Accumulation of Dinophysis Toxins in Bivalve Molluscs
Abstract
1. Introduction
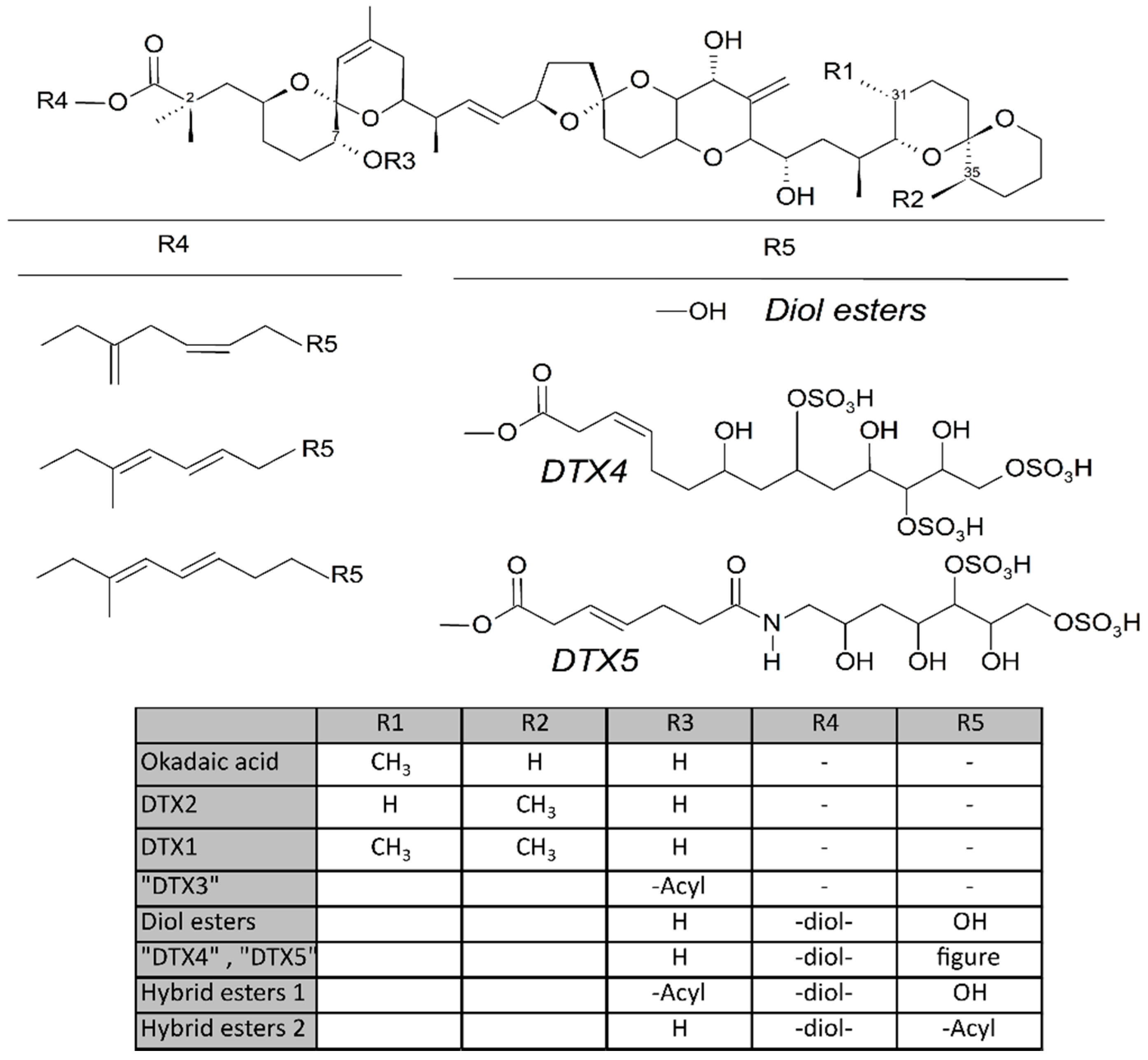
1.1. Dinophysis-Produced Toxins
1.2. Toxins in Phytoplankton
2. Ingestion
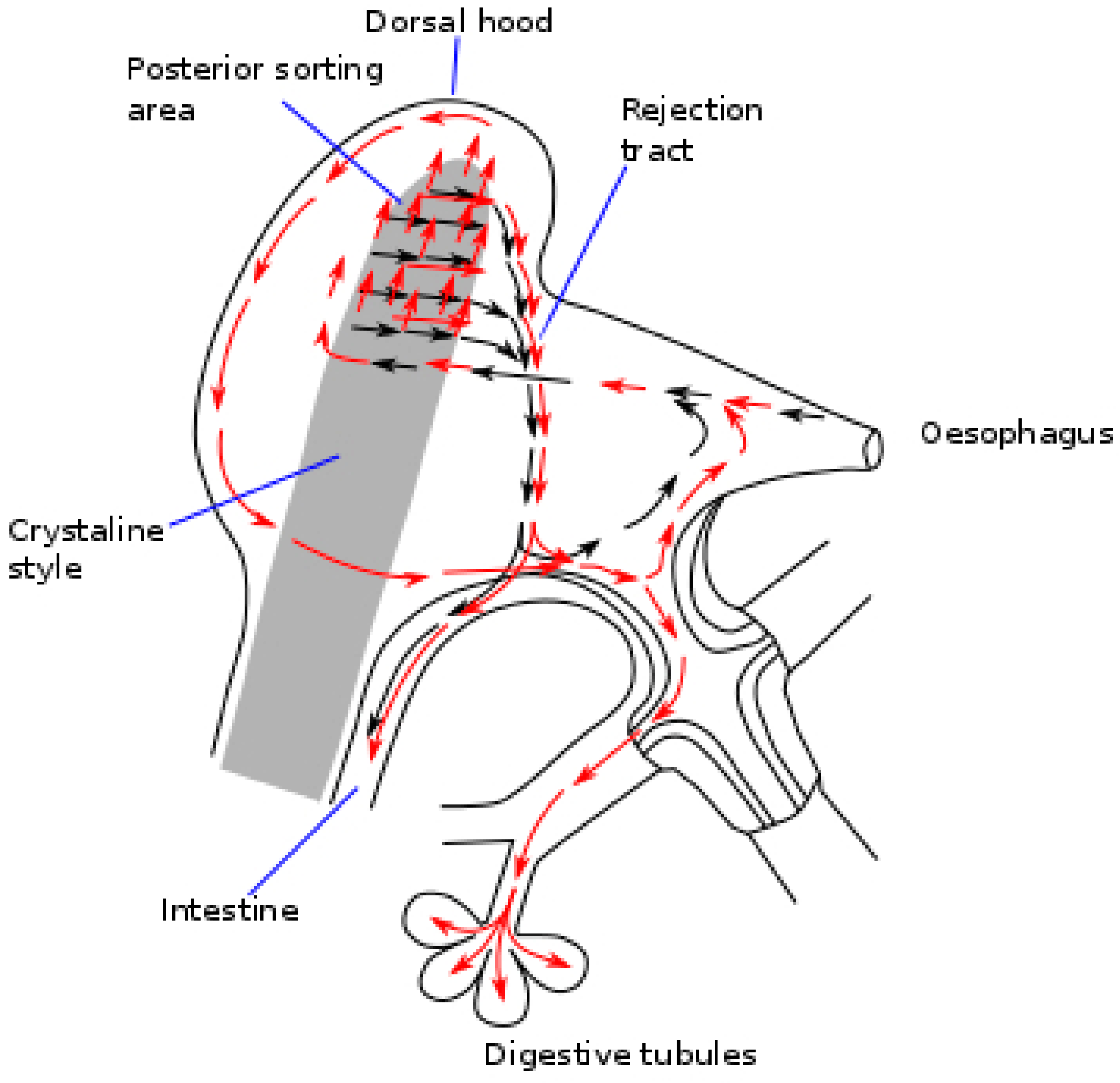
3. Post-Ingestive Selection and Regulation of Food Processing
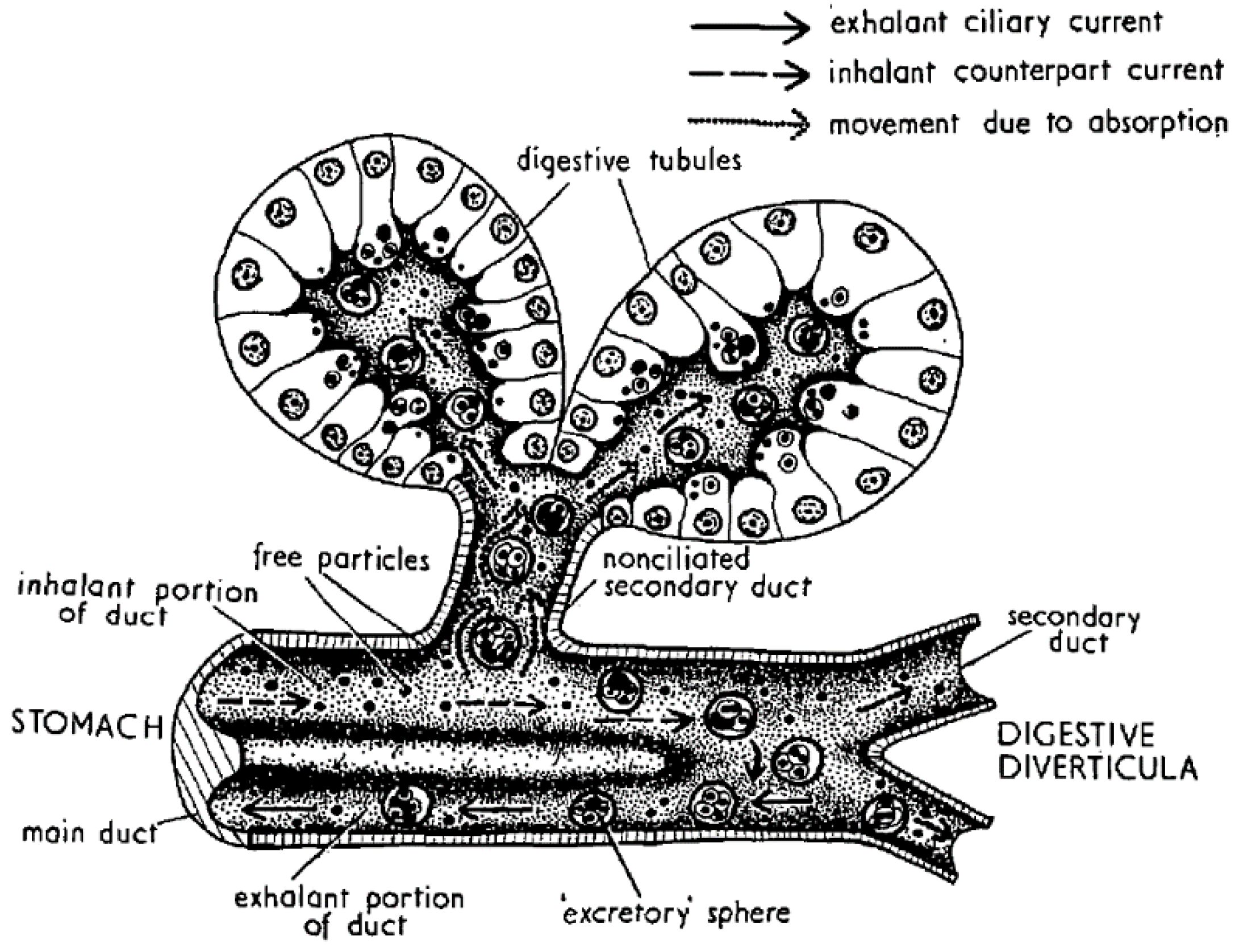
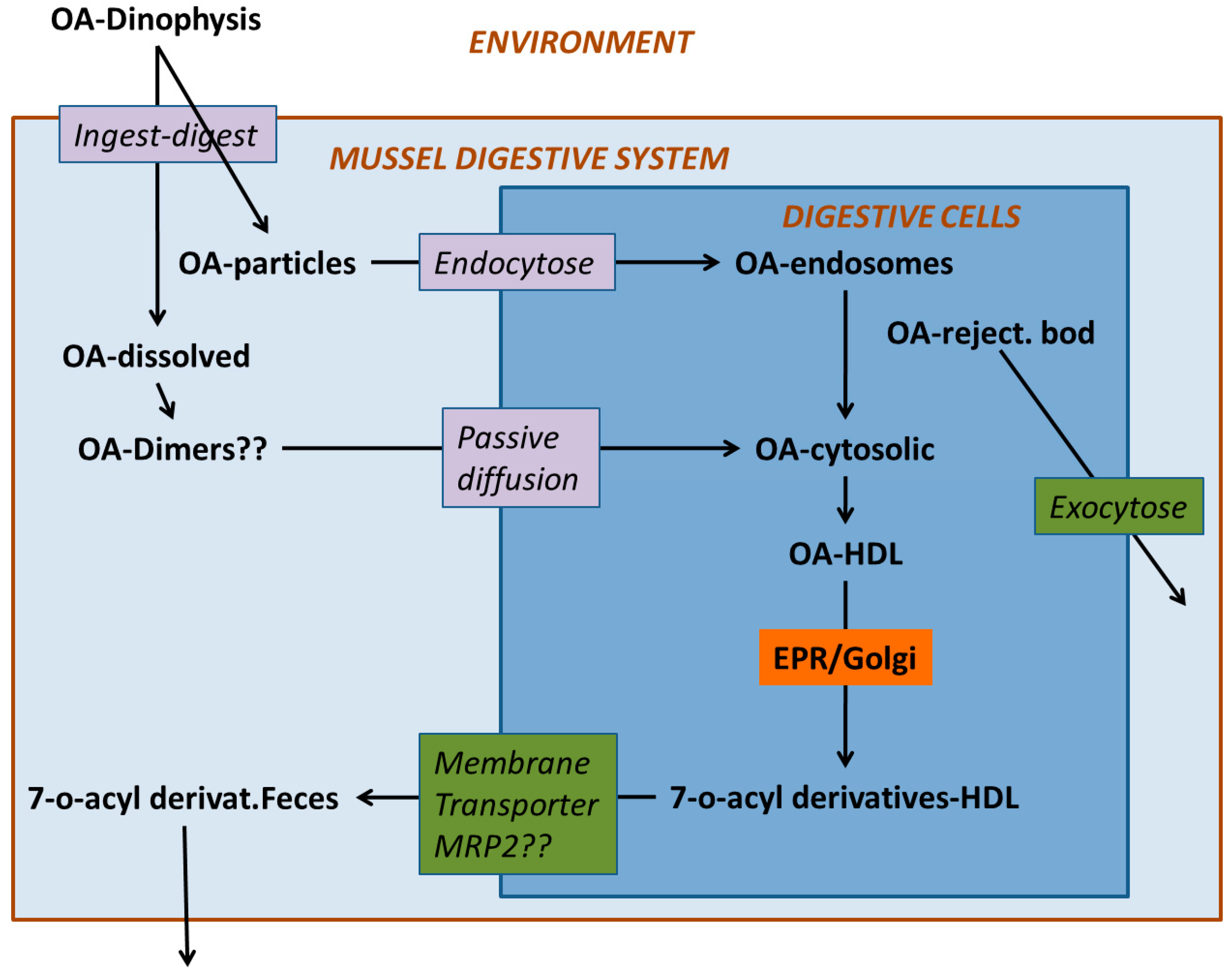
4. Digestion and Uptake
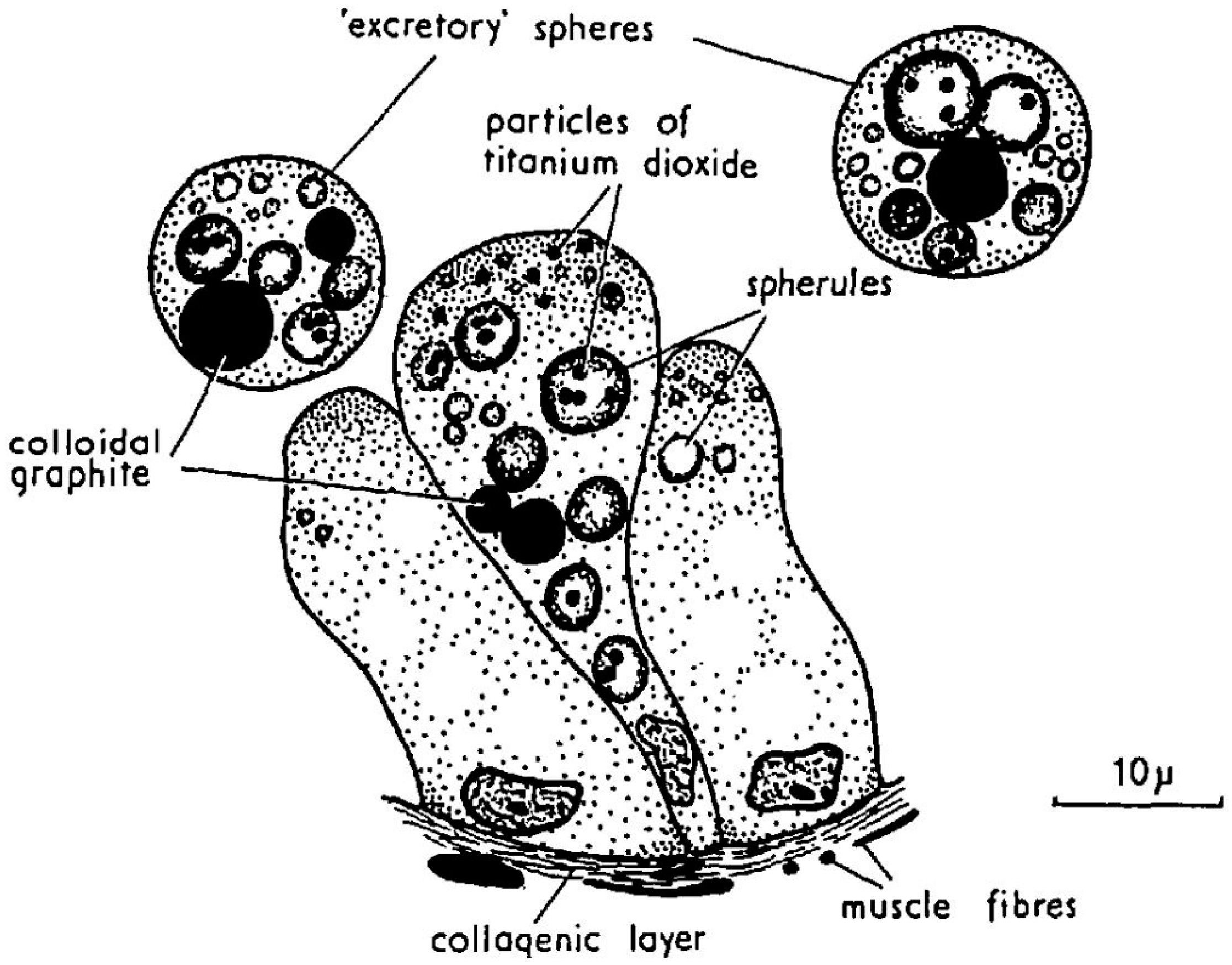
5. Compartmentalization
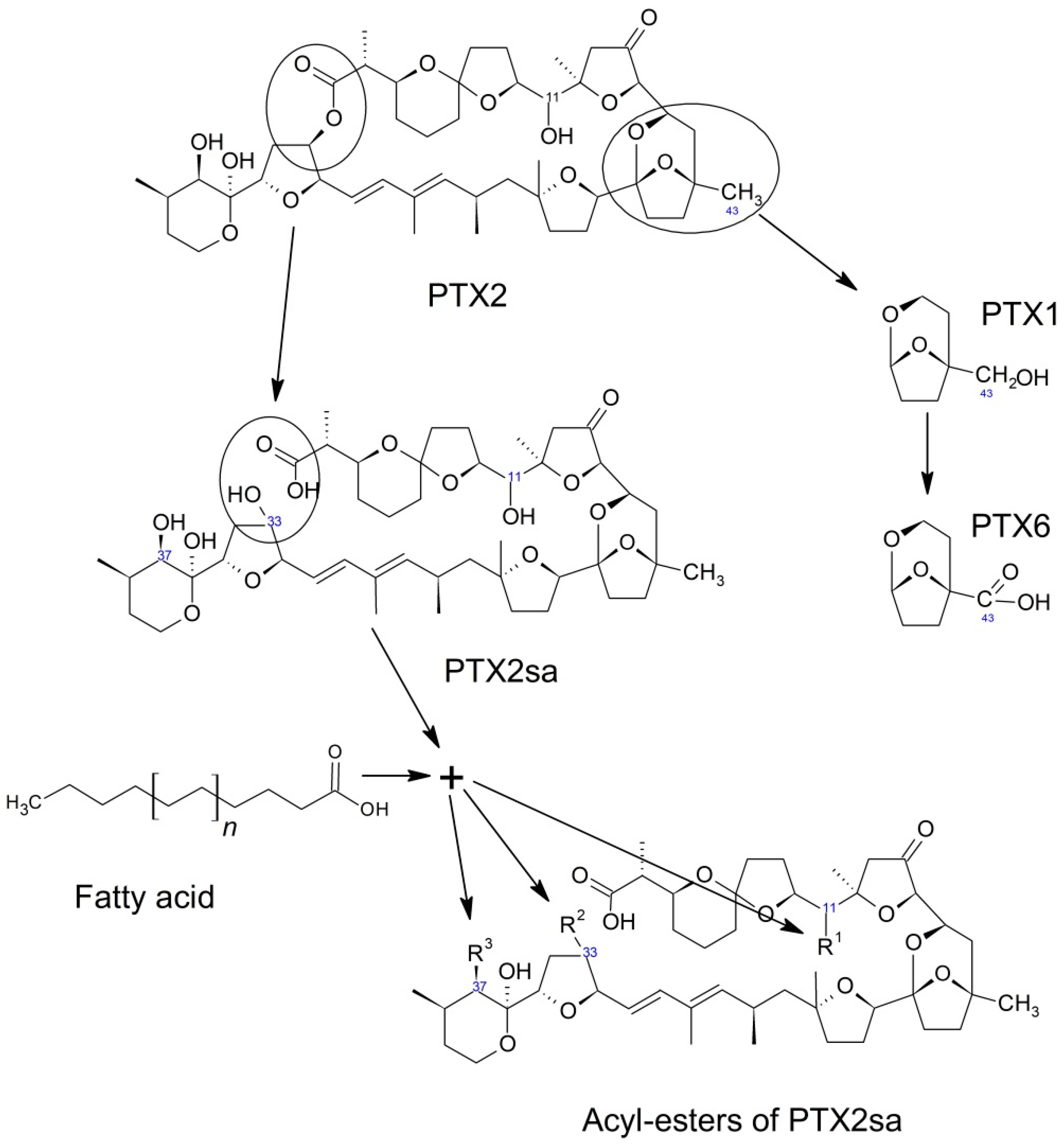
6. Transformation
7. Depuration
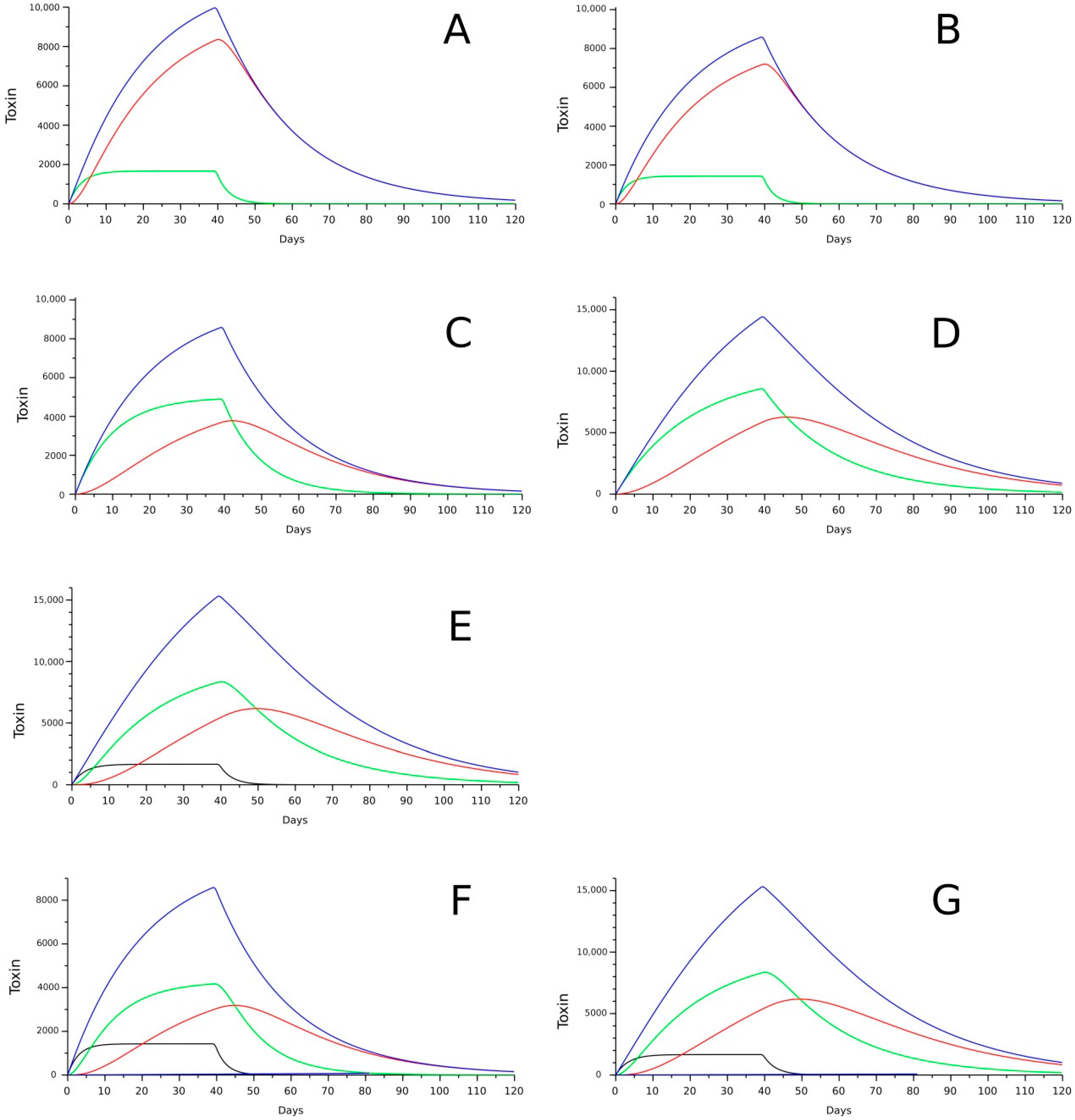
8. Accumulation Kinetics and Modeling
9. Perspectives
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yasumoto, T.; Oshima, Y.; Yamaguchi, M. Occurrence of a new type of shellfish poisoning in the Tohoku district. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1978, 44, 1249–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasumoto, T.; Oshima, Y.; Yamaguchi, M. Occurrence of a new type of toxic shellfish in Japan and chemical properties of the toxin. In Toxic Dinoflagellate Blooms; Taylor, D.L., Seliger, H.W., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1979; pp. 395–398. [Google Scholar]
