Beetroot Juice Supplementation as a Healthy Aging Strategy Through Improving Physical Performance and Cognitive Functions: A Systematic Review
Abstract
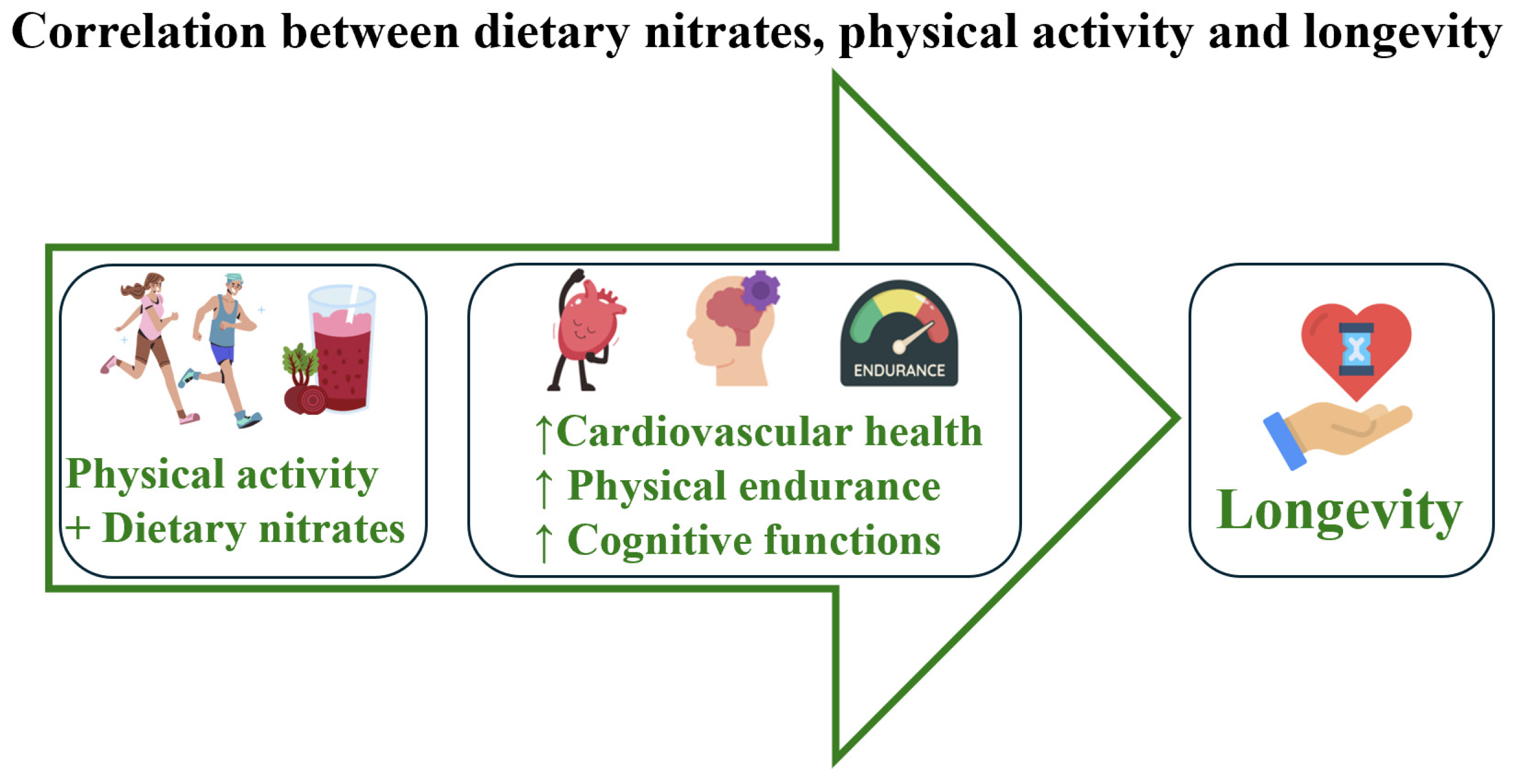
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Exclusion Criteria
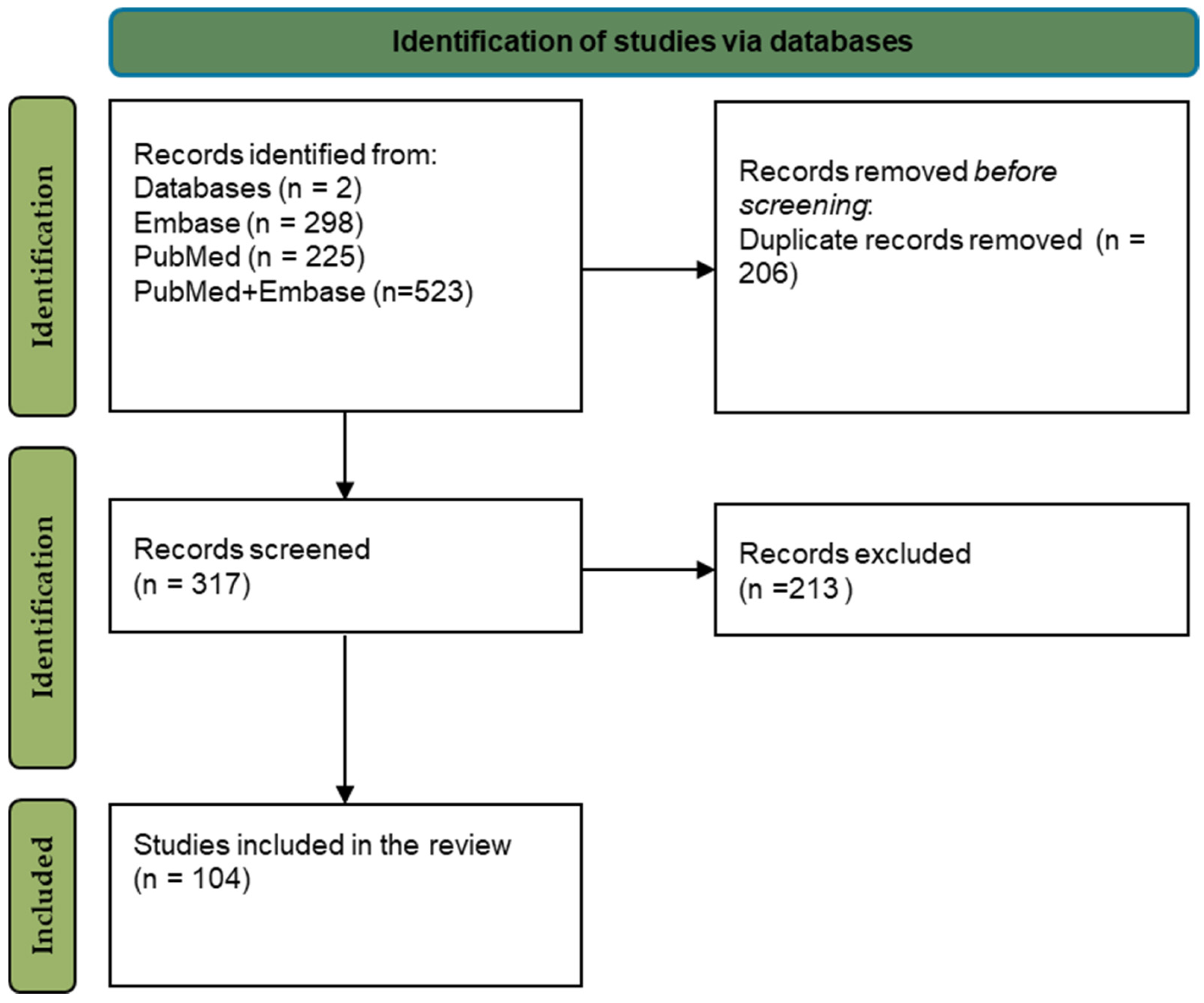
2.3. Search Results
3. Results
Analysis of Nitrates on Physical Activity and Cognitive Functions (Original Articles)
| Positive Effects of Supplementation (Acute/Short-Term) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Sample Size | Dose | Form | Duration | Results | |
| 1 | Ahmadpour A. et al. [53] | 10 men | PLA (<0.5 mmol NO3−) or BRJ 220 mL (~8.9 mmol NO3−) consumed 2.5 h before functional tests at 2800 m altitude. | Juice | Acute |
|
| 2 | Benjamim C.J.R. et al. [37] | 16 men | Beetroot extract (600 mg capsule) vs. placebo, taken 120 min before exercise. The participants ingested the opposite intervention (placebo or beetroot extract) on the third and final day to guarantee the study’scross-over. | Capsules | Acute (3 days; crossover). |
|
| 3 | Black M.I. et al. [54] | 11 individuals (10 men; 1 woman) | 7-day low NO3− diet, 3-day high NO3− diet, compared with a standard (control) NO3− diet; | Nitrates from food | Short-term dietary interventions: 7 days low NO3−, 3 days high NO3−, with controlled washout periods. |
|
| 4 | Bloomer R.J. et al. [55] | 10 men and 10 women | RRB1: Resync Recovery Blend, 1 serving (~7.5 g; ~4.2 g nitric oxide blend), single acute ingestion mixed with 12 fl oz water; RRB2: Resync Recovery Blend, 2 servings (~15 g; ~8.4 g nitric oxide blend), single acute ingestion mixed with 12 fl oz water; RCB1: Resync Collagen Blend, 1 serving (~21 g; ~2 g proprietary blend), single acute ingestion mixed with 12 fl oz water; PLA: Placebo, 7.5 g nitrate- and polyphenol-free powder mixed with 12 fl oz water. | Drink/juice | Acute |
|
| 5 | Cocksedge S.P. et al. [56] | 10 men | Nitrate-rich beetroot juice concentrate (210 mL containing ~18.6 mmol NO3−); 2.5 h before exercise on each testing. each trial was conducted on nine occasions over a 4–7 week timeframe, with beetroot (BR) or placebo (PL) consumed 2.5 h prior to each exercise test under normoxia, hypoxia, or hyperoxia. | Juice | Acute |
