The Role of Diet in Modulating Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis, and Psoriatic Arthritis
Abstract
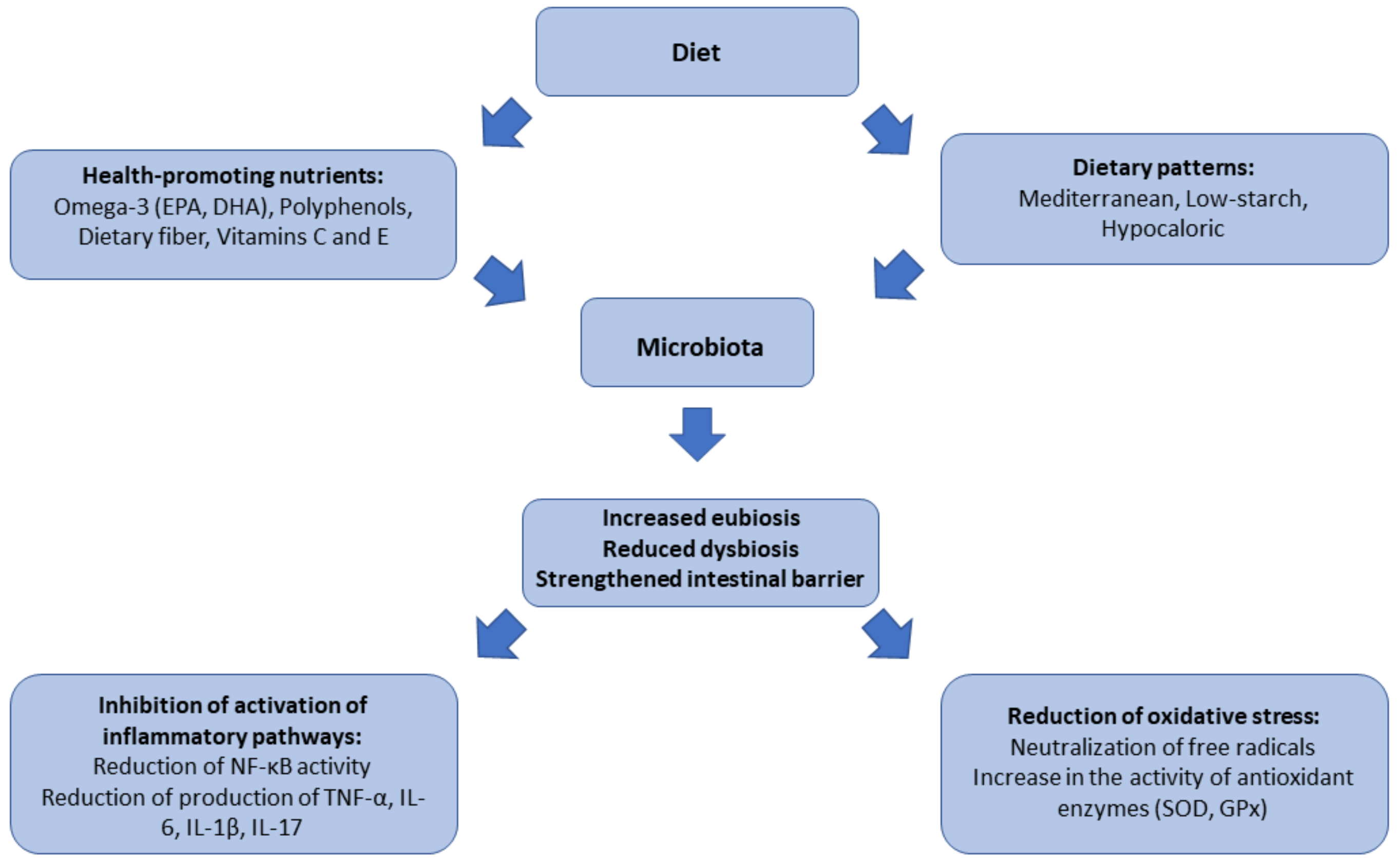
1. Introduction
2. Inflammation and Oxidative Processes in RA, AS, and PsA
3. Role of Histocompatibility Antigen in Ankylosing Spondylitis
4. Intersection of Psoriasis and Joint Inflammation
5. Impact of Metabolic Factors and Diet in PsA
6. The Role of Gut Microbiota in Inflammatory and Oxidative Processes
7. The Importance of the Mediterranean Diet in Modulating Inflammation and Oxidative Stress
8. The Significance of a Low-Starch Diet in Ankylosing Spondylitis
9. The Role of a Hypocaloric Diet in PsA
10. The Importance of Specific Dietary Components in Regulating Inflammation and Oxidative Stress
11. Perspectives and Challenges in the Use of Diet Therapy in Rheumatoid Diseases
12. Conclusions
13. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scott, I.C.; Whittle, R.; Bailey, J.; Twohig, H.; Hider, S.L.; Mallen, C.D.; Muller, S.; Jordan, K.P. Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriatic Arthritis, and Axial Spondyloarthritis Epidemiology in England from 2004 to 2020: An Observational Study Using Primary Care Electronic Health Record Data. Lancet Reg. 2022, 23, 100519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelsen, B.; Fiane, R.; Diamantopoulos, A.P.; Soldal, D.M.; Hansen, I.J.W.; Sokka, T.; Kavanaugh, A.; Haugeberg, G. A Comparison of Disease Burden in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriatic Arthritis and Axial Spondyloarthritis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhou, M.; Xu, T. Causal Effects of Rheumatoid Arthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis, Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis on Psoriasis: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2024, 17, 2583–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilski, R.; Kamiński, P.; Kupczyk, D.; Jeka, S.; Baszyński, J.; Tkaczenko, H.; Kurhaluk, N. Environmental and Genetic Determinants of Ankylosing Spondylitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilski, R.; Kupczyk, D.; Woźniak, A. Oxidative Imbalance in Psoriasis with an Emphasis on Psoriatic Arthritis: Therapeutic Antioxidant Targets. Molecules 2024, 29, 5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.A. Treatment Guidelines in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 48, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Xu, S. TNF Inhibitor Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Biomed. Rep. 2012, 1, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.J.; Perez-Chada, L.M.; Merola, J.F. TNF Inhibitor-Induced Psoriasis: Proposed Algorithm for Treatment and Management. J. Psoriasis Psoriatic Arthritis 2018, 4, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereda, C.A.; Nishishinya, M.B.; López, J.A.M.; Carmona, L. Efficacy and Safety of DMARDs in Psoriatic Arthritis: A Systematic Review. PubMed 2012, 30, 282–289. [Google Scholar]
- Can, M.; Aydın, S.Z.; Niğdelioğlu, A.; Atagündüz, P.; Direskeneli, H. Conventional DMARD Therapy (Methotrexate-sulphasalazine) May Decrease the Requirement of Biologics in Routine Practice of Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients: A Real-life Experience. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 15, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, L.J.; Zochling, J.; Boonen, A.; Singh, J.A.; Veras, M.M.; Ghogomu, E.T.; Jandu, M.B.; Tugwell, P.; Wells, G.A. TNF-Alpha Inhibitors for Ankylosing Spondylitis. Cochrane Libr. 2015, 4, CD005468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Li, Y.; Luo, W.-W.; Cheng, X.; Xiang, H.-R.; Zhang, Q.-Z.; He, J.; Peng, W.-X. The Risk of Adverse Effects of TNF-α Inhibitors in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Network Meta-Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 814429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila-Escalante, M.L.; Coop-Gamas, F.; Cervantes-Rodríguez, M.; Méndez-Iturbide, D.; Aranda-González, I.I. The Effect of Diet on Oxidative Stress and Metabolic Diseases—Clinically Controlled Trials. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsyth, C.; Kouvari, M.; D’Cunha, N.M.; Georgousopoulou, E.N.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Mellor, D.D.; Kellett, J.; Naumovski, N. The Effects of the Mediterranean Diet on Rheumatoid Arthritis Prevention and Treatment: A Systematic Review of Human Prospective Studies. Rheumatol. Int. 2017, 38, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adıgüzel, K.T.; Yurdakul, F.G.; Kürklü, N.S.; Yaşar, E.; Bodur, H. Relationship Between Diet, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation in Ankylosing Spondylitis. Arch. Rheumatol. 2021, 37, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfarlane, T.V.; Abbood, H.M.; Pathan, E.; Gordon, K.; Hinz, J.; Macfarlane, G.J. Relationship between Diet and Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Systematic Review. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 5, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaldo, G.; Pagano, I.; Grimaldi, M.; Marino, C.; Molettieri, P.; Santoro, A.; Stillitano, I.; Romano, R.; Montoro, P.; D’Ursi, A.M.; et al. Effect of Very-Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet on Psoriasis Patients: A Nuclear Magnetic Resonance-Based Metabolomic Study. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 20, 1509–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furst, A.; Gill, T. Exploring the Role of Gut Microbes in Spondyloarthritis: Implications for Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Strategies. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2024, 38, 101961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Wei, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Xie, Z.; Hai, Q.; Li, Z.; Qin, D. Gut Microbiota and Rheumatoid Arthritis: From Pathogenesis to Novel Therapeutic Opportunities. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1007165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Păsăran, E.-D.; Diaconu, A.E.; Oancea, C.; Bălănescu, A.-R.; Aurelian, S.M.; Homentcovschi, C. An Actual Insight into the Pathogenic Pathways of Ankylosing Spondylitis. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 12800–12812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alturaiki, W.; Alhamad, A.; Alturaiqy, M.; Mir, S.A.; Iqbal, D.; Dukhyil, A.A.B.; Alaidarous, M.; Alshehri, B.; Alsagaby, S.A.; Almalki, S.G.; et al. Assessment of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, IL-8, and CCL 5 Levels in Newly Diagnosed Saudi Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 25, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Sun, L.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, D.; He, D.; Nie, H. TNFαPromotes Th17 Cell Differentiation through IL-6 and IL-1βProduced by Monocytes in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 385352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monu, N.; Agnihotri, P.; Saquib, M.; Biswas, S. Targeting TNF-α-Induced Expression of TTR and RAGE in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Apigenin’s Mediated Therapeutic Approach. Cytokine 2024, 179, 156616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukazaki, H.; Kaito, T. The Role of the IL-23/IL-17 Pathway in the Pathogenesis of Spondyloarthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisălău, B.; Crînguș, L.-I.; Vreju, F.; Pârvănescu, C.; Firulescu, S.; Dinescu, Ș.; Ciobanu, D.; Tica, A.; Sandu, R.; Siloși, I.; et al. New Insights into IL-17/IL-23 Signaling in Ankylosing Spondylitis (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 3493–3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieper, J.; Poddubnyy, D.; Miossec, P. The IL-23-IL-17 Pathway as a Therapeutic Target in Axial Spondyloarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuz-Lieberman, N.; Markel, G.; Mizrahi, S.; Gazit, R.; Hanna, J.; Achdout, H.; Gruda, R.; Katz, G.; Arnon, T.I.; Battat, S.; et al. The Involvement of NK Cells in Ankylosing Spondylitis. Int. Immunol. 2005, 17, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yee, K.; Haroon, N. KIR3DL1 Interaction with HLA-B27 Is Altered by Ankylosing Spondylitis Associated ERAP1 and Enhanced by MHC Class I Cross-Linking. PubMed 2015, 20, 79–89. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Liu, B.; Lin, C.; Gu, J. Imbalance of Peripheral Lymphocyte Subsets in Patients With Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 696973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingappan, K. NF-κB in Oxidative Stress. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2017, 7, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Dutta, A.; Chakraborty, A. The Interaction of Oxidative Stress with MAPK, PI3/AKT, NF-κB, and DNA Damage Kinases Influences the Fate of γ-Radiation-Induced Bystander Cells. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2022, 725, 109302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marina, M.E.; Roman, I.I.; Constantin, A.-M.; Mihu, C.M.; Tătaru, A.D. VEGF Involvement in Psoriasis. Med. Pharm. Rep. 2015, 88, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerkowicz, A.; Socha, M.; Pietrzak, A.; Zubilewicz, T.; Krasowska, D. The Role of VEGF in Psoriasis: An Update. Acta Angiol. 2018, 24, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medovic, M.V.; Jakovljevic, V.L.; Zivkovic, V.I.; Jeremic, N.S.; Jeremic, J.N.; Bolevich, S.B.; Nikolic, A.B.R.; Milicic, V.M.; Srejovic, I.M. Psoriasis between Autoimmunity and Oxidative Stress: Changes Induced by Different Therapeutic Approaches. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 249834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eppinga, H.; Weiland, C.J.S.; Thio, H.B.; Van Der Woude, C.J.; Nijsten, T.E.C.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Konstantinov, S.R. Similar Depletion of ProtectiveFaecalibacterium Prausnitziiin Psoriasis and Inflammatory Bowel Disease, but Not in Hidradenitis Suppurativa. J. Crohns Colitis 2016, 10, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, S.-X.; Zhao, R.; Song, S.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Wang, C.-H.; Li, X.-F. Dysbiosis of the Gut Microbiota in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis Is Closely Related to Lymphocyte Subsets and Cytokines. Inflammation 2024, 47, 1220–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhaș, M.C.; Gavrilaș, L.I.; Candrea, R.; Cătinean, A.; Mocan, A.; Miere, D.; Tătaru, A. Gut Microbiota in Psoriasis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Li, Y.; Hou, H.; Zou, W.; Hu, L.; Gong, L.; Fan, W.; Wang, R.; Ibrahim, I.A.A.; Fan, S. Xanthorrhizol Ameliorates Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Freund’s Complete Adjuvant-Induced Rheumatoid Arthritis in Rats. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 194, 6423–6437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jah, N.; Jobart-Malfait, A.; Ermoza, K.; Noteuil, A.; Chiocchia, G.; Breban, M.; André, C. HLA–B27 Subtypes Predisposing to Ankylosing Spondylitis Accumulate in an Endoplasmic Reticulum–Derived Compartment Apart from the Peptide-Loading Complex. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 1534–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, J.; Sieper, J. Fifty Years after the Discovery of the Association of HLA B27 with Ankylosing Spondylitis. RMD Open 2023, 9, e003102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colbert, R.A.; Tran, T.M.; Layh-Schmitt, G. HLA-B27 Misfolding and Ankylosing Spondylitis. Mol. Immunol. 2013, 57, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sian, T.C.C.L.K.; Indumathy, S.; Halim, H.; Greule, A.; Cryle, M.J.; Bowness, P.; Rossjohn, J.; Gras, S.; Purcell, A.W.; Schittenhelm, R.B. Allelic Association with Ankylosing Spondylitis Fails to Correlate with Human Leukocyte Antigen B27 Homodimer Formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 20185–20195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Li, J.; He, C.; Li, D.; Tong, W.; Zou, Y.; Xu, W. Role of HLA-B27 in the Pathogenesis of Ankylosing Spondylitis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 1943–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, E.; Mellins, E.D.; Gershwin, M.E.; Nestle, F.O.; Adamopoulos, I.E. The IL-23/IL-17 Axis in Psoriatic Arthritis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecellio, M.; Hake, V.X.; Davidson, C.; Carena, M.C.; Wordsworth, B.P.; Selmi, C. The IL-17/IL-23 Axis and Its Genetic Contribution to Psoriatic Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 596086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Li, S.; Ying, S.; Tang, S.; Ding, Y.; Li, Y.; Qiao, J.; Fang, H. The IL-23/IL-17 Pathway in Inflammatory Skin Diseases: From Bench to Bedside. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 594735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stisen, Z.R.; Nielsen, S.M.; Skougaard, M.; Mogensen, M.; Jørgensen, T.S.; Dreyer, L.; De Wit, M.; Christensen, R.; Kristensen, L.E. Tolerability and Comparative Effectiveness of TNF, IL-17 and IL-23(P19) Inhibitors in Psoriatic Arthritis: A Target Trial Emulation Study. Rheumatology 2023, 63, 1543–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blauvelt, A.; Chiricozzi, A. The Immunologic Role of IL-17 in Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Pathogenesis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 55, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.C.; Hum, R.M.; Rogers, K.; Maglio, C.; Alam, U.; Zhao, S.S. Metabolic Syndrome and Psoriatic Arthritis: The Role of Weight Loss as a Disease-Modifying Therapy. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2024, 16, 1759720X241271886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, B.F.; Morimoto, M.A.; Gomes, C.M.F.; Klemz, B.N.C.; Genaro, P.S.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Damasceno, N.R.T.; Pinheiro, M.M. Dietetic Intervention in Psoriatic Arthritis: The DIETA Trial. Adv. Rheumatol. 2022, 62, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumthekar, A.; Ogdie, A. Obesity and Psoriatic Arthritis: A Narrative Review. Rheumatol. Ther. 2020, 7, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchnik, E.; Kruk, J.; Tuchowska, A.; Marchlewicz, M. The Impact of Diet and Physical Activity on Psoriasis: A Narrative Review of the Current Evidence. Nutrients 2023, 15, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wei, J.; Zhang, W.; Doherty, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, H.; Li, W.; Wang, N.; Lei, G.; Zeng, C. Gut Dysbiosis in Rheumatic Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 92 Observational Studies. EBioMedicine 2022, 80, 104055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bixio, R.; Bertelle, D.; Bertoldo, E.; Morciano, A.; Rossini, M. The Potential Pathogenic Role of Gut Microbiota in Rheumatic Diseases: A Human-Centred Narrative Review. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2023, 19, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purchiaroni, F.; Tortora, A.; Gabrielli, M.; Bertucci, F.; Gigante, G.; Ianiro, G.; Ojetti, V.; Scarpellini, E.; Gasbarrini, A. The Role of Intestinal Microbiota and the Immune System. PubMed 2013, 17, 323–333. [Google Scholar]
