Dietary Protein Intake Is a Determining Factor for Skeletal Muscle Mass in Japanese Older People with Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Subjects
2.2. Measurements
2.3. Statistical Analysis
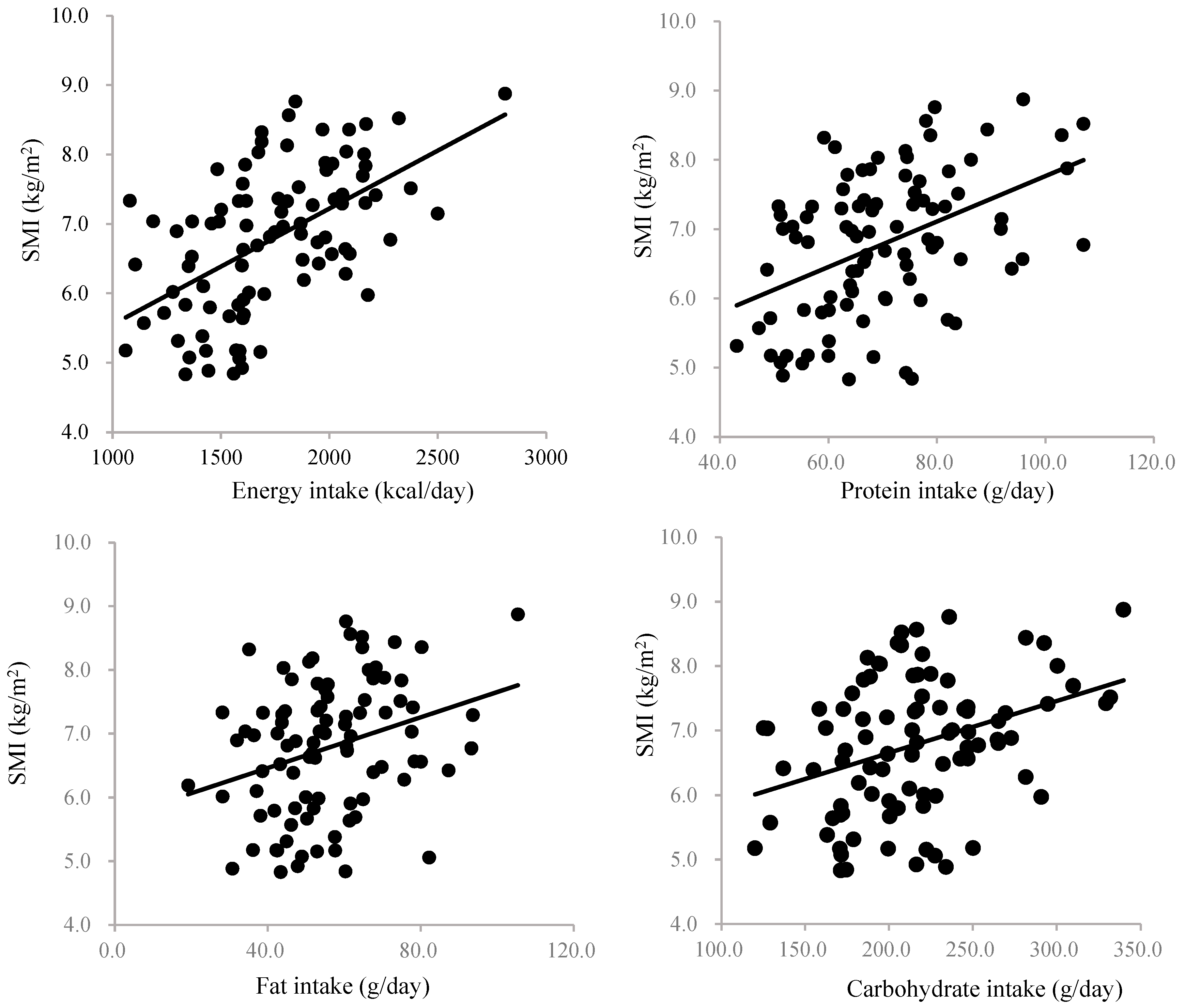
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Perspectives for Clinical Practice
4.2. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ballesteros-Pomar, M.D.; Gajete-Martín, L.M.; Pintor-de-la-Maza, B.; González-Arnáiz, E.; González-Roza, L.; García-Pérez, M.P.; González-Alonso, V.; García-González, M.A.; de Prado-Espinosa, R.; Cuevas, M.J.; et al. Disease-Related Malnutrition and Sarcopenia Predict Worse Outcome in Medical Inpatients: A Cohort Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Hao, Q.; Dong, B.; Yang, M. Malnutrition-sarcopenia syndrome predicts mortality in hospitalized older patients. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unaited Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs. World Population Prospects 2024: Summary of Results; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2024; p. 60. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, J.; Biolo, G.; Cederholm, T.; Cesari, M.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Morley, J.E.; Phillips, S.; Sieber, C.; Stehle, P.; Teta, D.; et al. Evidence-based recommendations for optimal dietary protein intake in older people: A position paper from the PROT-AGE Study Group. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2013, 14, 542–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyama, S.; Yamada, Y.; Makabe, N.; Fujita, H.; Araki, A.; Suzuki, A.; Seino, Y.; Shide, K.; Kimura, K.; Murotani, K.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of 6-Month High Dietary Protein Intake in Hospitalized Adults Aged 75 or Older at Nutritional Risk: An Exploratory, Randomized, Controlled Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shad, B.J.; Thompson, J.L.; Breen, L. Does the muscle protein synthetic response to exercise and amino acid-based nutrition diminish with advancing age? A systematic review. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 311, E803–E817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atherton, P.J.; Smith, K. Muscle protein synthesis in response to nutrition and exercise. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breen, L.; Phillips, S.M. Skeletal muscle protein metabolism in the elderly: Interventions to counteract the ‘anabolic resistance’ of ageing. Nutr. Metab. 2011, 8, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Abreu Silva, L.; de Vasconcelos Generoso, S.; da Rocha, V.M.; da Mata, L.A.C.; Castro, C.F.; Ribeiro, M.V.; Campolina, B.G.; Duarte, C.K. Association between nutrition intake and muscle mass in adult inpatients receiving nutrition support: A prospective cohort study. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2024, 48, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, N.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, X.; Liu, L.; Mo, Y.; Yao, X.; Wang, X.; Wiley, J.; Wang, X. Nutritional Status and Sarcopenia in Nursing Home Residents: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 17013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, S.S.Y.; Reijnierse, E.M.; Deen, P.; Trappenburg, M.C.; Meskers, C.G.M.; Maier, A.B. Nutrient Intake and Muscle Measures in Geriatric Outpatients. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2021, 40, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaegashi, A.; Kimura, T.; Hirata, T.; Ukawa, S.; Nakamura, K.; Okada, E.; Nakagawa, T.; Imae, A.; Tamakoshi, A. Association between Protein Intake and Skeletal Muscle Mass among Community-Dwelling Older Japanese: Results from the DOSANCO Health Study: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2008, 61, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, T.; Sakai, S.; Mori, K.; Ando, F.; Niino, N.; Shimokata, H. Nutritional assessments of 3-day dietary records in National Institute for Longevity Sciences--Longitudinal Study of Aging (NILS-LSA). J. Epidemiol. 2000, 10, S70–S76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Kobori, T. Association of a Combination of Sarcopenia and Type 2 Diabetes with Blood Parameters, Nutrient Intake, and Physical Activity: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miki, A.; Hashimoto, Y.; Matsumoto, S.; Ushigome, E.; Fukuda, T.; Sennmaru, T.; Tanaka, M.; Yamazaki, M.; Fukui, M. Protein Intake, Especially Vegetable Protein Intake, Is Associated with Higher Skeletal Muscle Mass in Elderly Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. J. Diabetes Res. 2017, 2017, 7985728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Kaji, A.; Sakai, R.; Takahashi, F.; Kawano, R.; Hamaguchi, M.; Fukui, M. Effect of Exercise Habit on Skeletal Muscle Mass Varies with Protein Intake in Elderly Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Lin, X.; Ma, J.; Li, M.; Chen, Y.; Fang, A.P.; Zhu, H.L. Dietary protein intake and changes in muscle mass measurements in community-dwelling middle-aged and older adults: A prospective cohort study. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 42, 2503–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsuka, R.; Kato, Y.; Tange, C.; Nishita, Y.; Tomida, M.; Imai, T.; Ando, F.; Shimokata, H.; Arai, H. Protein intake per day and at each daily meal and skeletal muscle mass declines among older community dwellers in Japan. Public Health Nutr. 2020, 23, 1090–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, C.; Toomey, C.; McCormack, W.G.; Francis, P.; Saunders, J.; Kerin, E.; Jakeman, P. Protein Supplementation at Breakfast and Lunch for 24 Weeks beyond Habitual Intakes Increases Whole-Body Lean Tissue Mass in Healthy Older Adults. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farsijani, S.; Morais, J.A.; Payette, H.; Gaudreau, P.; Shatenstein, B.; Gray-Donald, K.; Chevalier, S. Relation between mealtime distribution of protein intake and lean mass loss in free-living older adults of the NuAge study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| All Participants | Male | Female | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Participants | 91 | 53 | 38 |
| Age (year) | 70.3 ± 5.5 | 70.4 ± 5.4 | 70.3 ± 5.6 |
| Height (cm) | 159.9 ± 9.1 | 165.2 ± 7.1 | 152.4 ± 5.5 |
| Body weight (kg) | 61.5 ± 11.4 | 64.8 ± 9.7 | 56.7 ± 12.1 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.0 ± 3.6 | 23.7 ± 2.9 | 24.3 ± 4.4 |
| Body fat mass (kg) | 19.6 ± 7.3 | 18.0 ± 5.9 | 21.7 ± 8.4 |
| Fat-free mass (kg) | 41.9 ± 8.0 | 46.8 ± 6.0 | 35.0 ± 4.8 |
| SMI (kg/m2) | 6.8 ± 1.0 | 7.3 ± 0.8 | 6.0 ± 0.8 |
| HbA1c (%) | 7.6 ± 1.1 | 7.4 ± 1.0 | 7.9 ± 1.1 |
| Cr (mg/dL) | 0.84 ± 0.28 | 0.95 ± 0.95 | 0.69 ± 0.18 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 66.4 ± 17.3 | 65.3 ± 16.5 | 68.0 ± 18.4 |
| Energy intake (kcal/day) | 1726.0 ± 340.3 | 1828.3 ± 326.0 | 1583.2 ± 310.4 |
| Energy intake (kcal/kg/day) | 28.7 ± 6.1 | 28.4 ± 4.7 | 29.0 ± 7.7 |
