Abstract
Slow lorises are enigmatic animal that represent the only venomous primate lineage. Their defensive secretions have received little attention. In this study we determined the full length sequence of the protein secreted by their unique brachial glands. The full length sequences displayed homology to the main allergenic protein present in cat dander. We thus compared the molecular features of the slow loris brachial gland protein and the cat dander allergen protein, showing remarkable similarities between them. Thus we postulate that allergenic proteins play a role in the slow loris defensive arsenal. These results shed light on these neglected, novel animals.
Key Contribution:
We show the remarkable similarities between the proteins of cat dander allergen and slow loris brachial gland secretions. These proteins play a role in the defensive arsenal of both mammals.
1. Introduction
The origin and evolution of animal defensive and predatory toxins has been the subject of intense research [1], but that of mammals, possibly because of its infrequent occurrence, has been somewhat neglected. Employing venoms has evolved several times independently in mammals, including in solenodons, platypus, vampire bats, water shrews, and a group of primates, the slow lorises [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]. A slow loris when threatened, raises its arms over the head, bringing sebaceous glands located in the brachial region of the upper arm close to its mouth, the fluid from these brachial glands is mixed with saliva. The fluid is delivered in a bite with procumbent anterior incisors known as the toothcomb, which is believed to act as an effective venom delivery system [8]. Although ecological functions may vary, the toxin is certainly used for intraspecific competition [9]; use in defence against predators is possible but this requires future to determine. Bitten animals suffer from chronically non-healing wounds, leading to necrosis, septicaemia, lung oedema, and cellulitis [10,11]. Envenomation in humans may be followed by paraesthesia, haematuria, dyspnoea, extreme pain, and infection, and in the worst cases can lead to severe or even near-fatal anaphylactic shock [12,13,14]. Healing time may reach several months [13].
Despite this interest in the field, the nature of the secretions produced by the brachial glands of slow lorises has been studied only to a limited detail from captive animals. The secretions produce a characteristic odour that has been shown to be due to a complex array of over two hundred aromatic molecules [15]. While the aromatic compounds have been well-characterised, the protein secretions are known from only small N-terminal fragments details [15]. BLAST searches [16] revealed both chains to belong to the same allergenic protein family as does the Felis catus dander allergen Fel d1. Fel d1 is a 35 kDa secretoglobin protein produced by sebaceous, salivary, perianal, and lachrymal glands as well as squamous epithelial cells, and is distributed by F. catus over its fur during grooming and licking [17,18,19,20]. Structurally F. catus dander allergen Fel d1 is a heterodimer formed by three inter-chain disulphide bonds. Chain One is 70 residues while chain two is 90 or 92 residues long [21,22]. It has been shown that the two Chains One and Two are encoded for by different genes [23]. Two copies of this heterodimer non-covalently associate to form a larger homodimer consisting of Chains A and B. Several attempts have been made to determine the 3D-structure of F. catus dander allergen Fel d1 [24,25]. In principle, two ways exist to form a heterodimer from Chain One and Two: Chain One followed by Chain Two or vice versa. When recombinant proteins were investigated both chain arrangements yielded very similar biochemical, immunological, and structural results, even when compared to their natural counterpart [26]. Only Chain 1 + 2 arrangement resulted in forming homodimers [24,25]. Thus, Chain A and B each consists of a Chain 1 + 2 heterodimers.
The limited sequence information is insufficient to reconstruct the molecular evolutionary history of the slow loris brachial gland secreted proteins and therefore their relationship to F. catus dander allergen Fel d1 and other proteins within the broader allergen family. In this study, we therefore elucidate the full-length sequence of both chains of the Javan slow lorises’ (Nycticebus javanicus) brachial gland secreted proteins, with samples from wild animals. We discuss our findings in the light of available information from the cat F. catus dander allergens possibly leading to insights not only on the molecular evolution of mammalian allergens but also gaining a greater understanding how to treat humans when envenomated by slow lorises.
