Unknown Extracellular and Bioactive Metabolites of the Genus Alexandrium: A Review of Overlooked Toxins
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Alexandrium, a Potentially Toxic Genus
1.2. Ecology of Alexandrium
1.3. Taxonomy and Nomenclature of Alexandrium
1.4. Effects of Alexandrium on Marine Biota
2. Known Toxins of Alexandrium and Their Effects
2.1. Paralytic Shellfish Toxins
2.2. Cycloimines (Spirolides and Gymnodimines)
2.3. Goniodomins
| Species | PSP | Spiro-Imine | Gonodiomin | Trophy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. affine | ± a | P [21] | ||
| A. andersonii | ± b | M [21] | ||
| A. australiense | ± c | |||
| A. catenella | + d | − e | M [119] | |
| A. cohorticula | ± f | |||
| A. concavum | − g | |||
| A. diversaporum | − h | |||
| A. fragae | + i | |||
| A. fraterculus | − j | P [21] | ||
| A. hiranoi | + k | P [120] | ||
| A. insuetum | − l | P [121] | ||
| A. leei | ± m | |||
| A. margalefii | − n | P [120] | ||
| A. mediterraneum | − o | P [121] | ||
| A. minutum | ± p | M [119] | ||
| A. monilatum | − q | + r | ||
| A. ostenfeldii | ± s | ± s | M [122] | |
| A. pacificum | + t | P [121] | ||
| A. pohangense | − u | M [61] | ||
| A. pseudogonyaulax | − v | + v | M [120] | |
| A. tamarense | − w | M [123] | ||
| A. tamiyavanichii | + x | |||
| A. tamutum | − y | P [121] | ||
| A. taylorii | − z | − z | + z | P [120] |
3. Uncharacterised Extracellular Bioactivities
| Species | Hemolytic | Anti-Pathogen | Allelopathy | Anti-Grazer | Toxicity to Bivalves | Ichthyotoxic (Fishes) | Cytotoxic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. affine | [4] | [169] | [170] | ||||
| A. andersonii | [171] | [21] | [172] | ||||
| A. catenella | [173] a | [60] b | [164] c | [66] | [73] | ||
| A. fraterculus | [21] | ||||||
| A. insuetum | [121] | ||||||
| A. leei | [174] | ||||||
| A. margalefii | [121] | ||||||
| A. mediterraneum | [121] | ||||||
| A. minutum | [157] | [64] | [157] | [175] d | [68] | [176] e | |
| A. monilatum | [143] f | [177] f | |||||
| A. ostenfeldii | [163] | [85] | |||||
| A. pacificum | [178] g | [121] | |||||
| A. pohangense | [61] | ||||||
| A. pseudogonyaulax | [62] | [65] h | |||||
| A. tamarense | [173] i | [72] | [66] | ||||
| A. tamutum | [153] | [179] j | |||||
| A. taylorii | [180] k | [3] | [180] l | ||||
| Undefined strains of catenella/tamarense/ fundyense species complex | [181] m, [157] n | [182] o, [183] p |
3.1. Effect of BECs on Marine Organisms
3.1.1. Allelochemical Activities
Anti-Pathogen Activities
Effects on Protist Competitors
Anti-Grazing Activities
3.1.2. Toxicity towards Shellfish
3.1.3. Ichthyotoxicity
3.2. Methods for the Detection, Quantification and Study of BECs
3.2.1. Hemolytic Bioassay
3.2.2. Protistan Bioassay
3.2.3. Anti-Grazer Bioassay
3.2.4. Ichthyotoxicity Bioassays
3.3. State of the Art of Characterisation of Alexandrium BECs
3.3.1. Characterisation of BECs Based on Haemolytic and Allelochemical Properties
3.3.2. Ichthyotoxic BECs
3.3.3. BECs of Other Microalgal Species
4. Synthesis
4.1. Ecological Role of BECs
4.2. Toward the Essential Identification of BECs
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anderson, D.M.; Alpermann, T.J.; Cembella, A.D.; Collos, Y.; Masseret, E.; Montresor, M. The globally distributed genus Alexandrium: Multifaceted roles in marine ecosystems and impacts on human health. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 10–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wagoner, R.M.; Misner, I.; Tomas, C.R.; Wright, J.L.C. Occurrence of 12-methylgymnodimine in a spirolide-producing dinoflagellate Alexandrium peruvianum and the biogenetic implications. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 4243–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, U.; Krock, B.; Wietkamp, S.; Beran, A. A Mediterranean Alexandrium taylorii (Dinophyceae) strain produces goniodomin A and lytic compounds but not paralytic shellfish toxins. Toxins 2020, 12, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, U.; John, U. Toxic effects of Alexandrium spp. on heterotrophic dinoflagellates: An allelochemical defence mechanism independent of PSP-toxin content. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 230, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cembella, A.D. Harmful algal species fact sheets: Alexandrium. In Harmful Algal Blooms: A Compendium Desk Reference; Shumway, S.E., Burkholder, J.M., Morton, S.L., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 563–574. ISBN 978-1-118-99465-8. [Google Scholar]
- Chapelle, A.; Le Gac, M.; Labry, C.; Siano, R.; Quere, J.; Caradec, F.; Le Bec, C.; Nezan, E.; Doner, A.; Gouriou, J. The Bay of Brest (France), a new risky site for toxic Alexandrium minutum blooms and PSP shellfish contamination. Harmful Algae News 2015, 51, 4–5. [Google Scholar]
- Guallar, C.; Bacher, C.; Chapelle, A. Global and local factors driving the phenology of Alexandrium minutum (Halim) blooms and its toxicity. Harmful Algae 2017, 67, 44–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karasiewicz, S.; Chapelle, A.; Bacher, C.; Soudant, D. Harmful algae niche responses to environmental and community variation along the French coast. Harmful Algae 2020, 93, 101785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcés, E.; Bravo, I.; Vila, M.; Figueroa, R.I.; Masó, M.; Sampedro, N. Relationship between vegetative cells and cyst production during Alexandrium minutum bloom in Arenys de Mar harbour (NW Mediterranean). J. Plankton Res. 2004, 26, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapelle, A.; Le Bec, C.; Le Gac, M.; Labry, C.; Amzil, Z.; Guillou, L.; Dreanno, C.; Klouch, K.; Siano, R.; Pineau, L.; et al. Étude sur la Prolifération de la Microalgue Alexandrium Minutum en Rade de Brest. Projet Daoulex. Rapport d’avancement n° 2: Analyse des Traces Biologiques d’Alexandrium Minutum dans les sédiments de la Rade de Brest. 2014. Available online: https://archimer.ifremer.fr/doc/00191/30231/ (accessed on 1 November 2021).
- Carreto, J.I.; Benavides, H.R.; Negri, R.M.; Glorioso, P.D. Toxic red-tide in the Argentine Sea. phytoplankton distribution and survival of the toxic dinoflagellate Gonyaulax excavata in a frontal area. J. Plankton Res. 1986, 8, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallegraeff, G.M.; Steffensen, D.A.; Wetherbee, R. Three estuarine Australian dinoflagellates that can produce paralytic shellfish toxins. J. Plankton Res. 1988, 10, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitcher, G.C.; Cembella, A.D.; Joyce, L.B.; Larsen, J.; Probyn, T.A.; Ruiz Sebastián, C. The dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum in Cape Town harbour (South Africa): Bloom characteristics, phylogenetic analysis and toxin composition. Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, M.; Camp, J.; Garcés, E.; Masó, M.; Delgado, M. High resolution spatio-temporal detection of potentially harmful dinoflagellates in confined waters of the NW Mediterranean. J. Plankton Res. 2001, 23, 497–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D. A Diversity of harmful algal blooms in coastal waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 1009–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, D.W.; Pettigrew, N.R.; Thomas, A.C. On the nature of Alexandrium fundyense blooms in the Gulf of Maine. Deep. Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2005, 52, 2603–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, G.; Díaz, P.A.; Godoy, M.; Araya, M.; Ganuza, I.; Pino, R.; Álvarez, F.; Rengel, J.; Hernández, C.; Uribe, E.; et al. Paralytic shellfish toxins in surf clams Mesodesma donacium during a large bloom of Alexandrium catenella dinoflagellates associated to an intense shellfish mass mortality. Toxins 2019, 11, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, P.A.; Álvarez, G.; Varela, D.; Pérez-Santos, I.; Díaz, M.; Molinet, C.; Seguel, M.; Aguilera-Belmonte, A.; Guzmán, L.; Uribe, E.; et al. Impacts of harmful algal blooms on the aquaculture industry: Chile as a case study. Perspect. Phycol. 2019, 6, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattenrath, T.K.; Anderson, D.M.; Gobler, C.J. The influence of anthropogenic nitrogen loading and meteorological conditions on the dynamics and toxicity of Alexandrium fundyense blooms in a New York (USA) estuary. Harmful Algae 2010, 9, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, M.; Grazia, M.; Maso, M.; Gangemi, E.; Penna, A.; Sampedro, N.; Azzaro, F.; Camp, J.; Galluzzi, L. A comparative study on recurrent blooms of Alexandrium minutum in two Mediterranean coastal areas. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 673–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Jeong, H.J.; Kwon, J.E.; Kang, H.C.; Kim, J.H.; Jang, S.H.; Park, J.Y.; Yoon, E.Y.; Kim, J.S. Mixotrophic ability of the phototrophic dinoflagellates Alexandrium andersonii, A. affine, and A. fraterculus. Harmful Algae 2016, 59, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, P.J.; Tillmann, U. Mixotrophy among dinoflagellates—Prey selection, physiology and ecological imporance. In Dinoflagellates: Classification, Evolution, Physiology and Ecological Significance; DV, S.R., Ed.; Nova Science: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 201–260. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, D.M. Physiology and bloom dynamics of toxic Alexandrium species, with emphasis on life cycle transitions. In Physiology and Ecology of Harmful Algal Bloom; Anderson, D.M., Cembella, A., Hallegraeff, G.M., Eds.; NATO ASI Series; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1998; Volume G41, pp. 29–48. [Google Scholar]
- Richlen, M.L.; Zielinski, O.; Holinde, L.; Tillmann, U.; Cembella, A.; Lyu, Y.; Anderson, D.M. Distribution of Alexandrium fundyense (Dinophyceae) cysts in Greenland and Iceland, with an emphasis on viability and growth in the Arctic. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2016, 547, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillmann, U.; Bantle, A.; Krock, B.; Elbrächter, M.; Gottschling, M. Recommendations for epitypification of dinophytes exemplified by Lingulodinium polyedra and molecular phylogenetics of the Gonyaulacales based on curated rRNA sequence data. Harmful Algae 2021, 104, 101956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, Y. Alexandrium minutum nov. g. nov. sp. dinoflagellé provocant des «eaux rouges». Vie Milieu 1960, 11, 102–105. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, F.J.R.; Fukuyo, Y. The Neurotoxigenic Dinoflagellate Genus Alexandrium Halim: General Introduction. In Physiological Ecology of Harmful Algal Blooms; Anderson, D.M., Cembella, A.D., Hallegraeff, G.M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1998; pp. 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen, O. Plankton investigations in the waters round Iceland in 1903. Medd. Komm. Havunders. Kobenhaven Ser. Plankt. 1904, 1, 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Lebour, M.V. The Dinoflagellates of Northern Seas; Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom: Plymouth, UK, 1925. [Google Scholar]
- Whedon, W.F. Dinoflagellates of the San Francisco region. I. On the skeletal morphology of two new species, Gonyaulax catenella and G. acatenella. Univ. Calif. Publ. Zool. 1936, 41, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Loeblich, A.R., III; Loeblich, L.A. The systematics of Gonyaulax with special reference to the toxic species. In Toxic Dinoflagellate Blooms; Taylor, D.J., Seliger, H.H., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1979; pp. 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, F.J.R. The toxigenic gonyaulacoid dinoflagellates. In Toxic Dinoflagellate Blooms; Taylor, D.L., Seliger, H.H., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1979; pp. 47–56. [Google Scholar]
- Balech, E. The genus Alexandrium or Gonyaulax of the tamarensis group. In Toxic Dinoflagellates; Anderson, D.W., White, A.W., Baden, D.G., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Balech, E. Redescription of Alexandrium minutum Halim (Dinophyceae) type species of the genus Alexandrium. Phycologia 1989, 28, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balech, E. The Genus Alexandrium Halim (Dinoflagellata); Sherkin Island Marine Station: Cork, Ireland, 1995; Volume 452. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, S.A.; Hoppenrath, M.; Orr, R.J.S.; Bolch, C.; John, U.; Diwan, R.; Yauwenas, R.; Harwood, T.; de Salas, M.; Neilan, B.; et al. Alexandrium diversaporum sp. nov., a new non-saxitoxin producing species: Phylogeny, morphology and sxtA genes. Harmful Algae 2014, 31, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, A.S.; Jeong, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.Y. Description of the new phototrophic dinoflagellate Alexandrium pohangense sp. nov. from Korean coastal waters. Harmful Algae 2015, 46, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, S.; Oliveira, M.M.M.; Salgueiro, F.; Vilar, M.C.P.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O.; Menezes, M. Morphology and molecular phylogeny of a new PST-producing dinoflagellate species: Alexandrium fragae sp. nov. (Gonyaulacales, dinophyceae). Harmful Algae 2020, 95, 101793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, J.; Nguyen, N.L. Potentially Toxic Microalgae of Vietnamese Waters; Council for Nordic Publications in Botany: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2004; ISBN 8788702855. [Google Scholar]
