Sarcopenia Impairs Prognosis of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Role of Liver Functional Reserve and Tumor-Related Factors in Loss of Skeletal Muscle Volume
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients, Treatment, and Follow-Up Strategy
2.2. Image Analysis of Skeletal Muscle Volume and Definition of Sarcopenia
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics and Laboratory Data of Patients
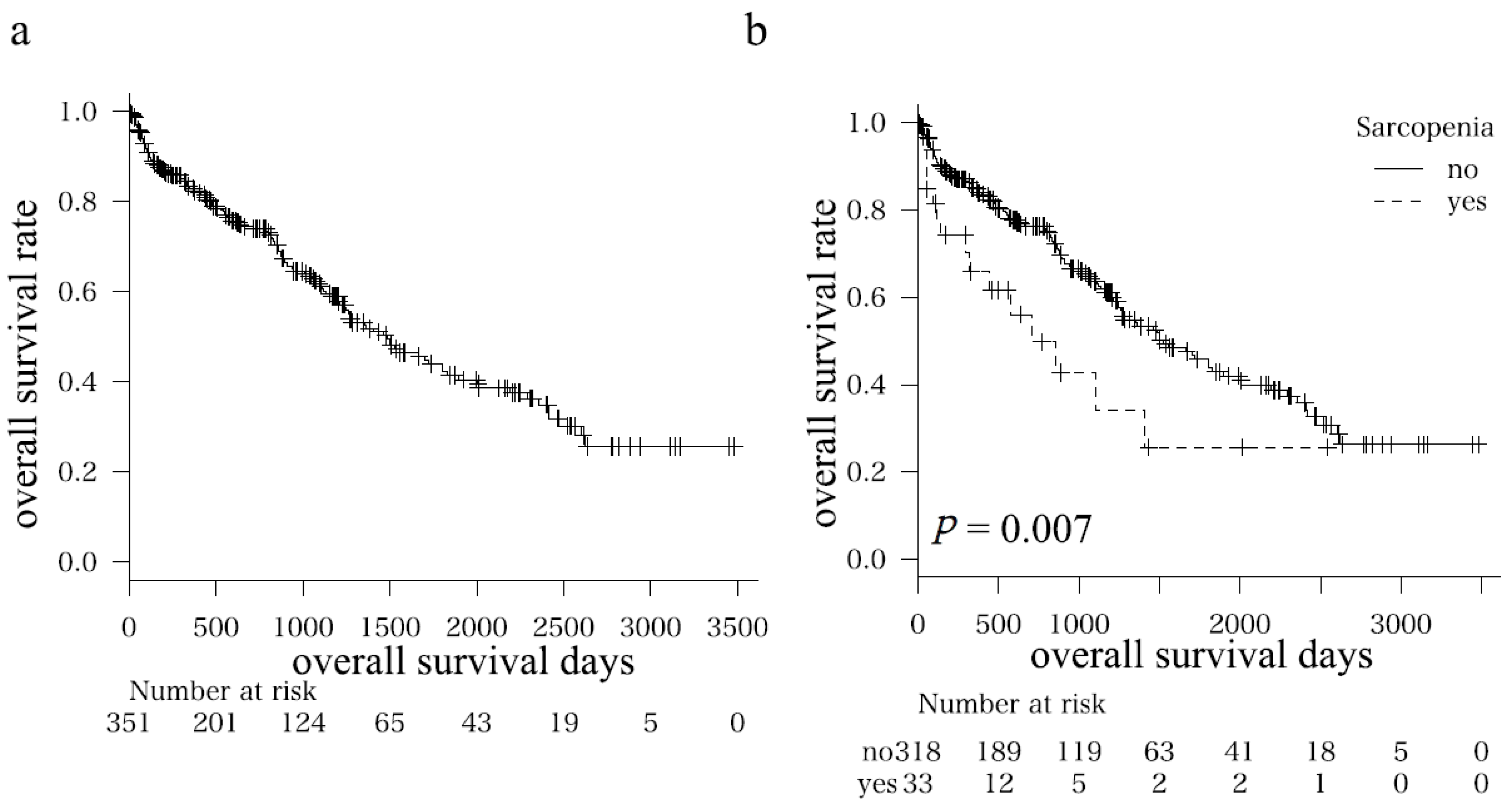
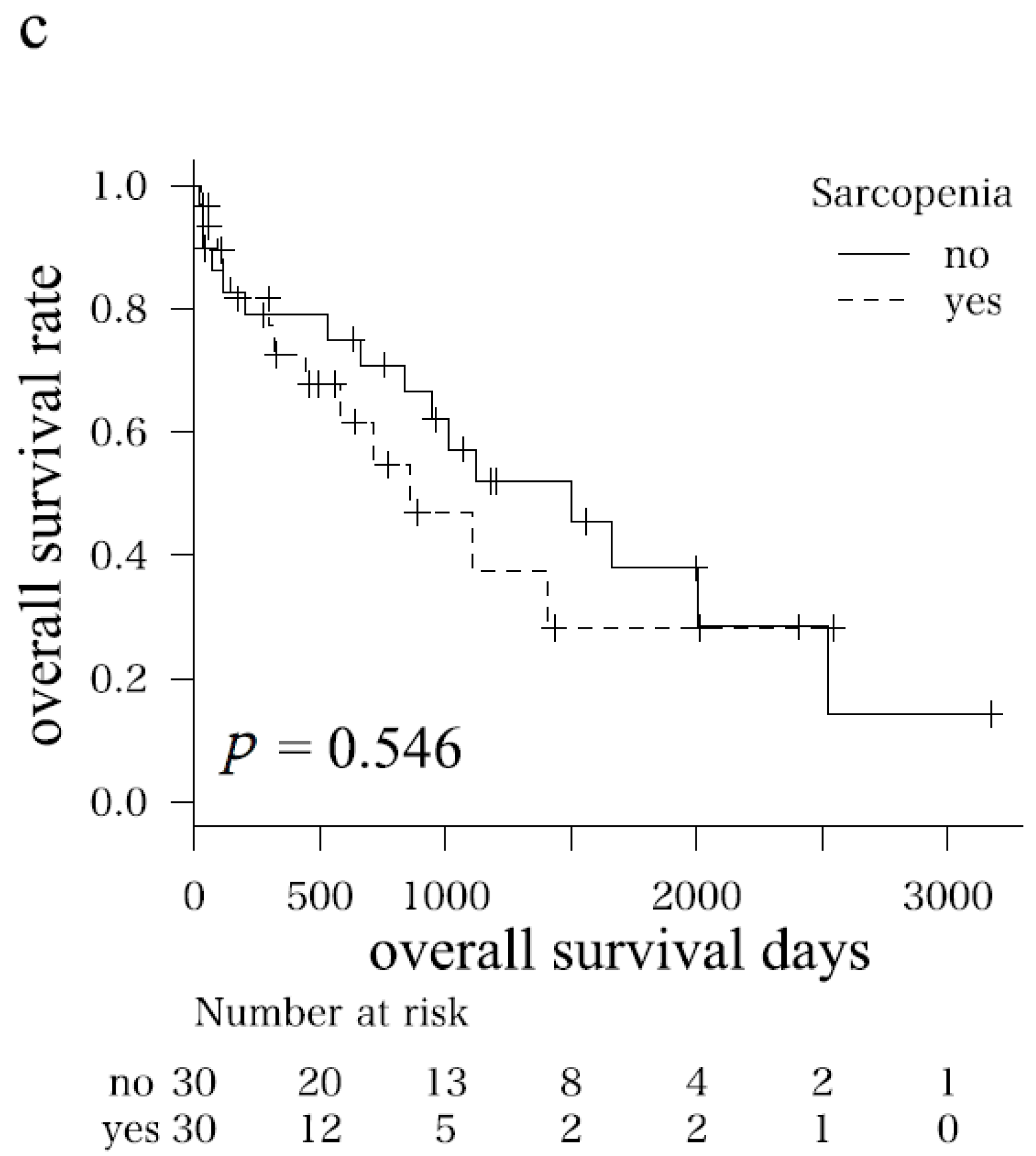
3.2. Comparison of Overall Survival in Sarcopenia and Non-Sarcopenia Groups before and after Adjustments for Possible Confounding Factors
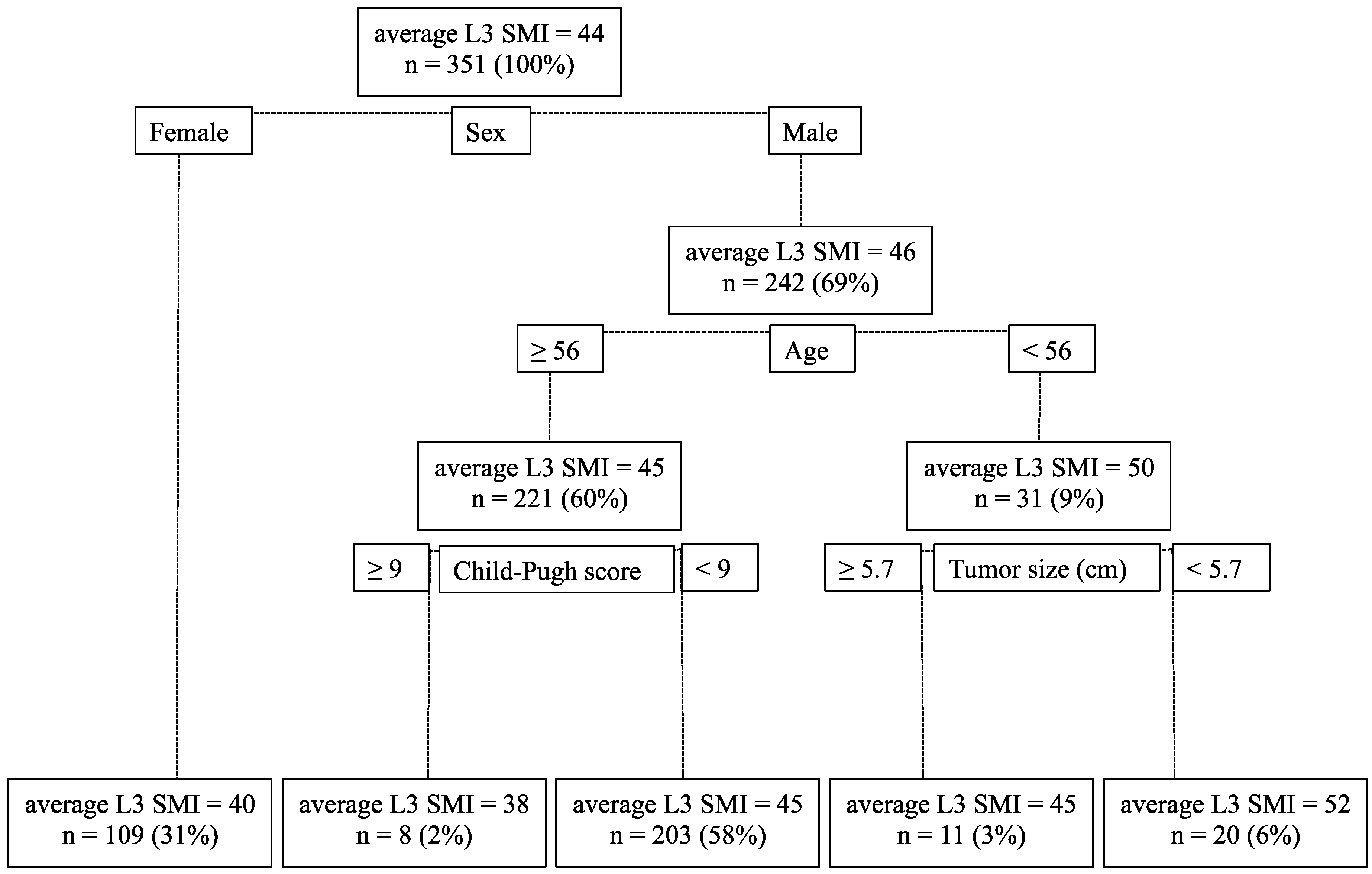
3.3. Significant Factors that Affect L3 SMI Based on Multiple Linear Regression Analysis and Tree-Based Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- A new prognostic system for hepatocellular carcinoma: A retrospective study of 435 patients: The cancer of the liver italian program (clip) investigators. Hepatology 1998, 28, 751–755.
