Abstract
The Southern Ocean is one of the most productive ecosystems in the world. It is an area heavily dependent on marine primary production and serving as a feeding ground for numerous seabirds and marine mammals. Therefore, the phytoplankton composition and presence of toxic species are of crucial importance. Fifteen monoclonal strains of Pseudo-nitzschia subcurvata, a diatom species endemic to the Southern Ocean, were established, which were characterized by morphological and molecular data and then analysed for toxin content. The neurotoxins domoic acid and iso-domoic acid C were present in three of the strains, which is a finding that represents the first evidence of these toxins in strains from Antarctic waters. Toxic phytoplankton in Antarctic waters are still largely unexplored, and their effects on the ecosystem are not well understood. Considering P. subcurvata’s prevalence throughout the Southern Ocean, these results highlight the need for further investigations of the harmful properties on the Antarctic phytoplankton community as well as the presence of the toxins in the Antarctic food web, especially in the light of a changing climate.
Key Contribution:
First report of domoic acid in Antarctic diatoms, which are probably frequent components of the Antarctic phytoplankton community and thereby the Antarctic foodweb. Domoic and and isodomoic acid C in equal amounts in Pseudo-nitzschia subcurvata cells.
1. Introduction
The unique Antarctic marine ecosystem is fueled by phytoplankton, particularly diatoms, capturing energy from the sun. The potentially toxic diatom genus Pseudo-nitzschia is among the most frequently encountered and dominant diatom genera in Antarctic waters, e.g., contributing 13–70% of diatom densities in the Weddell Sea [1,2]. Despite this, nothing is known about the toxicity of the genus in Antarctic waters [2,3], whereas Pseudo-nitzschia is a known producer of the neurotoxin domoic acid (DA) in temperate and tropical waters, causing amnesic shellfish poisoning in humans [1]. DA accumulates in a wide range of planktonic and benthic organisms across the marine food web, such as krill, copepods, fish, and bivalves [1]. In marine mammals, this can e.g., result in acute and chronic poisoning, with effects such as reduced reproduction, seizures, and death [4]. Worldwide monitoring efforts have linked several toxic Pseudo-nitzschia blooms to unusual, large-scale mortality events in a range of marine vertebrates including sea lions, whales, and seabirds [4,5,6]. However, the term “worldwide monitoring” does not include the polar regions, which are areas characterized by poorly known phytoplankton diversity and the absence of regular phytoplankton monitoring. Presently, 27 species of Pseudo-nitzschia can potentially produce DA [1,7,8,9]. In addition to DA, eight different DA isomers (A–H) exist, of which three (DA-IA, DA-IB, and DA-IC) are found in Pseudo-nitzschia [1,10,11].
The presently known Pseudo-nitzschia diversity in Antarctic waters is relatively low, which is based only on a restricted number of studies on morphological diversity. However, a high richness of unique rDNA gene sequences suggest a considerably larger Pseudo-nitzschia diversity [3]. Six different species have presently been recorded from Antarctic waters: three endemic for Antarctica (P. prolongatoides, P. subcurvata, and P. turgiduloides) while the remaining, P. lineola, P. heimii, and P. turgidula, are also found in other regions [1,2,12,13,14]. Until now, the few Antarctic strains studied (P. subcurvata, P. turgiduloides, and P. lineola) have shown no sign of DA production [12,13,14].
Nothing is known about the fate of the toxins in the Antarctic food web. The marine habitat of the Arctic is comparable to that of Antarctica. In the Arctic region, DA has been found in the gut and feces of all 13 different Alaskan marine mammal species examined and at levels high enough to have an impact on mammal health [5]. The lack of knowledge of toxic phytoplankton and toxin impact on the marine food web in Antarctica illustrates the inaccessibility of the region, not the relevance. Globally, harmful algal blooms are getting more frequent, which is probably linked to climate change [15]. If Pseudo-nitzschia species from Antarctica can produce DA, impacts on higher food web levels must be expected.
During two different cruises in Antarctic waters, several strains of Pseudo-nitzschia were established as clonal cultures, which were characterized using both morphological (TEM and SEM) and molecular data (Internal transcribed spacers (ITS) of ribosomal DNA (rDNA)) and studied for cellular DA content.
2. Results
In total, 15 monoclonal strains of P. subcurvata (Figure 1) were isolated and established in culture from samples originating from eight different stations during two separate sampling cruises in the Southern Ocean (Figure 2). Water temperatures varied between −1.58 and 2.46 °C, and salinities were stable, on average 33.98 ± 0.16. Silicate and nitrate peaked at station 31, close to the Antarctic mainland with levels of approximately 120 µM for both nutrients (Supplementary Table S1). Silicate levels were otherwise ranging between 25.95 and 66.72 µM, which were levels that were assumingly not limiting for diatom growth. Nitrate was found in relative high concentrations, except at stations 3, 4, and 5, where it was found in low levels (0.08–0.24 µM). Phosphate levels were stable around 1.61 µM ± 0.67, which are levels possibly limiting for growth in areas with high nitrogen levels.
