The Impact of T-2 Toxin on Vasoactive Intestinal Polypeptide-Like Immunoreactive (VIP-LI) Nerve Structures in the Wall of the Porcine Stomach and Duodenum
Abstract
1. Introduction
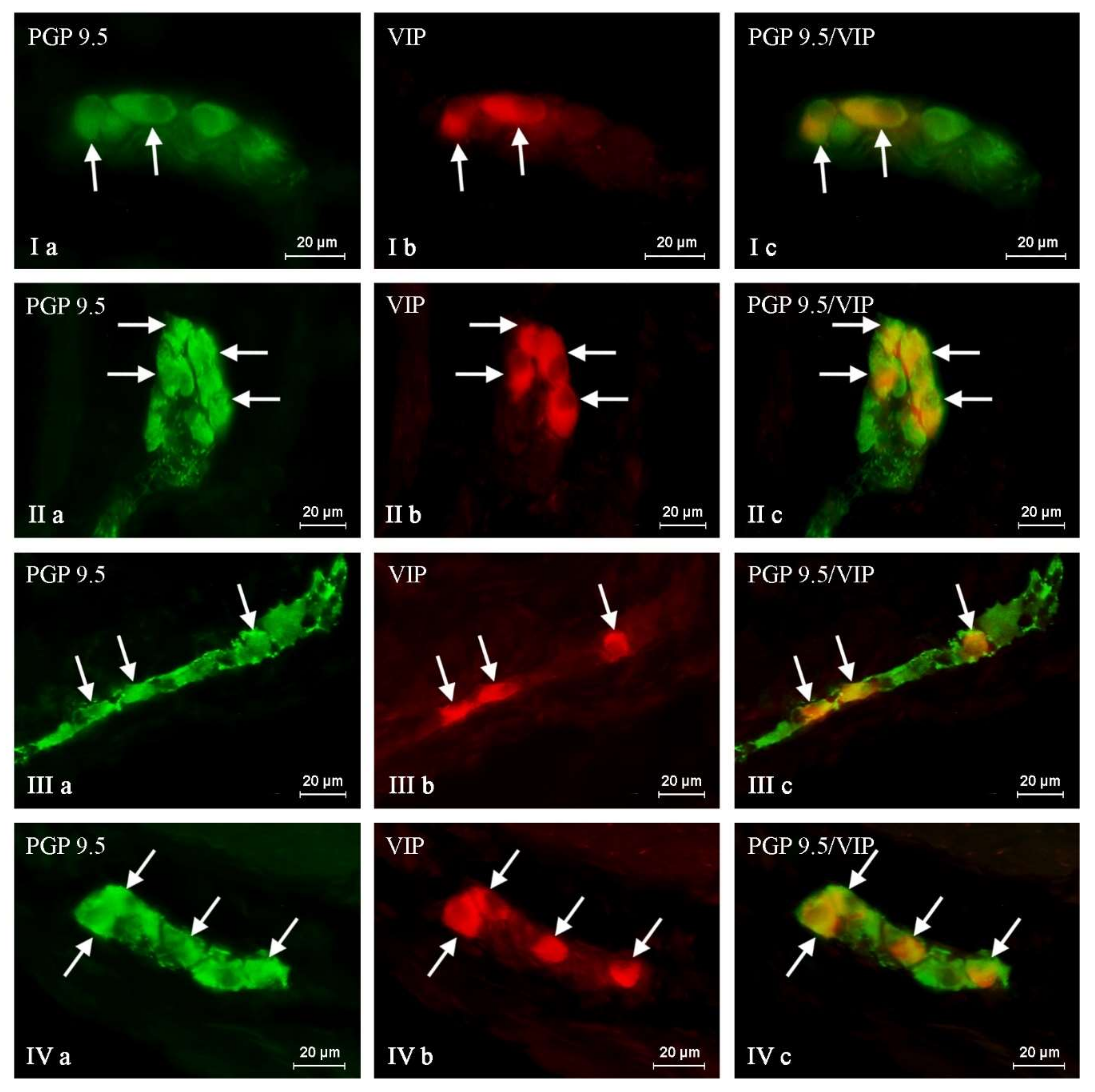
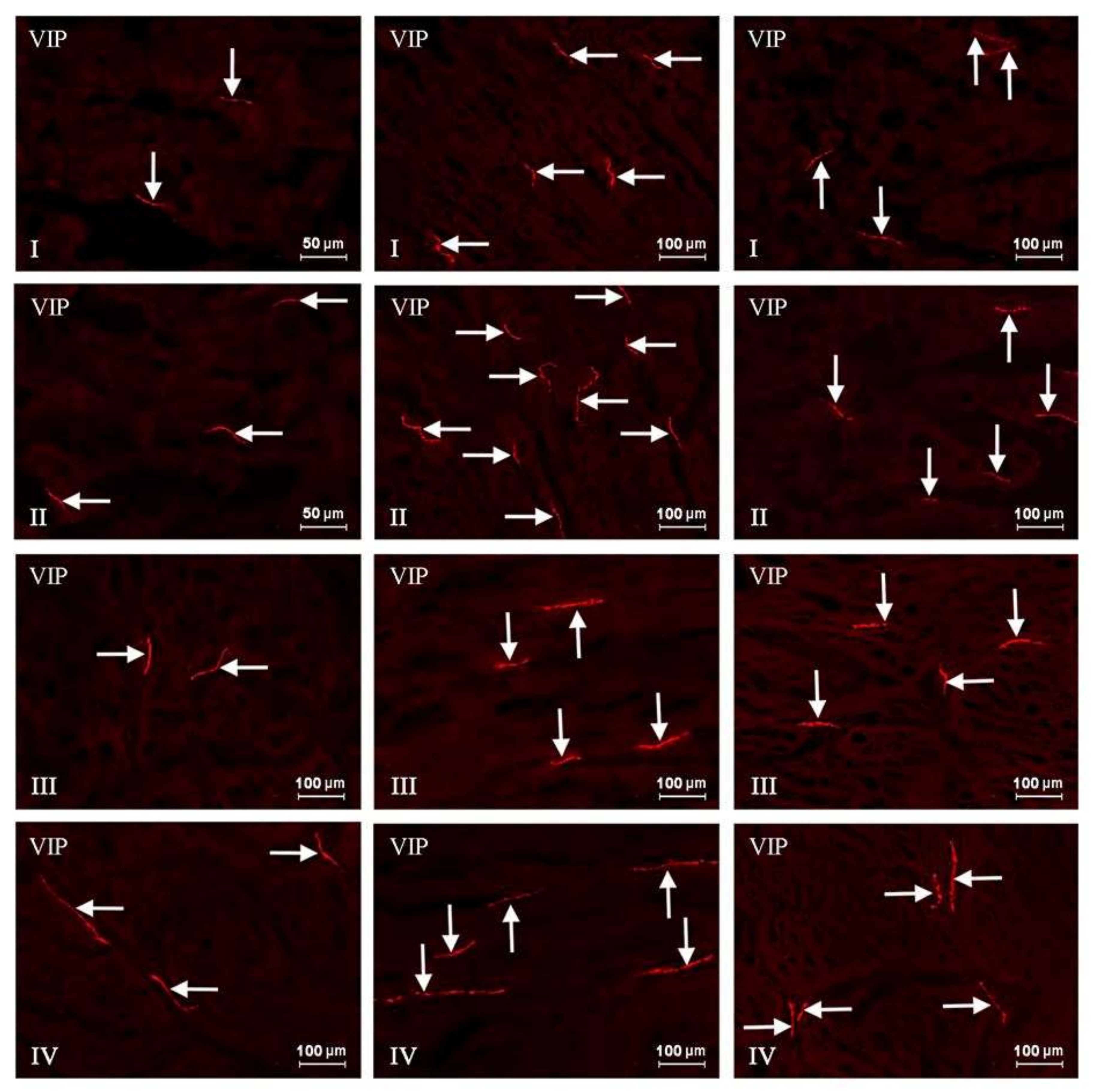
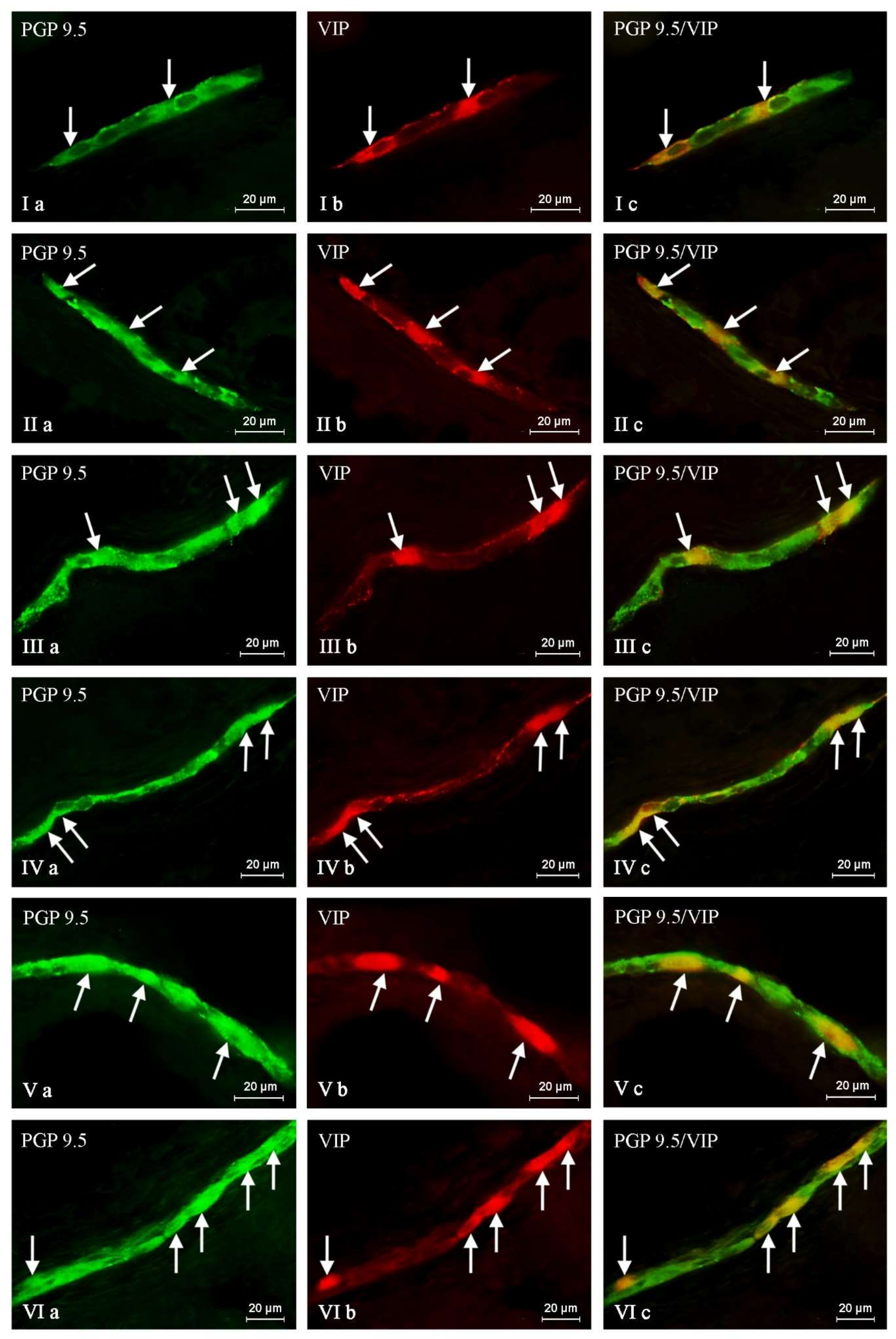
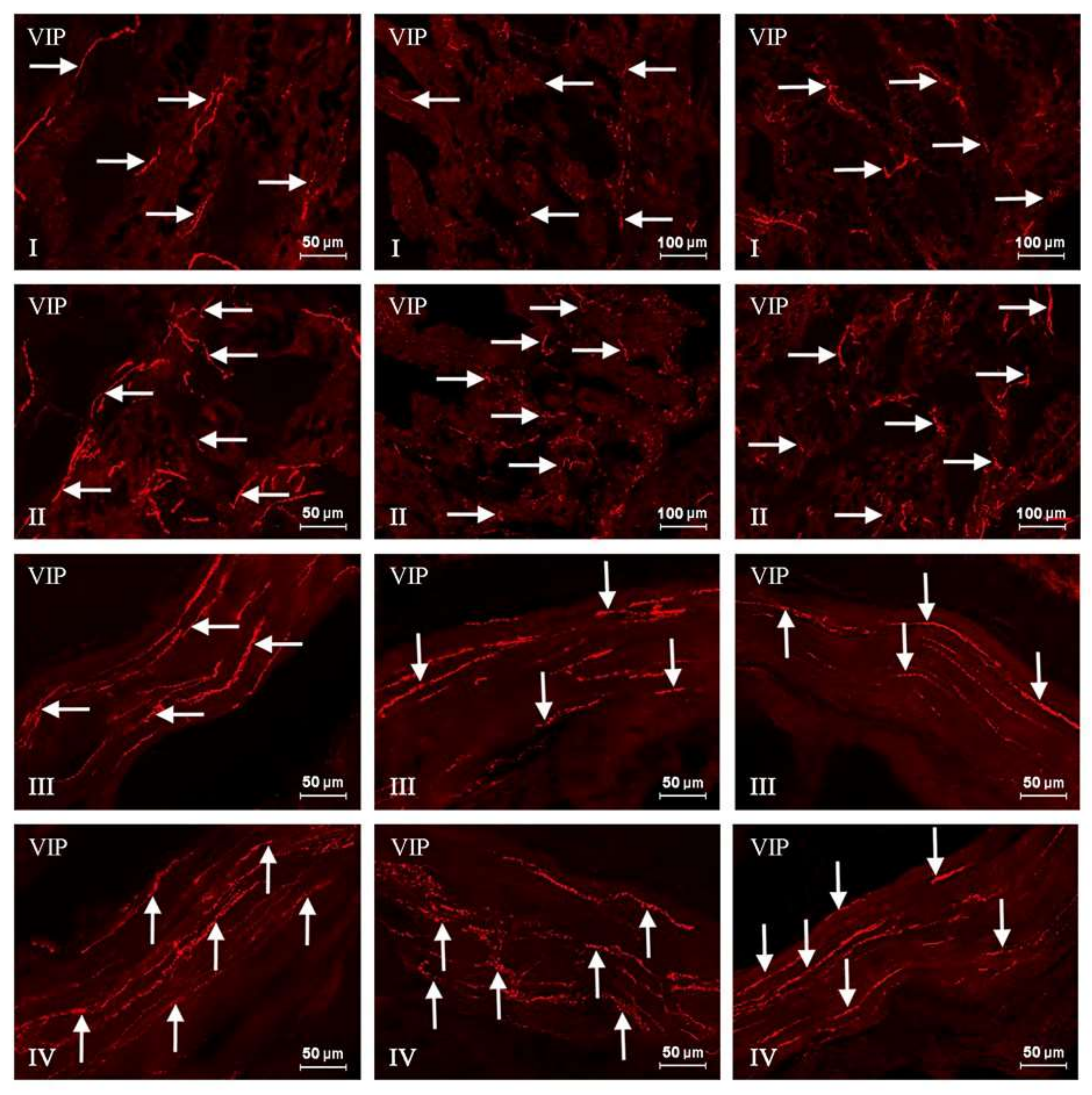
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lewis, L.; Onsongo, M.; Njapau, H.; Schurz-Rogers, H.; Luber, G.; Kieszak, S.; Nyamongo, J.; Backer, L.; Dahiye, A.M.; Misore, A.; et al. Kenya Aflatoxicosis Investigation Group. Aflatoxin contamination of commercial maize products during an outbreak of acute aflatoxicosis in eastern and central Kenya. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 1763–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Ruyck, K.; De Boevre, M.; Huybrechts, I.; De Saeger, S. Dietary mycotoxins, co-exposure, and carcinogenesis in humans: Short review. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2015, 766, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretti, A.; Logrieco, A.F.; Susca, A. Mycotoxins: An underhand food problem. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1542, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Makowska, K.; Obremski, K.; Zielonka, L.; Gonkowski, S. The Influence of Low Doses of Zearalenone and T-2 Toxin on Calcitonin Gene Related Peptide-Like Immunoreactive (CGRP-LI) Neurons in the ENS of the Porcine Descending Colon. Toxins 2017, 9, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, M.J.; Macáková, P.; Juan-García, A.; Font, G. Cytotoxic effects of mycotoxin combinations in mammalian kidney cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 2718–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, M.; Negi, B.; Kaushik, N.; Adhikari, A.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A.; Kaushik, N.K.; Choi, E.H. T-2 mycotoxin: Toxicological effects and decontamination strategies. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 33933–33952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makowska, K.; Gonkowski, S.; Zielonka, L.; Dabrowski, M.; Calka, J. T2 Toxin-Induced Changes in Cocaine- and Amphetamine-Regulated Transcript (CART)-Like Immunoreactivity in the Enteric Nervous System Within Selected Fragments of the Porcine Digestive Tract. Neurotox. Res. 2017, 31, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidner, M.; Huwel, S.; Ebert, F.; Schwerdtle, T.; Galla, H.J.; Humpf, H.U. Influence of T-2 and HT-2 toxin on the blood-brain barrier in vitro: New experimental hints for neurotoxic effects. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutsky, I.; Mor, N. Alimentary toxic aleukia (septic angina, endemic panmyelotoxicosis, alimentary hemorrhagic aleukia): T-2 toxin-induced intoxication of cats. Am. J. Pathol. 1981, 104, 189–191. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martin, L.J.; Doebler, J.A.; Anthony, A. Scanning cytophotometric analysis of brain neuronal nuclear chromatin changes in acute T-2 toxin-treated rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1986, 85, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonkowski, S.; Kamińska, B.; Landowski, P.; Całka, J. Immunohistochemical distribution of cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript peptide—Like immunoreactive (CART-LI) nerve fibers and various degree of co-localization with other neuronal factors in the circular muscle layer of human descending colon. Histol. Histopathol. 2013, 28, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makowska, K.; Gonkowski, S. The Influence of Inflammation and Nerve Damage on the Neurochemical Characterization of Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide-Like Immunoreactive (CGRP-LI) Neurons in the Enteric Nervous System of the Porcine Descending Colon. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furness, J.B.; Callaghan, B.P.; Rivera, L.R.; Cho, H.J. The enteric nervous system and gastrointestinal innervation: Integrated local and central control. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 817, 39–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makowska, K.; Gonkowski, S. Cocaine-And Amphetamine-Regulated Transcript (Cart) Peptide in Mammals Gastrointestinal System—A Review. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2017, 17, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Furness, J.B. Types of neurons in the enteric nervous system. J. Autonom. Nerv. Syst. 2000, 81, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasparek, M.S.; Fatima, J.; Iqbal, C.W.; Duenes, J.A.; Sarr, M.G. Role of VIP and Substance P in NANC innervation in the longitudinal smooth muscle of the rat jejunum -influence of extrinsic denervation. J. Surg. Res. 2007, 141, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rytel, L.; Palus, K.; Calka, J. Co-expression of PACAP with VIP, SP and CGRP in the porcine nodose ganglion sensory neurons. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2015, 44, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashima, M.; Morrison, K.J.; Vanhoutte, P.M. Hyperpolarization and relaxation of canine vascular smooth muscle to vasoactive intestinal polypeptide. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1997, 30, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Geldre, L.A.; Lefebvre, R.A. Interaction of NO and VIP in gastrointestinal smooth muscle relaxation. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2004, 10, 2483–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassar, C.F.; Abdallah, L.E.; Barada, K.A.; Atweh, S.F.; Saadé, N.F. Effects of intravenous vasoactive intestinal peptide injection on jejunal alanine absorption and gastric acid secretion in rats. Regul. Pept. 1995, 55, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burleigh, D.E.; Banks, M.R. Stimulation of intestinal secretion by vasoactive intestinal peptide and cholera toin. Auton. Neurosci. Basic Clin. 2007, 133, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaleczyc, J.; Klimczuk, M.; Franke-Radowiecka, A.; Sienkiewicz, W.; Majewski, M.; Łakomy, M. The distribution and chemical coding of intramural neurons supplying the porcine stomach—The study on normal pigs and on animals suffering from swine dysentery. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2007, 36, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arciszewski, M.B.; Sand, E.; Ekblad, E. Vasoactive intestinal peptide rescues cultured rat myenteric neurons from lipopolysaccharide induced cell death. Regul. Pept. 2008, 146, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pidsudko, Z.; Kaleczyc, J.; Wasowicz, K.; Sienkiewicz, W.; Majewski, M.; Zajac, W.; Lakomy, M. Distribution and chemical coding of intramural neurons in the porcine ileum during proliferative enteropathy. J. Comp. Pathol. 2008, 138, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonkowski, S.; Obremski, K.; Calka, J. The Influence of Low Doses of Zearalenone on Distribution of Selected Active Substances in Nerve Fibers within the Circular Muscle Layer of Porcine Ileum. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2015, 56, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasina, V.; Barbara, G.; Talamonti, L.; Stanghellini, V.; Corinaldesi, R.; Tonini, M.; de Ponti, F.; de Giorgio, R. Enteric neuroplasticity evoked by inflammation. Auton. Neurosci. 2006, 126–127, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonkowski, S.; Burlinski, P.; Calka, J. Proliferative enteropathy (PE)-induced changes in galanin-like immunoreactivity in the enteric nervous system of the porcine distal colon. Acta Vet. 2009, 59, 321–330. [Google Scholar]
- Gonkowski, S.; Burlinski, P.; Skobowiat, C.; Majewski, M.; Calka, J. Inflammation- And Axotomy-Induced Changes In Galanin-Like Immunoreactive (Gal-Li) Nerve Structures In The Porcine Descending Colon. Acta Vet. Hung. 2010, 58, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonkowski, S. Substance P as a neuronal factor in the enteric nervous system of the porcine descending colon in physiological conditions and during selected pathogenic processes. Biofactors 2013, 39, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmermans, J.P.; Adriaensen, D.; Cornelissen, W.; Scheuermann, D.W. Structural organization and neuropeptide distribution in the mammalian enteric nervous system, with special attention to those components involved in mucosal reflexes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Physiol. 1997, 118, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonkowski, S.; Wojtkiewicz, J.; Bossowska, A.; Kaleczyc, J.; Sienkiewicz, W.; Majewski, M. Proliferative enteropathy (PE)-induced changes in the number of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-immunoreactive (VIP-IR) neural elements in the porcine descending colon. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2004, 7, 53–55. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, N.; Rettenmeier, A.W.; Schmitz-Spanke, S. Recent advances in the use of Sus scrofa (pig) as a model system for proteomic studies. Proteomics 2011, 11, 776–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, R.J.; Schemann, M.; Santer, R.M.; Cowen, T. The effects of age on the overall population and on sub-populations of myenteric neurons in