Acteoside Ameliorates Hepatic Steatosis and Liver Injury in MASLD Mice Through Activation of PINK1/Parkin-Related Mitophagy Markers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
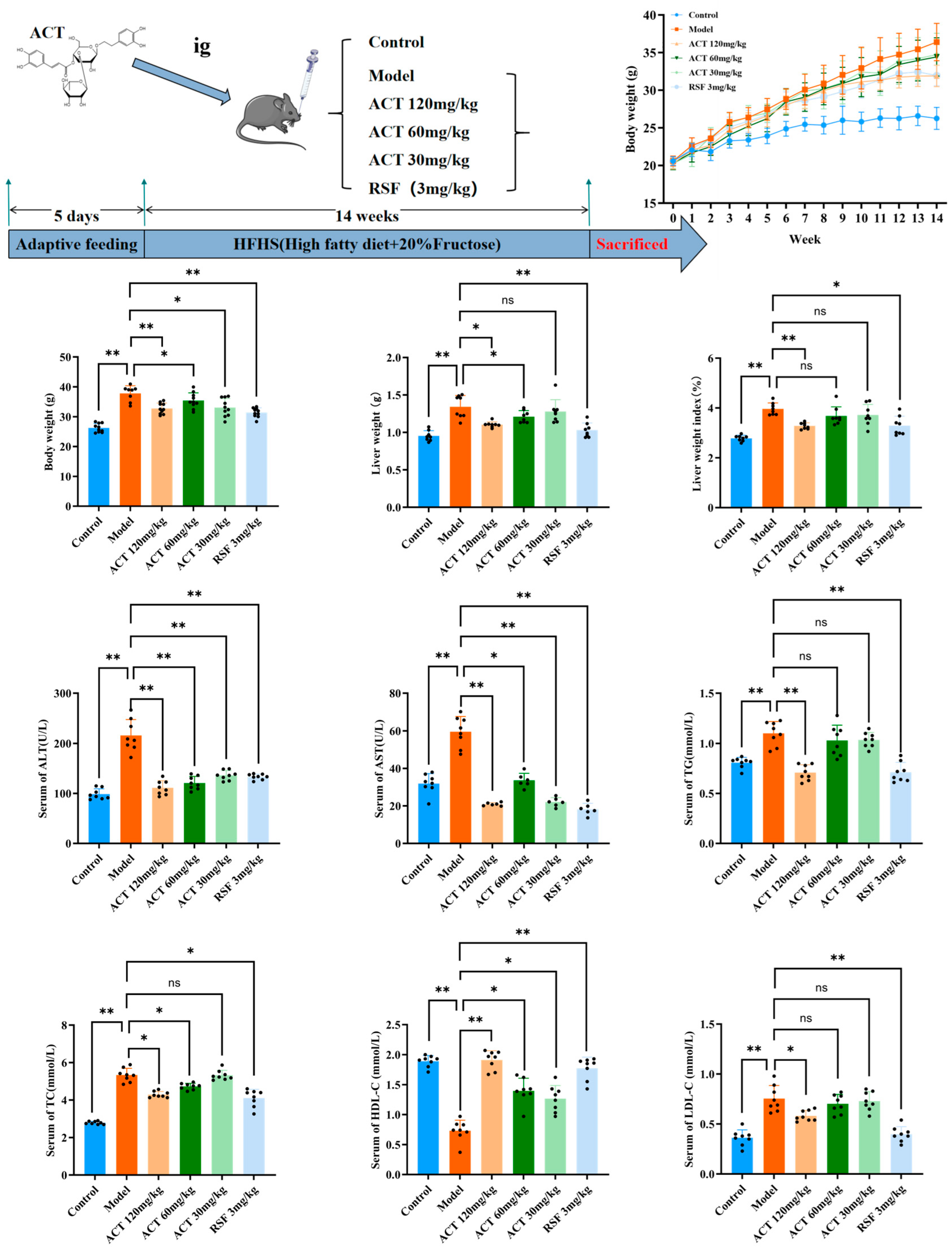
2.2. Animal Experiments
2.3. Serum Biochemical Assays
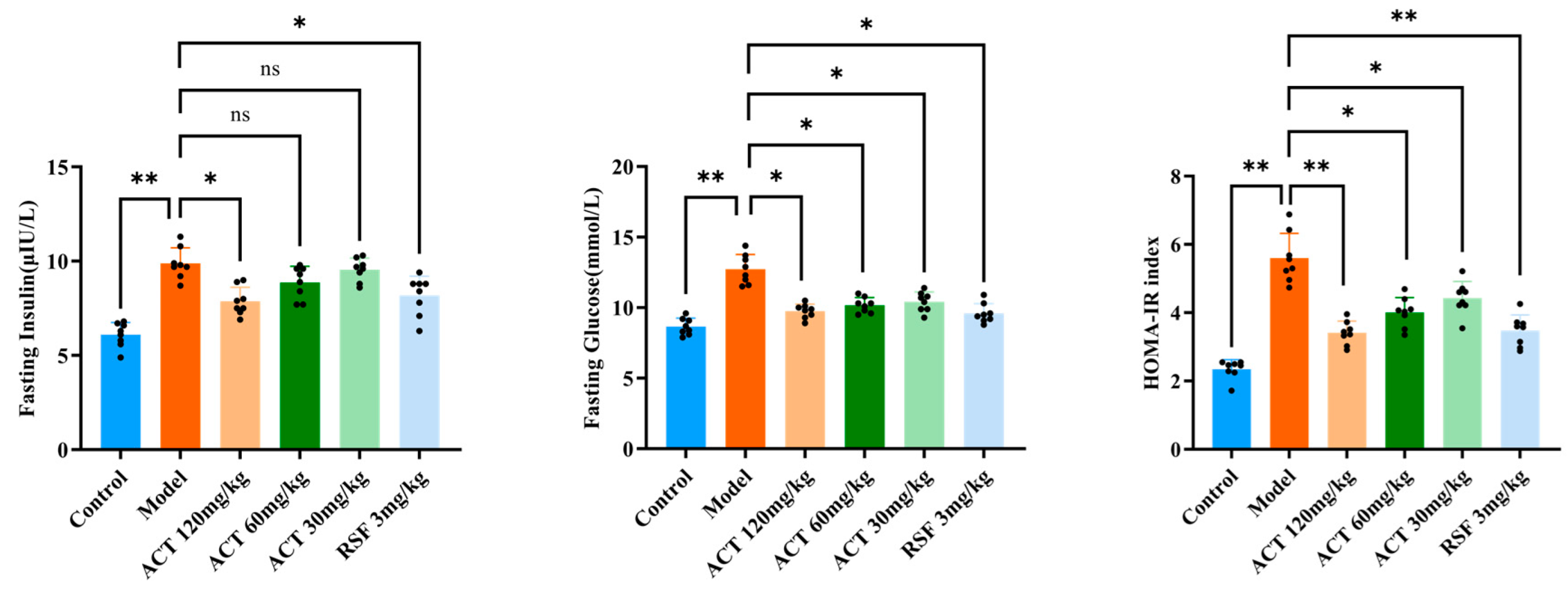
2.4. Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR) Assays
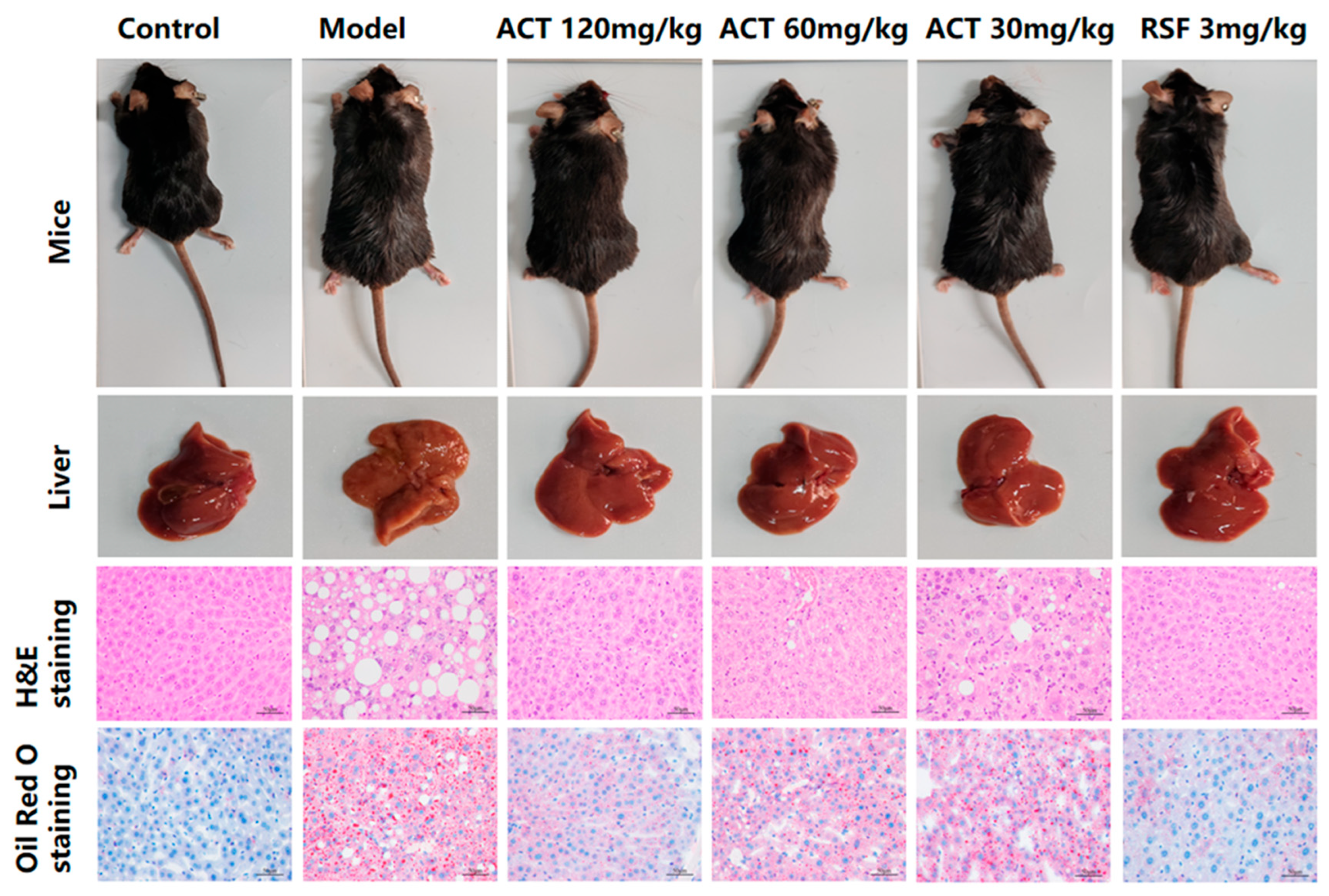
2.5. Histopathological Detection
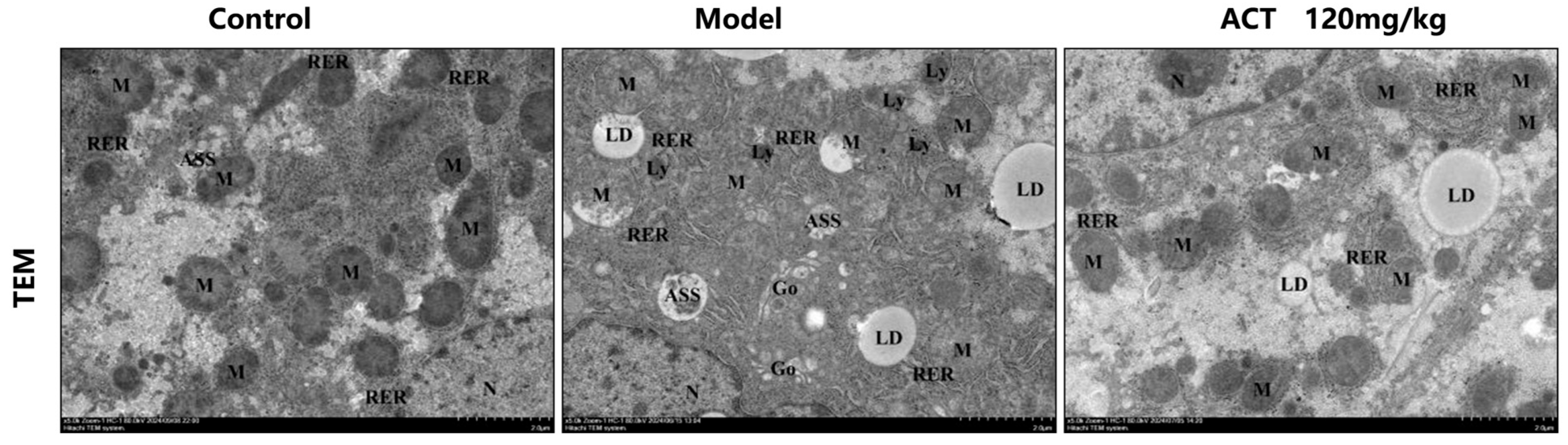
2.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy Assays
2.7. OS and Inflammatory Factors Detection
2.8. Western Blot (WB) Assays
2.9. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Assays
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Protective Effect of ACT Against Hepatic Steatosis in MASLD Mice
3.2. Effects of ACT on HOMA-IR in MASLD Mice
3.3. Effects of ACT on Liver Pathological Changes in MASLD Mice
3.4. Effects of ACT on Liver Tissue Ultrastructure in MASLD Mice
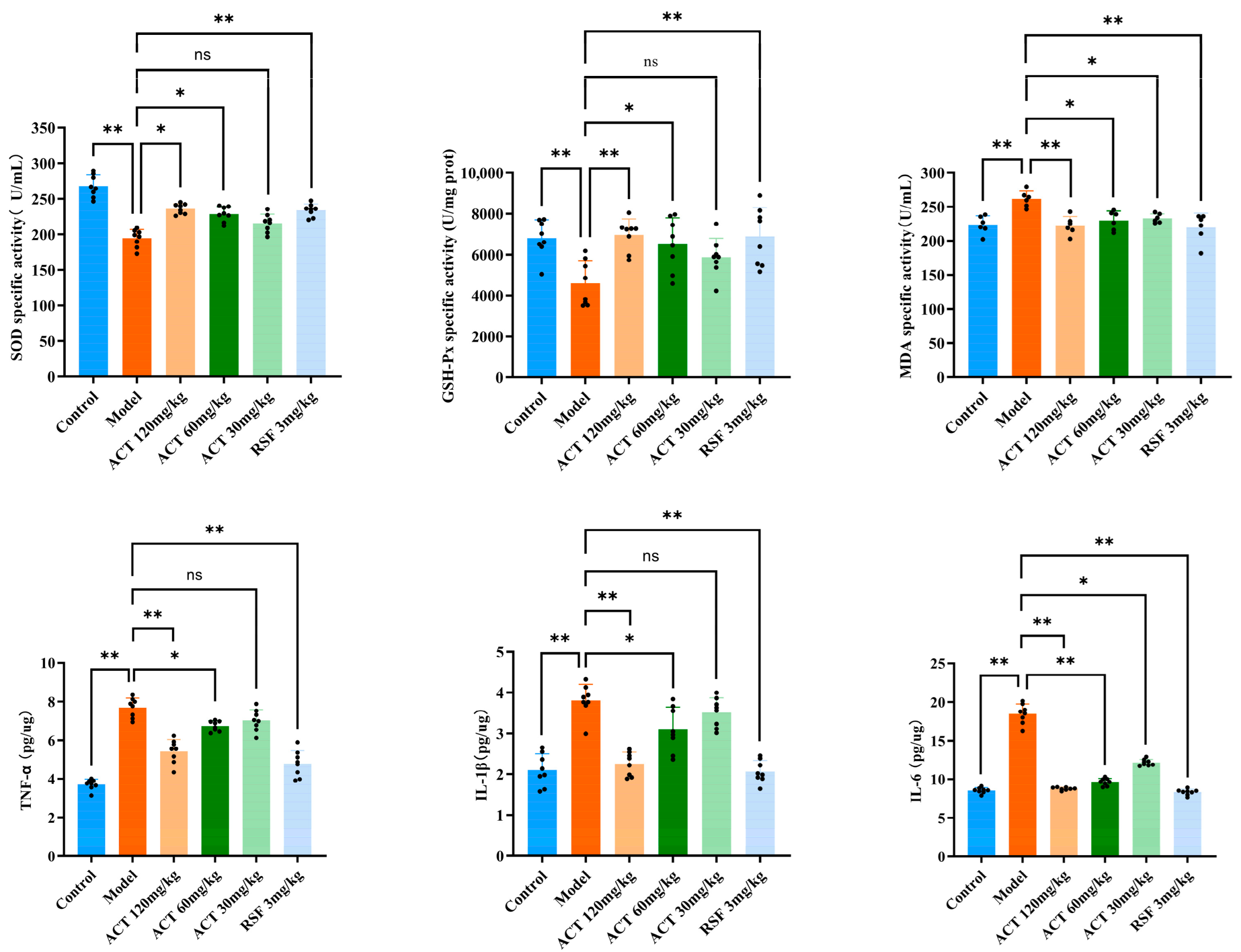
3.5. Effects of ACT Against OS and Inflammatory Factors in MASLD Mice
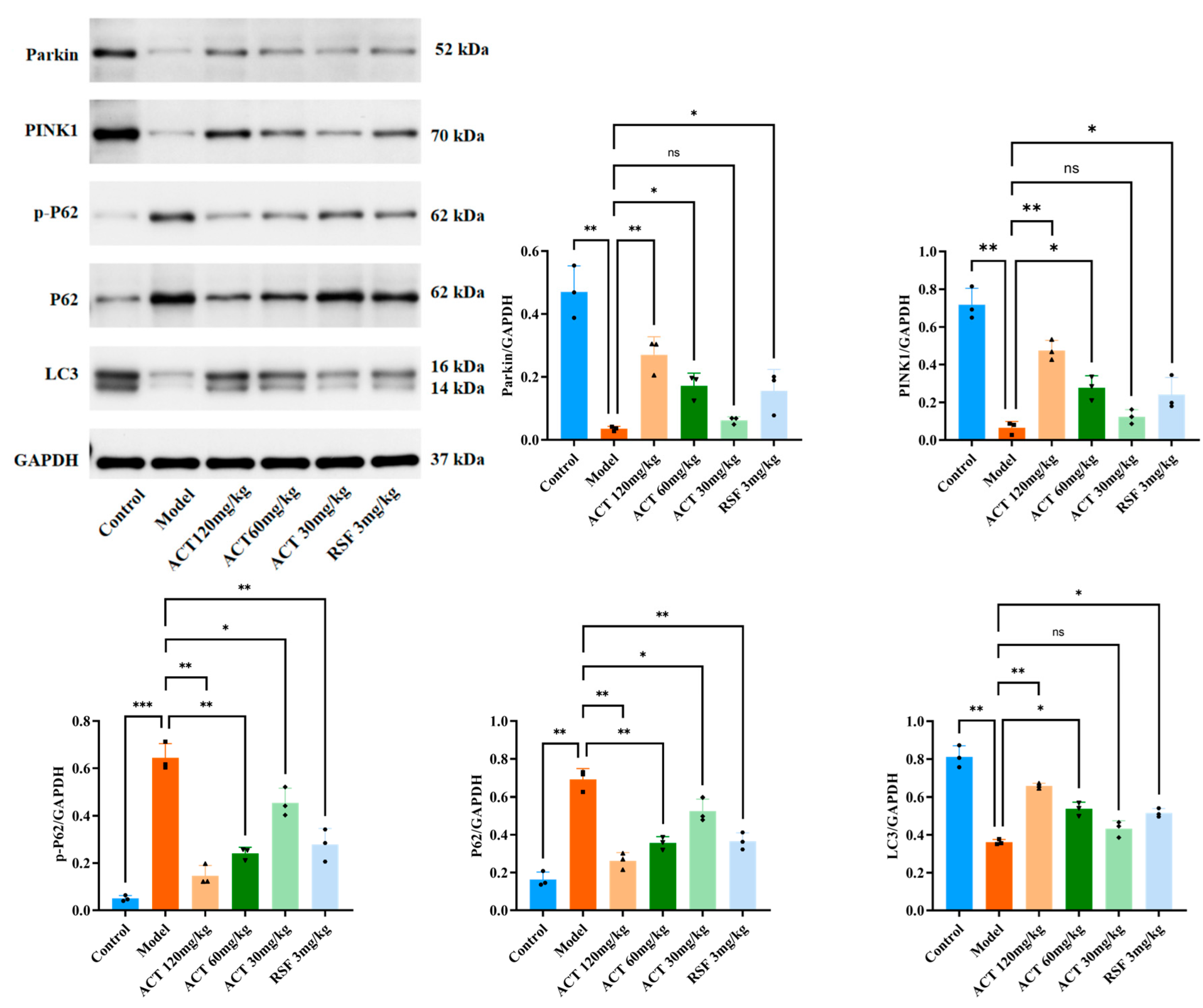
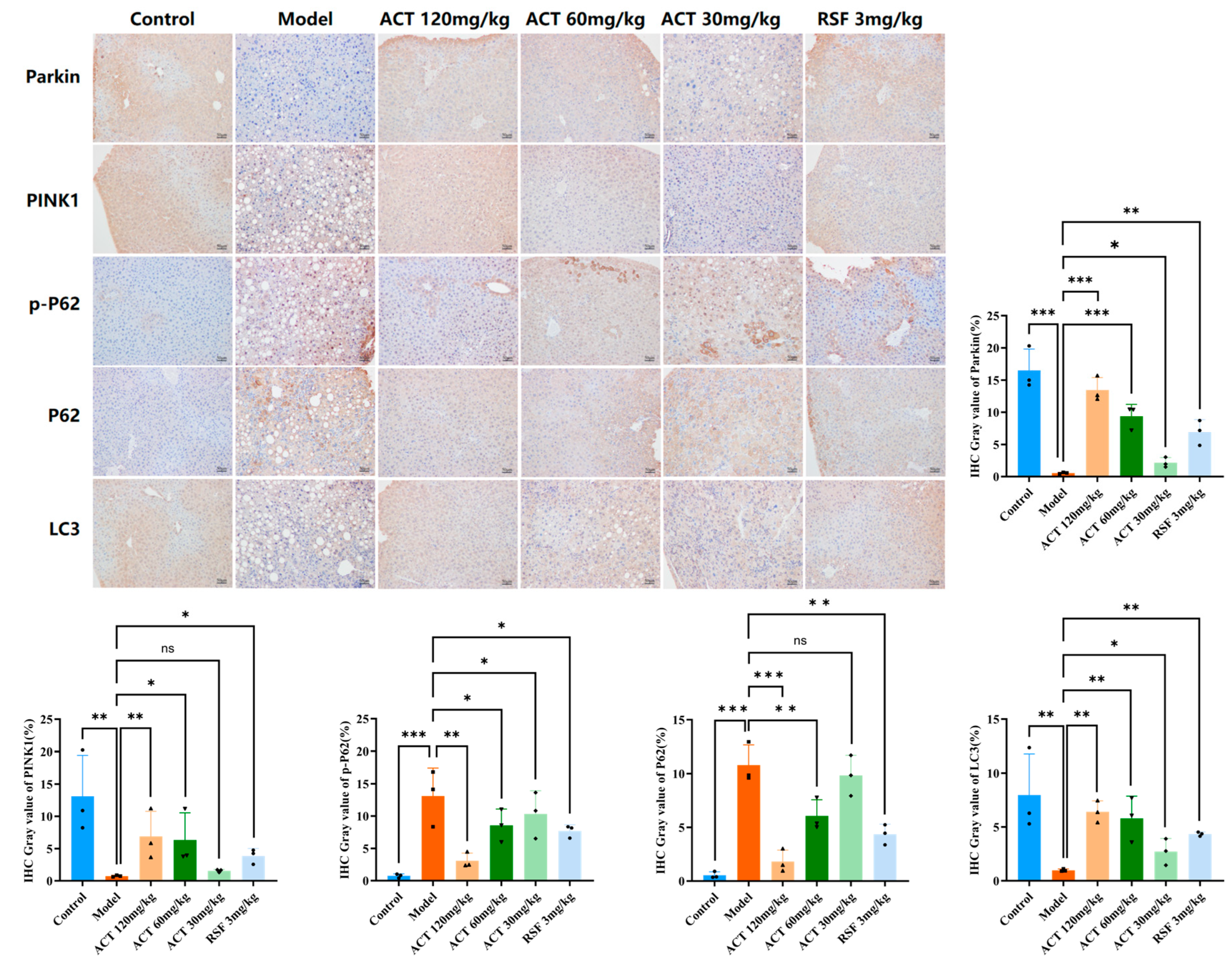
3.6. ACT’s Effects on the Expression of Mitophagy-Related Proteins Parkin, LC3, PINK1, P62, and p-P62 in MASLD Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Ayada, I.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Wen, T.; Ma, Z.; Bruno, M.J.; de Knegt, R.J.; Cao, W.; et al. Estimating Global Prevalence of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease in Overweight or Obese Adults. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, e573–e582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israelsen, M.; Francque, S.; Tsochatzis, E.A.; Krag, A. Steatotic liver disease. Lancet 2024, 404, 1761–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.J.; Lai, J.C.-T.; Wong, G.L.-H.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Yip, T.C.-F. Can we use old NAFLD data under the new MASLD definition? J. Hepatol. 2024, 80, e54–e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan, R.; Ali, A.H.; Ibdah, J.A. Mitochondrial Dysfunction Plays Central Role in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, T.M.; Cheng, L.; Wolf, D.M.; Ngo, J.; Segawa, M.; Zhu, X.; Strumwasser, A.R.; Cao, Y.; Clifford, B.L.; Ma, A.; et al. Parkin regulates adiposity by coordinating mitophagy with mitochondrial biogenesis in white adipocytes. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Sullivan, M.A.; Chen, W.; Jing, X.; Yu, H.; Li, F.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, Z.; et al. Quercetin ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) via the promotion of AMPK-mediated hepatic mitophagy. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2023, 120, 109414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Wu, X.; Liao, R. Mechanism and regulation of mitophagy in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A mini-review. Life Sci. 2023, 312, 121162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y. Mitochondrial metabolic dysfunction and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: New insights from pathogenic mechanisms to clinically targeted therapy. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, T.; Xie, H.; Pan, Y.; Ninomiya, K.; Yuan, D.; Jia, X.; Yoshikawa, M.; Nakamura, S.; Matsuda, H.; Muraoka, O. A Review of Biologically Active Natural Products from a Desert Plant Cistanche tubulosa. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 67, 675–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Z.; Liu, J.; Xu, Y.; Sun, H.; Qi, X.; Cong, M.; Zhang, X.; Yan, Y.; Liu, T. Protective effects of phenylethanol glycosides from Cistanche tubulosa against ALD through modulating gut microbiota homeostasis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025, 337, 118925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Sun, H.; Liu, J.; Cong, M.; Zhang, X.; Yan, Y.; Xia, Z.; Liu, T.; Zhao, J. Phenylethanol Glycoside from Cistanche tubulosa Attenuates BSA-Induced Liver Fibrosis in Rats by Modulating the Gut Microbiota-Liver Axis. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, T.; Ma, L.; Yan, M.; Zhao, Y.; Gu, Z.; Huang, Y. Protective Effect of Acteoside on Immunological Liver Injury Induced byBacillus Calmette-Guerinplus Lipopolysaccharide. Planta Medica 2009, 75, 1463–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wu, S.; Jiang, X.; Li, W.; Li, Q.