- Montresor, M.; John, U.; Beran, A.; Medlin, L.K. Alexandrium tamutum sp. nov. (Dinophyceae): A new nontoxic species in the genus Alexandrium. J. Phycol. 2004, 40, 398–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.; Kuribara, Y.; Fukuzawa, R.; Mimura, K.; Funaki, H.; Tanaka, K.; Watanabe, R.; Uchida, H.; Suzuki, T.; Adachi, M. First report of Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) associated with marine macroalgae off Japan: Diversity, distribution, and toxicity. Harmful Algae 2021, 104, 101924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Mertens, K.N.; Nézan, E.; Chomérat, N.; Bilien, G.; Iwataki, M.; Shin, H.H. Discovery of a new clade nested within the genus Alexandrium (Dinophyceae): Morpho-molecular characterization of Centrodinium punctatum (Cleve) F.J.R. Taylor. Protist 2019, 170, 168–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, F.; Artigas, L.F. Redefinition of the dinoflagellate genus Alexandrium based on Centrodinium: Reinstatement of Gessnerium and Protogonyaulax, and Episemicolon gen. nov. (Gonyaulacales, Dinophyceae). J. Mar. Biol. 2019, 2019, 1284104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.H.; Li, Z.; Réveillon, D.; Rovillon, G.A.; Mertens, K.N.; Hess, P.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, D.; et al. Centrodinium punctatum (Dinophyceae) produces significant levels of saxitoxin and related analogs. Harmful Algae 2020, 100, 101923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertens, K.N.; Adachi, M.; Anderson, D.M.; Band-Schmidt, C.J.; Bravo, I.; Brosnahan, M.L.; Bolch, C.J.S.; Calado, A.J.; Carbonell-Moore, M.C.; Chomérat, N.; et al. Morphological and phylogenetic data do not support the split of Alexandrium into four genera. Harmful Algae 2020, 98, 101902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilly, E.L.; Halanych, K.M.; Anderson, D.M. Phylogeny, biogeography, and species boundaries within the Alexandrium minutum group. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 1004–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilly, E.L.; Halanych, K.M.; Anderson, D.M. Species boundaries and global biogeography of the Alexandrium tamarense complex (Dinophyceae). J. Phycol. 2007, 43, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, U.; Litaker, R.W.; Montresor, M.; Murray, S.; Brosnahan, M.L.; Anderson, D.M. Formal revision of the Alexandrium tamarense species complex (dinophyceae) taxonomy: The introduction of five species with emphasis on molecular-based (rDNA) classification. Protist 2014, 165, 779–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lin, X.; Lin, S. DNA barcoding species in Alexandrium tamarense complex using ITS and proposing designation of five species. Harmful Algae 2014, 31, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholin, C.A.; Herzog, M.; Sogin, M.; Anderson, D.M. Identification of a group- and strain-specific genetic markers for globally distributed Alexandrium (dinophyceae). II. Sequence analysis of a fragment of the LSU rRNA gene. J. Phycol. 1994, 30, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, S.; Sampedro, N.; Larsen, J.; Moestrup, Ø.; Calado, A.J. Arguments against the proposal 2302 by John & al. to reject the name Gonyaulax catenella (Alexandrium catenella). Taxon 2015, 64, 634–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litaker, R.W.; Fraga, S.; Montresor, M.; Brosnahan, M.L.; Hoppenrath, M.; Murray, S.; Calado, A.J. A practical guide to new nomenclature for species within the “Alexandrium tamarense species complex”. Harmful Algae News 2018, 61, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Guiry, M.D.; Guiry, G.M. AlgaeBase. World-Wide Electronic Publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. 2021. Available online: https://www.algaebase.org (accessed on 7 December 2021).
- Hégaret, H.; Da Silva, P.M.; Wikfors, G.H.; Haberkorn, H.; Shumway, S.E.; Soudant, P. In Vitro interactions between several species of harmful algae and haemocytes of bivalve molluscs. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2011, 27, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, S.P.; Burkholder, J.A.M.; Shumway, S.E.; Hégaret, H.; Wikfors, G.H.; Frank, D. Effects of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium monilatum on survival, grazing and behavioral response of three ecologically important bivalve molluscs. Harmful Algae 2010, 9, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr, M.; Lair, S.; Michaud, S.; Scarratt, M.; Quilliam, M.; Lefaivre, D.; Robert, M.; Wotherspoon, A.; Michaud, R.; Ménard, N.; et al. Multispecies mass mortality of marine fauna linked to a toxic dinoflagellate bloom. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cembella, A.D.; Quilliam, M.A.; Lewis, N.I.; Bauder, A.G.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Thomas, K.; Jellett, J.; Cusack, R.R. The toxigenic marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense as the probable cause of mortality of caged salmon in Nova Scotia. Harmful Algae 2002, 1, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, U.; Alpermann, T.; John, U.; Cembella, A. Allelochemical interactions and short-term effects of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium on selected photoautotrophic and heterotrophic protists. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, U.; Hansen, P.J. Allelopathic effects of Alexandrium tamarense on other algae: Evidence from mixed growth experiments. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2009, 57, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattenrath-Lehmann, T.K.; Gobler, C.J. Allelopathic inhibition of competing phytoplankton by North American strains of the toxic dinoflagellate, Alexandrium fundyense: Evidence from field experiments, laboratory experiments, and bloom events. Harmful Algae 2011, 11, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, A.S.; Jeong, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Jang, S.H.; Lee, M.J.; Lee, K. Mixotrophy in the newly described dinoflagellate Alexandrium pohangense: A specialist for feeding on the fast-swimming ichthyotoxic dinoflagellate Cochlodinium polykrikoides. Harmful Algae 2015, 49, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blossom, H.E.; Daugbjerg, N.; Hansen, P.J. Toxic mucus traps: A novel mechanism that mediates prey uptake in the mixotrophic dinoflagellate Alexandrium pseudogonyaulax. Harmful Algae 2012, 17, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Jeong, H.J.; Lim, A.S.; Rho, J.R.; Lee, S.B. Killing potential protist predators as a survival strategy of the newly described dinoflagellate Alexandrium pohangense. Harmful Algae 2016, 55, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, M.; Marie, D.; Szymczak, J.; Toullec, J.; Bigeard, E.; Sourisseau, M.; Le Gac, M.; Guillou, L.; Jauzein, C. Dinophyceae can use exudates as weapons against the parasite Amoebophrya sp. (Syndiniales). ISME Commun. 2021, 1, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Hansen, P.; Nielsen, L.; Krock, B.; Tillmann, U.; Kiørboe, T. Distinctly different behavioral responses of a copepod, Temora longicornis, to different strains of toxic dinoflagellates, Alexandrium spp. Harmful Algae 2016, 62, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, V.A.; Langeloh, H.; Tillmann, U.; Krock, B.; Müller, A.; Bickmeyer, U.; Abele, D. Separate and combined effects of neurotoxic and lytic compounds of Alexandrium strains on Mytilus edulis feeding activity and hemocyte function. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 84, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borcier, E.; Morvezen, R.; Boudry, P.; Miner, P.; Charrier, G.; Laroche, J.; Hegaret, H. Effects of bioactive extracellular compounds and paralytic shellfish toxins produced by Alexandrium minutum on growth and behaviour of juvenile great scallops Pecten maximus. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 184, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrec, J.; Soudant, P.; Payton, L.; Tran, D.; Miner, P.; Lambert, C.; Goïc, N.L.; Huvet, A.; Quillien, V.; Boullot, F.; et al. Bioactive extracellular compounds produced by the dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum are highly detrimental for oysters. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 199, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castrec, J.; Hégaret, H.; Alunno-Bruscia, M.; Picard, M.; Soudant, P.; Petton, B.; Boulais, M.; Suquet, M.; Quéau, I.; Ratiskol, D.; et al. The dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum affects development of the oyster Crassostrea gigas, through parental or direct exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrec, J.; Hégaret, H.; Huber, M.; Le Grand, J.; Huvet, A.; Tallec, K.; Boulais, M.; Soudant, P.; Fabioux, C. The toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum impairs the performance of oyster embryos and larvae. Harmful Algae 2020, 92, 101744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrec, J.; Fabioux, C.; Le Goïc, N.; Boulais, M.; Soudant, P.; Hégaret, H. The toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum affects oyster gamete health and fertilization potential. Mar. Environ. Res. 2021, 169, 105401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, V.A.; Bickmeyer, U.; Tillmann, U.; Krock, B.; Müller, A.; Abele, D. In Vitro effects of paralytic shellfish toxins and lytic extracellular compounds produced by Alexandrium strains on hemocyte integrity and function in Mytilus edulis. Toxins 2021, 13, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardones, J.I.; Dorantes-Aranda, J.J.; Nichols, P.D.; Hallegraeff, G.M. Fish gill damage by the dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella from Chilean fjords: Synergistic action of ROS and PUFA. Harmful Algae 2015, 49, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricelj, V.M.; Shumway, S.E. Paralytic shellfish toxins in bivalve molluscs: Occurrence, transfer kinetics, and biotransformation. Rev. Fish. Sci. 1998, 6, 315–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Gigirey, B.; Soliño, L.; Bravo, I.; Rodríguez, F.; Casero, M.V.M. Paralytic and amnesic shellfish toxins impacts on seabirds, analyses and management. Toxins 2021, 13, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefebvre, K.A.; Quakenbush, L.; Frame, E.; Huntington, K.B.; Sheffield, G.; Stimmelmayr, R.; Bryan, A.; Kendrick, P.; Ziel, H.; Goldstein, T.; et al. Prevalence of algal toxins in Alaskan marine mammals foraging in a changing arctic and subarctic environment. Harmful Algae 2016, 55, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, H.; Meyer, K.F. Paralytic Shell-Fish Poisoning. Arch. Pathol. 1937, 24, 560–598. [Google Scholar]
- White, A.W. Seafood Toxins; Ragelis, E., Ed.; ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1984; pp. 171–180. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.Y.; Chou, H.N. Ichthyotoxicity studies of milkfish Chanos chanos fingerlings exposed to a harmful dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2001, 262, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, D.F.; Da Silva, P.M.; Barracco, M.A.; Soudant, P.; Hégaret, H. Effects of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum and its toxin (saxitoxin) on the functional activity and gene expression of Crassostrea gigas hemocytes. Harmful Algae 2013, 26, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, B.A.; Andersen, R.J.; Harrison, P.J. Feeding deterrent and toxicity effects of apo-fucoxanthinoids and phycotoxins on a marine copepod (Tigriopus californicus). Mar. Biol. 1997, 128, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhan, J.; Liu, L.; Gong, Y. Transcriptomic responses of Artemia salina exposed to an environmentally relevant dose of Alexandrium minutum cells or Gonyautoxin 2/3. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stivala, C.E.; Benoit, E.; Aráoz, R.; Servent, D.; Novikov, A.; Molgó, J.; Zakarian, A. Synthesis and biology of cyclic imine toxins, an emerging class of potent, globally distributed marine toxins. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 411–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Curtis, J.M.; Oshima, Y.; Quilliam, M.A.; Walter, J.A.; Watson-Wright, W.M.; Wright, J.L.C. Spirolides B and D, two novel macrocycles isolated from the digestive glands of shellfish. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1995, 97, 2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, P.J.; Cembella, A.D.; Moestrup, Ø. The marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii: Paralytic shellfish toxin concentration, composition, and toxicity to a tintinnid ciliate. J. Phycol. 1992, 28, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Burton, I.W.; Cembella, A.D.; Curtis, J.M.; Quilliam, M.A.; Walter, J.A.; Wright, J.L.C. Characterization of Spirolides A, C, and 13-Desmethyl C, New Marine Toxins Isolated from Toxic Plankton and Contaminated Shellfish. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, H.; Tillmann, U.; Harju, K.; Aversano, C.D.; Tartaglione, L.; Krock, B. Toxin variability estimations of 68 Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) strains from the Netherlands reveal a novel abundant gymnodimine. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieva, J.A.; Tebben, J.; Tillmann, U.; Wohlrab, S. Mass spectrometry-based characterization of new spirolides from Alexandrium ostenfeldii. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurhelle, C.; Nieva, J.; Tillmann, U.; Harder, T.; Krock, B.; Tebben, J. Identification of novel gymnodimines and spirolides from the marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aasen, J.; Mackinnon, S.L.; Leblanc, P.; Walter, J.A.; Hovgaard, P.; Aune, T.; Quilliam, M.A. Detection and identification of spirolides in Norwegian shellfish and plankton. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2005, 18, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciminiello, P.; Dell, C.; Fattorusso, E.; Magno, S.; Tartaglione, L.; Cangini, M.; Pompei, M.; Guerrini, F.; Boni, L.; Pistocchi, R. Toxin profile of Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) from the Northern Adriatic Sea revealed by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Toxicon 2006, 47, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackinnon, S.L.; Walter, J.A.; Quilliam, M.A.; Cembella, A.D.; Leblanc, P.; Burton, I.W.; Hardstaff, W.R.; Lewis, N.I. Spirolides isolated from Danish strains of the toxigenic dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, J.S.; Leblanc, P.; Lewis, N.I.; Munday, R.; Quilliam, M.A.; Mackinnon, S.L. Characterization of a dispiroketal spirolide subclass from Alexandrium ostenfeldii. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1237–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciminiello, P.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Iacovo, E.D.; Fattorusso, E.; Forino, M.; Grauso, L.; Tartaglione, L.; Guerrini, F.; Pezzolesi, L.; Pistocchi, R. Characterization of 27-hydroxy-13-desmethyl spirolide C and 27-oxo-13,19-didesmethyl spirolide C. Further insights into the complex Adriatic Alexandrium ostenfeldii toxin profile. Toxicon 2010, 56, 1327–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, U.; Kremp, A.; Tahvanainen, P.; Krock, B. Characterization of spirolide producing Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) from the western Arctic. Harmful Algae 2014, 39, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinder, V.A.; Tillmann, U.; Krock, B.; Delgado, A.L.; Krohn, T.; Garzón Cardona, J.E.; Metfies, K.; López Abbate, C.; Silva, R.; Lara, R. Plankton multiproxy analyses in the northern Patagonian shelf, Argentina: Community structure, phycotoxins, and characterization of toxic Alexandrium strains. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Rafuse, C.; Lewis, N.I.; Li, A.; Meng, F.; Beach, D.G.; McCarron, P. Screening of cyclic imine and paralytic shellfish toxins in isolates of the genus Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) from Atlantic Canada. Harmful Algae 2018, 77, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, T.; Satake, M.; Mackenzie, L.; Kaspar, H.F.; Yasumoto, T. Gymnodimine, a new marine toxin of unprecedented structure isolated from New Zealand oysters and the dinoflagellate, Gymnodinium sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 7093–7096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, T.; Satake, M.; MacKenzie, L.; Kaspar, H.F.; Yasumoto, T. Gymnodimine, A novel toxic imine isolated from the Foveaux Strait oysters and Gymnodinium sp. In Harmful Toxic Algal Bloom; Yasumoto, T., Oshima, Y., Fukuyo, Y., Eds.; Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Paris, France, 1996; pp. 495–498. [Google Scholar]
- Harju, K.; Koskela, H.; Kremp, A.; Suikkanen, S.; de la Iglesia, P.; Miles, C.O.; Krock, B.; Vanninen, P. Identification of gymnodimine D and presence of gymnodimine variants in the dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii from the Baltic Sea. Toxicon 2016, 112, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munday, R.; Selwood, A.I.; Rhodes, L. Acute toxicity of pinnatoxins E, F and G to mice. Toxicon 2012, 60, 995–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, P.; Alfonso, A.; Rodríguez, P.; Rubiolo, J.A.; Manuel, J.; Bermúdez, R.; Vieytes, M.R.; Botana, L.M. Pharmacokinetic and toxicological data of spirolides after oral and intraperitoneal administration. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourne, Y.; Radic, Z.; Aráoz, R.; Talley, T.T.; Benoit, E.; Servent, D.; Taylor, P.; Molgó, J.; Marchot, P. Structural determinants in phycotoxins and AChBP conferring high affinity binding and nicotinic AChR antagonism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6076–6081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, T.A.; Hepler, C.D.; Kombo, D.C.; Grinevich, V.P.; Kiser, M.N.; Hooker, D.N.; Zhang, J.; Mountfort, D.; Selwood, A.; Akireddy, S.R.; et al. Comparison of acetylcholine receptor interactions of the marine toxins, 13-desmethylspirolide C and gymnodimine. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 2238–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharrat, R.; Servent, D.; Girard, E.; Ouanounou, G.; Amar, M.; Marrouchi, R.; Benoit, E.; Molgó, J. The marine phycotoxin gymnodimine targets muscular and neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes with high affinity. J. Neurochem. 2008, 107, 952–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aráoz, R.; Ouanounou, G.; Iorga, B.I.; Alili, D.; Amar, M.; Benoit, E.; Molgo, J.; Servent, D.; Paris-saclay, I.N.; Yvette, G.; et al. The neurotoxic effect of 13, 19-didesmethyl and 13-desmethyl spirolide C phycotoxins is mainly mediated by nicotinic rather than muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 147, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieva, J.A.; Krock, B.; Tillmann, U.; Tebben, J.; Zurhelle, C. Gymnodimine A and 13-desMethyl spirolide C alter intracellular calcium levels via acetylcholine receptors. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, T.; Fukuyo, Y.; Tokuda, H.; Hirano, R. Sexual reproduction of Alexandrium hiranoi (Dinophyceae). Bull. Plankt. Soc. Jpn. 1993, 39, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, G.M.; Michaels, L.; Burkholder, P.R. Goniodomin, a new antibiotic from a dinoflagellate. J. Antibiot. 1968, 21, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, M.; Makabe, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Konosu, S.; Wälchli, M.R. Goniodomin A, a novel polyether macrolide from the dinoflagellate Goniodoma pseudogoniaulax. Tetrahedron Lett. 1988, 29, 1149–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.M.; Reece, K.S.; Stec, D.F.; Scott, G.P.; Jones, W.M.; Hobbs, P.L.M.; Harris, T.M. The toxin goniodomin, produced by Alexandrium spp., is identical to goniodomin A. Harmful Algae 2020, 92, 101707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsia, M.H.; Morton, S.L.; Smith, L.L.; Beauchesne, K.R.; Huncik, K.M.; Moeller, P.D.R. Production of goniodomin A by the planktonic, chain-forming dinoflagellate Alexandrium monilatum (Howell) Balech isolated from the Gulf Coast of the United States. Harmful Algae 2006, 5, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triki, H.Z.; Laabir, M.; Moeller, P.; Chomérat, N.; Daly-Yahia, O.K. First report of goniodomin A production by the dinoflagellate Alexandrium pseudogonyaulax developing in southern Mediterranean (Bizerte Lagoon, Tunisia). Toxicon 2016, 111, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, Y. Stereochemical Assignment of Goniodomin A, an Actin-Targeting Polyether Macrolide. Ph.D. Thesis, Tohoku University, Sendai, Japan, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, M.; Inoue, D.; Matsunaga, K.; Ohizumi, Y.; Ueda, H.; Asano, T.; Murakami, M.; Sato, Y. Goniodomin A, an antifungal polyether macrolide, exhibits antiangiogenic activities via inhibition of actin reorganization in endothelial cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2002, 116, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, J.M.; Mann, R.; Moeller, P.; Hsia, M.S. Mortality of the veined rapa whelk, Rapana Venosa, in relation to a bloom of Alexandrium monilatum in the York River, United States. J. Shellfish Res. 2009, 28, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espiña, B.; Cagide, E.; Louzao, M.C.; Vilariño, N.; Vieytes, M.R.; Takeda, Y.; Sasaki, M.; Botana, L.M. Cytotoxicity of goniodomin A and B in non contractile cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 251, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tainter, C.J.; Schley, N.D.; Harris, C.M.; Stec, D.F.; Song, A.K.; Balinski, A.; May, J.C.; Mclean, J.A.; Reece, K.S.; Harris, T.M. Algal toxin goniodomin A binds potassium ion selectively to yield a conformationally altered complex with potential biological consequences. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 1069–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hae, J.J.; Jae, Y.P.; Jae, H.N.; Myung, O.P.; Jeong, H.H.; Kyeong, A.S.; Jeng, C.; Chi, N.S.; Kwang, Y.L.; Won, H.Y. Feeding by red-tide dinoflagellates on the cyanobacterium Synechococcus. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2005, 41, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blossom, H.E.; Bædkel, T.D.; Tillmann, U.; Hansen, P.J. A search for mixotrophy and mucus trap production in Alexandrium spp. and the dynamics of mucus trap formation in Alexandrium pseudogonyaulax. Harmful Algae 2017, 64, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, A.S.; Jeong, H.J.; Ok, J.H. Five Alexandrium species lacking mixotrophic ability. Algae 2019, 34, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, D.M.; Anderson, D.M. Widespread phagocytosis of ciliates and other protists by marine mixotrophic and heterotrophic thecate dinoflagellates. J. Phycol. 1996, 32, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Yoo, Y.; Jeong, H.J.; Kim, M.S.; Kang, N.S.; Song, J.Y.; Shin, W.; Kim, K.Y.; Lee, K. Feeding by phototrophic red-tide dinoflagellates on the ubiquitous marine diatom Skeletonema costatum. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2009, 56, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, R.J.S.; Stüken, A.; Rundberget, T.; Eikrem, W.; Jakobsen, K.S. Improved phylogenetic resolution of toxic and non-toxic Alexandrium strains using a concatenated rDNA approach. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 676–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Ngoc, L. An autecological study of the potentially toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium affine isolated from Vietnamese waters. Harmful Algae 2004, 3, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciminiello, P.; Fattorusso, E.; Forino, M.; Montresor, M. Saxitoxin and neosaxitoxin as toxic principles of Alexandrium andersoni (Dinophyceae) from the Gulf of Naples, Italy. Toxicon 2000, 38, 1871–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzet, N.; Franco, J.M.; Raine, R. Morphogenetic diversity and biotoxin composition of Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) in Irish coastal waters. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 782–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Zeng, N.; Liu, T.; Yang, W.; Müller, A.; Krock, B. Morphology, toxicity, and phylogeny of Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) species along the coast of China. Harmful Algae 2013, 27, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savela, H.; Harju, K.; Spoof, L.; Lindehoff, E.; Meriluoto, J.; Vehniäinen, M.; Kremp, A. Quantity of the dinoflagellate sxtA4 gene and cell density correlates with paralytic shellfish toxin production in Alexandrium ostenfeldii blooms. Harmful Algae 2016, 52, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, S.A.; Wiese, M.; Neilan, B.A.; Orr, R.J.S.; de Salas, M.; Brett, S.; Hallegraeff, G. A reinvestigation of saxitoxin production and sxtA in the “non-toxic” Alexandrium tamarense Group V clade. Harmful Algae 2012, 18, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolch, C.J.S.; de Salas, M.F. A review of the molecular evidence for ballast water introduction of the toxic dinoflagellates Gymnodinium catenatum and the Alexandrium “tamarensis complex” to Australasia. Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 465–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallegraeff, G.M.; Bolch, C.; Blackburn, S.I.; Oshima, Y. Species of the toxigenic dinoflagellate genus Alexandrium in southeastern Australian waters. Bot. Mar. 1991, 34, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, J.E.; Park, G.; Dam, H.G. Relative importance of nitrogen sources, algal alarm cues and grazer exposure to toxin production of the marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella. Harmful Algae 2019, 84, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cembella, A.D.; Lewis, N.I.; Quilliam, M.A. The marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) as the causative organism of spirolide shellfish toxins. Phycologia 2000, 8884, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, L.; De Salas, M.; Adamson, J.; Beuzenberg, V. The dinoflagellate genus Alexandrium (Halim) in New Zealand coastal waters: Comparative morphology, toxicity and molecular genetics. Harmful Algae 2004, 3, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.J.; Kim, C.H.; Sako, Y. Paralytic shellfish poisoning toxin analysis of the genus Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) occurring in Korean coastal waters. Fish. Sci. 2005, 71, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaga, S.; Sekiguchi, K.; Yoshida, M.; Ogata, T. Occurrence and toxin production of Alexandrium spp. (Dinophyceae) in coastal waters of Iwate Prefecture, Japan. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 2006, 72, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gires, U.; Leaw, C.P.; Asmat, A.; Lim, P.T. Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) species in Malaysian waters. Harmful Algae 2002, 1, 265–275. [Google Scholar]