2. Results and Discussion
Through a combination of MS/MS sequencing and DNA sequencing, we obtained the first full-length sequences of brachial gland protein of N. javanicus, with the full nucleotide sequence of Chain-One determined as (tgtcccgccgtagaaaaacacgctaacctcttcctgaagggaaccactgatgaatttctcaattatgcgaaaaatttcgtaaaatcctctgcagtattggaaaatgctaagcaactgaagatgtgttccgacaataaactgacagaagaggataaggataatgtccagtctgggctggacaaaatatactcaagcaatttttgt) while Chain Two was sequenced using protein sequencing (Table 1).

Table 1.
Protein sequencing results for Chain 2.
We then compared them structurally to the homologous F. catus dander Fel d1 protein. To date, eight cat dander allergens have been found. They were named Fel d1 to Fel d8 [27,28]. Fel d1 belongs to the secretoglobulin family, Fel d2 is a serumalbumin, Fel d3 a cystatin, Fel d4 and 7 are lipocalins, Fel d5 and 6 are Ig antibodies of type A and M, respectively. Further, Fel d8 is a latherin. Despite Fel d1 Fel d4 is the second most prominent cat dander allergen with 63% of people allergic to cats have formed antibodies against [29]. Fel d1 was discovered in 1973 and is the most prominent of these allergens [30]. It accounts for 96% of cat allergies [31]. It is found in every house and public place, regardless of the presence of cats. Fel d1 has spread globally and was detected even in regions where cats most likely have never lived, i.e., the Greenland inland ice shelf. This has been associated with particle sizes of Fel d1 that can reach less than 4 cm in diameter and thus are susceptible to eolian distribution [32]. Fel d1 is produced by every cat but the amount produced varies greatly with race, age, and sex. Adult cats produce more Fel d1 than kittens and male cats more than females. Neutered cats probably produce similar amounts of Fel d1 than females [33]. It has been postulated that Siberian and Balinesian cats produced less Fel d1 than most other races. However, the body of data is still sparse and the topic remains unclear [27]. Any similarity of brachial gland protein of N. javanicus and cat allergen Fel d1 hints towards a better understanding of the mechanism of action of brachial gland protein of N. javanicus as well as possible treatments to slow loris bites in humans.
Sequence alignment of target to templates revealed that the cysteine residues are conserved indicating that disulfide bridges are conserved as well (Figure 1). The N. javanicus brachial gland protein chains are shorter than the F. catus allergen structures as Chain One is missing the first three N-terminal residues M0, E1, and I2 as well as the C-terminally located V71 to T76. Chain One of the N. javanicus brachial secretion protein contains 36 out of 68 identical residues corresponding to 52.9% sequence similarity. In Chain Two, 25 out of 70 residues (35.7%) are identical.

Figure 1.
Sequence alignment of Felis catus (Fc) dander allergen Fel d1 and Nycticebus javanicus (Nj) brachial gland secretion protein. Identical residues are shaded in grey.
In order to examine the structural evolution of the N. javanicus brachial secretion protein, the F. catus dander allergen Fel d1 structure template 2EJN was first downloaded from the protein databank (https://www.rcsb.org) [34] consisting of a heterodimeric homodimer (two non-covalently linked copies of a covalently linked heterodimer) (Figure 2). The F. catus dander allergen Fel d1 heterodimer consists of two chains (A and B) linked to each other by three disulfide bonds within each heterodimer. All three disulfide bonds link together in the format of Chain A cysteine1 – Chain B cysteine3; Chain A cysteine2 – Chain B cysteine3; and Chain A cystine3 – Chain B cysteine1. Each domain consists of eight α-helices, for each to Chain One and Two, respectively. A Ca2+-binding site at the domain interface consists of I125 of Domain A and D130 of Domain B as well as N89 from both Domain A and B and three water molecules [25]. The same structure contains a hydrophobic core consisting of six residues: F85 (Domain A and B), G131 (Domain A and B), and L132 (Domain A and B) that are surrounded by hydrogen bond forming amino acids. This core forms the central structural element of the dimerization site [25]. More remote Ca2+-binding Sites Two and Three involved D46 and M49 in each of the domains [25]. In addition, there is a glycosylation site at position N103, at a surface loop connecting helices H6 and H7 [21,35]. Of particular importance for interpreting the diversification of the N. javanicus brachial gland protein, cavities were identified at the same region in each domain of F. catus dander allergen Fel d1 2EJN [25]. The volume of these cavities differed significantly in size (350 Å3 in Domain A versus 730 Å3 in Domain B) due to the differing conformations of the eleven residue long stretch from E121 to G131 in both domains. Kaiser et al. hypothesised that these cavities may host progesterone [24,25]. This result would be in accordance to findings of uteroglobin and other orthologues such as CC16 (Clara cell secretory protein) and ABP (androgen-binding protein) that bind progesterone, PCB-derivatives (PCB: polychlorinated biphenyl) and androgen [36,37,38,39,40].
