Pharmacological Investigation of CC-LAAO, an L-Amino Acid Oxidase from Cerastes cerastes Snake Venom
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. In Vivo Study
2.1.1. General Observation
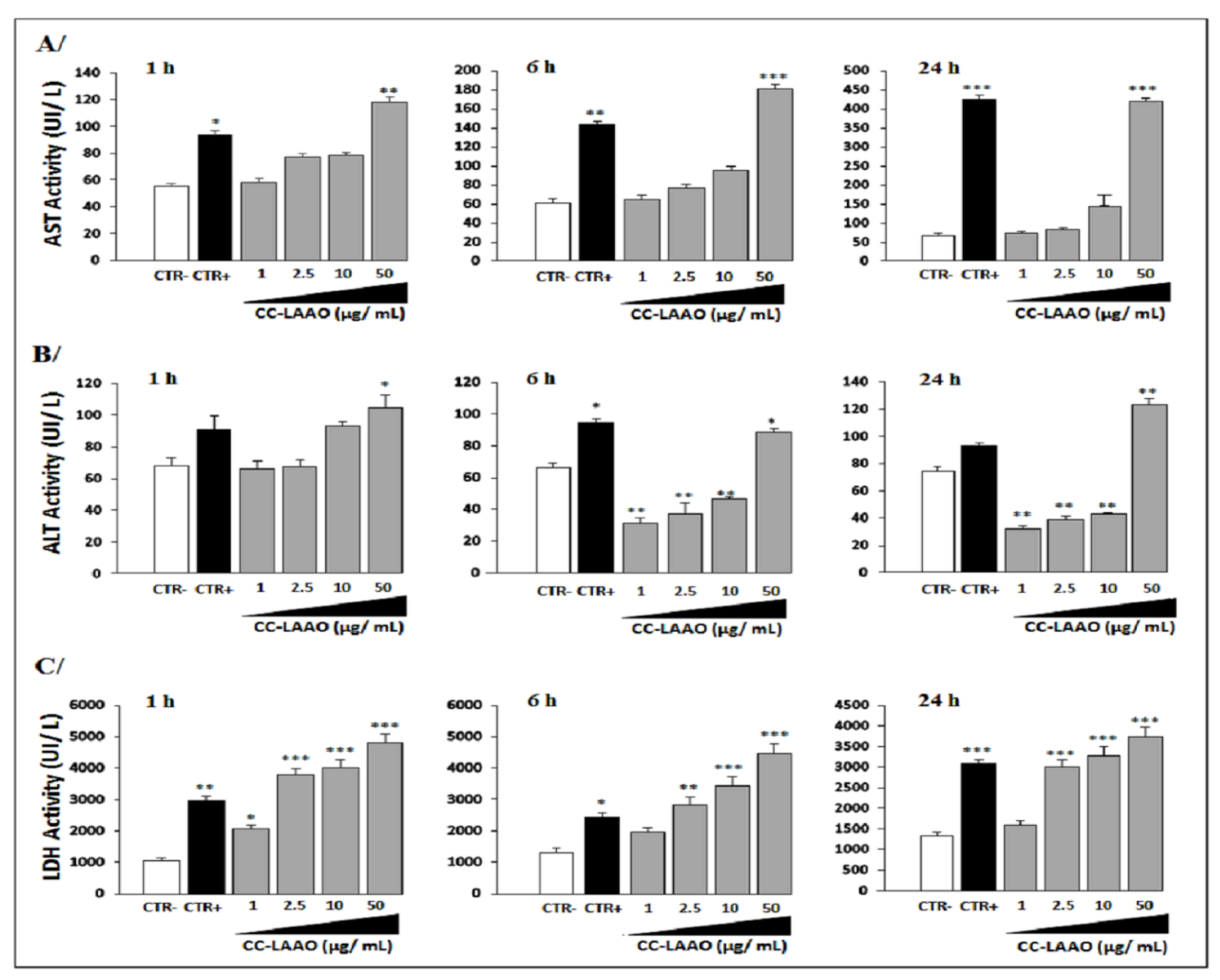
