A 14-Day Plant-Based Dietary Intervention Modulates the Plasma Levels of Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated MicroRNAs: A Bioinformatics-Guided Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Recruitment
2.2. Plant-Based Diet
2.3. Anthropometric Assessment
2.4. Blood Sample Collection
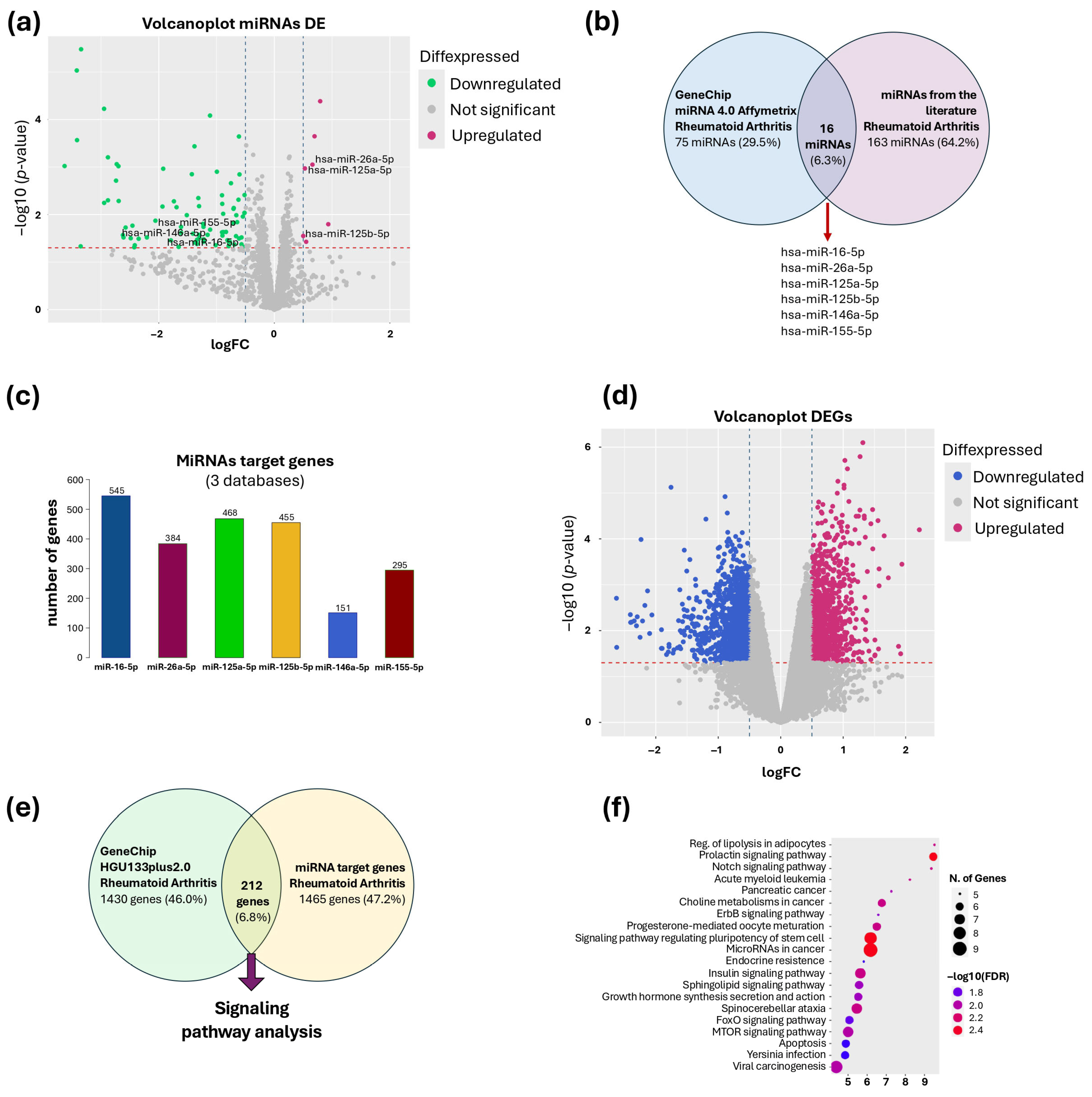
2.5. Selection of miRNAs
2.6. Prediction of miRNA Target Genes
2.7. Expression Microarray Analysis
2.8. Selection of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs)
2.9. Analysis of Signaling Pathways
2.10. miRNA Quantification
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RA | Rheumatoid Arthritis |
| miRNA | MicroRNA |
| DEGs | Differentially Expressed Genes |
| DEmiRNAs | Differentially Expressed microRNAs |
| RT-qPCR | Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| GEO | Gene Expression Omnibus |
| NCBI | National Center for Biotechnology Information |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| PBD | Plant-Based Diet |
| DAS28-CRP | Disease Activity Score of 28 Joints Using C-Reactive Protein |
| CRP | C-Reactive Protein |
| ESR | Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate |
| BIA | Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| REE | Resting Energy Expenditure |
| TEE | Total Energy Expenditure |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| SPSS | Statistical Package for the Social Sciences |
| PI3K/AKT | Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase/Protein Kinase B pathway |
| CTGF | Connective Tissue Growth Factor |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor Kappa B |
| RT | Reverse Transcription |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| ox-LDL | Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein |
References
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Xie, H.; Hong, F.; Yang, S. Role of MiRNAs in Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy. Cells 2023, 12, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, K.; Nossent, J.; Preen, D.; Keen, H.; Inderjeeth, C. The Global Prevalence of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Meta-Analysis Based on a Systematic Review. Rheumatol. Int. 2021, 41, 863–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; McInnes, I.B. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Lancet 2016, 388, 2023–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadell, A.K.E.; Bärebring, L.; Hulander, E.; Gjertsson, I.; Lindqvist, H.M.; Winkvist, A. Anti-Inflammatory Diet In Rheumatoid Arthritis (ADIRA)—A Randomized, Controlled Crossover Trial Indicating Effects on Disease Activity. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 111, 1203–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, A.M.; Dell’Oro, M.; Spoo, M.; Fischer, J.M.; Steckhan, N.; Jeitler, M.; Häupl, T.; Kandil, F.I.; Michalsen, A.; Koppold-Liebscher, D.A.; et al. To Eat or Not to Eat—An Exploratory Randomized Controlled Trial on Fasting and Plant-Based Diet in Rheumatoid Arthritis (NutriFast-Study). Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1030380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walrabenstein, W.; Wagenaar, C.A.; Van Der Leeden, M.; Turkstra, F.; Twisk, J.W.R.; Boers, M.; Van Middendorp, H.; Weijs, P.J.M.; Van Schaardenburg, D. A Multidisciplinary Lifestyle Program for Rheumatoid Arthritis: The ‘Plants for Joints’ Randomized Controlled Trial. Rheumatology 2023, 62, 2683–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulander, E.; Bärebring, L.; Turesson Wadell, A.; Gjertsson, I.; Calder, P.C.; Winkvist, A.; Lindqvist, H.M. Proposed Anti-Inflammatory Diet Reduces Inflammation in Compliant, Weight-Stable Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis in a Randomized Controlled Crossover Trial. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 3856–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkvist, A.; Bärebring, L.; Gjertsson, I.; Ellegård, L.; Lindqvist, H.M. A Randomized Controlled Cross-over Trial Investigating the Effect of Anti-Inflammatory Diet on Disease Activity and Quality of Life in Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Anti-Inflammatory Diet In Rheumatoid Arthritis (ADIRA) Study Protocol. Nutr. J. 2018, 17, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, W.J.; Mangels, A.R.; Fresán, U.; Marsh, K.; Miles, F.L.; Saunders, A.V.; Haddad, E.H.; Heskey, C.E.; Johnston, P.; Larson-meyer, E.; et al. The Safe and Effective Use of Plant-Based Diets with Guidelines for Health Professionals. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Peña, M.; González-Ramírez, J.; Bermúdez-Benítez, E.; Sánchez-Gloria, J.L.; Amezcua-Guerra, L.M.; Tavera-Alonso, C.; Guzmán-Martín, C.A.; Jacobo-Albavera, L.; Silveira-Torre, L.H.; Martínez-Martínez, L.A.; et al. Regulation of LncRNA NUTM2A-AS1 and CCR3 in the Clinical Response to a Plant-Based Diet in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Pilot Study. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, G.; Kehoe, L.; Flynn, A.; Walton, J. Plant-Based Diets: A Review of the Definitions and Nutritional Role in the Adult Diet. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2022, 81, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fam, V.W.; Charoenwoodhipong, P.; Sivamani, R.K.; Holt, R.R.; Keen, C.L.; Hackman, R.M. Plant-Based Foods for Skin Health: A Narrative Review. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2022, 122, 614–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwarith, J.; Kahleova, H.; Rembert, E.; Yonas, W.; Dort, S.; Calcagno, M.; Burgess, N.; Crosby, L.; Barnard, N.D. Nutrition Interventions in Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Potential Use of Plant-Based Diets. A Review. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 435408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, S.; Jaiswal, K.S.; Gupta, B. Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis with Dietary Interventions. Front. Nutr. 2017, 4, 301603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala-Climent, M.; López de Coca, T.; Guerrero, M.D.; Muñoz, F.J.; López-Ruíz, M.A.; Moreno, L.; Alacreu, M.; Dea-Ayuela, M.A. The Effect of an Anti-Inflammatory Diet on Chronic Pain: A Pilot Study. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1205526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayebi, A.; Soleimani, D.; Mostafaei, S.; Elahi, N.; Pahlavani, N.; Bagheri, A.; Elahi, H.; Mahmoudi, M.; Nachvak, S.M. Association between Dietary Inflammatory Index Scores and the Increased Disease Activity of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutr. J. 2022, 21, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juárez-Vicuña, Y.; Guzmán-Martín, C.A.; Martínez-Martínez, L.A.; Hernández-Díazcouder, A.; Huesca-Gómez, C.; Gamboa, R.; Amezcua-Guerra, L.M.; Chacon-Perez, M.; Amigo, M.C.; Sánchez-Muñoz, F. MiR-19b-3p