Purification and Characterization of Native and Vaccine Candidate Mutant Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Heat-Stable Toxins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
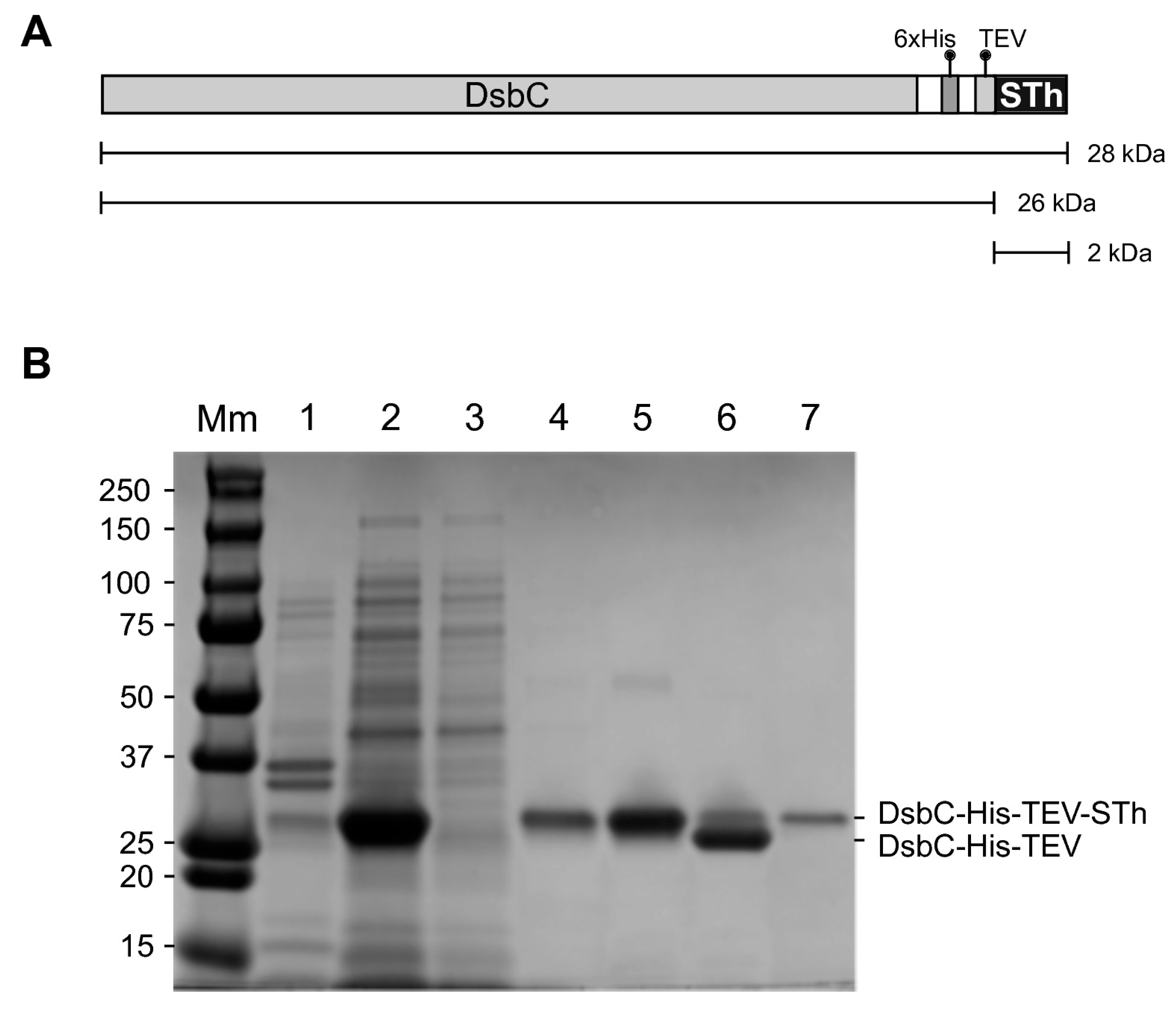
2.1. Expression and Purification of STh
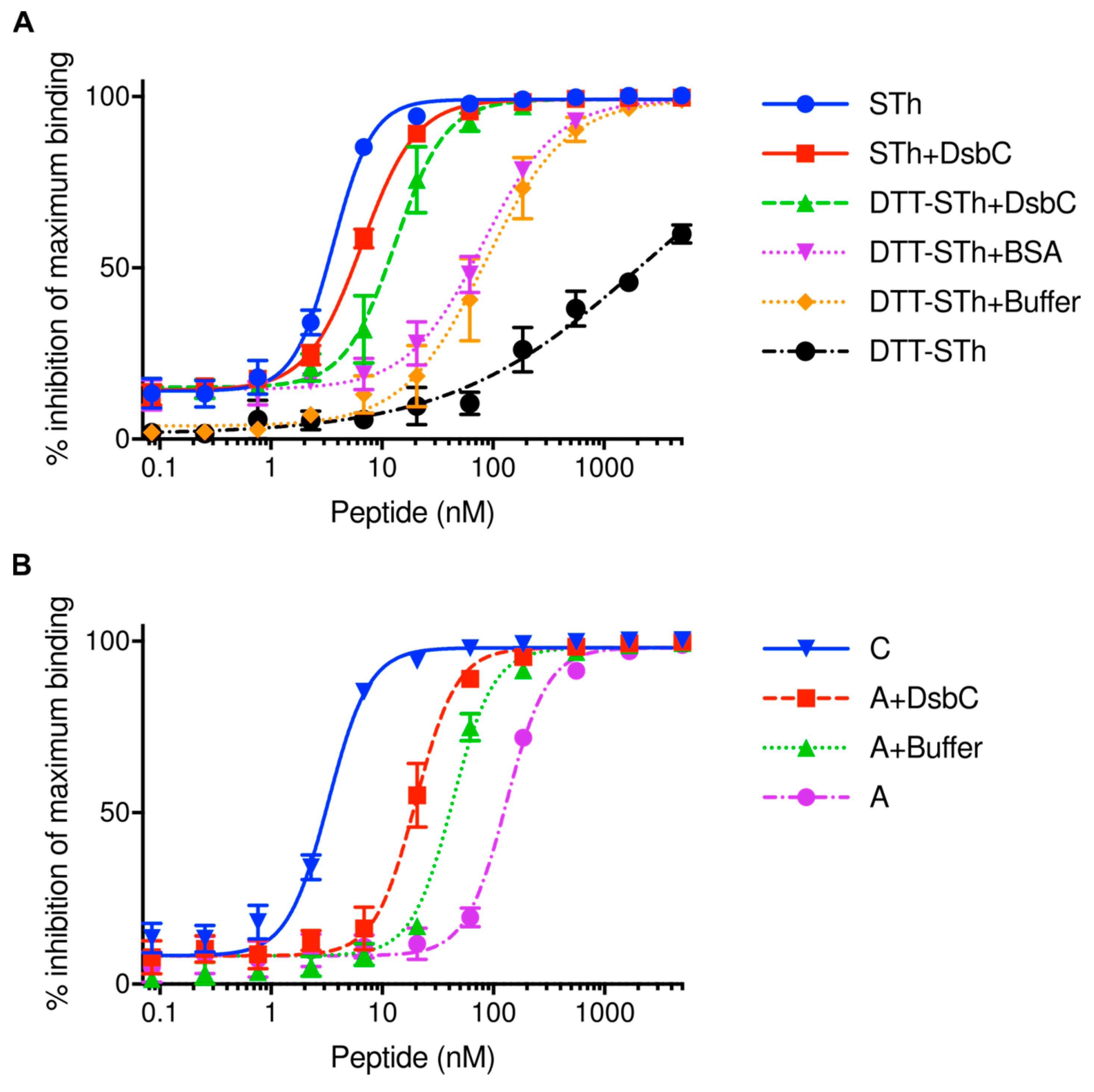
2.2. The Disulfide Isomerase DsbC Can Refold Misfolded STh In Vitro
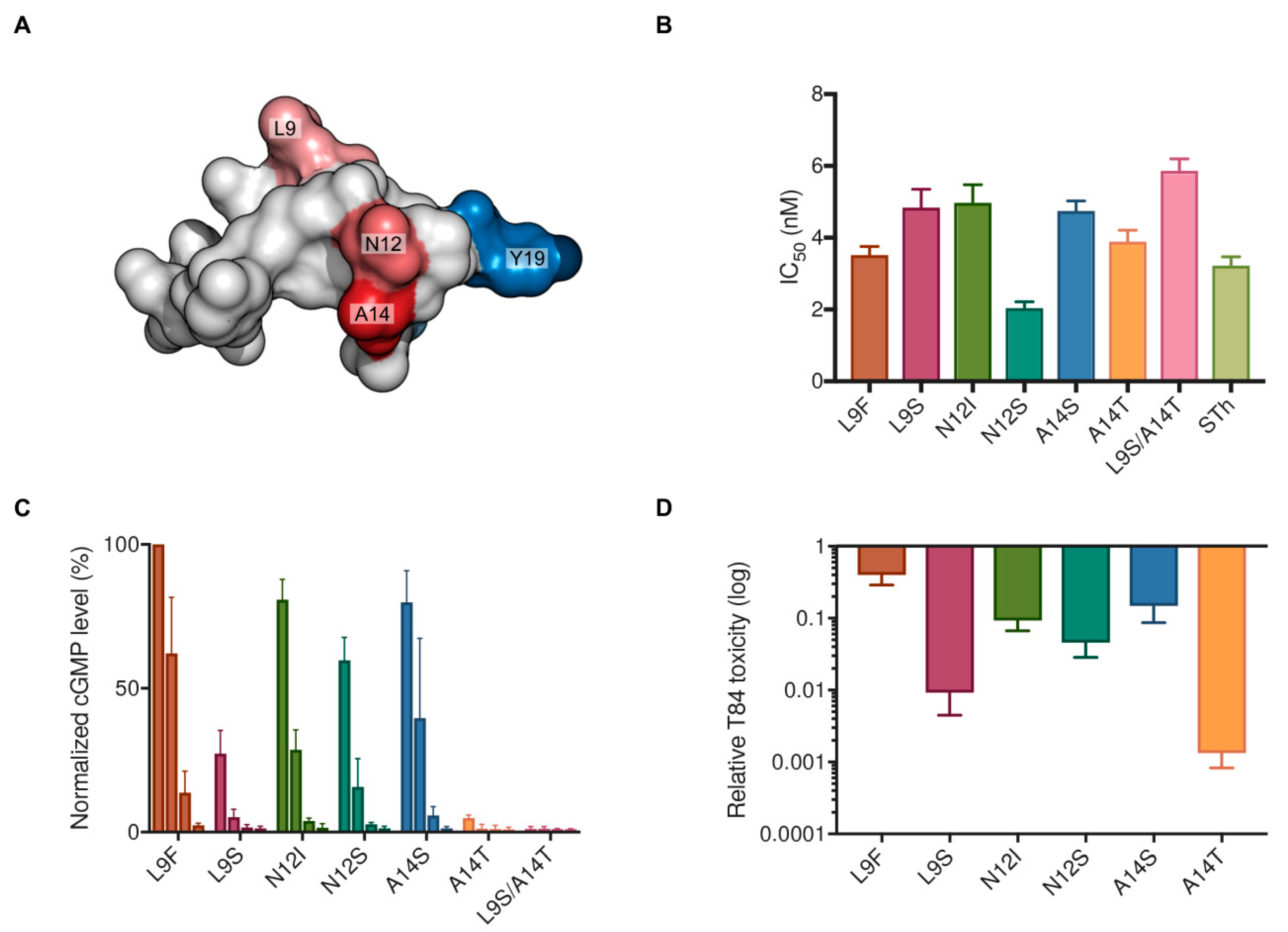
2.3. Characterization of Vaccine Candidate STh Mutants
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Construction of Native and Mutant ST Expression Vectors
4.2. Expression and Purification of DsbC-ST Fusion Proteins
4.3. Cleavage of DsbC-ST Fusion Proteins and Purification of ST Peptides
4.4. Competitive ST ELISA
4.5. T84 Cell Assay
4.6. Mass Spectrometry
4.7. Analytical Reversed-phase High-performance Liquid Chromatography
4.8. DsbC Assisted In Vitro Refolding of Denatured STh
4.9. Data and Statistical Analyses
5. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Future directions for research on enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli vaccines for developing countries. Wkly Epidemiol. Rec. 2006, 81, 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, C.L.F.; Rudan, I.; Liu, L.; Nair, H.; Theodoratou, E.; Bhutta, Z.A.; O’Brien, K.L.; Campbell, H.; Black, R.E. Global burden of childhood pneumonia and diarrhoea. Lancet 2013, 381, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2016, 388, 1459–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taxt, A.; Aasland, R.; Sommerfelt, H.; Nataro, J.; Puntervoll, P. Heat-stable enterotoxin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli as a vaccine target. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 1824–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vipin Madhavan, T.P.; Sakellaris, H. Colonization Factors of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 90, 155–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, M.K. Occurrence, distribution, and associations of O and H serogroups, colonization factor antigens, and toxins of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1997, 10, 569–584. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Steinsland, H.; Valentiner-Branth, P.; Perch, M.; Dias, F.; Fischer, T.K.; Aaby, P.; Mølbak, K.; Sommerfelt, H. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli infections and diarrhea in a cohort of young children in Guinea-Bissau. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 186, 1740–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porat, N.; Levy, A.; Fraser, D.; Deckelbaum, R.J.; Dagan, R. Prevalence of intestinal infections caused by diarrheagenic Escherichia coli in Bedouin infants and young children in Southern Israel. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1998, 17, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotloff, K.L.; Nataro, J.P.; Blackwelder, W.C.; Nasrin, D.; Farag, T.H.; Panchalingam, S.; Wu, Y.; Sow, S.O.; Sur, D.; Breiman, R.F.; et al. Burden and aetiology of diarrhoeal disease in infants and young children in developing countries (the Global Enteric Multicenter Study, GEMS): A prospective, case-control study. Lancet 2013, 382, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Platts-Mills, J.A.; Juma, J.; Kabir, F.; Nkeze, J.; Okoi, C.; Operario, D.J.; Uddin, J.; Ahmed, S.; Alonso, P.L.; et al. Use of quantitative molecular diagnostic methods to identify causes of diarrhoea in children: A reanalysis of the GEMS case-control study. Lancet 2016, 388, 1291–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platts-Mills, J.A.; Babji, S.; Bodhidatta, L.; Gratz, J.; Haque, R.; Havt, A.; McCormick, B.J.J.; McGrath, M.; Olortegui, M.P.; Samie, A.; et al. Pathogen-specific burdens of community diarrhoea in developing countries: A multisite birth cohort study (MAL-ED). Lancet Glob. Heal. 2015, 3, 564–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeois, A.L.; Wierzba, T.F.; Walker, R.I. Status of vaccine research and development for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Vaccine 2016, 34, 2880–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozaki, H.; Sato, T.; Kubota, H.; Hata, Y.; Katsube, Y.; Shimonishi, Y. Molecular structure of the toxin domain of heat-stable enterotoxin produced by a pathogenic strain of Escherichia coli. A putative binding site for a binding protein on rat intestinal epithelial cell membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 5934–5941. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Basu, N.; Arshad, N.; Visweswariah, S.S. Receptor guanylyl cyclase C (GC-C): regulation and signal transduction. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 334, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taxt, A.M.; Diaz, Y.; Bacle, A.; Grauffel, C.; Reuter, N.; Aasland, R.; Sommerfelt, H.; Puntervoll, P. Characterization of immunological cross-reactivity between enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli heat-stable toxin and human guanylin and uroguanylin. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 2913–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taxt, A.M.; Diaz, Y.; Aasland, R.; Clements, J.D.; Nataro, J.P.; Sommerfelt, H.; Puntervoll, P. Towards Rational Design of a Toxoid Vaccine against the Heat-Stable Toxin of Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 2016, 84, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clements, J.D. Construction of a nontoxic fusion peptide for immunization against Escherichia coli strains that produce heat-labile and heat-stable enterotoxins. Infect. Immun. 1990, 58, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cárdenas, L.; Clements, J.D. Development of mucosal protection against the heat-stable enterotoxin (ST) of Escherichia coli by oral immunization with a genetic fusion delivered by a bacterial vector. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 4629–4636. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pereira, C.M.; Guth, B.E.; Sbrogio-Almeida, M.E.; Castilho, B.A. Antibody response against Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin expressed as fusions to flagellin. Microbiology 2001, 147, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löwenadler, B.; Lake, M.; Elmblad, A.; Holmgren, E.; Holmgren, J.; Karlström, A.; Svennerholm, A.M. A recombinant Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin (STa) fusion protein eliciting anti-STa neutralizing antibodies. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1991, 66, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, C.; Francis, D.H.; Fang, Y.; Knudsen, D.; Nataro, J.P.; Robertson, D.C. Genetic fusions of heat-labile (LT) and heat-stable (ST) toxoids of porcine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli elicit neutralizing anti-LT and anti-STa antibodies. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Ruan, X.; Zhang, C.; Lawson, S.R.; Knudsen, D.E.; Nataro, J.P.; Robertson, D.C.; Zhang, W. Heat-labile- and Heat-stable-toxoid fusions (LTR192G-STaP13F) of human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli elicit neutralizing antitoxin antibodies. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 4002–4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, W. Escherichia coli K88ac fimbriae expressing heat-labile and heat-stable (STa) toxin epitopes elicit antibodies that neutralize cholera toxin and STa toxin and inhibit adherence of K88ac fimbrial E. coli. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2010, 17, 1859–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, T.; Takeda, Y.; Aimoto, S.; Takao, T.; Ikemura, H.; Shimonishi, Y.; Miwatani, T. Neutralization of activity of two different heat-stable enterotoxins (STh and STp) of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by homologous and heterologous antisera. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1983, 20, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockwood, D.E.; Robertson, D.C. Development of a competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin (STa). J. Immunol. Methods 1984, 75, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandwein, H.; Deutsch, A.; Thompson, M.; Giannella, R. Production of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect. Immun. 1985, 47, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zeng, W.; Azzopardi, K.; Hocking, D.; Wong, C.Y.; Robevska, G.; Tauschek, M.; Robins-Browne, R.M.; Jackson, D.C. A totally synthetic lipopeptide-based self-adjuvanting vaccine induces neutralizing antibodies against heat-stable enterotoxin from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Vaccine 2012, 30, 4800–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klipstein, F.A.; Engert, R.F.; Clements, J.D.; Houghten, R.A. Protection against human and porcine enterotoxigenic strains of Escherichia coli in rats immunized with a cross-linked toxoid vaccine. Infect. Immun. 1983, 40, 924–929. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Svennerholm, A.M.; Lundgren, A. Recent progress toward an enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli vaccine. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2012, 11, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, C.; Mateo, K.; Nataro, J.P.; Robertson, D.C.; Zhang, W. Modified heat-stable toxins (hSTa) of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli lose toxicity but display antigenicity after being genetically fused to heat-labile toxoid LT(R192G). Toxins 2011, 3, 1146–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staples, S.J.; Asher, S.E.; Giannella, R.A. Purification and characterization of heat-stable enterotoxin produced by a strain of E. coli pathogenic for man. J. Biol. Chem. 1980, 255, 4716–4721. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dreyfus, L.A.; Frantz, J.C.; Robertson, D.C. Chemical properties of heat-stable enterotoxins produced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli of different host origins. Infect. Immun. 