- Kudo, M.; Chung, H.; Osaki, Y. Prognostic staging system for hepatocellular carcinoma (clip score): Its value and limitations, and a proposal for a new staging system, the japan integrated staging score (jis score). J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 38, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poon, R.T. Prevention of recurrence after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma: A daunting challenge. Hepatology 2011, 54, 757–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Bru, C.; Bruix, J. Prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: The bclc staging classification. Semin. Liver Dis. 1999, 19, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, I.H. Sarcopenia: Origins and clinical relevance. J. Nutr. 1997, 127, 990S–991S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, N.; Nakagawa, H.; Kudo, Y.; Tateishi, R.; Taguri, M.; Watadani, T.; Nakagomi, R.; Kondo, M.; Nakatsuka, T.; Minami, T.; et al. Sarcopenia, intramuscular fat deposition, and visceral adiposity independently predict the outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado, C.M.; Lieffers, J.R.; McCargar, L.J.; Reiman, T.; Sawyer, M.B.; Martin, L.; Baracos, V.E. Prevalence and clinical implications of sarcopenic obesity in patients with solid tumours of the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts: A population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2008, 9, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabel, M.S.; Lee, J.; Cai, S.; Englesbe, M.J.; Holcombe, S.; Wang, S. Sarcopenia as a prognostic factor among patients with stage iii melanoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 18, 3579–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, B.H.; Birdsell, L.A.; Martin, L.; Baracos, V.E.; Fearon, K.C. Sarcopenia in an overweight or obese patient is an adverse prognostic factor in pancreatic cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 6973–6979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Vledder, M.G.; Levolger, S.; Ayez, N.; Verhoef, C.; Tran, T.C.; Ijzermans, J.N. Body composition and outcome in patients undergoing resection of colorectal liver metastases. Br. J. Surg. 2012, 99, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iritani, S.; Imai, K.; Takai, K.; Hanai, T.; Ideta, T.; Miyazaki, T.; Suetsugu, A.; Shiraki, M.; Shimizu, M.; Moriwaki, H. Skeletal muscle depletion is an independent prognostic factor for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 50, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, K.; Takai, K.; Hanai, T.; Ideta, T.; Miyazaki, T.; Kochi, T.; Suetsugu, A.; Shiraki, M.; Shimizu, M. Skeletal muscle depletion predicts the prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with sorafenib. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 9612–9624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanai, T.; Shiraki, M.; Nishimura, K.; Ohnishi, S.; Imai, K.; Suetsugu, A.; Takai, K.; Shimizu, M.; Moriwaki, H. Sarcopenia impairs prognosis of patients with liver cirrhosis. Nutrition 2015, 31, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanai, T.; Shiraki, M.; Ohnishi, S.; Miyazaki, T.; Ideta, T.; Kochi, T.; Imai, K.; Suetsugu, A.; Takai, K.; Moriwaki, H.; et al. Rapid skeletal muscle wasting predicts worse survival in patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Baeyens, J.P.; Bauer, J.M.; Boirie, Y.; Cederholm, T.; Landi, F.; Martin, F.C.; Michel, J.P.; Rolland, Y.; Schneider, S.M.; et al. Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis: Report of the european working group on sarcopenia in older people. Age Ageing 2010, 39, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, H.; Shiraki, M.; Hiramatsu, A.; Moriya, K.; Hino, K.; Nishiguchi, S. Japan society of hepatology guidelines for sarcopenia in liver disease (1st edition): Recommendation from the working group for creation of sarcopenia assessment criteria. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical practice guidelines for hepatocellular carcinoma—The Japan society of hepatology 2009 update. Hepatol. Res. Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Hepatol. 2010, 40, 2–144.
