Grape Seed Proanthocyanidin Extract Alleviates AflatoxinB1-Induced Immunotoxicity and Oxidative Stress via Modulation of NF-κB and Nrf2 Signaling Pathways in Broilers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
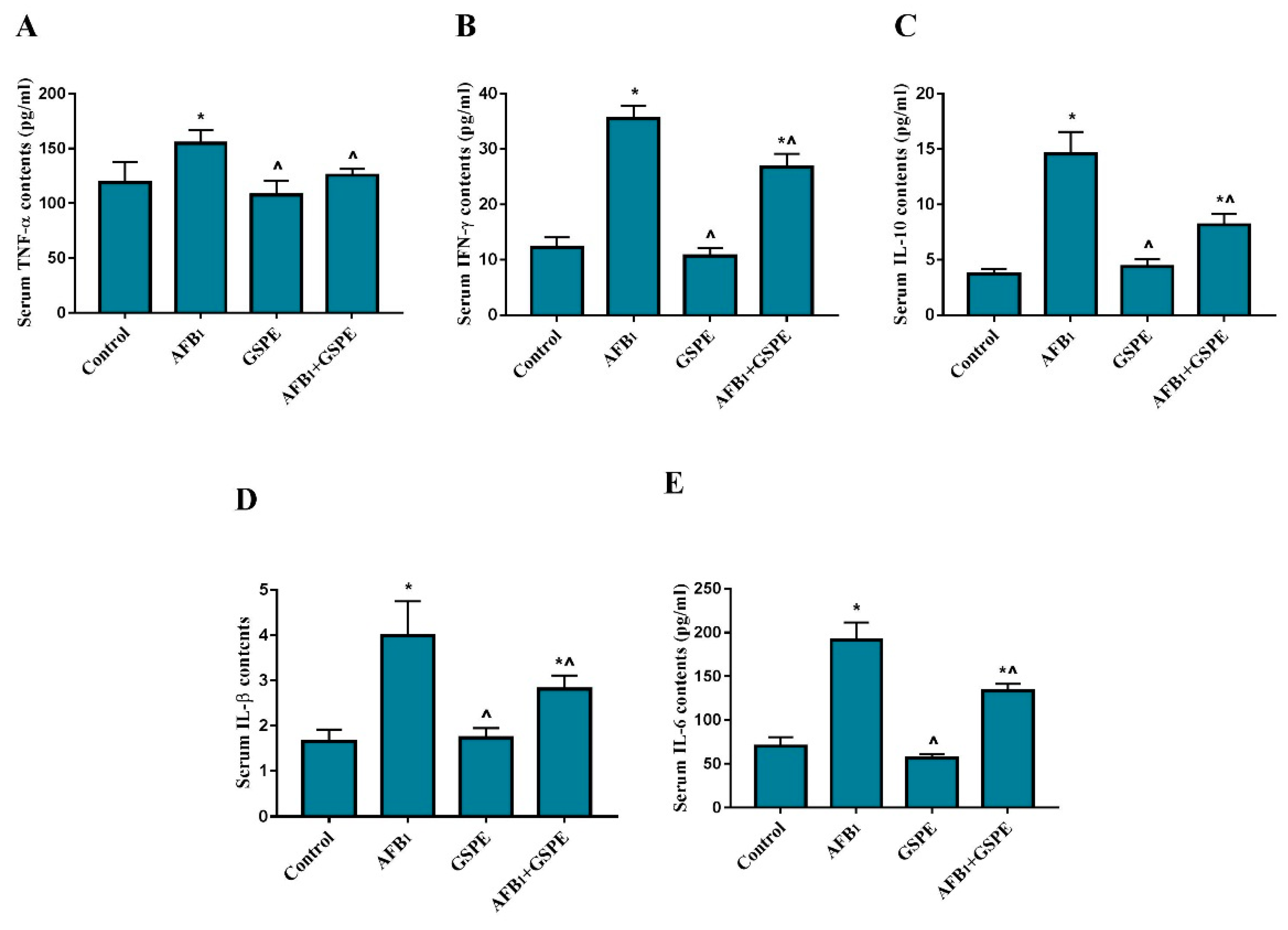
2.1. Serum Inflammatory Cytokines
2.2. Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Gene Expression
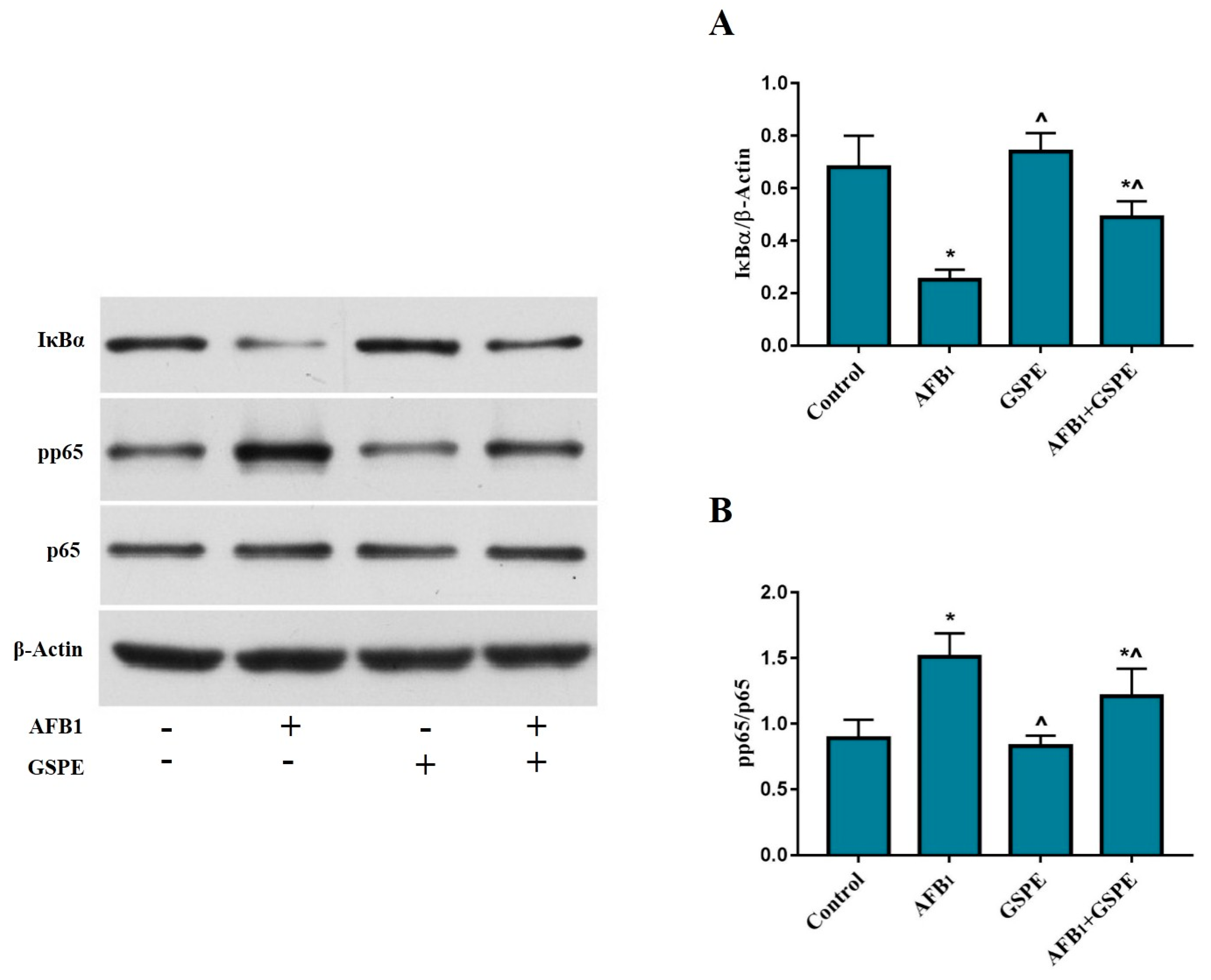
2.3. Effects of GSPE and AFB1 on the Degradation of IκBα and the Phosphorylation of NF-κB (p65)
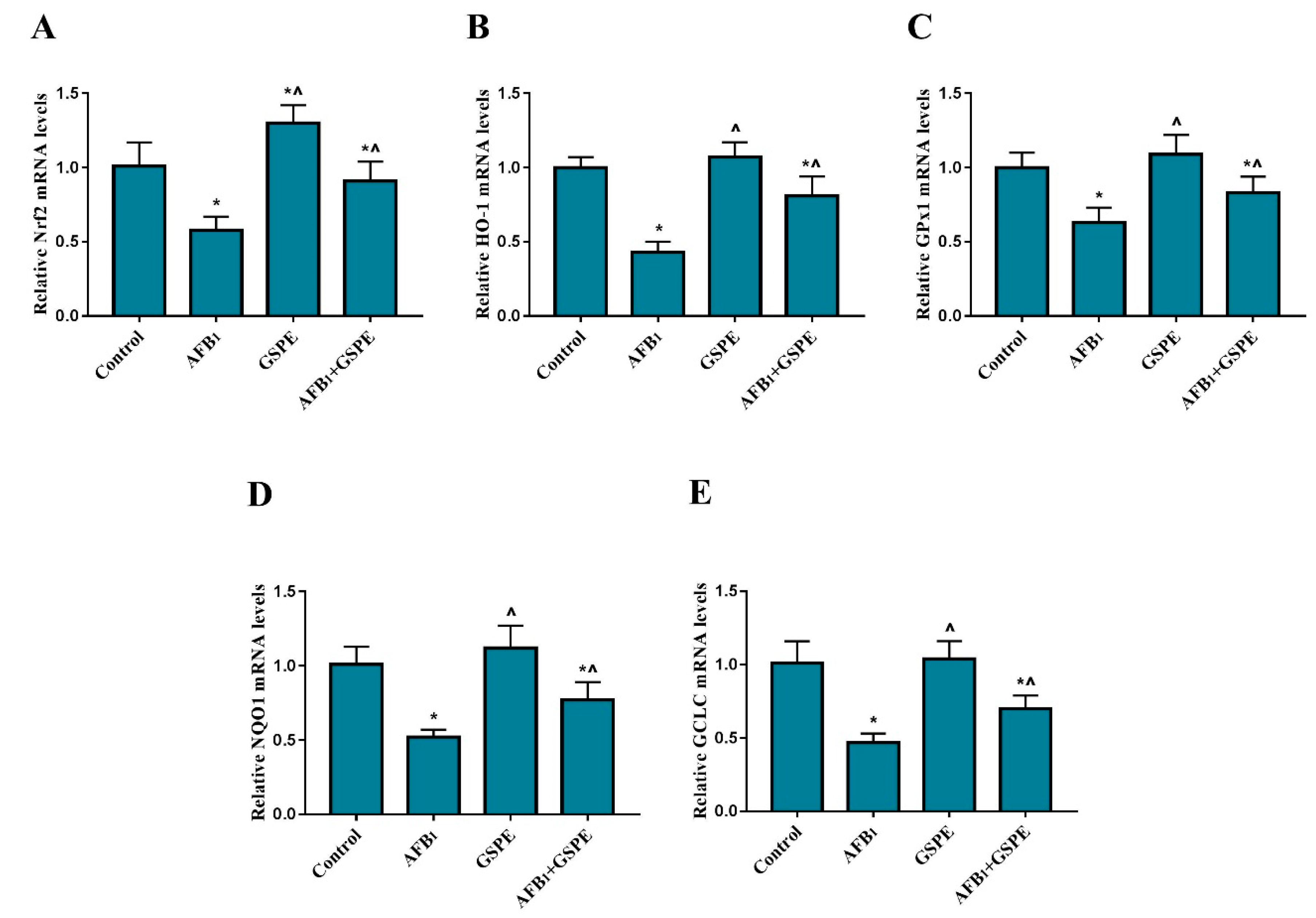
2.4. Nrf2 and Its Downstream Genes (HO-1, GPx1, NQO1, and GCLC) mRNA Expression
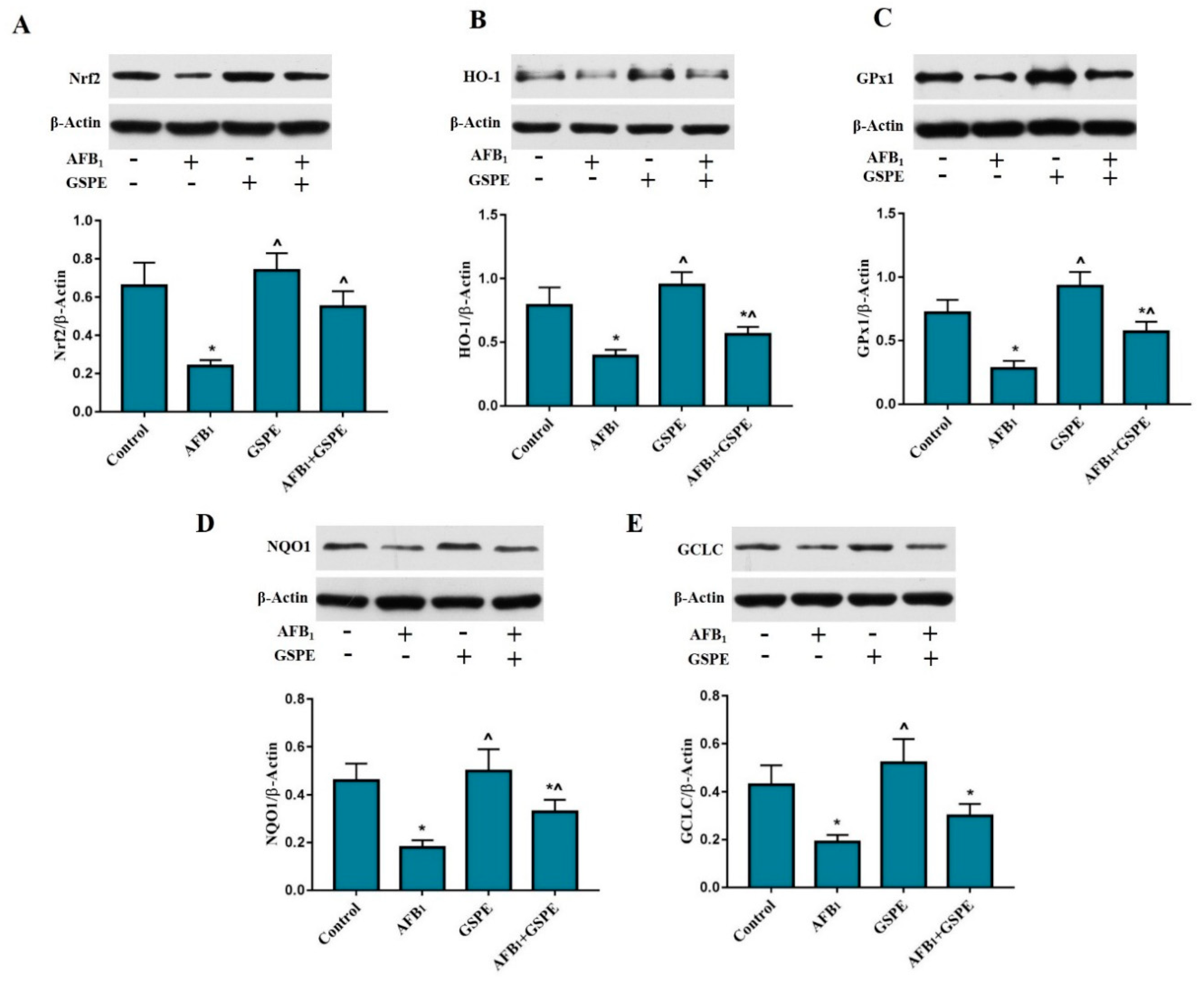
2.5. Nrf2 and Its Downstream Genes (HO-1, GPx1, NQO1, and GCLC) Protein Expression
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Material and Methods
5.1. Fungal Isolation
5.2. Aflatoxin B1 Production
5.3. Aflatoxin B1 Analysis
5.4. Compliance with Ethical Standards
5.5. Bird, Diets, and Management
5.6. Collection of Samples
5.7. Determination of Serum Cytokines
5.8. Total RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
5.9. Western Blot Analysis
5.10. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bünger, J.; Westphal, G.; Mönnich, A.; Hinnendahl, B.; Hallier, E.; Müller, M. Cytotoxicity of occupationally and environmentally relevant mycotoxins. Toxicology 2004, 202, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méndez, A. Decontamination of aflatoxin duckling feed with aqueous citric acid treatment. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2007, 135, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrar, M.; Anjum, F.M.; Butt, M.S.; Pasha, I.; Randhawa, M.A.; Saeed, F.; Waqas, K. Aflatoxins: Biosynthesis, occurrence, toxicity, and remedies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferenčík, M.; Ebringer, L. Modulatory effects of selenium and zinc on the immune system. Folia Microbiol. 2003, 48, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzallah, S.M. Aflatoxin B1 residues in eggs and flesh of laying hens fed aflatoxin B1 contaminated diet. Am. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2013, 8, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpsoy, L.; Yalvac, M.E.; Litwack, G. Key roles of vitamins a, c, and e in aflatoxin B1-induced oxidative stress. Vitam. Horm. Adv. Res. Appl. 2011, 86, 287–305. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, A.W. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans: International Agency for Research on Cancer; IARC: Lyon, France, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Stettler, P.M.; Sengstag, C. Liver carcinogen aflatoxin B1 as an inducer of mitotic recombination in a human cell line. Mol. Carcinog. 2001, 31, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.Y.; Qi, M.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, M.K.; Guo, J.; Liu, J.; Gu, C.Q.; Rajput, S.A.; Krumm, C.S.; Qi, D.S. Curcumin prevents aflatoxin b1 hepatoxicity by inhibition of cytochrome p450 isozymes in chick liver. Toxins 2016, 8, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meissonnier, G.M.; Pinton, P.; Laffitte, J.; Cossalter, A.M.; Gong, Y.Y.; Wild, C.P.; Bertin, G.; Galtier, P.; Oswald, I.P. Immunotoxicity of aflatoxin B1: Impairment of the cell-mediated response to vaccine antigen and modulation of cytokine expression. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 231, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunus, A.W.; Razzazifazeli, E.; Bohm, J. Aflatoxin B1 in affecting broiler’s performance, immunity, and gastrointestinal tract: A review of history and contemporary issues. Toxins 2011, 3, 566–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, T. The nuclear factor nf-kb pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 10, a001651. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, W.; Cui, H.; Peng, X.; Fang, J.; Liu, X.; Wu, B. Effect of vanadium on splenocyte apoptosis in broilers. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 2, 57–60. [Google Scholar]
- Subhashinie, K.; Johnson, T.J.; Zhou, H.; Li, X.; Nate, B.; Emma, B.; Megan, O.; Sandford, E.E.; Liu, P.; Nolan, L.K. Spleen transcriptome response to infection with avian pathogenic escherichia coli in broiler chickens. BMC Genomics 2011, 12, 469. [Google Scholar]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Nf-îºb, the first quarter-century: Remarkable progress and outstanding questions. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 203–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diks, S.H.; van Deventer, S.J.; Peppelenbosch, M.P. Lipopolysaccharide recognition, internalisation, signalling and other cellular effects. J. Endotoxin Res. 2001, 7, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzik, T.J.; Korbut, R.; Adamekguzik, T. Nitric oxide and superoxide in inflammation and immune regulation. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2003, 54, 469–487. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.; Fang, G.; Xuan, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Gang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Huang, K. Immunotoxicity of ochratoxin a and aflatoxin B1 in combination is associated with the nuclear factor kappa b signaling pathway in 3d4/21 cells. Chemosphere 2018, 199, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Yang, S.H.; Han, J.X.; Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, S.; Chen, X.; Guo, J.; Wang, J.; He, J.B. The protective effect of grape-seed proanthocyanidin extract on oxidative damage induced by zearalenone in kunming mice liver. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Yang, S.H.; Zhang, W.K.; Han, J.X.; Wang, Y.; He, J.B. Intervention of grape seed proanthocyanidin extract on the subchronic immune injury in mice induced by aflatoxin B1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Wahhab, M.A.; Aly, S.E. Antioxidants and radical scavenging properties of vegetable extracts in rats fed aflatoxin-contaminated diet. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 2409–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.M.; Shi, C.Y.; Lee, H.P.; Ong, C.N. Aflatoxin B1-induced lipid peroxidation in rat liver. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1994, 127, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumit, R.; Ji, E.K.; Roger, C.J. Aflatoxin B1 in poultry: Toxicology, metabolism and prevention. Res. Vet. Sci. 2010, 89, 325. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, D.; Mendicino, M.; Levy, G. Xenotransplantation: Just around the corner? Surgery 2001, 129, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Muhammad, I.; Li, W.; Sun, X.; Cheng, P.; Zhang, X. Sensitivity of arbor acres broilers and chemoprevention of aflatoxin B1-induced liver injury by curcumin, a natural potent inducer of phase-ii enzymes and Nrf2. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vipin, A.V.; Rao, R.; Kurrey, N.K.; Venkateswaran, G. Protective effects of phenolics rich extract of ginger against aflatoxin B1-induced oxidative stress and hepatotoxicity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 91, 415. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.M.; Wang, Y.; Tan, H.S.; Yu, T.; Fan, X.M.; Chen, P.; Zeng, H.; Huang, M.; Bi, H.C. Schisandrol b protects against acetaminophen-induced acute hepatotoxicity in mice via activation of the Nrf2/are signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2016, 37, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, I.G.; Min, K.C. Recent updates on acetaminophen hepatotoxicity: The role of Nrf2 in hepatoprotection. Toxicol. Res. 2013, 29, 165–172. [Google Scholar]