- Perini, F.; Galluzzi, L.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Iacovo, E.D.; Tartaglione, L.; Ricci, F.; Forino, M.; Ciminiello, P.; Penna, A. SxtA and sxtG gene expression and toxin production in the mediterranean Alexandrium minutum (Dinophyceae). Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5258–5276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geffroy, S.; Lechat, M.M.; Le Gac, M.; Rovillon, G.A.; Marie, D.; Bigeard, E.; Malo, F.; Amzil, Z.; Guillou, L.; Caruana, A.M.N. From the sxtA4 gene to saxitoxin production: What controls the variability among Alexandrium minutum and Alexandrium pacificum strains? Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.; Bresnan, E.; Graham, J.; Lacaze, J.P.; Turrell, E.; Collins, C. Distribution, diversity and toxin composition of the genus Alexandrium (dinophyceae) in Scottish waters. Eur. J. Phycol. 2010, 45, 375–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzet, N.; Franco, J.M.; Raine, R. Characterization of nontoxic and toxin-producing strains of Alexandrium minutum (Dinophyceae) in Irish coastal waters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 3333–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemons, G.P.; Pinion, J.P.; Bass, E.; Pham, D.V.; Sharif, M.; Wutoh, J.G. A hemolytic principle associated with the red-tide dinoflagellate Gonyaulax monilata. Toxicon 1980, 18, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemons, G.P.; Pham, D.V.; Pinion, J.P. Insecticidal activity of Gonyaulax (dinophyceae) cell powders and saxitoxin to the german cockroach. J. Phycol. 1980, 16, 305–307. [Google Scholar]
- Suikkanen, S.; Kremp, A.; Hautala, H.; Krock, B. Paralytic shellfish toxins or spirolides? The role of environmental and genetic factors in toxin production of the Alexandrium ostenfeldii complex. Harmful Algae 2013, 26, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, P.; Riobó, P.; Rodríguez, F.; Franco, J.M.; Bravo, I. Differences in the toxin profiles of Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) strains isolated from different geographic origins: Evidence of paralytic toxin, spirolide, and gymnodimine. Toxicon 2015, 103, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krock, B.; Tillmann, U.; Wen, Y.; Hansen, P.J.; Larsen, T.O.; Andersen, A.J.C. Development of a LC-MS/MS method for the quantification of goniodomins A and B and its application to Alexandrium pseudogonyaulax strains and plankton field samples of Danish coastal waters. Toxicon 2018, 155, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugliè, A.; Giacobbe, M.G.; Riccardi, E.; Bruno, M.; Pigozzi, S.; Mariani, M.A.; Satta, C.T.; Stacca, D.; Bazzoni, A.M.; Caddeo, T.; et al. Paralytic shellfish toxins and cyanotoxins in the Mediterranean: New data from sardinia and Sicily (Italy). Microorganisms 2017, 5, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hii, K.S.; Lim, P.T.; Tan, T.H.; Leaw, C.P. Characterization of the Saxitoxin Biosynthetic Starting Gene, sxta in the Toxic Dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamiyavanichii. In Proceedings of the 12th Symposium of the Malaysian Society of Applied Biology: Solutions to Global Challenges and Issues, Kuala Terengganu, Malaysia, 1–3 June 2012; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Menezes, M.; Varela, D.; De Oliveira Proença, L.A.; Da Silva Tamanaha, M.; Paredes, J. Identification of the toxic alga Alexandrium tamiyavanichi (dinophyceae) from Northeastern Brazil: A combined morphological and rDNA sequence (partial lsu and its) approach. J. Phycol. 2010, 46, 1239–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, P.T.; Ogata, T. Salinity effect on growth and toxin production of four tropical Alexandrium species (Dinophyceae). Toxicon 2005, 45, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, P.T.; Leaw, C.P.; Usup, G.; Kobiyama, A.; Koike, K.; Ogata, T. Effects of light and temperature on growth, nitrate uptake, and toxin production of two tropical dinoflagellates: Alexandrium tamiyavanichii and Alexandrium minutum (Dinophyceae). J. Phycol. 2006, 42, 786–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, U.; Krock, B.; Alpermann, T.J.; Cembella, A. Bioactive compounds of marine dinoflagellate isolates from western Greenland and their phylogenetic association within the genus Alexandrium. Harmful Algae 2016, 51, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremp, A.; Hansen, P.J.; Tillmann, U.; Savela, H.; Suikkanen, S.; Voß, D.; Barrera, F.; Jakobsen, H.H.; Krock, B. Distributions of three Alexandrium species and their toxins across a salinity gradient suggest an increasing impact of GDA producing A. pseudogonyaulax in shallow brackish waters of Northern Europe. Harmful Algae 2019, 87, 101622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, P.T.; Usup, G.; Leaw, C.P.; Ogata, T. First report of Alexandrium taylori and Alexandrium peruvianum (Dinophyceae) in Malaysia waters. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Tallec, K.; Soudant, P.; Lambert, C.; Le Grand, F.; Sarthou, G.; Jolley, D.; Hégaret, H. A rapid quantitative fluorescence-based bioassay to study allelochemical interactions from Alexandrium minutum. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 1598–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzul, G.; Seguel, M.; Guzman, L.; Denn, E.E. Comparison of allelopathic properties in 3 toxic Alexandrium species. J. Exp. Bot. 1999, 232, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, U.; Alpermann, T.L.; da Purificação, R.C.; Krock, B.; Cembella, A. Intra-population clonal variability in allelochemical potency of the toxigenic dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpermann, T.J.; Tillmann, U.; Beszteri, B.; Cembella, A.D.; John, U. Phenotypic variation and genotypic diversity in a planktonic population of the toxigenic marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense (Dinophyceae). J. Phycol. 2010, 46, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Waal, D.B.; Tillmann, U.; Martens, H.; Krock, B.; van Scheppingen, Y.; John, U. Characterization of multiple isolates from an Alexandrium ostenfeldii bloom in The Netherlands. Harmful Algae 2015, 49, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandenburg, K.M. Intraspecific trait variation and trade-offs within and across populations of a toxic dinoflagellate. Ecol. Lett. 2018, 21, 1561–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fistarol, G.O.; Legrand, C.; Selander, E.; Hummert, C.; Stolte, W.; Granéli, E. Allelopathy in Alexandrium spp.: Effect on a natural plankton community and on algal monocultures. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 35, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, U.; John, U.; Cembella, A. On the allelochemical potency of the marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii against heterotrophic and autotrophic protists. J. Plankton Res. 2007, 29, 527–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, U.; Tillmann, U.; Hulskotter, J.; Alpermann, T.J.; Wohlrab, S.; Van de Waal, D.B. Intraspecific facilitation by allelochemical mediated grazing protection within a toxigenic dinoflagellate population. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20141268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelong, A.; Haberkorn, H.; Le Goïc, N.; Hégaret, H.; Soudant, P. A new insight into allelopathic effects of Alexandrium minutum on photosynthesis and respiration of the diatom Chaetoceros neogracile revealed by photosynthetic-performance analysis and flow cytometry. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 62, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Tillmann, U. Nutrient starvation effects on the allelochemical potency of Alexandrium tamarense (Dinophyceae). Mar. Biol. 2012, 159, 1449–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blossom, H.E.; Markussen, B.; Daugbjerg, N.; Krock, B.; Norlin, A.; Hansen, P.J. The cost of toxicity in microalgae: Direct evidence from the dinoflagellate Alexandrium. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blossom, H.E.; Hansen, P.J. The loss of mixotrophy in Alexandrium pseudogonyaulax: Implications for trade-offs between toxicity, mucus trap production, and phagotrophy. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2021, 66, 528–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basti, L.; Nagai, S.; Go, J.; Okano, S.; Nagai, K.; Watanabe, R.; Suzuki, T.; Tanaka, Y. Differential inimical effects of Alexandrium spp. and Karenia spp. on cleavage, hatching, and two larval stages of Japanese pearl oyster Pinctada fucata martensii. Harmful Algae 2015, 43, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, N.; Nam, S.-E.; Shin, Y.K.; Rhee, J.-S. The dinoflagellate Alexandrium affine acutely induces significant modulations on innate immunity, hepatic function, and antioxidant defense system in the gill and liver tissues of red seabream. Aquat. Toxicol. 2021, 240, 105985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampedro, N.; Franco, J.M.; Zapata, M.; Riobó, P.; Garcés, E.; Penna, A.; Caillaud, A.; Diogène, J.; Cacho, E.; Camp, J. The toxicity and intraspecific variability of Alexandrium andersonii Balech. Harmful Algae 2013, 25, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansone, C.; Nuzzo, G.; Galasso, C.; Casotti, R.; Fontana, A.; Romano, G.; Ianora, A. The marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium andersoni induces cell death in lung and colorectal tumor cell lines. Mar. Biotechnol. 2018, 20, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschbach, E.; Scharsack, J.P.; John, U.; Medlin, L.K. Improved erythrocyte lysis assay in microtitre plates for senstiive detection and efficient measurement of haemolytic compounds from ichthyotoxic algae. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2001, 21, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.Z.; Kong, L.; Holmes, M.J. Dinoflagellate Alexandrium leei (Dinophyceae) from Singapore coastal waters produces a water-soluble ichthyotoxin. Mar. Biol. 2007, 150, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhl, A.R.; Martins, C.A.; Anderson, D.M. Toxicity of Alexandrium lusitanicum to gastropod larvae is not caused by paralytic-shellfish-poisoning toxins. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galasso, C.; Nuzzo, G.; Brunet, C.; Ianora, A.; Sardo, A.; Fontana, A.; Sansone, C. The marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum activates a mitophagic pathway in human lung cancer cells. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldrich, D.V.; Ray, S.M.; Wilson, W.B. Gonyaulax monilata: Population growth and development of toxicity in cultures. J. Protozool. 1967, 14, 636–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassudrie, M.; Soudant, P.; Nicolas, J.L.; Fabioux, C.; Lambert, C.; Miner, P.; Le Grand, J.; Petton, B.; Hégaret, H. Interaction between toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella exposure and disease associated with herpesvirus OsHV-1μVar in Pacific oyster spat Crassostrea gigas. Harmful Algae 2015, 45, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianora, A.; Turner, J.T.; Esposito, F.; Carotenuto, Y.; D’Ippolito, G.; Romano, G.; Fontana, A.; Guisande, C.; Miralto, A. Copepod egg production and hatching success is reduced by maternal diets of a non-neurotoxic strain of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2004, 280, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emura, A.; Matsuyama, Y.; Oda, T. Evidence for the production of a novel proteinaceous hemolytic exotoxin by dinoflagellate Alexandrium taylori. Harmful Algae 2004, 3, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, Y.; Fujita, M.; Kawano, S.; Baba, T. Effect of salinity on interspecific competition between the dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella and the raphidophyte Heterosigma akashiwo. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 81, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, Y.; Katsuo, D.; Nakayasu, S.; Salati, C.; Duan, J.; Zou, Y.; Matsuyama, Y.; Yamaguchi, K.; Oda, T. Purification and characterization of a novel high molecular weight exotoxin produced by red tide phytoplankton Alexandrium tamarense. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2008, 22, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satake, M.; Honma, D.; Watanabe, R.; Oshima, Y. Alexandrolide, a diatom growth inhibitor isolated from the dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella. Tetrahedron Lett. 2019, 23, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Allelopathy Society. Available online: https://allelopathy-society.osupytheas.fr/about/ (accessed on 7 December 2021).