- Mitsiopoulos, N.; Baumgartner, R.N.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Lyons, W.; Gallagher, D.; Ross, R. Cadaver validation of skeletal muscle measurement by magnetic resonance imaging and computerized tomography. J. Appl. Physiol. 1998, 85, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Austin, P.C. Propensity-score matching in the cardiovascular surgery literature from 2004 to 2006: A systematic review and suggestions for improvement. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2007, 134, 1128–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pociot, F.; Karlsen, A.E.; Pedersen, C.B.; Aalund, M.; Nerup, J.; European Consortium for I.G.S. Novel analytical methods applied to type 1 diabetes genome-scan data. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2004, 74, 647–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, M.; Muenz, D.G.; Chang, J.T.; Papaleontiou, M.; Haymart, M.R. Tree-based model for thyroid cancer prognostication. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 3737–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mir, O.; Coriat, R.; Blanchet, B.; Durand, J.P.; Boudou-Rouquette, P.; Michels, J.; Ropert, S.; Vidal, M.; Pol, S.; Chaussade, S.; et al. Sarcopenia predicts early dose-limiting toxicities and pharmacokinetics of sorafenib in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado, C.M.; Antoun, S.; Sawyer, M.B.; Baracos, V.E. Two faces of drug therapy in cancer: Drug-related lean tissue loss and its adverse consequences to survival and toxicity. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2011, 14, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.C.; Coombes, J.S.; Macdonald, G.A. Exercise capacity and muscle strength in patients with cirrhosis. Liver Transplant. 2012, 18, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plauth, M.; Cabre, E.; Riggio, O.; Assis-Camilo, M.; Pirlich, M.; Kondrup, J.; Ferenci, P.; Holm, E.; Vom Dahl, S.; Muller, M.J.; et al. Espen guidelines on enteral nutrition: Liver disease. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 25, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchesini, G.; Bianchi, G.; Merli, M.; Amodio, P.; Panella, C.; Loguercio, C.; Rossi Fanelli, F.; Abbiati, R. Nutritional supplementation with branched-chain amino acids in advanced cirrhosis: A double-blind, randomized trial. Gastroenterology 2003, 124, 1792–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriwaki, H.; Shiraki, M.; Fukushima, H.; Shimizu, M.; Iwasa, J.; Naiki, T.; Nagaki, M. Long-term outcome of branched-chain amino acid treatment in patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatol. Res. 2008, 38, S102–S106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muto, Y.; Sato, S.; Watanabe, A.; Moriwaki, H.; Suzuki, K.; Kato, A.; Kato, M.; Nakamura, T.; Higuchi, K.; Nishiguchi, S.; et al. Effects of oral branched-chain amino acid granules on event-free survival in patients with liver cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005, 3, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, H.K.; Raiser, S.N.; Vincent, K.R. The aging musculoskeletal system and obesity-related considerations with exercise. Ageing Res. Rev. 2012, 11, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossmann, M.; Hoermann, R.; Gani, L.; Chan, I.; Cheung, A.; Gow, P.J.; Li, A.; Zajac, J.D.; Angus, P. Low testosterone levels as an independent predictor of mortality in men with chronic liver disease. Clin. Endocrinol. 