Protective Effects of Ethanolic Extracts from Artichoke, an Edible Herbal Medicine, against Acute Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Animals
- (1)
- Control group: mice were gavaged with same volume of 0.9% saline twice per day (interval time, one hour).
- (2)
- EtOH group (model group): mice were gavaged with same volume of 0.9% saline and with 12 mL/kg body weight (BW) alcohol one hour after saline administration per day.
- (3)
- Positive control group (EtOH + bifendate): mice were gavaged with 0.36 g/kg BW of bifendate and with 12 mL/kg BW alcohol one hour after bifendate pretreatment each day.
- (4)
- Low-dose artichoke group (EtOH + artichoke 0.4): mice were gavaged with 0.4 g/kg BW of artichoke and with 12 mL/kg BW alcohol one hour after artichoke pretreatment each day.
- (5)
- Middle-dose artichoke group (EtOH + artichoke 0.8): mice were gavaged with 0.8 g/kg BW of artichoke and with 12 mL/kg BW alcohol one hour after artichoke pretreatment each day.
- (6)
- High-dose artichoke group (EtOH + artichoke 1.6): mice were gaveged with 1.6 g/kg BW of artichoke and with 12 mL/kg BW alcohol one hour after artichoke pretreatment each day.
2.3. Serum Biochemical Assays
2.4. Hepatic Antioxidant and Oxidative Stress Marker Assays
2.5. Histological Examination of Liver Tissue
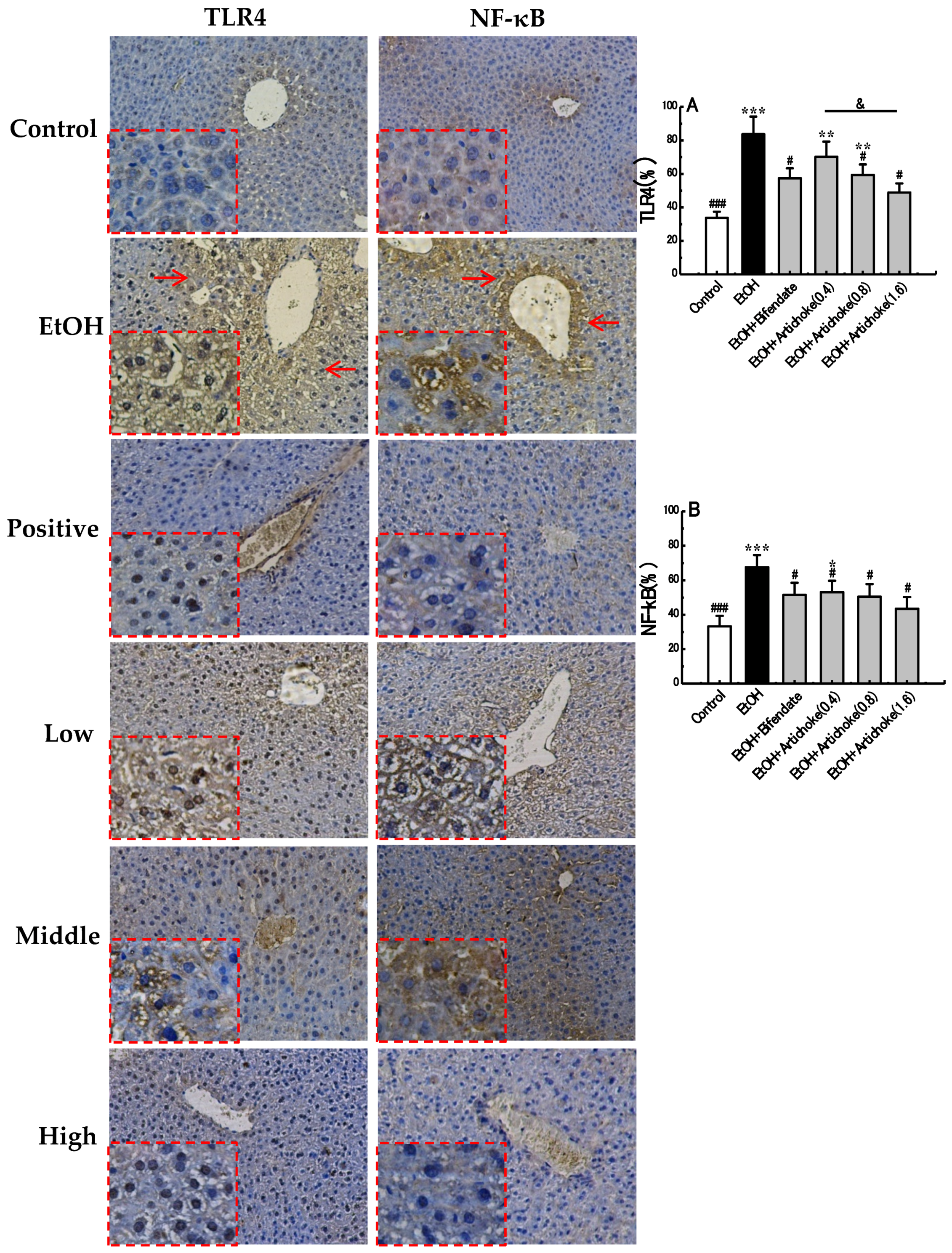
2.6. Immunohistochemical Analysis of TLR4 and NF-κB
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Liver Index of ICR Mice
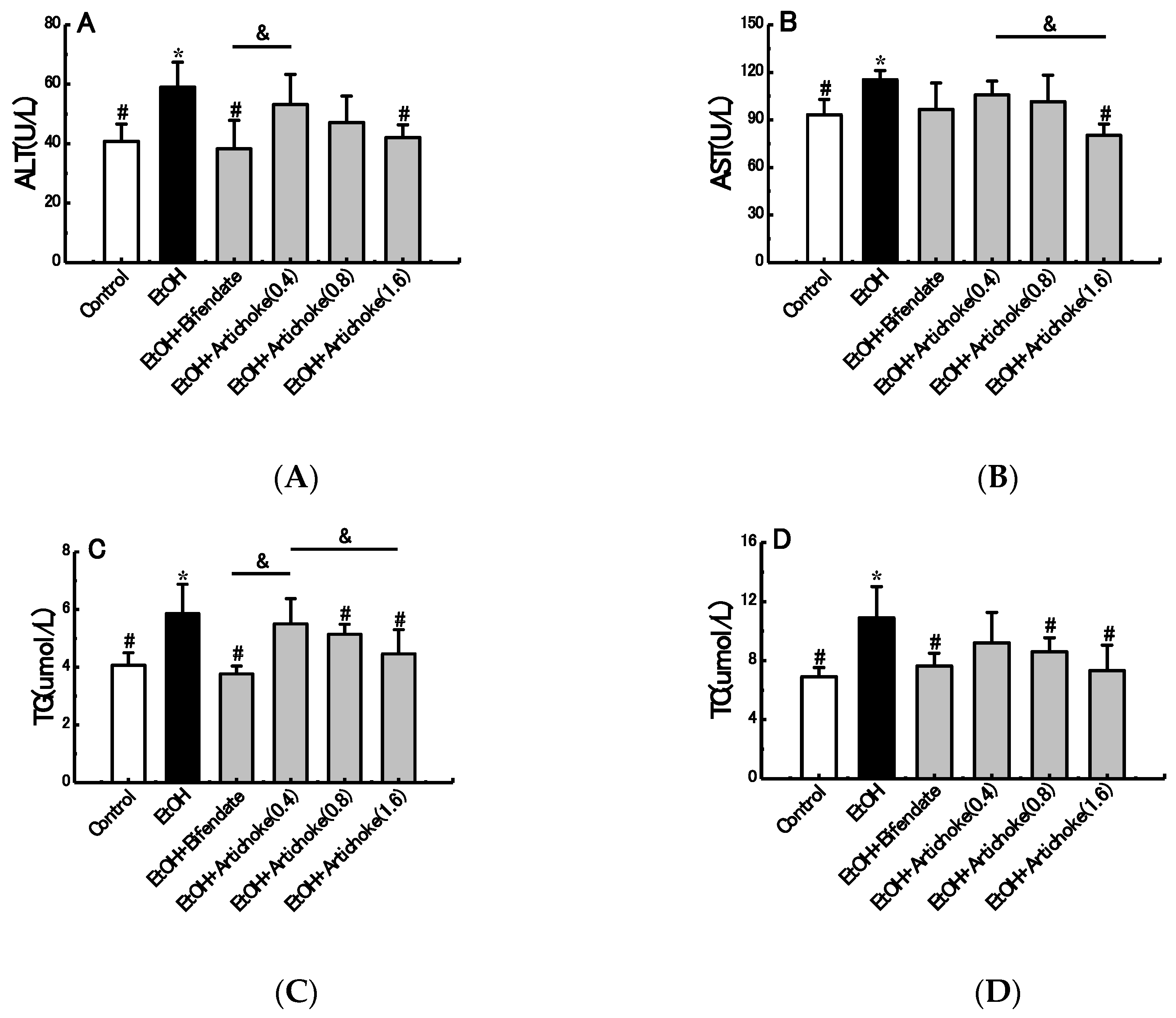
3.2. Serum Biochemical Markers
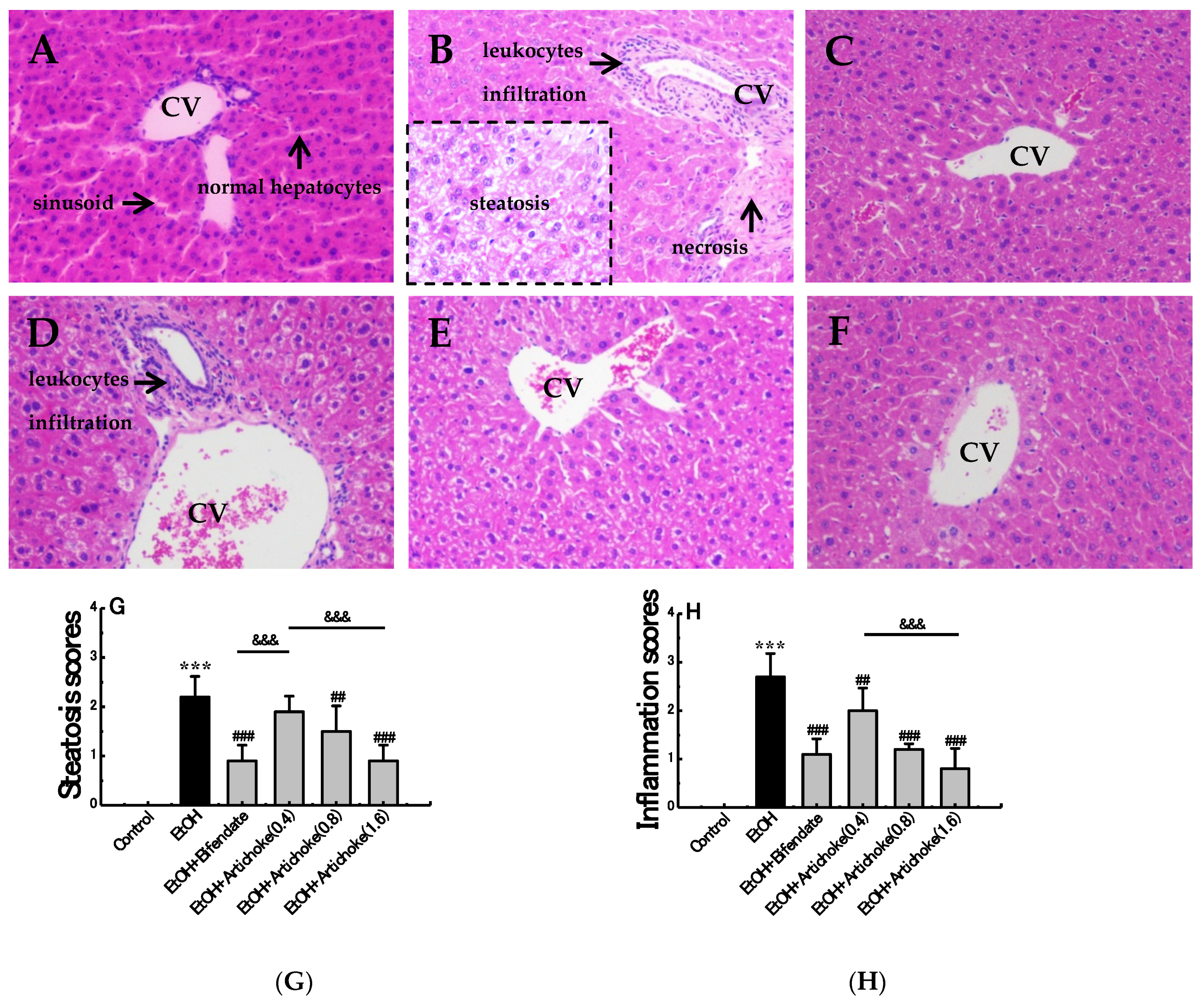
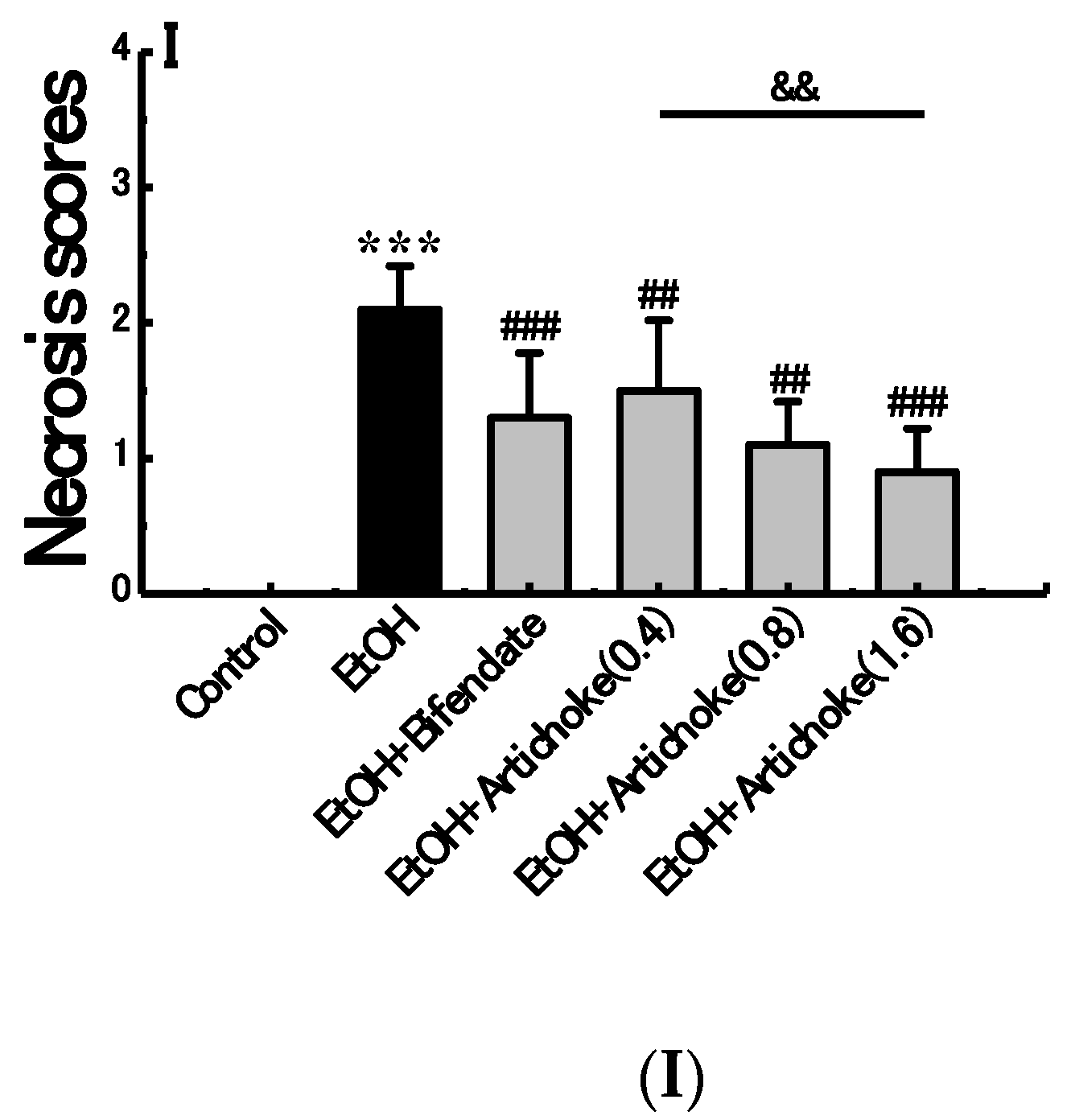
3.3. Histopathological Analysis
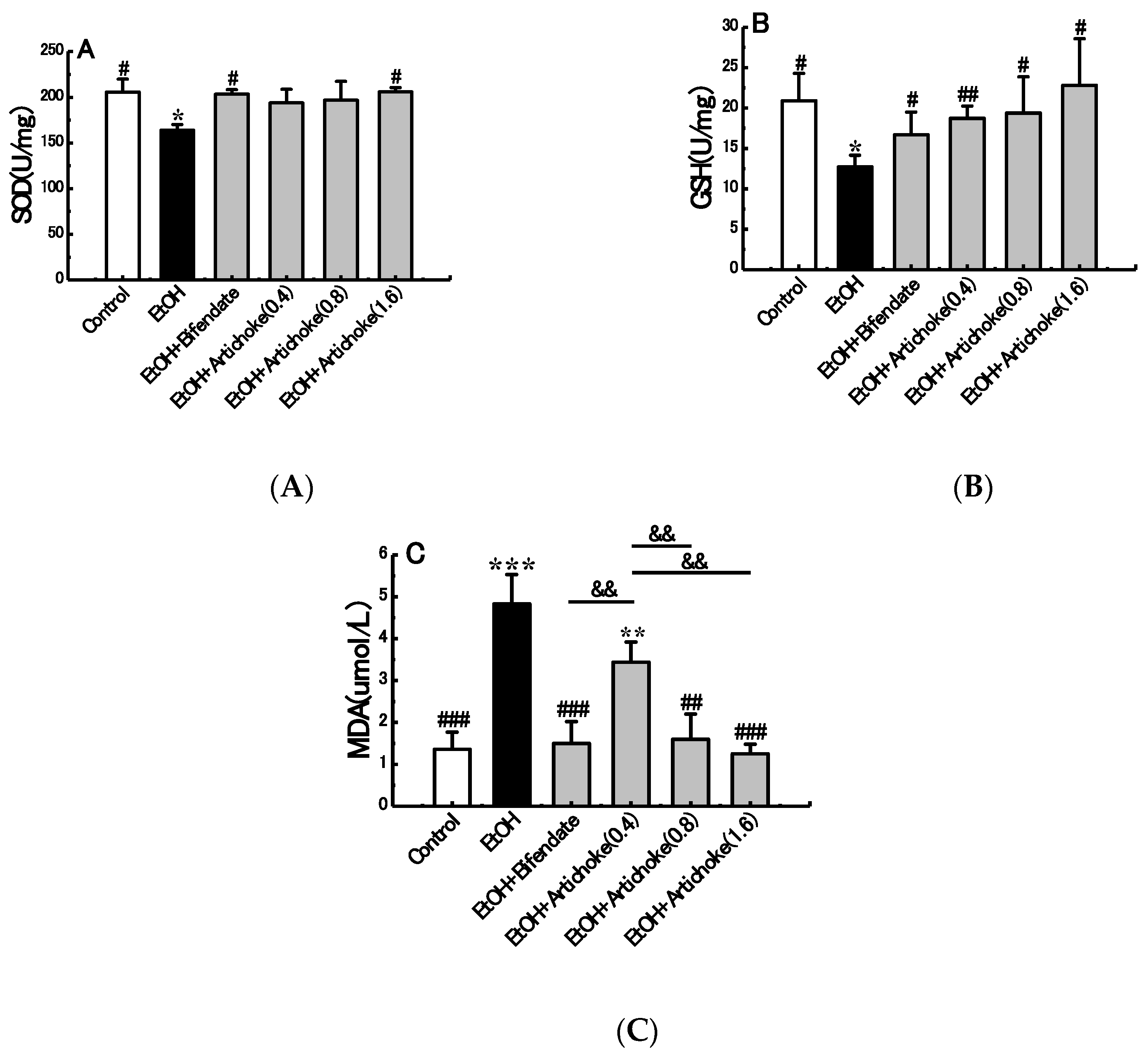
