High Diversity of Microcystin Chemotypes within a Summer Bloom of the Cyanobacterium Microcystis botrys
Abstract
1. Introduction
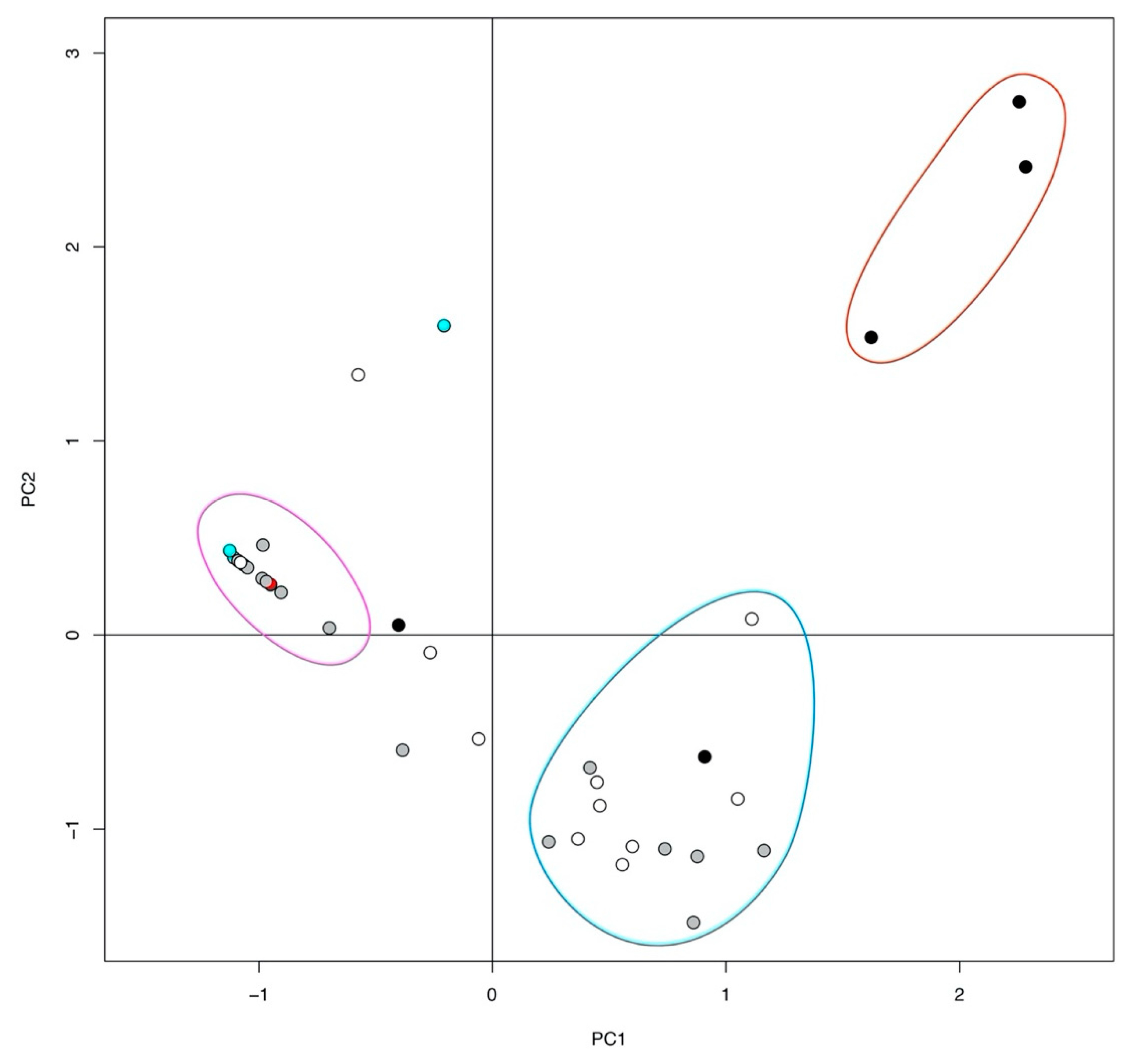
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Sampling and Isolation of Microcystis Colonies
4.2. Harvest of Microcystis botrys Strains
4.3. Extraction and LC-MS/MS Analysis
4.4. Statistical Analysis
4.5. Water Chemistry
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Visser, P.M.; Verspagen, J.M.H.; Sandrini, G.; Stal, L.J.; Matthijs, H.C.P.; Davis, T.W.; Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. How rising CO2 and global warming may stimulate harmful cyanobacterial blooms. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huisman, J.; Codd, G.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Ibelings, B.W.; Verspagen, J.M.H.; Visser, P.M. Cyanobacterial blooms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paerl, H.W.; Otten, T.G. Harmful Cyanobacterial Blooms: Causes, Consequences, and Controls. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 995–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. Blooms Like it Hot. Science 2008, 320, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neil, J.M.; Davis, T.W.; Burford, M.A.; Gobler, C.J. The rise of harmful cyanobacteria blooms: The potential roles of eutrophication and climate change. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosten, S.; Huszar, V.L.M.; Bécares, E.; Costa, L.S.; Donk, E.; Hansson, L.-A.; Jeppesen, E.; Kruk, C.; Lacerot, G.; Mazzeo, N.; et al. Warmer climates boost cyanobacterial dominance in shallow lakes. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2012, 18, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantzouki, E.; Lurling, M.; Fastner, J.; de Senerpont Domis, L.; Wilk-Wozniak, E.; Koreiviene, J.; Seelen, L.; Teurlincx, S.; Verstijnen, Y.; Krzton, W.; et al. Temperature Effects Explain Continental Scale Distribution of Cyanobacterial Toxins. Toxins 2018, 10, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W. Mitigating Toxic Planktonic Cyanobacterial Blooms in Aquatic Ecosystems Facing Increasing Anthropogenic and Climatic Pressures. Toxins 2018, 10, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berner, C.; Bertos-Fortis, M.; Pinhassi, J.; Legrand, C. Response of Microbial Communities to Changing Climate Conditions During Summer Cyanobacterial Blooms in the Baltic Sea. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konst, H.; McKercher, P.D.; Gorham, P.R.; Robertson, A.; Howell, J. Symptoms and Pathology Produced By Toxic Microcystis aeruginosa NRC-1 In Laboratory and Domestic Animals. Can. J. Comp. Med. Vet. Sci. 1965, 29, 221–228. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, R.M. The Toxicology of Microcystins. Toxicon 1998, 36, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartram, J.; Carmichael, W.W.; Chorus, I.; Jones, G.; Skulberg, O.M. Chapter 1: Introduction. In Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management; Chorus, I., Bartram, J., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999; p. 400. [Google Scholar]
- Codd, G.A.; Lindsay, J.; Young, F.M.; Morrison, L.F.; Metcalf, J.S. Harmful Cyanobacteria: From mass mortalities to management measures. In Harmful Cyanobacteria, 1st ed.; Huisman, J., Matthijs, H.C.P., Visser, P.M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 3, pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Catherine, A.; Bernard, C.; Spoof, L.; Bruno, M. Microcystins and Nodularins. In Handbook of Cyanobacterial Monitoring and Cyanotoxin Analysis, 1st ed.; Meriluoto, J., Spoof, L., Codd, G.A., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Humbert, J.