Anti-Nociceptive and Anti-Inflammation Effect Mechanisms of Mutants of Syb-prII, a Recombinant Neurotoxic Polypeptide
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Purification of the Syb-prII Protein
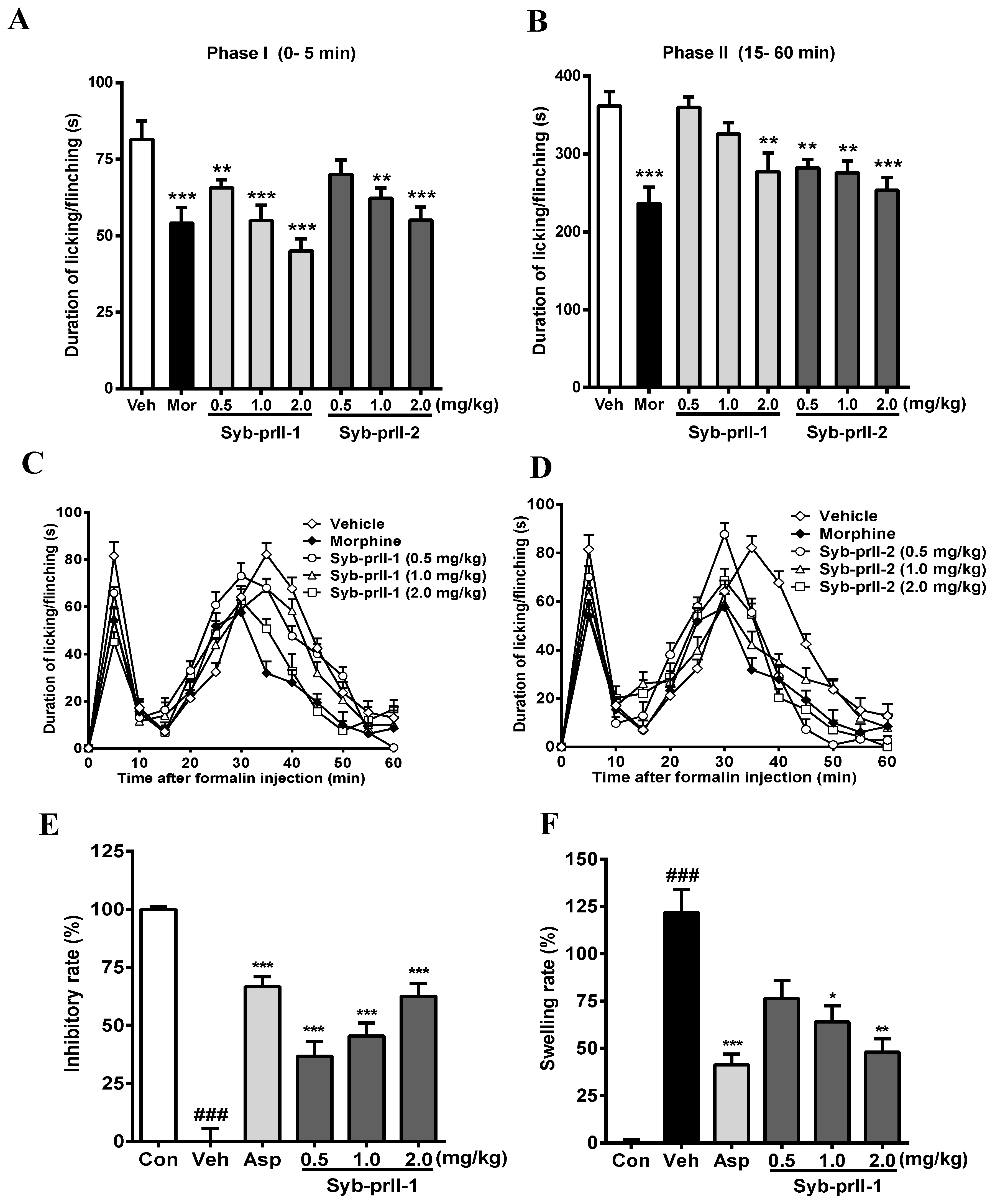
2.2. Effects of Syb-prII-1 and -2 in Inflammatory Animal Models
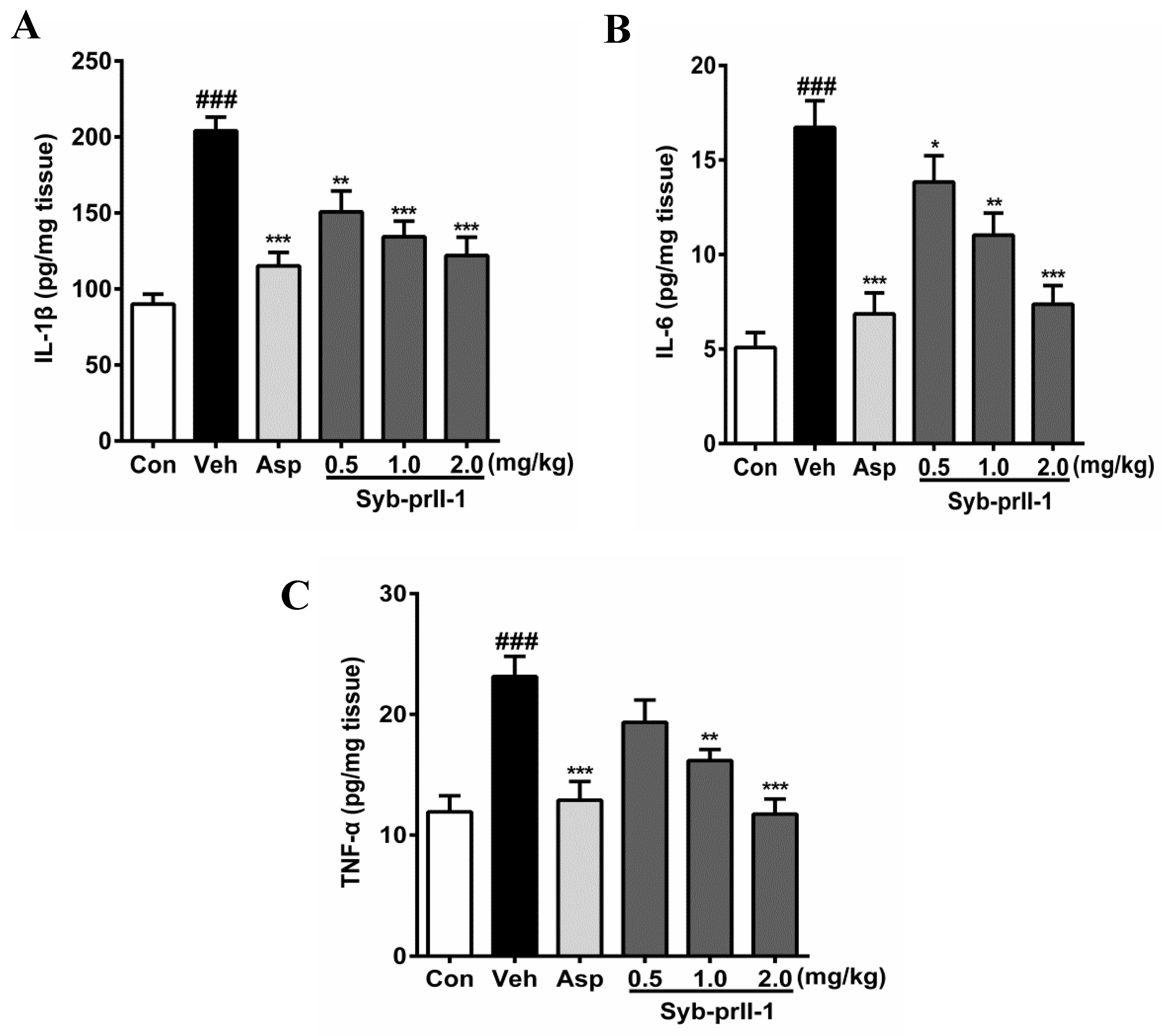
2.3. Syb-prII-1 Lowers the Secretion Levels of Inflammatory Factors
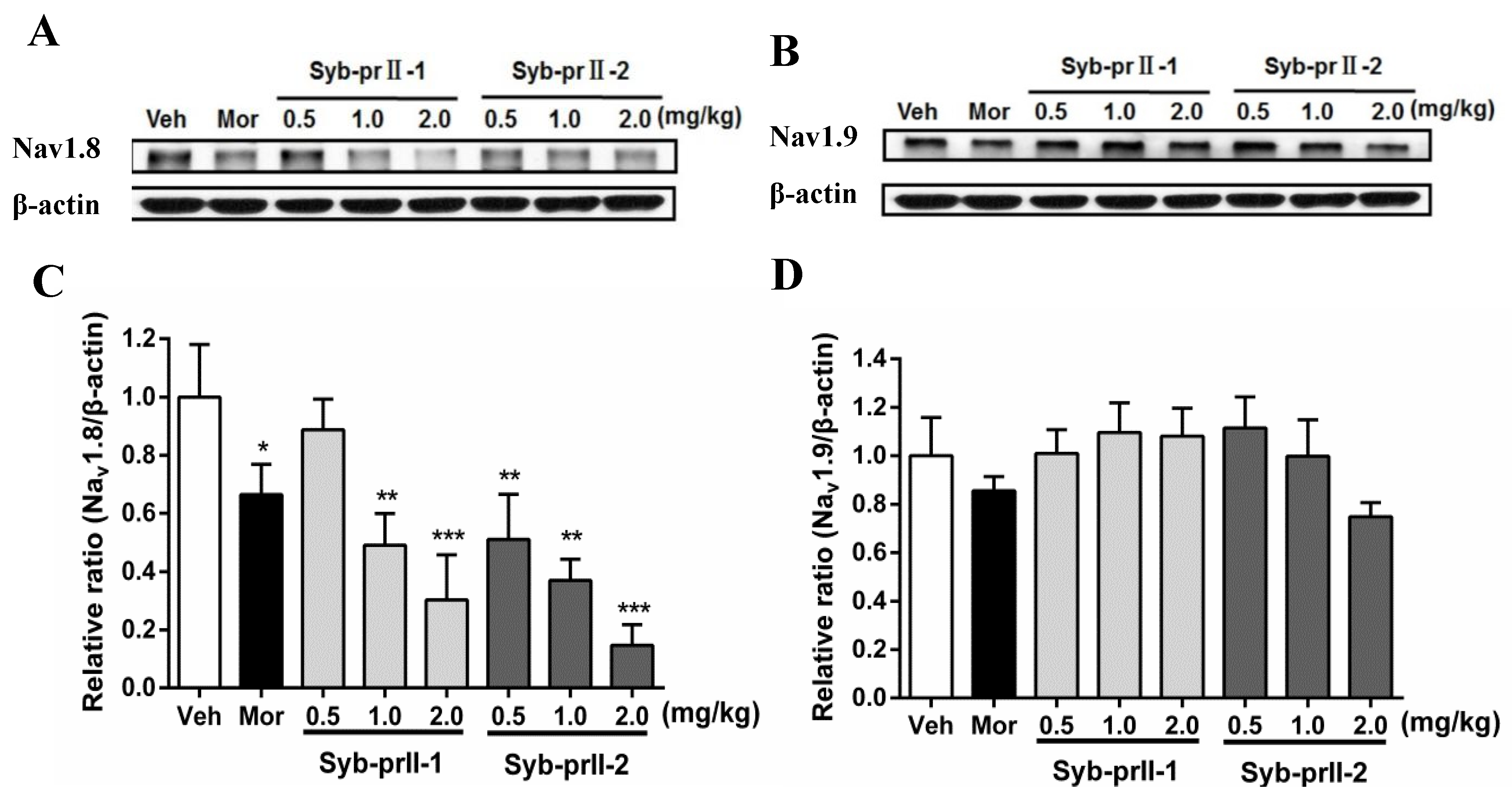
2.4. Syb-prII-1 Reduces the Expression of the TTX-R Sodium Channel, Nav1.8, and Nav1.9
2.5. Syb-prII-1 Reduces the Phosphorylation of MAPKs
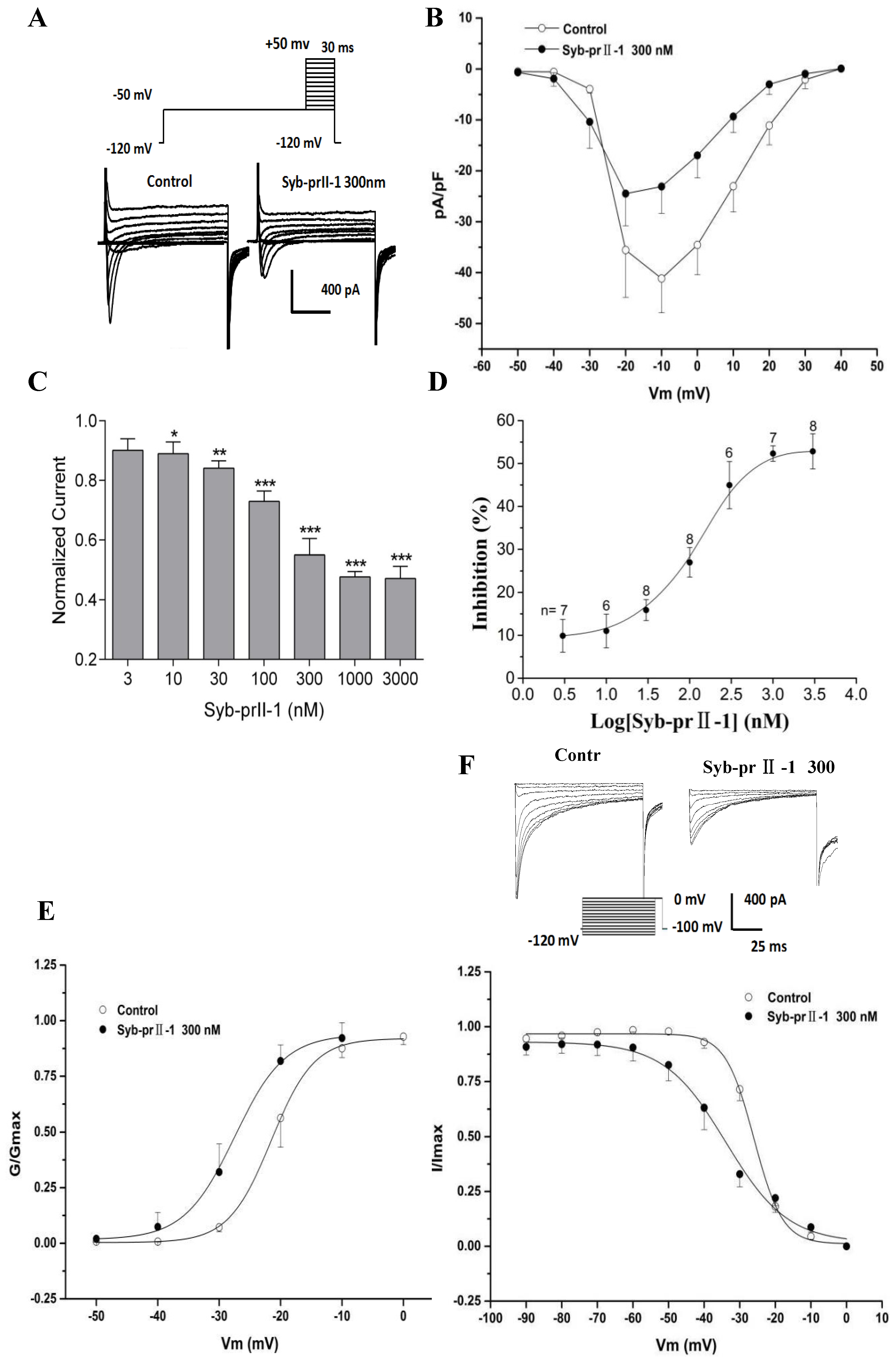
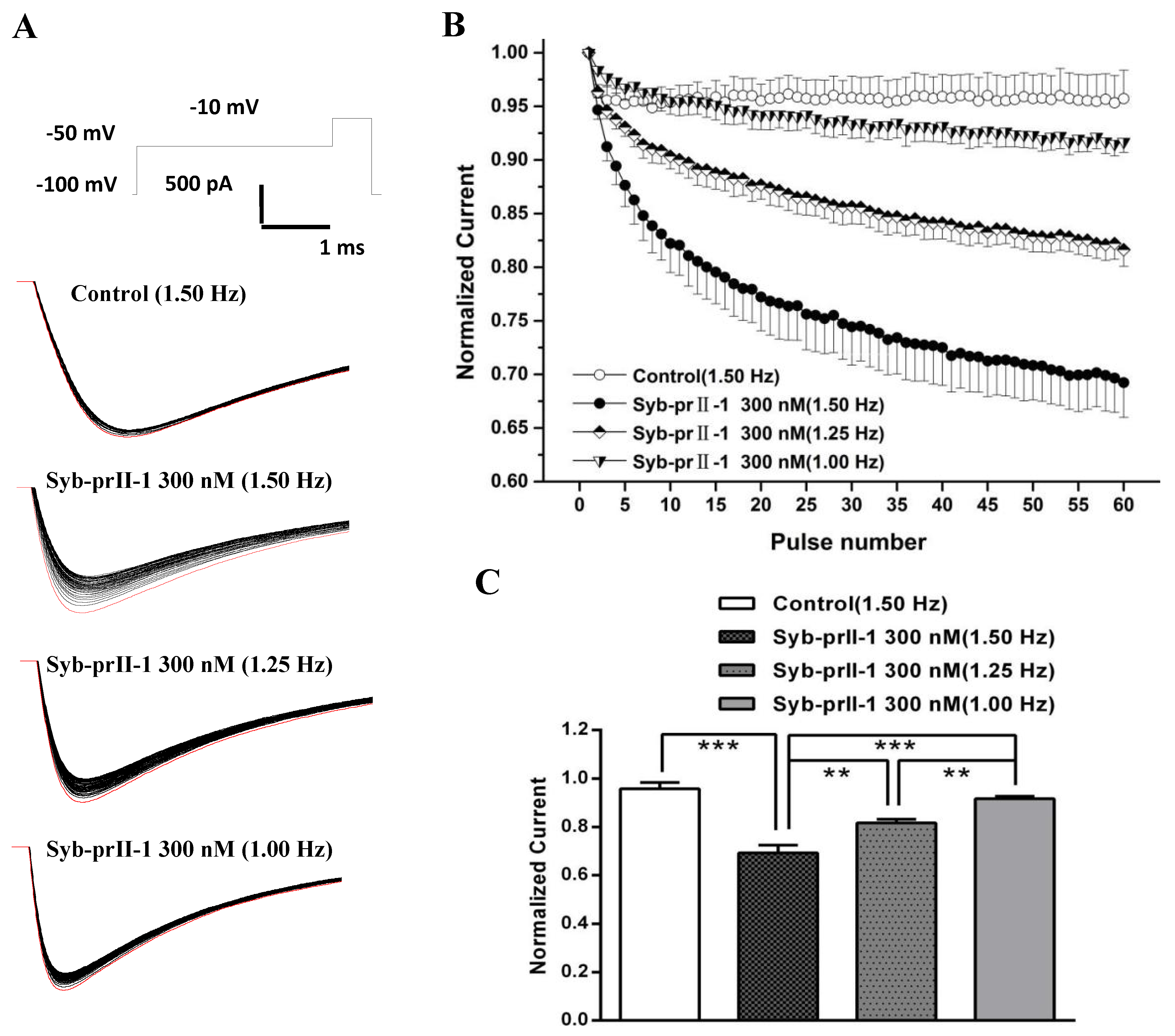
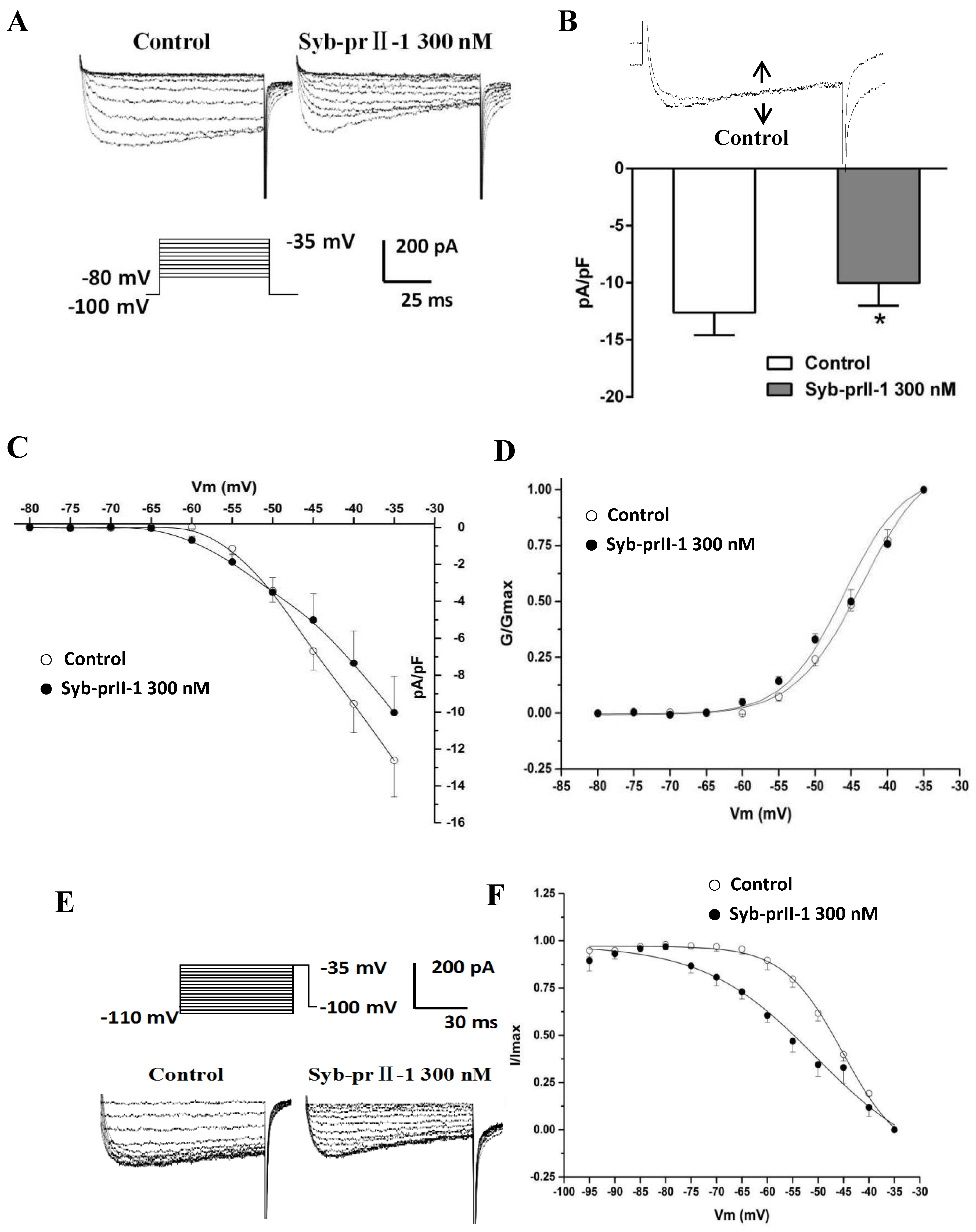
2.6. Effects of Syb-prII-1 on Nav1.8 Currents
2.7. Effects of Syb-prII-1 on Activation and Inactivation Kinetics of Nav1.8 Currents
2.8. Effects of Syb-prII-1 on the Frequency-Dependent Relationship of Nav1.8 Currents
2.9. Effects of Syb-prII-1 on Nav1.9 Currents
2.10. Effects of Syb-prII-1 on Activation and Inactivation Kinetics of Nav1.9 Currents
3. Discussion
3.1. The Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Syb-prII
3.2. Syb-prII-1 Regulates Neuronal Excitability of DRG Sensory Neurons via Nav1.8 and Nav1.9
3.3. The Regulation of Syb-prII on Nav1.8 and Nav1.9 via MAP Kinases
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Animals
5.2. Strains
5.3. Construction and Verification of the Expression Vectors pSYPU-3c/Syb-prII
5.4. Transformation and Verification of the Vectors
5.5. Expression of Recombinant Syb-prII
5.6. Purification of the Recombinant Scorpion Syb-prII
5.7. Formalin Test
5.8. Xylene-Induced Ear Edema in Mice
5.9. Biochemical Parameters
5.10. Extraction of Protein and Western Blot Analysis
5.11. Preparation of DRG Neurons
5.12. Electrophysiology
5.13. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anand, K.J.S. Consensus Statement for the Prevention and Management of Pain in the Newborn. Arch. Pediatrics Adolesc. Med. 2001, 155, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolf, C.J. What is this thing called pain? J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 