1983, 42, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aref, N.E.M.; Saeed, A.M. An enhanced protocol for expression and purification of heat-stable enterotoxin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2012, 26, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, X.; Robertson, D.C.; Nataro, J.P.; Clements, J.D.; Zhang, W. Characterization of heat-stable (STa) toxoids of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli fused to double mutant heat-labile toxin peptide in inducing neutralizing Anti-STa antibodies. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 1823–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiglmeier, P.R.; Berkner, H.; Seebahn, A.; Vogel, N.; Schreiber, R.; Wöhrl, B.M.; Schwarzinger, S.; Rösch, P. Prosequence switching: An effective strategy to produce biologically active E. coli heat-stable enterotoxin STh. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2014, 32, 1537–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nozach, H.; Fruchart-Gaillard, C.; Fenaille, F.; Beau, F.; Ramos, O.H.P.; Douzi, B.; Saez, N.J.; Moutiez, M.; Servent, D.; Gondry, M.; et al. High throughput screening identifies disulfide isomerase DsbC as a very efficient partner for recombinant expression of small disulfide-rich proteins in E. coli. Microb. Cell Fact. 2013, 12, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandre, R.M.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W. Passive antibodies derived from intramuscularly immunized toxoid fusion 3xSTa N12S -dmLT protect against STa+ enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) diarrhea in a pig model. Vaccine 2017, 35, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogomolovas, J.; Simon, B.; Sattler, M.; Stier, G. Screening of fusion partners for high yield expression and purification of bioactive viscotoxins. Protein Expr. Purif. 2009, 64, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapust, R.B.; Tözsér, J.; Copeland, T.D.; Waugh, D.S. The P1’ specificity of tobacco etch virus protease. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 294, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Berg, S.; Löfdahl, P.Å.; Härd, T.; Berglund, H. Improved solubility of TEV protease by directed evolution. J. Biotechnol. 2006, 121, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klint, J.K.; Senff, S.; Saez, N.J.; Seshadri, R.; Lau, H.Y.; Bende, N.S.; Undheim, E.A.B.; Rash, L.D.; Mobli, M.; King, G.F. Production of Recombinant Disulfide-Rich Venom Peptides for Structural and Functional Analysis via Expression in the Periplasm of E. coli. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PeptideSynthetics Peptide Mass Calculator. Available online: http://www.peptidesynthetics.co.uk/tools/ (accessed on 8 August 2017).