2.1.2. Effect of Acute Injection of CC-LAAO on Blood Biochemical Parameters
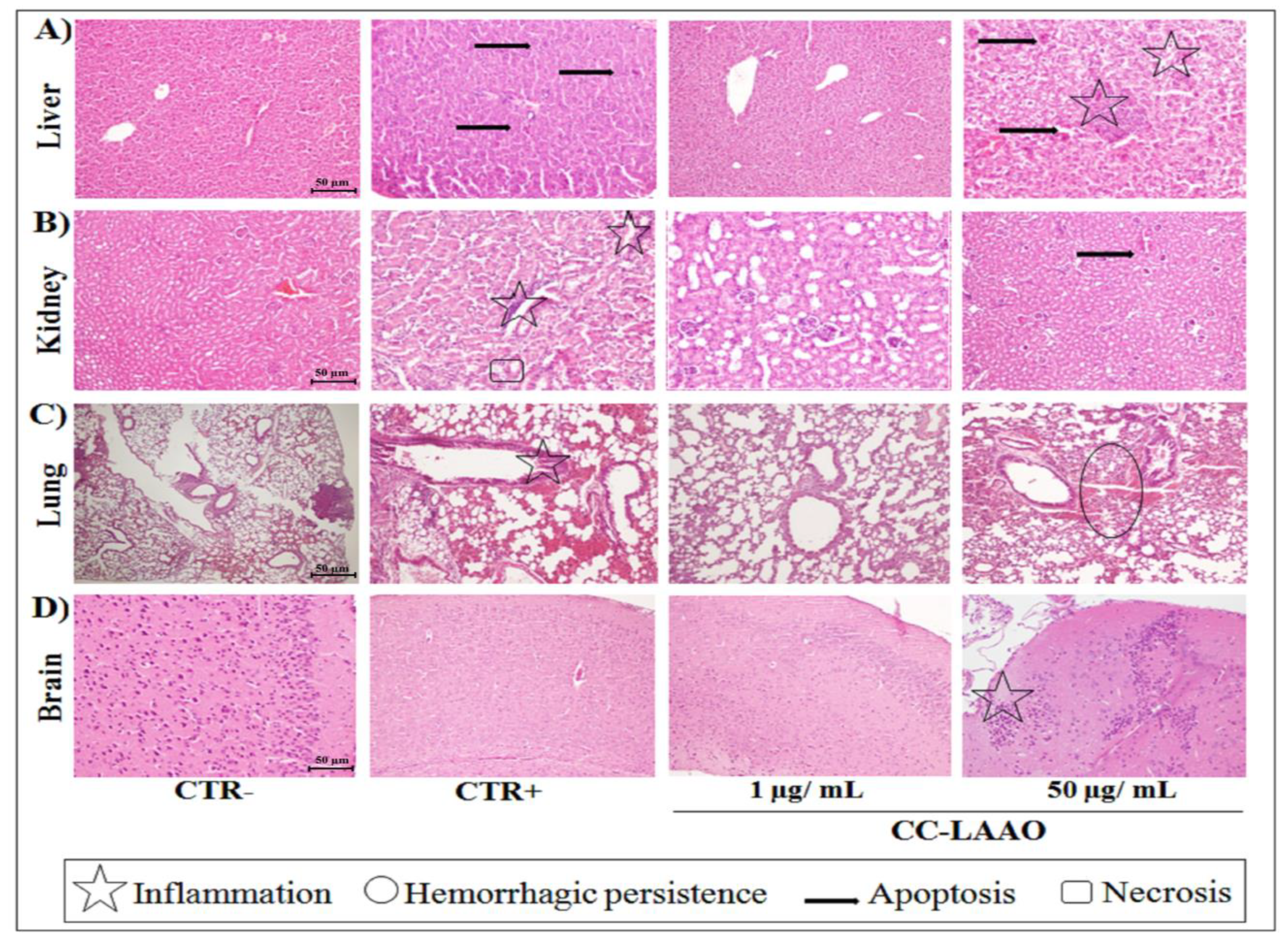
2.1.3. Effect of Acute Injection of CC-LAAO in Mouse Tissues
2.1.4. Edema-Inducing Activity
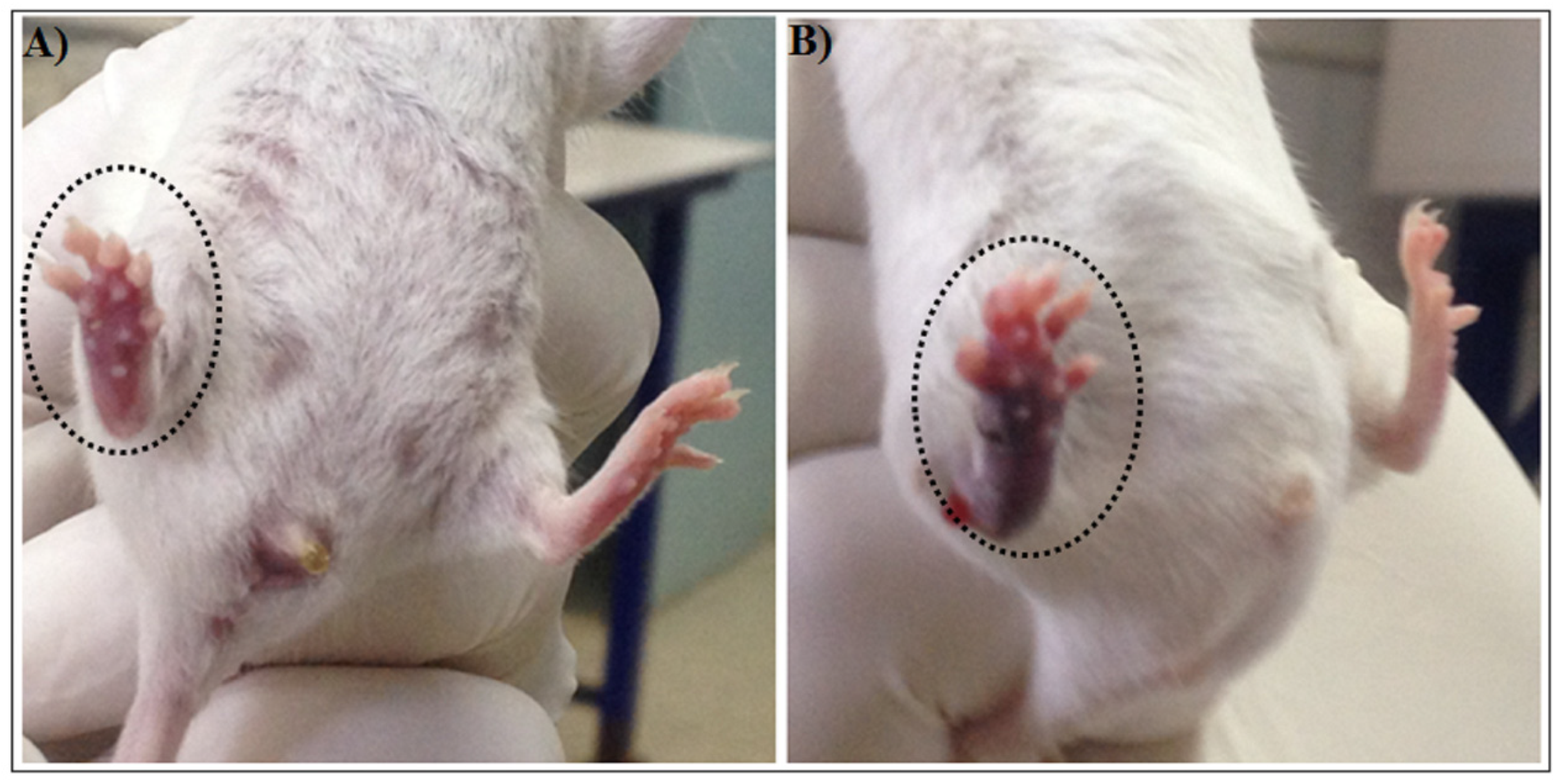