- Murata, M.; Shimatani, M.; Sugitani, H.; Oshima, Y.; Yasumoto, T. Isolation and structural elucidation of the causative toxin of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1982, 48, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, K.; Scheuer, P.; Tsukitani, Y.; Kikuchi, H.; Enden, V.; Clardy, J.; Gopichand, Y.; Schmitz, F. Okadaic acid, a cytotoxic polyether from two marine sponges of the genus Halichondria. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1981, 103, 2469–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangen, K. Shellfish poisoning and the ocurrence of potentially toxic dinoflagellates in Norwegian waters. Sarsia 1983, 68, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kat, M. Diarrhetic mussel poisoning in the Netherlands related to the dinoflagellate Dinophysis acuminata. Antonie Van Leeuenhoek 1983, 49, 417–427. [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai, M.; Yanagi, T.; Murata, M.; Yasumoto, T.; Kat, M.; Lassus, P.; Rodriguez-Vázquez, J.A. Okadaic acid as the causative toxin of Diarrhetic Shellfish Poisoning in Europe. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1986, 50, 2853–2857. [Google Scholar]
- Van Egmond, H.P.; Aune, T.; Lassus, P.; Speijers, G.J.A.; Waldock, M. Paralytic and diarrhoeic shellfish poisons: Occurrence in Europe, toxicity, analysis and regulation. J. Nat. Toxins 1993, 2, 41–82. [Google Scholar]
- James, K.J.; Carey, B.; O′Halloran, J.; van Pelt, F.N.A.M.; Skrabakova, Z. Shellfish toxicity: Human health implications of marine algal toxins. Epidemiol. Infect. 2010, 138, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain. Opinion of the Scientific Panel on Contaminants in the Food chain on a request from the European Commission on marine biotoxins in shellfish okadaic acid and analogues. EFSA J. 2008, 589, 1–62. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain. Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain on a request from the European Commission on Marine Biotoxins in Shellfish—Summary on regulated marine biotoxins. EFSA J. 2009, 1306, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. Commission Regulation (EU) No 15/2011. Amending Regulation (EC) No 2074/2005 as Regards Recognised Testing Methods for Detecting Marine Biotoxins in Live Bivalve Molluscs. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2011:006:0003:0006:EN:PDF (accessed on 24 October 2018).