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y. Acteoside alleviates salsolinol-induced Parkinson’s disease by inhibiting ferroptosis via activating Nrf2/SLC7A11/GPX4 pathway. Exp. Neurol. 2025, 385, 115084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wu, S.; Li, Q.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y. Targeting Ferroptosis: Acteoside as a Neuroprotective Agent in Salsolinol-Induced Parkinson’s Disease Models. Front. Biosci. 2025, 30, 26679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Li, Q.; Lang, W.; Li, W.; Jiang, X.; Wan, Z.; Sun, H.; Wang, H. Salsolinol Induces Parkinson’s Disease Through Activating NLRP3-Dependent Pyroptosis and the Neuroprotective Effect of Acteoside. Neurotox. Res. 2022, 40, 1948–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Zhang, S.J.; Tang, J.Y.; Deng, Y.; Kang, Y.; Zhang, X.H.; Lu, H.M.; Wang, Y.X.; Liu, W.J.; Ma, Y. Integrating network analysis and experimental validation to reveal the ferroptosis-associated mechanism of acteoside in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1660227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, J. Protective Effects of Isostrictiniin Against High-Fat, High-Sugar Diet-Induced Steatosis in MASLD Mice via Regulation of the AMPK/SREBP-1c/ACC Pathway. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Kimura, M.; Li, X.; Sulc, J.; Wang, Q.; Rodríguez-López, S.; Scantlebery, A.M.L.; Strotjohann, K.; Gallart-Ayala, H.; Vijayakumar, A.; et al. ACMSD inhibition corrects fibrosis, inflammation, and DNA damage in MASLD/MASH. J. Hepatol. 