One-Year Mortality After Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy: The Prognostic Role of Nutritional Biomarkers and Care Settings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Laboratory Measurements
2.4. PEG Procedure
2.5. Follow-Up Protocol
2.6. Outcome Measures
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Findings Associated with One-Year Mortality
3.3. Independent Predictors of One-Year Mortality
3.4. Diagnostic Performance of PNI and CAR in Predicting One-Year Mortality
3.5. Demographic and Clinical Findings According to Place of Residence
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations
4.2. Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rahnemai-Azar, A.A.; Rahnemaiazar, A.A.; Naghshizadian, R.; Kurtz, A.; Farkas, D.T. Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy: Indications, technique, complications and management. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 7739–7751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tae, C.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Joo, M.K.; Park, C.H.; Gong, E.J.; Shin, C.M.; Lim, H.; Choi, H.S.; Choi, M.; Kim, S.H.; et al. Clinical practice guidelines for percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy. Clin. Endosc. 2023, 56, 391–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I.H.; Cho, Y.K. Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy: Procedure, Complications and Management. Brain Neurorehabil. 2022, 15, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinar-Gutierrez, A.; Serrano-Aguayo, P.; Gutierrez, R.V.; Rey, S.G.; Gonzalez-Navarro, I.; Tatay-Dominguez, D.; Garrancho-Dominguez, P.; Remon-Ruiz, P.J.; Martinez-Ortega, A.J.; Mejias, V.N.; et al. Gastrostomies: Experience and complications with three modalities in a tertiary centre over a 26-year period. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1191204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucendo, A.J.; Friginal-Ruiz, A.B. Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy: An update on its indications, management, complications, and care. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2014, 106, 529–539. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, J.M.D.; Pedreira, L.C.; Goes, R.P.; Souza, M.A.A.; Baixinho, C.; Ortega, J.; De La Rosa, R.N.; Sousa, A.R.; Silva, V.A.D.; Pinto, I.S.; et al. Caregivers’ Mastery in Handling Gastrostomy at Home after Educational Intervention: Qualitative Descriptive Study. Healthcare 2024, 12, 2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrnes, C.; Mockler, D.; Lyons, L.; Loane, D.; Russell, E.; Bennett, A.E. A scoping review of best practices in home enteral tube feeding. Prim. Health Care Res. Dev. 2022, 23, e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, S.; Newcomb, M.; Hessler, J.; Siddiqui, F. Prophylactic versus reactive PEG tube placement in head and neck cancer. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 2014, 150, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, A.; Bardan, E.; Chowers, Y.; Sakhnini, E.; Fidder, H.H.; Bar-Meir, S.; Avidan, B. Risk factors for mortality in patients undergoing percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy. Endoscopy 2004, 36, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boylan, C.; Barrett, D.; Li, V.; Merrick, S.; Steed, H. Longitudinal complications associated with PEG: Rate and severity of 30-day and 1-year complications experienced by patients after primary PEG insertion. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2021, 43, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.; Oswal, M.; Samra, A.D.; Martin, H.; Burch, N.; Colby, J.; Lindahl, A.; Skelly, R. Mortality and Institutionalization After Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy in Parkinson’s Disease and Related Conditions. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2020, 7, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zopf, Y.; Konturek, P.; Nuernberger, A.; Maiss, J.; Zenk, J.; Iro, H.; Hahn, E.G.; Schwab, D. Local infection after placement of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tubes: A prospective study evaluating risk factors. Can. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 22, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahveci, G.; Çelik, S. Preparation, follow-up and discharge training of the patient fed with percutaneous endoskopic gasrostomy tube. J. Intensive Care Nurs. 2020, 24, 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- Ellez, H.I.; Keskinkilic, M.; Semiz, H.S.; Arayici, M.E.; Kisa, E.; Oztop, I. The Prognostic Nutritional Index (PNI): A New Biomarker for Determining Prognosis in Metastatic Castration-Sensitive Prostate Carcinoma. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.Y.; Wen, J.X.; Lu, M.T.; Jian, X.Y.; Wan, X.L.; Xu, Z.W.; Liang, J.Q.; Wu, J.D. Association Between Prognostic Nutritional Index and Prognosis in Patients With Heart Failure: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 918566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Yuan, X.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Li, W. Prognostic value of prognostic nutritional index in lung cancer: A meta-analysis. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 5298–5307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correa-Rodriguez, M.; Pocovi-Gerardino, G.; Callejas-Rubio, J.L.; Fernandez, R.R.; Martin-Amada, M.; Cruz-Caparros, M.G.; Ortego-Centeno, N.; Rueda-Medina, B. The Prognostic Nutritional Index and Nutritional Risk Index Are Associated with Disease Activity in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Nutrients 2019, 11, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ma, L.; Zhao, L.; Sheng, J.; Xu, Y.; Chen, J.; Yu, L.; Sun, Q.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, S.; et al. Association Between the Prognostic Nutritional Index and Cognitive Function Among Older Adults in the United States: A Population-Based Study. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2021, 83, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, Y.; Akino, K.; Nojima, M.; Himori, R.; Kikuchi, T.; Mita, H.; Nakamura, M.; Tsukuda, H.; Yamano, H.O.; Sasaki, Y.; et al. Prognostic nutritional index and early mortality with percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy. QJM 2018, 111, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, Y.; Maetani, I.; Shigoka, H.; Matsuda, T. Preprocedural control of nutritional status score and prediction of early death after percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy. JGH Open 2023, 7, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onodera, T.; Goseki, N.; Kosaki, G. Prognostic nutritional index in gastrointestinal surgery of malnourished cancer patients. Nihon Geka Gakkai Zasshi 1984, 85, 1001–1005. [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff, S.C.; Austin, P.; Boeykens, K.; Chourdakis, M.; Cuerda, C.; Jonkers-Schuitema, C.; Lichota, M.; Nyulasi, I.; Schneider, S.M.; Stanga, Z.; et al. ESPEN practical guideline: Home enteral nutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 468–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLong, E.R.; DeLong, D.M.; Clarke-Pearson, D.L. Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: A nonparametric approach. Biometrics 1988, 44, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenstein, I.; Shastri, Y.M.; Stein, J. Gastroenteric tube feeding: Techniques, problems and solutions. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 8505–8524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boullata, J.I.; Carrera, A.L.; Harvey, L.; Escuro, A.A.; Hudson, L.; Mays, A.; McGinnis, C.; Wessel, J.J.; Bajpai, S.; Beebe, M.L.; et al. ASPEN Safe Practices for Enteral Nutrition Therapy [Formula: See text]. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2017, 41, 15–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farag, S.; Georgy, S.S.; Fathy, M.; elSadek, A.; Abdulghani, K.O. Attitude and experience of neurologists towards percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy: An Egyptian study. Egypt. J. Neurol. Psychiatry Neurosurg. 2020, 56, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrag, S.P.; Sharma, R.; Jaik, N.P.; Seamon, M.J.; Lukaszczyk, J.J.; Martin, N.D.; Hoey, B.A.; Stawicki, S.P. Complications related to percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) tubes. A comprehensive clinical review. J. Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2007, 16, 407–418. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, P.; Cole, A.; Scolding, N.J.; Rice, C.M. Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy Tube Insertion in Neurodegenerative Disease: A Retrospective Study and Literature Review. Clin. Endosc. 2017, 50, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locher, J.L.; Bonner, J.A.; Carroll, W.R.; Caudell, J.J.; Kilgore, M.L.; Ritchie, C.S.; Roth, D.L.; Tajeu, G.S.; Yuan, Y.; Allison, J.J. Gastrostomy tube placement and use in patients with head and neck cancer. Head. Neck 2012, 34, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folwarski, M.; Klek, S.; Brzezinski, M.; Szlagatys-Sidorkiewicz, A.; Wyszomirski, A.; Meyer-Szary, J.; Skonieczna-Zydecka, K. Prevalence and Trends in Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy Placement: Results From a 10-Year, Nationwide Analysis. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 906409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezer, R.E.; Ozdemir Koken, Z.; Senol Celik, S. Home Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy Feeding: Difficulties and Needs of Caregivers, Qualitative Study. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2020, 44, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeykens, K.; Duysburgh, I.; Verlinden, W. Prevention and management of minor complications in percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2022, 9, e000975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroupa, R.; Jurankova, J.; Dastych, M.; Senkyrik, M.; Pavlik, T.; Prokesova, J.; Jecmenova, M.; Dolina, J.; Hep, A. Different clinical utility of oropharyngeal bacterial screening prior to percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in oncological and neurological patients. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 590891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, B.M.; Perring, P.; Engoren, M.; Sferra, J.J. Hospital and long-term outcome after percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy. Surg. Endosc. 2008, 22, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gumaste, V.V.; Bhamidimarri, K.R.; Bansal, R.; Sidhu, L.; Baum, J.; Walfish, A. Factors predicting early discharge and mortality in post-percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy patients. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2014, 27, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, G.; Rockey, D.; Gupta, S. High In-hospital mortality after percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy: Results of a nationwide population-based study. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 11, 1437–1444.e1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, D.L.; Miranda, L.E.C.; Lima, R.; Romero-Velez, G.; Chin, R.; Shadduck, P.P.; Sreeramoju, P. Factors Associated with Mortality after Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy. JSLS 2023, 27, e2023.00005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereketoğlu, M.A.; Haki, C. Survival Following Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy in Neurology Intensive Care Unit Patients. Harran Üniversitesi Tıp Fakültesi Derg. 2023, 20, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, R.; Batra, S.; Mancillas, O.L.; Wegner, R.; Grewal, N.; Williams, G.W. In-Hospital Mortality with Use of Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy in Traumatic Brain Injury Patients: Results of a Nationwide Population-Based Study. Neurocrit Care 2017, 26, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, R.; Kukreja, N.; Tse, A.; Pednekar, G.; Mouchli, A.; Young, L.; Didyuk, O.; Wegner, R.C.; Grewal, N.; Williams, G.W. Trends and Outcomes of Early Versus Late Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy Placement in Patients With Traumatic Brain Injury: Nationwide Population-based Study. J. Neurosurg. Anesthesiol. 2018, 30, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.Y.; Lai, J.N.; Kung, W.M.; Hung, C.H.; Yip, H.T.; Chang, Y.C.; Wei, C.Y. Nationwide Prevalence and Outcomes of Long-Term Nasogastric Tube Placement in Adults. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomberg, J.; Lagergren, P.; Martin, L.; Mattsson, F.; Lagergren, J. Albumin and C-reactive protein levels predict short-term mortality after percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in a prospective cohort study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2011, 73, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.; Lagergren, J.; Blomberg, J.; Johar, A.; Bosaeus, I.; Lagergren, P. Phase angle as a prognostic marker after percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) in a prospective cohort study. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 1013–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo, F.A.; da Costa, M.C.; Pelosi, A.D.; Martins, R.N.; Machado, L.; Francioni, E. Predicting outcomes and complications of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy. Endoscopy 2007, 39, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higaki, F.; Yokota, O.; Ohishi, M. Factors predictive of survival after percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in the elderly: Is dementia really a risk factor? Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 1011–1016; quiz 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenberg, K.; Eriksson, A.; Odensten, C.; Darehed, D. Mortality and complications after percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy: A retrospective multicentre study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022, 22, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyasato, Y.; Hanna, R.M.; Morinaga, J.; Mukoyama, M.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Prognostic Nutritional Index as a Predictor of Mortality in 101,616 Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gursoy, C.; Gursoy, G.; Demirbilek, S.G. C-reactive protein-albumin ratio and procalcitonin in predicting intensive care unit mortality in traumatic brain injury. Acute Crit. Care 2022, 37, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbeit, W.; Kadah, A.; Mari, A.; Mahamid, M.; Khoury, T. Simple Bedside Predictors of Survival after Percutaneous Gastrostomy Tube Insertion. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 2019, 1532918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duzenli, T.; Ketenci, M.; Akyol, T.; Koseoglu, H.; Tanoglu, A.; Kaplan, M.; Yazgan, Y. Predictive factors of complications and 30-day mortality in patients undergoing percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy: The utility of C-reactive protein to albumin ratio. Acta Gastroenterol. Belg. 2021, 84, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topcu, H.; Sezikli, İ.; Tutan, D.; Köseoğlu, H.; Topcu, R. Assessment of factors affecting mortality in patients with percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tube placement in the intensive care unit. J. Med. Palliat. Care 2023, 4, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | Mortality | Univariable Regression | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No n = 160 | Yes n = 76 | HR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Gender, n (%) | |||||
| Female | 102 (63.8) | 38 (50.0) | ref | ||
| Male | 58 (36.2) | 38 (50.0) | 1.55 | 0.98–2.43 | 0.056 |
| Age, years | 71.8 ± 17.7 | 74.3 ± 16.8 | 1.01 | 0.99–1.02 | 0.381 |
| Indications, n (%) | |||||
| Neurologic disorders | 120 (75.0) | 45 (59.2) | ref | ||
| Head and neck cancers | 19 (11.9) | 7 (9.2) | 1.04 | 0.47–2.31 | 0.920 |
| Other cancer | 7 (4.4) | 4 (5.3) | 1.48 | 0.53–4.12 | 0.451 |
| Hemorrhage | 9 (5.6) | 11 (14.5) | 2.47 | 1.28–4.78 | 0.007 * |
| Others | 5 (3.1) | 9 (11.8) | 2.90 | 1.41–5.94 | 0.004 * |
| Laboratory findings | |||||
| Albumin | 3.2 ± 0.6 | 2.7 ± 0.5 | 0.28 | 0.18–0.44 | <0.001 * |
| Lymphocytes | 1.8 (1.1–2.5) | 1.3 (0.9–2.0) | 0.7 | 0.53–0.91 | 0.008 * |
| CRP | 34.4 (11.9–75.4) | 57.4 (26.8–107.1) | 1.03 | 1.01–1.05 | 0.010 * |
| CAR | 11.1 (4.1–24.7) | 22.3 (10.0–46.5) | 1.1 | 1.05–1.16 | <0.001 * |
| PNI | 41.4 ± 8.0 | 34.3 ± 7.3 | 0.91 | 0.87–0.94 | <0.001 * |
| Feeding method, n (%) | |||||
| Pump | 137 (85.6) | 75 (98.7) | ref | ||
| Bolus | 23 (14.4) | 1 (1.3) | 0.10 | 0.01–0.69 | 0.020 * |
| Formula type | |||||
| Standard | 46 (28.7) | 14 (18.4) | ref | ||
| Hypercaloric | 54 (33.8) | 25 (32.9) | 1.43 | 0.74–2.74 | 0.288 |
| Diabetic | 40 (25.0) | 27 (35.5) | 1.91 | 1.01–3.64 | 0.049 * |
| Immunonutrition | 15 (9.4) | 5 (6.6) | 1.09 | 0.39–3.03 | 0.869 |
| Kidney specific | 5 (3.1) | 5 (6.6) | 2.33 | 0.84–6.47 | 0.105 |
| Variables | Mortality | Univariable Regression | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No n = 160 | Yes n = 76 | HR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Place of residence, n (%) | |||||
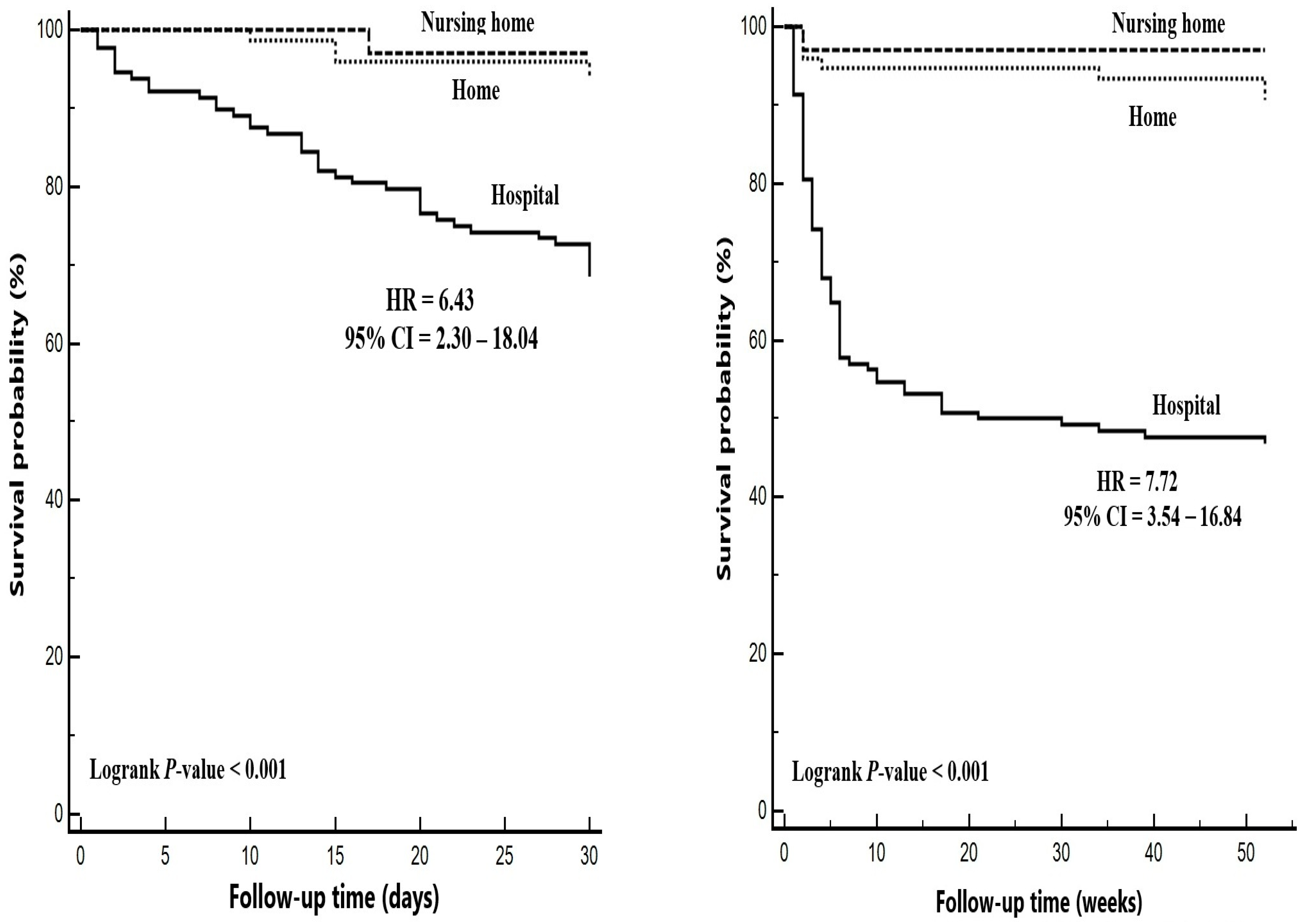
| Hospital | 60 (37.5) | 68 (89.5) | ref | ||
| Nursing home | 32 (20.0) | 1 (1.3) | 0.04 | 0.01–0.30 | 0.002 * |
| Home | 68 (42.5) | 7 (9.2) | 0.17 | 0.08–0.38 | <0.001 * |
| Characteristics of home caregivers | |||||
| Number of caregivers, n (%) | |||||
| One | 44 (64.7) | 2 (28.6) | ref | ||
| Two or more | 24 (35.3) | 5 (71.4) | 4.31 | 0.84–22.23 | 0.281 |
| Gender, n (%) | |||||
| Female | 55 (80.9) | 5 (71.4) | ref | ||
| Male | 13 (19.1) | 2 (28.6) | 1.56 | 0.30–8.07 | 0.592 |
| Age, years | 53.4 ± 10.9 | 54.0 ± 18.3 | 1.01 | 0.94–1.08 | 0.921 |
| Education, n (%) | |||||
| University | 8 (11.8) | 1 (14.3) | ref | ||
| High school | 14 (20.6) | 1 (14.3) | 0.56 | 0.04–8.97 | 0.683 |
| Primary school | 46 (67.6) | 5 (71.4) | 0.86 | 0.10–7.38 | 0.892 |
| PEG tube replacement, n (%) | |||||
| No | 103 (64.4) | 72 (94.7) | ref | ||
| Yes | 57 (35.6) | 4 (5.3) | 0.12 | 0.05–0.34 | <0.001 * |
| Number of replacements, n (%) | |||||
| One | 33 (20.6) | 4 (5.3) | ref | ||
| Two or more | 24 (15.0) | - | 0.02 | 0.01–82.89 | 0.362 |
| Minor complications, n (%) | |||||
| No | 103 (64.4) | 72 (94.7) | ref | ||
| Yes | 57 (35.6) | 4 (5.3) | 0.13 | 0.05–0.35 | <0.001 * |
| Wound infection | 14 (8.8) | - | 0.01 | 0.01–69.6 | 0.996 |
| Tube leakage | 10 (6.2) | - | 0.00 | 0.01–21.83 | 0.971 |
| Tube dislodgement | 30 (18.8) | 3 (3.9) | 0.18 | 0.06–0.56 | 0.003 * |
| Tube blockage | 3 (1.9) | 1 (1.3) | 0.48 | 0.07–3.47 | 0.470 |