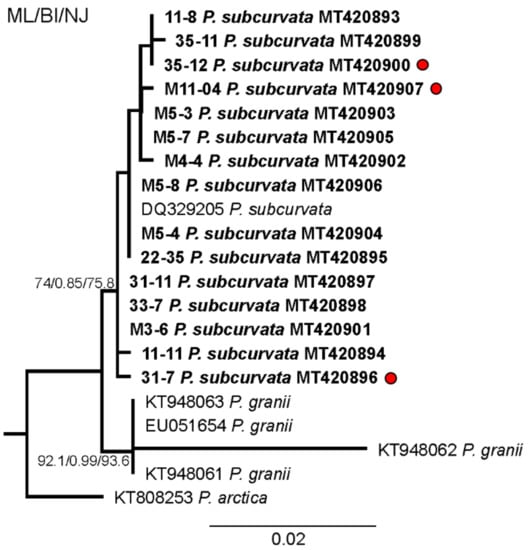
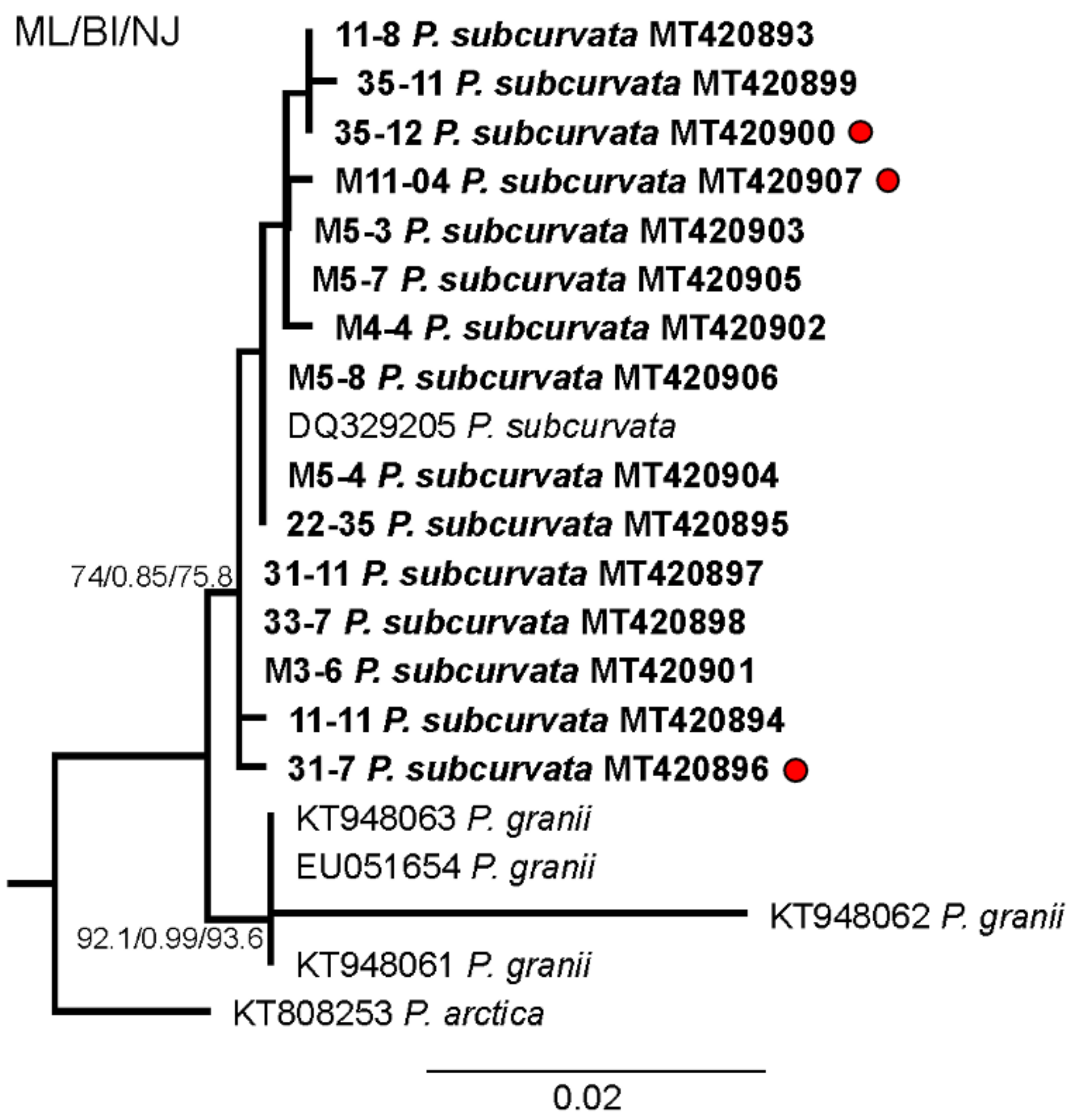
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic analysis based on maximum likelihood (ML) of the strains of P. subcurvata included in this study. Numbers at nodes represent the bootstrap values of an ML analysis with 1000 replicates/posterior probability of Bayesian inference (BI) analysis/bootstrap values of neighbour-joining (NJ) out of 10,000 replicates. The scale bar corresponds to two substitutions per 100 nucleotide positions.
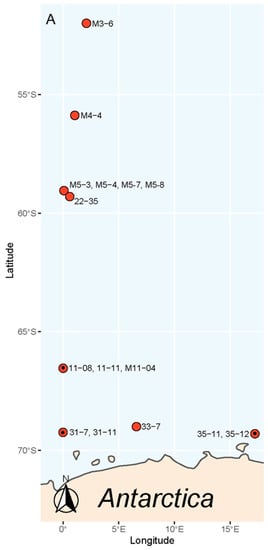
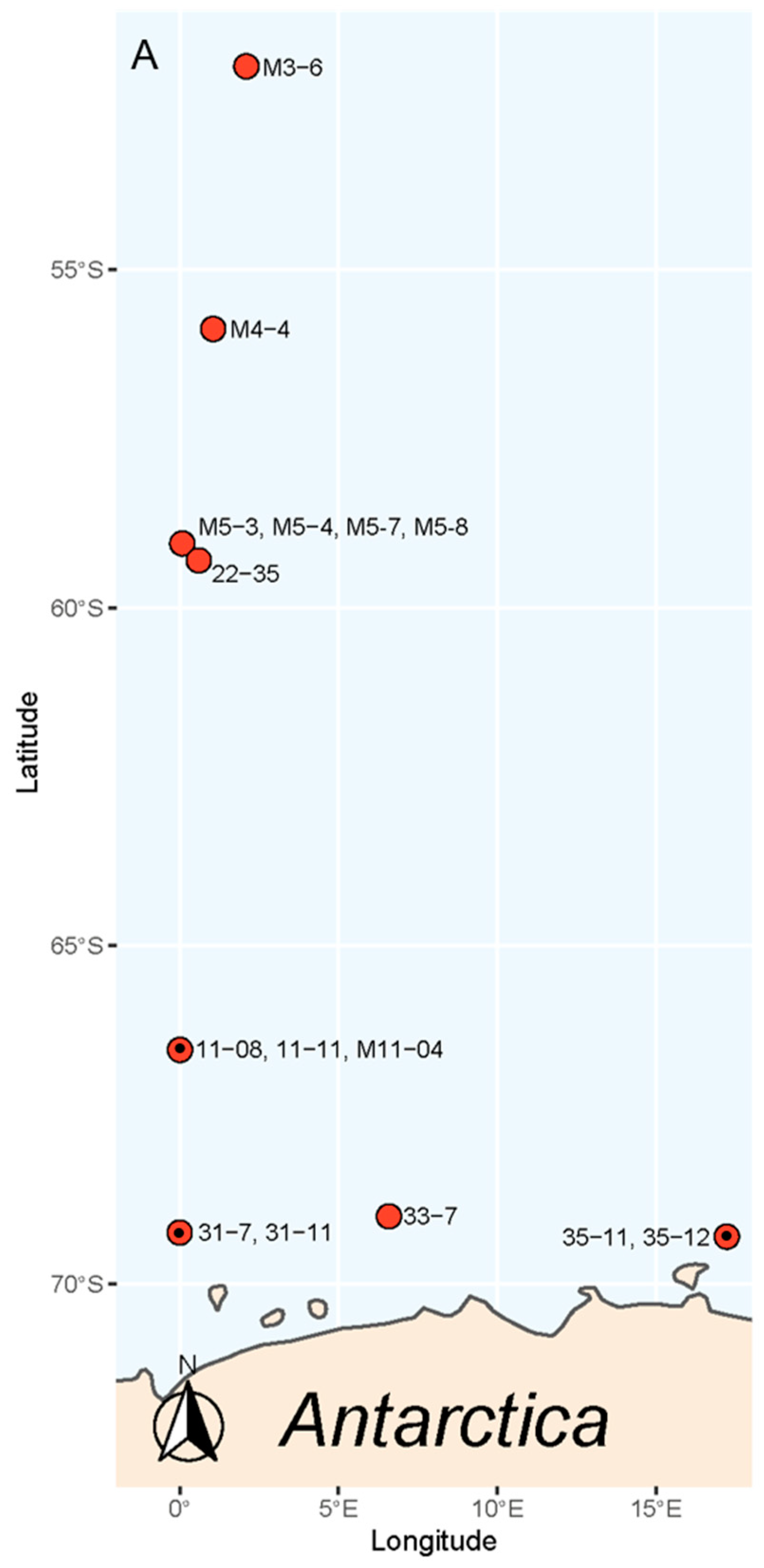
Figure 2.