2025, 82, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Guo, S.; Lai, X.; Xiao, Q.; Wu, X.; Pang, J.; Pei, L.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, L. α-Lack-SPI Alleviates MASLD in Rats via Regulating Hepatic Lipid Accumulation and Inflammation. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canivet, C.M.; Faure, S. Diagnosis and evaluation of metabolic dysfunction associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). Rev. Med. Interne 2024, 45, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Ye, S.; Li, T.; Huang, Y.; Cheryala, M.; Chen, S. Global burden of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: A systematic analysis of Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Chin. Med. J. 2025, 138, 2947–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hen, H.; Tang, Y.; Zhuang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, X. PINK1/Park2-Mediated Mitophagy Relieve Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Physiol. Res. 2024, 73, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.P.; Sun, H.L.; Zhang, X.D.; Guan, S.Q.; Pan, M. Mitochondrial viscosity, oxidative stress and autophagy responsive fluorescent Zn(II) complex for monitoring non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2025, 340, 126319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; Xiao, Y.; Wan, W.; Zou, H.; Yang, X. Mitochondrial dysfunction in fibrotic diseases: Research progress and MSC-exos therapy. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2025, 143, 104983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.P.; Cunningham, R.P.; Meers, G.M.; Johnson, S.A.; Wheeler, A.A.; Ganga, R.R.; Spencer, N.M.; Pitt, J.B.; Diaz-Arias, A.; Swi, A.I.A.; et al. Compromised hepatic mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation and reduced markers of mitochondrial turnover in human NAFLD. Hepatology 2022, 76, 1452–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-j.; Chen, Y.; Lin, J.-q.; Hu, R.; Liu, D.; Chen, J.-y.; Li, K.; Jiang, X.-y. Evidence summary of lifestyle interventions in adults with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Front. Nutr. 2025, 11, 1421386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kityania, S.; Nath, R.; Nath, D.; Patra, J.K.; Talukdar, A.D. Acteoside (Verbascoside): A Prospective Therapeutic Alternative against Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Inhibiting the Expression of AXL, FGFR, BRAF, TIE2 and RAF1 Targets. Comb. Chem. High. Throughput Screen. 2023, 26, 1907–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.-P.; Ma, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, S.-L.; Liu, T. Phenylethanol Glycosides from Cistanche tubulosa Suppress Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation and Block the Conduction of Signaling Pathways in TGF-β1/smad as Potential Anti-Hepatic Fibrosis Agents. Molecules 2016, 21, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, X.; Niu, D.