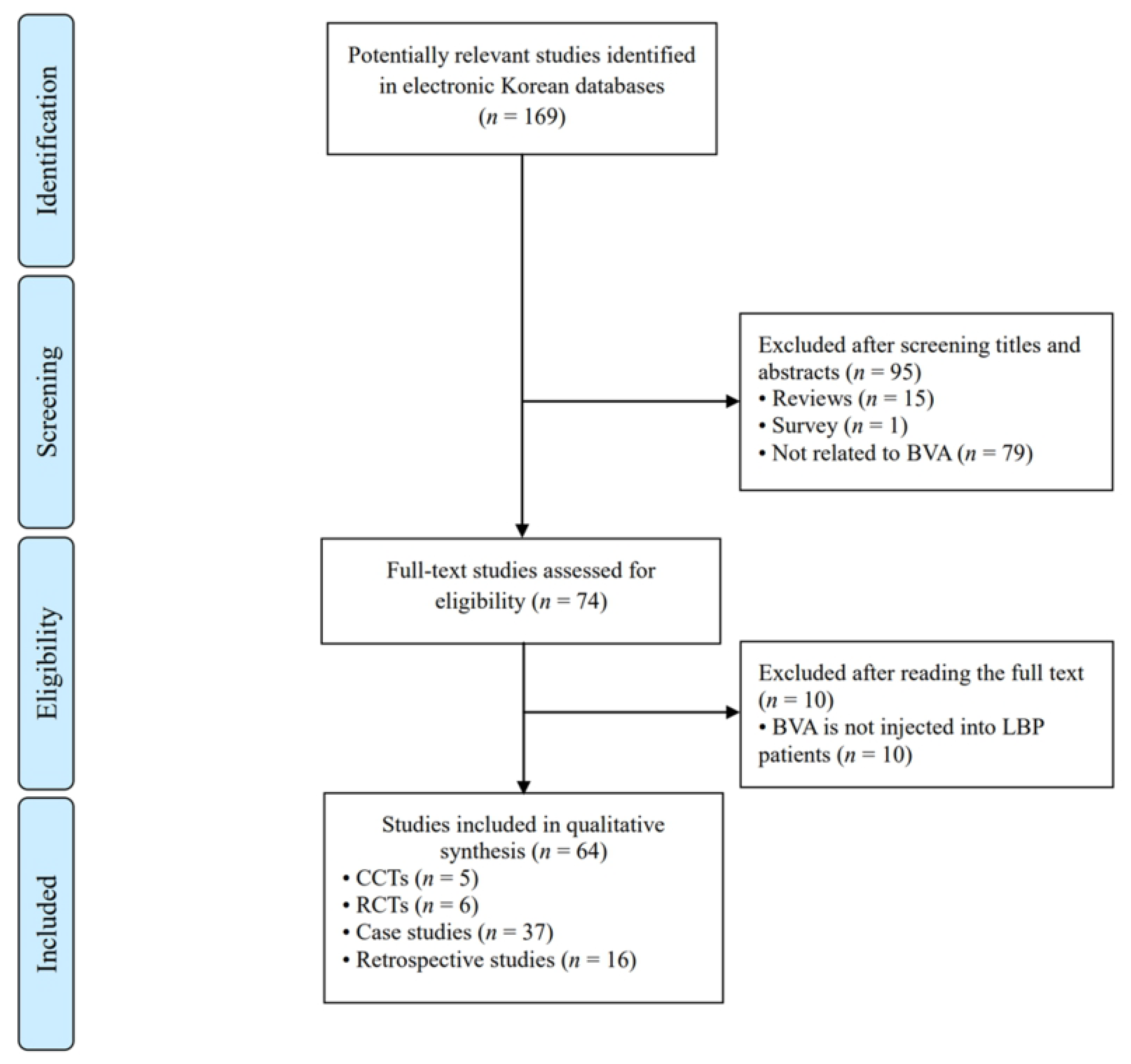
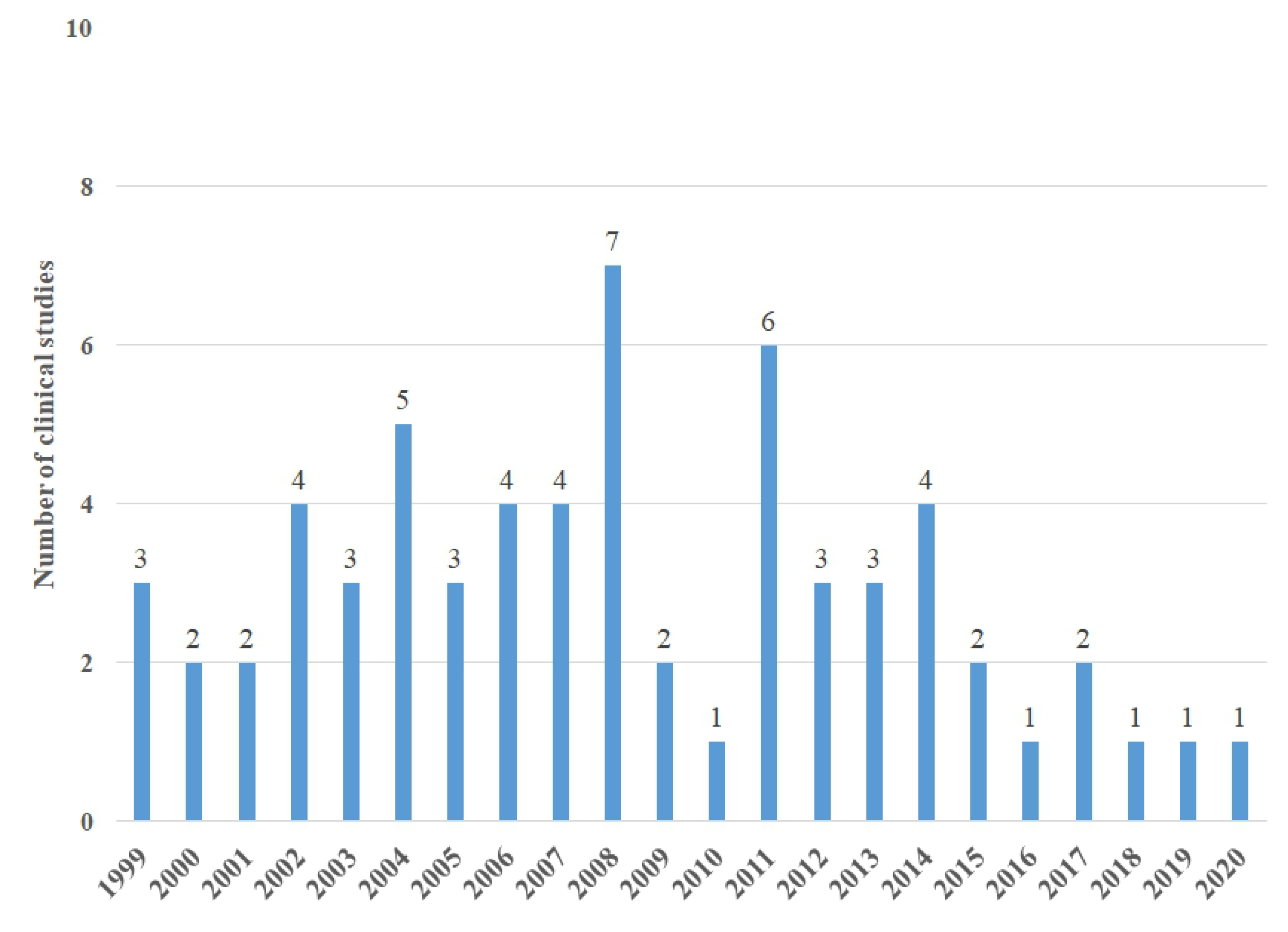
2.1. Study Description
2.2. Medical Conditions
2.3. Sample Size
2.4. BVA Intervention
2.5. Outcome Measures
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Data Sources and Searches
5.2. Study Selection
5.3. Data Extraction
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, D.H.; Han, S.R.; Choi, C.Y.; Sohn, M.J.; Lee, C.H. Efficacy of pulsed radiofrequency medial branch treatment in low back pain patients. J. Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2016, 29, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balagué, F.; Mannion, A.F.; Pellisé, F.; Cedraschi, C. Non-specific low back pain. Lancet 2012, 379, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, C.; Underwood, M.; Buchbinder, R. Non-specific low back pain. Lancet 2017, 389, 736–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; March, L.; Zheng, X.; Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Blyth, F.M.; Smith, E.; Buchbinder, R.; Hoy, D. Global low back pain prevalence and years lived with disability from 1990 to 2017: Estimates from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, G.E. Low back pain. Bull. World Health Organ. 2003, 81, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Manchikanti, L.; Singh, V.; Falco, F.J.; Benyamin, R.M.; Hirsch, J.A. Epidemiology of low back pain in adults. Neuromodulation 2014, 17 (Suppl. 2), 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, C.B.; Maher, C.G.; Pinto, R.Z.; Traeger, A.C.; Lin, C.C.; Chenot, J.F.; van Tulder, M.; Koes, B.W. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of non-specific low back pain in primary care: An updated overview. Eur. Spine J. 2018, 27, 2791–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roelofs, P.D.; Deyo, R.A.; Koes, B.W.; Scholten, R.J.; van Tulder, M.W. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for low back pain: An updated Cochrane review. Spine 2008, 33, 1766–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vonkeman, H.E.; van de Laar, M.A. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Adverse effects and their prevention. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 39, 294–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghildayal, N.; Johnson, P.J.; Evans, R.L.; Kreitzer, M.J. Complementary and alternative medicine use in the US adult low back pain population. Glob. Adv. Health Med. 2016, 5, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Jun, H.; Chae, Y.; Park, H.J.; Kim, B.H.; Chang, I.M.; Kang, S.K.; Lee, H.J. The practice of Korean medicine: An overview of clinical trials in acupuncture. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2005, 2, 325–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, D.; Lee, J.; Lee, Y.; Song, H.; Lee, C.; Hong, J. Therapeutic application of anti-arthritis, pain-releasing, and anti-cancer effects of bee venom and its constituent compounds. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 115, 246–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korea Pharmacopuncture Institute. Pharmacopuncturology, 3rd ed.; Hanmi Medical Publishing Co.: Seoul, Korea, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Health and Welfare; National Development Institute of Korean Medicine; Gallup Korea. 2020 Years National Survey for Traditional Korean Medicine (TKM) Usage; National Development Institute of Korean Medicine: Seoul, Korea, 2021; Available online: https://www.koms.or.kr/board/researchReport/view.do?post_no=185&menu_no=21 (accessed on 20 July 2022).
- Yook, T.H.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, S.H.; Jang, B.H.; Park, J.E.; Yoon, J.M. Institutionalization of Pharmacopuncture; Korea Pharmacopuncture Institute: Seoul, Korea, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, B.K.; Han, K.; Kwon, O.; Jo, D.J.; Lee, J.H. Efficacy of bee venom acupuncture for chronic low back pain: A randomized, double-blinded, sham-controlled trial. Toxins 2017, 9, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, B.-C.; Kong., J.C.; Park, T.-Y.; Yang, C.-Y.; Kang, K.-W.; Choi, S.-M. Bee venom acupuncture for chronic low back pain: A randomised, sham-controlled, triple-blind clinical trial. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2012, 4, e271–e280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Pittler, M.H.; Shin, B.C.; Kong, J.C.; Ernst, E. Bee venom acupuncture for musculoskeletal pain: A review. J. Pain 2008, 9, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.K.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, M.S.; Kim, J.I.; Wieland, L.S.; Shin, B.C. Randomized controlled trials on complementary and traditional medicine in the Korean literature. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2014, 2014, 194047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egger, M.; Zellweger-Zähner, T.; Schneider, M.; Junker, C.; Lengeler, C.; Antes, G. Language bias in randomised controlled trials published in English and German. Lancet 1997, 350, 326–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.C. Clinical study of Oriental medicine treatment with bee venom therapy of the extrusion type of herniated disc patient. J. Korea Acupunct. Moxibution Soc. 1999, 16, 285–293. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.D. Assessment of bee-venom acupuncture effect on herniated disc patients by rating scale. J. Korean Med. 1999, 20, 200–207. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.J.; Cho, M.R.; Kim, C.S. Clinical study on 100 patients of low back pain. J. Korea Acupunct. Moxibution Soc. 1999, 16, 119–135. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.C.; Cheon, M.N.; Yang, M.B. An experimental studies on the LFT, RFT of patients in Bee-venom Acupuncture. J. Korea Acupunct. Moxibution Soc. 2000, 17, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, H.S.; Park, D.S. A case of the bee venom herbal acupuncture for the patients with severe pain and sciatica due to HIVD of L-spine. J. Orient. Chr. Dis. 2000, 6, 144–149. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.I.; Lee, H.; Lee, B.C. Clinical studies on 20 cases of patient with bee venom acupuncture treatment. J. Heahwa Med. 2001, 10, 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.H.; Kim, C.H.; Seo, J.C.; Youn, H.M.; Jang, K.J.; Song, C.H.; Ahn, C.B. A case of the reduction of symptoms but no change on the CT scanning in HNP by Oriental Medical Treatment added Mori cortex-bee venom Acupuncture. J. Pharmacopunct. 2001, 4, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J.K.; Cho, G.C.; Park, Y.N.; Wang, W.H.; Jang, H.S. A clinical study on the patient of sequestrated disc treated by bee venom therapy-according to radiological change. J. Korean Acupunct. Moxibustion Soc. 2002, 19, 256–263. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, C.K.; An, C.S.; Kang, K.S.; Cho, A.R.; Kwon, K.R.; Kim, B.W. Clinical study on 1 case of Klippel-Trenaunay-Weber syndrome. J. Pharmacopunct. 2002, 5, 109–115. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, E.J.; Cho, H.Y.; Jin, J.D.; Shin, M.K.; Han, S.G.; Yang, G.Y.; Hwang, K.J.; Shin, Y.I.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, B.R. A Clinical study carried out common acupuncture therapy and Bee-Venom Acupuncture on HNP of L-spine. J. Korean Acupunct. Moxibustion Soc. 2002, 19, 54–64. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, I.R.; Choi, S.G.; Lim, H.J.; Seo, W.H. A clinical study on the case of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis(DISH) treated with traditional Korean Medicine, especially Korean bee-venom therapy. J. Korean Acupunct. Moxibustion Soc. 2002, 19, 225–233. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, H.J.; Hwang, O.; Kim, J.S.; Nam, S.S.; Kim, Y.S. Clinical evaluation of herniation of nucleus purposus patients treated by bee venom therapy. J. Korean Acupunct. Moxibustion Soc. 2003, 20, 36–72. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, W.S.; Lee, J.S.; Chung, S.H.; Kim, S.S. The effect of bee venom acupuncture on patient with herniation of nucleus pulposus of lumbar spine. J. Oriental. Rehab. Med. 2003, 13, 87–101. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, O.; Kim, J.S.; Jun, H.J.; Nam, S.S.; Kim, Y.S. Case report of spinal meningeal cyst patient treated with by bee venom therapy. J. Korean Acupunct. Moxibustion Soc. 2003, 20, 213–228. [Google Scholar]
- Cha, J.D.; Jung, S.M.; Kim, K.O.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, N.O. The comparision of effectiveness between acupuncture and its cotreatment with bee venom acua-acupuncture therapy on the treatment of herniation of nucleus pulpous. J. Korean Acupunct. Moxibustion Soc. 2004, 21, 149–158. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, G.M.; Lee, K.S.; Yeom, S.C.; Jang, J.H.; Yun, J.Y.; Hwang, B.C.; Kug, Y.S.; Jang, J.Y.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, Y.J.; et al. A clinical study of bee-venom acupuncture treatment on protrusion disc patients. J. Korean Acupunct. Moxibustion Soc. 2004, 20, 13–26. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.; Park, J.M.; Park, S.G.; Sim, W.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Shin, J.S. The effect of conservative treatment on Failed Back Surgery Syndrome. J. Oriental. Rehab. Med. 2004, 14, 149–159. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; So, K.S.; Choi, H.G.; Yeom, S.R.; Song, Y.S.; Kwon, Y.D. A case report on causalgia after lumbar partial laminectomy. J. Oriental. Rehab. Med. 2004, 14, 199–208. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, J.R.; Song, H.S. A clinical case study of the effect of bee-venom acupuncture on HNP. J. Korean Skelet. Jt. Med. 2004, 1, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.N.; Lim, J.A.; Lee, S.Y.; Yun, J.M.; Choi, S.Y.; Kim, H.H.; Kim, S.C.; Moon, H.C. A case of neurogenic bladder patient with lumbar disc herniation. J. Korean Acupunct. Moxibustion Soc. 2005, 4, 155–163. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.U.; Seo, B.M.; Yun, J.S.; Lee, Y.K.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, K.M.; Lim, S.C.; Seo, J.S.; Jung, T.Y.; Han, S.W. The comparison of bee venom herbal-acupuncture therapy between neighboring acupuncture points and neighboring-remote acupuncture points on the treatment of lumbar spine herniation of nucleus pulpous. J. Korean Acupunct. Moxibustion Soc. 2005, 22, 181–187. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.T.; Song, H.S. The effectiveness of bee venom acupuncture therapy on the treatment of sprain of L-Spine(a randomized controlled trial; double binding). J. Korean Acupunct. Moxibustion Soc. 2006, 22, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Rhee, S.H.; Cho, T.Y.; Jin, S.S.; Park, J.S.; Yeo, H.S.; Lim, H.H. The case report about herniation of inter-vertebral disc treated with bee venom acupuncture therapy. J. Korean Chuna Man. Med. Spine Nerves 2006, 1, 73–81. [Google Scholar]
- Cha, J.H.; Chang, S.Y.; Lee, T.H.; Owi, J.S.; Lee, E.U. The comparison of effectiveness between acupuncture and bee venom acupuncture on the treatment of acute lumbar herniation of intervertebral disc. J. Korean Acupunct. Moxibustion Soc. 2006, 9, 67–71. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.M.; Lee, J.Y.; Kwon, K.R.; Lee, H.S. Comparative study of acupuncture, bee venom acupuncture, and bee venom pharmacopuncture on the treatment of herniation of nucleus pulpous. J. Korean Acupunct. Moxibustion Soc. 2006, 23, 39–54. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, M.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Koh, D.H.; Song, W.S. The clinical report on 1 case of low back pain and radiational pain patient treated by Chuna traction and consevative treatment. J. Korean Chuna Man. Med. Spine Nerves 2006, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, G.J.; Lee, G.Y.; Jang, G.; Song, Y.K.; Lim, H.H. The case report of lumbar spinal stenosis treated with bee venom acupuncture therapy. J. Korean Chuna Man. Med. Spine Nerves 2007, 2, 49–57. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, T.H.; Chang, S.Y.; Chang, S.Y.; Cha, J.H.; Jung, K.H.; Lee, E.Y.; Roh, J.D. The comparison of effectiveness between bee venom and sweet bee venom therapy on low back pain with radiating pain. J. Pharmacopunct. 2007, 10, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.S.; Hong, K.E. Clinical study on 3 cases of HIVD patients treated by the Oriental medical conservative treatment. J. Korean Chuna Man. Med. Spine Nerves 2007, 2, 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H.; Kang, M.W.; Lee, S.Y. Effectiveness of bee-venom acupuncture and Ouhyul herbal acupuncture in herniation of nucleus pulposus-comparison with acupuncture therapy only. J. Korean Acupunct. Moxibustion Soc. 2007, 24, 197–205. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Jang, S.H.; Yoon, H.M.; Jang, K.J.; Ahn, C.B.; Kim, C.H.; Song, C.H.; Choi, H.N. The comparison of effectiveness between bee venom and sweet bee venom therapy on chronic lower back pain. J. Pharm. 2008, 11, 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, Y.D. Electrical acupuncture combined bee venom therapy for pain and disability induced intervertebral herniated disc of L-spine: A pilot study. Korean J. Orient. Physiol. Pathol. 2008, 22, 703–707. [Google Scholar]
- Youn, Y.S.; Park, W.S.; Ha, I.H.; Kim, J.W.; Kwon, H.J. A clinical study on the effect of Korean medical treatment for patients with lumbar disc herniation. J. Oriental. Rehab. Med. 2008, 18, 153–161. [Google Scholar]
- Youn, Y.S.; Lee, J.S.; Ha, I.H.; Kim, J.W.; Kwon, H.J. A comparative study with lumbar disc herniation under conservative treatment according to the duration. J. Oriental. Rehab. Med. 2008, 18, 135–145. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, H.C.; Lee, B.Y.; Lee, G.J.; Lim, H.H. The case report about Baastrup’s disease treated with conservative treatment. J. Oriental. Rehab. Med. 2008, 19, 201–210. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, S.M.; Park, C.K.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Sohn, S.C. The clinical study on effects of bee venom pharmacupuncture therapy in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis. J. Korean Acupunct. Moxibustion Soc. 2008, 25, 97–106. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.M.; Kim, Y.S.; Baek, Y.H.; Nam, S.S. The effects of acupuncture and bee-venom acupuncture on lumbar hypolordosis. J. Korean Acupunct. Moxibustion Soc. 2008, 25, 155–167. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, H.J.; Jeong, H.C.; Kim, H.J.; Park, Y.H.; Keum, D.H.; Lee, M.J. Clinical study for patients with lumbar disc herniation on change of magnetic resonance imaging after conservative treatment. J. Oriental. Rehab. Med. 2009, 19, 81–90. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, D.E.; Jung, I.M.; Yeom, S.R.; Kwon, Y.D. A clinical case of oriental medical treatment for the paraplegia after lumbar epidural nerve block. J. Oriental. Rehab. Med. 2009, 19, 219–228. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Min, K.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, S.J. The case report on 3 case of conservative treatment on failed back surgery syndrome. J. Korean Chuna Man. Med. Spine Nerves 2010, 5, 57–68. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.S.; Yang, K.Y.; Han, S.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Hwang, E.M. Effect of bee-venom acupuncture on low back pain by traffic accidents. J. Korean Chuna Man. Med. Spine Nerves 2011, 6, 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, G.M.; Moon, S.J.; Jun, K.S.; Shin, H.K.; Ko, Y.S. A clinical case of Oriental medical treatment on failed back surgery syndrome. J. Korean Chuna Man. Med. Spine Nerves 2011, 6, 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, Y.J. A clinical pilot study comparing sweet bee venom parallel treatment with only acupuncture treatment in patient diagnosed with lumbar spine sprain. J. Pharm. 2011, 14, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.W.; Kim, E.S.; Woo, J.H.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, J.S.; Nam, J.H.; Kim, K.W.; Koh, K.H.; Yoo, I.S. Clinical observation on 119 patients with lumbar spinal stenosis treatment with bee venom pharmacopuncture therapy. J. Korean Acupunct. Moxibustion Soc. 2011, 28, 21–31. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, H.Y.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.J.; Choi, Y.J.; Jung, T.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Lim, S.C.; Lee, Y.K.; Lee, B.H.; et al. Comparative study of effects on intracutaneous bee venom pharmacopuncture and intramuscular bee venom pharmacopuncture in lumbar disc herniation. J. Korean Acupunct. Moxibustion Soc. 2011, 28, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, E.; Kang, J.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Yoon, K.S.; Lee, H. The clinical study on effects of bee venom pharmacopuncture therapy in patients with FBSS(Failed back surgery syndrome). J. Korean Acupunct. Moxibustion Soc. 2011, 28, 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Ro, H.R.; Park, S.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Choo, W.J.; Han, S.W.; Kim, S.W.; Son, S.K.; Eom, T.W. The comparative study on the effects of ShinBaro pharmacopuncture treatment and bee venom pharmacopuncture treatment of patient with spondylolisthesis. J. Korean Chuna Man. Med. Spine Nerves 2012, 7, 53–61. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.H.; Park, W.H.; Cha, Y.Y. Comparative study of effects on bee venom pharmacopuncture and Ouhyul herbal acupuncture in low back pain caused by traffic accident. J. Oriental. Rehab. Med. 2012, 22, 177–184. [Google Scholar]
