Structural Analysis of Botulinum Neurotoxins Type B and E by Cryo-EM
Abstract
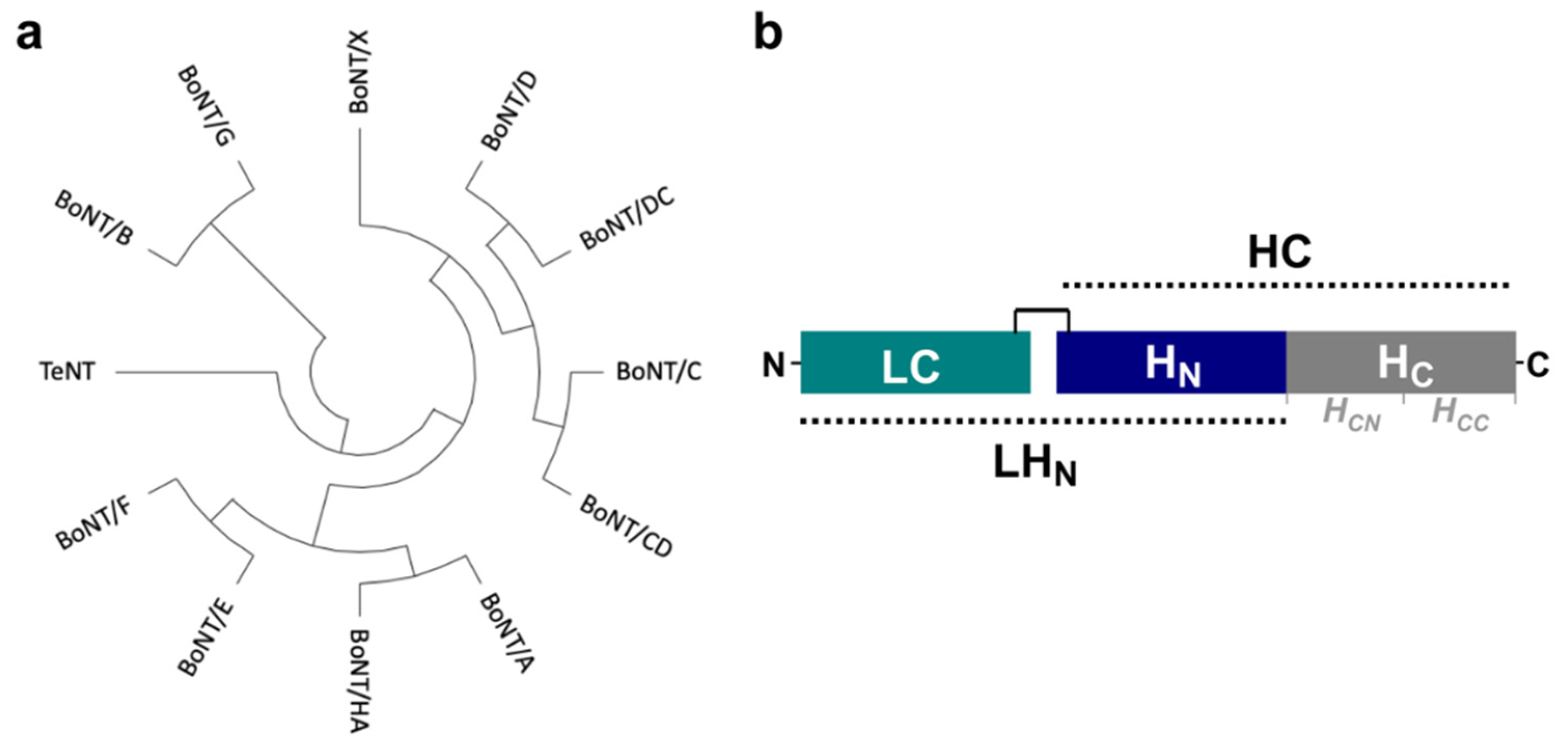
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
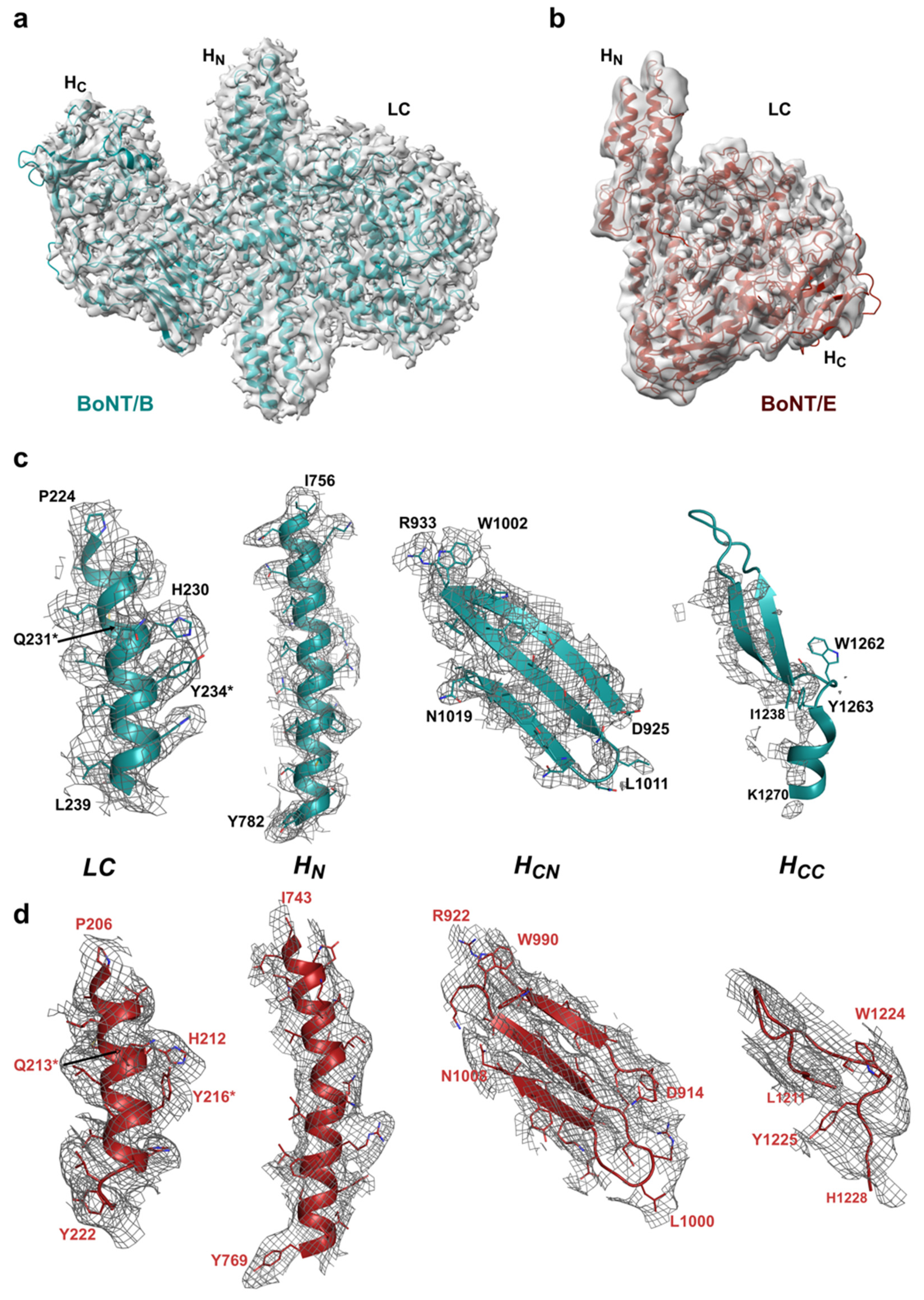
2.1. Single Particle Analysis by Cryo-Electron Microscopy
2.1.1. Data Collection and Analysis
2.1.2. Fitting of Protein Coordinates
2.2. Comparison with X-ray Crystal Structures
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Constructs
3.2. Protein Expression and Purification
3.3. Single Particle Cryo-Electron Microscopy
3.3.1. Cryo-EM Grid Preparation
3.3.2. Cryo-EM Imaging
3.3.3. Cryo-EM Data Processing
3.3.4. Model Building and Validation
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Williamson, C.H.; Sahl, J.W.; Smith, T.J.; Xie, G.; Foley, B.T.; Smith, L.A.; Fernández, R.A.; Lindström, M.; Korkeala, H.; Keim, P.; et al. Comparative genomic analyses reveal broad diversity in botulinum-toxin-producing Clostridia. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Masuyer, G.; Zhang, J.; Shen, Y.; Lundin, D.; Henriksson, L.; Miyashita, S.I.; Martinez-Carranza, M.; Dong, M.; Stenmark, P. Identification and characterization of a novel botulinum neurotoxin. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Masuyer, G.; Stenmark, P. Botulinum and tetanus neurotoxins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2019, 88, 811–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossetto, O.; Montecucco, C. Tables of toxicity of botulinum and tetanus neurotoxins. Toxins 2019, 11, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rasetti-Escargueil, C.; Popoff, M.R. Antibodies and vaccines against botulinum toxins: Available measures and novel approaches. Toxins 2019, 11, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stenmark, P.; Dupuy, J.; Imamura, A.; Kiso, M.; Stevens, R.C. Crystal structure of botulinum neurotoxin type A in complex with the cell surface co-receptor GT1b-insight into the toxin-neuron interaction. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berntsson, R.P.A.A.; Peng, L.; Dong, M.; Stenmark, P. Structure of dual receptor binding to botulinum neurotoxin B. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masuyer, G.; Davies, J.R.; Stenmark, P. Mechanism of ganglioside receptor recognition by botulinum neurotoxin serotype E. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binz, T.; Rummel, A. Cell entry strategy of clostridial neurotoxins. J. Neurochem. 2009, 109, 1584–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiki, T.; Kamata, Y.; Nemoto, Y.; Omori, A.; Ito, T.; Takahashi, M.; Kozaki, S. Identification of protein receptor for Clostridium botulinum type B neurotoxin in rat brain synaptosomes. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 10498–10503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiki, T.; Tokuyama, Y.; Kamata, Y.; Nemoto, Y.; Yoshida, A.; Sato, K.; Sekiguchi, M.; Takahashi, M.; Kozaki, S. The high-affinity binding of Clostridium botulinum type B neurotoxin to synaptotagmin II associated with gangliosides GT1b/GD1a. FEBS Lett. 1996, 378, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, M.; Richards, D.A.; Goodnough, M.C.; Tepp, W.H.; Johnson, E.A.; Chapman, E.R. Synaptotagmins I and II mediate entry of botulinum neurotoxin B into cells. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 162, 1293–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rummel, A.; Karnath, T.; Henke, T.; Bigalke, H.; Binz, T. Synaptotagmins I and II act as nerve cell receptors for botulinum neurotoxin G. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 30865–30870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, R.; Rummel, A.; Binz, T.; Brunger, A.T. Botulinum neurotoxin B recognizes its protein receptor with high affinity and specificity. Nature 2006, 444, 1092–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Q.; Arndt, J.W.; Dong, M.; Tepp, W.H.; Johnson, E.A.; Chapman, E.R.; Stevens, R.C. Structural basis of cell surface receptor recognition by botulinum neurotoxin B. Nature 2006, 444, 1096–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Tepp, W.H.; Liu, H.; Johnson, E.A.; Chapman, E.R. Mechanism of botulinum neurotoxin B and G entry into hippocampal neurons. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 179, 1511–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peng, L.; Berntsson, R.P.; Tepp, W.H.; Pitkin, R.M.; Johnson, E.A.; Stenmark, P.; Dong, M. Botulinum neurotoxin D-C uses synaptotagmin I and II as receptors, and human synaptotagmin II is not an effective receptor for type B, D-C and G toxins. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 3233–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Montal, M. Botulinum neurotoxin: A marvel of protein design. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 2010, 79, 591–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Südhof, T.C.; Rothman, J.E. Membrane fusion: Grappling with SNARE and SM proteins. Science 2009, 323, 474–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schiavo, G.; Matteoli, M.; Montecucco, C. Neurotoxins affecting neuroexocytosis. Physiol. Rev. 2000, 80, 717–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonfria, E.; Maignel, J.; Lezmi, S.; Martin, V.; Splevins, A.; Shubber, S.; Kalinichev, M.; Foster, K.; Picaut, P.; Krupp, J. The expanding therapeutic utility of botulinum neurotoxins. Toxins 2018, 10, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steward, L.; Brin, M.F.; Brideau-Andersen, A. Novel native and engineered botulinum neurotoxins. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2021, 263, 63–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donald, S.; Elliott, M.; Gray, B.; Hornby, F.; Lewandowska, A.; Marlin, S.; Favre-Guilmard, C.; Périer, C.; Cornet, S.; Kalinichev, M.; et al. A comparison of biological activity of commercially available purified native botulinum neurotoxin serotypes A1 to F1 in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2018, 6, e00446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eleopra, R.; Rinaldo, S.; Montecucco, C.; Rossetto, O.; Devigili, G. Clinical duration of action of different botulinum toxin types in humans. Toxicon 2020, 179, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pons, L.; Vilain, C.; Volteau, M.; Picaut, P. Safety and pharmacodynamics of a novel recombinant botulinum toxin E (rBoNT-E): Results of a phase 1 study in healthy male subjects compared with abobotulinumtoxinA (Dysport®). J. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 407, 116516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoelin, S.G.; Dhawan, S.S.; Vitarella, D.; Ahmad, W.; Hasan, F.; Abushakra, S. Safety and efficacy of EB-001, a novel type E botulinum toxin, in subjects with glabellar frown lines: Results of a phase 2, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Ascending-Dose Study. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 142, 847e–855e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacy, D.B.; Tepp, W.; Cohen, A.C.; DasGupta, B.R.; Stevens, R.C. Crystal structure of botulinum neurotoxin type A and implications for toxicity. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1998, 5, 898–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, S.; Eswaramoorthy, S. Structural analysis of the catalytic and binding sites of Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin B. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2000, 7, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaran, D.; Eswaramoorthy, S.; Furey, W.; Navaza, J.; Sax, M.; Swaminathan, S. Domain organization in Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin type E is unique: Its implication in faster translocation. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 386, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Meng, J.; Lawrence, G.W.; Zurawski, T.H.; Sasse, A.; Bodeker, M.O.; Gilmore, M.A.; Fernández-Salas, E.; Francis, J.; Steward, L.E.; et al. Novel chimeras of botulinum neurotoxins A and E unveil contributions from the binding, translocation, and protease domains to their functional characteristics. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 16993–17002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischer, A.; Garcia-Rodriguez, C.; Geren, I.; Lou, J.; Marks, J.D.; Nakagawa, T.; Montal, M. Molecular architecture of botulinum neurotoxin E revealed by single particle electron microscopy. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 3997–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masuyer, G.; Conrad, J.; Stenmark, P. The structure of the tetanus toxin reveals pH-mediated domain dynamics. EMBO Rep. 2017, 18, 1306–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madeira, F.; Park, Y.M.; Lee, J.; Buso, N.; Gur, T.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Basutkar, P.; Tivey, A.R.N.; Potter, S.C.; Finn, R.D.; et al. The EMBL-EBI search and sequence analysis tools APIs in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W636–W641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chaddock, J.A.; Herbert, M.H.; Ling, R.J.; Alexander, F.C.; Fooks, S.J.; Revell, D.F.; Quinn, C.P.; Shone, C.C.; Foster, K.A. Expression and purification of catalytically active, non-toxic endopeptidase derivatives of Clostridium botulinum toxin type A. Protein Expr. Purif. 2002, 25, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Meng, E.C.; Couch, G.S.; Croll, T.I.