2012, 77, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riggio, O.; Angeloni, S.; Ciuffa, L.; Nicolini, G.; Attili, A.F.; Albanese, C.; Merli, M. Malnutrition is not related to alterations in energy balance in patients with stable liver cirrhosis. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 22, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montano-Loza, A.J.; Meza-Junco, J.; Prado, C.M.; Lieffers, J.R.; Baracos, V.E.; Bain, V.G.; Sawyer, M.B. Muscle wasting is associated with mortality in patients with cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 166–173, 173.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | Total (n = 351) |
|---|---|
| Sex (male/female) | 242/109 |
| Age (years) | 70.4 ± 10.3 |
| Etiology (HBV/HCV/HBV + HCV/others) | 43/204/3/101 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.1 ± 3.4 |
| L3 SMI (cm2/m2) | 43.7 ± 8.6 |
| Sarcopenia (yes/no) | 33/318 |
| Child–Pugh score (5/6/7/8/9/10/11) | 179/84/52/20/9/6/1 |
| ALB (g/dL) | 3.6 ± 0.6 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 46.9 ± 44.3 |
| T-Bil (mg/dL) | 1.2 ± 1.0 |
| PLT (×104/μL) | 13.1 ± 7.8 |
| PT (%) | 85.3 ± 16.7 |
| FPG (mg/dL) | 110.6 ± 34.2 |
| HbA1c (%) | 6.0 ± 1.1 |
| AFP (ng/dL) | 11,557 ± 73,374 |
| PIVKA-II (mAU/mL) | 21,056 ± 125,773 |
| Tumor size (cm) | 4.2 ± 3.7 |
| Tumor number (1/≥2) | 193/158 |
| Vp (0/1/2/3/4) | 289/15/15/15/17 |
| Stage (I/II/III/IV) | 79/126/100/46 |
| Curability of initial treatment (yes/no) | 188/163 |
| Oral administration of BCAA (yes/no) | 153/198 |
| Co-existing diseases (yes/no) | |
| Renal disease | 22/329 |
| Heart disease | 45/306 |
| Respiratory disease | 16/335 |
| Neurologic disease | 22/329 |
| Malignant disease (except HCC) | 27/324 |
| Variables | Sarcopenia (n = 33) | Non-Sarcopenia (n = 318) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (male/female) | 30/3 | 212/106 | 0.003 |
| Age (years) | 72.6 ± 1.8 | 70.2 ± 0.6 | 0.197 |
| Etiology (HBV/HCV/HBV + HCV/other) | 3/22/0/8 | 40/182/3/93 | 0.868 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 20.8 ± 0.6 | 23.3 ± 0.2 | <0.0001 |
| L3 SMI (cm2/m2) | 30.8 ± 1.3 | 45.1 ± 0.4 | <0.0001 |
| Child–Pugh score (5/6/7/8/9/10/11) | 15/7/5/2/0/3/1 | 164/77/47/18/9/3/0 | 0.039 |
| ALB (g/dL) | 3.5 ± 0.1 | 3.6 ± 0.03 | 0.315 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 52.2 ± 7.7 | 46.4 ± 2.5 | 0.805 |
| T-Bil (mg/dL) | 1.6 ± 0.2 | 1.2 ± 0.06 | 0.045 |
| PLT (×104/μL) | 14.5 ± 1.4 | 13.0 ± 0.4 | 0.276 |
| PT (%) | 89.1 ± 2.9 | 84.9 ± 0.9 | 0.176 |
| FPG (mg/dL) | 113.3 ± 6.0 | 110.3 ± 2.0 | 0.958 |
| HbA1c (%) | 6.2 ± 0.2 | 6.0 ± 0.07 | 0.356 |
| AFP (ng/dL) | 4133 ± 12983 | 12,319 ± 4158 | 0.549 |
| PIVKA-II (mAU/mL) | 35,910 ± 21,910 | 19,475 ± 7149 | 0.476 |
| Tumor size (cm) | 5.6 ± 0.6 | 4.0 ± 0.2 | 0.020 |
| Tumor number (1/≥2) | 20/13 | 173/145 | 0.505 |
| Vp (0/1/2/3/4) | 24/1/2/2/4 | 265/14/13/13/13 | 0.040 |
| Stage (I/II/III/IV) | 8/7/12/6 | 71/117/88/42 | 0.303 |
| Curability of initial treatment (yes/no) | 12/21 | 176/142 | 0.039 |
| Oral administration of BCAA (yes/no) | 17/16 | 136/182 | 0.361 |
