The Failures of Ethnobotany and Phytomedicine in Delivering Novel Treatments for Snakebite Envenomation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Medicine or Magic?
3. Plant-Derived Medicines for Human Use
4. The Ethnobotanical Pharmacopeia Used for SBE
5. Consequences of Using Ineffective Traditional Treatments for SBE
6. Issues Associated with the Research on Therapeutic Efficacy of Plant Extracts for SBE
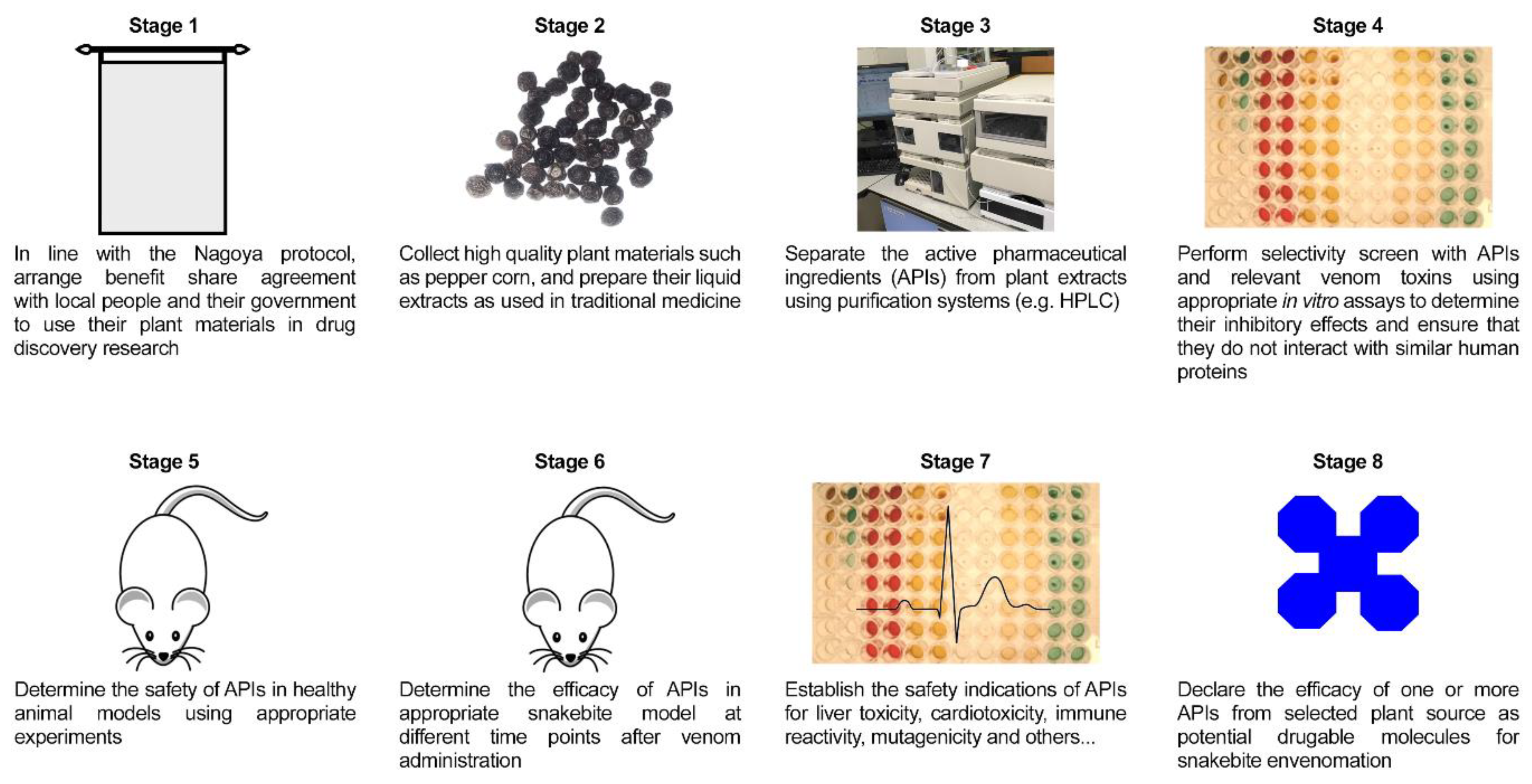
7. Approaches that Should Be Considered in Ethnobotany Research for SBE
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chippaux, J.P.; Goyffon, M. Venoms, Antivenoms and Immunotherapy. Toxicon 1998, 36, 823–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, H.F.; Layfield, H.J.; Vallance, T.; Patel, K.; Bicknell, A.B.; Trim, S.A.; Sakthivel, V. The urgent need to develop novel strategies for the diagnosis and treatment of snakebites. Toxins 2019, 11, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.S.; Wijesinghe, C.A.; Jayamanne, S.F.; Buckley, N.A.; Dawson, A.H.; Lalloo, D.G.; de Silva, H.J. Delayed psychological morbidity associated with snakebite envenoming. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawgood, B.J. Doctor Albert Calmette 1863–1933: Founder of Antivenomous Serotherapy and of Antituberculous BCG Vaccination. Toxicon 1999, 37, 1241–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.J.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J.; Wüster, W.; Ratanabanangkoon, K.; Paiva, O.; Brown, N.I.; Casewell, N.R.; Harrison, R.A.; Rowley, P.D.; et al. Ending the drought: New strategies for improving the flow of affordable, effective antivenoms in Asia and Africa. J. Proteom. 2011, 74, 1735–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habib, A.G.; Warrell, D.A. Antivenom therapy of carpet viper (Echis ocellatus) envenoming: Effectiveness and strategies for delivery in West Africa. Toxicon 2013, 69, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keyler, D.E.; Gawarammana, I.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Sellahewa, K.H.; McWhorter, K.; Malleappah, R. Antivenom for snakebite envenoming in Sri Lanka: The need for geographically specific antivenom and improved efficacy. Toxicon 2013, 69, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Bisht, G.S. Some novel folk treatments among the tribes of uttar pradesh. Anc. Sci. Life 1999, 18, 250. [Google Scholar]
- Owuor, B.O.; Mulemi, B.A.; Kokwaro, J.O. Indigenous snake bite remedies of the Luo of Western Kenya. J. Ethnobiol. 2005, 25, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, K.S.; Sharma, P.C.; Kishore, P. Tribal remedies for snakebite from orissa. Anc. Sci. Life 1986, 6, 122. [Google Scholar]
- Fry, B.G. Snakebite: When the human touch becomes a bad touch. Toxins 2018, 10, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murari, S.K.; Frey, F.J.; Frey, B.M.; Gowda, T.V.; Vishwanath, B.S. Use of Pavo cristatus feather extract for the better management of snakebites: Neutralization of inflammatory reactions. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 99, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanamandra, U.; Yanamandra, S. Traditional first aid in a case of snake bite: More harm than good. BMJ Case Rep. 2014, 2014, bcr2013202891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubab, K.V. An Indigenous Treatment for Snake-Bite. Ind. Med. Gaz. 1928, 63, 491. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kusari, P.; Kusari, S.; Spiteller, M.; Kayser, O. Implications of endophyte-plant crosstalk in light of quorum responses for plant biotechnology. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 5383–5390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rates, S.M.K. Plants as source of drugs. Toxicon 2001, 39, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, J.; Mujib, A.; Nasim, S.A.; Sharma, M.P. Screening of vincristine yield in ex vitro and in vitro somatic embryos derived plantlets of Catharanthus Roseus L. (G). Don. Sci. Hortic. 2009, 119, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, J.G.; Mahdi, A.J.; Mahdi, A.J.; Bowen, I.D. The historical analysis of aspirin discovery, its relation to the willow tree and antiproliferative and anticancer potential. Cell Prolif. 2006, 39, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durairaj, P.; Kamaraj, M.; Senthil Kumar, S. Ethnobotanical survey of folk plants for the treatment of snakebites in southern part of Tamil Nadu, India. Int. J. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 3, 72–78. [Google Scholar]
- Owuor, B.O.; Kisangau, D.P. Kenyan medicinal plants used as antivenin: A comparison of plant usage. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2006, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa Guimarães, N.; Freitas-de-Sousa, L.A.; Scheffer de Souza, M.C.; Oliveira de Almeida, P.D.; Dos-Santos, M.C.; Nunez, C.V.; de Oliveira, R.B.; Mourão, R.H.V.; de Moura, V.M. Evaluation of the anti-snakebite, antimicrobial and antioxidant potential of Philodendron megalophyllum Schott (Araceae), traditionally used in accidents caused by snakes in the western region of Pará, Brazil. Toxicon 2020, 184, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biondo, R.; Pereira, A.M.S.; Marcussi, S.; Pereira, P.S.; França, S.C.; Soares, A.M. Inhibition of enzymatic and pharmacological activities of some snake venoms and toxins by Mandevilla velutina (Apocynaceae) aqueous extract. Biochimie 2003, 85, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiyapuri, S.; Vaiyapuri, R.; Ashokan, R.; Ramasamy, K.; Nattamaisundar, K.; Jeyaraj, A.; Chandran, V.; Gajjeraman, P.; Baksh, M.F.; Gibbins, J.M.; et al. Snakebite and its socio-economic impact on the rural population of Tamil Nadu, India. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, Y.K.; Peshin, S.S. Do herbal medicines have potential for managing snake bite envenomation? Toxicol. Int. 2012, 19, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, H.F.; Vaiyapuri, R.; Gajjeraman, P.; Hutchinson, G.; Gibbins, J.M.; Bicknell, A.B.; Vaiyapuri, V. Challenges in diagnosing and treating snakebites in a rural population of Tamil Nadu, India: The views of clinicians. Toxicon 2017, 130, 44–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, W.F.; Hung, D.Z.; Tsai, W.J.; Lin, K.P.; Deng, J.F. Podophyllotoxin intoxication: Toxic effect of bajiaolian in herbal therapeutics. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 1992, 11, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, L.; He, Y.; Hao, J.-C.; Semotiuk, A.; Liu, Q.-R.; Mazari, P. Toxic pyrrolizidine alkaloids provide a warning sign to overuse of the ethnomedicine Arnebia benthamii. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 210, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, P.A.; Nipate, S.S.; Sonpetkar, J.M.; Salvi, N.C.; Waghmare, A.B.; Chaudhari, P.D. Anti-snake venom activities of ethanolic extract of fruits of Piper longum L. (Piperaceae) against Russell’s viper venom: Characterization of piperine as active principle. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 147, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, P.A.; Nipate, S.S.; Sonpetkar, J.M.; Salvi, N.C.; Waghmare, A.B.; Chaudhari, P.D. Production of high titre antibody response against Russell’s viper venom in mice immunized with ethanolic extract of fruits of Piper longum L. (Piperaceae) and piperine. Phytomedicine 2014, 21, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Katewa, S.S.; Sharma, S.K.; Galav, P.; Jain, V. Snakelore and indigenous snakebite remedies practiced by some tribals of Rajasthan. Indian J. Tradit. Knowl. 2011, 10, 258–268. [Google Scholar]
