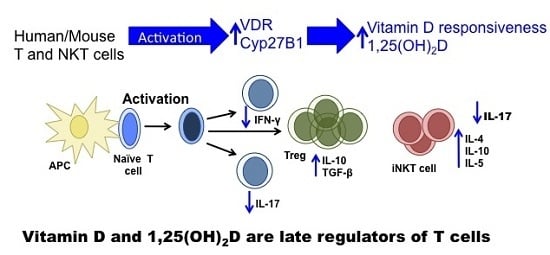
Vitamin D and 1,25(OH)2D Regulation of T cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. T Cells
3. Vitamin D and T Cells
4. Vitamin D Regulation of Mouse versus Human T Cells

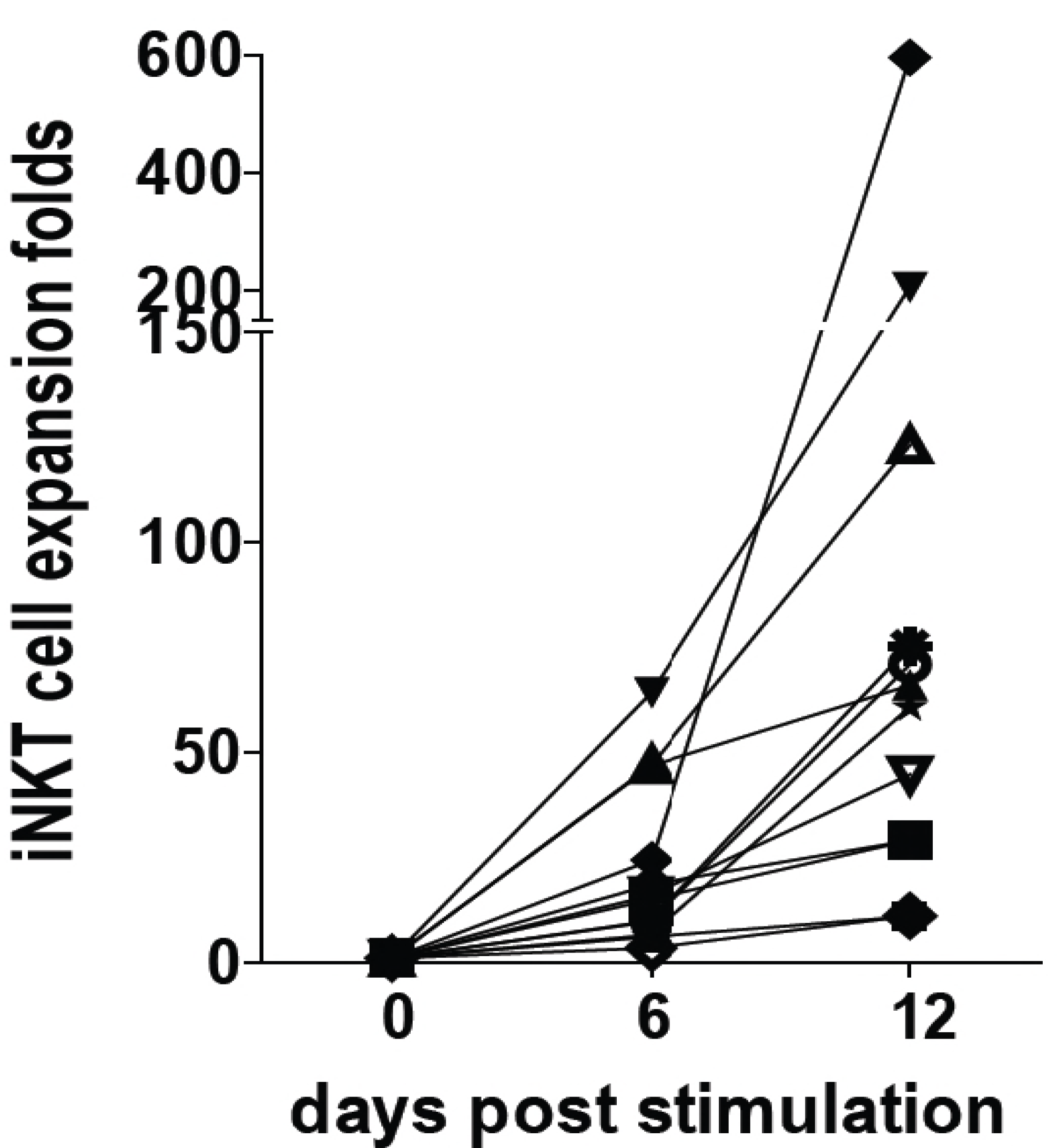
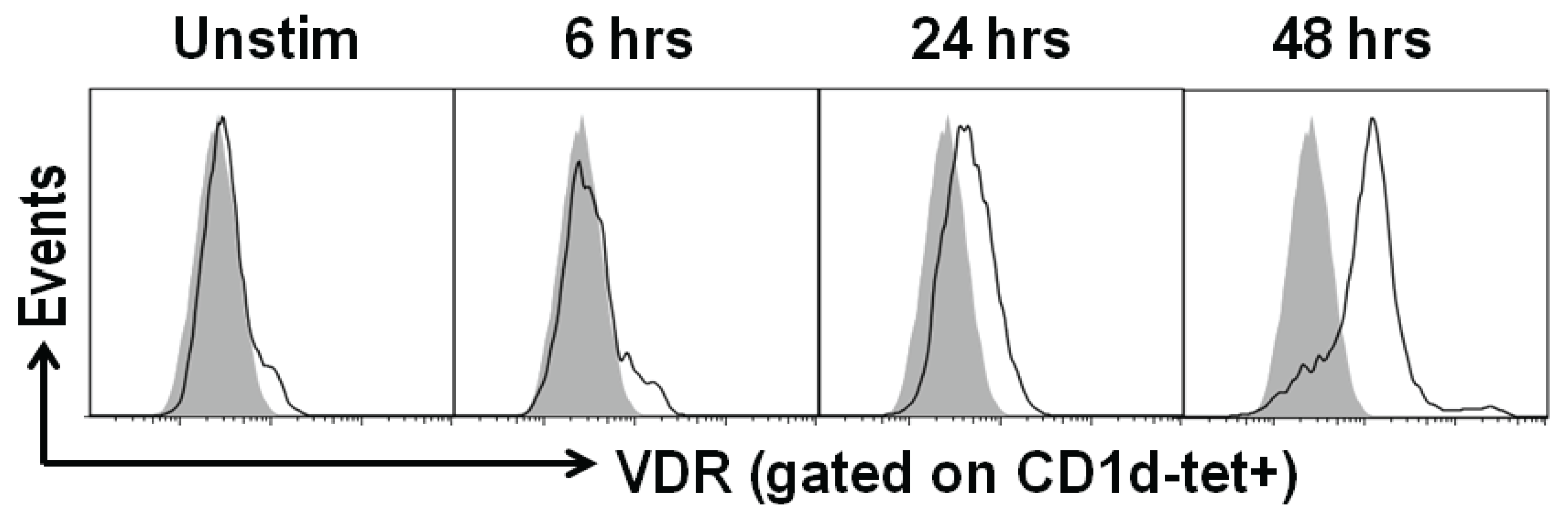
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interests
References
- Reeve, L.; Tanaka, Y.; DeLuca, H.F. Studies on the site of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin d3 synthesis in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 1983, 258, 3615–3617. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Christakos, S.; Ajibade, D.V.; Dhawan, P.; Fechner, A.J.; Mady, L.J. Vitamin D: Metabolism. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 38, 1–11,vii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLuca, H.F. Overview of general physiologic features and functions of vitamin d. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 1689S–1696S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pike, J.W.; Meyer, M.B. Fundamentals of vitamin d hormone-regulated gene expression. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 144, (Pt. A). 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, W.B.; Holick, M.F. Benefits and requirements of vitamin d for optimal health: A review. Altern. Med. Rev. 2005, 10, 94–111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Veldman, C.M.; Cantorna, M.T.; DeLuca, H.F. Expression of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin d(3) receptor in the immune system. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2000, 374, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swain, S.L.; McKinstry, K.K.; Strutt, T.M. Expanding roles for cd4(+) t cells in immunity to viruses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.S.; Macatonia, S.E.; Tripp, C.S.; Wolf, S.F.; O’Garra, A.; Murphy, K.M. Development of th1 cd4+ t cells through il-12 produced by listeria-induced macrophages. Science 1993, 260, 547–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haanen, J.B.; de Waal Malefijt, R.; Res, P.C.; Kraakman, E.M.; Ottenhoff, T.H.; de Vries, R.R.; Spits, H. Selection of a human t helper type 1-like t cell subset by mycobacteria. J. Exp. Med. 1991, 174, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maizels, R.M.; Hewitson, J.P.; Smith, K.A. Susceptibility and immunity to helminth parasites. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2012, 24, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, C.T.; Elson, C.O.; Fouser, L.A.; Kolls, J.K. The th17 pathway and inflammatory diseases of the intestines, lungs, and skin. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2013, 8, 477–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishigame, H.; Kakuta, S.; Nagai, T.; Kadoki, M.; Nambu, A.; Komiyama, Y.; Fujikado, N.; Tanahashi, Y.; Akitsu, A.; Kotaki, H.; et al. Differential roles of interleukin-17a and -17f in host defense against mucoepithelial bacterial infection and allergic responses. Immunity 2009, 30, 108–119. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda, J.L.; Mallevaey, T.; Scott-Browne, J.; Gapin, L. Cd1d-restricted inkt cells, the ‘swiss-army knife’ of the immune system. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2008, 20, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gratz, I.K.; Campbell, D.J. Organ-specific and memory treg cells: Specificity, development, function, and maintenance. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamura, C.; Nakayama, T. Role of nkt cells in allergic asthma. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2010, 22, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigby, W.F.; Stacy, T.; Fanger, M.W. Inhibition of t lymphocyte mitogenesis by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin d3 (calcitriol). J. Clin. Investig. 1984, 74, 1451–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provvedini, D.M.; Tsoukas, C.D.; Deftos, L.J.; Manolagas, S.C. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin d3 receptors in human leukocytes. Science 1983, 221, 1181–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoukas, C.D.; Provvedini, D.M.; Manolagas, S.C. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin d3: A novel immunoregulatory hormone. Science 1984, 224, 1438–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, M.T.; Lee, Y.K.; Maynard, C.L.; Oliver, J.R.; Bikle, D.D.; Jetten, A.M.; Weaver, C.T. Lineage-specific effects of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin d(3) on the development of effector cd4 t cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonstra, A.; Barrat, F.J.; Crain, C.; Heath, V.L.; Savelkoul, H.F.; O’Garra, A. 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin d3 has a direct effect on naive cd4(+) t cells to enhance the development of th2 cells. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 4974–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahon, B.D.; Wittke, A.; Weaver, V.; Cantorna, M.T. The targets of vitamin d depend on the differentiation and activation status of cd4 positive t cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2003, 89, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichler, J.; Gerstmayr, M.; Szepfalusi, Z.; Urbanek, R.; Peterlik, M.; Willheim, M. 1alpha,25(oh)2d3 inhibits not only th1 but also th2 differentiation in human cord blood t cells. Pediatr. Res. 2002, 52, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Staeva-Vieira, T.P.; Freedman, L.P. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin d3 inhibits ifn-gamma and il-4 levels during in vitro polarization of primary murine cd4+ t cells. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korf, H.; Wenes, M.; Stijlemans, B.; Takiishi, T.; Robert, S.; Miani, M.; Eizirik, D.L.; Gysemans, C.; Mathieu, C. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin d(3) curtails the inflammatory and t cell stimulatory capacity of macrophages through an il-10-dependent mechanism. Immunobiology. 2012, 217, 1292–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigmundsdottir, H.; Pan, J.; Debes, G.F.; Alt, C.; Habtezion, A.; Soler, D.; Butcher, E.C. Dcs metabolize sunlight-induced vitamin d3 to ‘program’ t cell attraction to the epidermal chemokine ccl27. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Bruce, D.; Cantorna, M.T. Vitamin d receptor expression controls proliferation of naive cd8+ t cells and development of cd8 mediated gastrointestinal inflammation. BMC Immunol. 2014, 15, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigby, W.F.; Yirinec, B.; Oldershaw, R.L.; Fanger, M.W. Comparison of the effects of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin d3 on t lymphocyte subpopulations. Eur. J. Immunol. 1987, 17, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuzefpolskiy, Y.; Baumann, F.M.; Penny, L.A.; Studzinski, G.P.; Kalia, V.; Sarkar, S. Vitamin d receptor signals regulate effector and memory cd8 t cell responses to infections in mice. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 2073–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce, D.; Cantorna, M.T. Intrinsic requirement for the vitamin d receptor in the development of cd8alphaalpha-expressing t cells. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 2819–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Cantorna, M.T. The vitamin d receptor is required for inkt cell development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5207–5212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Cantorna, M.T. Epigenetic reduction in invariant nkt cells following in utero vitamin d deficiency in mice. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 1384–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waddell, A.; Zhao, J.; Cantorna, M.T. Natural killer t cells can help mediate the protective effects of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin d3 in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice. Int. Immunol. 2015, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Zella, J.B.; McCary, L.C.; DeLuca, H.F. Oral administration of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin d3 completely protects nod mice from insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2003, 417, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregori, S.; Giarratana, N.; Smiroldo, S.; Uskokovic, M.; Adorini, L. A 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin d(3) analog enhances regulatory t-cells and arrests autoimmune diabetes in nod mice. Diabetes 2002, 51, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantorna, M.T.; Munsick, C.; Bemiss, C.; Mahon, B.D. 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol prevents and ameliorates symptoms of experimental murine inflammatory bowel disease. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 2648–2652. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Froicu, M.; Zhu, Y.; Cantorna, M.T. Vitamin d receptor is required to control gastrointestinal immunity in il-10 knockout mice. Immunology 2006, 117, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantorna, M.T.; Humpal-Winter, J.; DeLuca, H.F. In vivo upregulation of interleukin-4 is one mechanism underlying the immunoregulatory effects of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin d(3). Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2000, 377, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spach, K.M.; Nashold, F.E.; Dittel, B.N.; Hayes, C.E. Il-10 signaling is essential for 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin d3-mediated inhibition of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 6030–6037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantorna, M.T. Vitamin d, multiple sclerosis and inflammatory bowel disease. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2012, 523, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantorna, M.T.; McDaniel, K.; Bora, S.; Chen, J.; James, J. Vitamin d, immune regulation, the microbiota, and inflammatory bowel disease. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 2014, 239, 1524–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, J.H.; Chen, J.; Cantorna, M.T. Vitamin d regulation of immune function in the gut: Why do t cells have vitamin d receptors? Mol. Aspects Med. 2012, 33, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colin, E.M.; Asmawidjaja, P.S.; van Hamburg, J.P.; Mus, A.M.; van Driel, M.; Hazes, J.M.; van Leeuwen, J.P.; Lubberts, E. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin d3 modulates th17 polarization and interleukin-22 expression by memory t cells from patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2010, 62, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Eerden, B.C.; van der Heyden, J.C.; van Hamburg, J.P.; Schreuders-Koedam, M.; Asmawidjaja, P.S.; de Muinck Keizer-Schrama, S.M.; Boot, A.M.; Lubberts, E.; Drop, S.L.; van Leeuwen, J.P. A human vitamin d receptor mutation causes rickets and impaired th1/th17 responses. Bone 2014, 69, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keating, P.; Munim, A.; Hartmann, J.X. Effect of vitamin d on t-helper type 9 polarized human memory cells in chronic persistent asthma. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014, 112, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Zhou, X.J.; Hong, J.G. The effects of vitamin d on allergen-induced expression of interleukin-13 and interleukin-17 in cord blood cd4(+)t cells. Iran. J. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014, 13, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Zhao, J.; Cantorna, M.T. Invariant nkt cell defects in vitamin d receptor knockout mice prevents experimental lung inflammation. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 4907–4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittke, A.; Chang, A.; Froicu, M.; Harandi, O.F.; Weaver, V.; August, A.; Paulson, R.F.; Cantorna, M.T. Vitamin d receptor expression by the lung micro-environment is required for maximal induction of lung inflammation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 460, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari, O.; Stock, P.; Meyer, E.; Kronenberg, M.; Sidobre, S.; Nakayama, T.; Taniguchi, M.; Grusby, M.J.; DeKruyff, R.H.; Umetsu, D.T. Essential role of nkt cells producing il-4 and il-13 in the development of allergen-induced airway hyperreactivity. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittke, A.; Weaver, V.; Mahon, B.D.; August, A.; Cantorna, M.T. Vitamin d receptor-deficient mice fail to develop experimental allergic asthma. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 3432–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matheu, V.; Back, O.; Mondoc, E.; Issazadeh-Navikas, S. Dual effects of vitamin d-induced alteration of th1/th2 cytokine expression: Enhancing ige production and decreasing airway eosinophilia in murine allergic airway disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 112, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topilski, I.; Flaishon, L.; Naveh, Y.; Harmelin, A.; Levo, Y.; Shachar, I. The anti-inflammatory effects of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin d3 on th2 cells in vivo are due in part to the control of integrin-mediated t lymphocyte homing. Eur. J. Immunol. 2004, 34, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorman, S.; Judge, M.A.; Burchell, J.T.; Turner, D.J.; Hart, P.H. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin d3 enhances the ability of transferred cd4+ cd25+ cells to modulate t helper type 2-driven asthmatic responses. Immunology 2010, 130, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorman, S.; Judge, M.A.; Hart, P.H. Topical 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin d3 subverts the priming ability of draining lymph node dendritic cells. Immunology 2010, 131, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taher, Y.A.; van Esch, B.C.; Hofman, G.A.; Henricks, P.A.; van Oosterhout, A.J. 