Map of the area showing where each of the strains of P. subcurvata were isolated, stations marked with a dot (·) contained toxins. The strain name is given by the station.
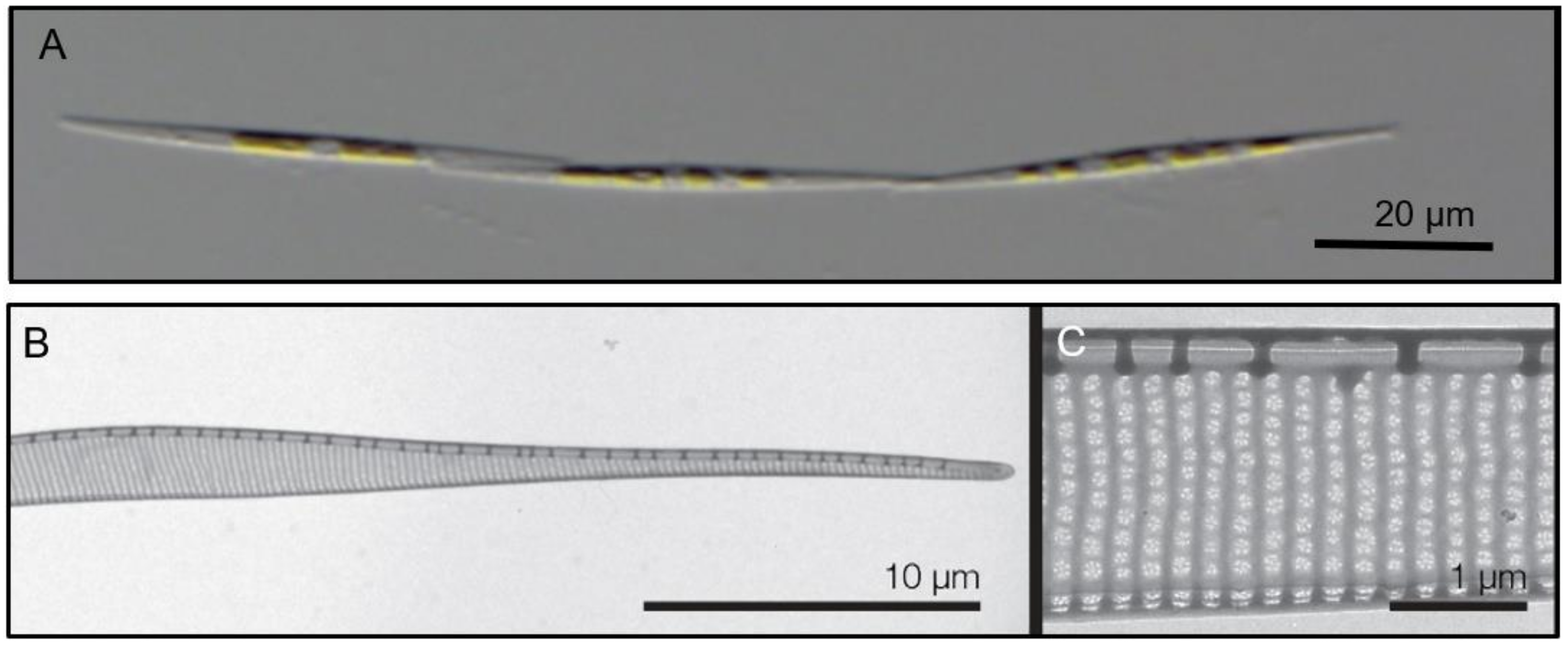
The monoclonal strains were identified based on qualitative and quantitative analyses of transmission electron micrographs of frustule structures (Figure 3). The analyses showed the subcurvate shape of cells, the absence of a central nodule, a fibula density of 12–20 in 10 µm, and a stria density of 40–50 in 10 µm. In combination with the presence of one row of poroids, with each poroid comprising four to eight sectors, morphological characters were in agreement with descriptions of P. subcurvata [16]. The phylogenetic analyses of ITS rDNA data showed the P. subcurvata strains to cluster in a clade comprising P. subcurvata from Genbank, with P. granii as a sister clade (Figure 1). Combined results from transmission electron microscopy and from ITS rDNA phylogenetic analyses revealed the identity of all 15 strains being P. subcurvata, with very limited variation in morphology and in their ITS rDNA data.
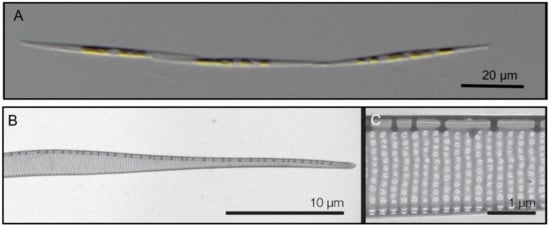
Figure 3.
(A) Light micrograph of a chain of P. subcurvata. (B,C) TEM micrographs of a P. subcurvata valve (M11-04) showing half part of diatom frustule, lack of central nodule, interstriae and fibulae, and one row of poroids with detailed poroid structure.