and MiR-20a-5p Are Associated with the Levels of Antiphospholipid Antibodies in Patients with Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Rheumatol. Int. 2021, 41, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Gatto, N.M.; Chen, Z.; Qiu, H.; Lee, G.; Duerksen-Hughes, P.; Fraser, G.; Wang, C. Vegetarian Diets, Circulating MiRNA Expression and Healthspan in Subjects Living in the Blue Zone. Precis. Clin. Med. 2020, 3, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, W.; Ge, G.; Peng, J.; Xu, Y.; Yang, H.; Bai, J.; Geng, D. Comprehensive Overview of MicroRNA Function in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Bone Res. 2023, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán-Martín, C.A.; Jiménez-Ortega, R.F.; Ortega-Springall, M.F.; Peña-Peña, M.; Guerrero-Ponce, A.E.; Vega-Memije, M.E.; Amezcua-Guerra, L.M.; Sánchez-Muñoz, F.; Springall, R. MiR-16-5p, MiR-21-5p, and MiR-155-5p in Circulating Vesicles as Psoriasis Biomarkers. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 6971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, J.; Upchurch, K.S. ACR/EULAR 2010 Rheumatoid Arthritis Classification Criteria. Rheumatology 2012, 51 (Suppl. 6), vi5–vi9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradowska-Gorycka, A.; Stypińska, B. MicroRNAs in Rheumatoid Arthritis: From Pathogenesis to Clinical Utility. In New Developments in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis; InTech: Vienna, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Blizzard, L.; Venn, A.; Jones, G.; Burgess, J.; Parameswaran, V.; Ding, C.; Antony, B. POS0191| THE VALUE OF MIR-20B, MIR-22, MIR-26A, MIR-125B AND MIR-221 IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 309–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kmiołek, T.; Paradowska-Gorycka, A. MiRNAs as Biomarkers and Possible Therapeutic Strategies in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cells 2022, 11, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormseth, M.; Solus, J.; Vickers, K.; Oeser, A.; Raggi, P.; Stein, C.M. SAT0125| Utility of Select Plasma Mirnas for Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Monitoring of Disease Activity and Cardiovascular Risk. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Li, J.; Zhao, H.; Shen, H.; Lin, J.; Zhao, M.; Gao, J.; Gong, T.; Ren, S.; Hong, L. MiR-146a and MiR-155 as Potential Biomarkers for Rheumatoid Arthritis and Disease Activity. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2018, 9, 1936–1943. [Google Scholar]
- Mantilla-Escalante, D.C.; López de las Hazas, M.C.; Crespo, M.C.; Martín-Hernández, R.; Tomé-Carneiro, J.; del Pozo-Acebo, L.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Bulló, M.; Dávalos, A. Mediterranean Diet Enriched in Extra-Virgin Olive Oil or Nuts Modulates Circulating Exosomal Non-Coding RNAs. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 4279–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, F.J.; Cardona-Alvarado, M.I.; Mercader, J.M.; Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Moreno, M.; Sabater, M.; Fuentes-Batllevell, N.; Ramírez-Chávez, E.; Ricart, W.; Molina-Torres, J.; et al. Circulating Profiling Reveals the Effect of a Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid-Enriched Diet on Common MicroRNAs. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 1095–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques-Rocha, J.L.; Milagro, F.I.; Mansego, M.L.; Zulet, M.A.; Bressan, J.; Martínez, J.A. Expression of Inflammation-Related MiRNAs in White Blood Cells from Subjects with Metabolic Syndrome after 8 Wk of Following a Mediterranean Diet–Based Weight Loss Program. Nutrition 2016, 32, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Huang, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, F.; Meng, S.; Wang, C. MicroRNA-125a-5p Partly Regulates the Inflammatory Response, Lipid Uptake, and ORP9 Expression in OxLDL-Stimulated Monocyte/Macrophages. Cardiovasc. Res. 2009, 83, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, A.; Saavedra, N.; Cavalcante, M.F.; Salazar, L.A.; Abdalla, D.S.P. Identification of MicroRNAs Involved in the Modulation of Pro-Angiogenic Factors in Atherosclerosis by a Polyphenol-Rich Extract from Propolis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 557, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Yu, F.; Wang, Y.; Hui, Y.; Carnevale, K.; Fu, M.; Lu, H.; Fan, D. MicroRNA-155 Deficiency Results in Decreased Macrophage Inflammation and Attenuated Atherogenesis in Apolipoprotein E-Deficient Mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Xing, S.; Liu, M.; Deng, W.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Huang, X.; Wu, C.; Guo, X.; et al. MiR-26a-5p Enhances Cells Proliferation, Invasion, and Apoptosis Resistance of Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes in Rheumatoid Arthritis by Regulating PTEN/PI3K/AKT Pathway. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20182192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Cao, S. Role of MicroRNA-26a in Cartilage Injury and Chondrocyte Proliferation and Apoptosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis Rats by Regulating Expression of CTGF. J. Cell Physiol. 2020, 235, 979–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran-Moguel, M.C.; Petarra-Del Rio, S.; Mayorquin-Galvan, E.E.; Zavala-Cerna, M.G. Rheumatoid Arthritis and miRNAs: A Critical Review through a Functional View. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 2474529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, M.B.; Sarangi, P.; Amit, S.; Senguttuvan, S.; Kumar, N.; Jayandharan, G.R. Targeted delivery of miR125a-5p and human Factor VIII attenuates molecular mediators of hemophilic arthropathy. Thromb. Res. 2023, 231, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Yuan, Q. miR-125 regulates PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis rats via PARP2. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20180890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Zeid, A.; Saad, M.; Soliman, E. MicroRNA 146a expression in rheumatoid arthritis: Association with tumor necrosis factor-alpha and disease activity. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2011, 15, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, C.; Xiang, X.; Qiu, W.; Guo, K. miR 155 promotes an inflammatory response in HaCaT cells via the IRF2BP2/KLF2/NF κB pathway in psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2024, 54, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| N = 23 | Baseline | 14 Days | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Female/Male sex | 22/1 | ||