- Yeon, C.H.; Park, H.G.; Yi, W.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Chung, S.H. The two cases report of bee venom injection on patient with low back pain maintaining after heating-conduction acupuncture therapy. J. Korean Chuna Man. Med. Spine Nerves 2012, 7, 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, J.H.; Kim, W.W.; Seong, I.H.; Lee, K.S.; Cho, C.Y.; Kum, C.J.; Kim, H.K.; Ha, I.H. The study on effectiveness of Oriental medicine treatment for lumbar disc herniation inpatients on 208 cases. J. Oriental. Rehab. Med. 2013, 23, 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, M.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, J.S.; Lim, S.C.; Lee, Y.K. A clinical case study about the patient of neurogenic claudication diagnosed spinal stenosis treated by bee venom therapy. J. Korean Skelet. Jt. Med. 2013, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Park, O.J.; Kim, S.G.; Lee, J.J.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, S.J.; Cho, N.G. The effect of Shinbaro and bee venom pharmacopuncture in treating lumbar disc herniation. Acupuncture 2013, 30, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.E.; Lee, C.I.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, H.J. Comparative study for therapeutic effects of the low back pain patients according to the bee venom pharmacopuncture-induced skin hyperseneitivity reaction and Sasang constitution. Acupuncture 2014, 31, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.M.; Yuk, D.I.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.I.; Jeon, J.H. A case of cauda equina syndrome cared with acupuncture, sweet bee venom pharmacopuncture, herbal medicine combined treatment. Acupuncture 2014, 31, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, H.S.; Lee, C.H.; Jeon, J.Y.; Lim, S.J.; Bae, Y.H.; Kim, H.S.; Song, J.H.; Kim, M.H.; Cho, C.Y.; Jung, Y.H. A case report on a patient with lumbar HIVD and femoroacetabular impingement, treated by bee venom pharmacopuncture and conservative Oriental medical treatment. J. Korean Chuna Man. Med. Spine Nerves 2014, 9, 81–92. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, H.K.; Park, S.A.; Ahn, C.B. The case study on 1 case of patients with ruptured intervertebral lumbar disc, treated with Korean medicine. J. East-West Med. 2014, 39, 21–32. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, M.J.; Lim, S.C.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, Y.K. A clinical case study of residual symptoms after decompression of traumatic compartment syndrome. Acupuncture 2015, 32, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.J.; Kim, S.W.; Jang, Y.J.; Hyun, M.K.; Lee, E.J.; Yoon, T.K.; Yang, M.S.; Wei, T.S. A case of Korean medical treatments for lumbar herniated intervertebral disc with piriformis muscle tenderness. J. Korean Skelet. Jt. Med. 2015, 12, 83–91. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.Y.; Seo, J.C.; Seo, Y.J.; Park, J.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, C.H.; Song, C.H.; Jang, K.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Yoon, H.M. The effect of Korean medical treatment with postural yinyang correction of temporomandibular joint on chronic low back pain. Korean J. Acupunct. 2016, 33, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ok, S.Y.; Sohn, S.A.; Lee, Y.J.; Shin, M.S. A case report of bee venom pharmacopuncture therapy at facet joint for the two patients with herniated intervertebral disc of lumbar spine. J. Korean Med. Rehabi. 2017, 27, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.H.; Kim, D.H.; Choi, H.M.; Kang, J.H.; Hyun, M.K. A case report of lumbar spinal stenosis improved with diarrhea-inducing treatment by Gamsui-mal and Korean medicine treatment. J. Korean Med. Rehabi. 2017, 27, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hwang, J.H.; Kim, D.H. Case report of two cases on effect of combined bee venom and CS pharmacopuncture with Korean medicine treatment on HIVD of L-spine. Korean J. Acupunct. 2018, 35, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, G.H.; Moon, H.Y.; Ju, A.R.; Choo, W.J.; Choi, Y.S.; Moon, Y.; Chai, J.; Shin, W. A case report on a patient with acute herniated lumbar disc due to coughing treated with megadose pharmacopuncture and combined Korean medicine. J. Int. Korean Med. 2019, 40, 1248–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bong, S.M.; Jang, W.S.; Kim, K.H. Effects of sweet bee venom pharmacopuncture combined with Korean medicine treatment for acute low back pain syndrome patients: A case report. Korean J. Acupunct. 2020, 37, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, W.I.; Kang, K.W.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, M.R.; Shin, J.S.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Shin, K.M.; Ha, I.H. Impact of acupuncture treatment on the lumbar surgery rate for low back pain in Korea: A nationwide matched retrospective cohort study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.J.; Shin, J.S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, M.R.; Park, K.B.; Lee, H.D.; Lee, Y.M.; Hong, J.W.; Ha, I.H. Usage report of pharmacopuncture in musculoskeletal patients visiting Korean medicine hospitals and clinics in Korea. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 17, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.D.; Park, H.J.; Chae, Y.; Lim, S. An overview of bee venom acupuncture in the treatment of arthritis. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2005, 2, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, S.H.; Oh, H.M.; Kwon, D.Y.; Yang, J.E.; Kim, B.J.; Ha, H.J.; Lim, E.J.; Oh, M.S.; Son, C.G.; Lee, E.J. Incidence rate of bee venom acupuncture related anaphylaxis: A systematic review. Toxins 2022, 26, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Jeong, H.; Lee, G.; Jang, S.; Yook, T. Characteristics of adverse events in bee venom therapy reported in South Korea: A survey study. Toxins 2021, 27, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| First Author | Study Design | Number of Patients | Medical Conditions | Intervention (Form, Concentration, Treatment Sessions and Dosage) | Adverse Events | Outcome Measure | Main Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lee (1999) [21] | Retrospective study | n = 12 | HIVD of L-spine patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.5 mg/mL 3. 1 session: n.r. 4. Total 1–9 sessions: n.r. | n.r. | 1. Symptom change (back pain) | 1. Improved |
