A Sensitive LC-MS/MS Method for Palytoxin Using Lithium Cationization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
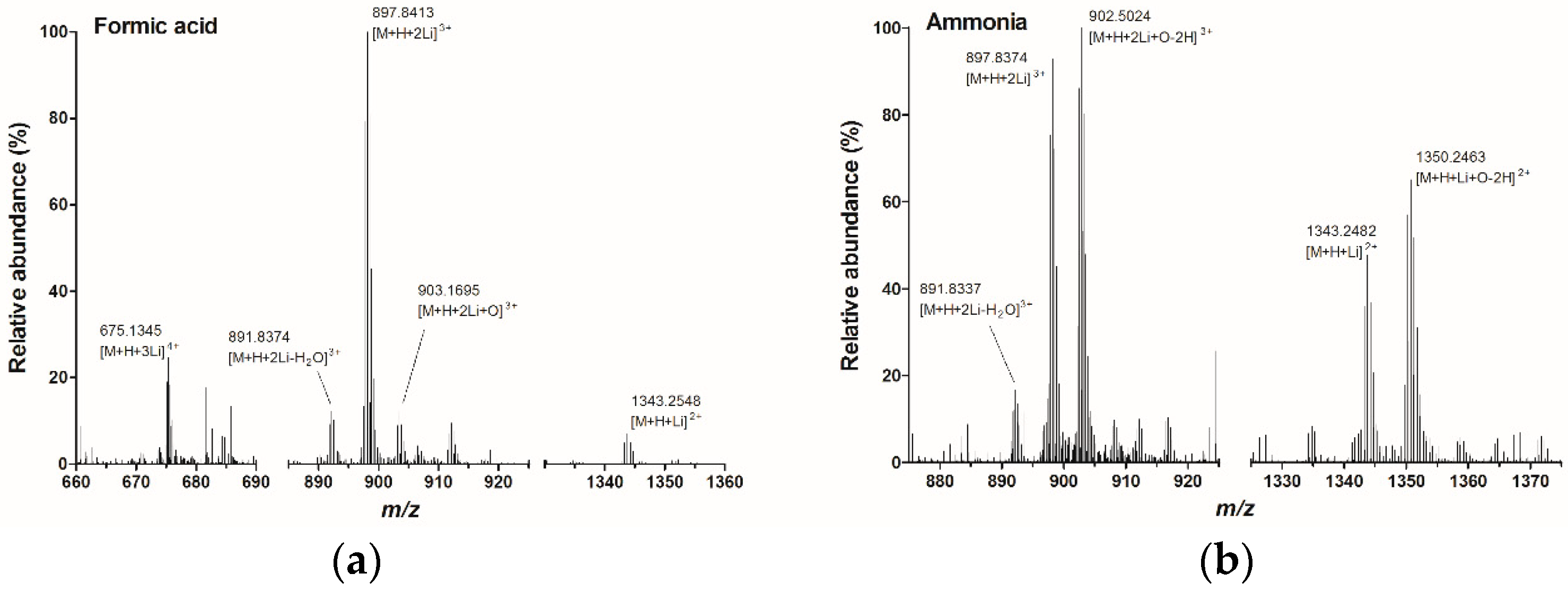
2.1. Infusion Experiments with High Resolution Mass Spectrometry
2.2. Fragmentation PlTX with High Resolution Mass Spectrometry
2.3. Chromatography
2.4. Sample Clean-Up
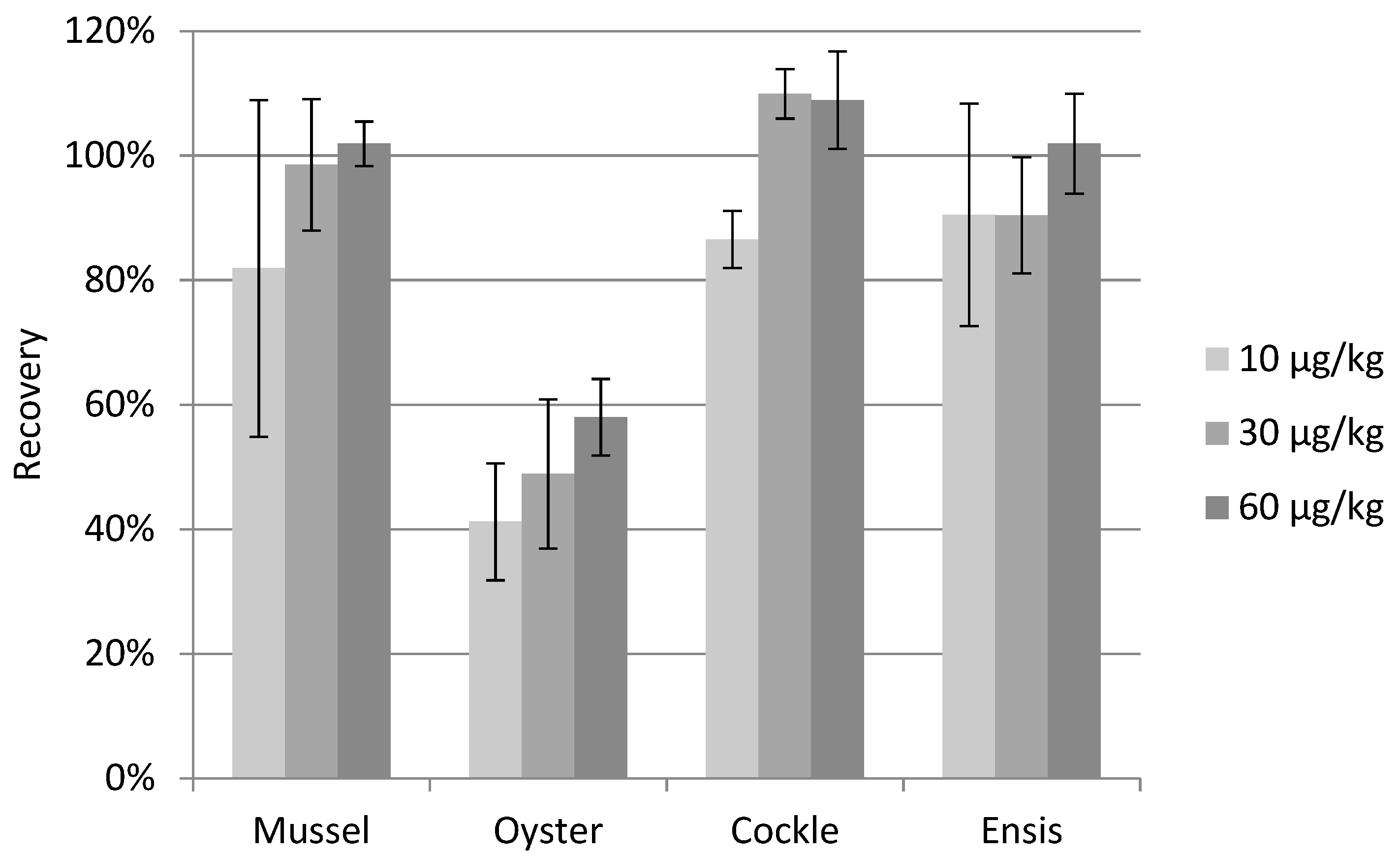
2.5. Method Validation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Materials
4.2. Preparation of Standards
4.3. Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Mass Spectrometry
4.3.1. Sample Clean-up
4.3.2. Liquid Chromatography Methods
4.3.3. High Resolution Mass Spectrometry
4.3.4. Triple Quad Mass Spectrometry
4.4. Method Validation
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Usami, M.; Satake, M.; Ishida, S.; Inoue, A.; Kan, Y.; Yasumoto, T. Palytoxin analogs from the dinoflagellate ostreopsis siamensis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 5389–5390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciminiello, P.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Dello Iacovo, E.; Fattorusso, E.; Forino, M.; Grauso, L.; Tartaglione, L.; Guerrini, F.; Pezzolesi, L.; Pistocchi, R.; et al. Isolation and structure elucidation of ovatoxin-a, the major toxin produced by ostreopsis ovata. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 1869–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, L.; Towers, N.; Briggs, L.; Munday, R.; Adamson, J. Uptake of palytoxin-like compounds by shellfish fed ostreopsis siamensis (dinophyceae). N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2002, 36, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenoir, S.; Ten-Hage, L.; Turquet, J.; Quod, J.-P.; Bernard, C.; Hennion, M.-C. First evidence of palytoxin analogues from an ostreopsis mascarenensis (dinophyceae) benthic bloom in southwestern indian ocean1. J. Phycol. 2004, 40, 1042–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, M.; Vilariño, N.; Louzao, M.C.; Molina, L.; López, Y.; Poli, M.; Botana, L.M. First identification of palytoxin-like molecules in the atlantic coral species palythoa canariensis. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 7438–7446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerbrat, A.S.; Amzil, Z.; Pawlowiez, R.; Golubic, S.; Sibat, M.; Darius, H.T.; Chinain, M.; Laurent, D. First evidence of palytoxin and 42-hydroxy-palytoxin in the marine cyanobacterium trichodesmium. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, L. World-wide occurrence of the toxic dinoflagellate genus ostreopsis schmidt. Toxicon 2011, 57, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aligizaki, K.; Katikou, P.; Milandri, A.; Diogène, J. Occurrence of palytoxin-group toxins in seafood and future strategies to complement the present state of the art. Toxicon 2011, 57, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciminiello, P.