|
| 6 | De Souza D.B. et al. [57] | 20 men | Beetroot juice (BJ; 500 mL, 16 mmol NO3−); 60 min before exercise; six exercise or PLA (açaí-flavored maltodextrin, equalized the caloric content of the BJ + 20 mL of beetroot to give flavor of the PLA) | Juice | Acute |
|
| 7 | Dumar A.M. et al. [58] | 10 men | Single dose of 70 mL concentrated beetroot juice (~400 mg NO3−), consumed 2 h prior to exercise. Participants consumed the full dose within 5 min; PLA (blackcurrant juice) | Juice | Acute |
|
| 8 | Esen O. et al. [59] | 12 men | NO3−-rich beetroot juice (NIT, 140 mL, ~12.8 mmol NO3−) or NO3−-depleted placebo (PLA, 140 mL, ~0.04 mmol NO3−), consumed 3 h before the Yo–Yo IR1 test. | Juice | Acute |
|
| 9 | Forbes S. et al. [60] | 14 women (including 9 using hormonal contraceptives; HC) | Nitrate-rich beetroot juice (140 mL containing ~13 mmol NO3−; 2,5 h before exercise or PLA (NO3−-free blackcurrant juice) | Juice | Acute |
|
| 10 | Garnacho-Castaño M.V. et al. [61] | 10 men | BRJ—140 mL (~12.8 mmol, ~808 mg NO3−), consumed 3 h before the 2000-m rowing ergometer test; or PLA (made by dissolving 2 g of powdered SUPER BEETROOT (~0.01 mmol, 0.620 mg of NO3−) in 1 L of water)) | Juice | Acute |
|
| 11 | Garnacho-Castaño M.V. et al. [43] | 11 men | Beetroot juice (BJ, 140 mL, ~12.8 mmol NO3−/808 mg) administered 3 h before exercise; or PLA (prepared by dissolving 2 g of powdered BJ (~ 0.01 mmol, 0.620 mg of NO3−) | Juice | Acute |
|
| 12 | Garnacho-Castaño M.V. et al. [62] | 12 men | Beetroot juice (140 mL; ~12.8 mmol NO3− (~808 mg)); 3 h before exercise (of each test) or PLA (prepared by dissolving 2 g of powdered BJ (~ 0.01 mmol, 0.620 mg of NO3−) | Juice | Acute |
|
| 13 | Hemmatinafar M. et al. [63] | 12 women | Beetroot juice (BRJ) vs. placebo (PLA), 50 mL per serving, 8 servings over 2 days (total 400 mL), ingested at 2, 6, 10, 14, 26, 30, 34, and 38 h post-exercise. | Juice | Acute (2-days) |
|
| 14 | Jiaqi Z. et al. [52] | 13 women | BJ 2.5 h before exercise; single dose 70 mL (~6.45 mmol NO3−) or double dose (2 × 70 mL; ~12.9 mmol NO3−). or PLA (BJ with extracted nitrates) | Juice | Acute |
|