| Kim (1999) [22] | Retrospective study | n = 22 | HIVD of L-spine patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.05 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.9 mL 4. Total 8 sessions: 7.2 mL | n.r. | 1. Symptom change (back pain) 2. L-spine MRI (degree of HIVD) 3. Satisfaction of patients | 1. Improved 2. Positive a 3. Improved |
| Park (1999) [23] | Case studies | n = 100 | Patients with lower back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: n.r. 3. 1 session: n.r. 4. Total session and dose: n.r. | n.r. | 1. SLR test | 1. Improved |
| Lee (2000) [24] | Case studies | n = 18 | Patients with back pain (degenerative arthritis and HIVD of L-spine) | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: n.r. 3. 1 session: n.r. 4. Total 21–64 sessions: n.r. | None | 1. Symptom change (back pain) | 1. Improved |
| Yun (2000) [25] | Case studies | n = 1 | HIVD of L-spine patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.3 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 1 mL 4. Total 20 sessions: 20 mL | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. L-spine ROM | 1. Improved 2. Improved |
| Kim (2001) [26] | Case studies | n = 19 | Patients with back pain (myofascial pain syndrome, HIVD of L-spine, degenerative spondylitis, and ankylosing spondylitis) | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: n.r. 3. 1 session: n.r. 4. Total 1–20 sessions: n.r. | n.r. | 1. Symptom change (back pain) | 1. Improved in 12 cases, not improved in 7 cases |
| Lee (2001) [27] | Case studies | n = 1 | HIVD of L-spine patient with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.03 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.5–1.4 mL 4. Total 13 sessions: 13.7 mL | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. L-spine ROM 3. L-spine CT (degree of HIVD) | 1. Improved 2. Improved 3. Not improved |
| Lim (2002) [28] | Case studies | n = 1 | Sequestrated disc patient with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.25 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.4–2.0 mL 4. Total 20 sessions: 8–40 mL | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. ODI for back pain 3. L-spine ROM | 1. Improved 2. Improved 3. Improved |
| Yoo (2002) [29] | Case studies | n = 1 | Klippel–Trenaunay–Weber syndrome patient with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.5 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.2–0.4 mL 4. Total 10 sessions: 2.0–4.0 mL | n.r. | 1. Symptom change (back pain) 2. DITI of back | 1. Improved 2. Improved |
| Bae (2002) [30] | Case studies | n = 1 | HIVD of L-spine patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.5 mg/mL 3. 1 session: n.r. 4. Total session and dosage: n.r. | n.r. | 1. SLR Test 2. Symptom change (back pain) | 1. Improved 2. Improved |
| Moon (2002) [31] | Case studies | n = 1 | Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis patient with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.1 mg/mL and 0.5 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.3–1.2 mL 4. Total session and dose: n.r. | n.r. | 1. SLR Test 2. Symptom change (back pain) | 1. Improved 2. Improved |
| Jun (2003) [32] | RCT | n = 45 | HIVD of L-spine patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.16 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.1–1.0 mL 4. Total above 12 sessions: above 1.2–12 mL | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. PRS for back pain 3. DITI of back | 1. Positive b 2. Positive b 3. Positive b |
| Chung (2003) [33] | Retrospective study | n = 24 | HIVD of L-spine patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.05 mg/mL (1–2 visit), 0.1 mg/mL (3 visit), 0.2 mg/mL (4 visit), 0.4 mg/mL (5–6 visit) 3. 1 session: 0.05 mL 4. Total 6 sessions: 0.3 mL | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. ODI for back pain 3. L-spine ROM | 1. Positive b 2. Positive b 3. Positive a |
| Hwang (2003) [34] | Case studies | n = 1 | Spinal meningeal cyst patient with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.16 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.08 mL 4. Total 21 sessions: 1.68 mL | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. PRS for back pain 3. L-spine MRI (degree of HIVD) 4. L-spine ROM | 1. Improved 2. Improved 3. Improved 4. Improved |
| Cha (2004) [35] | CCT | n = 29 | HIVD of L-spine patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.1 mg/mL, 0.25 mg/mL or 0.5 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.05 mL 4. Total 7 sessions: 0.35 mL | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. ODI for back pain | 1. Positive c 2. Positive c |
| Lee (2004) [36] | Retrospective study | n = 20 | HIVD of L-spine patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.05 mg/mL or 0.25 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.1–1.5 mL 4. Total 9 sessions: 0.9–13.5 mL | Fever in 3 cases | 1. VAS for back pain 2. Grade classification of recovery degree | 1. Positive c 2. Improved |
| Lee (2004) [37] | Case studies | n = 1 | Failed back surgery syndrome patient with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.125 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.3–1 mL 4. Total 10 sessions: 8.4 mL | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. ODI for back pain 3. Physical examination | 1. Improved 2. Improved 3. Improved |
| Lee (2004) [38] | Case studies | n = 1 | Causalgia patient after lumbar partial laminectomy with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.5 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.3 mL 4. Total 44 sessions: 13.2 mL | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain | 1. Improved |