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: Structure visualization for researchers, educators, and developers. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebschner, D.; Afonine, P.V.; Baker, M.L.; Bunkóczi, G.; Chen, V.B.; Croll, T.I.; Hintze, B.; Hung, L.W.; Jain, S.; McCoy, A.J.; et al. Macromolecular structure determination using X-rays, neutrons and electrons: Recent developments in Phenix. Acta Crystallogr. D Struct. Biol. 2019, 75, 861–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stancombe, P.R.; Masuyer, G.; Birch-Machin, I.; Beard, M.; Foster, K.A.; Chaddock, J.A.; Acharya, K.R. Engineering botulinum neurotoxin domains for activation by toxin light chain. FEBS J. 2012, 279, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breidenbach, M.A.; Brunger, A.T. Substrate recognition strategy for botulinum neurotoxin serotype A. Nature 2004, 432, 925–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuyer, G.; Stancombe, P.; Chaddock, J.A.; Acharya, K.R. Structures of engineered Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin derivatives. Acta Cryst. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2011, 67, 1466–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Handing, K.B.; Niedzialkowska, E.; Shabalin, I.G.; Kuhn, M.L.; Zheng, H.; Minor, W. Characterizing metal-binding sites in proteins with X-ray crystallography. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 1062–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elad, N.; Bellapadrona, G.; Houben, L.; Sagi, I.; Elbaum, M. Detection of isolated protein-bound metal ions by single-particle cryo-STEM. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 11139–11144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brunger, A.T.; Breidenbach, M.A.; Jin, R.; Fischer, A.; Santos, J.S.; Montal, M. Botulinum neurotoxin heavy chain belt as an intramolecular chaperone for the light chain. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, 1191–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eswaramoorthy, S.; Sun, J.; Li, H.; Singh, B.R.; Swaminathan, S. Molecular Assembly of Clostridium botulinum progenitor M complex of type E. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krissinel, E. Enhanced fold recognition using efficient short fragment clustering. J. Mol. Biochem. 2012, 1, 76–85. [Google Scholar]
- Eswaramoorthy, S.; Kumaran, D.; Keller, J.; Swaminathan, S. Role of metals in the biological activity of Clostridium botulinum neurotoxins. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 2209–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Rumpel, S.; Zhou, J.; Strotmeier, J.; Bigalke, H.; Perry, K.; Shoemaker, C.B.; Rummel, A.; Jin, R. Botulinum neurotoxin is shielded by NTNHA in an interlocked complex. Science 2012, 335, 977–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaur, S.; Gomez-Blanco, J.; Khalifa, A.A.Z.; Adinarayanan, S.; Sanchez-Garcia, R.; Wrapp, D.; McLellan, J.S.; Bui, K.H.; Vargas, J. Local computational methods to improve the interpretability and analysis of cryo-EM maps. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punjani, A.; Rubinstein, J.L.; Fleet, D.J.; Brubaker, M.A. cryoSPARC: Algorithms for rapid unsupervised cryo-EM structure determination. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, V.B.; Arendall, W.B., 3rd; Headd, J.J.; Keedy, D.A.; Immormino, R.M.; Kapral, G.J.; Murray, L.W.; Richardson, J.S.; Richardson, D.C. MolProbity: All-atom structure validation for macromolecular crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D 2010, 66, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| LC | LHN | HC | Full-Length | BoNT-NTNH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BoNT/A | 1XTF | 2W2D | 2VU9 | 3BTA | 3V0B |
| BoNT/B | 2ETF | 2XHL | 1Z0H | 1EPW | - |
| BoNT/C | 1QN0 | - | 3N7K | - | - |
| BoNT/CD | (=C) | - | 3PME | - | - |
| BoNT/D | 2FPQ | 5BQN | 3OGG,3N7J,3OBR | - | - |
| BoNT/DC | (=D) | (=D) | 3AZW | - | - |
| BoNT/E | 1T3A | 7K7Y | 7OVW | 3FFZ | 4ZKT |
| BoNT/F | 2A8A | - | 3FUQ | - | - |
| BoNT/G | 1ZB7 | - | 3MPP,2VXR | - | - |
| BoNT/HA | 6BVD | - | 5V38 | - | - |
| BoNT/X | 6F47 | - | - | - | - |
| TeNT | 1YVG | - | 1AF9 | 5N0B | N/A |
| BoNT/B | BoNT/E | |
|---|---|---|
| Data collection and processing | ||
| Nominal magnification | 130,000 | 165,000 |
| Voltage (kV) | 300 | 300 |
| Electron exposure (e/Å2) | 57.3 | 55 |
| Defocus range (µm) | −1.9–−3.5 | −0.5–−3 |
| Pixel size (Å) | 1.09 | 0.86 |
| Number of images | 2252 | 18,282 |
| Symmetry imposed | C1 | C1 |
| Particles picked | 2,420,309 | 1,096,741 |
| Particles refined | 286,802 | 284,390 |
| Map resolution (Å) | 3.6 | 3.7 |
| FSC threshold | 0.143 | 0.143 |
| Map sharpening B factor | −151.9 | −100 |
| Refinement | ||
| Initial model used (PDB code) | 1EPW | 3FFZ |
| Model composition | ||
| Nonhydrogen atoms | 10,660 | 9996 |
| Protein residues | 1291 | 1233 |
| Ligand | 0 | 0 |
| B factors (Å2) | 160 | 54 |
| R.m.s.d. Bond lengths (Å) | 0.002 | 0.007 |
| R.m.s.d. Bond angles (°) | 0.552 | 1.118 |
| Validation | ||
| MolProbity score | 1.82 | 2.82 |
| Clash score | 8.21 | 18.19 |
| Poor rotamers (%) | 0 | 6.2 |
| Ramachandran statistics: | ||
| Favoured (%) | 94.5 | 86.6 |
| Outliers (%) | 0 | 0.5 |
| PDB/EMDB ID | 7QFQ/13947 | 7QFP/13946 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Košenina, S.; Martínez-Carranza, M.; Davies, J.R.; Masuyer, G.; Stenmark, P. Structural Analysis of Botulinum Neurotoxins Type B and E by Cryo-EM. Toxins 2022, 14, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14010014
Košenina S, Martínez-Carranza M, Davies JR, Masuyer G, Stenmark P. Structural Analysis of Botulinum Neurotoxins Type B and E by Cryo-EM. Toxins. 2022; 14(1):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14010014
Chicago/Turabian StyleKošenina, Sara, Markel Martínez-Carranza, Jonathan R. Davies, Geoffrey Masuyer, and Pål Stenmark. 2022. "Structural Analysis of Botulinum Neurotoxins Type B and E by Cryo-EM" Toxins 14, no. 1: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14010014
APA StyleKošenina, S., Martínez-Carranza, M., Davies, J. R., Masuyer, G., & Stenmark, P. (2022). Structural Analysis of Botulinum Neurotoxins Type B and E by Cryo-EM. Toxins, 14(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14010014