- Chan, A.T.; Andersen, R.J.; Le Blanc, M.J.; Harrison, P.J. Algal plating as a tool for investigating allelopathy among marine microalgae. Mar. Biol. 1980, 59, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, C.; Rengefors, K.; Fistarol, G.O.; Granéli, E. Allelopathy in phytoplankton—Biochemical, ecological and evolutionary aspects. Phycologia 2003, 42, 406–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, E.M.; Legrand, C.; Rengefors, K.; Tillmann, U. Allelochemical interactions among aquatic primary producers. In Chemical Ecology in Aquatic Systems; Brönmark, C., Hansson, L.A., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 196–209. [Google Scholar]
- Flynn, K.J.; Stoecker, D.K.; Mitra, A.; Raven, J.A.; Glibert, P.M.; Hansen, P.J.; Granéli, E.; Burkholder, J.M. Misuse of the phytoplankton-zooplankton dichotomy: The need to assign organisms as mixotrophs within plankton functional types. J. Plankton Res. 2013, 35, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, K.J.; Mitra, A.; Anestis, K.; Anschütz, A.A.; Calbet, A.; Ferreira, G.D.; Gypens, N.; Hansen, P.J.; John, U.; Martin, J.L.; et al. Mixotrophic protists and a new paradigm for marine ecology: Where does plankton research go now? J. Plankton Res. 2019, 41, 375–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulin, R.X.; Hogan, S.; Poulson-ellestad, K.L.; Brown, E. Karenia brevis allelopathy compromises the lipidome, membrane integrity, and photosynthesis of competitors. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granéli, E.; Hansen, P.J. Allelopathy in Harmful Algae: A mechanism to compete for resources. In Ecology of Harmful Algae; Granéli, E., Turner, J.T., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 189–201. [Google Scholar]
- Chambouvet, A.; Morin, P.; Marie, D.; Guillou, L. Control of toxic marine dinoflagellate blooms by serial parasitic killers. Science 2008, 322, 1254–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissbach, A.; Tillmann, U.; Legrand, C. Allelopathic potential of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense on marine microbial communities. Harmful Algae 2010, 10, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Krock, B.; Tillmann, U.; Cembella, A. Preliminary characterization of extracellular allelochemicals of the toxic marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense using a Rhodomonas salina bioassay. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 497–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.-W.; Li, D.-W.; Lu, Y.; Chen, J.; Liang, J.-J.; Zhang, L.; Yang, W.-D.; Liu, J.-S.; Lu, S.-H.; Li, H.-Y. Molecular exploration of algal interaction between the diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum and the dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. Algal Res. 2016, 17, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.R.; Kubanek, J. Harmful alga trades off growth and toxicity in response to cues from dead phytoplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2020, 65, 1723–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selander, E.; Thor, P.; Toth, G.; Pavia, H. Copepods induce paralytic shellfish toxin production in marine dinoflagellates. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2006, 273, 1673–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, H.; Van de Waal, D.B.; Brandenburg, K.M.; Krock, B.; Tillmann, U. Salinity effects on growth and toxin production in Alexandrium ostenfeldii from The Netherlands. J. Plankton Res. 2016, 38, 1302–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Holland, A.; Planquette, H.; González Santana, D.; Whitby, H.; Soudant, P.; Sarthou, G.; Hégaret, H.; Jolley, D.F. Effects of copper on the dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum and its allelochemical potency. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 210, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyczkowski, E.R.; Karp-Boss, L. Allelopathic effects of Alexandrium fundyense (Dinophyceae) on Thalassiosira cf. gravida (Bacillariophyceae): A matter of size. J. Phycol. 2014, 50, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, P.J. The red tide dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense: Effects on behaviour and growth of a tintinnid ciliate. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1989, 53, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Krock, B.; Tillmann, U.; Bickmeyer, U.; Graeve, M.; Cembella, A. Mode of action of membrane-disruptive lytic compounds from the marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. Toxicon 2011, 58, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, M.; Tallec, K.; Soudant, P.; Le Grand, F.; Donval, A.; Lambert, C.; Sarthou, G.; Jolley, D.F.; Hégaret, H. Allelochemicals from Alexandrium minutum induce rapid inhibition and modify the membranes from Chaetoceros muelleri. Algal Res. 2018, 35, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Peltekis, A.; González-Fernández, C.; Hégaret, H.; Bailleul, B. Allelochemicals of Alexandrium minutum: Kinetics of membrane disruption and photosynthesis inhibition in a co-occurring diatom. Harmful Algae 2021, 103, 101997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thingstad, T.F.; Havskum, H.; Garde, K.; Riemann, B. On the strategy of "eating your competitor": A mathematical analysis of algal mixotrophy. Ecology 1996, 77, 2108–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoecker, D.; Tillmann, U.; Graneli, E. Phagotrophy in harmful algae. In Ecology of Harmful Algae; Granéli, E., Turner, J.T., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006; pp. 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, H.S.; Wikfors, G.H.; Dam, H.G. Reactive oxygen species are linked to the toxicity of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium spp. to protists. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 66, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulco, V.K. Harmful effects of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense on the tintinnids Favella taraikaensis and Eutintinnus sp. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2007, 87, 1085–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, K.; Cho, H.J.; Jacobson, D.M. Observations of the feeding behavior and growth rates of the heterotrophic dinoflagellate Polykrikos kofoidii (Polykrikaceae, Dinophyceae). Phycologia 2000, 39, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.C.; Jin Jeong, H.; So Jin, K.; You, J.H.; Hee Ok, J. Differential feeding by common heterotrophic protists on 12 different Alexandrium species. Harmful Algae 2018, 78, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, U.; John, U.; Krock, B.; Cembella, A. Allelopathic effects of bioactive compounds produced by harmful algae. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Harmful Algae, Copenhagen, Denmark, 4–8 September 2006; Moestrup, O., Doucette, G., Enevoldsen, H., Godhe, A., Hallegraeff, G., Luckas, B., Lundholm, N., Lewis, J., Rengefors, K., Sellner, K., Eds.; International Society for the Study of Harmful Algae and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2008; pp. 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Lasley-Rasher, R.S.; Nagel, K.; Angra, A.; Yen, J. Intoxicated copepods: Ingesting toxic phytoplankton leads to risky behaviour. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 283, 20160176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncalli, V.; Turner, J.T.; Kulis, D.; Anderson, D.M.; Lenz, P.H. The effect of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium fundyense on the fitness of the calanoid copepod Calanus finmarchicus. Harmful Algae 2016, 51, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergkvist, J.; Selander, E. Induction of toxin production in dinoflagellates: The grazer makes a difference. Oecologia 2008, 156, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selander, E.; Kubanek, J.; Hamberg, M.; Andersson, M.X.; Cervin, G.; Pavia, H. Predator lipids induce paralytic shellfish toxins in bloom-forming algae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 6395–6400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selander, E.; Fagerberg, T.; Wohlrab, S.; Pavia, H. Fight and flight in dinoflagellates? Kinetics of simultaneous grazer-induced responses in Alexandrium tamarense. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2012, 57, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colin, S.P.; Dam, H.G. Effects of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium fundyense on the copepod Acartia hudsonica: A test of the mechanisms that reduce ingestion rates. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 248, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.T. Planktonic marine copepods and harmful algae. Harmful Algae 2014, 32, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Kiørboe, T. Toxic dinoflagellates produce true grazer deterrents. Ecology 2018, 99, 2240–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagøein, E.; Miranda, A.; Reguera, B.; Franco, J.M. Effects of two paralytic shellfish toxin producing dinoflagellates on the pelagic harpacticoid copepod Euterpina acutifrons. Mar. Biol. 1996, 126, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, R.A.F.; Figueiredo, G.M.; Valentin, J.L.; da Silva Scardua, P.M.; Hégaret, H. Immunological and physiological responses of the periwinkle Littorina littorea during and after exposure to the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 160, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, S.E.; Bricelj, V.M.; Lambert, C.; Paillard, C. Deleterious effects of a nonPST bioactive compound(s) from Alexandrium tamarense on bivalve hemocytes. Mar. Biol. 2008, 154, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banno, K.; Oda, T.; Nagai, K.; Nagai, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Basti, L. Deleterious effects of harmful dinoflagellates and raphidophytes on egg viability and spermatozoa swimming velocity in the Japanese pearl oyster Pinctada fucata martensii. J. Shellfish Res. 2018, 37, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supono, S.; Knowles, G.; Bolch, C. Toxicity and histopathological effects of toxic dinoflagellate, Alexandrium catenella exudates on larvae of blue mussel, Mytilus galloprovincialis, and Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas. J. Ilm. Perikan. Dan Kelaut. 2020, 12, 5965741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guéguen, M.; Bardouil, M.; Baron, R.; Lassus, P.; Truquet, P.; Massardier, J. Detoxification of Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas fed on diets of Skeletonema costatum with and without silt, following PSP contamination by Alexandrium minutum. Aquat. Living Ressources 2008, 20, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberkorn, H.; Lambert, C.; Le Goïc, N.; Quéré, C.; Bruneau, A.; Riso, R.; Auffret, M.; Soudant, P. Cellular and biochemical responses of the oyster Crassostrea gigas to controlled exposures to metals and Alexandrium minutum. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 147, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Goïc, N.; Hégaret, H.; Boulais, M.; Béguel, J.P.; Lambert, C.; Fabioux, C.; Soudant, P. Flow cytometric assessment of morphology, viability, and production of reactive oxygen species of Crassostrea gigas oocytes. Application to Toxic dinoflagellate (Alexandrium minutum) exposure. Cytom. Part A 2014, 85, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pousse, É.; Flye-Sainte-Marie, J.; Alunno-Bruscia, M.; Hégaret, H.; Rannou, É.; Pecquerie, L.; Marques, G.M.; Thomas, Y.; Castrec, J.; Fabioux, C.; et al. Modelling paralytic shellfish toxins (PST) accumulation in Crassostrea gigas by using Dynamic Energy Budgets (DEB). J. Sea Res. 2019, 143, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.L.; LeGresley, M.M.; Haya, K.; Sephton, D.H.; Burridge, L.E.; Page, F.H.; Chang, B.D. Salmon mortalities associated with a bloom of Alexandrium fundyense in 2003 in the Bay of Fundy, and subsequent early warning approaches for industry. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2006, 28, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.L.; LeGresley, M.M.; Hanke, A.; Page, F.H. Alexandrium fundyense-red tides, PSP shellfish toxicity, salmon mortalities and human illnesses in 2003-04–before and after. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Harmful Algae, Copenhagen, Denmark, 4–8 September 2006; Moestrup, O., Doucette, G., Enevoldsen, H., Godhe, A., Hallegraeff, G., Luckas, B., Lundholm, N., Lewis, J., Rengefors, K., Sellner, K., et al., Eds.; International Society for the Study of Harmful Algae and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2008; pp. 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Burridge, L.E.; Martin, J.L.; Lyons, M.C.; Legresley, M.M. Lethality of microalgae to farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Aquaculture 2010, 308, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranston, E.R.; Webber, D.F.; Larsen, J. The first description of the potentially toxic dinoflagellate, Alexandrium minutum in Hunts Bay. Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, C.; Clement, A.; Aguilera, A. Summer Alexandrium catenella bloom and the impact on fish farming, in the XI Aysén Region, Chile. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Harmful Algae, Copenhagen, Denmark, 4–8 September 2006; Moestrup, O., Doucette, G., Enevoldsen, H., Godhe, A., Hallegraeff, G., Luckas, B., Lundholm, N., Lewis, J., Rengefors, K., Sellner, K., et al., Eds.; International Society for the Study of Harmful Algae and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2008; pp. 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie, C.H.; Bates, S.S.; Martin, J.L.; Haigh, N.; Howland, K.L.; Lewis, N.I.; Locke, A.; Peña, A.; Poulin, M.; Rochon, A.; et al. Three decades of Canadian marine harmful algal events: Phytoplankton and phycotoxins of concern to human and ecosystem health. Harmful Algae 2021, 102, 101852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, T.; Kodama, M. Ichthyotoxicity found in cultured media of Protogonyaulax spp. Mar. Biol. 1986, 92, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ye, Q.; Gu, H.-F.; Li, H.-Y.; Lv, S.-H.; Liu, J.-S.; Yang, W.-D. Variability in the allelopathic action of the Alexandrium tamarense species complex along the coast of China. Harmful Algae 2015, 47, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.D.; Xie, J.; van Rijssel, M.; Li, H.Y.; Liu, J.S. Allelopathic effects of Alexandrium spp. on Prorocentrum donghaiense. Harmful Algae 2010, 10, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Gan, C.; Huang, J.; Zou, C.; Li, H.; Liu, J.; Yang, W. Variability of Prorocentrum donghaiense response to allelopathic action from Alexandrium pacificum in laboratory culture. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2021, 39, 1305–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Krock, B.; Tillmann, U.; Muck, A.; Wielsch, N.; Svatoš, A.; Cembella, A. Isolation of activity and partial characterization of large non-proteinaceous lytic allelochemicals produced by the marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. Harmful Algae 2011, 11, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanen, P.; Suikkanen, S.; Kremp, A. Allelopathic activity of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii: Intra-population variability and response of co-occurring dinoflagellates. Harmful Algae 2014, 39, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blossom, H.E.; Andersen, N.G.; Rasmussen, S.A.; Hansen, P.J. Stability of the intra- and extracellular toxins of Prymnesium parvum using a microalgal bioassay. Harmful Algae 2014, 32, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, B.W. Effects of size and concentration of food particles on the feeding behavior of the marine planktonic copepod Calanus pacificus1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1972, 17, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMott, W.R.; Zhang, Q.-X.; Carmichael, W.W. Effects of toxic cyanobacteria and purified toxins on the survival and feeding of a copepod and three species of Daphnia. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1991, 36, 1346–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, R.A.F.; Fernandes, T.; Dos Santos, L.N.; Nascimento, S.M. Toxicity of benthic dinoflagellates on grazing, behavior and survival of the brine shrimp Artemia salina. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anne-Sophie, P.; Julie, R.; Laurence, G.G.; Sophie, M.; Eva, T.; Thomas, O.P.; Rodolphe, L.; Stéphane, G. Effects of the toxic dinoflagellate Ostreopsis cf. ovata on survival, feeding and reproduction of a phytal harpacticoid copepod. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2019, 516, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel, L.M.; Silva, L.H.S.; Faassen, E.J.; Lürling, M.; Ger, K.A. Copepod prey selection and grazing efficiency mediated by chemical and morphological defensive traits of cyanobacteria. Toxins 2020, 12, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segner, H. Fish cell lines as a tool in aquatic toxicology. EXS 1998, 86, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.E.J.; Dayeh, V.R.; Schirmer, K.; Bols, N.C. Applications and potential uses of fish gill cell lines: Examples with RTgill-W1. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol.-Anim. 2009, 45, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorantes-Aranda, J.J.; Waite, T.D.; Godrant, A.; Rose, A.L.; Tovar, C.D.; Woods, G.M.; Hallegraeff, G.M. Novel application of a fish gill cell line assay to assess ichthyotoxicity of harmful marine microalgae. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardones, J.I.; Shabala, L.; Shabala, S.; Dorantes-Aranda, J.J.; Seger, A.; Hallegraeff, G.M. Fish gill damage by harmful microalgae newly explored by microelectrode ion flux estimation techniques. Harmful Algae 2018, 80, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Goïc, N.; Hégaret, H.; Fabioux, C.; Miner, P.; Suquet, M.; Lambert, C.; Soudant, P. Impact of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella on Pacific oyster reproductive output: Application of flow cytometry assays on spermatozoa. Aquat. Living Resour. 2013, 26, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Roux, F.; Wegner, K.M.; Polz, M.F. Oysters and vibrios as a model for disease dynamics in wild animals. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 568–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petton, B.; Boudry, P.; Alunno-Bruscia, M.; Pernet, F. Factors influencing disease-induced mortality of Pacific oysters Crassostrea gigas. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2015, 6, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M. Allelochemical Interactions between the Dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum and the Diatom Chaetoceros muelleri. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Bretagne occidentale, Brest, France, University of Wollongong, Wollongong, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dorantes-Aranda, J.J.; Seger, A.; Mardones, J.I.; Nichols, P.D.; Hallegraeff, G.M. Progress in understanding algal bloom-mediated fish kills: The role of superoxide radicals, phycotoxins and fatty acids. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.; Nichols, P.D.; Hamilton, B.; Lewis, R.J.; Hallegraeff, G.M. Ichthyotoxicity of Chattonella marina (Raphidophyceae) to damselfish (Acanthochromis polycanthus): The synergistic role of reactive oxygen species and free fatty acids. Harmful Algae 2003, 2, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolf, J.E.; Bachvaroff, T.R.; Krupatkina, D.N.; Nonogaki, H.; Brown, P.J.P.; Lewitus, A.J.; Harvey, H.R.; Place, A.R. Species specificity and potential roles of Karlodinium micrum toxin. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2006, 28, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolf, J.E.; Krupatkina, D.; Bachvaroff, T.; Place, A.R. Karlotoxin mediates grazing by Oxyrrhis marina on strains of Karlodinium veneficum. Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 400–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeds, J.R.; Place, A.R. Sterol-specific membrane interactions with the toxins from Karlodinium micrum (Dinophyceae)—A strategy for self-protection? Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2006, 28, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbay, G.; Chambliss, S.S.; Wikfors, G.H.; Adolf, J.E.; Chintapenta, L.K.; Place, A.R. The growth response of Prorocentrum minimum Pavill. (Dinophyta) to karlotoxin exposure. Int. J. Algae 2014, 16, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Place, A.R.; Bowers, H.A.; Bachvaroff, T.R.; Adolf, J.E.; Deeds, J.R.; Sheng, J. Karlodinium veneficum-The little dinoflagellate with a big bite. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.; Malkiel, E.; Katz, J.; Adolf, J.E.; Place, A.R. A dinoflagellate exploits toxins to immobilize prey prior to ingestion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2082–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, S.A.; Binzer, S.B.; Hoeck, C.; Meier, S.; De Medeiros, L.S.; Andersen, N.G.; Place, A.; Nielsen, K.F.; Hansen, P.J.; Larsen, T.O. Karmitoxin: An amine-containing polyhydroxy-polyene toxin from the marine dinoflagellate Karlodinium armiger. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1287–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
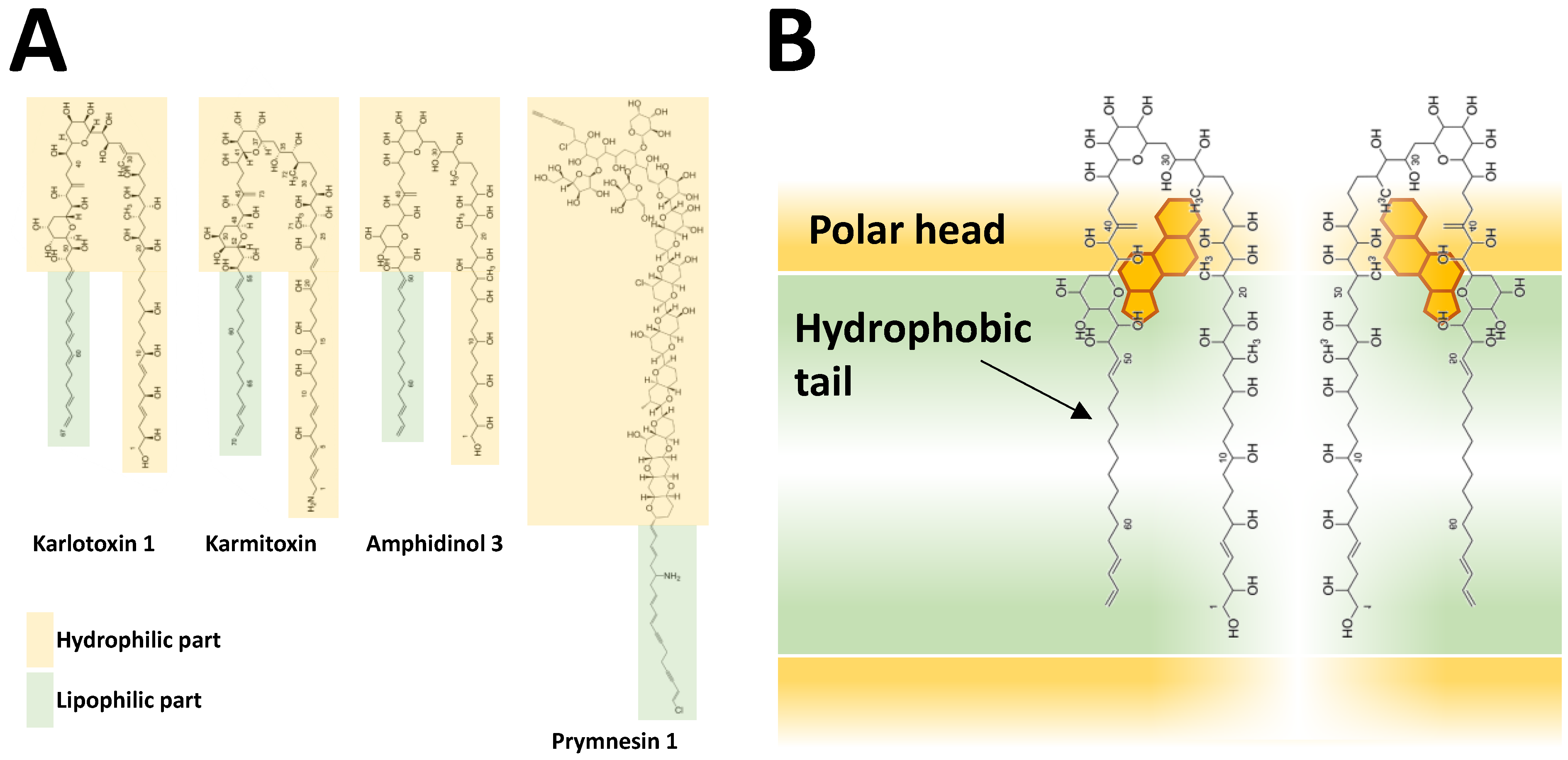
- Wellkamp, M.; García-Camacho, F.; Durán-Riveroll, L.M.; Tebben, J.; Tillmann, U.; Krock, B. LC-MS/MS method development for the discovery and identification of amphidinols produced by Amphidinium. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, G.K.; Matsumori, N.; Konoki, K.; Murata, M.; Tachibana, K. Chemical structures of amphidinols 5 and 6 isolated from marine dinoflagellate Amphidinium klebsii and their cholesterol-dependant membrane disruption. J. Mar. Biotechnol. 1997, 5, 124–128. [Google Scholar]
- Binzer, S.B.; Svenssen, D.K.; Daugbjerg, N.; Alves-de-Souza, C.; Pinto, E.; Hansen, P.J.; Larsen, T.O.; Varga, E. A-, B- and C-type prymnesins are clade specific compounds and chemotaxonomic markers in Prymnesium parvum. Harmful Algae 2019, 81, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igarashi, T.; Satake, M.; Yasumoto, T. Structures and partial stereochemical assignments for prymnesin-1 and prymnesin-2: Potent hemolytic and ichthyotoxic glycosides isolated from the red tide alga Prymnesium parvum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 8499–8511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blossom, H.E.; Rasmussen, S.A.; Andersen, N.G.; Larsen, T.O.; Nielsen, K.F.; Hansen, P.J. Prymnesium parvum revisited: Relationship between allelopathy, ichthyotoxicity, and chemical profiles in 5 strains. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 157, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rein, K.S.; Snyder, R.V. The biosynthesis of polyketide metabolites by dinoflagellates. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 59, 93–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellmann, R.; Stüken, A.; Orr, R.J.S.; Svendsen, H.M.; Jakobsen, K.S. Biosynthesis and molecular genetics of polyketides in marine dinoflagellates. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1011–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tidgewell, K.; Clark, B.R.; Gerwick, W.H. The natural products chemistry of cyanobacteria. In Comprehensive Natural Products II Chemistry and Biology; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; Volume 2, pp. 141–188. ISBN 978-0-08-045382-8. [Google Scholar]
- Rein, K.S.; Borrone, J. Polyketides from dinoflagellates: Origins, pharmacology and biosynthesis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.-B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1999, 124, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Altares, M. Structural Diversity of Microalgal Marine Toxins; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 78. [Google Scholar]
- Mooney, B.D.; Hallegraeff, G.M.; Place, A.R. Ichthyotoxicity of four species of gymnodinioid dinoflagellates (Kareniaceae, Dinophyta) and purified karlotoxins to larval sheepshead minnow. Harmful Algae 2011, 9, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galimany, E.; Place, A.R.; Jutson, M.; Pipe, R.K. The effects of feeding Karlodinium veneficum (PLY # 103; Gymnodinium veneficum Ballantine) to the blue mussel Mytilus edulis. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoecker, D.K.; Adolf, J.E.; Place, A.R.; Glibert, P.M.; Meritt, D.W. Effects of the dinoflagellates Karlodinium veneficum and Prorocentrum minimum on early life history stages of the eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica). Mar. Biol. 2008, 154, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Talapatra, S.; Katz, J.; Tester, P.A.; Waggett, R.J.; Place, A.R. Algal toxins alter copepod feeding behavior. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waggett, R.J.; Tester, P.A.; Place, A.R. Anti-grazing properties of the toxic dinoflagellate Karlodinium veneficum during predator–prey interactions with the copepod Acartia tonsa. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 366, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Adolf, J.E.; Bachvaroff, T.; Place, A.R.; Coats, D.W. The interplay between host toxins and parasitism by Amoebophrya. Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Place, A.R.; Bai, X.; Kim, S.; Sengco, M.R.; Coats, D.W.; Larsen, D.B.J.; Ge, H.; Balech, M.L.; Inoue, H.; Balech, F.; et al. Dinoflagellate host-parasite sterol profile dictate karlotoxin sensitivity. J. Phycol. 2009, 385, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Wagoner, R.M.; Deeds, J.R.; Satake, M.; Ribeiro, A.A.; Place, A.R.; Wright, J.L.C. Isolation and characterization of karlotoxin 1, a new amphipathic toxin from Karlodinium veneficum. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 6457–6461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeds, J.R.; Hoesch, R.E.; Place, A.R.; Kao, J.P.Y. The cytotoxic mechanism of karlotoxin 2 (KmTx 2) from Karlodinium veneficum (Dinophyceae). Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 159, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, A.L.; Oh, J.; Place, A.R.; Hamann, M.T. Stereochemical studies of the karlotoxin class using NMR spectroscopy and DP4 chemical-shift analysis: Insights into their mechanism of action. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 15705–15710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, M.; Inoue, K. The mechanism of the action of Prymnesium toxin on membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 1974, 352, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackett, J.D.; Wisecaver, J.H.; Brosnahan, M.L.; Kulis, D.M.; Anderson, D.M.; Bhattacharya, D.; Plumley, F.G.; Erdner, D.L. Evolution of saxitoxin synthesis in cyanobacteria and dinoflagellates. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 30, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusick, K.D.; Sayler, G.S. An overview on the marine neurotoxin, saxitoxin: Genetics, moleculartargets, methods of detection and ecological functions. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 991–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, T.; Jenkinson, I.R. Notes on Alexandrium population dynamics. J. Plankton Res. 1997, 19, 551–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, U. Kill and eat your predator: A winning strategy of the planktonic flagellate Prymnesium parvum. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2003, 32, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berge, T.; Poulsen, L.K.; Moldrup, M.; Daugbjerg, N.; Hansen, P.J. Marine microalgae attack and feed on metazoans. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1926–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driscoll, W.W.; Hackett, J.D.; Ferrière, R. Eco-evolutionary feedbacks between private and public goods: Evidence from toxic algal blooms. Ecol. Lett. 2016, 19, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonsson, P.R.; Pavia, H.; Toth, G. Formation of harmful algal blooms cannot be explained by allelopathic interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 11177–11182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breier, R.E.; Lalescu, C.C.; Waas, D.; Wilczek, M.; Mazza, M.G. Emergence of phytoplankton patchiness at small scales in mild turbulence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 12112–12117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, W.M.; Climent, E.; Barry, M.; De Lillo, F.; Boffetta, G.; Cencini, M.; Stocker, R. Turbulence drives microscale patches of motile phytoplankton. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, J.D.; Secchi, E.; Rusconi, R.; Stocker, R. Not just going with the flow: The effects of fluid flow on bacteria and plankton. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 35, 213–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basterretxea, G.; Font-Muñoz, J.S.; Tuval, I. Phytoplankton orientation in a turbulent ocean: A microscale perspective. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Yang, X.; Zheng, T.; Hong, H. An efficient method to obtain axenic cultures of Alexandrium tamarense-a PSP-producing dinoflagellate. J. Microbiol. Methods 2007, 69, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaberc-porekar, V.; Menart, V. Perspectives of immobilized-metal affinity chromatography. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2001, 49, 335–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.L.; Stauber, J.L.; Wilson, M.R.; Jolley, D.F. The use of immobilised metal affinity chromatography (IMAC) to compare expression of copper-binding proteins in control and copper-exposed marine microalgae. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
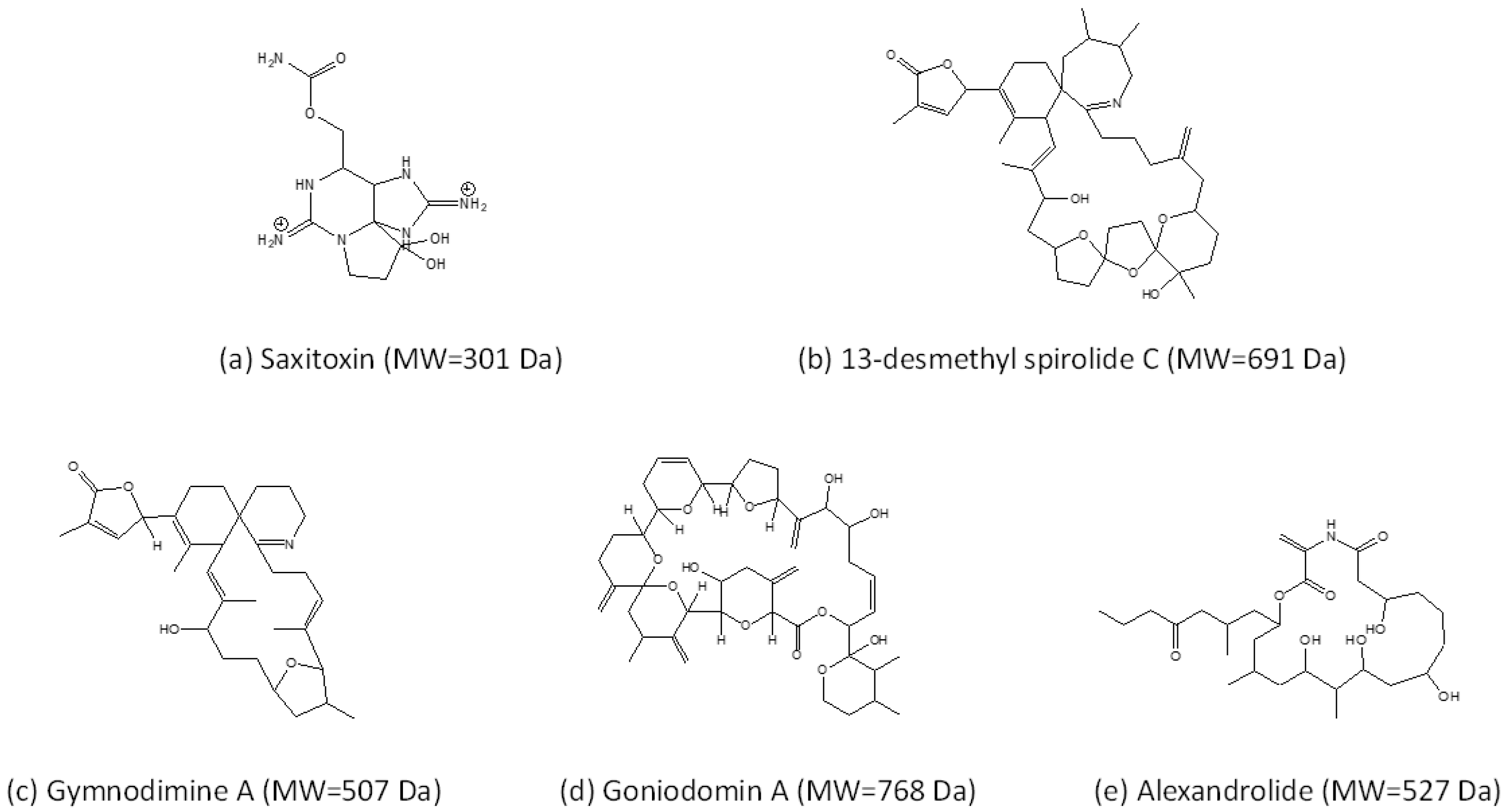
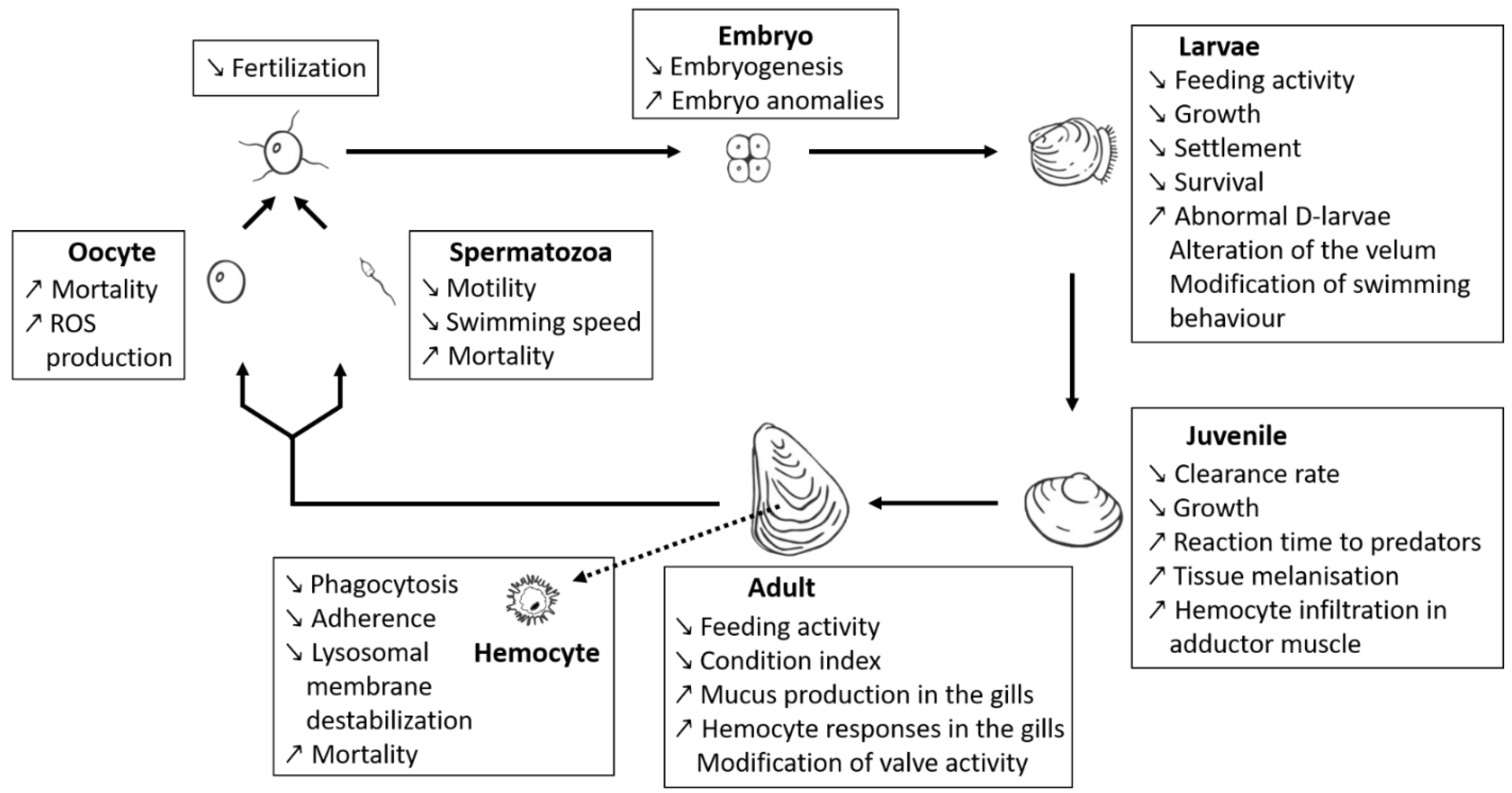
| Species | Bioactivity (Target Cell) | Sample | Method | Purification Steps | Chemical Analysis | Study | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. andersonii | Cytotoxic (Anti-cancer) | C | Bioassay guided purification | MeOH extraction | SPE Chromabond HR-X (CH3CN/H2O 7:3 and CH2Cl2/CH3OH 9:1) | Staining, NMR, LC-MS | [172] | ||||
| A. catenella | Protist (Rhodomonas salina) | F | Bioassay guided purification | SPE C18 (80% MeOH) | Evaporation and redisolvation in water | HPLC C8 (18–19 min) | or | HILIC (7.5–8.5 min) | MALDI-TOF MS, Triple quadrupole and orbitrap MS, enzyme digestion, SEC | [194, 239] | |
| A. catenella | Rainbow trout gill cell line | F, C | Targeted characterisation of FA and ROS | Crude cell extract | GC-FID, Enzyme detection | [73] | |||||
| A. catenella | Rainbow trout gill cell line | C | Comparative extractions, targeted characterisation of ROS | Comparative extractions in solvent | Enzyme detection, enzyme digestion | [255] | |||||
| “A. catenella” a | Protist (Skeletonema costatum) | F | Bioassay guided purification | SPE Amberlite XAD-2 (MeOH) | SPE Sep-pak ODS (MeOH 75%) | SPE Develosil ODS UG-5 (75% MeOH) | HR-FAB MS, NMR, staining | [183] | |||
| “A. catenella” b | Protists (Tiarina fusus and Polykrikos kofoidii) | F | Tests on the filtrate | Enzyme digestion, antioxidant addition | [207] | ||||||
| A. leei | Whole fish (Lates calcarifer) | F | Tests on the filtrate and liquid/liquid partitioning | Liquid partitioning water/hexane/ ethyl acetate | Evaporation and dissolution in DMSO | [174] | |||||
| A. minutum | Protist (Chaetoceros muelleri) | F | Bioassay guided purification | SPE C18 (80% MeOH) | HPLC C18, CH3CN gradient (17.5–20.6 min) | Evaporation and dissolution in MeOH | HPLC C18, CH3CN gradient (8.5–9 min) | Evaporation and dissolution in MeOH | GC-FID, HPLC-MS | [254] | |
| A. minutum | Protist (Chaetoceros muelleri) | F | Tests on the filtrate | [165] | |||||||
| A. minutum | Cytotoxic (Anti-cancer) | C | Bioassay guided purification | Aqueous extraction | SPE Chromabond HR-X (CH3CN/H2O 7:3) | Ultrafiltration (>10 kDa) | Staining, NMR, HPAEC | [176] | |||
| A. pacificumc | Protist (Phaeodactylum tricornutum) | F | Non-guided purification, characterisation of extracts | Precipitation pH 10–11 | Redisolvation of precipitate in 1 N HCl | Dialysis (1 kDa) | Lyophilisation | Dissolution in MeOH | UPLC-MALDI-MS | [195] | |
| A. tamarensed | Protists (Tiarina fusus and Polykrikos kofoidii) | F | Tests on the filtrate | Enzyme digestion, antioxidant addition | [207] | ||||||
| “A. tamarense” e | Hemolytic and cytotoxic | F | Bioassay guided purification | Ultrafiltration (>200 kDa) | Ammonium sulfate 100% (precipitate) | Dissolution in water, dialysis | Centrifugation (supernatant) | Lyophilisation and dissolution in PBS | FPLC Superdex-200 | SDS-PAGE, staining, amino acid and sugar analysis | [182] |
| A. tamutumf | Copepods and cytotoxic (sea urchin) | C | Targeted characterisation of AA, FA and PUSCA | Crude cell extract | HPLC, GC-MS, NMR | [179] | |||||
| “A. taylorii” g | Hemolytic, cytotoxic and shrimp (Artemia salina) | F | Bioassay guided purification | Ultrafiltration >10 kDa | Ammonium sulfate 100% (precipitate) | Dissolution in PBS, dialysis | Centrifugation (supernatant) | Staining, enzyme digestion | [180] | ||
| Chemical Properties | Chemical Nature | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species or Complex | Bioactivity (Target Cell) | Solubility | pH Sensitivity | Thermal Sensitivity | Light Sensitivity | Proteic | Saccharide | Fatty Acids | Reactive Oxygen Species | Molecular Size (Da) or Formula | Other Informations | Study |
| A. andersoni | Cytotoxic (Anti-cancer) | Mid to slightly hydrophilic | Can be frozen (−80 °C) | Detected | Intracellular. Two active fractions. Detection of polar lipids. | [172] | ||||||
| A. catenella | Protist (Rhodomonas salina) | Amphiphatic | Relatively resistant [3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12] Lytic activity max at 8 | Resistant [−20° to 60], Sensitive (95 °C) | Resistant | No | Detected (Traces) | 7–15 kDa | Large non-proteinaceous non-polysaccharide compounds | [194, 239] | ||
| A. catenella | Rainbow trout gill cell line | Resistant [7,8,9] | Resistant [17–85 °C] | Sensitive | PUFA (DHA) detected | Yes | Hypothesis of ROS and peroxidation products | [73] | ||||
| A. catenella | Rainbow trout gill cell line | Hydrophilic | Yes | [255] | ||||||||
| “A. catenella” a | Protist (Skeletonema costatum) | Hydrophobic | No | No | No | C28H49NO8 | “Alexandrolide” | [183] | ||||
| “A. catenella” b | Protists (T. fusus and P. kofoidii) | No | Yes | Hypothesis of ROS and peroxidation products | [207] | |||||||
| A. leei | Whole fish (Lates calcarifer) | Hydrophilic | Resistant to freezing and boiling | [174] | ||||||||
| A. minutum | Protist (Chaetoceros muelleri) | Amphiphatic | Can be frozen (−20 °C) | No | 200–700 Da | Molecular size not confirmed by ultrafiltration | [254] | |||||
| A. minutum | Protist (Chaetoceros muelleri) | Sensitive (100 °C) | [165] | |||||||||
| A. minutum | Cytotoxic (Anti-cancer) | Hydrophilic | Can be frozen (−80 °C) | Detected | Detected | >20 kDa | Intracellular. Hypothesis of glycoprotein. | [176] | ||||
| A. pacificumc | Protist (P. tricornutum) | Polypeptides detected | 1021 Da < size < 1600 Da | Detection of esters and organic acids. Molecular size not confirmed by ultrafiltration. | [195] | |||||||
| A. tamarensed | Protists (T. fusus and P. kofoidii) | Yes | Yes | Hypothesis of ROS and peroxidation products | [207] | |||||||
| “A. tamarense” e | Hemolytic and cytotoxic | Can be frozen (−80 °C) | No | Detected | 1000 kDa | “AT-toxin” | [182] | |||||
| A. Tamutumf | Copepods and cytotoxic (sea urchin) | Amino acid detected | Detected | Absence of PUSCA | [179] | |||||||
| “A. taylori” g | Hemolytic, cytotoxic and shrimp (A. salina) | Sensitive (100 °C) Not active at 4 °C | Yes | >10 kDa | [180] | |||||||
| Species | Strain | Type of Toxin | Effects against Protist Competitors or Grazers | Anti-Parasitic Activity | Toxicity to Bivalves |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. minutum | CCMI1002 | Lytic | +++ | +++ | +++ |
| A. minutum | AM89BM | Lytic + PST | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| A. minutum | Da1257 | PST | − | + | − |
| A. catenella | Alex2 | Lytic + PST | +++ | / | ++ |
| A. catenella | Alex5 | PST | − | / | + |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Long, M.; Krock, B.; Castrec, J.; Tillmann, U. Unknown Extracellular and Bioactive Metabolites of the Genus Alexandrium: A Review of Overlooked Toxins. Toxins 2021, 13, 905. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13120905
Long M, Krock B, Castrec J, Tillmann U. Unknown Extracellular and Bioactive Metabolites of the Genus Alexandrium: A Review of Overlooked Toxins. Toxins. 2021; 13(12):905. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13120905
Chicago/Turabian StyleLong, Marc, Bernd Krock, Justine Castrec, and Urban Tillmann. 2021. "Unknown Extracellular and Bioactive Metabolites of the Genus Alexandrium: A Review of Overlooked Toxins" Toxins 13, no. 12: 905. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13120905
APA StyleLong, M., Krock, B., Castrec, J., & Tillmann, U. (2021). Unknown Extracellular and Bioactive Metabolites of the Genus Alexandrium: A Review of Overlooked Toxins. Toxins, 13(12), 905. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13120905