3742–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowe, R.K.; Ellis, G.I.; Harrison, J.L.; Bachstetter, A.D.; Corder, G.F.; Eldik, L.J.V.; Taylor, B.K.; Marti, F.; Lifshitz, J. Diffuse traumatic brain injury induces prolonged immune dysregulation and potentiates hyperalgesia following a peripheral immune challenge. Mol. Pain 2016, 12, 1744806916647055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colloca, L.; Ludman, T.; Bouhassira, D.; Baron, R.; Dickenson, A.H.; Yarnitsky, D.; Freeman, R.; Truini, A.; Attal, N.; Finnerup, N.B. Neuropathic pain. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholz, J.; Woolf, C.J. Can we conquer pain? Nat. Neurosci. 2002, 5, 1062–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pleuvry, B.J.; Lauretti, G.R. Biochemical aspects of chronic pain and its relationship to treatment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1996, 71, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Rodriguez, L.; Garcia-Martinez, O.; Morales, M.A.; Rodriguez-Perez, L.; Rubio-Ruiz, B.; Ruiz, C. Effects of indomethacin, nimesulide, and diclofenac on human MG-63 osteosarcoma cell line. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2012, 14, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prendini, L.; Wheeler, W.C. Scorpion higher phylogeny and classification, taxonomic anarchy, and standards for peer review in online publishing. Cladistics Int. J. Willi Hennig Soc. 2010, 21, 446–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plessis, L.H.D.; Elgar, D.; Plessis, J.L.D. Southern African scorpion toxins: An overview. Toxicon Off. J. Int. Soc. Toxinol. 2008, 51, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, M.S.; Reichling, D.B.; Shuster, M.J.; Levine, J.D. Hyperalgesic agents increase a tetrodotoxin-resistant Na+ current in nociceptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 1108–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamboulian, S.; Choi, J.S.; Ahn, H.S.; Chang, Y.W.; Tyrrell, L.; Black, J.A.; Waxman, S.G.; Dib-Hajj, S.D. ERK1/2 mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylates sodium channel Na(v)1.7 and alters its gating properties. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummins, T.R.; Dibhajj, S.D.; Black, J.A.; Akopian, A.N.; Wood, J.N.; Waxman, S.G. A Novel Persistent Tetrodotoxin-Resistant Sodium Current in SNS-Null and Wild-Type Small Primary Sensory Neurons. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 1713–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, S.D.; Cavanaugh, D.J.; Lee, H.; Anderson, D.J.; Basbaum, A.I. Pain behavior in the formalin test persists after ablation of the great majority of C-fiber nociceptors. Pain 2010, 151, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobuisson, D.; Dennis, S.G. The formalin test: A quantitative study of the analgesic effects of morphine, meperidine, and brain stem stimulation in rats and cats. Pain 1977, 4, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, F.V.; Franklin, K.B.; Westbrook, R.F. The formalin test: Scoring properties of the first and second phases of the pain response in rats. Pain 1995, 60, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickenson, A.H.; Sullivan, A.F. Peripheral origins and central modulation of subcutaneous formalin-induced activity of rat dorsal horn neurons. Neurosci. Lett. 1987, 83, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.; Meng, D. Chemical constituents from Stauntonia brachyanthera Hand–Mazz. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2013, 48, 182–185. [Google Scholar]
- Abdala, S.; Dévora, S.; Martínherrera, D.; Pérezpaz, P. Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activity of Sambucus palmensis link, an endemic Canary Island species. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, Y.F.; Lin, Z.X.; Xu, X.Y.; Su, Z.R.; Chen, J.N.; Lai, X.P.; Ip, S.P. Effect of Rhizoma Polygonati on 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-acetate-induced ear edema in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 142, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean-Michel, D. The process of identifying and understanding cytokines: From basic studies to treating rheumatic diseases. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2004, 18, 31–45. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseinzadeh, H.; Haddadkhodaparast, M.H.; Arash, A.R. Antinociceptive, antiinflammatory and acute toxicity effects of Salvia leriifolia Benth seed extract in mice and rats. Phytother. Res. 2003, 17, 422–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, G.R.; Talbot, J.; Lotufo, C.M.; Cunha, F.Q.; Cunha, T.M.; Ferreira, S.H. Fractalkine mediates inflammatory pain through activation of satellite glial cells. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 11193–11198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.H.; Zang, Y.; Chen, X.; Pang, R.P.; Xu, J.T.; Zhou, X.; Wei, X.H.; Li, Y.Y.; Xin, W.J.; Qin, Z.H. TNF-α contributes to up-regulation of Nav1.3 and Nav1.8 in DRG neurons following motor fiber injury. Pain 2010, 151, 266–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Pang, R.P.; Shen, K.F.; Zimmermann, M.; Xin, W.J.; Li, Y.Y.; Liu, X.G. TNF-α enhances the currents of voltage gated sodium channels in uninjured dorsal root ganglion neurons following motor nerve injury. Exp. Neurol. 2011, 227, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, K.F.; Zhu, H.Q.; Wei, X.H.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.Y.; Pang, R.P.; Liu, X.G. Interleukin-10 down-regulates voltage gated sodium channels in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 247, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, S.D.; Ahn, H.S.; Yang, Y.; Han, C.; Seal, R.P.; Wood, J.N.; Waxman, S.G.; Dibhajj, S.D. Na(v)1.8 expression is not restricted to nociceptors in mouse peripheral nervous system. Pain 2012, 153, 2017–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuoka, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Yamanaka, H.; Obata, K.; Dai, Y.; Noguchi, K. Comparative study of the distribution of the alpha-subunits of voltage-gated sodium channels in normal and axotomized rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. J. Comp. Neurol. 