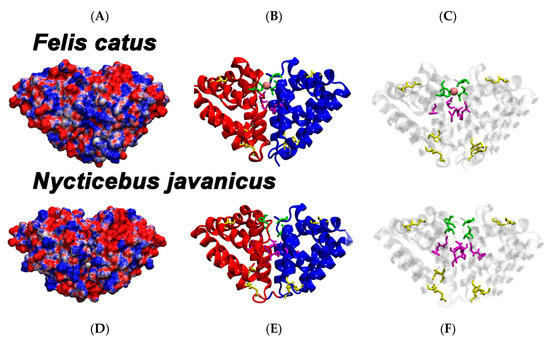
Figure 2.
Molecular modelling comparison of Felis catus dander allergen Fel d1 (top, A–C) and Nycticebus javanicus brachial gland secretion protein (bottom, D–F). A and D show the electrostatic surface of both proteins. Positive charges are depicted in blue, negative charges in red. B and E show cartoon representations of the same proteins. Domain A is shown in red, Domain B in blue. C and F are identical to B and E, but with transparent tertiary structure. B, C, E, and F: disulfide bridges are highlighted in yellow. B and C: N89 and I125 of Domain A and N89 and D130 of Domain B form the Ca2+ binding site at the domain interface in F. catus. These four residues are shown in green with the Ca2+ ion in pink. Six amino acids forming the hydrophobic core at the interface of Domains A and B are coloured in magenta (F85, G131, and L132 in both Domains A and B, respectively) E and F: possible Ca2+ binding in N. javanicus involves T81 and T117 of Domain A and T81 and D123 of Domain B. The hydrophobic core may consist of G77, D123, and I124 in both Domains A and B. D123 as a charged amino acid is expected to affect the interface in N. javanicus.
When modelled, as the N. javanicus brachial gland protein chains are shorter than the F. catus allergen chains, the structures shown for both proteins appear slightly different in shape, despite being superimposed and rotated the same way, but overall the structures are highly similar (Figure 2), which is reflective not only of shared molecular evolutionary history but suggestive of similar functionality. In the N. javanicus brachial secretion protein the critical residue for PLA2 inhibition D44 (homologous residue D46 in Fel d1) is held in position by two salt bridges from K40 and K52. In F. catus dander allergen Fel d1 the homologous stabilizing residues are K42 and K54.
Comparative examination of the Ca2+-binding site revealed that in the F. catus dander allergen Fel d1, the Ca2+-binding site 1 is located in a prominent position at the contact area between Domains A and B. Four residues form Ca2+-binding site 1: the side chain carbonyl atom of N89 and backbone carbonyl atom of I125 of Domain A as well as the side chain carbonyl atoms of N89 and D130 of Domain B. Since the N. javanicus brachial secretion protein was modelled without Ca2+-ions present, the attractive force of Ca2+ is missing, affecting the side-chain placement of T81(A), T81(B), and D123(B). Like I125 in F. catus dander allergen Fel d1, the respective T117 (A) orients its backbone carbonyl toward Ca2+-binding Site One. Despite these differences in side chain orientation, we postulate that Ca2+-binding Site One is also present in the dimerization area of the N. javanicus brachial secretion protein.
Comparative examination of the hydrophobic core revealed that the F. catus dander allergen Fel d1 a hydrophobic core made of six residues, namely F85, G131, and L132 of both Domains A and B [25]. In the N. javanicus brachial secretion protein this interdomain region is not all hydrophobic: G77 (A and B), D123 (A and B), I124 (A and B). Moreover, it is differently shaped. Where in F. catus dander allergen Fel d1 the large phenylalanine side chain reaches deep into the cavity, in the N. javanicus brachial secretion protein there is a glycine. By contrast, the position homologous to G131 of F. catus dander allergen Fel d1 is in the N. javanicus brachial secretion protein occupied by D123. We postulate that for the N. javanicus brachial secretion protein the hydrophobic core, therefore, differs from that of the allergen of F. catus.