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Nan, F.; Jiang, S.; Wang, B. Gut microbiota induces hepatic steatosis by modulating the T cells balance in high fructose diet mice. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.T.; Cui, W.; Kong, L.; Yang, X. Efficacy of Sitagliptin on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in High-fat-diet-fed Diabetic Mice. Curr. Med. Sci. 2022, 42, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, S.M.; Park, G.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Jeong, D.Y.; Kang, J.; Lee, H.J. Beneficial Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum Strains on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in High Fat/High Fructose Diet-Fed Rats. Nutrients 2020, 12, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Zhang, F.; Meng, D.; Zhang, X.; Feng, Y.; Yin, G.; Liang, P.; Chen, S.; Liu, H. Mechanism of Action and Related Natural Regulators of Nrf2 in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2024, 21, 1300–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Lin, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, F.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Zhu, X.; Guo, X.; Tang, Y.; Yao, P. Frataxin-Mediated PINK1-Parkin-Dependent Mitophagy in Hepatic Steatosis: The Protective Effects of Quercetin. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, e1800164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, H.; Chao, X.; Williams, J.; Fulte, S.; Li, T.; Yang, L.; Ding, W.-X. Autophagy in liver diseases: A review. Mol. Asp. Med. 2021, 82, 100973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Cong, M.; Qi, X.; Sun, H.; Zhang, X.; Yan, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhao, J. Acteoside Ameliorates Hepatic Steatosis and Liver Injury in MASLD Mice Through Activation of PINK1/Parkin-Related Mitophagy Markers. Nutrients 2026, 18, 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu18010118
Cong M, Qi X, Sun H, Zhang X, Yan Y, Liu T, Zhao J. Acteoside Ameliorates Hepatic Steatosis and Liver Injury in MASLD Mice Through Activation of PINK1/Parkin-Related Mitophagy Markers. Nutrients. 2026; 18(1):118. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu18010118
Chicago/Turabian StyleCong, Meili, Xinxin Qi, Hongguang Sun, Xinxuan Zhang, Yunxin Yan, Tao Liu, and Jun Zhao. 2026. "Acteoside Ameliorates Hepatic Steatosis and Liver Injury in MASLD Mice Through Activation of PINK1/Parkin-Related Mitophagy Markers" Nutrients 18, no. 1: 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu18010118
APA StyleCong, M., Qi, X., Sun, H., Zhang, X., Yan, Y., Liu, T., & Zhao, J. (2026). Acteoside Ameliorates Hepatic Steatosis and Liver Injury in MASLD Mice Through Activation of PINK1/Parkin-Related Mitophagy Markers. Nutrients, 18(1), 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu18010118