| Protein intake (g/day) | 69.7 ± 14.4 | 72.1 ± 14.1 | 66.2 ± 14.2 |
| Protein intake (g/kg/day) | 1.16 ± 0.29 | 1.13 ± 0.24 | 1.21 ± 0.34 |
| Fat intake (g/day) | 55.9 ± 15.8 | 57.5 ± 15.8 | 53.6 ± 15.8 |
| Carbohydrate intake (g/day) | 215.6 ± 46.6 | 225.7 ± 48.6 | 201.4 ± 40.1 |
| Ratio of energy intake in breakfast (%) | 24.5 ± 7.3 | 24.5 ± 8.3 | 24.4 ± 5.6 |
| Ratio of energy intake in lunch (%) | 31.7 ± 7.3 | 31.1 ± 8.9 | 32.5 ± 4.2 |
| Ratio of energy intake in dinner (%) | 39.0 ± 8.6 | 40.3 ± 9.7 | 37.0 ± 6.4 |
| Ratio of energy intake in snack (%) | 4.9 ± 5.3 | 4.0 ± 4.9 | 6.1 ± 5.6 |
| Comorbidity | |||
| Diabetic neuropathy [n (%)] | 57 (62.6) | 32 (60.4) | 25 (65.8) |
| Diabetic retinopathy [n (%)] | 42 (46.2) | 24 (45.3) | 18 (47.4) |
| Diabetic nephropathy [n (%)] | 29 (31.9) | 17 (32.1) | 12 (31.6) |
| Hypertension [n (%)] | 56 (61.5) | 33 (62.3) | 23 (60.5) |
| Dyslipidemia [n (%)] | 52 (57.1) | 30 (56.6) | 22 (57.9) |
| Chronic kidney disease [n (%)] | 13 (14.3) | 8 (15.1) | 5 (13.2) |
| Heart failure [n (%)] | 4 (4.4) | 2 (3.8) | 2 (5.3) |
| Cardiovascular disease [n (%)] | 19 (20.9) | 10 (18.9) | 9 (23.7) |
| Malignant tumors [n (%)] | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Medications | |||
| Antihypertensive drugs [n (%)] | 48 (52.7) | 27 (50.9) | 21 (55.3) |
| Antihyperlipidemic drugs [n (%)] | 46 (50.5) | 24 (45.3) | 22 (57.9) |
| Antihyperglycemic drugs [n (%)] | 77 (84.6) | 44 (83.0) | 33 (86.8) |
| Insulin [n (%)] | 27 (29.7) | 17 (32.1) | 10 (26.3) |
| Steroid [n (%)] | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standardized Regression Coefficient | p-Value | Standardized Regression Coefficient | p-Value | |
| Age | - | - | −0.265 | 0.001 |
| Gender | −0.640 | <0.001 | −0.602 | <0.001 |
| Nonprotein calories | - | - | - | - |
| Protein intake | - | - | 0.193 | 0.015 |
| Fat intake | - | - | - | - |
| Carbohydrate intake | - | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moyama, S.; Yamazaki, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Makabe, N.; Hamamoto, Y.; Kurose, T.; Yamada, Y.; Kuwata, H.; Seino, Y. Dietary Protein Intake Is a Determining Factor for Skeletal Muscle Mass in Japanese Older People with Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2025, 17, 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17040731
Moyama S, Yamazaki Y, Takahashi T, Makabe N, Hamamoto Y, Kurose T, Yamada Y, Kuwata H, Seino Y. Dietary Protein Intake Is a Determining Factor for Skeletal Muscle Mass in Japanese Older People with Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients. 2025; 17(4):731. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17040731
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoyama, Shota, Yuji Yamazaki, Takuya Takahashi, Noboru Makabe, Yoshiyuki Hamamoto, Takeshi Kurose, Yuichiro Yamada, Hitoshi Kuwata, and Yutaka Seino. 2025. "Dietary Protein Intake Is a Determining Factor for Skeletal Muscle Mass in Japanese Older People with Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study" Nutrients 17, no. 4: 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17040731
APA StyleMoyama, S., Yamazaki, Y., Takahashi, T., Makabe, N., Hamamoto, Y., Kurose, T., Yamada, Y., Kuwata, H., & Seino, Y. (2025). Dietary Protein Intake Is a Determining Factor for Skeletal Muscle Mass in Japanese Older People with Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients, 17(4), 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17040731