the rat small intestine. J. Anat. 1998, 192, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinschmidt, S.; Nolte, I.; Hewicker-Trautwein, M. Structural and functional changes of neuronal and glial components of the feline enteric nervous system in cats with chronic inflammatory and non-inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Res. Vet. Sci. 2011, 91, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenneman, D.E.; Philips, T.M.; Hauser, J.; Hill, J.M.; Spong, C.Y.; Gozes, I. Complex array of cytokines released by vasoactive intestinal peptide. Neuropeptides 2003, 37, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vota, D.; Aguero, M.; Grasso, E.; Hauk, V.; Gallino, L.; Soczewski, E.; Pérez Leirós, C.; Ramhorst, R. Progesterone and VIP cross-talk enhances phagocytosis and anti-inflammatory profile in trophoblast-derived cells. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2017, 443, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obremski, K.; Gonkowski, S.; Wojtacha, P. Zearalenone-induced changes in the lymphoid tissue and mucosal nerve fibers in the porcine ileum. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2015, 18, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bednarska, O.; Walter, S.A.; Casado-Bedmar, M.; Ström, M.; Salvo-Romero, E.; Vicario, M.; Mayer, E.A.; Keita, Å.V. Vasoactive Intestinal Polypeptide and Mast Cells Regulate Increased Passage of Colonic Bacteria in Patients With Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 948–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchgessner, A.L.; Dodd, J.; Gershon, M.D. Markers shared between dorsal root and enteric ganglia. J. Comp. Neurol. 1988, 276, 607–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Beier, R.C.; Shen, J.; De Smet, D.; De Saeger, S.; Zhang, S. T-2 toxin, a trichothecene mycotoxin: Review of toxicity, metabolism, and analytical methods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 3441–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, I.M.; Mar, W.C. Effect of T-2 toxin on lipid peroxidation in rats: Elevation of conjugated diene formation. Toxicol. Lett. 1988, 40, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shifrin, V.I.; Anderson, P. Trichothecene mycotoxins trigger a ribotoxic stress response that activates c-jun N-terminal kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and induces apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 13985–13992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Fitzpatrick, D.W.; Wilson, J.R. Effects of the trichothecene mycotoxin T-2 toxin on neurotransmitters and metabolites in discrete areas of the rat brain. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1998, 36, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehata, S.; Kiyosawa, N.; Makino, T.; Atsumi, F.; Ito, K.; Yamoto, T.; Teranishi, M.; Baba, Y.; Uetauka, K.; Nakayama, H.; et al. Morphological and microarray analysis of T-2 toxin-induced rat fetal brain lesion. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2004, 42, 1727–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, K.; Uetsuka, K. Mechanisms of mycotoxin-induced neurotoxicity through oxidative stress-associated pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 5213–5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenneman, D.E.; Nicol, T.; Warren, D.; Bowers, L.M. Vasoactive intestinal peptide: A neurotrophic releasing agent and an astroglial mitogen. J. Neurosci. Res. 1990, 25, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazillis, M.; Gonzalez, B.J.; Billardon, C.; Lombet, A.; Fraichard, A.; Samarut, J.; Gressens, P.; Vaudry, H.; Rostène, W. VIP and PACAP induce selective neuronal differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 19, 798–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passemard, S.; Sokolowska, P.; Schwendimann, L.; Gressens, P. VIP-induced neuroprotection of the developing brain. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 1036–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangon, C.M.; Dicou, E.; Goursaud, S.; Mounien, L.; Jégou, S.; Janet, T.; Muller, J.M.; Lelièvre, V.; Gressens, P. Mechanisms of VIP-induced neuroprotection against neonatal excitotoxicity. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1070, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gressens, P.; Marret, S.; Hill, J.M.; Brenneman, D.E.; Gozes, I.; Fridkin, M.; Evrard, P. Vasoactive intestinal peptide prevents excitotoxic cell death in the murine developing brain. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carniglia, L.; Ramírez, D.; Durand, D.; Saba, J.; Turati, J.; Caruso, C.; Scimonelli, T.N.; Lasaga, M. Neuropeptides and Microglial Activation in Inflammation, Pain, and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 5048616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekharan, B.; Nezami, B.G.; Srinivasan, S. Emerging neuropeptide targets in inflammation: NPY and VIP. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2013, 304, G949–G957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandgren, K.; Lin, Z.; Ekblad, E. Differential effects of VIP and PACAP on survival of cultured adult rat myenteric neurons. Regul. Pept. 2003, 111, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, J.; Pasmans, F.; Verbrugghe, E.; Vandenbroucke, V.; De Baere, S.; Meyer, E.; Haesebrouck, F.; De Backer, P.; Croubels, S. Porcine intestinal epithelial barrier disruption by the Fusarium mycotoxins deoxynivalenol and T-2 toxin promotes transepithelial passage of doxycycline and paromomycin. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obremski, K.; Zielonka, L.; Gajecka, M.; Jakimiuk, E.; Bakuła, T.; Baranowski, M.; Gajecki, M. Histological estimation of the small intestine wall after administration of feed containing deoxynivalenol, T-2 toxin and zearalenone in the pig. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2008, 11, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moriez, R.; Abdo, H.; Chaumette, T.; Faure, M.; Lardeux, B.; Neunlist, M. Neuroplasticity and neuroprotection in enteric neurons: Role of epithelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 382, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganea, D.; Hooper, K.M.; Kong, W. The neuropeptide vasoactive intestinal peptide: Direct effects on immune cells and involvement in inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Acta Physiol 2015, 213, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, M.; Munoz-Elias, E.J.; Gomariz, R.P.; Ganea, D. Vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide enhance IL-10 production by murine macrophages: In vitro and in vivo studies. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 1707–1716. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Delgado, M.; Pozo, D.; Ganea, D. The significance of vasoactive intestinal peptide in immunomodulation. Pharmacol. Rev. 2004, 56, 249–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obremski, K.; Podlasz, P.; Zmigrodzka, M.; Winnicka, A.; Woźny, M.; Brzuzan, P.; Jakimiuk, E.; Wojtacha, P.; Gajecka, M.; Zielonka, Ł.; et al. The effect of T-2 toxin on percentages of CD4+, CD8+, CD4+ CD8+ and CD21+ lymphocytes, and mRNA expression levels of selected cytokines in porcine ileal Peyer’s patches. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2013, 16, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| STOMACH | Group C | Group T2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CML 1 | 4.26 ± 0.21 | 5.17 ± 0.11 * | |
| MP | CB 2 | 37.56± 0.84 | 42.85 ± 0.74 * |
| NF 3 | + | + | |
| SP | CB 2 | 36.78 ± 0.4 | 43.83 ± 1.18 * |
| NF 3 | − | + | |
| S/ML 1 | 2.84 ± 0.07 | 4.15 ± 0.15 * | |
| DUDODENUM | Group C | Group T2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CML 1 | 17.08 ± 0.08 | 21.22 ± 0.24 * | |
| MP | CB 2 | 31.45 ± 0.77 | 39.24 ± 1.02 * |
| NF 3 | + | ++ | |
| OSP | CB 2 | 32.43 ± 1.83 | 40.59 ± 0.67 * |
| NF 3 | ++ | ++ | |
| ISP | CB 2 | 28.50 ± 1.17 | 35.42 ± 1.52 * |
| NF 3 | + | ++ | |
| S/ML 1 | 32.35 ± 0.32 | 39.97 ± 1.23 * | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Makowska, K.; Obremski, K.; Gonkowski, S. The Impact of T-2 Toxin on Vasoactive Intestinal Polypeptide-Like Immunoreactive (VIP-LI) Nerve Structures in the Wall of the Porcine Stomach and Duodenum. Toxins 2018, 10, 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10040138
Makowska K, Obremski K, Gonkowski S. The Impact of T-2 Toxin on Vasoactive Intestinal Polypeptide-Like Immunoreactive (VIP-LI) Nerve Structures in the Wall of the Porcine Stomach and Duodenum. Toxins. 2018; 10(4):138. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10040138
Chicago/Turabian StyleMakowska, Krystyna, Kazimierz Obremski, and Slawomir Gonkowski. 2018. "The Impact of T-2 Toxin on Vasoactive Intestinal Polypeptide-Like Immunoreactive (VIP-LI) Nerve Structures in the Wall of the Porcine Stomach and Duodenum" Toxins 10, no. 4: 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10040138
APA StyleMakowska, K., Obremski, K., & Gonkowski, S. (2018). The Impact of T-2 Toxin on Vasoactive Intestinal Polypeptide-Like Immunoreactive (VIP-LI) Nerve Structures in the Wall of the Porcine Stomach and Duodenum. Toxins, 10(4), 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10040138