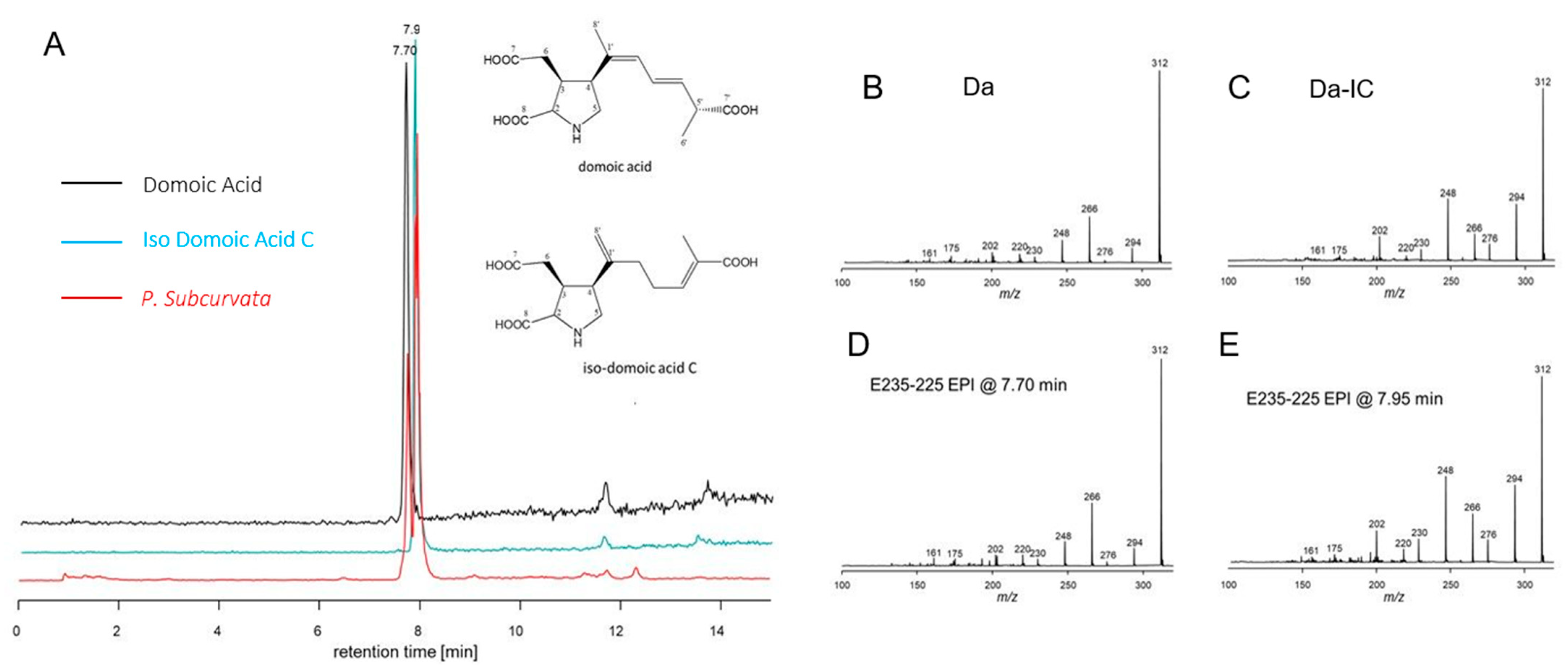
Toxin analyses of all 15 strains sampled in the early stationary growth phase revealed the presence of DA and iso-domoic acid C (DA-IC) in three of the 15 P. subcurvata strains (31-7, 35-12, and M11-04) (Figure 2 and Figure 4, and Table 1). The toxic strains were collected at stations 31, 35, and 11 (Figure 2 and Supplementary Table S1), which are all stations close to the Antarctic mainland. Five non-toxic strains were also isolated from the same area close to the Antarctic mainland. Further away from the Antarctic mainland (Figure 2), all seven strains were found to be non-toxic or with toxins at levels below the detection level.
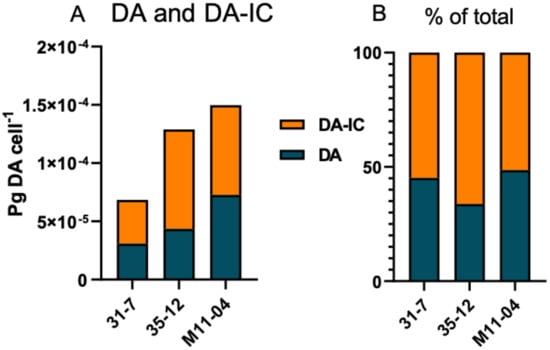
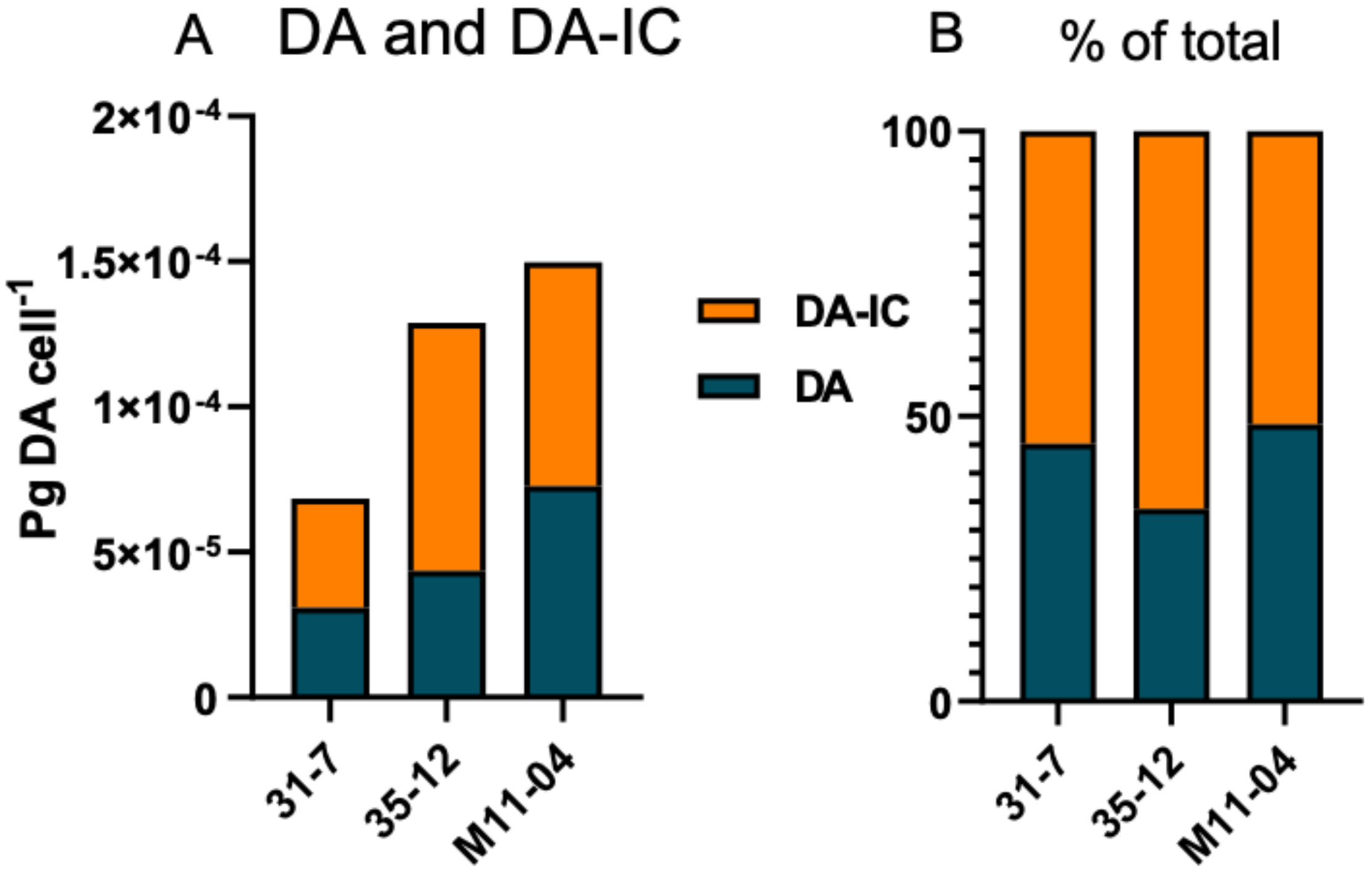
Figure 4.