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain. Marine biotoxins in shellfish—Pectenotoxin group: Marine biotoxins in shellfish—Pectenotoxin group. EFSA J. 2009, 7, 1109. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández, M.L.; Shumway, S.E.; Blanco, J. Management of shellfish resources. In Manual on Harmful Marine Microalgae; Hallegraeff, G.M., Anderson, A.D., Anderson, D.M., Eds.; UNESCO Publishing: Paris, France, 2003; pp. 657–692. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco, J.; Correa, J.; Muñíz, S.; Mariño, C.; Martín, H.; Arévalo, F. Evaluación del impacto de los métodos y niveles utilizados para el control de toxinas en el mejillón. Revista Galega dos Recursos Mariños 2013, 3, 1–55. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.S.; Igarashi, T.; Fraga, S.; Dahl, E.; Hovgaard, P.; Yasumoto, T. Determination of diarrhetic shellfish toxins in various dinoflagellate species. J. Appl. Phycol. 1989, 1, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fux, E.; Smith, J.L.; Tong, M.; Guzmán, L.; Anderson, D.M. Toxin profiles of five geographical isolates of Dinophysis spp. from North and South America. Toxicon 2011, 57, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uribe, J.C.; García, C.; Rivas, M.; Lagos, N. First report of diarrhetic shellfish toxins in Magellanic fjord, Southern Chile. J. Shellfish Res. 2001, 20, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, M.; McIntyre, L.; Ritson, M.; Stone, J.; Bronson, R.; Bitzikos, O.; Rourke, W.; Galanis, E.; Team, O. Outbreak of Diarrhetic Shellfish Poisoning Associated with Mussels, British Columbia, Canada. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1669–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Mendoza, E.; Sánchez-Bravo, Y.A.; Turner, A.; Blanco, J.; O’Neil, A.; Mancera-Flores, J.; Pérez-Brunius, P.; Rivas, D.; Almazán-Becerril, A.; Peña-Manjarrez, J.L. Lipophilic toxins in Mediterranean Mussels from the northwest coast of Baja California, México. Toxicon 2014, 90, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmody, E.P.; James, K.J.; Kelly, S.S. Dinophysistoxin-2: The predominant diarrhetic shellfish toxin in Ireland. Toxicon 1996, 34, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, J.; Fernández, M.L.; Mariño, J.; Reguera, B.; Miguez, A.; Maneiro, J.; Cacho, E.; Martínez, A. From Dinophysis spp. toxicity to DSP outbreaks: Apreliminary model of toxin accumulation in mussels. In Harmful Marine Algal Blooms; Lassus, P., Arzul, G., Erard-Le Denn, E., Gentien, P., Marcaillou-Le Baut, C., Eds.; Lavoisier: Paris, France, 1995; pp. 777–782. [Google Scholar]
- Gago, A.; Rodriguez-Vázquez, J.A.; Thibault, P.; Quilliam, M.A. Simultaneus occurrence of diarrhetic and paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins in Spanish mussels in 1993. Nat. Toxins 1996, 4, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, P.; Sampayo, M.A. DTX-2 in Portuguese bivalves. In Harmful and Toxic Algal Blooms; Yasumoto, T., Oshima, Y., Fukuyo, Y., Eds.; IOC of UNESCO: Sendai, Japan, 1996; pp. 539–542. [Google Scholar]
- Aune, T.; Larsen, S.; Aasen, J.A.B.; Rehmann, N.; Satake, M.; Hess, P. Relative Toxicity of Dinophysistoxin-2 (DTX-2) Compared With Okadaic Acid, Based on Acute Intraperitoneal Toxicity in Mice. Toxicon 2007, 49, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanji-Rapkova, M.; O′Neill, A.; Maskrey, B.H.; Coates, L.; Teixeira Alves, M.; Kelly, R.J.; Hatfield, R.G.; Rowland-Pilgrim, S.J.; Lewis, A.M.; Algoet, M.; et al. Variability and profiles of lipophilic toxins in bivalves from Great Britain during five and a half years of monitoring: Okadaic acid, dinophysis toxins and pectenotoxins. Harmful Algae 2018, 77, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgarch, A.; Vale, P.; Rifai, S.; Fassouane, A. Detection of Diarrheic Shellfish Poisoning and Azaspiracid Toxins in Moroccan Mussels: Comparison of the LC-MS Method with the Commercial Immunoassay Kit. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armi, Z.; Turki, S.; Trabelsi, E.; Ceredi, A.; Riccardi, E.; Milandri, A. Occurrence of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP) toxins in clams (Ruditapes decussatus) from Tunis north lagoon. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 5085–5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavela-Vrancic, M.; Mestrovic, V.; Marasovic, I.; Gillman, M.; Furey, A.; James, K.J. DSP toxin profile in the coastal waters of the central Adriatic Sea. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1601–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, P.; Sampayo, M.A. Dinophysistoxin-2: A rare diarrhoeic toxin associated with Dinophysis acuta. Toxicon 2000, 38, 1599–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draisci, R.; Giannetti, L.; Lucentini, L.; Marchiafava, C.; James, K.J.; Bishop, A.G.; Healy, B.M.; Kelly, S.S. Isolation of a new okadaic acid analog from phytoplankton implicated in diarrhetic shellfish poisoning. J. Chromatogr. 1998, 798, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Doyle, J.; Jackson, D.M.; Marr, J.; Nixon, E.; Pleasance, S.; Quilliam, M.A.; Walter, J.A.; Wright, J.L.C. Isolation of a new diarrhetic shellfish poison from Irish mussels. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1992, 40, 39–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Marr, J.; de Freitas, A.S.W.; Quilliam, M.A.; Walter, J.A.; Wright, J.L.C.; Pleasance, S. New diol esters isolated from cultures of Prorocentrum lima and Prorocentrum concavum. J. Nat. Prod. 1992, 55, 1631–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Curtis, J.M.; Walter, J.A.; McLachlan, J.L.; Wright, J.L.C. Two new water-soluble dsp toxin derivatives from the dinoflagellate Prorocentrum maculosum: Possible storage and excretion products. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 9273–9276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Curtis, J.M.; Walter, J.A.; Wright, J.L.C. Identification of DTX-4, A New water-soluble phosphatase inhibitor from the toxic dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1995, 5, 597–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.M.; LeBlanc, P.; Burton, I.W.; Walter, J.A.; McCarron, P.; Melanson, J.E.; Strangman, W.K.; Wright, J.L.C. Sulfated diesters of okadaic acid and DTX-1: Self-protective precursors of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP) toxins. Harmful Algae 2017, 63, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Chen, J.H.; Shen, H.H.; He, X.P.; Li, G.J.; Song, X.C.; Zhou, D.S.; Sun, C.J. Profiling of Extracellular Toxins Associated with Diarrhetic Shellfish Poison in Prorocentrum lima Culture Medium by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Mass Spectrometry. Toxins 2017, 9, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torgersen, T.; Miles, C.O.; Rundberget, T.; Wilkins, A.L. New Esters of Okadaic Acid in Seawater and Blue Mussels (Mytilus edulis). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 9628–9635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, P.G.; Daranas, A.H.; Fernandez, J.J.; Souto, M.L.; Norte, M. DTX5c, a new OA sulphate ester derivative from cultures of Prorocentrum belizeanum. Toxicon 2006, 47, 920–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Beuzenberg, V.; MacKenzie, A.L.; Quilliam, M.A. Discovery of okadaic acid esters in the toxic dinoflagellate Dinophysis acuta from New Zealand using liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 18, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miles, C.O.; Wilkins, A.L.; Hawkes, A.D.; Jensen, D.J.; Cooney, J.M.; Larsen, K.; Petersen, D.; Rise, F.; Beuzenberg, V.; MacKenzie, A.L. Isolation and identification of a cis-C-8-diol-ester of okadaic acid from Dinophysis acuta in New Zealand. Toxicon 2006, 48, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizarro, G.; Paz, B.; Franco, J.; Suzuki, T.; Reguera, B. First detection of Pectenotoxin-11 and confirmation of OA-D8 diol-ester in Dinophysis acuta from European waters by LC-MS/MS. Toxicon 2008, 52, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, L.; Olson, R.; Sosik, H.M.; Abraham, A.; Henrichs, D.W.; Hyatt, C.; Buskey, E.J. First harmful Dinophysis (Dinophyceae, Dinophysiales) bloom in the U.S. is revealed by automated imaging flow cytometry. J. Phycol. 2010, 46, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroño, A.; Arevalo, F.; Fernandez, M.; Maneiro, J.; Pazos, Y.; Salgado, C.; Blanco, J. Accumulation and transformation of DSP toxins in mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis during a toxic episode caused by Dinophysis acuminata. Aquat. Toxicol. 2003, 62, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Walter, J.A.; LeBlanc, P.; MacKinnon, S.; Miles, C.O.; Wilkins, A.L.; Munday, R.; Beuzenberg, V.; MacKenzie, L.; Jensen, D.J.; et al. Identification of Pectenotoxin-11 as 34S-Hydroxypectenotoxin-2, a New Pectenotoxin Analogue in the Toxic Dinoflagellate Dinophysis acuta from New Zealand. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2006, 19, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miles, C.O.; Wilkins, A.L.; Samdal, I.A.; Sandvik, M.; Petersen, D.; Quilliam, M.A.; Naustvoll, L.J.; Jensen, D.J.; Cooney, J.M. A novel pectenotoxin, PTX-12, in Dinophysis spp. and shellfish from Norway. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2004, 17, 1423–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draisci, R.; Lucentini, L.; Giannetti, L.; Boria, P.; Poletti, R. First report of pectenotoxin-2 (PTX-2) in algae (Dinophysis fortii) related to seafood poisoning in Europe. Toxicon 1996, 34, 923–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daiguji, M.; Satake, M.; James, K.J.; Bishop, A.; MacKenzie, L.; Naoki, H.; Yasumoto, T. Structures of new pectenotoxin analogs, pectenotoxin-2 seco acid and 7-epi-pectenotoxin-2 seco acid, isolated from a dinoflagellate and greenshell mussels. Chem. Lett. 1998, 7, 653–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Mitsuya, T.; Matsubara, H.; Yamasaki, M. Determination of pectenotoxin-2 after solid-phase extraction from seawater and from the dinoflagellate Dinophysis fortii by liquid chromatography with electrospray mass spectrometry and ultraviolet detection. Evidence of oxidation of pectenotoxin-2 to pectenotoxin-6 in scallop. J Chomatogr. A 1998, 815, 155–160. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, T.; Miyazono, A.; Baba, K.; Sugawara, R.; Kamiyama, T. LC-MS/MS analysis of okadaic acid analogues and other lipophilic toxins in single-cell isolates of several Dinophysis species collected in Hokkaido, Japan. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Miyazono, A.; Okumura, Y.; Kamiyama, T. LC-MS/MS Analysis of Lipophilic Toxins in Japanese Dinophysis Species. Available online: http://www.pices.int/publications/presentations/PICES_15/Ann15_W4/W4_Suzuki.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2018).