2.1.5. Hemorrhagic Activity
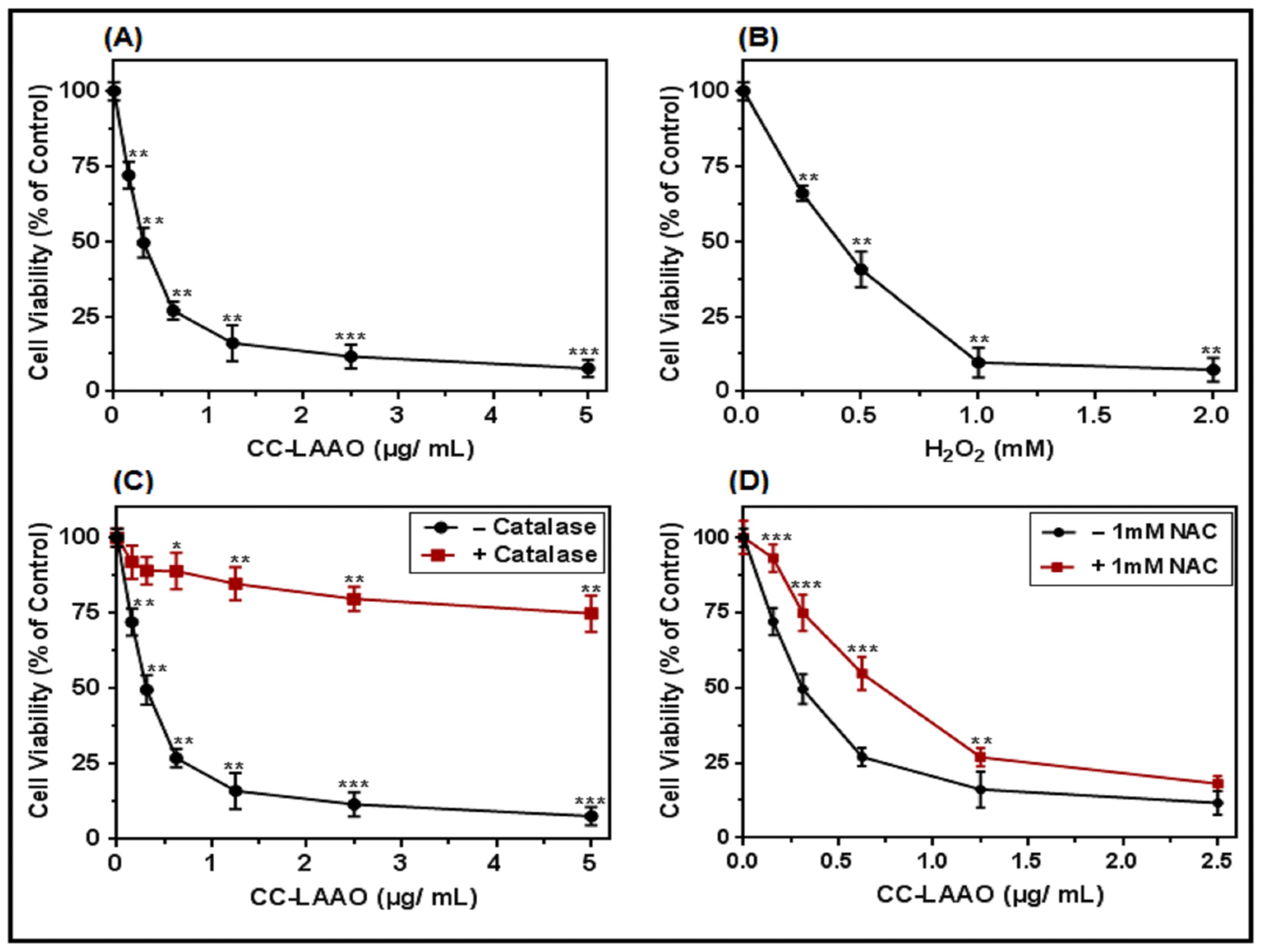
2.2. CC-LAAO Effects on U87 Cell Viability
2.3. Apoptosis-Induction Effect
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Biological and Chemical Material
5.2. Cells
5.3. In Vivo Assessment of CC-LAAO Biological Effects on Mice Models
5.3.1. Lethal Dose determination
5.3.2. Assessment of CC-LAAO toxicity
In Vivo Experimental Procedure
- Group 1 (CTR−): received 100 µL of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) 1×.