| Variables | Multivariable Regression | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| PNI | 0.93 | 0.89–0.97 | <0.001 * |
| Place of residence | |||
| Hospital | ref | ||
| Nursing home | 0.07 | 0.01–0.48 | 0.007 * |
| Home | 0.20 | 0.07–0.54 | 0.002 * |
| PEG tube replacement | 0.20 | 0.07–0.54 | 0.002 * |
| −2Log Likelihood = 669.2 | |||
| Variables | Place of Residence | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hospital | Nursing Home | Home | ||
| n = 128 | n = 33 | n = 75 | ||
| Gender, n (%) | ||||
| Female | 71 (55.5) | 26 (78.8) | 43 (57.3) | 0.048 * |
| Male | 57 (44.5) | 7 (21.2) | 32 (42.7) | |
| Age, years | 72.5 ± 16.6 | 79.6 ± 13.6 | 69.8 ± 19.5 | 0.027 * |
| Indications, n (%) | ||||
| Neurologic disorders | 83 (64.8) | 31 (93.9) | 51 (68.0) | <0.001 * |
| Head and neck cancers | 9 (7.0) | 1 (3.0) | 16 (21.3) | |
| Other cancer | 7 (5.5) | 1 (3.0) | 3 (4.0) | |
| Hemorrhage | 17 (13.3) | - | 3 (4.0) | |
| Others | 12 (9.4) | - | 2 (2.7) | |
| Laboratory findings | ||||
| Albumin | 2.9 ± 0.5 | 3.1 ± 0.5 | 3.2 ± 0.7 | 0.003 * |
| Lymphocytes | 1.7 (1.0–2.2) | 1.7 (0.9–2.6) | 1.7 (0.9–2.2) | 0.947 |
| CRP | 47.8 (22.4–97.8) | 33.2 (8.4–93.0) | 35.2 (11.9–67.4) | 0.055 |
| CAR | 17.3 (7.6–35.6) | 11.5 (3.1–24.1) | 12.0 (4.2–20.1) | 0.019 * |
| PNI | 37.2 ± 7.9 | 40.6 ± 7.1 | 40.8 ± 8.8 | 0.040 * |
| Feeding method, n (%) | ||||
| Pump | 128 (100.0) | 33 (100.0) | 51 (68.0) | <0.001 * |
| Bolus | - | - | 24 (32.0) | |
| Formula type | ||||
| Standard | 25 (19.5) | 13 (39.4) | 22 (29.3) | 0.130 |
| Hypercaloric | 47 (36.7) | 7 (21.2) | 25 (33.3) | |
| Diabetic | 42 (32.8) | 8 (24.2) | 17 (22.7) | |
| Immunonutrition | 9 (7.0) | 2 (6.1) | 9 (12.0) | |
| Kidney specific | 5 (3.9) | 3 (9.1) | 2 (2.7) | |
| PEG tube replacement, n (%) | ||||
| No | 109 (85.2) | 14 (42.4) | 52 (69.3) | <0.001 * |
| Yes | 19 (14.8) | 19 (57.6) | 23 (30.7) | |
| Number of replacements, n (%) | ||||
| One | 16 (84.2) | 9 (47.4) | 12 (52.2) | 0.041 * |
| Two or more | 3 (15.8) | 10 (52.6) | 11 (47.8) | |
| Minor complications, n (%) | ||||
| No | 109 (85.2) | 14 (42.4) | 52 (69.3) | <0.001 * |
| Yes | 19 (14.8) | 19 (57.6) | 23 (30.7) | |
| Wound infection | 3 (2.3) | 7 (21.2) | 4 (5.3) | <0.001 * |
| Tube leakage | 3 (2.3) | 2 (6.1) | 5 (6.7) | |
| Tube dislodgement | 11 (8.6) | 10 (30.3) | 12 (16.0) | |
| Tube blockage | 2 (1.6) | - | 2 (2.7) | |
| 30-day mortality, n (%) | 41 (32.0) | 1 (3.0) | 4 (5.3) | <0.001 * |
| One-year mortality, n (%) | 68 (53.1) | 1 (3.0) | 7 (9.3) | <0.001 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bilgiç, N.M.; Kahveci, G.; Özşenel, E.B.; Basat, S. One-Year Mortality After Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy: The Prognostic Role of Nutritional Biomarkers and Care Settings. Nutrients 2025, 17, 904. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17050904
Bilgiç NM, Kahveci G, Özşenel EB, Basat S. One-Year Mortality After Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy: The Prognostic Role of Nutritional Biomarkers and Care Settings. Nutrients. 2025; 17(5):904. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17050904
Chicago/Turabian StyleBilgiç, Nermin Mutlu, Güldan Kahveci, Ekmel Burak Özşenel, and Sema Basat. 2025. "One-Year Mortality After Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy: The Prognostic Role of Nutritional Biomarkers and Care Settings" Nutrients 17, no. 5: 904. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17050904
APA StyleBilgiç, N. M., Kahveci, G., Özşenel, E. B., & Basat, S. (2025). One-Year Mortality After Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy: The Prognostic Role of Nutritional Biomarkers and Care Settings. Nutrients, 17(5), 904. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17050904