- De Roodt, A.R.; Litwin, S.; Angel, S.O. Hydrolysis of DNA by 17 snake venoms. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2003, 135, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, A. Testing of natural remedies for natural toxins. Toxicon 2003, 41, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Albulescu, L.-O.; Bittenbinder, M.A.; Somsen, G.W.; Vonk, F.J.; Casewell, N.R.; Kool, J. Neutralizing effects of small molecule inhibitors and metal chelators on coagulopathic viperinae snake venom toxins. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rucavado, A.; Escalante, T.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Effect of the metalloproteinase inhibitor batimastat in the systemic toxicity induced by Bothrops asper snake venom: Understanding the role of metalloproteinases in envenomation. Toxicon 2004, 43, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenbroucke, R.E.; Libert, C. Is there new hope for therapeutic matrix metalloproteinase inhibition? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 904–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rofes, L.; Arreola, V.; Martin, A.; Clavé, P. Effect of oral piperine on the swallow response of patients with oropharyngeal dysphagia. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 49, 1517–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, J.; Swain, B.C.; Tripathy, U. In silico investigation of spice molecules as potent inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachtel, L.W.; Cole, L.J. Who expert committee on biological standardization. Seventeenth report. World Health Organ. Tech. Rep. Ser. 1964, 293, 1–86. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, A.; Marikar, F.; Murugananthan, A.; Agampodi, S. Awareness and perceptions on prevention, first aid and treatment of snakebites among Sri Lankan farmers: A knowledge practice mismatch? J. Occup. Med. Toxicol. 2014, 9, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsantrizos, Y.S. The design of a potent inhibitor of the hepatitis C virus NS3 protease: BILN 2061–From the NMR tube to the clinic. Biopolym. Pept. Sci. Sect. 2004, 76, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, M.; Hamilton, C. The nagoya protocol on access to genetic resources and the fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from their utilization to the convention on biological diversity. Rev. Eur. Comm. Int Environ. Law. 2011, 20, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trim, S.A.; Trim, C.M.; Williams, H.F.; Vaiyapuri, S. The Failures of Ethnobotany and Phytomedicine in Delivering Novel Treatments for Snakebite Envenomation. Toxins 2020, 12, 774. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12120774
Trim SA, Trim CM, Williams HF, Vaiyapuri S. The Failures of Ethnobotany and Phytomedicine in Delivering Novel Treatments for Snakebite Envenomation. Toxins. 2020; 12(12):774. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12120774
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrim, Steven A., Carol M. Trim, Harry F. Williams, and Sakthivel Vaiyapuri. 2020. "The Failures of Ethnobotany and Phytomedicine in Delivering Novel Treatments for Snakebite Envenomation" Toxins 12, no. 12: 774. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12120774
APA StyleTrim, S. A., Trim, C. M., Williams, H. F., & Vaiyapuri, S. (2020). The Failures of Ethnobotany and Phytomedicine in Delivering Novel Treatments for Snakebite Envenomation. Toxins, 12(12), 774. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12120774