- Del Socorro Romero-Figueroa, M.; Ramírez-Durán, N.; Montiel-Jarquín, A.J.; Horta-Baas, G. Gut-Joint Axis: Gut Dysbiosis Can Contribute to the Onset of Rheumatoid Arthritis via Multiple Pathways. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1092118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, D.; Song, X.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C.-Y.; Zhang, S.-X. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1376525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, C.; Liu, L.; He, J.; Zhu, C.; Zheng, F.; Dai, W.; Hong, X.; Liu, D.; Tang, D.; et al. Analysis of Gut Microbiota and Metabolites in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Identification of Potential Biomarkers. Aging 2021, 13, 23689–23701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Ouyang, Y.; Lu, N.; Li, N. The NF-κB Signaling Pathway, the Microbiota, and Gastrointestinal Tumorigenesis: Recent Advances. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.; Lee, A.R.; Kim, H.; Jhun, J.; Lee, S.-Y.; Choi, J.W.; Jeong, Y.; Park, M.S.; Ji, G.E.; Cho, M.-L.; et al. Faecalibacterium Prausnitzii Alleviates Inflammatory Arthritis and Regulates IL-17 Production, Short Chain Fatty Acids, and the Intestinal Microbial Flora in Experimental Mouse Model for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2023, 25, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.; Jhun, J.; Lee, S.-Y.; Na, H.S.; Choi, J.; Cho, K.-H.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, A.R.; Park, S.-J.; You, H.J.; et al. Therapeutic Potential of a Novel Bifidobacterium Identified Through Microbiome Profiling of RA Patients with Different RF Levels. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 736196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klingberg, E.; Magnusson, M.K.; Strid, H.; Deminger, A.; Ståhl, A.; Sundin, J.; Simrén, M.; Carlsten, H.; Öhman, L.; Forsblad-d’Elia, H. A Distinct Gut Microbiota Composition in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis Is Associated with Increased Levels of Fecal Calprotectin. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olejniczak-Staruch, I.; Ciążyńska, M.; Sobolewska-Sztychny, D.; Narbutt, J.; Skibińska, M.; Lesiak, A. Alterations of the Skin and Gut Microbiome in Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Deng, Y.; He, Q.; Yang, K.; Li, J.; Xiang, W.; Liu, H.; Zhu, X.; Chen, H. Safety and Efficacy of Probiotic Supplementation in 8 Types of Inflammatory Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 34 Randomized Controlled Trials. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 961325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Chen, J.; Huang, X.-L.; Fang, G.-S.; Yang, L.-J.; Duan, Y.; Wang, J. The Association of HLA-B27 and Klebsiella Pneumoniae in Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Systematic Review. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 117, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, F.; Wang, T.; Li, Q.; Xiong, Y.; Zeng, Y. Association between Klebsiella Pneumoniae and Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 25, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, T.; Ebringer, A. Ankylosing Spondylitis Is Linked to Klebsiella—The Evidence. Clin. Rheumatol. 2006, 26, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Yu, J.; Zhou, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Hu, J.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zeng, F.; Yue, C.; et al. Intestinal Dysbiosis Exacerbates the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis-like Phenotype through Changes in Fatty Acid Metabolism. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Wang, L.; Ji, X.; Wang, Y.; Hu, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Liao, S.; Yan, Y.; Zhu, J.; et al. Dietary Fiber Intake Influences Changes in Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Status. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergne-Salle, P.; Salle, L.; Fressinaud-Marie, A.C.; Descamps-Deplas, A.; Montestruc, F.; Bonnet, C.; Bertin, P. Diet and Disease Activity in Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis: SpondyloArthritis and NUTrition Study (SANUT). Nutrients 2022, 14, 4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; Funasaka, Y.; Saeki, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Kanda, N. Dietary Fiber Inulin Improves Murine Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-like Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbicz, J.; Całyniuk, B.; Górski, M.; Buczkowska, M.; Piecuch, M.; Kulik, A.; Rozentryt, P. Nutritional Therapy in Persons Suffering from Psoriasis. Nutrients 2021, 14, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, H.; Wu, P.; Yang, S.; Xue, W.; Xu, B.; Zhang, S.; Tang, B.; Xu, D. Akkermansia Muciniphila: A Promising Probiotic against Inflammation and Metabolic Disorders. Virulence 2024, 15, 2375555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsetseri, M.-N.; Silman, A.J.; Keene, D.J.; Dakin, S.G. The Role of the Microbiome in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Review. Rheumatol. Adv. Pract. 2023, 7, rkad034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, J.D.; Chen, C.-Y.; Knox, N.C.; Marrie, R.-A.; El-Gabalawy, H.; De Kievit, T.; Alfa, M.; Bernstein, C.N.; Van Domselaar, G. A Comparative Study of the Gut Microbiota in Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases—Does a Common Dysbiosis Exist? Microbiome 2018, 6, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picchianti-Diamanti, A.; Panebianco, C.; Salemi, S.; Sorgi, M.L.; Di Rosa, R.; Tropea, A.; Sgrulletti, M.; Salerno, G.; Terracciano, F.; D’Amelio, R.; et al. Analysis of Gut Microbiota in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: Disease-Related Dysbiosis and Modifications Induced by Etanercept. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, H.-I.; Li, J.