- James, K.J.; Bishop, A.G.; Draisci, R.; Palleschi, L.; Marchiafava, C.; Ferretti, E.; Satake, M.; Yasumoto, T. Liquid chromatographic methods for the isolation and identification of new pectenotoxin-2 analogues from marine phytoplankton and shellfish. J. Chromatogr. 1999, 844, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, K.; Takizawa, A.; Tubaro, A.; Sidari, L.; Loggia, R.D.; Yasumoto, T. Fluorometric analysis of pectenotoxin-2 in microalgal samples by high performance liquid chromatography. Nat. Toxins 1999, 7, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M.L.; Reguera, B.; González-Gil, S.; Míguez, A. Pectenotoxin-2 in single-cell isolates of Dinophysis caudata and Dinophysis acuta from the Galician Rías (NW Spain). Toxicon 2006, 48, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamiyama, T.; Suzuki, T. Production of dinophysistoxin-1 and pectenotoxin-2 by a culture of Dinophysis acuminata (Dinophyceae). Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, S.; Suzuki, T.; Nishikawa, T.; Kamiyama, T. Differences in the production and excretion kinetics of okadaic acid, dinophysistoxin-1, and pectenotoxin-2 between cultures of Dinophysis acuminata and Dinophysis fortii isolated from western Japan. J. Phycol. 2011, 47, 1326–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKenzie, L.; Beuzenberg, V.; Holland, P.; McNabb, P.; Suzuki, T.; Selwood, A. Pectenotoxin and okadaic acid-based toxin profiles in Dinophysis acuta and Dinophysis acuminata from New Zealand. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabro, E.; Almandoz, G.O.; Ferrari, M.E.; Hoffmeyer, M.S.; Pettigrosso, R.E.; Uibrig, R.; Krock, B. Co-occurrence of Dinophysis tripos and pectenotoxins in Argentinean shelf waters. Harmful Algae 2015, 42, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, P.; Sampayo, M.A. Pectenotoxin-2 seco acid, 7-epi-pectenotoxin-2 seco acid and pectenotoxin-2 in shellfish and plankton from Portugal. Toxicon 2002, 40, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Puente, P.; Fidalgo Sáez, M.J.; Hamilton, B.; Furey, A.; James, K.J. Studies of polyether toxins in the marine phytoplankton, Dinophysis acuta, in Ireland using multiple tandem mass spectrometry. Toxicon 2004, 44, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, J.; Álvarez, G.; Uribe, E. Identification of pectenotoxins in plankton, filter feeders, and isolated cells of a Dinophysis acuminata with an atypical toxin profile from Chile. Toxicon 2007, 49, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, L.T.; Krock, B.; Hansen, P.J. Effects of light and food availability on toxin production, growth and photosynthesis in Dinophysis acuminata. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 471, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Li, M.; Qiu, J.; Song, J.; Ji, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, S.; Che, Y. Effect of Suspended Particulate Matter on the Accumulation of Dissolved Diarrhetic Shellfish Toxins by Mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) under Laboratory Conditions. Toxins 2018, 10, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossignoli, A.E. Acumulación de Toxinas DSP en el mejillón Mytilus galloprovincialis. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Santiago de Compostela, Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, K.Y.; Hiro, M.; Kimura, S.; Fujiki, H.; Imanishi, Y. Permeability of a non-TPA-type tumor promoter, okadaic acid, through lipid bilayer membrane. Carcinogenesis 1990, 11, 1171–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daranas, A.H.; Cruz, P.G.; Creus, A.H.; Norte, M.; Fernández, J.J. Self-assembly of okadaic acid as a pathway to the cell. Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 4191–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jauffrais, T.; Kilcoyne, J.; Herrenknecht, C.; Truquet, P.; Sechet, V.; Miles, C.O.; Hess, P. Dissolved azaspiracids are absorbed and metabolized by blue mussels (Mytilus edulis). Toxicon 2013, 65, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dame, R.F. Bivalve Filter Feeders: In Estuarine and Coastal Ecosystem Processes; Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 33. [Google Scholar]
- Gosling, E. Marine Bivalve Molluscs; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Møhlenberg, F.; Riisgård, H.U. Efficiency of particle retention in 13 species of suspension feeding bivalves. Ophelia 1978, 17, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riisgård, H.U. Efficiency of particle retention and filtration rate in 6 species of Northeast American bivalves. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1988, 45, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahl, O. Particle retention and relation between water transport and oxygen uptake in Chlamys opercularis (L.) (Bivalvia). Ophelia 1972, 10, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobral, P.; Widdows, J. Effects of increasing current velocity, turbidity and particle-size selection on the feeding activity and scope for growth of Ruditapes decussatus from Ria Formosa, southern Portugal. J. Exp. Mar.Biol. Ecol. 2000, 245, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguera, B.; Riobó, P.; Rodríguez, F.; Díaz, P.; Pizarro, G.; Paz, B.; Franco, J.; Blanco, J. Dinophysis Toxins: Causative Organisms, Distribution and Fate in Shellfish. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 394–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias, J.I.P.; Urrutia, M.B.; Navarro, E.; Alvarez-Jorna, P.; Larretxea, X.; Bougrier, S.; Heral, M. Variability of feeding processes in the cockle Cerastoderma edule (L.) in response to changes in seston concentration and composition. J. Exp. Mar.Biol. Ecol. 1996, 197, 121–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitcher, G.C.; Krock, B.; Cembella, A.D. Accumulation of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning toxins in the oyster Crassostrea gigas and the mussel Choromytilus meridionalis in the southern Benguela ecosystem. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2011, 33, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Altares, M.; Casanova, A.; Fernández-Tejedor, M.; Diogène, J.; De La Iglesia, P. Bloom of Dinophysis spp. dominated by D. sacculus and its related diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP) outbreak in Alfacs Bay (Catalonia, NW Mediterranean Sea): Identification of DSP toxins in phytoplankton, shellfish and passive samplers. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2016, 6, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, K.J.; Suzuki, T.; Kang, Y.S.; Ho Kim, P.; Song, K.C.; Lee, T.S. Seasonal Variability of Lipophilic Shellfish Toxins in Bivalves and Waters, and Abundance of Dinophysis spp. in Jinhae Bay, Korea. J. Shellfish Res. 2010, 29, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacem, I.; Bouaïcha, N.; Hajjem, B. Comparison of okadaic acid profiles in mussels and oysters collected in Mediterranean lagoon, Tunisia. Int.J. Biol. 2010, 2, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comeau, L.A.; Pernet, F.; Tremblay, R.; Bates, S.S.; LeBlanc, A. Comparison of eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica) and blue mussel (Mytilus edulis) filtration rates at low temperatures. Can. Tech. Rep. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2008, 2810, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- McFarland, K.; Donaghy, L.; Volety, A.K. Effect of acute salinity changes on hemolymph osmolality and clearance rate of the non-native mussel, Perna viridis, and the native oyster, Crassostrea virginica, in Southwest Florida. Aquat. Invasions 2013, 8, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cranford, P.J.; Ward, J.E.; Shumway, S.E. Bivalve filter feeding: Variability and limits of the aquaculture biofilter. In Shellfish Aquaculture and the Environment; Shumway, S.E., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 81–124. [Google Scholar]
