Heat-Stable Enterotoxins of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and Their Impact on Host Immunity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Heat-Stable Enterotoxins of ETEC from Human and Animal Origin
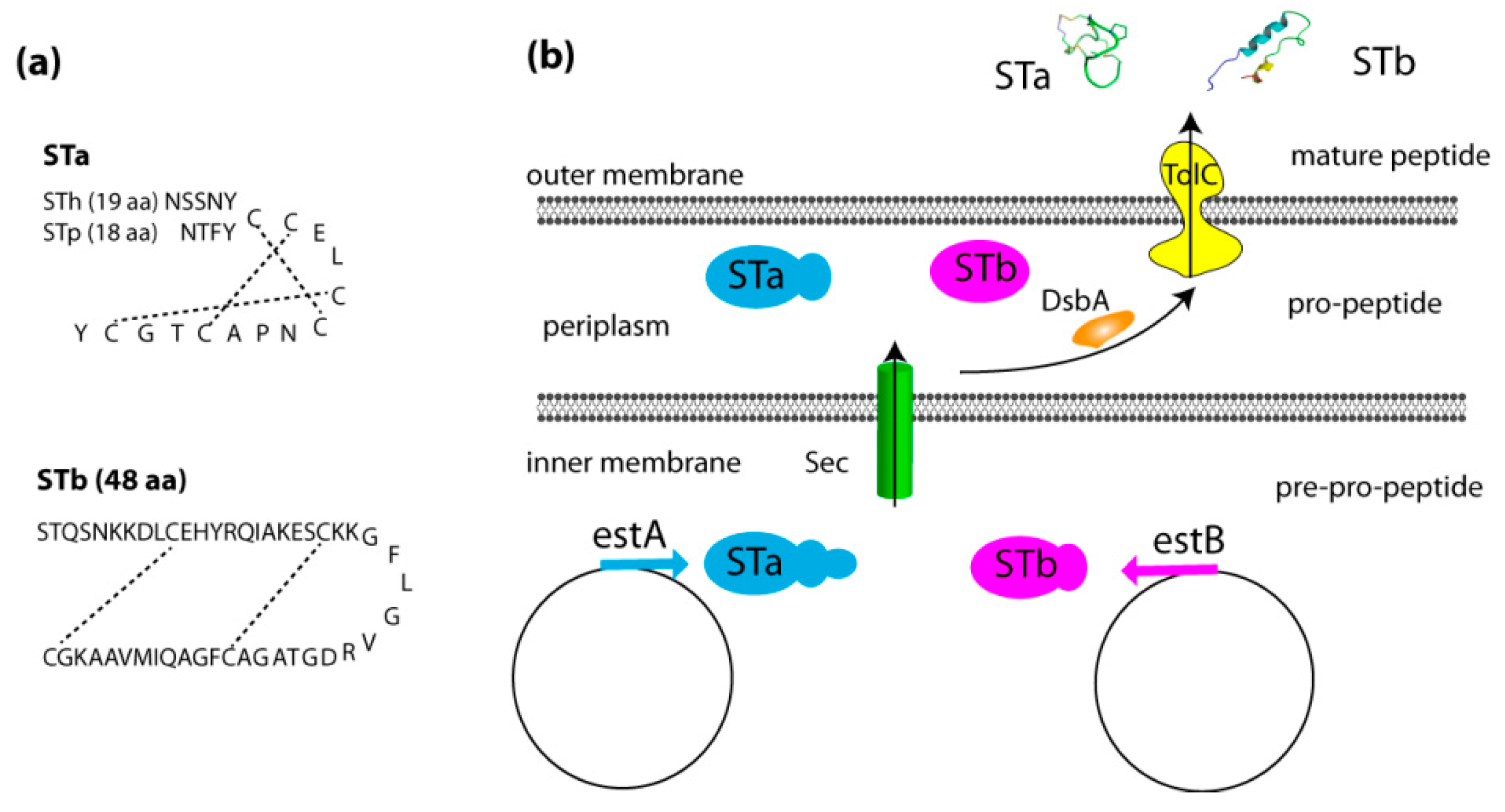
2.1. Genetics, Structure, and Secretion of Heat-Stable Enterotoxins
2.2. Molecular Mechanisms of STs Induced Diarrhea
2.3. Impact on Enterocytes and the Intestinal Immune System
2.4. STs-Based Vaccines to Combat Human and Animal ETEC Induced Diarrhea
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kotloff, K.L.; Nataro, J.P.; Blackwelder, W.C.; Nasrin, D.; Farag, T.H.; Panchalingam, S.; Wu, Y.; Sow, S.O.; Sur, D.; Breiman, R.F.; et al. Burden and aetiology of diarrhoeal disease in infants and young children in developing countries (the Global Enteric Multicenter Study, GEMS): A prospective, case-control study. Lancet 2013, 382, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, R.; Hill, D.R.; DuPont, H.L. Traveler’s diarrhea: A clinical review. JAMA 2015, 313, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Platts-Mills, J.A.; Juma, J.; Kabir, F.; Nkeze, J.; Okoi, C.; Operario, D.J.; Uddin, J.; Ahmed, S.; Alonso, P.L.; et al. Use of quantitative molecular diagnostic methods to identify causes of diarrhoea in children: A reanalysis of the GEMS case-control study. Lancet 2016, 388, 1291–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, M. Intestinal ion transport and the pathophysiology of diarrhea. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 931–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapar, N.; Sanderson, I.R. Diarrhoea in children: An interface between developing and developed countries. Lancet 2004, 363, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Oza, S.; Hogan, D.; Perin, J.; Rudan, I.; Lawn, J.E.; Cousens, S.; Mathers, C.; Black, R.E. Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality in 2000-13, with projections to inform post-2015 priorities: An updated systematic analysis. Lancet 2015, 385, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.D.; DuPont, H.L. Etiology of travellers’ diarrhea. J. Travel Med. 2017, 24, S13–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, I.A.; Troeger, C.; Blacker, B.F.; Rao, P.C.; Brown, A.; Atherly, D.E.; Brewer, T.G.; Engmann, C.M.; Houpt, E.R.; Kang, G.; et al. Morbidity and mortality due to shigella and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli diarrhoea: The Global Burden of Disease Study 1990-2016. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrant, R.L.; DeBoer, M.D.; Moore, S.R.; Scharf, R.J.; Lima, A.A. The impoverished gut—A triple burden of diarrhoea, stunting and chronic disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrant, R.L.; Oria, R.B.; Moore, S.R.; Oria, M.O.; Lima, A.A. Malnutrition as an enteric infectious disease with long-term effects on child development. Nutr. Rev. 2008, 66, 487–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddle, M.S.; Gutierrez, R.L.; Verdu, E.F.; Porter, C.K. The chronic gastrointestinal consequences associated with campylobacter. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2012, 14, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosangadi, D.; Smith, P.G.; Giersing, B.K. Considerations for using ETEC and Shigella disease burden estimates to guide vaccine development strategy. Vaccine 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, B.; Fekete, P.Z. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) in farm animals. Vet. Res. 1999, 30, 259–284. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dubreuil, J.D.; Isaacson, R.E.; Schifferli, D.M. Animal Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. EcoSal Plus 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaper, J.B.; Nataro, J.P.; Mobley, H.L. Pathogenic escherichia coli. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Mentzer, A.; Tobias, J.; Wiklund, G.; Nordqvist, S.; Aslett, M.; Dougan, G.; Sjoling, A.; Svennerholm, A.M. Identification and characterization of the novel colonization factor CS30 based on whole genome sequencing in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharat, V.B.; Ahmed, M.; Jiang, Z.D.; Riddle, M.S.; DuPont, H.L. Colonization Factors in Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Strains in Travelers to Mexico, Guatemala, and India Compared with Children in Houston, Texas. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 96, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, B.; Fekete, P.Z. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in veterinary medicine. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2005, 295, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Kuhlmann, F.M.; Chakraborty, S.; Bourgeois, A.L.; Foulke-Abel, J.; Tumala, B.; Vickers, T.J.; Sack, D.A.; DeNearing, B.; Harro, C.D.; et al. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-blood group A interactions intensify diarrheal severity. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 3298–3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, M.; Geens, M.; Schauvliege, S.; Gasthuys, F.; van der Meulen, J.; Dubreuil, J.D.; Goddeeris, B.M.; Niewold, T.; Cox, E. Role of heat-stable enterotoxins in the induction of early immune responses in piglets after infection with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran, A.R.; Carraro-Lacroix, L.R.; Bezerra, C.N.; Cornejo, M.; Norambuena, K.; Toledo, F.; Araos, J.; Pardo, F.; Leiva, A.; Sanhueza, C.; et al. Escherichia coli Heat-Stable Enterotoxin Mediates Na+/H+ Exchanger 4 Inhibition Involving cAMP in T84 Human Intestinal Epithelial Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0146042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbrugghe, E.; Van Parys, A.; Leyman, B.; Boyen, F.; Arnouts, S.; Lundberg, U.; Ducatelle, R.; Van den Broeck, W.; Yekta, M.A.; Cox, E.; et al. Heat-labile enterotoxin of Escherichia coli promotes intestinal colonization of Salmonella enterica. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 43, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, K.P.; Randolph, M.M.; Fleckenstein, J.M. Importance of heat-labile enterotoxin in colonization of the adult mouse small intestine by human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berberov, E.M.; Zhou, Y.; Francis, D.H.; Scott, M.A.; Kachman, S.D.; Moxley, R.A. Relative importance of heat-labile enterotoxin in the causation of severe diarrheal disease in the gnotobiotic piglet model by a strain of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli that produces multiple enterotoxins. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 3914–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasaro, M.; Rodrigues, J.; Mathias-Santos, C.; Guth, B.; Balan, A.; Sbrogio-Almeida, M.; Ferreira, L. Genetic diversity of heat-labile toxin expressed by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains isolated from humans. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 2400–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobling, M.G.; Holmes, R.K. Type II heat-labile enterotoxins from 50 diverse Escherichia coli isolates belong almost exclusively to the LT-IIc family and may be prophage encoded. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobling, M.G. The chromosomal nature of LT-II enterotoxins solved: A lambdoid prophage encodes both LT-II and one of two novel pertussis-toxin-like toxin family members in type II enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. FEMS Pathog. Dis. 2016, 74, ftw001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiglmeier, P.R.; Rosch, P.; Berkner, H. Cure and curse: E. coli heat-stable enterotoxin and its receptor guanylyl cyclase C. Toxins 2010, 2, 2213–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bölin, I.; Wiklund, G.; Qadri, F.; Torres, O.; Bourgeois, A.L.; Savarino, S.; Svennerholm, A.-M. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli with STh and STp genotypes is associated with diarrhea both in children in areas of endemicity and in travelers. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 3872–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joffre, E.; von Mentzer, A.; Svennerholm, A.M.; Sjoling, A. Identification of new heat-stable (STa) enterotoxin allele variants produced by human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC). Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2016, 306, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Przedpelski, A.; Tepp, W.H.; Pellett, S.; Johnson, E.A.; Barbieri, J.T. Heat-labile enterotoxin IIa, a platform to deliver heterologous proteins into neurons. MBio 2015, 6, e00734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joffré, E.; von Mentzer, A.; El Ghany, M.A.; Oezguen, N.; Savidge, T.; Dougan, G.; Svennerholm, A.-M.; Sjöling, Å. Allele variants of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin are globally transmitted and associated with colonization factors. J. Bacteriol. 2015, 197, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osek, J. Prevalence of virulence factors of Escherichia coli strains isolated from diarrheic and healthy piglets after weaning. Vet. Microbiol. 