| Yoo (2004) [39] | Case studies | n = 1 | HIVD of L-spine patient with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.05 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.3–0.6 mL 4. Total 22 sessions: n.r. | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain | 1. Improved |
| Kim (2005) [40] | Case studies | n = 1 | Neurogenic bladder after lumbar disc herniation with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.5 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.2–1.0 mL 4. Total 17 sessions: 12.4 mL | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. Physical examination | 1. Improved 2. Improved |
| Kim (2005) [41] | Retrospective study | n = 15 | HIVD of L-spine patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.5 mg/mL, 0.25 mg/mL or 0.1 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.1–1 mL 4. Total session and dosage: n.r. | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. Symptom change (back pain) | 1. Improved 2. Improved |
| Kim (2005) [42] | RCT | n = 30 | Back sprain patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0,3 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 1 mL 4. Total 5 sessions: 5 mL | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. ODI for back pain | 1. Improved 2. Improved |
| Lee (2006) [43] | Case studies | n = 1 | HIVD of L-spine patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.3 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.8 mL 4. Total 6 sessions: 4.8 mL | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. L-spine ROM | 1. Improved 2. Improved |
| Cha (2006) [44] | CCT | n = 18 | HIVD of L-spine patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.25 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.2–1.4 mL 4. Total 2–15 sessions: 0.4–21 mL | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. L-spine ROM | 1. Improved 2. Improved |
| Yu (2006) [45] | Retrospective study | n = 35 | HIVD of L-spine patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.25 mg/mL or 0.5 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.1–1.0 mL 4. Total session and dosage: n.r. | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. ODI for back pain 3. SLR test 4. L-spine ROM 5. Symptom change (back pain) | 1. Improved 2. Improved 3. Improved 4. Improved 5. Improved |
| Kang (2006) [46] | Case studies | n = 1 | Patients with lower back pain (lumbar spinal stenosis and HIVD of L-spine) | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.3 mg/mL or 2 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.03–0.3 mL 4. Total 17 sessions: 0.51–5.1 mL | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain | 1. Improved |
| Lee (2007) [47] | Case studies | n = 1 | Lumbar spinal stenosis patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.3 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.04 mL 4. Total 20 sessions: 0.8 mL | n.r. | 1. ODI for back pain 2. VAS for back pain 3. L-spine MRI (degree of stenosis) | 1. Improved 2. Improved 3. Improved |
| Lee (2007) [48] | Retrospective study | n = 10 | HIVD of L-spine patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.1 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.6 mL 4. Total 4 sessions: 2.4 mL | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. SLR test | 1. Improved 2. Improved |
| Seo (2007) [49] | Case studies | n = 3 | HIVD of L-spine patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.005–5.0 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.08–0.2 mL 4. Total 2–10 sessions: 0.32–0.1 mL | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. PRS for back pain 3. SLR test | 1. Improved 2. Improved 3. Improved |
| Lee (2007) [50] | Retrospective study | n = 60 | HIVD of L-spine patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.05 mg/mL 3. 1 session: n.r. 4. Total session and dosage: n.r. | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. Symptom change (back pain) 3. SLR test | 1. Improved 2. Improved 3. Improved |
| Kim (2008) [51] | RCT | n = 19 | Patients with lower back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.1 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.5 mL (1 and 2 visit), 0.7 mL(3 and 4 visit) 4. Total 4 sessions: 2.4 mL | Itching in 0.85 ± 1.72 cases | 1. VAS for back pain 2. ODI for back pain | 1. Positive c 2. Positive c |
| Kwon (2008) [52] | Retrospective study | n = 13 | HIVD of L-spine patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.5 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.2 mL 4. Total 12 sessions: 2.4 mL | Itching in 8 cases | 1. VAS for back pain 2. RMDQ | 1. Positive a 2. Positive a |
| Youn (2008) [53] | Retrospective study | n = 20 | HIVD of L-spine patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.125 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 1 mL 4. Total 7 sessions: 7 mL | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. ODI for back pain 3. Quality of life (SF-36) | 1. Positive a 2. Positive b 3. Positive b |
| Youn (2008) [54] | Retrospective study | n = 36 | HIVD of L-spine patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.125 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 1 mL 4. Total 8 sessions: 8 mL | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. ODI for back pain 3. Quality of life (SF-36) | 1. Positive a 2. Positive a 3. Positive a |
| Cho (2008) [55] | Case studies | n = 1 | Baastrup’s disease patient with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.125 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 1 mL 4. Total 34 sessions: 34 mL | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. ODI for back pain | 1. Improved 2. Improved |