-R.; Liu, C.-C.; Liu, P.-Y.; Chen, H.-H.; Chen, Y.-M.; Lan, J.-L.; Chen, D.-Y. An Association of Gut Microbiota with Different Phenotypes in Chinese Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, D.; Jia, H.; Feng, Q.; Wang, D.; Liang, D.; Wu, X.; Li, J.; Tang, L.; Li, Y.; et al. The Oral and Gut Microbiomes Are Perturbed in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Partly Normalized after Treatment. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itsiopoulos, C.; Mayr, H.L.; Thomas, C.J. The Anti-Inflammatory Effects of a Mediterranean Diet: A Review. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care. 2022, 25, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsigalou, C.; Konstantinidis, T.; Paraschaki, A.; Stavropoulou, E.; Voidarou, C.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Mediterranean Diet as a Tool to Combat Inflammation and Chronic Diseases. An Overview. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Y.; Salliot, C.; Gelot, A.; Gambaretti, J.; Mariette, X.; Boutron-Ruault, M.; Seror, R. Mediterranean Diet and Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Findings from the French E3N-EPIC Cohort Study. Arthritis Rheum. 2020, 73, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, J.; Fialho, M.; Santos, R.; Peixoto-Plácido, C.; Madeira, T.; Sousa-Santos, N.; Virgolino, A.; Santos, O.; Carneiro, A.V. Is Olive Oil Good for You? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on Anti-Inflammatory Benefits from Regular Dietary Intake. Nutrition 2019, 69, 110559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosillo, M.Á.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Sánchez-Hidalgo, M.; Fernández-Bolaños, J.G.; Alarcón-De-La-Lastra, C.; Ferrándiz, M.L. Anti-Inflammatory and Joint Protective Effects of Extra-Virgin Olive-Oil Polyphenol Extract in Experimental Arthritis. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 25, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.; Sepodes, B.; Rocha, J.; Direito, R.; Fernandes, A.; Brites, D.; Freitas, M.; Fernandes, E.; Bronze, M.; Figueira, M.E. Protective Effects of Hydroxytyrosol-Supplemented Refined Olive Oil in Animal Models of Acute Inflammation and Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 26, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, T.; Sánchez-Hidalgo, M.; Castejón, M.L.; Rosillo, M.Á.; González-Benjumea, A.; Alarcón-De-La-Lastra, C. Dietary Oleocanthal Supplementation Prevents Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Mice. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Critselis, E.; Tsiampalis, T.; Damigou, E.; Georgousopoulou, E.; Barkas, F.; Chrysohoou, C.; Skoumas, J.; Pitsavos, C.; Liberopoulos, E.; Tsioufis, C.; et al. High Fish Intake Rich in N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Reduces Cardiovascular Disease Incidence in Healthy Adults: The ATTICA Cohort Study (2002–2022). Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1158140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardar, S.; Buduneli, E.; TürkogLu, O.; Berdeli, A.H.; Baylas, H.; Başkesen, A.; Atilla, G. Therapeutic Versus Prophylactic Plus Therapeutic Administration of Omega-3 Fatty Acid on Endotoxin-Induced Periodontitis in Rats. J. Periodontol. 2004, 75, 1640–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Qin, J.; Wei, P.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Fu, L.; Li, S.; Ma, C.; Cong, B. Effects of Leukotriene B4 and Prostaglandin E2 on the Differentiation of Murine Foxp3+ T Regulatory Cells and Th17 Cells. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2009, 80, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, U.N. Essential Fatty Acids and Their Metabolites in the Pathobiology of Inflammation and Its Resolution. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behl, T.; Mehta, K.; Sehgal, A.; Singh, S.; Sharma, N.; Ahmadi, A.; Arora, S.; Bungau, S. Exploring the Role of Polyphenols in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 62, 5372–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, T.M.; Kabisch, S.; Pfeiffer, A.F.H.; Weickert, M.O. The Effects of the Mediterranean Diet on Health and Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charneca, S.; Ferro, M.; Vasques, J.; Carolino, E.; Martins-Martinho, J.; Duarte-Monteiro, A.M.; Dourado, E.; Fonseca, J.E.; Guerreiro, C.S. The Mediterranean Diet, and Not Dietary Inflammatory Index, Is Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease Activity, the Impact of Disease and Functional Disability. Eur. J. Nutr. 2023, 62, 2827–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caso, F.; Navarini, L.; Carubbi, F.; Picchianti-Diamanti, A.; Chimenti, M.S.; Tasso, M.; Currado, D.; Ruscitti, P.; Ciccozzi, M.; Annarumma, A.; et al. Mediterranean Diet and Psoriatic Arthritis Activity: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study. Rheumatol. Int. 2019, 40, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsimbri, P.; Grivas, A.; Papadavid, E.; Tzannis, K.; Flouda, S.; Moysidou, G.-S.; Kosmetatou, M.; Kapniari, I.; Fanouriakis, A.; Boumpas, D.T. Mediterranean Diet and Exercise Are Associated with Better Disease Control in Psoriatic Arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2024, 43, 2877–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ometto, F.; Ortolan, A.; Farber, D.; Lorenzin, M.; Dellamaria, G.; Cozzi, G.; Favero, M.; Valentini, R.; Doria, A.; Ramonda, R. Mediterranean Diet in Axial Spondyloarthritis: An Observational Study in an Italian Monocentric Cohort. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 23, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebringer, A.; Wilson, C. The Use of a Low Starch Diet in the Treatment of Patients Suffering from Ankylosing Spondylitis. Clin. Rheumatol. 1996, 15, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, T.; Wilson, C.; Ebringer, A. The Link between Ankylosing Spondylitis, Crohn’s Disease, Klebsiella, and Starch Consumption. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 872632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Xian, C.; Lu, H. A Possible Role of Intestinal Microbiota in the Pathogenesis of Ankylosing Spondylitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, A.; Arnadottir, S.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Aphale, A.; Sigmarsdottir, A.A.; Gunnarsson, S.I.; Steinsson, J.T.; Elder, J.T.; Valdimarsson, H. Obesity in Psoriasis: Leptin and Resistin as Mediators of Cutaneous Inflammation. Br. J. Dermatol 2008, 159, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirichenko, T.V.; Markina, Y.V.; Bogatyreva, A.I.; Tolstik, T.V.; Varaeva, Y.R.; Starodubova, A.V. The Role of Adipokines in Inflammatory Mechanisms of Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Gaffen, S.L. IL-17 in Obesity and Adipogenesis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2010, 21, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manna, P.; Jain, S.K. Obesity, Oxidative Stress, Adipose Tissue Dysfunction, and the Associated Health Risks: Causes and Therapeutic Strategies. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2015, 13, 423–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, M.J. On the Immunometabolic Role of NF-κB in Adipocytes. Immunometabolism 2022, 4, e220003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, M.; Simon, J.C.; Saalbach, A. Psoriasis: Obesity and Fatty Acids. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, K.S.; Bowen, K.J.; Tindall, A.M.; Sullivan, V.K.; Johnston, E.A.; Fleming, J.A.; Kris-Etherton, P.M. The Effect of Inflammation and Insulin Resistance on Lipid and Lipoprotein Responsiveness to Dietary Intervention. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2020, 4, nzaa160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, A.R.; Siegel, M.; Bagel, J.; Cordoro, K.M.; Garg, A.; Gottlieb, A.; Green, L.J.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Koo, J.; Lebwohl, M.; et al. Dietary Recommendations for Adults With Psoriasis or Psoriatic Arthritis From the Medical Board of the National Psoriasis Foundation. JAMA Dermatol. 2018, 154, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, A.; Saad, A.; Draz, R. Effect of Low-Calorie Diet on Psoriasis Severity Index, Triglycerides, Liver Enzymes, and Quality of Life in Psoriatic Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Reumatologia/Rheumatology 2023, 61, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch-Sierra, N.; Valle, C.G.-D.; Salom, C.; Zaragoza-Villena, B.; Perea-Galera, L.; Falcón-Tapiador, R.; Rovira-Llopis, S.; Morillas, C.; Monleón, D.; Bañuls, C. Effect of a Very Low-Calorie Diet on Oxidative Stress, Inflammatory and Metabolomic Profile in Metabolically Healthy and Unhealthy Obese Subjects. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsimbri, P.; Korakas, E.; Kountouri, A.; Ikonomidis, I.; Tsougos, E.; Vlachos, D.; Papadavid, E.; Raptis, A.; Lambadiari, V. The Effect of Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Capacity of Diet on Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Phenotype: Nutrition as Therapeutic Tool? Antioxidants 2021, 10, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Megna, M.; Cacciapuoti, S.; Frias-Toral, E.; Fabbrocini, G.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A.; Muscogiuri, G. Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet (VLCKD) in Patients with Psoriasis and Obesity: An Update for Dermatologists and Nutritionists. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 62, 398–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiphorou, E.; Philippou, E. Nutrition and Its Role in Prevention and Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2023, 22, 103333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popa, S.L.; Dumitrascu, D.I.; Brata, V.D.; Duse, T.A.; Florea, M.D.; Ismaiel, A.; Muntean, L.M.; Grad, S. Nutrition in Spondyloarthritis and Related Immune-Mediated Disorders. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crupi, R.; Cuzzocrea, S. Role of EPA in Inflammation: Mechanisms, Effects, and Clinical Relevance. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candreva, T.; Kühl, C.M.C.; Burger, B.; Anjos, M.B.P.D.; Torsoni, M.A.; Consonni, S.R.; Crisma, A.R.; Fisk, H.L.; Calder, P.C.; De Mato, F.C.P.; et al. Docosahexaenoic Acid Slows Inflammation Resolution and Impairs the Quality of Healed Skin Tissue. Clin. Sci. 2019, 133, 2345–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, R.; Ross, R.P.