| Co-existing diseases (yes/no) | |||
| Renal disease | 2/31 | 20/298 | 1.000 |
| Heart disease | 5/28 | 40/278 | 0.593 |
| Respiratory disease | 0/33 | 16/302 | 0.381 |
| Neurologic disease | 6/27 | 16/302 | 0.011 |
| Malignant disease (except HCC) | 0/33 | 27/291 | 0.093 |
| Variables | Sarcopenia (n = 30) | Non-Sarcopenia (n = 30) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (male/female) | 27/3 | 28/2 | 1.000 |
| Age (years) | 71.8 ± 9.7 | 73.0 ± 10.7 | 0.642 |
| Etiology (HBV/HCV/HBV + HCV/other) | 3/21/0/6 | 3/20/1/6 | 0.918 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 20.7 ± 3.0 | 23.2 ± 2.8 | 0.002 |
| L3 SMI (cm2/m2) | 30.5 ± 6.4 | 46.8 ± 7.4 | <0.0001 |
| Child–Pugh score (5/6/7/8/9/10/11) | 14/7/5/2/0/1/1 | 14/9/6/0/1/0/0 | 0.660 |
| ALB (g/dL) | 3.6 ± 0.7 | 3.6 ± 0.6 | 0.984 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 48.8 ± 57.7 | 41.8 ± 22.7 | 0.543 |
| T-Bil (mg/dL) | 1.4 ± 1.0 | 1.0 ± 0.5 | 0.106 |
| PLT (×104/μL) | 14.5 ± 13.0 | 13.4 ± 4.9 | 0.656 |
| PT (%) | 89.8 ± 14.4 | 87.7 ± 15.5 | 0.589 |
| FPG (mg/dL) | 114.8 ± 40.2 | 113.6 ± 47.9 | 0.918 |
| HbA1c (%) | 6.3 ± 1.6 | 5.8 ± 1.2 | 0.226 |
| AFP (ng/dL) | 3531 ± 12,997 | 1480 ± 4268 | 0.423 |
| PIVKA-II (mAU/mL) | 22,979 ± 89,165 | 10,893 ± 46,387 | 0.518 |
| Tumor size (cm) | 5.0 ± 3.9 | 4.4 ± 3.8 | 0.534 |
| Tumor number (1/≥2) | 18/12 | 18/12 | 1.000 |
| Vp (0/1/2/3/4) | 24/1/2/1/2 | 22/3/1/2/2 | 0.852 |
| Stage (I/II/III/IV) | 8/7/10/5 | 7/11/5/7 | 0.427 |
| Curability of initial treatment (yes/no) | 12/18 | 17/13 | 0.301 |
| Variables | Std. Coefficient | Std. Error | t Value | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 46.94 | 3.06 | 15.33 | <0.0001 |
| Age | −0.10 | 0.04 | −2.44 | 0.015 |
| Sex (vs. man) | 5.20 | 0.95 | 5.46 | <0.0001 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Imai, K.; Takai, K.; Watanabe, S.; Hanai, T.; Suetsugu, A.; Shiraki, M.; Shimizu, M. Sarcopenia Impairs Prognosis of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Role of Liver Functional Reserve and Tumor-Related Factors in Loss of Skeletal Muscle Volume. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9101054
Imai K, Takai K, Watanabe S, Hanai T, Suetsugu A, Shiraki M, Shimizu M. Sarcopenia Impairs Prognosis of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Role of Liver Functional Reserve and Tumor-Related Factors in Loss of Skeletal Muscle Volume. Nutrients. 2017; 9(10):1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9101054
Chicago/Turabian StyleImai, Kenji, Koji Takai, Satoshi Watanabe, Tatsunori Hanai, Atsushi Suetsugu, Makoto Shiraki, and Masahito Shimizu. 2017. "Sarcopenia Impairs Prognosis of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Role of Liver Functional Reserve and Tumor-Related Factors in Loss of Skeletal Muscle Volume" Nutrients 9, no. 10: 1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9101054
APA StyleImai, K., Takai, K., Watanabe, S., Hanai, T., Suetsugu, A., Shiraki, M., & Shimizu, M. (2017). Sarcopenia Impairs Prognosis of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Role of Liver Functional Reserve and Tumor-Related Factors in Loss of Skeletal Muscle Volume. Nutrients, 9(10), 1054. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9101054