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Forino, M. Chemistry of palytoxin and its analogues. In Phycotoxins: Chemistry and Biochemistry, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 85–111. [Google Scholar]
- Tartaglione, L.; Dello Iacovo, E.; Mazzeo, A.; Casabianca, S.; Ciminiello, P.; Penna, A.; Dell’Aversano, C. Variability in toxin profiles of the mediterranean ostreopsis cf. Ovata and in structural features of the produced ovatoxins. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 13920–13928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeds, J.R.; Schwartz, M.D. Human risk associated with palytoxin exposure. Toxicon 2010, 56, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, L.T.; Charlton, N.P. Prevalence and characteristics of inhalational and dermal palytoxin exposures reported to the national poison data system in the U.S. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 55, 107–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durando, P.; Ansaldi, F.; Oreste, P.; Moscatelli, P.; Marensi, L.; Grillo, C.; Gasparini, R.; Icardi, G. Ostreopsis ovata and human health: Epidemiological and clinical features of respiratory syndrome outbreaks from a two-year syndromic surveillance, 2005–06, in North-West Italy. Wkly. Releases (1997–2007) 2007, 12, 3212. [Google Scholar]
- Snoeks, L.; Veenstra, J. Family with fever after cleaning a sea aquarium. Ned. Tijdschr. Geneeskd. 2012, 156, A4200. [Google Scholar]
- Patocka, J.; Nepovimova, E.; Wu, Q.; Kuca, K. Palytoxin congeners. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 92, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, E.; Ishii, T.; Nishimura, M. Palytoxin-induced increase in cytosolic-free Ca2+ in mouse spleen cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 465, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiles, J.S.; Vick, J.A.; Christensen, M.K. Toxicological evaluation of palytoxin in several animal species. Toxicon 1974, 12, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa, S.; Del Favero, G.; De Bortoli, M.; Vita, F.; Soranzo, M.R.; Beltramo, D.; Ardizzone, M.; Tubaro, A. Palytoxin toxicity after acute oral administration in mice. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 191, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Scientific opinion on marine biotoxins in shellfish–palytoxin group. EFSA J. 2009, 1393, 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Riobó, P.; Franco, J.M. Palytoxins: Biological and chemical determination. Toxicon 2011, 57, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonso, A.; Fernández-Araujo, A.; Alfonso, C.; Caramés, B.; Tobio, A.; Louzao, M.C.; Vieytes, M.R.; Botana, L.M. Palytoxin detection and quantification using the fluorescence polarization technique. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 424, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolas, J.; Bovee, T.F.H.; Kamelia, L.; Rietjens, I.M.C.M.; Hendriksen, P.J.M. Exploration of new functional endpoints in neuro-2a cells for the detection of the marine biotoxins saxitoxin, palytoxin and tetrodotoxin. Toxicol. in Vitro 2015, 30, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brovedani, V.; Sosa, S.; Poli, M.; Forino, M.; Varello, K.; Tubaro, A.; Pelin, M. A revisited hemolytic assay for palytoxin detection: Limitations for its quantitation in mussels. Toxicon 2016, 119, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraga, M.; Vilariño, N.; Louzao, M.C.; Fernández, D.A.; Poli, M.; Botana, L.M. Detection of palytoxin-like compounds by a flow cytometry-based immunoassay supported by functional and analytical methods. Ana. Chim. Acta 2016, 903, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciminiello, P.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Dello Iacovo, E.; Forino, M.; Tartaglione, L. Liquid chromatography–high-resolution mass spectrometry for palytoxins in mussels. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 1463–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Altares, M.; Tartaglione, L.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Carnicer, O.; de la Iglesia, P.; Forino, M.; Diogène, J.; Ciminiello, P. The novel ovatoxin-g and isobaric palytoxin (so far referred to as putative palytoxin) from ostreopsis cf. Ovata (nw mediterranean sea): Structural insights by lc-high resolution msn. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 1191–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selwood, A.I.; van Ginkel, R.; Harwood, D.T.; McNabb, P.S.; Rhodes, L.R.; Holland, P.T. A sensitive assay for palytoxins, ovatoxins and ostreocins using lc-ms/ms analysis of cleavage fragments from micro-scale oxidation. Toxicon 2012, 60, 810–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelin, M.; Forino, M.; Brovedani, V.; Tartaglione, L.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Pistocchi, R.; Poli, M.; Sosa, S.; Florio, C.; Ciminiello, P.; et al. Ovatoxin-a, a palytoxin analogue isolated from ostreopsis cf. Ovata fukuyo: Cytotoxic activity and elisa detection. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 1544–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asam, M.R.; Glish, G.L. Tandem mass spectrometry of alkali cationized polysaccharides in a quadrupole ion trap. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 1997, 8, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaley, L.; Herrera, L.C.; Melanson, J.E. Quantitative analysis of tag in oils using lithium cationization and direct-infusion esi tandem mass spectrometry. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2015, 92, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Bristow, A.W.T.; O’Connor, P.B. The competitive influence of Li+, Na+, K+, Ag+, and H+ on the fragmentation of a pegylated polymeric excipient. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 26, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Cook, K.D. Oxidation artifacts in the electrospray mass spectrometry of aβ peptide. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 2031–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, A.D.; Dhanji-Rapkova, M.; Algoet, M.; Suarez-Isla, B.A.; Cordova, M.; Caceres, C.; Murphy, C.J.; Casey, M.; Lees, D.N. Investigations into matrix components affecting the performance of the official bioassay reference method for quantitation of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins in oysters. Toxicon 2012, 59, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EU Reference Laboratories for Residues of Pesticides. Sante/11945/2015-Guidance Document on Analytical Quality Control and Method Validation Procedures for Pesticides Residues Analysis in Food and Feed. Available online: https://www.accredia.it/en/documento/guidance-sante-119452015-guidance-document-on-analytical-quality-control-and-method-validation-procedures-for-pesticides-residues-analysis-in-food-and-feed/ (accessed on 14 December 2018).
- Moreiras, G.; Leão, J.M.; Gago-Martínez, A. Design of experiments for the optimization of electrospray ionization in the lc-ms/ms analysis of ciguatoxins. J. Mass Spectrom. 2018, 53, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klijnstra, M.D.; Gerssen, A. A Sensitive LC-MS/MS Method for Palytoxin Using Lithium Cationization. Toxins 2018, 10, 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10120537
Klijnstra MD, Gerssen A. A Sensitive LC-MS/MS Method for Palytoxin Using Lithium Cationization. Toxins. 2018; 10(12):537. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10120537
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlijnstra, Mirjam D., and Arjen Gerssen. 2018. "A Sensitive LC-MS/MS Method for Palytoxin Using Lithium Cationization" Toxins 10, no. 12: 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10120537
APA StyleKlijnstra, M. D., & Gerssen, A. (2018). A Sensitive LC-MS/MS Method for Palytoxin Using Lithium Cationization. Toxins, 10(12), 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10120537




