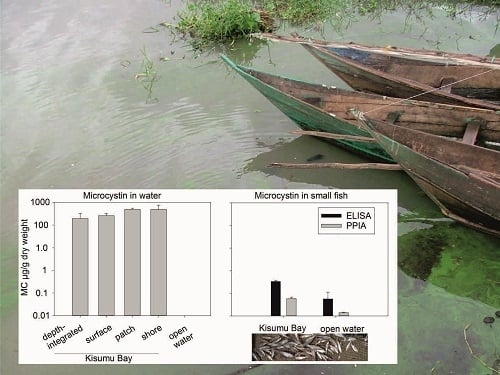
Microcystin Content in Phytoplankton and in Small Fish from Eutrophic Nyanza Gulf, Lake Victoria, Kenya
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Spatial Variation of Physical-Chemical Parameters
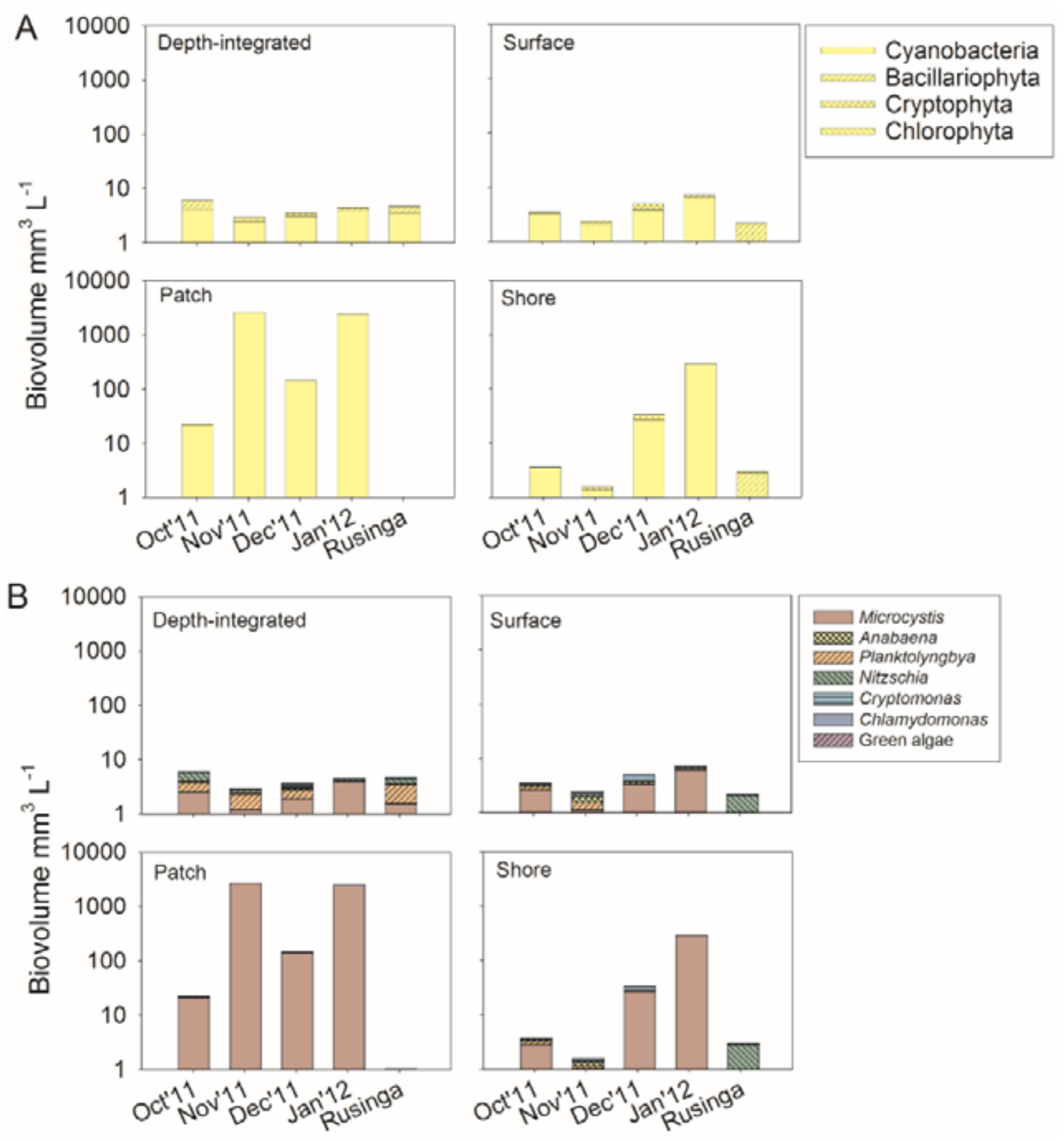
2.2. Phytoplankton Composition
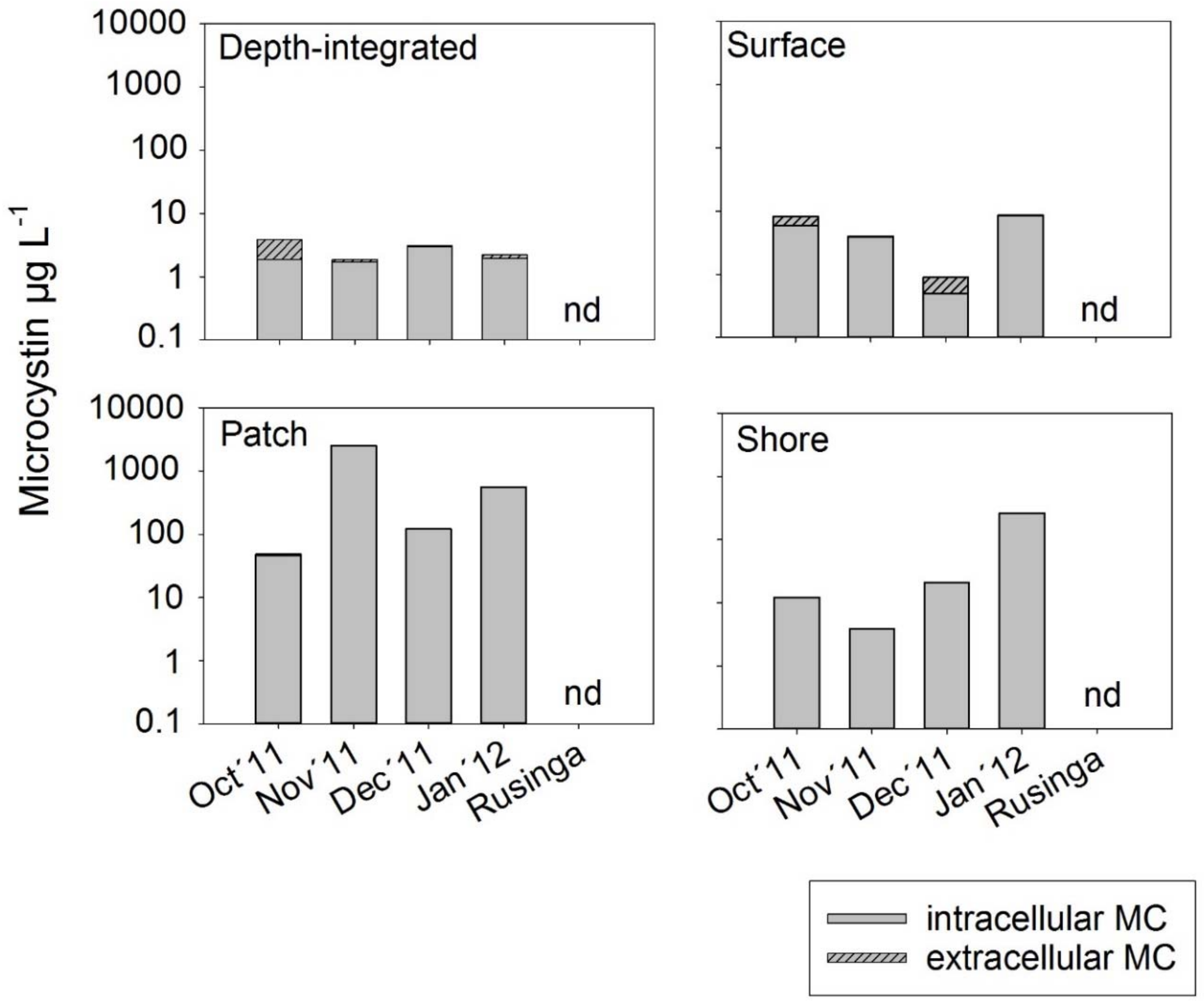
2.3. Microcystin Concentrations in Water
2.4. Small Fish Species Composition
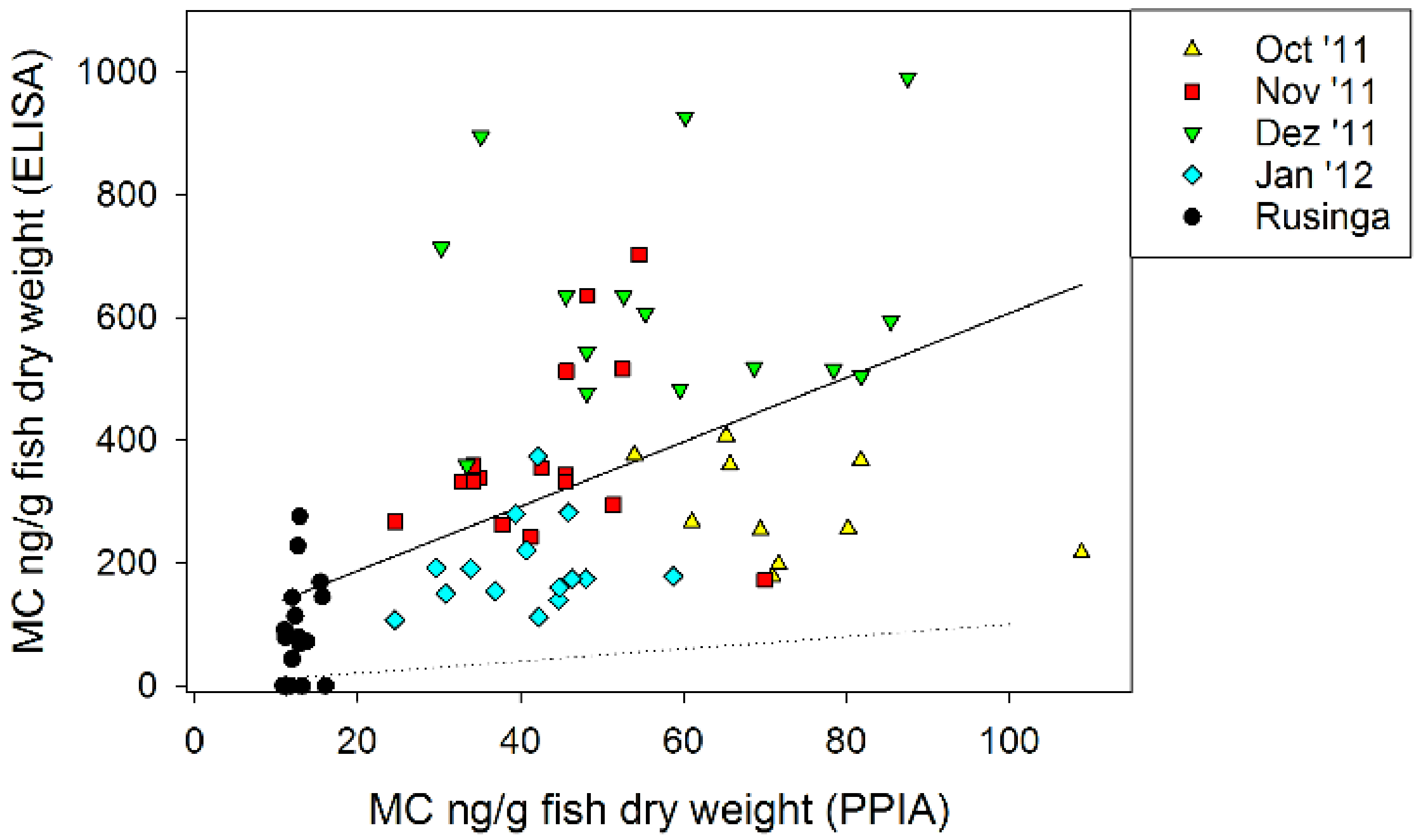
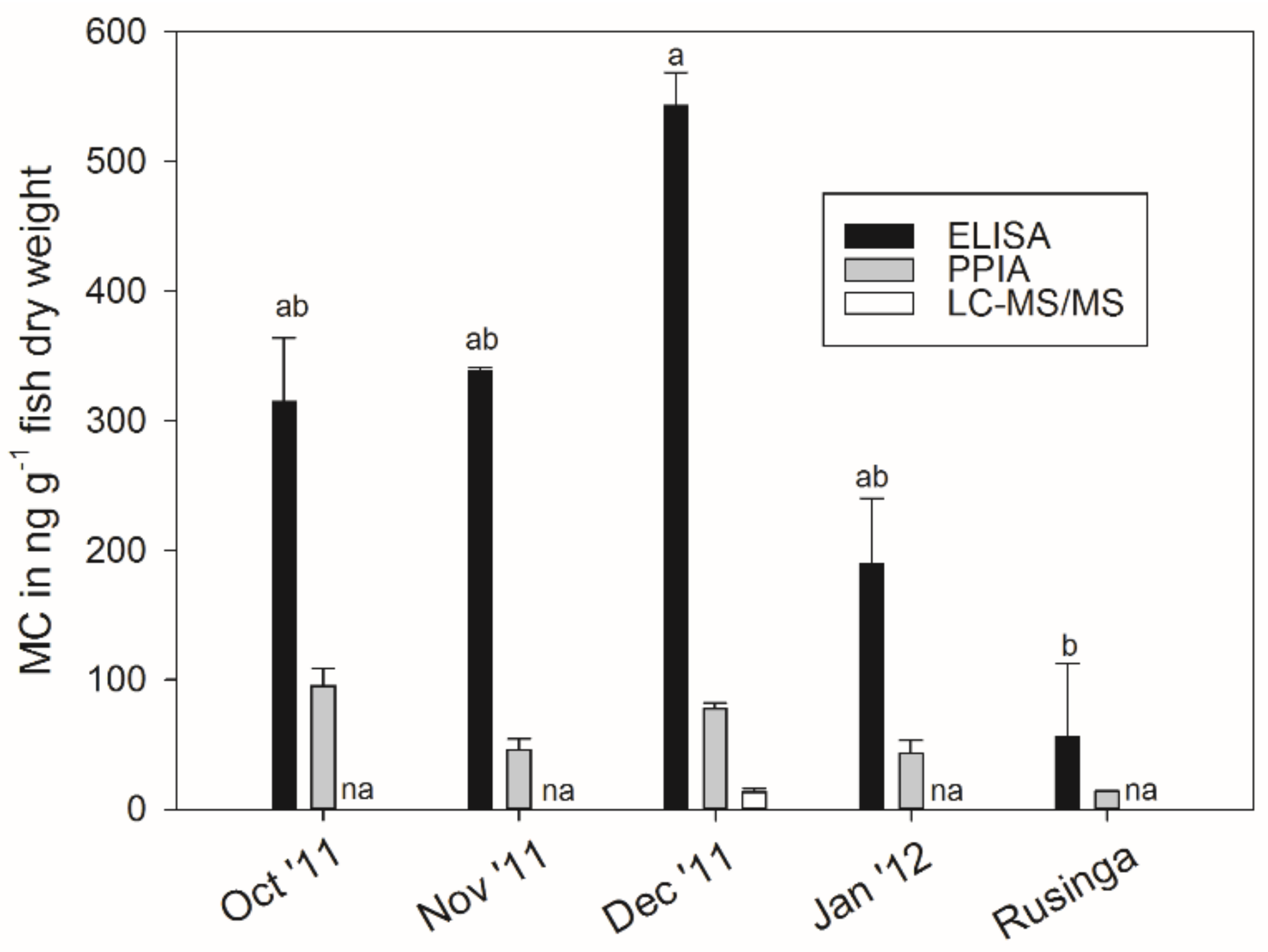
2.5. Microcystin Content in Small Fish as Determined by Biological and Chemical-Analytical Methods
2.6. Microcystin Content in Small Fish in Relation to MC in Phytoplankton
3. Discussion
3.1. Eutrophication and Spatial Variability of Phytoplankton Composition
3.2. Spatial Variability of Microcystin Concentration in Water
3.3. Microcystin Content in Small Fish as Determined by Biological and Chemical-Analytical Methods
3.4. Microcystin Content in Small Fish
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
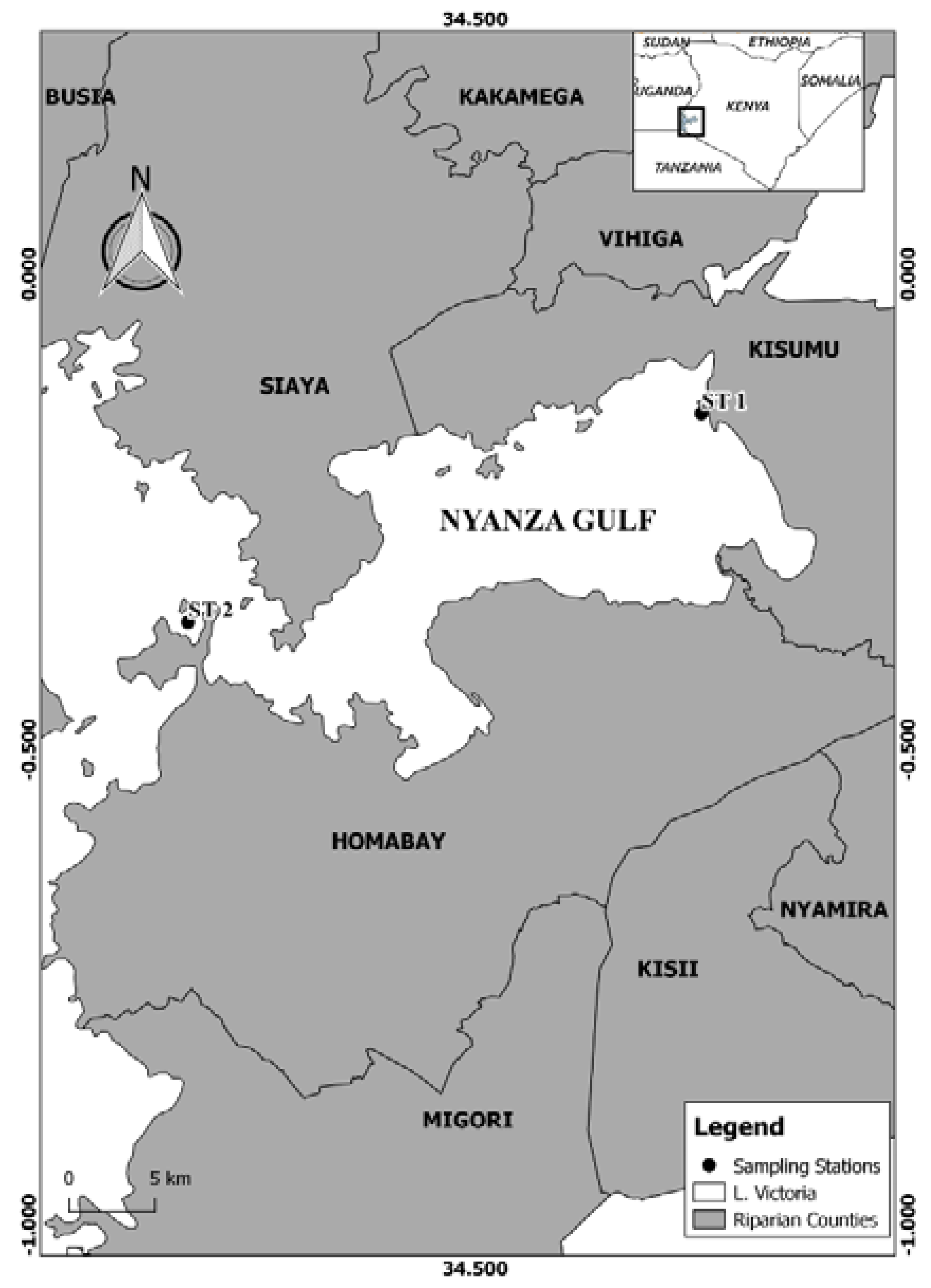
5.1. Study Area and Sampling
5.2. Phytoplankton Composition and Abundance
5.3. Microcystin Determination in Water
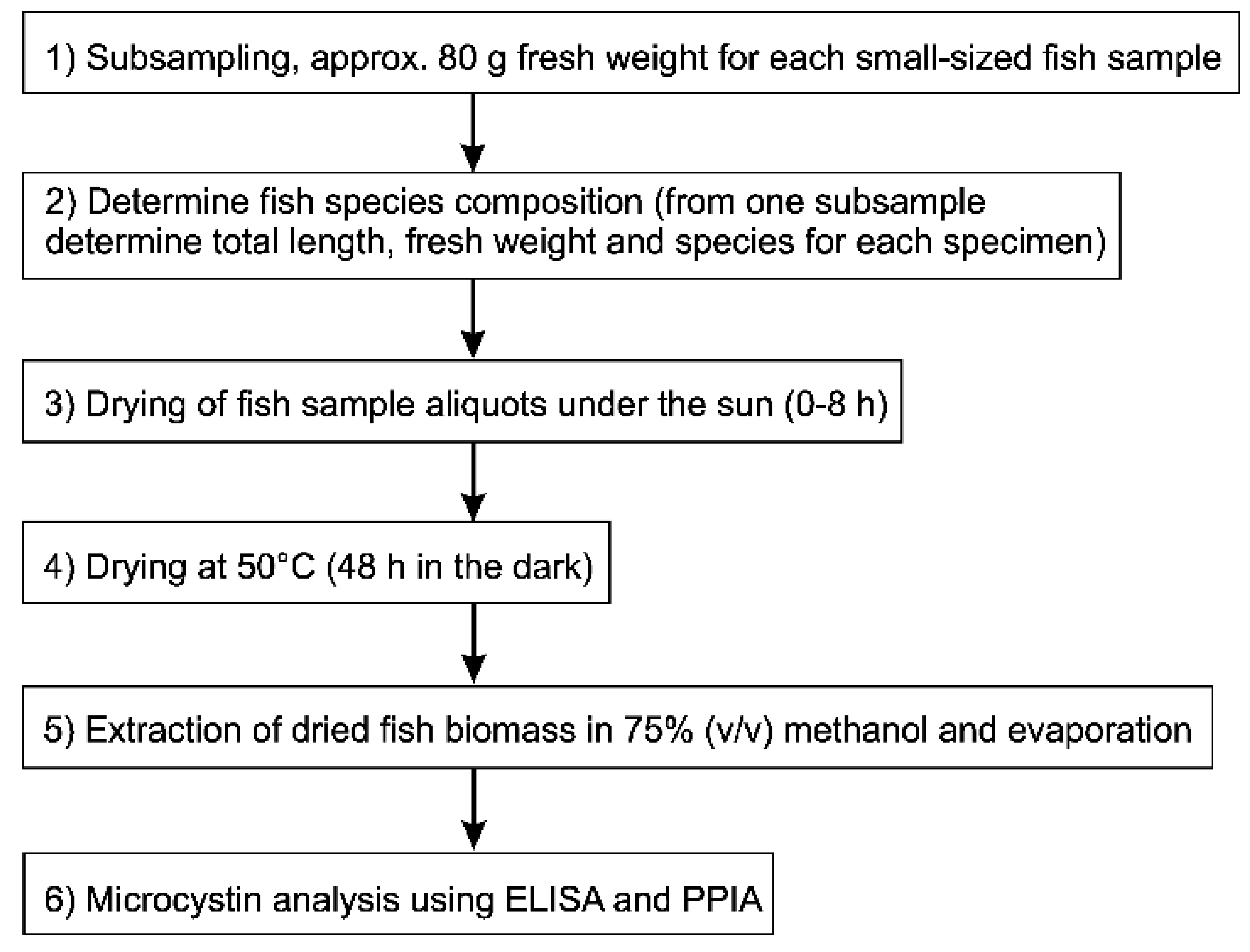
5.4. Fish Sampling
5.5. Microcystin Analysis in Small Fish
5.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Verschuren, D.; Johnson, T.C.; Kling, H.J.; Edgington, D.N.; Leavitt, P.R.; Brown, E.T.; Talbot, M.R.; Hecky, R.E. History and timing of human impact on Lake Victoria, East Africa. Proc. R. Soc. B 2001, 269, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecky, R.E.; Muggide, R.; Ramlal, P.S.; Talbot, M.R.; Kling, G.W. Multiple stressors cause rapid ecosystem change in Lake Victoria. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 19–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamatamah, R.A.; Hecky, R.E.; Duthie, H. The atmospheric deposition of phosphorus in Lake Victoria (East Africa). Biogeochemistry 2005, 73, 325–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbonde, A.S.; Sitoki, L.; Kurmayer, R. Phytoplankton composition and microcystin concentrations in open and closed bays of Lake Victoria, Tanzania. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2015, 18, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gikuma-Njuru, P.; Hecky, R.E.; Guildford, S.J.; MacIntyre, S. Spatial variability of nutrient concentrations, fluxes, and ecosystem metabolism in Nyanza Gulf and Rusinga Channel, Lake Victoria (East Africa). Limnol. Oceanogr. 