- Sykiotis, G.P.; Habeos, I.G.; Samuelson, A.V.; Bohmann, D. The role of the antioxidant and longevity-promoting Nrf2 pathway in metabolic regulation. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2011, 14, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Surh, Y.J. Nrf2 as a novel molecular target for chemoprevention. Cancer Lett. 2005, 224, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggler, A.L.; Gay, K.A.; Mesecar, A.D. Molecular mechanisms of natural products in chemoprevention: Induction of cytoprotective enzymes by Nrf2. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2008, 52, S84–S94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, F.; Fu, J.; Xu, Y.; Hou, Y.; Kou, H.H.; Zhai, C.; Nelson, M.B.; Zhang, Q. An overview of chemical inhibitors of the Nrf2—are signaling pathway and their potential applications in cancer therapy. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 99, 544–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, S.; Utan, A.; Speroni, E.; Cervellati, R.; Piva, G.; Prandini, A.; Guerra, M.C. Carnosic acid from rosemary extracts: A potential chemoprotective agent against aflatoxin B1. An in vitro study. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2007, 27, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavin, C.; Marin-Kuan, M.; Langouet, S.; Bezencon, C.; Guignard, G.; Verguet, C.; Piguet, D.; Holzhauser, D.; Cornaz, R.; Schilter, B. Induction of Nrf2-mediated cellular defenses and alteration of phase i activities as mechanisms of chemoprotective effects of coffee in the liver. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 1239–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, J.D.; Mcmahon, M.; Chowdhry, S.; Dinkovakostova, A.T. Cancer chemoprevention mechanisms mediated through the keap1-Nrf2 pathway. Antioxid Redox Signal 2010, 13, 1713–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, J.; Qu, Z.; Fang, H.; Fu, L.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zang, H.; Wang, W. Effects of grape seed proanthocyanidin extract on pentylenetetrazole-induced kindling and associated cognitive impairment in rats. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 34, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ashmawy, I.M.; Saleh, A.; Salama, O.M. Effects of marjoram volatile oil and grape seed extract on ethanol toxicity in male rats. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2007, 101, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouédraogo, M.; Charles, C.; Ouédraogo, M.; Guissou, I.P.; Stévigny, C.; Duez, P. An overview of cancer chemopreventive potential and safety of proanthocyanidins. Nutr. Cancer 2011, 63, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.C.; Yin, J.; Zhou, B.; Liu, Y.T.; Yu, Y.; Li, G.Q. Grape seed proanthocyanidin protects liver against ischemia/reperfusion injury by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 7468–7477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, N.; Zou, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wang, H.F.; Dai, M.G. Antioxidant properties of proanthocyanidins attenuate carbon tetrachloride (ccl4)-induced steatosis and liver injury in rats via cyp2e1 regulation. J. Med. Food 2014, 17, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, N.; Dang, M.; He, J. Proanthocyanidins attenuation of chronic lead-induced liver oxidative damage in kunming mice via the Nrf2/are pathway. Nutrients 2016, 8, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, S.A.; Sun, L.; Zhang, N.; Khalil, M.M.; Gao, X.; Ling, Z.; Zhu, L.; Khan, F.A.; Zhang, J.; Qi, D. Ameliorative effects of grape seed proanthocyanidin extract on growth performance, immune function, antioxidant capacity, biochemical constituents, liver histopathology and aflatoxin residues in broilers exposed to aflatoxin B1. Toxins 2017, 9, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ma, Q.G.; Zhao, L.H.; Wei, H.; Duan, G.X.; Zhang, J.Y.; Ji, C. Effects of lipoic acid on immune function, the antioxidant defense system, and inflammation-related genes expression of broiler chickens fed aflatoxin contaminated diets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 5649–5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Yan, L.; Yu, F.; Zhao, L.; Hua, W.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, J. Molecular mechanisms of lipoic acid protection against aflatoxin B1-induced liver oxidative damage and inflammatory responses in broilers. Toxins 2015, 7, 5435–5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.; Kwon, H.S.; Bang, B.R.; Lee, Y.S.; Park, M.Y.; Moon, K.A.; Kim, T.B.; Lee, K.Y.; Moon, H.B.; Cho, Y.S. Grape seed proanthocyanidin extract attenuates allergic inflammation in murine models of asthma. J. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 32, 1292–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subarnas, A.; Wagner, H. Analgesic and anti-inflammatory activity of the proanthocyanidin shellegueain a from polypodium feei mett. Phytomedicine 2000, 7, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.F.; Zoheir, K.M.; Abdelhamied, H.E.; Attia, S.M.; Bakheet, S.A.; Ashour, A.E.; Abdallah, A.R. Grape seed proanthocyanidin extract protects against carrageenan-induced lung inflammation in mice through reduction of pro-inflammatory markers and chemokine expressions. Inflammation 2014, 37, 500–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.M.; Koh, J.; Ji, W.K.; Lee, C.; Koh, S.J.; Kim, B.G.; Lee, K.L.; Im, J.P.; Kim, J.S. Nf-kappa b activation correlates with disease phenotype in crohn’s disease. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Kong, C.; Yang, X.; Cui, X.; Lin, X.; Zhe, Z. Protein kinase c-α (pkcα) modulates cell apoptosis by stimulating nuclear translocation of nf-kappa-b p65 in urothelial cell carcinoma of the bladder. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 432. [Google Scholar]
- Didonato, J.A.; Mercurio, F.; Karin, M. Phosphorylation of i kappa b alpha precedes but is not sufficient for its dissociation from nf-kappa b. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1995, 15, 1302–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otterbein, L.E.; Choi, A.M.K. Heme oxygenase: Colors of defense against cellular stress. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2000, 279, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffit, J.S.; Aleksunes, L.M.; Kardas, M.J.; Slitt, A.L.; Klaassen, C.D.; Manautou, J.E. Role of nad(p)h:Quinone oxidoreductase 1 in clofibrate-mediated hepatoprotection from acetaminophen. Toxicology 2007, 230, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, D.D.; Lekli, I.; Teissier, P.; Bak, I.; Tosaki, A. Role of haeme oxygenase-1 in resolution of oxidative stress-related pathologies: Focus on cardiovascular, lung, neurological and kidney disorders. Acta Physiol. 2012, 204, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulcahy, R.T.; Wartman, M.A.; Bailey, H.H.; Gipp, J.J. Constitutive and beta-naphthoflavone-induced expression of the human gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase heavy subunit gene is regulated by a distal antioxidant response element/tre sequence. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 7445–7454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Jin, W.; Shi, H. Oligomeric proanthocyanidins protects a549 cells against H2O2-induced oxidative stress via the Nrf2-are pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 39, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidtheydt, M.; Abdelhadi, A.; Magan, N.; Geisen, R. Complex regulation of the aflatoxin biosynthesis gene cluster of aspergillus flavus in relation to various combinations of water activity and temperature. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 135, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Sun, L.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, J.; Guo, J.; Li, C.; Rajput, S.A.; Qi, D. Effects of nutrients in substrates of different grains on aflatoxin B1 production by aspergillus flavus. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 7232858. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Xiao, Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, L.; Sun, L.; Zhang, N.; Khalil, M.M.; Rajput, S.A.; Qi, D. Prenatal exposure to zearalenone disrupts reproductive potential and development via hormone-related genes in male rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 16, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.H.; Lei, M.Y.; Zhang, N.Y.; Zhao, L.; Krumm, C.S.; Qi, D.S. Hepatotoxic effects of mycotoxin combinations in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 74, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.H.; Lei, M.Y.; Zhang, N.Y.; Gao, X.; Li, C.; Krumm, C.S.; Qi, D.S. Individual and combined cytotoxic effects of aflatoxin B1, zearalenone, deoxynivalenol and fumonisin B1 on brl 3a rat liver cells. Toxicon 2015, 95, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ingredients | Percentage % |
|---|---|
| Corn | 58.3 |
| Soybean meal | 30.2 |
| Fish meal | 5.6 |
| Soybean oil | 2.3 |
| Dicalcium phosphate | 1.2 |
| Lime stone | 1.00 |
| Salt | 0.2 |
| Methionine | 0.2 |
| Premix 1 | 1.00 |
| Total | 100.00 |
| Calculated chemical composition | |
| Crude protein | 21.87 |
| Metabolisable energy (MJ/kg) | 13.45 |
| Lysine | 1.14 |
| Methionine | 0.40 |
| Methionine + Cystine | 0.94 |
| Calcium | 0.95 |
| Available phosphorus | 0.49 |
| Target Gene | Primer | Primer Sequence (5′→3′) | Accession No. |
|---|---|---|---|