- Bricelj, V.M.; Lee, J.H.; Cembella, A.D. Influence of dinoflagellate cell toxicity on uptake and loss of paralytic shellfish toxins in the northern quahog Mercenaria mercenaria. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1991, 74, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafra, L., Jr.; Bricelj, V.; Ouellette, C.; Léger, C.; Bates, S. Mechanisms contributing to low domoic acid uptake by oysters feeding on Pseudo-nitzschia cells. I. Filtration and pseudofeces production. Aquat. Biol. 2009, 6, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basti, L.; Uchida, H.; Kanamori, M.; Matsushima, R.; Suzuki, T.; Nagai, S. Mortality and pathology of Japanese scallop, Patinopecten (Mizuhopecten) yessoensis, and noble scallop, Mimachlamys nobilis, fed monoclonal culture of PTX-producer, Dinophysis caudata. In Marine and Freshwater Harmful Algae, Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Harmful Algae, Wellington, New Zealand, Wellington, New Zealand, 27–31 October 2014; Cawthron Institute and International Society for the Study of Harmful Algae (ISSHA): Nelson, New Zealand, 2014; pp. 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Pillet, S.; Houvenaghel, G. Influence of experimental toxification by DSP producing microalgae, Prorocentrum lima, on clearance rate in blue mussels Mytilus edulis. In Harmful Marine Algal Blooms; Lassus, P., Arzul, G., Erard, E., Gentien, P., Marcaillou, C., Eds.; Lavoisier Publishing/Intercept Ltd.: Paris, France, 1995; pp. 481–486. [Google Scholar]
- Sampayo, M.A.; Alvito, P.; Franca, S.; Sousa, I. Dinophysis spp. toxicity and relation to accompanying species. In Toxic Marine Phytoplankton; Granéli, E., Sundström, B., Edler, L., Anderson, D.M., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 215–220. [Google Scholar]
- Haamer, J. Presence of the phycotoxin okadaic acid in mussel (Mytilus edulis) in relation to nutrient composition in a Swedish coastal water. J. Shellfish Res. 1995, 14, 209–216. [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen, C.B. Bivalve Filter Feeding: Hydrodynamics, Bioenergetics, Physiology and Ecology; Olsen & Olsen: Fredensborg, Denmark, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Iglesias, J.I.P.; Navarro, E.; Alvarez Jorna, P.; Armentia, I. Feeding, particle selection and absorption in cockles Cerastoderma edule (L.) exposed to variable conditions of food concentration and quality. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1992, 162, 177–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumway, S.E.; Cucci, T.L.; Lesser, M.P.; Bourne, N.; Bunting, B. Particle clearance and selection in three species of juvenile scallops. Aquac. Int. 1997, 5, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumway, S.E.; Cucci, T.L.; Newell, R.C.; Yentsch, C.M. Particle selection, ingestion, and absorption in filter-feeding bivalves. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1985, 9, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.E.; Shumway, S.E. Separating the grain from the chaff: Particle selection in suspension- and deposit-feeding bivalves. J. Exp. Mar.Biol. Ecol. 2004, 300, 83–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricelj, V.M.; Ward, J.E.; Cembella, A.D.; MacDonald, B.A. Application of video-endoscopy to the study of bivalve feeding on toxic dinoflagellates. In Harmful Algae; Reguera, B., Blanco, J., Fernández, M.L., Wyatt, T., Eds.; Xunta de Galicia and IOC of UNESCO: Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 1998; pp. 453–456. [Google Scholar]
- Defossez, J.M.; Hawkins, A.J.S. Selective feeding in shellfish: Size-dependent rejection of large particles within pseudofaeces from Mytilus edulis, Ruditapes philippinarum and Tapes decussatus. Mar. Biol. 1997, 129, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidari, L.; Nichetto, P.; Cok, S.; Sosa, S.; Tubaro, A.; Honsell, G.; DellaLoggia, R. Phytoplankton selection by mussels, and diarrhetic shellfish poisoning. Mar. Biol. 1998, 131, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pino-Querido, A.; Alvarez-Castro, J.M.; Guerra-Varela, J.; Toro, M.A.; Vera, M.; Pardo, B.G.; Fuentes, J.; Blanco, J.; Martinez, P. Heritability estimation for okadaic acid algal toxin accumulation, mantle color and growth traits in Mediterranean mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis). Aquaculture 2015, 440, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, G. Observations on the Stomach and Digestive Diverticula of the Lamellibranchia: I. The Anisomyaria and Eulamellibranchia. Q. J. Microsc. Sci. 1955, s3-96, 517–537. [Google Scholar]
- Purchon, R.D. The stomach in the bivalvia. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1987, 316, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, A.J.S.; Navarro, E.; Iglesias, J.I.P. Comparative allometries of gut-passage time, gut content and metabolic faecal loss in Mytilus edulis and Cerastoderma edule. Mar. Biol. 1990, 105, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, E.; Iglesias, J.I.P. Infaunal Filter-Feeding Bivalves and the Physiological Response to Short-Term Fluctuations in Food Availability and Composition. In Bivalve Filter Feeders; Dame, R.F., Ed.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; pp. 25–56. [Google Scholar]
- Moroño, A.; Franco, J.; Miranda, M.; Reyero, M.I.; Blanco, J. The effect of mussel size, temperature, seston volume, food quality and volume-specific toxin concentration on the uptake rate of PSP toxins by mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis LmK). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2001, 257, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guéguen, M.; Lassus, P.; Laabir, M.; Bardouil, M.; Baron, R.; Séchet, V.; Truquet, P.; Amzil, Z.; Barillé, L. Gut passage times in two bivalve molluscs fed toxic microalgae: Alexandrium minutum, A. catenella and Pseudo-nitzschia calliantha. Aquat. Living Res. 2008, 21, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brillant, M.G.; MacDonald, B.A. Postingestive selection in the sea scallop, Placopecten magellanicus (Gmelin): the role of particle size and density. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2000, 253, 211–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricelj, V.M.; Bass, A.E.; Lopez, G.R. Absorption and gut passage time of microalgae in a suspension feeder: an evaluation of the 51Cr: 14C twin tracer technique. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1984, 17, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayne, B.L. Feeding physiology of bivalves: Time-dependence and compensation for changes in food availability. In Bivalve Filter Feeders; Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Bauder, A.G.; Cembella, A.D. Viability of the toxic dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima following ingestion and gut passage in the bay scallop Argopecten irradians. J. Shellfish Res. 2000, 19, 321–324. [Google Scholar]
- Bauder, A.G.; Cembella, A.D.; Bricelj, V.M.; Quilliam, M.A. Uptake and fate of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning toxins from the dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima in the bay scallop Argopecten irradians. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 213, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossignoli, A.E.; Fernández, D.; Acosta, C.P.; Blanco, J. Microencapsulation of okadaic acid as a tool for studying the accumulation of DSP toxins in mussels. Mar. Environ. Res. 2011, 71, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windust, A.J.; Hu, T.M.; Wright, J.L.C.; Quilliam, M.A.; McLachlan, J.L. Oxidative metabolism by Thalassiosira weissflogii (Bacillariophyceae) of a diol-ester of okadaic acid, the diarrhetic shellfish poisoning. J. Phycol. 2000, 36, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quilliam, M.A.; Hardstaff, W.R.; Ishida, N.; McLachlan, J.L.; Reeves, A.R.; Ross, N.W.; Windust, A.J. Production of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP) toxins by Prorocentrum lima in culture and development of analytical methods. In Harmful and Toxic Algal Blooms; Yasumoto, T., Oshima, Y., Fukuyo, Y., Eds.; IOC of UNESCO: Sendai, Japan, 1996; pp. 289–292. [Google Scholar]
- Quilliam, M.A.; Ishida, N.; McLachlan, J.L.; Ross, N.W.; Windust, A.J. Analytical Methods for Diarrhetic Shellfish Poisoning (DSP) Toxins and A Study of Toxin Production by Prorocentrum lima in Culture. UJNR Technical Report No. 24 1996; pp. 101–106. Available online: https://repository.library.noaa.gov/view/noaa/12555/noaa_12555_DS1.pdf?#page=101 (accessed on 18 May 2018).