- Group 2 (CTR+): Mice received Cerastes cerastes crude venom at a dose of 6 µg in 100 µL PBS, which represented half of LD50 on Swiss mice [42].
- Group 3 (M1): received CC-LAAO at 1 µg/mL
- Group 4 (M2): received CC-LAAO at 2.5 µg/mL
- Group 5 (M3): received CC-LAAO at 10 µg/mL
- Group 6 (M4): received CC-LAAO at 50 µg/mL.
Biochemical Parameters Study
Histological Examination
Edema-Inducing Activity Assay
Hemorrhagic Activity Assay
5.4. Antitumor Activity of CC-LAAO on In Vitro Models
5.4.1. Cell Culture and Cell Growth Conditions
5.4.2. Cell Morphology Analysis and Viability Assay
5.4.3. Apoptosis Quantification by Flow Cytometry Analysis
5.5. Statistical Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kasturiratne, A.; Wickremasinghe, A.R.; de Silva, N.; Gunawardena, N.K.; Pathmeswaran, A.; Premaratna, R.; Savioli, L.; Lalloo, D.G.; de Silva, H.J. The Global Burden of Snakebite: A Literature Analysis and Modelling Based on Regional Estimates of Envenoming and Deaths. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ojeda, P.G.; Ramírez, D.; Alzate-Morales, J.; Caballero, J.; Kaas, Q.; González, W. Computational Studies of Snake Venom Toxins. Toxins 2017, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Da Silva, S.L.; Rowan, E.; Albericio, F.; Stabeli, R.G.; Calderon, L.; Soares, A. Animal Toxins and Their Advantages in Biotechnology and Pharmacology. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 951561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slagboom, J.; Kool, J.; Harrison, R.; Casewell, N.R. Haemotoxic snake venoms: Their functional activity, impact on snakebite victims and pharmaceutical promise. Br. J. Haematol. 2017, 177, 947–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hiu, J.J.; Yap, M.K.K. Cytotoxicity of snake venom enzymatic toxins: Phospholipase A2 and l-amino acid oxidase. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2020, 48, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Markland, F.S.; Swenson, S. Snake venom metalloproteinases. Toxicon 2013, 62, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldrini-França, J.; Cologna, C.T.; Pucca, M.B.; Bordon, K.D.C.F.; Amorim, F.G.; Anjolette, F.A.P.; Cordeiro, F.A.; Wiezel, G.A.; Cerni, F.A.; Pinheiro-Junior, E.L.; et al. Minor snake venom proteins: Structure, function and potential applications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 2017, 1861, 824–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izidoro, L.F.M.; Sobrinho, J.C.; Mendes, M.M.; Costa, T.R.; Grabner, A.N.; Rodrigues, V.D.M.; Da Silva, S.L.; Zanchi, F.B.; Zuliani, J.P.; Fernandes, C.F.C.; et al. Snake Venom L-Amino Acid Oxidases: Trends in Pharmacology and Biochemistry. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 196754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Souza, L.L.; Stransky, S.; Guerra-Duarte, C.; Flor-Sá, A.; Schneider, F.S.; Kalapothakis, E.; Chávez-Olórtegui, C. Determination of Toxic Activities inBothropsspp. Snake Venoms Using Animal-Free Approaches Correlation Between In Vitro Versus In Vivo Assays. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 147, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, F.C.; Stransky, S.; Guerra-Duarte, C.; de Souza, D.L.N.; Vivas-Ruiz, D.E.; Yarlequé, A.; Sanchez, E.O.F.; Chávez-Olórtegui, C.; Braga, V. L-amino acid oxidase from Bothrops atrox snake venom triggers autophagy, apoptosis and necrosis in normal human keratinocytes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paloschi, M.V.; Pontes, A.S.; Soares, A.; Zuliani, J.P. An Update on Potential Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Actions of Snake Venom L-amino Acid Oxidases (LAAOs). Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 2520–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, T.R.; Amstalden, M.K.; Ribeiro, D.L.; Menaldo, D.L.; Sartim, M.; Aissa, A.F.; Antunes, L.M.; Sampaio, S.V. CR-LAAO causes genotoxic damage in HepG2 tumor cells by oxidative stress. Toxicology 2018, 404–405, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkafi-Koubaa, Z.; Jebali, J.; Othman, H.; Morjen, M.; Aissa, I.; Zouari-Kesentini, R.; Bazaa, A.; Ellefi, A.A.; Majdoub, H.; Srairi-Abid, N.; et al. A thermoactive l-amino acid oxidase from Cerastes cerastes snake venom: Purification, biochemical and molecular characterization. Toxicon 2014, 89, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkafi-Koubaa, Z.; Aissa, I.; Morjen, M.; Kharrat, N.; El Ayeb, M.; Gargouri, Y.; Srairi-Abid, N.; Marrakchi, N. Interaction of a snake venom l-amino acid oxidase with different cell types membrane. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 82, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geniez, P. Snakes of Europe, North Africa and the Middle East: A Photographic Guide; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Ghezala, H.; Snouda, S. Hemorrhagic stroke following a fatal envenomation by a horned viper in Tunisia. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2015, 21, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessentini-Zouari, R.; Jebali, J.; Taboubi, S.; Srairi-Abid, N.; Morjen, M.; Kallech-Ziri, O.; Bezzine, S.; Marvaldi, J.; Ayeb, M.E.L.; Marrakchi, N.; et al. CC-PLA2-1 and CC-PLA2-2, two Cerastes cerastes venom-derived phospholipases A2, inhibit angiogenesis both in vitro and in vivo. Lab. Investig. 2010, 90, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marrakchi, N.; Barbouche, R.; Guermazi, S.; Karoui, H.; Bon, C.; El Ayeb, M. Cerastotin, a Serine Protease from Cerastes Cerastes Venom, with Platelet-Aggregating and Agglutinating Properties. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 1997, 247, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Mabrouk, H.; Zouari-Kessentini, R.; Montassar, F.; Koubaa, Z.A.-; Messaadi, E.; Guillonneau, X.; ElAyeb, M.; Srairi-Abid, N.; Luis, J.; Micheau, O.; et al. CC5 and CC8, two homologous disintegrins from Cerastes cerastes venom, inhibit in vitro and ex vivo angiogenesis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 86, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Liu, S.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, M.-Z. Past decade study of snake venom l-amino acid oxidase. Toxicon 2012, 60, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.K.; Bay, B.H.; Gopalakrishnakone, P. L-amino acid oxidase from snake venom and its anticancer potential. Toxicon 2018, 144, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedoya-Medina, J.; Mendivil-Perez, M.; Rey-Suarez, P.; Jimenez-Del-Rio, M.; Núñez, V.; Velez-Pardo, C. L-amino acid oxidase isolated from Micrurus mipartitus snake venom (MipLAAO) specifically induces apoptosis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells mostly via oxidative stress-dependent signaling mechanism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 134, 1052–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oukkache, N.; El Jaoudi, R.; Ghalim, N.; Chgoury, F.; Bouhaouala-Zahar, B.; El Mdaghri, N.; Sabatier, J.-M. Evaluation of the Lethal Potency of Scorpion and Snake Venoms and Comparison between Intraperitoneal and Intravenous Injection Routes. Toxins 2014, 6, 1873–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, N.H.; Saifuddin, M.N. Substrate specificity of king cobra (Ophiophagus hannah) venom L-amino acid oxidase. Int. J. Biochem. 1991, 23, 323–327. [Google Scholar]