3.4. Hepatic Antioxidant and Oxidative Stress Markers
3.5. TLR4 and NF-κB Expression Levels
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Szabo, G. Gut–liver axis in alcoholic liver disease. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Han, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Pan, S.; Liang, S.; Wang, S. Plasma metabonomic analysis reveals the effects of salvianic acid on alleviating acute alcoholic liver damage. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 36732–36741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaratani, H.; Tsujimoto, T.; Douhara, A.; Takaya, H.; Moriya, K.; Namisaki, T.; Noguchi, R.; Yoshiji, H.; Fujimoto, M.; Fukui, H. The effect of inflammatory cytokines in alcoholic liver disease. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 495156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.-W.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, D.-Y.; Zhang, X.-J.; Hu, Y.-J.; Li, P.; Su, H.; Wan, J.-B. The hepatoprotective effect of aqueous extracts of penthorum chinense pursh against acute alcohol-induced liver injury is associated with ameliorating hepatic steatosis and reducing oxidative stress. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 1510–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Bataller, R. Alcoholic liver disease: Pathogenesis and new therapeutic targets. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1572–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R.; Kaneider, N.C. Pathways of liver injury in alcoholic liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 1159–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akira, S.; Uematsu, S.; Takeuchi, O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 2006, 124, 783–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilmore, T.D. Introduction to nf-kappab: Players, pathways, perspectives. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6680–6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, S.; Yamazaki, T.; Kawano, Y.; Miura, S.; Ezaki, O. Fish oil fed prior to ethanol administration prevents acute ethanol-induced fatty liver in mice. J. Hepatol. 2008, 49, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hritz, I.; Mandrekar, P.; Velayudham, A.; Catalano, D.; Dolganiuc, A.; Kodys, K.; Kurt-Jones, E.; Szabo, G. The critical role of toll-like receptor (TLR) 4 in alcoholic liver disease is independent of the common TLR adapter MyD88. Hepatology 2008, 48, 1224–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purohit, V.; Gao, B.; Song, B.J. Molecular mechanisms of alcoholic fatty liver. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2009, 33, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Q.; Wang, P.; Wang, Z.; Smith, A.J. Cytidine-phosphate-guanosine oligonucleotides induce interleukin-8 production through activation of TLR9, MyD88, NF-κB, and ERK pathways in odontoblast cells. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suk, K.T.; Kim, M.Y.; Baik, S.K. Alcoholic liver disease: Treatment. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 12934–12944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Shea, R.S.; Dasarathy, S.; McCullough, A.J.; Practice Guideline Committee of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases; Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology. Alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology 2010, 51, 307–328. [Google Scholar]
- Massey, V.L.; Arteel, G.E. Acute alcohol-induced liver injury. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leggio, L.; Kenna, G.A.; Ferrulli, A.; Zywiak, W.H.; Caputo, F.; Swift, R.M.; Addolorato, G. Preliminary findings on the use of metadoxine for the treatment of alcohol dependence and alcoholic liver disease. Hum. Psychopharmacol. 2011, 26, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, S.Y.; Yang, R.; Dong, H.; Yu, Z.L.; Ko, K.M. Bifendate treatment attenuates hepatic steatosis in cholesterol/bile salt- and high-fat diet-induced hypercholesterolemia in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 552, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Rai, A.; Reddy, N.D.; Raj, P.V.; Jain, P.; Deshpande, P.; Mathew, G.; Kutty, N.G.; Udupa, N.; Rao, C.M. Silymarin liposomes improves oral bioavailability of silybin besides targeting hepatocytes, and immune cells. Pharmacol. Rep. 2014, 66, 788–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pistón, M.; Machado, I.; Branco, C.S.; Cesio, V.; Heinzen, H.; Ribeiro, D.; Fernandes, E.; Chisté, R.C.; Freitas, M. Infusion, decoction and hydroalcoholic extracts of leaves from artichoke (cynara cardunculus L. Subsp. Cardunculus) are effective scavengers of physiologically relevant ros and rns. Food Res. Int. 2014, 64, 150–156. [Google Scholar]
- Bianco, V.V. Present Situation and Future Potential of Artichoke in the Mediterranean Basin; International Society for Horticultural Science (ISHS): Leuven, Belgium, 2005; pp. 39–58. [Google Scholar]