- Morton, B. Feeding and digestion in Bivalvia. In The Mollusca. Physiology Part 2; Saleuddin, A.S.M., Wilbur, K.M., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 65–147. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández, M.L.; Miguez, A.; Moroño, A.; Cacho, E.; Martínez, A.; Blanco, J. Detoxification of low polarity toxins (DTX3) from mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis in Spain. In Harmful Algae; Reguera, B., Blanco, J., Fernández, M.L., Wyatt, T., Eds.; Xunta de Galicia & Intergovernmental Oceanografic Comission of UNESCO: Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 1998; pp. 449–452. [Google Scholar]
- MacKenzie, L.A.; Selwood, A.I.; Marshall, C. Isolation and characterization of an enzyme from the Greenshell (TM) mussel Perna canaliculus that hydrolyses pectenotoxins and esters of okadaic acid. Toxicon 2012, 60, 406–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fux, E. Development and Evaluation of Passive Sampling and LC-MS Based Techniques for the Detection and Monitoring of Lipophilic Marine Toxins in Mesocosm and Field Studies. Ph.D. Thesis, The Marine Institute, School of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Dublin, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Rossignoli, A.E.; Blanco, J. Subcellular distribution of okadaic acid in the digestive gland of Mytilus galloprovincialis: First evidences of lipoprotein binding to okadaic acid. Toxicon 2010, 55, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guéguen, M.; Duinker, A.; Marcaillou, C. A first approach to localizing biotoxins in mussel digestive glands. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Molluscan Shellfish Safety, Nantes, France, 14–19 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, M.N.; Willows, R.I. A model for cellular uptake and intracellular behaviour of particulate-bound micropollutants. Mar. Environ. Res. 1998, 46, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedes, F. Sampling and partitioning of neutral organic contaminants in surface waters with regard to legislation, environmental quality and flux estimations. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 1994, 57, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossignoli, A.; Blanco, J. Cellular distribution of okadaic acid in the digestive gland of Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lamarck, 1819). Toxicon 2008, 52, 957–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstein, J.E. Fine structure of the digestive tubule of the eastern oyster, Crassostrea virginica (Gmelin, 1791). J. Shellfish Res. 1995, 14, 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Jonas, A. Lipoprotein structure. In Biochemistry of Lipids, Lipoproteins and Membranes, 4th ed.; Vance, D.E., Vance, J.E., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 483–504. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco, J.; Mariño, C.; Martín, H.; Acosta, C.P. Anatomical distribution of Diarrhetic Shellfish Poisoning (DSP) toxins in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Toxicon 2007, 50, 1011–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcaillou, C.; Haure, J.; Mondeguer, F.; Courcoux, A.; Dupuy, B.; Penisson, C. Effect of food supply on the detoxification in the blue mussel, Mytilus edulis, contaminated by diarrhetic shellfish toxins. Aquat. Living Resour. 2010, 23, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edebo, L.; Lange, S.; Li, X.P.; Allenmark, S.; Lindgren, K.; Thompson, R. Seasonal, geographic and individual variation of okadaic acid content in cultivated mussels in Sweden. Apmis 1988, 96, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarron, P.; Kilcoyne, J.; Hess, P. Effects of cooking and heat treatment on concentration and tissue distribution of okadaic acid and dinophysistoxin-2 in mussels (Mytilus edulis). Toxicon 2008, 51, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madigan, T.L.; Lee, K.G.; Padula, D.J.; McNabb, P.; Pointon, A.M. Diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP) toxins in South Australian shellfish. Harmful Algae 2006, 5, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, P.; McMahon, T.; Slattery, D.; Swords, D.; Dowling, G.; McCarron, M.; Clarke, D.; Gibbons, W.; Silke, W.; O’Cinneide, M. Use of LC-MS testing to identify lipophilic toxins, to stablish local trends and interspecies differences and to test the comparability of LC-MS testing with mouse bioassay: An example from the Irish Biotoxin Monitoring Programme 2001. In Molluscan Shellfish Safety, Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Molluscan Shellfish Safety, Xunta De Galicia, Spain, 4–8 June 2002; Villalba, A., Reguera, B., Romalde, J.L., Beiras, R., Eds.; Consellería de Pesca e Asuntos Marítimos, Xunta de Galicia and IOC of UNESCO: Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 2003; pp. 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Vale, P. Differential Dynamics of Dinophysistoxins and Pectenotoxins, Part II: Offshore Bivalve Species. Toxicon 2006, 47, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kameneva, P.A.; Krasheninina, E.A.; Slobodskova, V.V.; Kukla, S.P.; Orlova, T.Y. Accumulation and Tissue Distribution of Dinophysitoxin-1 and Dinophysitoxin-3 in the Mussel Crenomytilus grayanus Feeding on the Benthic Dinoflagellate Prorocentrum foraminosum. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, J.; Álvarez, G.; Rengel, J.; Díaz, R.; Mariño, C.; Martín, H.; Uribe, E. Accumulation and Biotransformation of Dinophysis Toxins by the Surf Clam Mesodesma donacium. Toxins 2018, 10, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Ota, H.; Yamasaki, M. Direct evidence of transformation of dinophysistoxin-1 to 7-O-acyl-dinophysistoxin-1 (Dinophysis-3) in the scallop Patinopecten yessoensis. Toxicon 1999, 37, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossignoli, A.E.; Fernández, D.; Regueiro, J.; Mariño, C.; Blanco, J. Esterification of okadaic acid in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Toxicon 2011, 57, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konoki, K.; Onoda, T.; Watanabe, R.; Cho, Y.; Kaga, S.; Suzuki, T.; Yotsu-Yamashita, M. In Vitro Acylation of Okadaic Acid in the Presence of Various Bivalves′ Extracts. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 300–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vale, P. Detailed profiles of 7-O-acyl esters in plankton and shellfish from the Portuguese coast. J. Chomatogr. A 2006, 1128, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quilliam, M.A.; Vale, P.; Sampayo, M.A.M. Direct detection of acyl esters of okadaic acid and dinophysistoxin-2 in Portuguese shellfish by LC-MS. In Molluscan Shellfish Safety; Villalba, A., Reguera, B., Romalde, J., Beiras, R., Eds.; Consellería de Pesca e Asuntos Marıtimos da Xunta de Galicia and IOC of UNESCO: Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 2003; pp. 67–73. [Google Scholar]
- Iglesia, P.; Fonollosa, E.; Diogène, J. Assessment of acylation routes and structural characterisation by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry of semi-synthetic acyl ester analogues of lipophilic marine toxins. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2014, 28, 2605–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Kamiyama, T.; Okumura, Y.; Ishihara, K.; Matsushima, R.; Kaneniwa, M. Liquid-chromatographic hybrid triple–quadrupole linear-ion-trap MS/MS analysis of fatty-acid esters of dinophysistoxin-1 in bivalves and toxic dinoflagellates in Japan. Fish. Sci. 2009, 75, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgersen, T.; Wilkins, A.L.; Rundberget, T.; Miles, C.O. Characterization of fatty acid esters of okadaic acid and related toxins in blue mussels (Mytilus edulis) from Norway. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 22, 1127–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marr, J.; Hu, T.; Pleasance, S.; Quilliam, M.A.; Wright, J.L.C. Detection of new 7-O-acyl derivatives of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning toxins by liquid chromatography- mass spectometry. Toxicon 1992, 30, 1621–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, P. Profiles of fatty acids and 7-O-acyl okadaic acid esters in bivalves: Can bacteria be involved in acyl esterification of okadaic acid? Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 151, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trainer, V.L.; Moore, L.; Bill, B.; Adams, N.; Harrington, N.; Borchert, J.; da Silva, D.; Eberhart, B. Diarrhetic Shellfish Toxins and Other Lipophilic Toxins of Human Health Concern in Washington State. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1815–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torgersen, T.; Sandvik, M.; Lundve, B.; Lindegarth, S. Profiles and levels of fatty acid esters of okadaic acid group toxins and pectenotoxins during toxin depuration. Part II: Blue mussels (Mytilus edulis) and flat oyster (Ostrea edulis). Toxicon 2008, 52, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindegarth, S.; Torgersen, T.; Lundve, B.; Sandvik, M. Differential retention of Okadaic Acid (OA) group toxins and Pectenotoxins (PTX) in the blue mussel, Mytilus edulis (L.), and european flat oyster, Ostrea edulis (L.). J. Shellfish Res. 2009, 28, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, K.; Scanlon, S.; Jensen, L.B. Diarrhetic Shellfish Poisoning Toxin Esters in Danish Blue Mussels and Surf Clams. Food Addit. Contam. 2005, 22, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Quilliam, M.A. LC-MS/MS Analysis of Diarrhetic Shellfish Poisoning (DSP) Toxins, Okadaic Acid and Dinophysistoxin Analogues, and Other Lipophilic Toxins. Anal. Sci. 2011, 27, 571–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Mitsuya, T. Comparison of dinophysistoxin-1 and esterified dinophysistoxin-1 (dinophysistoxin-3) contents in the scallop Patinopecten yessoensis and the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Toxicon 2001, 39, 905–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.; Pruzzo, M.; Rodriguez-Unda, M.; Contreras, C.; Lagos, N. First evidence of Okadaic acid acyl-derivative and Dinophysistoxin-3 in mussel samples collected in Chiloe Island, Southern Chile. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 35, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vale, P.; Sampayo, M.A. Esterification of DSP toxins by Portuguese bivalves from the northwest coast determined by LC-MS-a widespread phenomenon. Toxicon 2002, 40, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, J.; Moroño, A.; Fernández, M.L. Toxic episodes in shellfish, produced by lipophilic phycotoxins: an overview. Revista Galega dos Recursos Mariños 2005, 1, 1–70. [Google Scholar]