| Jeong (2008) [56] | Case studies | n = 16 | Lumbar spinal stenosis patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.2 mg/mL or 0.5 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.8–1.0 mL 4. Total session and dosage: n.r. | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. ODI for back pain 3. Symptom change (back pain) | 1. Improved 2. Improved 3. Improved |
| Kim (2008) [57] | CCT | n = 33 | Lumbar hyperlordosis patient with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.16 mg/mL 3. 1 session: n.r. 4. Total session and dosage: n.r. | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. ODI for back pain 3. L-spine X-ray (degree of hyperlordosis) | 1. Improved 2. Improved 3. Improved |
| Kwon (2009) [58] | Retrospective study | n = 35 | HIVD of L-spine patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.125 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 1 mL 4. Total 24 sessions: 24 mL | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. ODI for back pain 3. L-spine CT (degree of HIVD) | 1. Positive a 2. Positive a 3. Improved |
| Yu (2009) [59] | Case studies | n = 1 | Failed back surgery syndrome patient with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.3 mg/mL or 0.5 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.02–0.5 mL 4. Total 9 sessions: 2.5 mL | Local redness, itching, and edema in 1 case | 1. VAS for back pain 2. Symptom change (back pain) | 1. Improved 2. Improved |
| Lee (2010) [60] | Case studies | n = 3 | Failed back surgery syndrome patient with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.125 mg/mL or 0.25 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.2–1 mL 4. Total 18–34 sessions: 3.6–34 mL | n.r. | 1. NRS for back pain 2. Physical examination | 1. Improved 2. Improved |
| Lee (2011) [61] | RCT | n = 34 | Car accident patients with lower back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.05 mg/mL or 0.1 mL/mL 3. 1 session: 0.2–1.0 mL 4. Total 8 sessions: 1.6–8.0 mL | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. ODI for back pain | 1. Positive b 2. Positive a |
| Lim (2011) [62] | Case studies | n = 1 | Failed back surgery syndrome patient with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.01 mg/mL or 0.25 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.6 mL 4. Total 11–13 sessions: 6.6–7.8 mL | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. ODI for back pain 3. SF-MPQ | 1. Improved 2. Improved 3. Improved |
| Shin (2011) [63] | CCT | n = 36 | Back sprain patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.1 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.1 mL 4. Total 8–13 sessions: 0.8–25 mL | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain | 1. Positive c |
| Han (2011) [64] | Case studies | n = 119 | Lumbar spinal stenosis patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.13 mg/mL or 0.25 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.8–1.0 mL 4. Total session and dosage: n.r. | n.r. | 1. NRS for back pain 2. ODI for back pain 3. Symptom change (back pain) | 1. Improved 2. Improved 3. Improved |
| Shin(2011) [65] | RCT | n = 34 | HIVD of L-spine patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.1 mg/mL or 0.25 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.2–1.0 mL 4. Total session and dosage: n.r. | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. Aberdeen LBP scale | 1. Improved 2. Improved |
| Cho (2011) [66] | Case studies | n = 30 | Failed back surgery syndrome patient with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.05 mg/mL, 0.1 mg/mL or 0.5 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.4–1.0 mL 4. Total session and dosage: n.r. | n.r. | 1. NRS for back pain 2. Symptom change 3. SLR test | 1. Improved 2. Improved 3. Improved |
| Ro (2012) [67] | RCT | n = 30 | Spondylolisthesis patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.1 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.2–1.0 mL 4. Total 14 sessions: 2.8–14 mL | n.r. | 1. NRS for back pain 2. ODI for back pain | 1. Positive c 2. Positive c |
| Kim (2012) [68] | CCT | n = 20 | Car accident patients with lower back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.1 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 1.0 mL 4. Total 8 sessions: 8.0 mL | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. Patient condition grade 3. Five-point Likert scale | 1. Improved 2. Improved 3. Improved |
| Yeon (2012) [69] | Case studies | n = 2 | Patients with lower back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.05 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.3 mL 4. Total 1 session: 0.3 mL | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. L-spine ROM 3. SLR test | 1. Improved 2. Improved 3. Improved |
| Jung (2013) [70] | Retrospective study | n = 208 | HIVD of L-spine patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.1 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 1 mL 4. Total 8–32 sessions: 8–32 mL | n.r. | 1. NRS for back pain 2. ODI for back pain 3. SLR test 4. L-spine ROM | 1. Positive c 2. Positive c 3. Positive c 4. Positive c |
| Ji (2013) [71] | Case studies | n = 1 | Lumbar spinal stenosis patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.1 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.8 mL 4. Total 18 sessions: 14.4 mL | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. Start time of claudication 3. DITI of back | 1. Improved 2. Improved 3. Improved |
| Park (2013) [72] | Retrospective study | n = 10 | HIVD of L-spine patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.1 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 1 mL 4. Total session and dosage: n.r. | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. PRS for back pain 3. ODI for back pain 4. DITI of back | 1. Improved 2. Improved 3. Improved 4. Improved |
| Lee (2014) [73] | Retrospective study | n = 62 | Patients with lower back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.05 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.1–0.6 mL 4. Total 6 sessions: 0.6–2.1 mL | Skin hypersensitivity (edema, rash, and itching) in 22 cases | 1. VAS for back pain 2. ODI for back pain | 1. Positive a 2. Positive c |