| Primer | Nucleotide Sequence |
|---|---|
| STh-F | tgtaatcctgcttgtaccgggtgctattaaGGCGCCATGGGCAAAGTG |
| STp-F | taatcctgcttgtgctggttgctattaaGGCGCCATGGGCAAAGTG |
| STh-N12I-F | tgtatccctgcttgtaccgggtgctattaaGGCGCCATGGGCAAAGTG |
| STh-N12S-F | tgtagccctgcttgtaccgggtgctattaaGGCGCCATGGGCAAAGTG |
| STh-A14S-F | tgtaatcctagctgtaccgggtgctattaaGGCGCCATGGGCAAAGTG |
| STh-A14T(a)-F | tgtaatcctacttgtaccgggtgctattaaGGCGCCATGGGCAAAGTG |
| STh-A14T(b)-F | tgtaatcctacatgtaccgggtgctattaaGGCGCCATGGGCAAAGTG |
| DsbC-TAA-F | taaGCCATGGGCAAAGTGAGC |
| STh-R | acacaattcacagcagtaattgctactattCTGAAAATAAAGATTCTCGCTACCCG |
| STp-R | caacacaattcacagcagtagaaggtattCTGAAAATAAAGATTCTCGCTACCCG |
| STh-L9A-R | acatgcttcacagcagtaattgctactattCTGAAAATAAAGATTCTCGCTACCCG |
| STh-L9F-R | acaaaattcacagcagtaattgctactattCTGAAAATAAAGATTCTCGCTACCCG |
| STh-L9N-R | acagttttcacagcagtaattgctactattCTGAAAATAAAGATTCTCGCTACCCG |
| STh-L9S-R | acaactttcacagcagtaattgctactattCTGAAAATAAAGATTCTCGCTACCCG |
| STh-N12S-R | acacagttcacagcagtaattgctactattCTGAAAATAAAGATTCTCGCTACCCG |
| DsbC-TAA-R | GCCCTGAAAATAAAGATTCTCGC |
| Plasmid | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer | ST Variant |
|---|---|---|---|
| pET-DsbC-STh | STh-F | STh-R | STh |
| pET-DsbC-STp | STp-F | STp-R | STp |
| pET-DsbC-STh-L9A | STh-F | STh-L9A-R | STh-L9A |
| pET-DsbC-STh-L9F | STh-F | STh-L9F-R | STh-L9F |
| pET-DsbC-STh-L9N | STh-F | STh-L9N-R | STh-L9N |
| pET-DsbC-STh-L9S | STh-F | STh-L9S-R | STh-L9S |
| pET-DsbC-STh-N12S | STh-N12S-F | STh-N12S-R | STh-N12S |
| pET-DsbC-STh-N12I | STh-N12I-F | STh-R | STh-N12I |
| pET-DsbC-STh-A14S | STh-A14S-F | STh-R | STh-A14S |
| pET-DsbC-STh-A14T | STh-A14T(a)-F | STh-R | STh-A14T |
| pET-DsbC-STh-L9S/A14T | STh-A14T(b)-F | STh-L9S-R | STh-L9S/A14T |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Govasli, M.L.; Diaz, Y.; Zegeye, E.D.; Darbakk, C.; Taxt, A.M.; Puntervoll, P. Purification and Characterization of Native and Vaccine Candidate Mutant Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Heat-Stable Toxins. Toxins 2018, 10, 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10070274
Govasli ML, Diaz Y, Zegeye ED, Darbakk C, Taxt AM, Puntervoll P. Purification and Characterization of Native and Vaccine Candidate Mutant Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Heat-Stable Toxins. Toxins. 2018; 10(7):274. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10070274
Chicago/Turabian StyleGovasli, Morten L., Yuleima Diaz, Ephrem Debebe Zegeye, Christine Darbakk, Arne M. Taxt, and Pål Puntervoll. 2018. "Purification and Characterization of Native and Vaccine Candidate Mutant Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Heat-Stable Toxins" Toxins 10, no. 7: 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10070274
APA StyleGovasli, M. L., Diaz, Y., Zegeye, E. D., Darbakk, C., Taxt, A. M., & Puntervoll, P. (2018). Purification and Characterization of Native and Vaccine Candidate Mutant Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Heat-Stable Toxins. Toxins, 10(7), 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10070274