Comparative examination of the dimerization site revealed that the two heterodimeric Domains A and B of F. catus dander allergen Fel d1 and that of the N. javanicus brachial secretion protein form a homodimer. The interface between the two domains consists of 21 amino acids of Domain A (S29, A31, Y73, G74, G77, T81, D83, I86, F90, T117, G118, K119, T120, D123, I124, I126, G127, A130, I131, I136, I137) and 20 residues of Domain B (same residues, except I137). Accessible surface area was calculated for both domains separately and the homodimer (Table 2). As expected, the number of solvent exposed surface atoms decreases upon dimerization. This is reflected in a 14% decrease of total accessible area as compared to the two separate heterodimeric Domains A and B.

Table 2.
Accessible surface area of isolated heterodimer Domains A and B and the homodimer. Surface areas were calculated using InterProSurf [41].
Comparative examination of the glycosylation site revealed that in F. catus dander allergen Fel d1 the glycosylation site N103 lies in the surface loop between helices H6 and H7. The corresponding residue in the N. javanicus brachial secretion protein is S95. Serine can be O-glycosylated and therefore glycosylation may occur at the same structural position as in F. catus dander allergen Fel d1 structure 2EJN.
Kaiser et al. postulated immunoglobulin E (IgE)-binding to solvent exposed residues [24]. IgE is an antibody that is known to play a crucial role in type I hypersensitivity. Type I hypersensitivity has been linked to allergic asthma, sinusitis, allergic rhinitis, food allergies, chronic urticaria, and atopic dermatitis. It is involved in allergen response, e.g. bee stings or anaphylactic drugs [42]. The apparent similarity of residues in F. catus dander allergen Fel d1, and the N. javanicus brachial secretion protein hints toward a similar function. F. catus dander allergen Fel d1 was identified several decades ago and is responsible for the immunoglobulin IgE-response in 90–95% of patients who are allergic to F. catus [31,43]. The body of work carried out in this study revealed that not only F. catus dander allergen Fel d1 may be able to trigger an immune response. A number of proteins exist in evolutionary distant animals that potentially can act similar to the major F. catus allergen. Of particular note is the molecular similarity between the N. javanicus brachial secretion protein and F. catus dander allergen Fel d1 which suggests a functional similarity that is consistent with known reactions to Nycticebus bites. We postulate that approaches to treat cat allergy, such as desensitization, may work for researchers and caretakers of slow lorises as well [44,45,46]. Furthermore, understanding the causes of allergic reactions up to anaphylactic shock greatly enhances chances for successful treatment of slow loris’ bites.
Future work should investigate the potential role of immunological feedback loops that are overstimulated and may explain the festering, non-healing wounds characteristic of slow loris bites. Treatment with cat antiallergens may be a starting point.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Brachial Gland Secretion
We obtained brachial gland secretions of Nycticebus javanicus from wild slow lorises studied at the ecological research station in Cipaganti, Garut Regency, West Java, Indonesia (S7°6’6–7°7’0& E 107°46’0–107°46’5). We collected samples used here from April 2012 to June 2014, during which time we captured the animals for health checks associated with a radio-tracking project [47]. After capture, we manually held the non-anaesthetized animals and gently used a sterile swab to collect the brachial secretion (supplementary video 1). Each swab was then contained, sealed with parafilm, and frozen at −80 °C. Samples were exported from Indonesia to Australia in August 2016 with approval from the Indonesian Ministry of Forestry, Indonesia’s CITES Management Authority, and Australia’s Department of Environment. The work was conducted under the RISTEK research permits 039/SIP/FRP/SM/11/2012, 11/TKPIPA/FRP/SM/11/2013, and 163/SPP/RPB/WU/5/2014. The Animal Ethics Subcommittee of Oxford Brookes University’s University Research Ethics Committee approved this research.