-F.; Fastner, J. Ecology of Cyanobacteria. In Handbook of Cyanobacterial Monitoring and Cyanotoxin Analysis, 1st ed.; Meriluoto, J., Spoof, L., Codd, G.A., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- De Figueiredo, D.R.; Azeiteiro, U.M.; Esteves, S.M.; Goncalves, F.J.; Pereira, M.J. Microcystin-producing blooms-a serious global public health issue. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2004, 59, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, K.; Sano, T.; Kubota, R.; Kobayashi, N.; Tahara, M.; Obama, T.; Sugimoto, N.; Nishimura, T.; Ikarashi, Y. Effects of the amino acid constituents of microcystin variants on cytotoxicity to primary cultured rat hepatocytes. Toxins 2014, 6, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivonen, K.; Jones, G. Chapter 3: Cyanobacterial Toxins. In Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management; Chorus, I., Bartram, J., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Welker, M.; von Döhren, H. Cyanobacterial peptides-nature’s own combinatorial biosynthesis. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 30, 530–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, W.W.; Beasley, V.; Bunner, D.L.; Eloff, J.N.; Falconer, I.; Gorham, P.; Harada, K.-I.; Krishnamurthy, T.; Min-Juan, Y.; Moore, R.E.; et al. Naming of Cyclic Heptapeptide Toxins of Cyanobacteria (Blue-Green Algae). Toxicon 1988, 26, 971–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizawa, T.; Asayama, M.; Fujii, K.; Harada, K.-i.; Shirai, M. Genetic Analysis of the Peptide Synthetase Genes for a Cyclic Heptapeptide Microcystin in Microcystis spp. J. Biochem. 1999, 126, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillett, D.; Dittmann, E.; Erhard, M.; von Döhren, H.; Börner, T.; Neilan, B.A. Structural organization of microcystin biosynthesis in Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806: An integrated peptide-polyketide synthetase system. Chem. Biol. 2000, 7, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizawa, T.; Ueda, A.; Asayama, M.; Fujii, K.; Harada, K.-i.; Ochi, K.; Shirai, M. Polyketide Synthase Gene Coupled to the Peptide Synthetase Module Involved in the Biosynthesis of the Cyclic Heptapeptide Microcystin. J. Biochem. 2000, 127, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, G.; Fastner, J.; Erhard, M.; Börner, T.; Dittmann, E. Microcystin Biosynthesis in Planktothrix: Genes, Evolution, and Manipulation. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhiainen, L.; Vakkilainen, T.; Siemer, B.L.; Buikema, W.; Haselkorn, R.; Sivonen, K. Genes coding for hepatotoxic heptapeptides (microcystins) in the cyanobacterium Anabaena strain 90. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoof, L.; Catherine, A. Appendix 3 Tables of Microcystins and Nodularins. In Handbook of Cyanobacterial Monitoring and Cyanotoxin Analysis, 1st ed.; Meriluoto, J., Spoof, L., Codd, G.A., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Welker, M.; Brunke, M.; Preussel, K.; Lippert, I.; von Dohren, H. Diversity and distribution of Microcystis (Cyanobacteria) oligopeptide chemotypes from natural communities studied by single-colony mass spectrometry. Microbiology 2004, 150, 1785–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puddick, J.; Prinsep, M.R.; Wood, S.A.; Kaufononga, S.A.; Cary, S.C.; Hamilton, D.P. High levels of structural diversity observed in microcystins from Microcystis CAWBG11 and characterization of six new microcystin congeners. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5372–5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinta-Kanto, J.M.; Konopko, E.A.; DeBruyn, J.M.; Bourbonniere, R.A.; Boyer, G.L.; Wilhelm, S.W. Lake Erie Microcystis: Relationship between microcystin production, dynamics of genotypes and environmental parameters in a large lake. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.S.; Li, Z.; Kang, Y.H.; Shin, H.H.; Joo, J.H.; Han, M.S. Distinct Bloom Dynamics of Toxic and Non-toxic Microcystis (Cyanobacteria) Subpopulations in Hoedong Reservoir (Korea). Microb. Ecol. 2018, 75, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neilan, B.A.; Pearson, L.A.; Muenchhoff, J.; Moffitt, M.C.; Dittmann, E. Environmental conditions that influence toxin biosynthesis in cyanobacteria. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 1239–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rantala, A.; Fewer, D.P.; Hisbergues, M.; Rouhiainen, L.; Vaitomaa, J.; Börner, T.; Sivonen, K. Phylogenetic evidence for the early evolution of microcystin synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, A.; Kinnear, S. Interpreting the possible ecological role(s) of cyanotoxins: Compounds for competitive advantage and/or physiological aide? Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2239–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, L.A.; Dittmann, E.; Mazmouz, R.; Ongley, S.E.; D’Agostino, P.M.; Neilan, B.A. The genetics, biosynthesis and regulation of toxic specialized metabolites of cyanobacteria. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilliges, Y.; Kehr, J.C.; Meissner, S.; Ishida, K.; Mikkat, S.; Hagemann, M.; Kaplan, A.; Borner, T.; Dittmann, E. The cyanobacterial hepatotoxin microcystin binds to proteins and increases the fitness of Microcystis under oxidative stress conditions. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ger, K.A.; Faassen, E.J.; Pennino, M.G.; Lurling, M. Effect of the toxin (microcystin) content of Microcystis on copepod grazing. Harmful Algae 2016, 52, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, P.T.; Jones, G.J. Relationship between microcystin production and cell division rates in nitrogen-limited Microcystis aeruginosa cultures. Limnol. Ocanogr. 1998, 43, 1604–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardinaal, W.E.A.; Janse, I.; Kamst-van Agterveld, M.; Meima, M.; Snoek, J.; Mur, L.R.; Huisman, J.; Zwart, G.; Visser, P.M. Microcystis genotype succession in relation to microcystin concentrations in freshwater lakes. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2007, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Merwe, D. Cyanobacterial (Blue-Green Algae) Toxins. In Handbook of Toxicology of Chemical Warfare Agents; Elsevier: Kidlington, UK, 2015; pp. 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y.-T.; Chen, Y.-H.; Wang, T.-S.; Yen, H.-K.; Lin, T.-F. A qPCR-Based Tool to Diagnose the Presence of Harmful Cyanobacteria and Cyanotoxins in Drinking Water Sources. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alström, T.; Holmström, K.; Holmström, C.; Davidsson, T.; Björklund, H. Vombsjön Faktasammanställning 2017 (Lake Vomb, A Compilation of Information); Kävlingeåns vattenråd: Landskrona, Sweden, 2017; p. 55. [Google Scholar]
- Ekvall, M.K.; de la Calle Martin, J.; Faassen, E.J.; Gustafsson, S.; Lürling, M.; Hansson, L.-A. Synergistic and species-specific effects of climate change and water colour on cyanobacterial toxicity and bloom formation. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 2414–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrutia-Cordero, P.; Ekvall, M.K.; Hansson, L.A. Controlling Harmful Cyanobacteria: Taxa-Specific Responses of Cyanobacteria to Grazing by Large-Bodied Daphnia in a Biomanipulation Scenario. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briand, E.; Yepremian, C.; Humbert, J.F.; Quiblier, C. Competition between microcystin- and non-microcystin-producing Planktothrix agardhii (cyanobacteria) strains under different environmental conditions. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 3337–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briand, E.; Escoffier, N.; Straub, C.; Sabart, M.; Quiblier, C.; Humbert, J.-F. Spatiotemporal changes in the genetic diversity of a bloom-forming Microcystis aeruginosa (cyanobacteria) population. ISME J. 2009, 3, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabart, M.; Pobel, D.; Briand, E.; Combourieu, B.; Salencon, M.J.; Humbert, J.F.; Latour, D. Spatiotemporal Variations in Microcystin Concentrations and in the Proportions of Microcystin-Producing Cells in Several Microcystis aeruginosa Populations. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2010, 76, 4750–4759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joung, S.-H.; Oh, H.-M.; You, K.-A. Dynamic variation of toxic and non-toxic Microcystis proportion in the eutrophic Daechung Reservoir in Korea. J. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurmayer, R.; Kutzenberger, T. Application of Real-Time PCR for Quantification of Microcystin Genotypes in a Population of the Toxic Cyanobacterium Microcystis sp. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2003, 69, 6723–6730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, L.-A.; Gustafsson, S.; Rengefors, K.; Bomark, L. Cyanobacterial chemical warfare affects zooplankton community composition. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 1290–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonk, L.; Welker, M.; Huisman, J.; Visser, P.M. Production of cyanopeptolins, anabaenopeptins, and microcystins by the harmful cyanobacteria Anabaena 90 and Microcystis PCC 7806. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agha, R.; Cires, S.; Wormer, L.; Dominguez, J.A.; Quesada, A. Multi-scale strategies for the monitoring of freshwater cyanobacteria: Reducing the sources of uncertainty. Water Res 2012, 46, 3043–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drugă, B.; Welker, M.; Sesărman, A.; Hegedus, A.; Coman, C.; Sicora, C.; Dragoş, N. Molecular characterization of microcystin-producing cyanobacteria from Romanian fresh waters. Eur. J. Phycol. 2013, 48, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welker, M.; Marsalek, B.; Sejnohova, L.; von Dohren, H. Detection and identification of oligopeptides in Microcystis (cyanobacteria) colonies: Toward an understanding of metabolic diversity. Peptides 2006, 27, 2090–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welker, M.; Šejnohová, L.; Némethová, D.; von Döhren, H.; Jarkovský, J.; Maršálek, B. Seasonal shifts in chemotype composition of Microcystis sp. communities in the pelagial and the sediment of a shallow reservoir. Limnol. Ocanogr. 2007, 52, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agha, R.; Quesada, A. Oligopeptides as Biomarkers of Cyanobacterial Subpopulations. Toward an Understanding of Their Biological Role. Toxins 2014, 6, 1929–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoof, L.; Blaszczyk, A.; Meriluoto, J.; Ceglowska, M.; Mazur-Marzec, H. Structures and Activity of New Anabaenopeptins Produced by Baltic Sea Cyanobacteria. Mar. Drugs 2015, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurmayer, R.; Deng, L.; Entfellner, E. Role of toxic and bioactive secondary metabolites in colonization and bloom formation by filamentous cyanobacteria Planktothrix. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handbook of Cyanobacterial Monitoring and Cyanotoxin Analysis, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: London, UK, 2017.