(A) Domoic acid (DA) and iso-domoic acid C (DA-IC) profiles of the three toxic strains, absolute amounts. (B) Relative amounts of DA and DA-IC of the three toxic strains.

Table 1.
Table overview of the toxin content, limit of detection, cell number in the DA sample pellet, and cell volume of the three toxin-containing strains.
The total cellular DA amount ranged from 6.85 × 10−5 to 1.5 × 10−4 pg DA cell-1 (Figure 4, Table 1). Apart from DA, an isobaric compound was registered. Collision-induced dissociation (CID) spectra of DA and the isobaric compound differed only with differences between fragment intensities (Figure 5). The high similarity of the CID spectra of DA and the compound led to the hypothesis that the compound was an isomer of DA. This hypothesis was verified by an analytical standard of DA-IC, which was received from Pearse Mc Carron of the NRC-IMB in Halifax, NS, Canada, showing the same retention time and CID spectrum as the compound from the toxic P. subcurvata strains (Figure 5). DA-IC was found in all three strains, in amounts ranging from 3.76 × 10−5 to 8.54 × 10−5 pg DA-IC cell-1 (Figure 4). Domoic acid accounted for approximately half of the total DA content in all three strains, with relative amounts ranging from 51% to 66% (Figure 4B). When comparing the cellular content of total-DA (DA+DA-IC), strain 31-7 contained less than 35-12 and M11-04 (p < 0.05), but no statistical testing was possible due the lack of replicate DA samples.
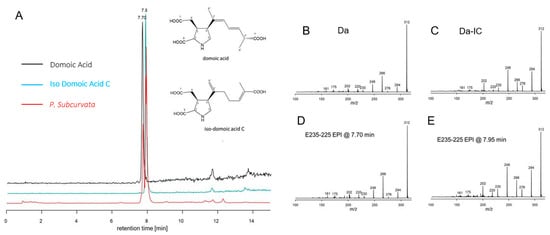
Figure 5.
(A) Extracted ion chromatograms (m/z 312 > 266) of domoic acid (black), iso-domoic acid C (green), and of compounds found in strain M11-04 (red) and structures of DA and DA-IC. (B) Collision-induced dissociation (CID) spectrum of DA (C) CID spectrum of DA-IC, (D) CID spectrum of compound m/z 312 eluting at 7.70 min of strain M11-04, and (E) CID spectrum of compound m/z 312 eluting at 7.95 min of strain M11-04.
Cell volumes of the three toxic strains varied from 162.5 to 235.8 µm3. Taking differences in cell volume into consideration, the toxin levels per cell volume showed M11-04 and 35-12 as being more potent toxin producers pr. cell volume. Total toxin content varied from 2.9 × 10−7 total DA pr. µm3 in 31-7 and peaked in M11-04 with 8.7 × 10−7 total DA pr. µm3.
3. Discussion
The finding of both DA and DA-IC in three Antarctic strains of P. subcurvata represents the first evidence of these toxins in Antarctic phytoplankton strains (Figure 4, Table 1). The presence of three toxic and twelve non-toxic strains of P. subcurvata explains the previous records of Antarctic Pseudo-nitzschia species as non-toxic [14,17]. Until now, only a total of seven strains of Pseudo-nitzschia species from Antarctic waters have been examined for DA content, i.e., four strains of P. subcurvata, two strains of P. turgiduloides, and one strain of P. lineola [14,17]. Hence, the present study triples the total number of Pseudo-nitzschia strains studied, and furthermore, detection levels might be lower in present-day studies than in studies published in early 1990s. As we found DA in three of 15 strains, the results revealed high intraspecific variation in total DA content and high likelihood of isolating and analysing non-toxic strains of possibly toxic species. These results support previous findings of high intraspecific diversity in toxin levels in other Pseudo-nitzschia species [1]. The time range covered by the sampling of the toxic strains (Supplementary Table S1) indicates the presence of toxic strains as frequent components of the Antarctic phytoplankton community. The strain containing most toxin (M11-04) is the oldest strain; however, the amounts are low in all strains but relatively comparable to other small toxic Pseudo-nitzschia species (Table 2), even though comparisons should be made with caution, as the species might be cultured under different conditions. The three toxic strains were all isolated close to the Antarctic mainland, along with five non-toxic strains, whereas all seven strains isolated farther away from the mainland were non-toxic, which is a finding that could suggest a difference in toxicity between populations of P. subcurvata but could simply also be a coincidence due to the relatively small number of strains examined.

Table 2.
Comparative species to P. subcurvata and their levels of toxins measured in laboratory (max and min if available). The species are selected based on the criteria: DA assessments without induction factors and small species.
Our evidence of DA and DA-IC in Antarctic phytoplankton supports previous findings of DA being present in the water column of the Southern Ocean during a large-scale iron fertilizer experiment in 2002 in a concentration of up to 220 ng L−1 [12]. They linked the presence of DA to the Pseudo-nitzschia species P. granii, as it was one of four and the dominant Pseudo-nitzschia species present during the experiment. P. subcurvata was not present in the water samples during the time of the experiment. Adding the finding of toxic P. subcurvata to the extremely limited number of studies in this area, as well as the report of DA in the water column coinciding with the presence of P. granii, it is reasonable to suggest that more toxigenic Pseudo-nitzschia species might be present in the Southern Ocean. Calculations suggest that P. granii contained orders of magnitude (0.85 pg cell−1) more toxin during the oceanic iron fertilizer experiment than P. subcurvata from the current investigation, indicating that some Pseudo-nitzschia species in the Southern Ocean can attain higher DA contents depending on the environmental conditions (see below). The toxic content in the strains included in the current study were low but comparable to other strains in non-inducing conditions; see Table 1 [1]. P. granii and P. subcurvata are genetically very similar, and they cluster together in the phylogenetic analysis (Figure 1) [8]. The P. granii cells analyzed during the iron-fertilizer experiment were under toxin-inducing conditions, with high iron concentrations, possibly grazer presence, and in competition with other phytoplankton species [1,12]. Taking these inducing conditions or the absence of them into consideration, it is possible that P. subcurvata comprises similar toxic potential as P. granii. Different chemical, physical, and biological factors can affect the toxicity of Pseudo-nitzschia cells, inducing higher toxicity e.g., under the depletion of silicate and phosphate and the presence of herbivorous grazers [1,11,15,28]. Therefore, future studies exploring the toxigenic potential of Antarctic Pseudo-nitzschia strains could be relevant.