| β-Actin | Forward Reverse | CCCGCAAATGCTCTAAACC CCAATCCTGTCTTGTTTTATGC | L08165 |
| IL-1β | Forward Reverse | GGTCAACATCGCCACCTACA CATACGAGATGCAAACCAGCAA | NM_204524.1 |
| IL-6 | Forward Reverse | GGTGATAAATCCCGATGAAGT TCTCCATAAACGAAGTAAAGTCTC | NM_204628 |
| IFNγ | Forward Reverse | TGAGCCAGATTGTTTCGATG TCCTTTTGAAACTCGGAGGA | NM_205149 |
| TNFα | Forward Reverse | TGTGTATGTGCAGCAACCCGTAGT GGCATTGCAATTTGGACAGAAGT | AY765397.1 |
| Nrf2 | Forward Reverse | GATGTCACCCTGCCCTTAG CTGCCACCATGTTATTCC | NM_205117 |
| HO-1 | Forward Reverse | GGTCCCGAATGAATGCCCTTG ACCGTTCTCCTGGCTCTTGG | HM237181.1 |
| GPx1 | Forward Reverse | GACCAACCCGCAGTACATCA GAGGTGCGGGCTTTCCTTTA | NM_001277853.1 |
| NQO1 | Forward Reverse | CAGTGGCATGCACCCAGGGAA GCATGCCCCTTTTAGCCTTGGCA | NM_001277619.1 |
| GCLC | Forward Reverse | AGTGCTGAGTGGCGAAGAAGT GCAGCCTCTTGCCTCCTCTT | XM_419910.5 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rajput, S.A.; Sun, L.; Zhang, N.-Y.; Khalil, M.M.; Ling, Z.; Chong, L.; Wang, S.; Rajput, I.R.; Bloch, D.M.; Khan, F.A.; et al. Grape Seed Proanthocyanidin Extract Alleviates AflatoxinB1-Induced Immunotoxicity and Oxidative Stress via Modulation of NF-κB and Nrf2 Signaling Pathways in Broilers. Toxins 2019, 11, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11010023
Rajput SA, Sun L, Zhang N-Y, Khalil MM, Ling Z, Chong L, Wang S, Rajput IR, Bloch DM, Khan FA, et al. Grape Seed Proanthocyanidin Extract Alleviates AflatoxinB1-Induced Immunotoxicity and Oxidative Stress via Modulation of NF-κB and Nrf2 Signaling Pathways in Broilers. Toxins. 2019; 11(1):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11010023
Chicago/Turabian StyleRajput, Shahid Ali, Lvhui Sun, Ni-Ya Zhang, Mahmoud Mohamed Khalil, Zhao Ling, Li Chong, Shuai Wang, Imran Rashid Rajput, Dost Muhammad Bloch, Farhan Anwar Khan, and et al. 2019. "Grape Seed Proanthocyanidin Extract Alleviates AflatoxinB1-Induced Immunotoxicity and Oxidative Stress via Modulation of NF-κB and Nrf2 Signaling Pathways in Broilers" Toxins 11, no. 1: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11010023
APA StyleRajput, S. A., Sun, L., Zhang, N.-Y., Khalil, M. M., Ling, Z., Chong, L., Wang, S., Rajput, I. R., Bloch, D. M., Khan, F. A., Shaukat, A., & Qi, D. (2019). Grape Seed Proanthocyanidin Extract Alleviates AflatoxinB1-Induced Immunotoxicity and Oxidative Stress via Modulation of NF-κB and Nrf2 Signaling Pathways in Broilers. Toxins, 11(1), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11010023