2013, 58, 774–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calamari, D.; Akech, M.O.; Ochumba, P.B.O. Pollution of Winam Gulf, Lake Victoria, Kenya: A case study for preliminary risk assessment. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 1995, 1, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kling, H.J.; Mugidde, R.; Hecky, R.E. Recent changes in the phytoplankton community of Lake Victoria in response to eutrophication. In The Great Lakes of the World (GLOW): Food Web, Health and Integrity; Munawar, M., Hecky, R.E., Eds.; Ecovision World Monograph Series; Backhuys Publishers: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 47–65. ISBN 978-0-9921007-8-0. [Google Scholar]
- Meriluoto, J.; Spoof, L.; Codd, G.A. Handbook of Cyanobacterial Monitoring and Cyanotoxin Analysis; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2017; p. 576. ISBN 9781119068747. [Google Scholar]
- Sitoki, L.; Kurmayer, R.; Rott, E. Spatial variation of phytoplankton composition, biovolume, and resulting microcystin concentrations in the Nyanza Gulf (Lake Victoria, Kenya). Hydrobiologia 2012, 691, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humbert, J.-F.; Fastner, J. Ecology of cyanobacteria. In Handbook of Cyanobacterial Monitoring and Cyanotoxin Analysis; Meriluoto, J., Spoof, L., Codd, G.A., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2017; pp. 9–18. ISBN 9781119068747. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, C.S.; Oliver, R.L.; Walsby, A.E. Cyanobacterial dominance: The role of buoyancy regulation in dynamic lake environments. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1987, 21, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.R.; Wilhelm, S.W.; Boyer, G.L. The fate of microcystins in the environment and challenges for monitoring. Toxins 2014, 6, 3354–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svircev, Z.; Drobac, D.; Tokodi, N.; Mijovic, B.; Codd, G.A.; Meriluoto, J. Toxicology of microcystins with reference to cases of human intoxications and epidemiological investigations of exposures to cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 621–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okello, W.; Kurmayer, R. Seasonal development of cyanobacteria and microcystin production in Ugandan freshwater lakes. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 2011, 16, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okello, W.; Portmann, C.; Erhard, M.; Gademann, K.; Kurmayer, R. Occurrence of microcystin-producing cyanobacteria in Ugandan freshwater habitats. Environ. Toxicol. 2010, 25, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Xie, P.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, T. Transfer, distribution and bioaccumulation of microcystins in the aquatic food web in Lake Taihu, China, with potential risks to human health. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2191–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotton, B.; Guillard, J.; Anneville, O.; Maréchal, M.; Savichtcheva, O.; Domaizon, I. Trophic transfer of microcystins through the lake pelagic food web: Evidence for the role of zooplankton as a vector in fish contamination. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 466, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, J.D.; Franklin, R.B.; Garman, G.; McIninch, S.; Porter, A.J.; Bukaveckas, P.A. Exposure to the cyanotoxin microcystin arising from interspecific differences in feeding habits among fish and shellfish in the James River Estuary, Virginia. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 5194–5202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semyalo, R.; Rohrlack, T.; Naggawa, C.; Nyakairu, G.W. Microcystin concentrations in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) caught from Murchison Bay, Lake Victoria and Lake Mburo: Uganda. Hydrobiologia 2010, 638, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibelings, B.W.; Chorus, I. Accumulation of cyanobacterial toxins in freshwater “seafood” and its consequences for public health: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 150, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semyalo, R.; Rohrlack, T.; Kayiira, D.; Kizito, Y.S.; Byarujali, S.; Nyakairu, G.; Larsson, P. On the diet of Nile tilapia in two eutrophic tropical lakes containing toxin producing cyanobacteria. Limnologica 2011, 41, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyakairu, G.W.; Nagawa, C.B.; Mbabazi, J. Assessment of cyanobacteria toxins in freshwater fish: A case study of Murchison Bay (Lake Victoria) and Lake Mburo, Uganda. Toxicon 2010, 55, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poste, A.E.; Hecky, R.E.; Guildford, S.J. Evaluating microcystin exposure risk through fish consumption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 5806–5811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality. Fourth Edition Incorporating the First Addendum; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; p. 541. ISBN 978-92-4-154995-0. [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe, D.M.; Wandera, S.B.; Chapman, L.J. Life history change in response to fishing and an introduced predator in the East African cyprinid Rastrineobola argentea. Evol. Appl. 2012, 5, 677–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abila, R.O. Assessment of fisheries products values along Kenya’s export marketing chain. In FAO Fisheries Technical Report; No. 819; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2007; p. 262. [Google Scholar]
- Wangechi, K.S.; Muigai, A.W.T.; Ouma, S.O. The Impact of evolution and socio-economics of commercially exploited fish stock: A Review on Rastrineobola argentea in Lake Victoria. J. Food Secur. 2015, 3, 82–86. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, R.; Imberger, J. Phytoplankton patchiness in Winam Gulf, Lake Victoria: A study using principal component analysis of in situ fluorescent excitation spectra. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okely, P.; Imberger, J.; Antenucci, P.J. Processes affecting horizontal mixing and dispersion in Winam Gulf, Lake Victoria. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 1865–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gikuma-Njuru, P.; Hecky, R.E. Nutrient concentrations in Nyanza Gulf, Lake Victoria, Kenya: Light limits algal demand and abundance. Hydrobiologia 2005, 534, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, K.; Kumagai, M.; Vincent, W.F.; Tsujimura, S.; Nakahara, H. Transport and accumulation of bloom-forming cyanobacteria in a large, mid-latitude lake: The gyre-Microcystis hypothesis. Limnology 2002, 3, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khisa, P.; Romero, J.R.; Imberger, J.; Ewing, T.; Antenucci, J.; Njuguna, H.; Okungu, J. The effect of the Mbita Causeway on water currents in the region of Rusinga Channel, Winam Gulf, Lake Victoria: A 3D modelling study with ELCOM. In Proceedings of the 11th World Lakes Conference, Nairobi, Kenya, 31 October–4 November 2005; Odada, E.O., Olago, D.O., Ochola, W., Ntiba, M., Wandiga, S., Gichuki, N., Oyieke, H., Eds.; Ministry of Water and Irrigation: Nairobi, Kenya, 2005; pp. 74–78. [Google Scholar]