2010, 510, 188–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renganathan, M.; Cummins, T.R.; Waxman, S.G. Contribution of Nav1.8 Sodium Channels to Action Potential Electrogenesis in DRG Neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2001, 86, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coggeshall, R.E.; Tate, S.; Carlton, S.M. Differential expression of tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channels Nav1.8 and Nav1.9 in normal and inflamed rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 355, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, J.A.; Liu, S.; Tanaka, M.; Cummins, T.R.; Waxman, S.G. Changes in the expression of tetrodotoxin-sensitive sodium channels within dorsal root ganglia neurons in inflammatory pain. Pain 2004, 108, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porreca, F.; Lai, J.; Di, B.; Wegert, S.; Ossipov, M.H.; Eglen, R.M.; Kassotakis, L.; Novakovic, S.; Rabert, D.K.; Sangameswaran, L. A comparison of the potential role of the tetrodotoxin-insensitive sodium channels, PN3/SNS and NaN/SNS2, in rat models of chronic pain. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 7640–7644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.W.; Hsu, C.K.; Hsieh, C.L.; Yang, J.; Lin, Y.W. Probing the Effects and Mechanisms of Electroacupuncture at Ipsilateral or Contralateral ST36-ST37 Acupoints on CFA-induced Inflammatory Pain. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, S.K.; Mikusa, J.P.; Hernandez, G.; Baker, S.; Shieh, C.C.; Neelands, T.; Zhang, X.F.; Niforatos, W.; Kage, K.; Han, P. Involvement of the TTX-resistant sodium channel Nav 1.8 in inflammatory and neuropathic, but not post-operative, pain states. Pain 2006, 123, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvis, M.F.; Honore, P.; Shieh, C.C.; Chapman, M.; Joshi, S.; Zhang, X.F.; Kort, M.; Carroll, W.; Marron, B.; Atkinson, R. A-803467, a potent and selective Nav1.8 sodium channel blocker, attenuates neuropathic and inflammatory pain in the rat. Channels 2007, 104, 8520–8525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priest, B.T.; Murphy, B.A.; Lindia, J.A.; Diaz, C.; Abbadie, C.; Ritter, A.M.; Liberator, P.; Iyer, L.M.; Kash, S.F.; Kohler, M.G. Contribution of the Tetrodotoxin-Resistant Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel NaV1.9 to Sensory Transmission and Nociceptive Behavior. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9382–9387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dib-Hajj, S.D.; Tyrrell, L.; Black, J.A.; Waxman, S.G. NaN, a Novel Voltage-Gated Na Channel, is Expressed Preferentially in Peripheral Sensory Neurons and Down-Regulated after Axotomy. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 8963–8968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaya, F.; Wang, H.; Costigan, M.; Allchorne, A.J.; Hatcher, J.P.; Egerton, J.; Stean, T.; Morisset, V.; Grose, D.; Chessell, I.P.; et al. The voltage-gated sodium channel Na(v)1.9 is an effector of peripheral inflammatory pain hypersensitivity. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 12852–12860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrison, S.R.; Weyer, A.D.; Barabas, M.E.; Beutler, B.A.; Stucky, C.L. A gain-of-function voltage-gated sodium channel 1.8 mutation drives intense hyperexcitability of A- and C-fiber neurons. Pain 2014, 155, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.Y.; Liu, B.L.; Zang, K.K.; Yang, L.; Xu, H.; Pan, H.L.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.Q. Dexmedetomidine inhibits Tetrodotoxin-resistant Na v 1.8 sodium channel activity through G i/o-dependent pathway in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Mol. Brain 2015, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obata, K.; Noguchi, K. MAPK activation in nociceptive neurons and pain hypersensitivity. Life Sci. 2004, 74, 2643–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obata, K.; Yamanaka, H.; Dai, Y.; Mizushima, T.; Fukuoka, T.; Tokunaga, A.; Noguchi, K. Differential activation of MAPK in injured and uninjured DRG neurons following chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve in rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2015, 20, 2881–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chattopadhyay, M.; Mata, M.; Fink, D.J. Continuous delta opioid receptor activation reduces neuronal voltage gated sodium channel (NaV1.7) levels through activation of protein kinase C in painful diabetic neuropathy. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 6652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudmon, A.; Choi, J.S.; Tyrrell, L.; Black, J.A.; Rush, A.M.; Waxman, S.G.; Dibhajj, S.D. Phosphorylation of sodium channel Na(v)1.8 by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase increases current density in dorsal root ganglion neurons. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 3190–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrasquillo, Y.; Gereau, R.W. Activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase in the amygdala modulates pain perception. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 1543–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Z.Y.; Gerner, P.; Woolf, C.J.; Ji, R.R. ERK is sequentially activated in neurons, microglia, and astrocytes by spinal nerve ligation and contributes to mechanical allodynia in this neuropathic pain model. Pain 2005, 114, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres, C.; Hasenauer, J.; Ahn, H.S.; Joseph, E.K.; Isensee, J.; Theis, F.J.; Allgöwer, F.; Levine, J.D.; Dib-Hajj, S.D.; Waxman, S.G. Wound-healing growth factor, basic FGF, induces Erk1/2-dependent mechanical hyperalgesia. Pain 2013, 154, 2216–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milligan, E.D.; Twining, C.; Chacur, M.; Biedenkapp, J.; O’Connor, K.; Poole, S.; Tracey, K.; Martin, D.; Maier, S.F.; Watkins, L.R. Spinal glia and proinflammatory cytokines mediate mirror-image neuropathic pain in rats. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Z.Y.; Wen, Y.R.; Zhang, D.R.; Borsello, T.; Bonny, C.; Strichartz, G.R.; Decosterd, I.; Ji, R.R. A peptide c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) inhibitor blocks mechanical allodynia after spinal nerve ligation: Respective roles of JNK activation in primary sensory neurons and spinal astrocytes for neuropathic pain development and maintenance. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 3551–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunskaar, S.; Hole, K. The formalin test in mice: Dissociation between inflammatory and non-inflammatory pain. Pain 1987, 30, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.Q.; Feng, Z.; Guan, S.M.; Chen, J. Antisense-Mediated Knockdown of NaV1.8, but Not NaV1.9, Generates Inhibitory Effects on Complete Freund’s Adjuvant-Induced Inflammatory Pain in Rat. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Name | Oligonucleotide Sequence (5′-3′) | Orientation |
|---|---|---|
| Syb-prII-1-F | GGTGGTTGCTCTTCCAACGATGGATATATAAGAGGAAGTAACGGGATGCAAG | Sense |
| Syb-prII-2-F | GGTGGTTGCTCTTCCAACGATGGATATATAAGAGAGAAGAGATGGATGCAAG | Sense |
| Syb-prII-R | CCGGAATTCTTAGCCACCGCATGTATTACTTTCAG | Antisense |
| Antibody | Molecule Weight | Vendor |
|---|---|---|
| Nav1.8 | 220 kDa | Abcam |
| Nav1.9 | 202 kDa | Alomone |
| P-ERK1/2 | 42 kDa (up) 40 kDa (down) | Cell Signaling |
| ERK1/2 | 42 kDa (up) 40 kDa (down) | Cell Signaling |
| P-JNK1/2 | 54 kDa (up) 46 kDa (down) | Cell Signaling |
| JNK1/2 | 54 kDa (up) 46 kDa (down) | Cell Signaling |
| P-P38 | 43 kDa | Cell Signaling |
| P38 | 40 kDa | Cell Signaling |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Ban, M.; Bai, F.; Chen, J.; Jin, X.; Song, Y. Anti-Nociceptive and Anti-Inflammation Effect Mechanisms of Mutants of Syb-prII, a Recombinant Neurotoxic Polypeptide. Toxins 2019, 11, 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11120699
Li C, Ban M, Bai F, Chen J, Jin X, Song Y. Anti-Nociceptive and Anti-Inflammation Effect Mechanisms of Mutants of Syb-prII, a Recombinant Neurotoxic Polypeptide. Toxins. 2019; 11(12):699. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11120699
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chunli, Mengqi Ban, Fei Bai, Jianzhao Chen, Xiaoquan Jin, and Yongbo Song. 2019. "Anti-Nociceptive and Anti-Inflammation Effect Mechanisms of Mutants of Syb-prII, a Recombinant Neurotoxic Polypeptide" Toxins 11, no. 12: 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11120699
APA StyleLi, C., Ban, M., Bai, F., Chen, J., Jin, X., & Song, Y. (2019). Anti-Nociceptive and Anti-Inflammation Effect Mechanisms of Mutants of Syb-prII, a Recombinant Neurotoxic Polypeptide. Toxins, 11(12), 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11120699