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin d3 potentiates the beneficial effects of allergen immunotherapy in a mouse model of allergic asthma: Role for il-10 and tgf-beta. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 5211–5221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigby, W.F.; Noelle, R.J.; Krause, K.; Fanger, M.W. The effects of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin d3 on human t lymphocyte activation and proliferation: A cell cycle analysis. J. Immunol. 1985, 135, 2279–2286. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Joshi, S.; Pantalena, L.C.; Liu, X.K.; Gaffen, S.L.; Liu, H.; Rohowsky-Kochan, C.; Ichiyama, K.; Yoshimura, A.; Steinman, L.; Christakos, S.; et al. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin d3 ameliorates th17 autoimmunity via transcriptional modulation of interleukin-17a. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 31, 3653–3669. [Google Scholar]
- Kongsbak, M.; von Essen, M.R.; Boding, L.; Levring, T.B.; Schjerling, P.; Lauritsen, J.P.; Woetmann, A.; Odum, N.; Bonefeld, C.M.; Geisler, C. Vitamin d up-regulates the vitamin d receptor by protecting it from proteasomal degradation in human cd4+ t cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Healy, K.D.; Frahm, M.A.; DeLuca, H.F. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin d3 up-regulates the renal vitamin d receptor through indirect gene activation and receptor stabilization. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2005, 433, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooi, J.H.; McDaniel, K.L.; Weaver, V.; Cantorna, M.T. Murine cd8+ t cells but not macrophages express the vitamin d 1alpha-hydroxylase. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 25, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kongsbak, M.; von Essen, M.R.; Levring, T.B.; Schjerling, P.; Woetmann, A.; Odum, N.; Bonefeld, C.M.; Geisler, C. Vitamin d-binding protein controls t cell responses to vitamin d. BMC Immunol. 2014, 15, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrat, F.J.; Cua, D.J.; Boonstra, A.; Richards, D.F.; Crain, C.; Savelkoul, H.F.; de Waal-Malefyt, R.; Coffman, R.L.; Hawrylowicz, C.M.; O’Garra, A. In vitro generation of interleukin 10-producing regulatory cd4(+) t cells is induced by immunosuppressive drugs and inhibited by t helper type 1 (th1)- and th2-inducing cytokines. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cantorna, M.T.; Snyder, L.; Lin, Y.-D.; Yang, L. Vitamin D and 1,25(OH)2D Regulation of T cells. Nutrients 2015, 7, 3011-3021. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7043011
Cantorna MT, Snyder L, Lin Y-D, Yang L. Vitamin D and 1,25(OH)2D Regulation of T cells. Nutrients. 2015; 7(4):3011-3021. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7043011
Chicago/Turabian StyleCantorna, Margherita T., Lindsay Snyder, Yang-Ding Lin, and Linlin Yang. 2015. "Vitamin D and 1,25(OH)2D Regulation of T cells" Nutrients 7, no. 4: 3011-3021. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7043011
APA StyleCantorna, M. T., Snyder, L., Lin, Y.-D., & Yang, L. (2015). Vitamin D and 1,25(OH)2D Regulation of T cells. Nutrients, 7(4), 3011-3021. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7043011