| Age (years) | 56 (51–63) | ||
| Weight (kg) | 65.50 (60.75–83.05) | 64.70 (59.25–83.65) | 0.014 |
| Waist-to-hip radio | 0.88 (0.84–0.94) | 0.89 (0.84–0.92) | 0.313 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 29.50 (25.80–33.05) | 29.20 (25.15–32.75) | 0.001 |
| % Body fat | 44.40 (37.10–48.05) | 45.00 (37.25–49.40) | 0.736 |
| %Visceral fat | 10.00 (7.50–12.00) | 10.00 (7.00–12.50) | 0.052 |
| Serum glucose (mg/dL) | 92.00 (82.50–104.00) | 87.00 (80.00–99.00) | 0.022 |
| Serum uric acid (mg/dL) | 4.91 (3.90–5.81) | 4.98 (4.19–5.61) | 0.543 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 180.00 (144.00–211.00) | 155.00 (141.00–199.00) | 0.0034 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 47.50 (41.65–60.40) | 46.50 (41.10–56.80) | 0.363 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 134.00 (106.00–174.00) | 130.00 (107.50–176.00) | 0.243 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 5.61 (3.38–8.96) | 4.78 (2.35–7.40) | 0.020 |
| ESR (mm/h) | 17.00 (7.50–33.50) | 15.00 (8.00–25.00) | 0.149 |
| Swollen joints | 5.00 (3.00–8.00) | 3.00 (1.50–4.50) | 0.005 |
| Tender joints | 7.00 (2.50–8.00) | 3.00 (1.00–3.50) | <0.0001 |
| DAS28-CRP | 4.04 (3.33–4.72) | 3.43 (2.92–3.60) | <0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peña-Peña, M.; Bermúdez-Benítez, E.; Sánchez-Gloria, J.L.; Rada, K.M.; Mora-Ramírez, M.; Amezcua-Guerra, L.M.; Ballinas-Verdugo, M.A.; Tavera-Alonso, C.; Guzmán-Martín, C.A.; Jacobo-Albavera, L.; et al. A 14-Day Plant-Based Dietary Intervention Modulates the Plasma Levels of Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated MicroRNAs: A Bioinformatics-Guided Pilot Study. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2222. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17132222
Peña-Peña M, Bermúdez-Benítez E, Sánchez-Gloria JL, Rada KM, Mora-Ramírez M, Amezcua-Guerra LM, Ballinas-Verdugo MA, Tavera-Alonso C, Guzmán-Martín CA, Jacobo-Albavera L, et al. A 14-Day Plant-Based Dietary Intervention Modulates the Plasma Levels of Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated MicroRNAs: A Bioinformatics-Guided Pilot Study. Nutrients. 2025; 17(13):2222. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17132222
Chicago/Turabian StylePeña-Peña, Mario, Elyzabeth Bermúdez-Benítez, José L. Sánchez-Gloria, Karla M. Rada, Mauricio Mora-Ramírez, Luis M. Amezcua-Guerra, Martha A. Ballinas-Verdugo, Claudia Tavera-Alonso, Carlos A. Guzmán-Martín, Leonor Jacobo-Albavera, and et al. 2025. "A 14-Day Plant-Based Dietary Intervention Modulates the Plasma Levels of Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated MicroRNAs: A Bioinformatics-Guided Pilot Study" Nutrients 17, no. 13: 2222. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17132222
APA StylePeña-Peña, M., Bermúdez-Benítez, E., Sánchez-Gloria, J. L., Rada, K. M., Mora-Ramírez, M., Amezcua-Guerra, L. M., Ballinas-Verdugo, M. A., Tavera-Alonso, C., Guzmán-Martín, C. A., Jacobo-Albavera, L., Domínguez-López, A., Jiménez-Ortega, R. F., Silveira, L. H., Martínez-Martínez, L. A., & Sánchez-Muñoz, F. (2025). A 14-Day Plant-Based Dietary Intervention Modulates the Plasma Levels of Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated MicroRNAs: A Bioinformatics-Guided Pilot Study. Nutrients, 17(13), 2222. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17132222