The current study is consistent with a large-scale study in the transect of the east Atlantic Ocean, detecting dissolved DA in the Southern Ocean [29]. The highest dissolved DA concentration was found around the equator; dissolved DA was detectable in all surface water samples as south as 70° S [29]. This knowledge adds to the pivotal importance of studying DA presence and impact in global as well as Antactic ecosystems.
The present study is the second report of DA-IC in diatoms (Figure 5, Table 1), the first study was on P. australis isolated close to New Zealand, and the exact cellular amount is not described [10,30]. In the present study, levels of DA-IC exceeded the DA level in all three strains (Figure 4). However, previous studies on a subtropical diatom of another genus, Nitzschia navis-varingica, showed similar high relative amounts of isomers. In one study, DA-IA and DA-IB were found in concentrations of approximately 50% of the total DA content [31]. The limited knowledge on isomers of domoic acid is most likely reflecting a monitoring focus on DA and therefore limited focus on the presence of isomers, because DA is regulated in seafood production and because we know very little about the isomers. Isomers of DA are not regulated globally in industrial seafood production. The toxic potential of DA-IC is debated; one study suggested it to be one-third of DA [11], whereas another study on isomers from P. australis assessed the binding affinity for DA-IC compared to DA and found it 240-fold less potent. A third study found DA-IC to be 20 times less potent than DA [32]. Conclusively, more studies are needed to elucidate the true toxic potential of DA-IC.
Our findings support previous detections of DA in water samples in the Southern Ocean [12]. P. subcurvata is an endemic, widely distributed, and frequent component of the marine ecosystem in Antarctica [2]. Other Pseudo-nitzschia species have been recorded and are abundant in Antarctic waters, illustrating the relevance of expanding studies to more Pseudo-nitzschia species, which could also comprise both toxic and non-toxic clones. The temperature optimum for the Antarctic P. subcurvata is interestingly around 8 ℃, which is well above the present temperatures of the area [33]. As global temperatures are increasing, toxic P. subcurvata will, according to a study, enhance its competitive advantage and thus represent an increasing threat for Antarctic fauna [33]. The toxicity and frequency of harmful algae blooms are often hypothesized as increasing with global ocean warming [33]. Other factors can also enhance the toxic potential of the Pseudo-nitzschia community in the Antarctic region, like variation in nutrient availability, presence of toxin-inducing grazers (e.g., krill and copepods), variation in salinity, and pH of the ocean. These are factors known to affect the toxic potential of Pseudo-nitzschia communities, and the combined effect of these factors is largely unexplored [1] and completely unknown in the context of Antarctic species.
The present study shows, for the first time, DA presence in Pseudo-nitzschia strains from Antarctica. The Antarctic Southern Ocean is one of the most productive ecosystems in the world. The area is serving as a feeding ground for many seabirds and marine mammals. The area is especially important to the humpback whale (Megaptera novaeangliae) and the southern right whale (Eubalena australis). Both are dependent on the Antarctic region to feed on krill before the long fasting periods, which they spend calving at lower latitudes [34,35]. However, krill is an important vector for DA [15], and DA can cross the placental barrier of pregnant marine mammals [15]. This raises concern for the accumulation of DA in marine mammals in the Antarctic region [4,34,35]. Thus, toxigenic blooms of DA-producing diatoms have the potential to disturb a marine ecosystem, which is already susceptible to the effects of climate change. Thus, the effort of further mapping and exploring DA and Pseudo-nitzschia species in the Southern Ocean is of major importance.
4. Materials and Methods
Water samples and physiochemical parameters were collected with a conductivity, temperature, depth sampler (CTD) at depths of 10–15 m (Supplementary Table S1). The samples were collected between 51.99° S as the most northern and 69.3° S as the southern locality. Strains were isolated from water sampled at different localities (Figure 2, Supplementary Table S1) close to the Antarctic mainland. Monoclonal strains were established by isolation of single cells or chains. Strains were cultured in 55 mL flasks in L1 medium with salinity 30 at 4 °C and 120-µmol photons m−2 s−1 cool white light.
Cultures were harvested for toxin analyses at a density of 350,000–750,000 cells mL−1 in early stationary phase. All cultures were harvested for toxin analysis in April 2019; for this reason, some cultures were approximately 1.5 years and others were approximately 4 months (see Supplementary Table S1). A 40–45 mL well-mixed sample from each culture was centrifuged at 4 °C, 1811× g for 15 min, and the cell pellet was pooled and centrifuged once again at 1811× g for 15 min, the supernatant was the removed, and the pellet was stored at −20 °C until further analysis. Nutrient analysis was done using a QuAAtro Seal AutoAnalyzer following standard colorimetric techniques. The accuracy of the analysis was evaluated via the measurement of KANSO LTD Japan Certified Reference Materials, and corrections were applied if required.
For toxin analysis, 300–400 µL extraction solvent was added to the harvested pellet, vortexed, and solution transferred to cryotubes. Extraction was carried out following [36] and transferred to HPLC glass vials, sealed, and frozen until analysis. DA contents were measured using liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS-MS) [36].
Strains were identified as P. subcurvata by morphological studies (Figure 3) and molecular analyses of the ITS rDNA regions (ITS1, 5.8S and ITS2 ribosomal DNA) (Figure 1). DNA was extracted from cell pellets using the CTAB method [37]. For amplification of ITS rDNA, the primer pair used was forward: ITS1 (5′-TCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGG-3′) and reverse: ITS4 (5′-TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC-3′) or the newly designed ITS4Ps (5′-TCCTCCGCTTAATTATATGC-3′). PCR reactions were done in 25 µl reactions containing 1.5 mM MgCl2, 0.8 mM dNTPs (deoxyribose adenosine triphosphate) [VWR #733-1363], 0.5 units’ polymerase [VWR #733-1301], and 0.4 µM primers using 36 cycles and 55 °C as the annealing temperature. The PCR products were sent to Macrogen (Macrogen Europe, Amsterdam, NL) for purification and sequencing in both directions. Sequence analysis (trimming, assembly, BLAST) was done with Geneious version 2020.0.3 (Biomatters Ltd., Auckland, New Zealand).