| 15 | Jurado-Castro J.M. et al. [64] | 11 men | 70 mL beetroot juice (BJ; 400 mg NO3−, 6.4 mmol/L or NO3−-depleted placebo, consumed 120 min before resistance training sessions. | Juice | Acute |
|
| 16 | Jurado-Castro J.M. et al. [35] | 14 women (2 on contraceptives) | 70 mL NO3−-rich beetroot juice (BRJ; 400 mg nitrate) or NO3−-depleted placebo, consumed 2 h before exercise (during each visit—3 visits) | Juice | Acute |
|
| 17 | Macuh M. et al. [65] | 15 men | 70 mL concentrated beetroot juice (~400 mg nitrate)) or nitrate-depleted placebo (~0 mg nitrate), consumed 2 h before exercise | Juice | Acute |
|
| 18 | Miraftabi H. et al. [41] | 8 men | four experimental trials: BJ-400, BJ-800, PL, CON; 2.5 h before the tests, each participant ingested either one bottle of 60 mL BJ + one bottle of 60 mL of PL or two bottles of BJ (120 mL) (=400 mg NO3− per bottle) or depleted dried powder NO3− for PL (1 g of dried powder of BJ dissolved in 1 L of water + lemon juice for taste) | Juice | Acute |
|
| 19 | Neteca J. et al. [42] | 18 women | BJG- 50 mL of nitrate-rich beetroot juice concentrate (~6.2 mmol of nitrates (NO3−) consumed once before second exercise test; or PLA (nitrate-free beverage). | Juice | Acute |
|
| 20 | Ranchal-Sanchez A. et al. [66] | 12 men | Beetroot juice (70 mL containing ~400 mg NO3− per serving); 120 min before exercise, single acute dose, across three visits; or PLA (blackcurrant juice with depleted nitrates) | Juice | Acute |
|
| 21 | Rodríguez-Fernández A. et al. [34] | 18 men | Beetroot juice (BJ), 140 mL total (2 × 70 mL concentrated shots; ~800 mg NO3−otal); ingested 2.5 h prior to testing or PLA (2 × 70 mL providing <0.1 mmol NO3−) | Juice | Acute |
|
| 22 | Rowland S.N. et al. [67] | 12 men | Beetroot juice 2 × 70 mL (~13 mmol NO3−) with breakfast 2.5 h before exercise at morning (08:00), afternoon (12:00), or evening (15:00). Six experimental conditions, PL and BR in the morning (started at 08:00; PL-MORN and BR-MORN), afternoon (started at 12:00; PL-AFT, BR-AFT) and evening (started at 15:00; PL-EVE and BR-EVE). | Juice | Acute |
|
| 23 | Serra-Payá N. et al. [68] | 11 men | 140 mL Beet-It-Pro Elite Shot (~808 mg NO3− (~12.8 mmol)), 3 h prior to testing or PLA (2 g of powdered BJ (~0.01 mmol, 0.620 mg of NO3−, dissolved in 1 L of water + lemon juice for flavor)). | Juice | Acute |