- Bregge-Silva, C.; Nonato, M.C.; de Albuquerque, S.; Ho, P.L.; de Azevedo, I.L.J.; Diniz, M.R.V.; Lomonte, B.; Rucavado, A.; Díaz, C.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; et al. Isolation and biochemical, functional and structural characterization of a novel l-amino acid oxidase from Lachesis muta snake venom. Toxicon 2012, 60, 1263–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.-F.; Yang, H.-W.; Wei, X.-L.; Qiao, L.-Y.; Wang, W.-Y.; He, S.-H. Purification, characterization and biological activities of the l-amino acid oxidase from Bungarus fasciatus snake venom. Toxicon 2009, 54, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.K.; Saviola, A.J.; Burns, P.D.; Mackessy, S.P. Apoptosis induction in human breast cancer (MCF-7) cells by a novel venom l-amino acid oxidase (Rusvinoxidase) is independent of its enzymatic activity and is accompanied by caspase-7 activation and reactive oxygen species production. Apoptosis 2015, 20, 1358–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.-L.; Wei, J.-F.; Li, T.; Qiao, L.-Y.; Liu, Y.-L.; Huang, T.; He, S.-H. Purification, characterization and potent lung lesion activity of an l-amino acid oxidase from Agkistrodon blomhoffii ussurensis snake venom. Toxicon 2007, 50, 1126–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.A.; Stoevab, S.; Abbasia, A.; Alam, J.M.; Kayedb, R.; Faigled, M.; Neumeisterd, B.; Voelterb, W. Isolation, Structural, and Functional Characterization of an Apoptosis-Inducing -Amino Acid Oxidase from Leaf-Nosed Viper (Eristocophis macmahoni) Snake Venom. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2000, 384, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazo, F.; Vivas-Ruiz, D.E.; Sandoval, G.A.; Rodriguez, E.; Kozlova, E.E.; Oliveira, F.C.; Chávez-Olórtegui, C.; Severino, R.; Yarlequé, A.; Sanchez, E.F. Biochemical, biological and molecular characterization of an L-Amino acid oxidase (LAAO) purified from Bothrops pictus Peruvian snake venom. Toxicon 2017, 139, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.-F.; Wei, Q.; Lu, Q.-M.; Tai, H.; Jin, Y.; Wang, W.-Y.; Xiong, Y.-L. Purification, characterization and biological activity of an L-amino acid oxidase from Trimeresurus mucrosquamatus venom. Sheng Wu Hua Xue Yu Sheng Wu Wu Li Xue Bao Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2003, 35, 219–224. [Google Scholar]
- Zamuner, S.; Teixeira, C. Cell adhesion molecules involved in the leukocyte recruitment induced by venom of the snakeBothrops jararaca. Mediat. Inflamm. 2002, 11, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alves, R.M.; Feliciano, P.R.; Sampaio, S.V.; Nonato, M.C. A rational protocol for the successful crystallization ofL-amino-acid oxidase fromBothrops atrox. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2011, 67, 475–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Souza, D.H.; Eugenio, L.M.; Fletcher, J.E.; Jiang, M.-S.; Garratt, R.C.; Oliva, G.; Selistre-De-Araujo, H.S. Isolation and Structural Characterization of a Cytotoxic L-Amino Acid Oxidase from Agkistrodon contortrix laticinctus Snake Venom: Preliminary Crystallographic Data. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1999, 368, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.-K.; Yoshii, Y.; Hyodo, A.; Tsurushima, H.; Saito, A.; Harakuni, T.; Li, Y.-P.; Kariya, K.; Nozaki, M.; Morine, N. Apoptotic effect in the glioma cells induced by specific protein extracted from Okinawa Habu (Trimeresurus flavoviridis) venom in relation to oxidative stress. Toxicol. Vitr. 2003, 17, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, R.M.; Antonucci, G.A.; Paiva, H.H.; Cintra, A.C.O.; Franco, J.J.; Mendonça-Franqueiro, E.P.; Dorta, D.J.; Giglio, J.R.; Rosa, J.C.; Fuly, A.L.; et al. Evidence of caspase-mediated apoptosis induced by l-amino acid oxidase isolated from Bothrops atrox snake venom. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2008, 151, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, C.; Maciel, T.; Burin, S.; Ambrósio, L.; Ghisla, S.; Sampaio, S.; Castro, F. l-Amino acid oxidase isolated from Calloselasma rhodostoma snake venom induces cytotoxicity and apoptosis in JAK2V617F-positive cell lines. Rev. Bras. Hematol. Hemoter. 