Additional sequences of ITS rDNA were downloaded from GenBank and aligned using MAFFT with subsequent alignment masking, as implemented in GUIDANCE2 (34). The GUIDANCE alignment score was 0.99. The masked alignment (columns below confidence score of 0.93 were removed) was trimmed by hand and included 724 characters. The alignment was uploaded to the ATGC bioinformatics platform for PhyML 3.0 analysis with Smart Model Selection (best model was HKY85+I), using the Akaike Information Criterion and performing 1000 bootstrap replicates. Bayesian Inference was performed with MrBayes 3.2.6 using the HKY85+I model as implemented in Geneious® 2020.1.2. The following settings were used: four simultaneous Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) run for 1,000,000 generations, sampling every 1000 generations. The first 25% of trees were discarded as burn-in. Finally, a neighbor-joining tree was built, using the HKY model and 10,000 bootstrap replicates as implemented in Geneious Prime® 2020.1.2.
Cultures were rinsed for morphological analyses during March and April 2019, leaving some cultures 1.5 years old and others approximately 4 months old; the method used was [37]: a drop of the material was mounted on carbon-coated grids and left to dry. The grids were inspected in a transmission electron microscope (TEM) (JEOL 1010, Tokyo, Japan). For SEM (JEOL JSM 6335F, Tokyo, Japan), a few drops of rinsed material were mounted on round cover glasses and glued to metal stubs with double-sticky tape. The stubs were dried, sputter-coated with gold/palladium, and examined.
A minimum of three different valves from each culture was measured and included in the species determination.
Cell volume calculation: Volume = (0.6 × L × W2) + (0.4 × 0.5 × L × W2).
Where L is the cell length and W is the width of the cell.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6651/13/2/93/s1, Table S1: Detailed overview of the strains included in this study. Date of isolation, location for specific water sample, temperature, salinity and nutrient levels when available.
Author Contributions
A.J.O. and A.L. carried out the experiment and identification, A.A. performed the D.N.A. analysis, N.L. supervised experiment and manuscript, A.J.O. wrote the manuscript with support from A.L., A.A. and N.L. B.K. carried out the analysis of domoic acid and iso domoic acid, B.B. and S.L.E. sampled and isolated the cultures. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was partially financed by the Helmholtz-Gemeinschaft Deutscher Forschungszentren through the research program PACES II of the Alfred Wegener Institut-Helmholtz Zentrum für Polar- und Meeresforschung. The work was supported by The Danish Research Council grant number 9040-00248B to N.L.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data available in a publicly accessible repository that does not issue DOIs. Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: [Figure 1 GenBank Accession numbers].
Acknowledgments
We thank Pearse McCarron of the NRC-IMB in Halifax, NS, Canada for provision of the standard of DA-IC, and Øjvind Moestrup for his assistance with TEM. We are grateful for Sharyn Ossebaar (NIOZ), Laura Wischnewski, and Sinhué Torres-Valdez (AWI) for nutrients, salinity, temperature assessments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Bates, S.S.; Hubbard, K.A.; Lundholm, N.; Montresor, M.; Leaw, C.P. Pseudo-nitzschia, Nitzschia, and domoic acid: New research since 2011. Harmful Algae 2018, 79, 3–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almandoz, G.O.; Ferreyra, G.A.; Schloss, I.R.; Dogliotti, A.I.; Rupolo, V.; Paparazzo, F.E.; Esteves, J.L.; Ferrario, M.E. Distribution and ecology of Pseudo-nitzschia species (Bacillariophyceae) in surface waters of the Weddell Sea (Antarctica). Polar Biol. 2008, 31, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malviya, S.; Malviya, S.; Scalco, E.; Audic, S.; Vincent, F.; Veluchamy, A.; Poulain, J.; Wincker, P.; Iudicone, D.; de Vargas, C.; et al. Insights into global diatom distribution and diversity in the world’s ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 11, E1516–E1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, K.A.; Quakenbush, L.; Frame, E.; Huntington, K.B.; Sheffield, G.; Stimmelmayr, R.; Bryan, A.; Kendrick, P.; Ziel, H.; Goldstein, T.; et al. Prevalence of algal toxins in Alaskan marine mammals foraging in a changing arctic and subarctic environment. Harmful Algae 2016, 55, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, K.A.; Quakenbush, L.; Frame, E.; Huntington, K.B.; Sheffield, G.; Stimmelmayr, R.; Bryan, A.; Kendrick, P.; Ziel, H.; Goldstein, T.; et al. Epidemiology of Domoic Acid Poisoning in Brown Pelicans (Pelecanus occidentalis) and Brandt’ s Cormorants (Phalacrocorax penicillatus) in California. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 1993, 24, 54–62. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, T.; Zabka, T.S.; DeLong, R.L.; Wheeler, E.A.; Ylitalo, G.; Bargu, S.; Silver, M.; Leighfield, T.; Van Dolah, F.; Langlois, G.; et al. The role of domoic acid in abortion and premature parturition of California sea lions (Zalophus caufornianus) on San Miguel island, California. J. Wildl. Dis. 2009, 45, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobler, C.J. Climate Change and Harmful Algal Blooms: Insights and perspective. Harmful Algae 2020, 91, 101731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.C.; Tan, S.N.; Teng, S.T.; Lundholm, N.; Orive, E.; David, H.; Quijano-Scheggia, S.; Leong, S.C.Y.; Wolf, M.; Bates, S.S.; et al. Phylogeny and species delineation in the marine diatom Pseudo-nitzschia (Bacillariophyta) using cox1, LSU, and ITS2 rRNA genes: A perspective in character evolution. J. Phycol. 2018, 54, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.C.; Lundholm, N.; Teng, S.T.; Li, A.; Wang, C.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y. Occurrence of Pseudo-nitzschia species and associated domoic acid production along the Guangdong coast, South China Sea. Harmful Algae 2020, 98, 101899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, P.T.; Selwood, A.I.; Mountfort, D.O.; Wilkins, A.L.; McNabb, P.; Rhodes, L.L.; Doucette, G.J.; Mikulski, C.M.; King, K.L. Isodomoic acid C, an unusual amnesic shellfish poisoning toxin from Pseudo-nitzschia australis. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2005, 18, 814–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant, P.M.; Holland, P.T.; Mountfort, D.O.; Kerr, D.S. In vivo seizure induction and pharmacological preconditioning by domoic acid and isodomoic acids A., B. and C. Neuropharmacology 2008, 55, 1412–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, M.W.; Bargu, S.; Coale, S.L.; Benitez-Nelson, C.R.; Garcia, A.C.; Roberts, K.J.; Sekula-Wood, E.; Bruland, K.W.; Coale, K.H. Toxic diatoms and domoic acid in natural and iron enriched waters of the oceanic Pacific. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 2010, 107, 20762–20767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, M.E.; Licea, S. Species of the genus Pseudo-nitzschia (Bacillariophyta) in Antarctic waters: Morphology and distribution. Nov. Hedwig. 