- DeMott, W.R.; Moxter, F. Foraging Cyanobacteria by Copepods: Responses to Chemical Defense and Resource Abundance. Ecology 1991, 72, 1820–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMott, W.R.; Zhang, Q.-x.; Carmichael, W.W. Effects of toxic cyanobacteria and purified toxins on the survival and feeding of a copepod and three species of Daphnia. Limnol. Ocanogr. 1991, 36, 1346–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harke, M.J.; Jankowiak, J.G.; Morrell, B.K.; Gobler, C.J. Transcriptomic Responses in the Bloom-Forming Cyanobacterium Microcystis Induced During Exposure to Zooplankton. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urrutia-Cordero, P.; Agha, R.; Cires, S.; Lezcano, M.A.; Sanchez-Contreras, M.; Waara, K.O.; Utkilen, H.; Quesada, A. Effects of harmful cyanobacteria on the freshwater pathogenic free-living amoeba Acanthamoeba castellanii. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 130–131, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meissner, S.; Steinhauser, D.; Dittmann, E. Metabolomic analysis indicates a pivotal role of the hepatotoxin microcystin in high light adaptation of Microcystis. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 1497–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacinavicius, F.R.; Pacheco, A.B.F.; Chow, F.; Verissimo da Costa, G.C.; Kalume, D.E.; Rigonato, J.; Schmidt, E.C.; Sant’Anna, C.L. Different ecophysiological and structural strategies of toxic and non-toxic Microcystis aeruginosa (cyanobacteria) strains assessed under culture conditions. Algal Res. 2019, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briand, E.; Bormans, M.; Quiblier, C.; Salencon, M.J.; Humbert, J.F. Evidence of the cost of the production of microcystins by Microcystis aeruginosa under differing light and nitrate environmental conditions. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blossom, H.E.; Markussen, B.; Daugbjerg, N.; Krock, B.; Norlin, A.; Hansen, P.J. The Cost of Toxicity in Microalgae: Direct Evidence from the Dinoflagellate Alexandrium. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardinaal, W.E.; Tonk, L.; Janse, I.; Hol, S.; Slot, P.; Huisman, J.; Visser, P.M. Competition for light between toxic and nontoxic strains of the harmful cyanobacterium Microcystis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 2939–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, T.W.; Berry, D.L.; Boyer, G.L.; Gobler, C.J. The effects of temperature and nutrients on the growth and dynamics of toxic and non-toxic strains of Microcystis during cyanobacteria blooms. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, T.W.; Harke, M.J.; Marcoval, M.A.; Goleski, J.; Orano-Dawson, C.; Berry, D.L.; Gobler, C.J. Effects of nitrogenous compounds and phosphorus on the growth of toxic and non-toxic strains of Microcystis during cyanobacterial blooms. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2010, 61, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblanc Renaud, S.; Pick, F.R.; Fortin, N. Effect of light intensity on the relative dominance of toxigenic and nontoxigenic strains of Microcystis aeruginosa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 7016–7022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suominen, S.; Brauer, V.S.; Rantala-Ylinen, A.; Sivonen, K.; Hiltunen, T. Competition between a toxic and a non-toxic Microcystis strain under constant and pulsed nitrogen and phosphorus supply. Aquat. Ecol. 2017, 51, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, T.D.; Smith, V.H.; Graham, J.L.; Van de Waal, D.B.; Tedesco, L.P.; Clercin, N. Combined effects of nitrogen to phosphorus and nitrate to ammonia ratios on cyanobacterial metabolite concentrations in eutrophic Midwestern USA reservoirs. Inland Waters 2016, 6, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffin, J.D.; Davis, T.W.; Smith, D.J.; Baer, M.M.; Dick, G.J. Interactions between nitrogen form, loading rate, and light intensity on Microcystis and Planktothrix growth and microcystin production. Harmful Algae 2018, 73, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newell, S.E.; Davis, T.W.; Johengen, T.H.; Gossiaux, D.; Burtner, A.; Palladino, D.; McCarthy, M.J. Reduced forms of nitrogen are a driver of non-nitrogen-fixing harmful cyanobacterial blooms and toxicity in Lake Erie. Harmful Algae 2019, 81, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillard, R.R.L.; Lorenzen, C.J. Yellow-green algae with chlorophyllide C1,2. J. Phycol. 1972, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staub, R. Ernährungsphysiologisch-autökologische Untersuchungen an der planktischen Blaualge Oscillatoria rubescens DC. Schweiz. Z. Hydrol. 1961, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM Corp. SPSS Statistics for Macintosh; Version 25.0, Release 25.0.0.1; IBM Corp: Armonk, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- RStudio; 1.1.453; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2018; Available online: https://rstudio.com/products/rstudio/ (accessed on 10 October 2019).