- Wittemer, S.M.; Ploch, M.; Windeck, T.; Muller, S.C.; Drewelow, B.; Derendorf, H.; Veit, M. Bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of caffeoylquinic acids and flavonoids after oral administration of artichoke leaf extracts in humans. Phytomedicine 2005, 12, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegener, T.; Fintelmann, V. Pharmacological properties and therapeutic profile of artichoke (cynara scolymus L.). Wien. Med. Wochenschr. 1999, 149, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Joy, J.F.; Haber, S.L. Clinical uses of artichoke leaf extract. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2007, 64, 1904, 1906–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moglia, A.; Lanteri, S.; Comino, C.; Acquadro, A.; de Vos, R.; Beekwilder, J. Stress-induced biosynthesis of dicaffeoylquinic acids in globe artichoke. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 8641–8649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wider, B.; Pittler, M.H.; Thompson-Coon, J.; Ernst, E. Artichoke leaf extract for treating hypercholesterolaemia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 7, CD003335. [Google Scholar]
- Heidarian, E.; Soofiniya, Y. Hypolipidemic and hypoglycemic effects of aerial part of cynara scolymus in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Med. Plants Res. 2011, 5, 2717–2723. [Google Scholar]
- Yasukawa, K.; Matsubara, H.; Sano, Y. Inhibitory effect of the flowers of artichoke (cynara cardunculus) on TPA-induced inflammation and tumor promotion in two-stage carcinogenesis in mouse skin. J. Nat. Med. 2010, 64, 388–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebhardt, R. Inhibition of cholesterol biosynthesis in HepG2 cells by artichoke extracts is reinforced by glucosidase pretreatment. Phytother. Res. 2002, 16, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, L.W.; Wang, L.K.