3.2. MS/MS
Protein was first desalted on C8 column, and resuspended in 100 mM ammonium bicarbonate. Protein was reduced with 10 mM DTT, 95 °C, 15 min, cooled to room temperature, and alkylated with iodoacetamide (25 mM final concentration) for 30 min, RT in the dark. Additional DTT (1ul, 100 uM) was added to quench excess iodoacetamide. The sample was split into aliquots, and digestion was performed overnight at 37 °C with either trypsin, chymotrypsin, AspN, GluC or LysC. Samples were ziptipped (C18, 0.6 ul resin, MerckMillipore) before analysis by mass spectrometry.
3.3. LC-MS/MS Analysis
Peptides were separated using reversed-phase chromatography on a Shimadzu Prominence nanoLC system. Using a flow rate of 30 µL/min, samples were desalted on an Agilent C18 trap (0.3 × 5 mm, 5 µm) for 3 min, followed by separation on a Vydac Everest C18 (300 A, 5 µm, 150 mm × 150 µm) column at a flow rate of 1 µL/min. A gradient of 10–60% buffer B over 30 min where buffer A = 1 % ACN / 0.1% FA and buffer B = 80% ACN / 0.1% FA was used to separate peptides. Eluted peptides were directly analyzed on a TripleTof 5600 instrument (ABSciex) using a Nanospray III interface. Gas and voltage settings were adjusted as required. MS TOF scan across m/z 350–1800 was performed for 0.5 sec followed by information dependent acquisition of up to 20 peptides across m/z 40–1800 (0.05 sec per spectra).
LC-MS/MS data was de novo sequenced using PeaksStudio software, with enzyme specified based on sample, mass tolerance of 20 ppm, fragment mass tolerance of 0.1 Da, and variable modifications including oxidation of methionine, and carbamidomethylation set as fixed modification. Resulting de novo sequences were manually curated and validated, with sequences BLAST searched to determine other proteins with similarity.
3.4. mRNA
The 3’ rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE) first strand cDNA was synthesized from 34 ng total RNA using the FirstChoice RLM-RACE kit (Ambion), following the manufacturer’s instructions. The resulting cDNA was used as template in a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using a forward primer (F) designed from the partial α-chain venom peptide sequence and a reverse 3’RACE outer primer supplied in the FirstChoice RLM-RACE kit (Ambion). The known peptide sequence was reverse-translated into a nucleotide sequence for primer design. Primer sequences were F=5’-GGTGGAAAAACATGCGAAC-3’ and 3’RACE outer primer = 5’-GCGAGCACAGAATTAATACGACT-3’. The PCR reaction was performed using FastStart Taq DNA polymerase (Roche) with 3’RACE-cDNA as template under the following cycling conditions: 95 °C for 4 min, followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 30 s, 58 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 1 min and a final elongation step at 72 °C for 7 min. PCR products were analyzed and purified after separation on a 1% agarose gel using a QIAquick Gel Extraction kit (Qiagen) and cloned into vector pCR2.1 (Invitrogen) for sequencing by the Australian Genome Research Facility using an M13 forward primer.
3.5. Modeling
In order to structurally modelling of Chain 1 + 2 heterodimers and homodimers of Chain A and B, the target sequence was aligned to the template sequence of the major F. catus allergen Fel d1 in Swiss PDB Viewer [48]. The major F. catus allergen Fel d1 template structures 1ZKR and 2EJN [24,25] were downloaded from the PDB (www.rcsb.org) [34]. It was used as the template for all molecules in this study. The target sequences A and B were aligned to the template and target to template sequence alignments were exported in gapped FASTA-format from SPDBV [48]. The alignment was read in Chimera (University of San Francisco), version 1.8 [49]. Models were created using MODELLER [50] through UCSF Chimera as a Graphical User Interface. Due to the overall high sequence identity between target and template the series of models obtained from MODELLER were very similar. Therefore, the first model with the lowest overall energy was chosen. The model structures were generated in SPDBV [48] and side chains were cleaned up by following energy minimization of 20 and two times 100 steps of steepest descent minimization as implemented in SPDBV. Interface residues were identified by calculating contact surfaces of neighbouring domains in the homodimer using InterProSurf [51]. Hydrophobic patches were identified by calculating the respective surfaces in SPDBV. Surface charges were calculated using the APBS-algorithm [52] as implemented in VMD [53]. The calculated potential-maps were loaded to the protein under inspection. Surfaces were visualized applying the “surf” option and colouring method “volume” in VMD. The range for positive (blue) to negative charges (red) was set to −20.00 and 20.00, respectively.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.G.F.; methodology, H.S., L.R, B.G.F.; investigation, H.S., L.R., K.B., J.S.D., W.W., R.J.L., H.F.K., B.G.F.; resources, K.A.-I.N, J.R.-M., R.M., B.G.F.; writing—original draft preparation, H.S., K.A.-I.N., J.R.-M., B.G.F.; writing—review and editing, H.S., K.A.-I.N, J.R.-M., L.R, K.B., J.S.D., W.W., A.N., V.N., P.M., R.M., R.J.L., H.F.K., B.G.F.; supervision, B.G.F.; project administration, K.A.-I.N., B.G.F.; funding acquisition, K.A.-I.N., B.G.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Cleveland Zoo and Zoo Society, Leverhulme Trust (RPG-084) and People’s Trust for Endangered Species. This work was also funded by NHMRC Project APP1072113 to R.L and the Science and Technology Development Fund, Macau SAR (File no. 019/2017/A1) to H.F.K.