- Mazur-Marzec, H.; Bertos-Fortis, M.; Torunska-Sitarz, A.; Fidor, A.; Legrand, C. Chemical and Genetic Diversity of Nodularia spumigena from the Baltic Sea. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synergy Software KaleidaGraph; Version 4.5. Available online: http://www.synergy.com/wordpress_650164087/ (accessed on 10 October 2019).



| Strain Prefix | Sampling Date | Water Temp at 0.5 m Depth (°C) | Colonies Isolated | Cultures Established | Cultures Analyzed | Number of MC Producing Strains |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 2014-06-30 | 19 | 143 | 35 | 25 | 5 |
| S2 | 2014-07-14 | 20 | 192 | 33 | 25 | 2 |
| S3 | 2014-08-03 | 26 | 192 | 35 | 27 | 4 |
| S4 | 2014-08-25 | 18 | 148 | 35 | 30 | 14 |
| S5 | 2014-09-08 | 19 | 168 | 30 | 23 | 12 |
| Sampling Date (2014) | Toxigenic Strain ID | Microcystin Variants | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MC-WR | [Asp3]MC-ThTyrR | MC-RY | MC-RR | MC? | [Asp3] MC-RY | MC-FR | [Asp3] MC-RR | [Dha7] MC-RR | MC-HilR | [Ser1] MC-VR | MC-LR | [Asp3Dhb7] MC-LR | MC? | MC? | MC? | MC? | MC? | ||
| m/z [M+H]+ | 1035 | 861 | 528 | 1031 | 509 | 502 | |||||||||||||
| June 30 | S1-58 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||
| S1-79 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||||||
| S1-117 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||
| S1-119 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||
| S1-160 | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||||||||||
| July 14 | S2-127 | ● | |||||||||||||||||
| S2-164 | ● | ||||||||||||||||||
| August 3 | S3-36 | ● | |||||||||||||||||
| S3-55 | ● | ||||||||||||||||||
| S3-56 | ● | ||||||||||||||||||
| S3-165 | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||||||||
| August 25 | S4-16 | ● | |||||||||||||||||
| S4-30 | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||||||||
| S4-41 | ● | ||||||||||||||||||
| S4-59 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||||
| S4-98 | ● | ||||||||||||||||||
| S4-101 | ● | ||||||||||||||||||
| S4-105 | ● | ||||||||||||||||||
| S4-113 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||||||||
| S4-129 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||||||
| S4-141 | ● | ● | |||||||||||||||||
| S4-177 | ● | ● | |||||||||||||||||
| S4-179 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||||
| S4-184 | ● | ||||||||||||||||||
| S4-190 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||||
| September 8 | S5-21 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||||
| S5-23 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||||
| S5-34 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||||
| S5-73 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||
| S5-74 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||||||||
| S5-79 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||||||
| S5-93 | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||||||||
| S5-106 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||||
| S5-110 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||||||
| S5-144 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||||
| S5-152 | ● | ||||||||||||||||||
| S5-163 | ● | ||||||||||||||||||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Johansson, E.; Legrand, C.; Björnerås, C.; Godhe, A.; Mazur-Marzec, H.; Säll, T.; Rengefors, K. High Diversity of Microcystin Chemotypes within a Summer Bloom of the Cyanobacterium Microcystis botrys. Toxins 2019, 11, 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11120698
Johansson E, Legrand C, Björnerås C, Godhe A, Mazur-Marzec H, Säll T, Rengefors K. High Diversity of Microcystin Chemotypes within a Summer Bloom of the Cyanobacterium Microcystis botrys. Toxins. 2019; 11(12):698. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11120698
Chicago/Turabian StyleJohansson, Emma, Catherine Legrand, Caroline Björnerås, Anna Godhe, Hanna Mazur-Marzec, Torbjörn Säll, and Karin Rengefors. 2019. "High Diversity of Microcystin Chemotypes within a Summer Bloom of the Cyanobacterium Microcystis botrys" Toxins 11, no. 12: 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11120698
APA StyleJohansson, E., Legrand, C., Björnerås, C., Godhe, A., Mazur-Marzec, H., Säll, T., & Rengefors, K. (2019). High Diversity of Microcystin Chemotypes within a Summer Bloom of the Cyanobacterium Microcystis botrys. Toxins, 11(12), 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11120698