- Vale, P. Differential Dynamics of Dinophysistoxins and Pectenotoxins Between Blue Mussel and Common Cockle: A Phenomenon Originating From the Complex Toxin Profile of Dinophysis acuta. Toxicon 2004, 44, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villar-González, A.; Rodríguez-Velasco, M.L.; Ben-Gigirey, B.; Botana, L.M. Lipophilic toxin profile in Galicia (Spain): 2005 toxic episode. Toxicon 2007, 49, 1129–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Mackenzie, L.; Stirling, D.; Adamson, J. Conversion of pectenotoxin-2 to pectenotoxin-2 seco acid in the New Zealand scallop, Pecten novaezelandiae. Fish. Sci. 2001, 67, 506–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; MacKenzie, L.; Stirling, D.; Adamson, J. Pectenotoxin-2 seco acid: A toxin converted from pectenotoxin-2 by the New Zealand Greenshell mussels, Perna canaliculus. Toxicon 2001, 39, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, C.O.; Wilkins, A.L.; Munday, R.; Dines, M.H.; Hawkes, A.D.; Briggs, L.R.; Sandvik, M.; Jensen, D.J.; Cooney, J.M.; Holland, P.T.; et al. Isolation of pectenotoxin-2 from Dinophysis acuta and its conversion to pectenotoxin-2 seco acid, and preliminary assessment of their acute toxicities. Toxicon 2004, 43, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKenzie, L.; Holland, P.; McNabb, P.; Beuzenberg, V.; Selwood, A.; Suzuki, T. Complex toxin profiles in phytoplankton and Greenshell mussels (Perna canaliculus), revealed by LC–MS/MS analysis. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1321–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M.L.; Míguez, A.; Martínez, A.; Moroño, A.; Arévalo, F.; Pazos, Y.; Salgado, C.; Correa, J.; Blanco, J.; González-Gil, S.; et al. First report of Pectenotoxin-2 in phytoplankton net-hauls and mussels from the Galician Rías Baixas (NW Spain) during proliferations of Dinophysis acuta and Dinophysis caudata. In Molluscan Shellfish Safety; Villalba, A., Reguera, B., Romalde, J., Beiras, R., Eds.; Consellería de Pesca e Asuntos Marítimos da Xunta de Galicia and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 2003; pp. 75–83. [Google Scholar]
- Amzil, Z.; Sibat, M.; Royer, F.; Masson, N.; Abadie, E. Report on the First Detection of Pectenotoxin-2, Spirolide-A and Their Derivatives in French Shellfish. Mar. Drugs 2007, 5, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Jin, T.; Shirota, Y.; Mitsuya, T.; Okumura, Y.; Kamiyama, T. Quantification of Lipophilic Toxins Associated With Diarrhetic Shellfish Poisoning in Japanese Bivalves by Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry and Comparison With Mouse Bioassay. Fish. Sci. 2005, 71, 1370–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Igarashi, T.; Ichimi, K.; Watai, M.; Suzuki, M.; Ogiso, E.; Yasumoto, T. Kinetics of Diarrhetic Shellfish Poisoning Toxins, Okadaic Acid, Dinophysistoxin-1, Pectenotoxin-6 and Yessotoxin in Scallops Patinopecten yessoensis. Fish. Sci. 2005, 71, 948–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T. Lipophilic Toxins, Pectenotoxins, and Yessotoxins: Chemistry, Metabolism, and Detection. In Seafood and Freshwater Toxins: Pharmacology, Physiology, and Detection; Botana, L.M., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Ratón, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 627–656. [Google Scholar]
- Janer, G.; Lavado, R.; Thibaut, R.; Porte, C. Effects of 17β-estradiol exposure in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis: A possible regulating role for steroid acyltransferases. Aquat. Toxicol. 2005, 75, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janer, G.; Mesia-Vela, S.; Porte, C.; Kauffman, F.C. Esterification of vertebrate-type steroids in the Eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica). Steroids 2004, 69, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkins, A.L.; Rehmann, N.; Torgersen, T.; Rundberget, T.; Keogh, M.; Petersen, D.; Hess, P.; Rise, F.; Miles, C.O. Identification of fatty acid esters of pectenotoxin-2 seco acid in blue mussels (Mytilus edulis) from Ireland. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 5672–5678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez-Ulloa, V.; Fernandez-Tajes, J.; Aguiar-Pulido, V.; Prego-Faraldo, M.V.; Florez-Barros, F.; Sexto-Iglesias, A.; Mendez, J.; Eirin-Lopez, J.M. Unbiased high-throughput characterization of mussel transcriptomic responses to sublethal concentrations of the biotoxin okadaic acid. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Escauriaza, R. Identificación de genes implicados en la eliminación de biotoxinas en el mejillón Mytilus galloprovincialis Lmk.: clonación y expresion de los cDNA que codifican para dos proteinas transportadoras ABC de la subfamilia B (proteínas MDR). Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade de Santiago de Compostela, Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lozano, V. Identificación de genes implicados en la eliminación de biotoxinas en el mejillón Mytilus galloprovincialis Lmk.: clonación y expresion de los cDNA que codifican para tres proteinas transportadoras ABC pertenecientes a las subfamilias C (proteínas MRP) y G. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade de Santiago de Compostela, Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Luedeking, A.; Koehler, A. Regulation of expression of multixenobiotic resistance (MXR) genes by environmental factors in the blue mussel Mytilus edulis. Aquat. Toxicol. 2004, 69, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luedeking, A.; Van Noorden, C.J.F.; Koehler, A. Identification and characterisation of a multidrug resistance-related protein mRNA in the blue mussel Mytilus edulis. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 286, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eufemia, N.; Epel, D. Induction of the multixenobiotic defense mechanism (MXR), P-glycoprotein, in the mussel Mytilus californianus as a general cellular response to environmental stresses. Aquat. Toxicol. 2000, 49, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldstein, T.; Nelson, N.; Mokady, O. Cloning and expression of MDR transporters from marine bivalves, and their potential use in biomonitoring. Mar. Environ. Res. 2006, 62, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingtong, S.; Chitramvong, Y.; Janvilisri, T. ATP-Binding Cassette Multidrug Transporters in Indian-Rock Oyster Saccostrea Forskali and Their Role in the Export of an Environmental Organic Pollutant Tributyltin. Aquat. Toxicol. 2007, 85, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurelec, B. The multixenobiotic resistance mechanism in aquatic organisms. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 1992, 22, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luckenbach, T.; Epel, D. ABCB-and ABCC-type transporters confer multixenobiotic resistance and form an environment-tissue barrier in bivalve gills. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2008, 294, R1919–R1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, M.; Navarro, A.; Luckenbach, T.; Piña, B.; Barata, C. Characterization of the multixenobiotic resistance (MXR) mechanism in embryos and larvae of the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) and studies on its role in tolerance to single and mixture combinations of toxicants. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 101, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Wang, J.; Chen, W.C.; Li, H.Y.; Liu, J.S.; Jiang, T.; Yang, W.D. P-glycoprotein expression in Perna viridis after exposure to Prorocentrum lima, a dinoflagellate producing DSP toxins. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 39, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, J.; Fernández, M.L.; Míguez, A.; Moroño, A. Okadaic acid depuration in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis: One- and two-compartment models and the effect of environmental conditions. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 176, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroño, A.; Fernández, M.L.; Franco, J.M.; Martínez, A.; Reyero, I.; Míguez, A.; Cacho, E.; Blanco, J. PSP and DSP detoxification kinetics in mussel, Mytilus galloprovincialis: Effect of environmental parameters and body weight. In Harmful Algae; Reguera, B., Blanco, J., Fernández, M.L., Wyatt, T., Eds.; Xunta de Galicia and IOC of UNESCO: Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 1998; pp. 445–448. [Google Scholar]
- Poletti, R.; Viviani, R.; Casadei, C.; Lucentini, L.; Giannetti, L.; Funari, E.; Draisci, R. Decontamination dynamics of mussels naturally contaminated with diarrhetic toxins relocated to a basin of the Adriatic Sea. In Harmful and Toxic Algal Blooms; Yasumoto, T., Oshima, Y., Fukuyo, Y., Eds.; IOC of UNESCO: Paris, France, 1996; pp. 429–432. [Google Scholar]
- Marcaillou-Le Baut, C.; Bardin, B.; Bardouil, M.; Bohec, M.; Le Denn, E.; Masselin, P.; Truquet, P. DSP depuration rates of mussels reared in a laboratory and an aquaculture pond. In Toxic Phytoplankton Blooms in the Sea; Smayda, T.J., Shimizu, Y., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993; pp. 531–535. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, L.T.; Hansen, P.J.; Krock, B.; Vismann, B. Accumulation, transformation and breakdown of DSP toxins from the toxic dinoflagellate Dinophysis acuta in blue mussels, Mytilus edulis. Toxicon 2016, 117, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botelho, M.J.; Vale, C.; Joaquim, S.; Costa, S.T.; Soares, F.; Roque, C.; Matias, D. Combined effect of temperature and nutritional regime on the elimination of the lipophilic toxin okadaic acid in the naturally contaminated wedge shell Donax trunculus. Chemosphere 2018, 190, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, M.; Teo, S.; Lee, F.; Khoo, H. Persistent low concentratrions of diarrhetic shellfish toxins in green mussels Perna viridis from the Johor Strait, Singapure: First record of diarrhetic shellfish toxins from South-East Asia. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 181, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, J. Modelling as a mitigation strategy for harmful algal blooms. In Shellfish Safety and Quality; Shumway, S.E., Rodrick, G.E., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 200–227. [Google Scholar]
- Svensson, S. Depuration of Okadaic acid (Diarrhetic Shellfish Toxin) in mussels, Mytilus edulis (Linnaeus), feeding on different quantities of nontoxic algae. Aquaculture 2003, 218, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penry, D.L. Digestive kinematics of suspension-feeding bivalves: Modeling and measuring particle-processing in the gut of Potamocorbula amurensis. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 197, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pousse, É.; Flye-Sainte-Marie, J.; Alunno-Bruscia, M.; Hégaret, H.; Rannou, É.; Pecquerie, L.; Marques, G.M.; Thomas, Y.; Castrec, J.; Fabioux, C. Modelling paralytic shellfish toxins (PST) accumulation in Crassostrea gigas by using Dynamic Energy Budgets (DEB). J. Sea Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blanco, J. Accumulation of Dinophysis Toxins in Bivalve Molluscs. Toxins 2018, 10, 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10110453
Blanco J. Accumulation of Dinophysis Toxins in Bivalve Molluscs. Toxins. 2018; 10(11):453. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10110453
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlanco, Juan. 2018. "Accumulation of Dinophysis Toxins in Bivalve Molluscs" Toxins 10, no. 11: 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10110453
APA StyleBlanco, J. (2018). Accumulation of Dinophysis Toxins in Bivalve Molluscs. Toxins, 10(11), 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10110453