2016, 38, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, K.K.; Ler, S.G.; Gunaratne, J.; Bay, B.H.; Ponnampalam, G. In vitro cytotoxicity of L-amino acid oxidase from the venom of Crotalus mitchellii pyrrhus. Toxicon 2017, 139, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, T.R.; Menaldo, D.L.; Zoccal, K.F.; Burin, S.M.; Aissa, A.F.; De Castro, F.A.; Faccioli, L.H.; Antunes, L.M.G.; Sampaio, S.V. CR-LAAO, an L-amino acid oxidase from Calloselasma rhodostoma venom, as a potential tool for developing novel immunotherapeutic strategies against cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep42673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.L.; Fung, S.Y.; Chung, I.; Pailoor, J.; Cheah, S.H.; Tan, N.H. King Cobra (Ophiophagus hannah) Venom L-Amino Acid Oxidase Induces Apoptosis in PC-3 Cells and Suppresses PC-3 Solid Tumor Growth in a Tumor Xenograft Mouse Model. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 11, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abidin, S.A.Z.; Rajadurai, P.; Chowdhury, E.H.; Othman, I.; Naidu, R. Cytotoxic, Anti-Proliferative and Apoptosis Activity of l-Amino Acid Oxidase from Malaysian Cryptelytrops purpureomaculatus (CP-LAAO) Venom on Human Colon Cancer Cells. Molecules 2018, 23, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krifi, M.N.; Marrakchi, N.; El Ayeb, M.; Dellagi, K. Effect of Some Variables on theIn VivoDetermination of Scorpion and Viper Venom Toxicities. Biologicals 1998, 26, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartels, H.; Böhmer, M.; Heierli, C. Serum kreatininbestimmung ohne enteiweissen. Clin. Chim. Acta 1972, 37, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sells, P.G.; Richards, A.M.; Laing, G.D.; Theakston, R.D.G. The use of hens’ eggs as an alternative to the conventional in vivo rodent assay for antidotes to haemorrhagic venoms. Toxicon 1997, 35, 1413–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| CTR− | CTR+ | CC-LAAO | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 µg/mL | 2.5 µg/mL | 10 µg/mL | 50 µg/mL | |||
| 1 h | 0.56 ± 0.07 | 0.815 ± 0.78 * | 0.66 ± 0.06 | 0.63 ± 0.07 | 0.89 ± 0.09 * | 0.965 ± 0.09 ** |
| 6 h | 0.63 ± 0.06 | 1.05 ± 0.098 ** | 0.891 ± 0.08 * | 0.899 ± 0.06 * | 1.002 ± 0.09 ** | 1.23 ± 0.3 ** |
| 24 h | 0.63 ± 0.07 | 1.35 ± 0.58 *** | 0.963 ± 0.07 * | 0.963 ± 0.08 * | 1.263 ± 0.1 ** | 1.55 ± 0.78 *** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdelkafi-Koubaa, Z.; ELBini-Dhouib, I.; Souid, S.; Jebali, J.; Doghri, R.; Srairi-Abid, N.; Essafi-Benkhadir, K.; Micheau, O.; Marrakchi, N. Pharmacological Investigation of CC-LAAO, an L-Amino Acid Oxidase from Cerastes cerastes Snake Venom. Toxins 2021, 13, 904. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13120904
Abdelkafi-Koubaa Z, ELBini-Dhouib I, Souid S, Jebali J, Doghri R, Srairi-Abid N, Essafi-Benkhadir K, Micheau O, Marrakchi N. Pharmacological Investigation of CC-LAAO, an L-Amino Acid Oxidase from Cerastes cerastes Snake Venom. Toxins. 2021; 13(12):904. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13120904
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdelkafi-Koubaa, Zaineb, Ines ELBini-Dhouib, Soumaya Souid, Jed Jebali, Raoudha Doghri, Najet Srairi-Abid, Khadija Essafi-Benkhadir, Olivier Micheau, and Naziha Marrakchi. 2021. "Pharmacological Investigation of CC-LAAO, an L-Amino Acid Oxidase from Cerastes cerastes Snake Venom" Toxins 13, no. 12: 904. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13120904
APA StyleAbdelkafi-Koubaa, Z., ELBini-Dhouib, I., Souid, S., Jebali, J., Doghri, R., Srairi-Abid, N., Essafi-Benkhadir, K., Micheau, O., & Marrakchi, N. (2021). Pharmacological Investigation of CC-LAAO, an L-Amino Acid Oxidase from Cerastes cerastes Snake Venom. Toxins, 13(12), 904. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13120904