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Luo, L.P.; Song, J.C.; Gong, Z.J. Betaine protects against high-fat-diet-induced liver injury by inhibition of high-mobility group box 1 and toll-like receptor 4 expression in rats. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2013, 58, 3198–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.X.; Lai, L.N.; Zhang, H.Y.; Bi, Y.H.; Meng, L.; Li, X.J.; Tian, X.X.; Wang, L.M.; Fan, Y.M.; Zhao, Z.F.; et al. Effect of artesunate supplementation on bacterial translocation and dysbiosis of gut microbiota in rats with liver cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 2949–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Yang, M.; Huang, W.; Wang, Y.; Yang, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Z. Composition, antioxidant activities and hepatoprotective effects of the water extract of ziziphus jujuba cv. Jinsixiaozao. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 6511–6522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, J.; Ratner, M.; Shaw, M.; Bailey, W.; Schomaker, S. The current state of serum biomarkers of hepatotoxicity. Toxicology 2008, 245, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, O.R.; Pani, G.; Borrello, S.; Colavitti, R.; Cravero, A.; Farre, S.; Galeotti, T. Oxidative stress and antioxidant defenses in ethanol-induced cell injury. Mol. Asp. Med. 2004, 25, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afonso, V.; Champy, R.; Mitrovic, D.; Collin, P.; Lomri, A. Reactive oxygen species and superoxide dismutases: Role in joint diseases. Jt. Bone Spine 2007, 74, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, R.B.; Tian, K.; Cao, Y.W.; Bao, J.L.; Wang, M.; He, C.; Hu, Y.; Su, H.; Wan, J.B. Protective effect of panax notoginseng saponins on acute ethanol-induced liver injury is associated with ameliorating hepatic lipid accumulation and reducing ethanol-mediated oxidative stress. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 2413–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Matos, D.G.; Furnus, C.C. The importance of having high glutathione (GSH) level after bovine in vitro maturation on embryo development: Effect of β-mercaptoethanol, cysteine and cystine. Theriogenology 2000, 53, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Ye, Y.; Kang, J.; Yao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, W.; Gao, M.; Dai, Y.; Xin, Y.; Wang, Q.; et al. l-theanine prevents alcoholic liver injury through enhancing the antioxidant capability of hepatocytes. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuma, D.J. Role of malondialdehyde-acetaldehyde adducts in liver injury. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2002, 32, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akira, S.; Takeda, K.; Kaisho, T. Toll-like receptors: Critical proteins linking innate and acquired immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Signaling to nf-kappab by toll-like receptors. Trends Mol. Med. 2007, 13, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palsson-McDermott, E.M.; O’Neill, L.A. Signal transduction by the lipopolysaccharide receptor, toll-like receptor-4. Immunology 2004, 113, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Treatment Group | Dosage (g/kg) | Liver Weight (g) | Initial Body Weight (g) | Final Body Weight (g) | Liver Index (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | _ | 1.75 ± 0.22 | 26.46 ± 0.64 | 36.96 ± 4.26 # | 4.78 ± 0.64 # |
| EtOH | _ | 1.53 ± 0.17 | 26.24 ± 0.70 | 29.94 ± 2.98 * | 5.20 ± 0.22 * |
| EtOH + Bifendate | 0.36 | 1.53 ± 0.18 | 26.17 ± 0.95 | 30.18 ± 2.13 * | 5.05 ± 0.38 |
| Low-dose artichoke | 0.4 | 1.47 ± 0.23 | 26.35 ± 0.72 | 28.79 ± 3.00 * | 5.12 ± 0.64 |
| Middle-dose artichoke | 0.8 | 1.57 ± 0.20 | 26.39 ± 0.52 | 29.06 ± 2.03 * | 5.04 ± 0.44 |
| High-dose artichoke | 1.6 | 1.54 ± 0.12 | 25.94 ± 0.85 | 29.84 ± 1.27 * | 5.14 ± 0.31 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, X.; Wei, R.; Deng, A.; Lei, T. Protective Effects of Ethanolic Extracts from Artichoke, an Edible Herbal Medicine, against Acute Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury in Mice. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1000. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9091000
Tang X, Wei R, Deng A, Lei T. Protective Effects of Ethanolic Extracts from Artichoke, an Edible Herbal Medicine, against Acute Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury in Mice. Nutrients. 2017; 9(9):1000. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9091000
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Xuchong, Ruofan Wei, Aihua Deng, and Tingping Lei. 2017. "Protective Effects of Ethanolic Extracts from Artichoke, an Edible Herbal Medicine, against Acute Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury in Mice" Nutrients 9, no. 9: 1000. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9091000
APA StyleTang, X., Wei, R., Deng, A., & Lei, T. (2017). Protective Effects of Ethanolic Extracts from Artichoke, an Edible Herbal Medicine, against Acute Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury in Mice. Nutrients, 9(9), 1000. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9091000