|
| 24 | Tan R. et al. [69] | 14 men | 2 × 70 mL doses per day of concentrated NO3−-rich beetroot juice (BR: ~5.9 mmol of NO3− per 70 mL). Experimental days (day 1 and 4 of each supplementation period): 2 × 70 mL of allocated beverage 2.5 h before exercise. Days 2 and 3 of each supplementation period: 1 × 70 mL beverage twice a day; or PLA (nitrate-depleted BR) | Juice | 2 × 4 days |
|
| 25 | Tatlici A. et al. [70] | 8 men | Second visit of the trial: 2 × 70 mL beetroot juice; Third visit of the trial: 2 × 70 mL beetroot juice, 150 min prior to testing or PLA (140 mL of cherry + lemon juice). | Juice | Acute |
|
| 26 | Tatlici A. et al. [71] | 8 men | Beetroot juice (BJ), 2 × 70 mL shots (~140 mL), 150 min before exercise or PLA (140 mL of cherry + lemon juice). | Juice | Acute |
|
| 27 | Thurston T.S. et al. [72] | 11 men | Single daily dose for 2 days prior to experimental trial, plus a double dose 2 h before exercise (Nitrate-rich beetroot concentrate; 70 mL; 4.1 mmol NO3−) or PLA (nitrate-stripped; 0.03 mmol of NO3−). | Juice | Short term (3-day supplementation period; single doses for 2 days and double dose 2 h prior to exercise.) |
|
| 28 | Volino-Souza M. et al. [73] | 9 women and 4 men | Beetroot juice (BJ), 140 mL containing ~8.12 ± 3.61 mmol NO3−; consumed 150 min before exercise or PLA (depleted nitrate beetroot juice; ~0.08 ± 0.76 mmol of nitrate). | Juice | Acute |
|
| 29 | Wei C. et al. [50] | 8 men and 3 women | 2 bottles of NO3− depleted BR (placebo, PL) (~0.08 mmol NO3−, 2 × 70 mL); 1 bottle of NO3− rich BR (~6.4 mmol NO3−, 1 × 70 mL); 2 bottles of NO3−− rich BR (~12.8 mmol NO3−, 2 × 70 mL); 3 bottles of NO3−− rich BR (~19.2 mmol NO3−, 3 × 70 mL); 1.3 g KNO3 (~12.8 mmol NO3− mixed with 300 mL deionized water on separate laboratory visits. | Juice | Five visits over a period of 17–35 days |
|
| 30 | Williams T.D. et al. [49] | 11 men | Beetroot juice -70 mL containing ~400 mg NO3−; 2 h before exercise, within 5 min or PLA (blackcurrat juice). | Juice | Acute |
|
| 31 | Wong T.H. et al. [74] | 17 men | Two trials—2 × 285 mL of either ISO-BR (isotonic beetroot juice) or BR drink 3 h before testing Both contained 6.45 mmol, 400 mg, per 285 mL serving; 9 mg/100 mL of ascorbic acid was added into the ISO-BR drink. | Juice | Acute |