- Kurmayer, R.; Christiansen, G.; Chorus, I. The abundance of microcystin-producing genotypes correlates positively with colony size in Microcystis and determines its microcystin net production in Lake Wannsee. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurmayer, R.; Dittmann, E.; Fastner, J.; Chorus, I. Diversity of microcystin genes within a population of the toxic cyanobacterium Microcystis. In Lake Wannsee (Berlin, Germany). Microb. Ecol. 2002, 43, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, J.L.; Jones, J.R. Microcystin distribution in physical size class separations of natural plankton communities. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2007, 23, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, M.; Xie, M.; Liu, M.; Luo, L.; Li, P.; Kong, F. Differences in microcystin production and genotype composition among Microcystis colonies of different sizes in Lake Taihu. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5659–5669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testai, E.; Buratti, F.M.; Funari, E.; Manganelli, M.; Vichi, S.; Arnich, N.; Biré, R.; Fessard, V.; Sialehaamoa, A. Review and analysis of occurrence, exposure and toxicity of cyanobacteria toxins in food. EFSA Support. Publ. 2016, 13, 998E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadel-Six, S.; Moyenga, D.; Magny, S.; Trotereau, S.; Edery, M.; Krys, S. Detection of free and covalently bound microcystins in different tissues (liver, intestines, gills, and muscles) of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry: Method Characterization. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 185, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.L.; Schulz, K.L.; Zimba, P.V.; Boyer, G.L. Possible mechanism for the foodweb transfer of covalently bound microcystins. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 757–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, J.R.; Shaskus, M.; Estenik, J.F.; Oesch, C.; Khidekel, R.; Boyer, G.L. Variations in the microcystin content of different fish species collected from a eutrophic lake. Toxins 2013, 5, 992–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isumbisho, M.; Petit, P.; Gashagaza, J.B.; Moreau, J. The feeding habit of the Cyprinidae Rastrineobola argentea in its new habitat, Lakes Bulera and Ruhondo, two Rwandan lakes (Eastern Africa). Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawton, L.A.; Robertson, P.K.J. Physico-chemical treatment methods for the removal of microcystins (cyanobacterial hepatotoxins) from potable waters. Chem. Soc. Rev. 1999, 28, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, L.C.V.; Peralta-Zamora, P.; Campos, F.R.; Pontarolo, R. Photocatalytic degradation of microcystin-LR in aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 1552–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Organization for Standardization. Water Quality—Measurement of Biochemical Parameters—Spectrometric Determination of the Chlorophyll—A Concentration; ISO 10260; ISO: Geneve, Switzerland, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel, R.G.; Likens, G.E. Limnological Analyses, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000; p. 429. ISBN 978-1-4757-3250-4. [Google Scholar]
- Talling, J.F. The phytoplankton of Lake Victoria (East Africa). Arch. Hydrobiol. Beih. Ergeb. Limnol. 1987, 25, 229–56. [Google Scholar]
- Komárek, J.; Kling, H. Variation in six planktonic cyanophyte genera in Lake Victoria (East Africa). Algol. Stud. 1991, 61, 21–45. [Google Scholar]
- Cronberg, G.; Annadotter, H. Manual on Aquatic Cyanobacteria; A Photo Guide and Synopsis of Their Toxicology; International Society for the Study of Harmful Algae (ISSHA) and United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation (UNESCO): Copenhagen, Denmark, 2006; p. 106. ISBN 8799082705. [Google Scholar]
- Lawton, L.; Marsalek, B.; Padisak, J.; Chorus, I. Determination of cyanobacteria in the laboratory. In Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water; A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management; Chorus, I., Bartram, J., Eds.; WHO: London, UK, 1999; pp. 347–368. ISBN 0-419-23930-8. [Google Scholar]
- Fastner, J.; Flieger, I.; Neumann, U. Optimised extraction of microcystins from field samples—A comparison of different solvents and procedures. Water Res. 1998, 32, 3177–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.E.; Gossiaux, D.C.; Höök, T.O.; Berry, J.P.; Landrum, P.F.; Dyble, J.; Guildford, S.J. Evaluation of the human health threat associated with the hepatotoxin microcystin in the muscle and liver tissues of yellow perch (Perca flavescens). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2008, 65, 1487–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, J.S.; Hyenstrand, P.; Beattie, K.A.; Codd, G.A. Effects of physicochemical variables and cyanobacterial extracts on the immunoassay of microcystin-LR by two ELISA kits. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 89, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, J.; Carmichael, W.W. Use of a colorimetric protein phosphatase inhibition assay and enzyme linked immunosorbent assay for the study of microcystins and nodularins. Toxicon 1994, 32, 1495–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Date | Temp. (°C) | Cond. (µS/cm) | pH | Secchi (cm) | Chlorophyll a (µg/L) | Total Phytoplankton Biovolume (mm3/L) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface | Integrated | Patch | Shore | Surface | Integrated | Patch | Shore | |||||
| Kisumu Bay (ST1) | ||||||||||||
| 27 October 2011 | 25.3 ± 0.1 | 153 ± 0.4 | 6.5 ± 0.3 | 25 | 50 | 14 | 1038 | 128 | 3.5 | 3.9 | 22.4 | 3.7 |
| 8 November 2011 | n.d | 159 ± 0.1 | 6.3 ± 0.2 | 15 | 20 | 17 | 274 | 18 | 2.4 | 2.1 | 264 | 1.6 |
| 5 December 2011 | 24.9 ± 0.3 | 130 ± 0.3 | 6.5 ± 0.1 | 27 | 19 | 10 | 845 | 73 | 5.0 | 3.0 | 145 | 34 |
| 10 January 2012 | 25.5 ± 0.2 | 134 ± 0.3 | n.d | 7 | 44 | 30 | 4382 | 1737 | 7.3 | 4.5 | 2467 | 291 |
| Rusinga Channel (ST2) | ||||||||||||
| 9 January 2012 | 25.8 ± 0.1 | 106 ± 0.1 | n.d | 85 | 13 | 14 | n/a | 15 | 2.2 | 2.6 | n/a | 3.0 |
| Structural Variant | Retention (min) | Surface | Integrated | Patch | Shore | p-Value 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proportion | ||||||
| MC-YR | 17.06–17.26 | 40 ± 5 a,b | 26 ± 6 b | 45 ± 2 a | 33 ± 4 a,b | 0.015 |
| MC-LR | 18.34–18.52 | 28 ± 4 | 18 ± 4 | 29 ± 2 | 26 ± 4 | 0.136 |
| MC m/z 1052 | 23.95–24.16 | 25 ± 9 | 51 ± 12 | 16 ± 1 | 31 ± 9 | 0.05 |
| MC m/z 1002 | 25.0–25.07 | 7 ± 3 | 6 ± 2 | 11 ± 2 | 9 ± 2 | 0.463 |
| Concentration (µg/L) | ||||||
| MC-YR | 17.06–17.26 | 0.6 ± 0.4 a,b | 0.5 ± 0.1 b | 343 ± 186 a | 29 ± 17 a,b | <0.001 |
| MC-LR | 18.34–18.52 | 1.3 ± 0.3 b | 0.4 ± 0.1 b | 210 ± 102 a | 22 ± 12 a,b | <0.001 |
| MC m/z 1052 | 23.95–24.16 | 1.4 ± 0.6 b | 1.2 ± 0.3 b | 160 ± 94 a | 17 ± 9 a,b | <0.001 |
| MC m/z 1002 | 25.0–25.07 | 0.6 ± 0.5 b | 0.2 ± 0.04 b | 111 ± 60 a | 9 ± 5 a,b | <0.001 |