| Kim(2014) [74] | Case studies | n = 1 | Cauda equina syndrome patient with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.1 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.5–2.0 mL 4. Total 18 sessions: 9–36 mL | n.r. | 1. Symptom change (back pain) 2. L-spine MRI (cauda equine syndrome) | 1. Improved 2. Improved |
| Kim (2014) [75] | Case studies | n = 1 | HIVD of L-spine and femoroacetabular impingement patient with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.1 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.1–0.3 mL 4. Total 35 sessions: 3.5–10.5 mL | n.r. | 1. NRS for back pain 2. ODI for back pain 3. SLR test 4. Quality of life (EQ-5D) | 1. Improved 2. Improved 3. Improved 4. Improved |
| Kwon (2014) [76] | Case studies | n = 1 | HIVD of L-spine patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.1 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.7 mL 4. Total 7 sessions: 4.9 mL | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. ODI for back pain 3. L-spine MRI (degree of HIVD) | 1. Improved 2. Improved 3. Improved |
| Ji (2015) [77] | Case studies | n = 1 | Back pain patient after decompression of traumatic compartment syndrome | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.05 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.4 mL 4. Total 63 sessions: 25.2 mL | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. L-spine ROM | 1. Improved 2. Improved 3. Improved |
| Yang (2015) [78] | Case studies | n = 1 | HIVD of L-spine patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.1 mg/mL 3. 1 session: n.r. 4. Total session and dosage: n.r. | None | 1. VAS for back pain 2. ODI for back pain | 1. Improved 2. Improved |
| Kim (2016) [79] | Retrospective study | n = 40 | Patients with lower back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: n.r. 3. 1 session: 0.5 mL 4. Total 8 sessions: 4.0 mL | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. ODI for back pain | 1. Positive a 2. Positive a |
| Ok (2017) [80] | Case studies | n = 2 | HIVD of L-spine patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: n.r. 3. 1 session: 1.5 mL 4. Total 12–16 sessions: 18–24 mL | n.r. | 1. NRS for back pain 2. SLR test 3. RMDQ | 1. Improved 2. Improved 3. Improved |
| Nam (2017) [81] | Case studies | n = 4 | HIVD of L-spine patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.05 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 1 mL 4. Total 2–8 sessions: 2–8 mL | n.r. | 1. VAS for back pain 2. ODI for back pain | 1. Improved 2. Improved |
| Hwang (2018) [82] | Case studies | n = 2 | HIVD of L-spine patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.1 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 0.1–0.3 mL 4. Total 5–8 sessions: 0.5–2.4 mL | Mild chilling, local rash, itching in 2 cases | 1. NRS for back pain 2. ODI for back pain 3. RMDQ | 1. Improved 2. Improved 3. Improved |
| Ryu (2019) [83] | Case studies | n = 1 | HIVD of L-spine patients with back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: n.r. 3. 1 session: 0.2–1.5 mL 4. Total 16 sessions: 20.5 mL | n.r. | 1. NRS for back pain 2. ODI for back pain 3. L-spine MRI (degree of HIVD) 4. SLR test 5. Quality of life (EQ-5D) | 1. Improved 2. Improved 3. Improved 4. Improved 5. Improved |
| Bong (2020) [84] | Case studies | n = 3 | Patients with lower back pain | 1. Form: injection 2. Concentration: 0.1 mg/mL 3. 1 session: 1 mL 4. Total 8–9 sessions: 8–9 mL | None | 1. NRS for back pain 2. ODI for back pain 3. Quality of life (EQ-5D) | 1. Improved 2. Improved 3. Improved |
| Medical Conditions | Number of Papers (N (%)) | Number of Patients (Mean) |
|---|---|---|
| HIVD of L-spine patients with back pain | 30 (47.7) | 22.17 ± 38.4 |
| Back pain | 6 (9.2) | 37.7 ± 38.2 |
| Failed back surgery syndrome patients with back pain | 5 (7.7) | 7.2 ± 12.8 |
| Lumbar spinal stenosis patients with back pain | 4 (6.2) | 34.3 ± 56.9 |
| Car accident patients with lower back pain | 2 (3.1) | 27 ± 9.9 |
| Back sprain patients with back pain | 2 (3.1) | 33 ± 4.2 |
| Conditions of Participants | Concentration (mg/mL) | Dosage | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dosage Per 1 Session (mL) | Dosage for Total Session (mL) | ||
| HIVD of L-spine patients with back pain | 0.01–5.0 | 0.02–2.0 | 0.3–40.0 |
| Back pain | 0.05–0.5 | 0.03–1.0 | 0.51–5.1 |
| Failed back surgery syndrome patients with back pain | 0.05–0.25 | 0.1–2.0 | 0.5–21 |
| Lumbar spinal stenosis patients with back pain | 0.05–0.5 | 0.3–1.2 | 14.4 |
| Car accident patients with lower back pain | 0.1–0.3 | 0.5–0.8 | 0.35–4.8 |
| Back sprain patients with back pain | 0.05 | 0.9 | 7.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sung, S.-H.; Han, J.-E.; Lee, H.-J.; Park, M.; Lee, J.-Y.; Jang, S.; Park, J.-K.; Lee, G. Clinical Studies of Bee Venom Acupuncture for Lower Back Pain in the Korean Literature. Toxins 2022, 14, 524. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14080524
Sung S-H, Han J-E, Lee H-J, Park M, Lee J-Y, Jang S, Park J-K, Lee G. Clinical Studies of Bee Venom Acupuncture for Lower Back Pain in the Korean Literature. Toxins. 2022; 14(8):524. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14080524
Chicago/Turabian StyleSung, Soo-Hyun, Ji-Eun Han, Hee-Jung Lee, Minjung Park, Ji-Yeon Lee, Soobin Jang, Jang-Kyung Park, and Gihyun Lee. 2022. "Clinical Studies of Bee Venom Acupuncture for Lower Back Pain in the Korean Literature" Toxins 14, no. 8: 524. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14080524
APA StyleSung, S.-H., Han, J.-E., Lee, H.-J., Park, M., Lee, J.-Y., Jang, S., Park, J.-K., & Lee, G. (2022). Clinical Studies of Bee Venom Acupuncture for Lower Back Pain in the Korean Literature. Toxins, 14(8), 524. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14080524