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Stanton, C. Fatty Acids from Fish: The Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Long-Chain Omega-3 Fatty Acids. Nutr. Rev. 2010, 68, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, R.; Konkel, A.; Mehling, H.; Blossey, K.; Gapelyuk, A.; Wessel, N.; Von Schacky, C.; Dechend, R.; Muller, D.N.; Rothe, M.; et al. Dietary Omega-3 Fatty Acids Modulate the Eicosanoid Profile in Man Primarily via the CYP-Epoxygenase Pathway. J. Lipid. Res. 2014, 55, 1150–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chacon, A.C.; Phillips, B.E.; Chacon, M.A.; Brunke-Reese, D.; Kelleher, S.L.; Soybel, D.I. Oral Omega-3 Fatty Acids Promote Resolution in Chemical Peritonitis. J. Surg. Res. 2016, 206, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Wen, J.; Bai, X.-C.; Chen, T.-Y.; Zheng, R.-C.; Zhou, G.-B.; Ma, J.; Feng, J.-Y.; Zhong, B.-L.; Li, Y.-M. Endogenous N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Protect against Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-like Inflammation via the IL-17/IL-23 Axis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 9, 2097–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, S.; Schmidt, E.; Schlemmer, A.; Rasmussen, C.; Johansen, M.; Christensen, J. Beneficial Effect of N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Inflammation and Analgesic Use in Psoriatic Arthritis: A Randomized, Double Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 47, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowska, B.; Maślińska, M. The Place of Omega-3 and Omega-6 Acids in Supplementary Treatment of Inflammatory Joint Diseases. Reumatologia/Rheumatology 2020, 58, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchlewicz, M.; Polakowska, Z.; Maciejewska-Markiewicz, D.; Stachowska, E.; Jakubiak, N.; Kiedrowicz, M.; Rak-Załuska, A.; Duchnik, M.; Wajs-Syrenicz, A.; Duchnik, E. Fatty Acid Profile of Erythrocyte Membranes in Patients with Psoriasis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zang, Y. Effects of Omega-3 Supplementation on Lipid Metabolism, Inflammation, and Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Clin. Rheumatol. 2024, 43, 2479–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigaux, J.; Mathieu, S.; Nguyen, Y.; Sanchez, P.; Letarouilly, J.-G.; Soubrier, M.; Czernichow, S.; Flipo, R.-M.; Sellam, J.; Daïen, C. Impact of Type and Dose of Oral Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplementation on Disease Activity in Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2022, 24, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Moscoso, D.I.; Porter, J.; Krishnareddy, S.; Abrams, J.A.; Seres, D.; Chong, D.H.; Freedberg, D.E. Relationship Between Dietary Fiber Intake and Short-Chain Fatty Acid–Producing Bacteria During Critical Illness: A Prospective Cohort Study. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2019, 44, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tayyeb, J.Z.; Popeijus, H.E.; Mensink, R.P.; Konings, M.C.J.M.; Mokhtar, F.B.A.; Plat, J. Short-Chain Fatty Acids (Except Hexanoic Acid) Lower NF-kB Transactivation, Which Rescues Inflammation-Induced Decreased Apolipoprotein A-I Transcription in HepG2 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Hu, X.; Yao, J.; Cao, W.; Zou, Z.; Wang, L.; Qin, H.; Zhong, D.; Li, Y.; Xue, P.; et al. The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Inflammatory Skin Diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1083432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Lu, G.; Wang, H. Advances in the Mechanism of Action of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Psoriasis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 141, 112928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.-H.; Lee, Y.; Song, E.-J.; Lee, D.; Jang, S.-Y.; Byeon, H.R.; Hong, M.-G.; Lee, S.-N.; Kim, H.-J.; Seo, J.-G.; et al. Faecalibacterium Prausnitzii Prevents Hepatic Damage in a Mouse Model of NASH Induced by a High-Fructose High-Fat Diet. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1123547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petro, T.M. Regulatory Role of Resveratrol on Th17 in Autoimmune Disease. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2010, 11, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limagne, E.; Lançon, A.; Delmas, D.; Cherkaoui-Malki, M.; Latruffe, N. Resveratrol Interferes with IL1-β-Induced Pro-Inflammatory Paracrine Interaction Between Primary Chondrocytes and Macrophages. Nutrients 2016, 8, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.M.; Oliveira, M.I.; Sette, L.; Almeida, C.R.; Oliveira, M.J.; Barbosa, M.A.; Santos, S.G. Resveratrol as a Natural Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Molecule: Implications to Dendritic Cells and Their Crosstalk with Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangels, D.R.; Mohler, E.R. Catechins as Potential Mediators of Cardiovascular Health. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, P.; Khanna, D. Green Tea Catechins: Defensive Role in Cardiovascular Disorders. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2013, 11, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traber, M.G.; Stevens, J.F. Vitamins C and E: Beneficial Effects from a Mechanistic Perspective. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 51, 1000–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gęgotek, A.; Skrzydlewska, E. Ascorbic Acid as Antioxidant. Vitam. Horm. 2022, 121, 247–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudabadi, M.M.S.; Rahbar, A.R. Effect of EPA and Vitamin C on Superoxide Dismutase, Glutathione Peroxidase, Total Antioxidant Capacity and Malondialdehyde in Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Oman. Med. J. 2014, 29, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, H.; Qing, Z.; Guo, H.; Zhang, R.; Ma, J. Effect of Vitamin E Supplementation in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 77, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilari, S.; Proietti, S.; Milani, F.; Vitiello, L.; Muscoli, C.; Russo, P.; Bonassi, S. Dietary Patterns, Oxidative Stress, and Early Inflammation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Comparing Mediterranean, Vegan, and Vegetarian Diets. Nutrients 2025, 17, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioia, C.; Lucchino, B.; Tarsitano, M.G.; Iannuccelli, C.; Di Franco, M. Dietary Habits and Nutrition in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Can Diet Influence Disease Development and Clinical Manifestations? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadell, A.K.; Bärebring, L.; Hulander, E.; Gjertsson, I.; Lindqvist, H.M.; Winkvist, A. Anti-Inflammatory Diet In Rheumatoid Arthritis (ADIRA)—A Randomized, Controlled Crossover Trial Indicating Effects on Disease Activity. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 111, 1203–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Microbiota | Impact on Disease | References |
|---|---|---|
| Prevotella copri | RA—inflammatory induction through the activation of Th17 lymphocytes and IL-17 production; possible cross-reaction with autoantigens. | [53,59,74] |
| Escherichia coli | PsA—LPS translocation, IL-23/IL-17 pathway activation; increase in proinflammatory cytokines. | [37,73] |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | AS—activation of IL-23/IL-17 pathway; stimulation of IL-17 production. | [65,66] |
| Faecalibacterium prausnitzii | Common for RA, AS, and PsA—SCFA production, anti-inflammatory activity, enhancement of intestinal barrier. | [53,59] |
| Collinsella aerofaciens | RA—increased intestinal permeability, induction of inflammation, activation of NF-κB. | [53,58] |
| Lactobacillus salivarius | RA—reduction in proinflammatory cytokines, increase in the number of Treg lymphocytes. | [36,69] |
| Lactobacillus plantarum | RA—reduction in disease activity, reduction in IL-17 and TNF-α. | [36,53] |
| Roseburia faecis | RA—anti-inflammatory effect, reduction in RF and ACPA, improvement of the intestinal barrier. | [75,76] |
| Akkermansia muciniphila | RA—improvement of the intestinal barrier, anti-inflammatory effect, reduction in intestinal permeability. | [69,77] |
| Eggerthella lenta | RA—induction of inflammation, increased activity in proinflammatory cytokines. | [58,78] |
| Aspect | Mediterranean Diet | Plant-Based Hypocaloric Diet |
|---|---|---|
| Main Components | Vegetables, fruits, whole grains, olive oil, fish, nuts, and small amounts of dairy and red meat | Vegetables, fruits, legumes, whole grains, nuts, and seeds |
| Protein Sources | Fish, poultry, legumes, and limited dairy | Legumes, tofu, tempeh, nuts, and seeds |
| Fat Sources | Olive oil, nuts, and fish | Nuts, seeds, and plant oils (e.g., flaxseed oil, canola oil) |
| Fat Profile | High monounsaturated fats and moderate omega-3 intake | Very high in polyunsaturated fats (plant-based omega-3) |
| Fiber Content | Moderate to high | Very high |
| Polyphenol Content | High (from fruits, vegetables, olive oil, and wine) | Very high (from a wide variety of plant foods) |
| Key Anti-Inflammatory Components | Olive oil (oleocanthal), omega-3 fatty acids from fish, and polyphenols | Polyphenols, fiber, phytochemicals (e.g., isoflavones) |
| Anti-Inflammatory Potential | High | Very high |
| Typical Limitations | Limited intake of red meat, sugars, and saturated fats | Excludes animal products (in vegan diet), and potential risk of B12, iron, and calcium deficiencies |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kupczyk, D.; Bilski, R.; Szeleszczuk, Ł.; Mądra-Gackowska, K.; Studzińska, R. The Role of Diet in Modulating Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis, and Psoriatic Arthritis. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17091603
Kupczyk D, Bilski R, Szeleszczuk Ł, Mądra-Gackowska K, Studzińska R. The Role of Diet in Modulating Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis, and Psoriatic Arthritis. Nutrients. 2025; 17(9):1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17091603
Chicago/Turabian StyleKupczyk, Daria, Rafał Bilski, Łukasz Szeleszczuk, Katarzyna Mądra-Gackowska, and Renata Studzińska. 2025. "The Role of Diet in Modulating Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis, and Psoriatic Arthritis" Nutrients 17, no. 9: 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17091603
APA StyleKupczyk, D., Bilski, R., Szeleszczuk, Ł., Mądra-Gackowska, K., & Studzińska, R. (2025). The Role of Diet in Modulating Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis, and Psoriatic Arthritis. Nutrients, 17(9), 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17091603