| Barbus sp. | Haplochromis sp. | L. niloticus | R. argentea | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number (Proportion) | ||||
| ST1, October 2011 | 26 (33) | 2 (2.6) | 6 (7.8) | 43 (55.5) |
| ST1, November 2011 | 17 (10) | 2 (2.2) | 51 (30.5) | 97 (58) |
| ST1, December 2011 | 3 (2.5) | 0 | 44 (37.3) | 71 (60.2) |
| ST1, January 2012 | 19 (13) | 0 | 18 (12.6) | 106 (74.1) |
| ST2, January 2012 | 1 (0.1) | 0 | 6 (4.2) | 137 (95.1) |
| Fresh weight (g) | ||||
| ST1, October 2011 | 1.2 ± 0.1 (0.1–2.6) | (0.3–0.4) | 0.7 ± 0.3 (0.2–1.9) | 0.5 ± 0.1 (0.3–1.7) |
| ST1, November 2011 | 1 ± 0.1 (0.4–2.4) | (0.5–1.2) | 0.8 ± 0.1 (0.2–4.2) | 0.6 ± 0.1 (0.1–1.6) |
| ST1, December 2011 | 1.4 ± 0.3 (1.1–2) | - | 0.6 ± 0.1 (0.1–4.6) | 0.6 ± 0 (0.1–1.2) |
| ST1, January 2012 | 0.7 ± 0.1 (0.3–1.9) | - | 0.3 ± 0.0 (0.1–0.7) | 0.5 ± 0 (0.1–1.3) |
| ST2, January 2012 | 1.2 | - | 1.8 ± 0.2 (1.3–2.3) | 0.5 ± 0 (0.1–1.5) |
| Total length (mm) | ||||
| ST1, October 2011 | 47 ± 3 (19–64) | (26–30) | 35 ± 5 (21–53) | 44 ± 1 (30–56) |
| ST1, November 2011 | 48 ± 2 (38–65) | (31–40) | 37 ± 2 (12–70) | 36 ± 2 (10–58) |
| ST1, December 2011 | 56 ± 4 (51–63) | - | 34 ± 2 (17–70) | 44 ± 1 (20–56) |
| ST1, January 2012 | 40 ± 2 (29–60) | - | 30 ± 3 (17–62) | 36 ± 1 (4–60) |
| ST2, January 2012 | 56 | - | 58 ± 2 (50–61) | 40 ± 1 (27–56) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Simiyu, B.M.; Oduor, S.O.; Rohrlack, T.; Sitoki, L.; Kurmayer, R. Microcystin Content in Phytoplankton and in Small Fish from Eutrophic Nyanza Gulf, Lake Victoria, Kenya. Toxins 2018, 10, 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10070275
Simiyu BM, Oduor SO, Rohrlack T, Sitoki L, Kurmayer R. Microcystin Content in Phytoplankton and in Small Fish from Eutrophic Nyanza Gulf, Lake Victoria, Kenya. Toxins. 2018; 10(7):275. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10070275
Chicago/Turabian StyleSimiyu, Benard Mucholwa, Steve Omondi Oduor, Thomas Rohrlack, Lewis Sitoki, and Rainer Kurmayer. 2018. "Microcystin Content in Phytoplankton and in Small Fish from Eutrophic Nyanza Gulf, Lake Victoria, Kenya" Toxins 10, no. 7: 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10070275
APA StyleSimiyu, B. M., Oduor, S. O., Rohrlack, T., Sitoki, L., & Kurmayer, R. (2018). Microcystin Content in Phytoplankton and in Small Fish from Eutrophic Nyanza Gulf, Lake Victoria, Kenya. Toxins, 10(7), 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10070275