Acknowledgments
We thank Indonesia RISTEK and the regional Perhutani and BKSDA for authorising the fieldwork portion of this study.
Conflicts of Interest
Declare The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fry, B.G.; Roelants, K.; Champagne, D.E.; Scheib, H.; Tyndall, J.D.; King, G.F.; Nevalainen, T.J.; Norman, J.A.; Lewis, R.J.; Norton, R.S.; et al. The toxicogenomic multiverse: Convergent recruitment of proteins into animal venoms. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2009, 10, 483–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casewell, N.R.; Petras, D.; Card, D.C.; Suranse, V.; Mychajliw, A.M.; Richards, D.; Koludarov, I.; Albulescu, L.O.; Slagboom, J.; Hempel, B.F.; et al. Solenodon genome reveals convergent evolution of venom in eulipotyphlan mammals. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 25745–25755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casewell, N.R.; Wuster, W.; Vonk, F.J.; Harrison, R.A.; Fry, B.G. Complex cocktails: The evolutionary novelty of venoms. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2013, 28, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakumanu, R.; Hodgson, W.C.; Ravi, R.; Alagon, A.; Harris, R.J.; Brust, A.; Alewood, P.F.; Kemp-Harper, B.K.; Fry, B.G. Vampire Venom: Vasodilatory Mechanisms of Vampire Bat (Desmodus rotundus) Blood Feeding. Toxins 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligabue-Braun, R.; Verli, H.; Carlini, C.R. Venomous mammals: A review. Toxicon 2012, 59, 680–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, D.H.; Sunagar, K.; Undheim, E.A.; Ali, S.A.; Alagon, A.C.; Ruder, T.; Jackson, T.N.; Pineda Gonzalez, S.; King, G.F.; Jones, A.; et al. Dracula’s children: Molecular evolution of vampire bat venom. J. Proteom. 2013, 89, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rode-Margono, J.E.; Nekaris, K.A. Cabinet of Curiosities: Venom Systems and Their Ecological Function in Mammals, with a Focus on Primates. Toxins 2015, 7, 2639–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alterman, L. Toxins and toothcombs: Potential allospecific chemical defenses in Nycticebus and Perodicticus. In Creatures of the Dark: The Nocturnal Prosimians; Alterman, L., Doyle, G.A., Izard, M.K., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 413–424. [Google Scholar]
- Nekaris, K.A.; Moore, R.S.; Rode, E.J.; Fry, B.G. Mad, bad and dangerous to know: The biochemistry, ecology and evolution of slow loris venom. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop Dis. 2013, 19, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, G.; Lukas, K.E.; Kuhar, C.; Dennis, P.M. A retrospective review of mortality in lorises and pottos in North American zoos 1980–2010. Endanger. Species Res. 2014, 23, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streicher, U. Aspects of Ecology and Conservation of the Pygmy Loris Nycticebus Pygmaeus in Vietnam; Ludwig-Maximilian-Universitat Munchen: Munich, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Fung, H.T.; Wong, O.F. Clinical quiz: A potentially toxic primate bite. Hong Kong J. Emerg. Med. 2016, 23, 301–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, M.; Weldon, A.; Poindexter, S.A.; Gibson, N.; Nekaris, K.A.I. Survey of practitioners handling slow lorises (Primates: Nycticebus): An assessment of the harmful effects of slow loris bites. J. Venom. Res. 2018, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Madani, G.; Nekaris, K.A. Anaphylactic shock following the bite of a wild Kayan slow loris (Nycticebus kayan): Implications for slow loris conservation. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop Dis. 2014, 20, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagey, L.; Fry, B.G.; Snyder, H. Talking Defensively: A Dual Use for the Brachial Gland Exudate of Slow and Pygmy Lorises. In Developments in Primatology; Gursky, N., Ed.; Kluwer: South Holland, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schaffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, M.C.; Baer, H.; Ohman, J.L., Jr. A comparative study of the allergens of cat urine, serum, saliva, and pelt. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1985, 76, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charpin, C.; Mata, P.; Charpin, D.; Lavaut, M.N.; Allasia, C.; Vervloet, D. Fel d I allergen distribution in cat fur and skin. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1991, 88, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klug, J.; Beier, H.M.; Bernard, A.; Chilton, B.S.; Fleming, T.P.; Lehrer, R.I.; Miele, L.; Pattabiraman, N.; Singh, G. Uteroglobin/Clara cell 10-kDa family of proteins: Nomenclature committee report. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 923, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Milligen, F.J.; Vroom, T.M.; Aalberse, R.C. Presence of Felis domesticus allergen I in the cat’s salivary and lacrimal glands. Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol. 1990, 92, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffort, O.A.; Carreira, J.; Nitti, G.; Polo, F.; Lombardero, M. Studies on the biochemical structure of the major cat allergen Felis domesticus I. Mol. Immunol. 1991, 28, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, A.K.; Schou, C.; Roepstorff, P. Determination of isoforms, N-linked glycan structure and disulfide bond linkages of the major cat allergen Fel d1 by a mass spectrometric approach. Biol. Chem. 1997, 378, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, I.J.; Craig, S.; Pollock, J.; Yu, X.B.; Morgenstern, J.P.; Rogers, B.L. Expression and genomic structure of the genes encoding FdI, the major allergen from the domestic cat. Gene 1992, 113, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, L.; Gronlund, H.; Sandalova, T.; Ljunggren, H.G.; van Hage-Hamsten, M.; Achour, A.; Schneider, G. The crystal structure of the major cat allergen Fel d 1, a member of the secretoglobin family. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 37730–37735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, L.; Velickovic, T.C.; Badia-Martinez, D.; Adedoyin, J.; Thunberg, S.; Hallen, D.; Berndt, K.; Gronlund, H.; Gafvelin, G.; van Hage, M.; et al. Structural characterization of the tetrameric form of the major cat allergen Fel d 1. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 370, 714–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gronlund, H.; Bergman, T.; Sandstrom, K.; Alvelius, G.; Reininger, R.; Verdino, P.; Hauswirth, A.; Liderot, K.; Valent, P.; Spitzauer, S.; et al. Formation of disulfide bonds and homodimers of the major cat allergen Fel d 1 equivalent to the natural allergen by expression in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 40144–40151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, S.K.; Leung, D.Y.M. Dog and Cat Allergies: Current State of Diagnostic Approaches and Challenges. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2018, 10, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.; O’Neil, S.E.; Hales, B.J.; Chai, T.L.; Hazell, L.A.; Tanyaratsrisakul, S.; Piboonpocanum, S.; Thomas, W.R. Two newly identified cat allergens: The von Ebner gland protein Fel d 7 and the latherin-like protein Fel d 8. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2011, 156, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.; Butler, A.J.; Hazell, L.A.; Chapman, M.D.; Pomes, A.; Nickels, D.G.; Thomas, W.R. Fel d 4, a cat lipocalin allergen. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2004, 34, 1732–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohman, J.L.; Lowell, F.C.; Bloch, K.J. Allergens of mammalian origin: Characterization of allergen extracted from cat pelts. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1973, 52, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Ree, R.; van Leeuwen, W.A.; Bulder, I.; Bond, J.; Aalberse, R.C. Purified natural and recombinant Fel d 1 and cat albumin in in vitro diagnostics for cat allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1999, 104, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custovic, A.; Simpson, A.; Pahdi, H.; Green, R.M.; Chapman, M.D.; Woodcock, A. Distribution, aerodynamic characteristics, and removal of the major cat allergen Fel d 1 in British homes. Thorax 1998, 53, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalil-Colome, J.; de Andrade, A.D.; Birnbaum, J.; Casanova, D.; Mege, J.L.; Lanteaume, A.; Charpin, D.; Vervloet, D. Sex difference in Fel d 1 allergen production. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1996, 98, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgenstern, J.P.; Griffith, I.J.; Brauer, A.W.; Rogers, B.L.; Bond, J.F.; Chapman, M.D.; Kuo, M.C. Amino acid sequence of Fel dI, the major allergen of the domestic cat: Protein sequence analysis and cDNA cloning. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 9690–9694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, H.J.; Nordlund-Moller, L.; Nord, M.; Gustafsson, J.; Lund, J.; Gillner, M. Structural basis for calcium binding by uteroglobins. J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 256, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beato, M. Binding of steroids to uteroglobin. J. Steroid Biochem 1976, 7, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emes, R.D.; Riley, M.C.; Laukaitis, C.M.; Goodstadt, L.; Karn, R.C.; Ponting, C.P. Comparative evolutionary genomics of androgen-binding protein genes. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1516–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hard, T.; Barnes, H.J.; Larsson, C.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Lund, J. Solution structure of a mammalian PCB-binding protein in complex with a PCB. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1995, 2, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez de Haro, M.S.; Perez Martinez, M.; Garcia, C.; Nieto, A. Binding of retinoids to uteroglobin. FEBS Lett. 1994, 349, 249–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negi, S.S.; Schein, C.H.; Oezguen, N.; Power, T.D.; Braun, W. InterProSurf: A web server for predicting interacting sites on protein surfaces. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 3397–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, H.J.; Sutton, B.J.; Beavil, A.J.; Beavil, R.L.; McCloskey, N.; Coker, H.A.; Fear, D.; Smurthwaite, L. The biology of IGE and the basis of allergic disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 21, 579–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleine-Tebbe, J.; Kleine-Tebbe, A.; Jeep, S.; Schou, C.; Lowenstein, H.; Kunkel, G. Role of the major allergen (Fel d I) in patients sensitized to cat allergens. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 1993, 100, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyaraj, E.; Gardner, C.; Filipi, I.; Cramer, K.; Sherrill, S. Reduction of active Fel d1 from cats using an antiFel d1 egg IgY antibody. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2019, 7, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uermosi, C.; Zabel, F.; Manolova, V.; Bauer, M.; Beerli, R.R.; Senti, G.; Kundig, T.M.; Saudan, P.; Bachmann, M.F. IgG-mediated down-regulation of IgE bound to mast cells: A potential novel mechanism of allergen-specific desensitization. Allergy 2014, 69, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Kepley, C.L.; Zhang, K.; Terada, T.; Yamada, T.; Saxon, A. A chimeric human-cat fusion protein blocks cat-induced allergy. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 446–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poindexter, S.A.; Nekaris, K.A.I. Vertical clingers and gougers: Rapid acquisition of adult limb proportions facilitates feeding behaviours in young Javan slow lorises (Nycticebus javanicus). Mammalian Biology-Zeitschrift für Säugetierkunde 2017, 87, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guex, N.; Peitsch, M.C.; Schwede, T. Automated comparative protein structure modeling with SWISS-MODEL and Swiss-PdbViewer: A historical perspective. Electrophoresis 2009, 30 (Suppl. 1), S162–S173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera--a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput Chem 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sali, A.; Blundell, T.L. Comparative protein modelling by satisfaction of spatial restraints. J. Mol. Biol. 1993, 234, 779–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negri, L.; Lattanzi, R.; Giannini, E.; Melchiorri, P. Bv8/Prokineticin proteins and their receptors. Life Sci. 2007, 81, 1103–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, N.A.; Sept, D.; Joseph, S.; Holst, M.J.; McCammon, J.A. Electrostatics of nanosystems: Application to microtubules and the ribosome. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 10037–10041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).