2006, 130, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, S.H.; Fryxell, G.A. Phytoplankton in the Weddell Sea, Antarctica: Composition, abundance and distribution in water-column assemblages of the marginal ice-edge zone during austral autumn. Mar. Biol. Int. J. Life Ocean. Coast. Waters 1993, 116, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargu, S.; Powell, C.; Coale, S.; Busman, M.; Doucette, G.; Silver, M. Domoic acid detection in krill: A potential vector in marine food webs. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 237, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasle, G. Nitzschia and Fragilariopsis species studied in the light and electron microscopes. I. Some marine species of the groups Nitzschiella and Lanceolatae. Det Nor. Vidensk. Akad. Oslo Mat. 1964, 16, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Fryxell, G.A.; Garza, S.A.; Roelke, D.L. Auxospore formation in an Antarctic clone of Nitzschia subcurvate, Hasle. Diatom Res. 1991, 6, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trick, C.G.; Bill, B.D.; Cochlan, W.P.; Wells, M.L.; Trainer, V.L.; Pickell, L.D. Iron enrichment stimulates toxic diatom production in high-nitrate, low-chlorophyll areas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 2010, 107, 5887–5892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, L.; White, D.; Syhre, M.; Atkinson, M. Pseudo-nitzschia species isolated from New Zealand coastal waters: Domoic acid production in vitro and links with shellfish toxicity. In Harmful Toxic Algal Bloom; Yasumoto, T., Oshima, Y., Fukuyo, Y., Eds.; The Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Paris, France, 1996; pp. 155–158. [Google Scholar]
- Lundholm, N.; Bates, S.S.; Baugh, K.A.; Bill, B.D.; Connell, L.B.; Léger, C.; Trainer, V.L. Cryptic and pseudo-cryptic diversity in diatoms-with descriptions of Pseudo-nitzschia hasleana sp. nov. and P. fryxelliana sp. nov. 1. J. Phycol. 2012, 48, 436–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trainer, V.L.; Wells, M.L.; Cochlan, W.P.; Trick, C.G.; Bill, B.D.; Baugh, K.A.; Beall, B.F.; Herndon, J.; Lundholmf, N. An ecological study of a massive bloom of toxigenic Pseudo-nitzschia cuspidata off the Washington State coast. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 1461–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J. Population dynamics and toxicity of various species of Dinophysis and Nitzschia from the southern Gulf of St. Lawrence. Can. Tech. Rep. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1991, 1799, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Baugh, K.A.; Bush, J.M.; Bill, B.D.; Lefebvre, K.A.; Trainer, V.L. Estimates of specific toxicity in several Pseudo-nitzschia species from the Washington coast, based on culture and field studies. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2006, 28, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschandreou, K.K.; Papaefthimiou, D.; Katikou, P.; Kalopesa, E.; Panou, A.; Nikolaidis, G. Morphology, phylogeny and toxin analysis of Pseudo-nitzschia pseudodelicatissima (Bacillariophyceae) isolated from the Thermaikos Gulf, Greece. Phycologia 2010, 49, 260–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryabushko, L.I.; Besiktepe, S.; Ediger, D.; Yilmaz, D.; Zenginer, A.; Ryabushko, V.I.; Lee, R.I. Toxic diatom of Pseudo-nitzschia calliantha Lundholm, Moestrup et Hasle from the Black Sea: Morphology, taxonomy, ecology. Mar. Ecol. J. ECOSI Gidrofiz. 2008, 7, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Thessen, A.; Bowers, H.; Stoeckera, D. Intra- and interspecies differences in growth and toxicity of Pseudo-nitzschia while using different nitrogen sources. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 792–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerino, F.; Orsini, L.; Sarno, D.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Tartaglione, L.; Zingone, A. The alternation of different morphotypes in the seasonal cycle of the toxic diatom Pseudo-nitzschia galaxiae. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundholm, N.; Krock, B.; John, U.; Skov, J.; Cheng, J.; Pančić, M.; Wohlrab, S.; Rigby, K.; Nielsen, T.G.; Selander, E.; et al. Induction of domoic acid production in diatoms—Types of grazers and diatoms are important. Harmful Algae 2018, 79, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geuer, J.K.; Krock, B.; Leefmann, T.; Koch, B.P. Quantification, extractability and stability of dissolved domoic acid within marine dissolved organic matter. Mar. Chem. 2019, 215, 103669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, L.L.; Holland, P.T.; Adamson, J.; McNabb, P.; Selwood, A.I. Production of a new isomer of domoic acid by New Zealand isolates of the diatom Pseudo-nitzschia australis. In Molluscan Shellfish Safety; Xunta Galicia IOC UNESCO: Paris, France, 2003; Volume 2003, pp. 43–58. [Google Scholar]
- Kotaki, Y.; Furio, E.F.; Satake, M.; Lundholm, N.; Katayama, T.; Koike, K.; Fulgueras, V.P.; Bajarias, F.A.; Takata, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; et al. Production of isodomoic acids A and B as major toxin components of a pennate diatom Nitzschia navis-varingica. Toxicon 2005, 46, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meda, M.; Kodama, T.; Tanaka, T.; Yoshizumi, H.; Takemoto, T.; Nomoto, K.; Fujita, T. Structures of isodomoic acids A, B and C novel insecticidal amino acids from the red alga Chondria armata. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1986, 34, 4892–4895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Qu, P.; Fu, F.; Tennenbaum, N.; Tatters, A.O.; Hutchins, D.A. Understanding the blob bloom: Warming increases toxicity and abundance of the harmful bloom diatom Pseudo-nitzschia in California coastal waters. Harmful Algae 2017, 67, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, V.C.; Degrati, M.; Sastre, V.; Santinelli, N.; Krock, B.; Krohn, T.; Dans, S.L.; Hoffmeyer, M.S. Domoic acid in a marine pelagic food web: Exposure of southern right whales Eubalaena australis to domoic acid on the Península Valdés calving ground, Argentina. Harmful Algae 2017, 68, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riekkola, L.; Zerbini, A.N.; Andrews, O.; Andrews-Goff, V.; Baker, C.S.; Chandler, D.; Childerhouse, S.; Clapham, P.; Dodémont, R.; Donnelly, D.; et al. Application of a multi-disciplinary approach to reveal population structure and Southern Ocean feeding grounds of humpback whales. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krock, B.; Tillmann, U.; John, U.; Cembella, A. LC-MS-MS aboard ship: Tandem mass spectrometry in the search for phycotoxins and novel toxigenic plankton from the North Sea. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 392, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundholm, N.; Daugbjerg, N.; Moestrup, Ø. Phylogeny of the Bacillariaceae with emphasis on the genus Pseudo-nitzschia (Bacillariophyceae) based on partial LSU rDNA. Eur. J. Phycol. 2002, 37, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).