1999, 68, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, N.; Arshad, N.; Visweswariah, S.S. Receptor guanylyl cyclase C (GC-C): Regulation and signal transduction. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 334, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaandrager, A.B. Structure and function of the heat-stable enterotoxin receptor/guanylyl cyclase C. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2002, 230, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foreman, D.T.; Martinez, Y.; Coombs, G.; Torres, A.; Kupersztoch, Y.M. TolC and DsbA are needed for the secretion of STB, a heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 1995, 18, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousset, E.; Harel, J.; Dubreuil, J.D. Sulfatide from the pig jejunum brush border epithelial cell surface is involved in binding of Escherichia coli enterotoxin b. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 5650–5658. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fekete, P.Z.; Schneider, G.; Olasz, F.; Blum-Oehler, G.; Hacker, J.H.; Nagy, B. Detection of a plasmid-encoded pathogenicity island in F18+ enterotoxigenic and verotoxigenic Escherichia coli from weaned pigs. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 293, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taillon, C.; Nadeau, E.; Mourez, M.; Dubreuil, J.D. Heterogeneity of Escherichia coli STb enterotoxin isolated from diseased pigs. J. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 57, 887–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Mentzer, A.; Connor, T.R.; Wieler, L.H.; Semmler, T.; Iguchi, A.; Thomson, N.R.; Rasko, D.A.; Joffre, E.; Corander, J.; Pickard, D. Identification of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) clades with long-term global distribution. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, H.; Kameyama, M.; Baba, T.; Fujii, Y.; Okamoto, K. Maturation pathway of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin I: Requirement of DsbA for disulfide bond formation. J. Bacteriol. 1994, 176, 2906–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Luo, Q.; Davis, S.M.; Westra, C.; Vickers, T.J.; Fleckenstein, J.M. Molecular Determinants of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Heat-Stable Toxin Secretion and Delivery. Infect. Immun. 2018, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Gao, Z.; Guzman-Verduzco, L.M.; Tachias, K.; Kupersztoch, Y.M. Secretion of the STA3 heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: Extracellular delivery of Pro-STA is accomplished by either Pro or STA. Mol. Microbiol. 1992, 6, 3521–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batisson, I.; der Vartanian, M. Extracellular DsbA-insensitive folding of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin STa in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 10582–10589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, S.M.; Scott-Tucker, A.; Cooper, L.M.; Henderson, I.R. Weapons of mass destruction: Virulence factors of the global killer enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 263, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubreuil, J.D. The whole Shebang: The gastrointestinal tract, Escherichia coli enterotoxins and secretion. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2012, 14, 71–82. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, T.A.; Wu, X.Y.; Barchia, I.; Bettelheim, K.A.; Driesen, S.; Trott, D.; Wilson, M.; Chin, J.J. Comparison of virulence gene profiles of Escherichia coli strains isolated from healthy and diarrheic swine. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 4782–4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, M.; Hellemans, A.; Cox, E. Optimization of a small intestinal segment perfusion model for heat-stable enterotoxin A induced secretion in pigs. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2013, 152, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erume, J.; Berberov, E.M.; Kachman, S.D.; Scott, M.A.; Zhou, Y.; Francis, D.H.; Moxley, R.A. Comparison of the contributions of heat-labile enterotoxin and heat-stable enterotoxin b to the virulence of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in F4ac receptor-positive young pigs. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 3141–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaandrager, A.B.; Tilly, B.C.; Smolenski, A.; Schneider-Rasp, S.; Bot, A.G.; Edixhoven, M.; Scholte, B.J.; Jarchau, T.; Walter, U.; Lohmann, S.M.; et al. cGMP stimulation of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator Cl- channels co-expressed with cGMP-dependent protein kinase type II but not type Ibeta. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 4195–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaandrager, A.B.; Smolenski, A.; Tilly, B.C.; Houtsmuller, A.B.; Ehlert, E.M.; Bot, A.G.; Edixhoven, M.; Boomaars, W.E.; Lohmann, S.M.; de Jonge, H.R. Membrane targeting of cGMP-dependent protein kinase is required for cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator Cl- channel activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 1466–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, A.C.; de Sauvage, F.J.; Dong, Y.J.; Wagner, J.A.; Goeddel, D.V.; Gardner, P. Activation of intestinal CFTR Cl- channel by heat-stable enterotoxin and guanylin via cAMP-dependent protein kinase. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostedgaard, L.S.; Baldursson, O.; Welsh, M.J. Regulation of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator Cl- channel by its R domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 7689–7692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagorda, A.; Guerra, L.; Di Sole, F.; Hemle-Kolb, C.; Cardone, R.A.; Fanelli, T.; Reshkin, S.J.; Gisler, S.M.; Murer, H.; Casavola, V. Reciprocal PKA regulatory interactions between CFTR and NHE3 in a renal polarized epithelial cell model. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 21480–21488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves, C.; Berthiaume, F.; Mourez, M.; Dubreuil, J.D. Escherichia coli STb toxin binding to sulfatide and its inhibition by carragenan. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 281, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labrie, V.; Beausoleil, H.E.; Harel, J.; Dubreuil, J.D. Binding to sulfatide and enterotoxicity of various Escherichia coli STb mutants. Microbiology 2001, 147, 3141–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellstrom, B.; Savignac, M.; Gomez-Villafuertes, R.; Naranjo, J.R. Ca2+-operated transcriptional networks: Molecular mechanisms and in vivo models. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 421–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, K.; Edin, S.; Antonsson, A.; Grundstrom, T. Calmodulin-dependent kinase II mediates T cell receptor/CD3- and phorbol ester-induced activation of IkappaB kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 36008–36013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubreuil, J.D. Escherichia coli STb toxin and colibacillosis: Knowing is half the battle. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 278, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erume, J.; Wijemanne, P.; Berberov, E.M.; Kachman, S.D.; Oestmann, D.J.; Francis, D.H.; Moxley, R.A. Inverse relationship between heat stable enterotoxin-b induced fluid accumulation and adherence of F4ac-positive enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in ligated jejunal loops of F4ab/ac fimbria receptor-positive swine. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 161, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harville, B.A.; Dreyfus, L.A. Involvement of 5-hydroxytryptamine and prostaglandin E2 in the intestinal secretory action of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin B. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peterson, J.W.; Whipp, S.C. Comparison of the mechanisms of action of cholera toxin and the heat-stable enterotoxins of Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 1452–1461. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dubreuil, J.D. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli targeting intestinal epithelial tight junctions: An effective way to alter the barrier integrity. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 113, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngendahayo Mukiza, C.; Dubreuil, J.D. Escherichia coli heat-stable toxin b impairs intestinal epithelial barrier function by altering tight junction proteins. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 2819–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassour, H.; Dubreuil, J.D. Escherichia coli STb enterotoxin dislodges claudin-1 from epithelial tight junctions. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourgeois, A.L.; Wierzba, T.F.; Walker, R.I. Status of vaccine research and development for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Vaccine 2016, 34, 2880–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundgren, A.; Jertborn, M.; Svennerholm, A.M. Induction of long term mucosal immunological memory in humans by an oral inactivated multivalent enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli vaccine. Vaccine 2016, 34, 3132–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taxt, A.; Aasland, R.; Sommerfelt, H.; Nataro, J.; Puntervoll, P. Heat-stable enterotoxin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli as a vaccine target. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 1824–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleckenstein, J.; Sheikh, A.; Qadri, F. Novel antigens for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli vaccines. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2014, 13, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleckenstein, J.M.; Rasko, D.A. Overcoming enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli pathogen diversity: Translational molecular approaches to inform vaccine design. In Vaccine Design; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 363–383. [Google Scholar]
- Nadeau, E.; Fairbrother, J.M.; Zentek, J.; Belanger, L.; Tremblay, D.; Tremblay, C.L.; Rohe, I.; Vahjen, W.; Brunelle, M.; Hellmann, K.; et al. Efficacy of a single oral dose of a live bivalent E. coli vaccine against post-weaning diarrhea due to F4 and F18-positive enterotoxigenic E. coli. Vet. J. 2017, 226, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirhoseini, A.; Amani, J.; Nazarian, S. Review on pathogenicity mechanism of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and vaccines against it. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 117, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; You, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, X. Protective immunity of a Multivalent Vaccine Candidate against piglet diarrhea caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) in a pig model. Vaccine 2018, 36, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Q.; Huang, J.; Xiao, N.; Seo, H.; Zhang, W. Neutralizing Anti-Heat-Stable Toxin (STa) Antibodies Derived from Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Toxoid Fusions with STa Proteins Containing N12S, L9A/N12S, or N12S/A14T Mutations Show Little Cross-Reactivity with Guanylin or Uroguanylin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e01737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govasli, M.L.; Diaz, Y.; Zegeye, E.D.; Darbakk, C.; Taxt, A.M.; Puntervoll, P. Purification and Characterization of Native and Vaccine Candidate Mutant Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Heat-Stable Toxins. Toxins 2018, 10, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puntervoll, P.; Clements, J.; Diaz, Y.; Nataro, J.; Taxt, A.; Zhang, W.; Aasland, R.; Sommerfelt, H. Rational Design of a Vaccine against the Heat-Stable Toxin of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli; Vaccines for Enteric Diseases: Bangkok, Thailand, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Sack, D.A. Progress and hurdles in the development of vaccines against enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in humans. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2012, 11, 677–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, C.; Francis, D.H.; Fang, Y.; Knudsen, D.; Nataro, J.P.; Robertson, D.C. Genetic fusions of heat-labile (LT) and heat-stable (ST) toxoids of porcine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli elicit neutralizing anti-LT and anti-STa antibodies. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, X.; Sack, D.A.; Zhang, W. Genetic fusions of a CFA/I/II/IV MEFA (multiepitope fusion antigen) and a toxoid fusion of heat-stable toxin (STa) and heat-labile toxin (LT) of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) retain broad anti-CFA and antitoxin antigenicity. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rausch, D.; Ruan, X.; Nandre, R.; Duan, Q.; Hashish, E.; Casey, T.A.; Zhang, W. Antibodies derived from a toxoid MEFA (multiepitope fusion antigen) show neutralizing activities against heat-labile toxin (LT), heat-stable toxins (STa, STb), and Shiga toxin 2e (Stx2e) of porcine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC). Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 202, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandre, R.; Ruan, X.; Lu, T.; Duan, Q.; Sack, D.; Zhang, W. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Adhesin-Toxoid Multiepitope Fusion Antigen CFA/I/II/IV-3xSTaN12S-mnLTG192G/L211A-Derived Antibodies Inhibit Adherence of Seven Adhesins, Neutralize Enterotoxicity of LT and STa Toxins, and Protect Piglets against Diarrhea. Infect. Immun. 2018, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmgren, J.; Czerkinsky, C. Mucosal immunity and vaccines. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Qadri, F.; Kansal, R.; Rasko, D.A.; Sheikh, A.; Fleckenstein, J.M. Conservation and immunogenicity of novel antigens in diverse isolates of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, S.; Randall, A.; Vickers, T.J.; Molina, D.; Harro, C.D.; DeNearing, B.; Brubaker, J.; Sack, D.A.; Bourgeois, A.L.; Felgner, P.L. Human experimental challenge with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli elicits immune responses to canonical and novel antigens relevant to vaccine development. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 40, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devriendt, B.; De Geest, B.G.; Goddeeris, B.M.; Cox, E. Crossing the barrier: Targeting epithelial receptors for enhanced oral vaccine delivery. J. Control. Release 2012, 160, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zegeye, E.D.; Govasli, M.L.; Sommerfelt, H.; Puntervoll, P. Development of an enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli vaccine based on the heat-stable toxin. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Z.; Mc Cafferty, S.; Combes, F.; Huysmans, H.; De Temmerman, J.; Gitsels, A.; Vanrompay, D.; Catani, J.P.; Sanders, N.N. mRNA therapeutics deliver a hopeful message. Nano Today 2018, 23, 16–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söderholm, J.D. Gut immunology: Nanoparticles ferry gut antigens. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2015, 10, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, S.K.; Wang, Y.Y.; Hanes, J. Mucus-penetrating nanoparticles for drug and gene delivery to mucosal tissues. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.S.; Suzuki, K.; Cho, H.; Youn, Y.S.; Bae, Y.H. Oral Nanoparticles Exhibit Specific High-Efficiency Intestinal Uptake and Lymphatic Transport. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 8893–8900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadwick, S.; Kriegel, C.; Amiji, M. Nanotechnology solutions for mucosal immunization. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aref, N.M.; Nasr, M.; Osman, R. Construction and immunogenicity analysis of nanoparticulated conjugate of heat-stable enterotoxin (STa) of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.; Zeng, J.; Jian, M.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y. Nanoparticulated heat-stable (STa) and heat-labile B subunit (LTB) recombinant toxin improves vaccine protection against enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli challenge in mouse. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2013, 115, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Enterotoxins | Variants | Encoding Gene | Location of Genes | Host Specificity | Receptor | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heat-labile enterotoxin (LT) | LTIh | eltAB | plasmid | humans | GM1a | [25,31,32] |
| LTIp | eltAB | plasmid | piglets | GM1a | [31,33] | |
| LTIIa | eltAB | chromosome, prophages | water-buffalo, humans | GD1b | [27,30,31] | |
| LTIIb | eltAB | chromosome, prophages | unknown | GD1a | [27,30,31] | |
| LTIIc | eltAB | chromosome, prophages | humans, calves | GM1a | [26,27,31] | |
| Heat-stable enterotoxin (STa) | STp | estA1, estA5, estA6 | plasmids | piglets, calves, humans | GC-C | [30,34] |
| STh | estA2, estA3/4, estA7 | plasmids | humans | GC-C | [30,34,35] | |
| Heat-stable enterotoxin (STb) | STb | estB | plasmids | post-weaning pigs | sulfatide | [36,37] |
| STbH12N | estBC34A | plasmids | post-weaning pigs | sulfatide | [38,39] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Zhong, Z.; Luo, Y.; Cox, E.; Devriendt, B. Heat-Stable Enterotoxins of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and Their Impact on Host Immunity. Toxins 2019, 11, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11010024
Wang H, Zhong Z, Luo Y, Cox E, Devriendt B. Heat-Stable Enterotoxins of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and Their Impact on Host Immunity. Toxins. 2019; 11(1):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11010024
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Haixiu, Zifu Zhong, Yu Luo, Eric Cox, and Bert Devriendt. 2019. "Heat-Stable Enterotoxins of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and Their Impact on Host Immunity" Toxins 11, no. 1: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11010024
APA StyleWang, H., Zhong, Z., Luo, Y., Cox, E., & Devriendt, B. (2019). Heat-Stable Enterotoxins of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and Their Impact on Host Immunity. Toxins, 11(1), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11010024