|
| 32 | Yuschen X. et al. [75] | 12 men | 2.5 h before exercise- Nitrate-rich beetroot juice (NRBRJ): 70 mL shot 400 containing 400 mg NO3− or PLA (prune juice). | Juice | Acute |
|
| Positive Effects of Supplementation (Chronic) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Sample size | Dose | Form | Duration | Results | |
| 1 | Burgos J. et al. [76] | 32 men | I-placebo group (PLG); II-CIT (citrulline) group (CITG): 3 g/day (3 × 1 g) gelatin capsules III-nitrate-rich beetroot extract group (BRG); 3 gelatin capsules of 700 mg a day (5:1 beetroot extract equivalent to 3500 mg of whole dried root, standardized to contain 0.3% betanin providing 100 mg of NO3−) IV-CIT-BR group (CIT-BRG). | Capsules | Chronic (9 weeks) |
|
| 2 | Burgos J. et al. [77] | 32 men | 6 capsules/day: (I) placebo group (PLG); (II) CIT (citrulline) group (3 × 1 g CIT; CITG); (III): nitrate-rich beetroot extract group (3 × 700 mg; 100 mg of NO3−; BRG) and (IV) CIT-BR group (CIT- BRG) | Capsules | Chronic (9 weeks) |
|
| 3 | Daab W. et al. [36] | 13 men | Beetroot juice (BET; 150 mL per serving, 250 mg NO3−/serving), consumed twice daily (08:00 and 18:00) for 7 consecutive days, including 3 days pre-exercise, on the trial day, and 3 days post-exercise or PLA (nonspecified) | Juice | Chronic (7-days) |
|
| 4 | de Oliveira G.V. et al. [78] | 14 men | 100 g of beetroot-based nutritional gel (BG; 12.2 ± 0.2 mmol of nitrate); On the second and third visit: a single dose of BG after measuring maximal forearm muscle isometric strength; Then 120 min before exercise, ingestion of the supplement; or PLA (nitrate-depleted BG gel). | Gel | Chronic, 8-day supplementation |
|
| 5 | Esen O. et al. [79] | 14 men | 2 × 70 mL/day (~12.8 mmol/day NO3−) for 5 days; on the experimental trial day, both shots were taken together 2.5 h before testing; or PLA (nitrate-depleted beetroot juice). | Juice | Chronic (5-day supplementation) with acute dosing on the test day |
|
| 6 | Esen O. et al. [80] | 14 men | NO3−-rich beetroot juice (BRJ; NIT: 2 × 70 mL/day, ~12.8 mmol/day NO3−) or NO3−-depleted BRJ as placebo (PLA; 2 × 70 mL/day, ~0.08 mmol/day NO3−). For days 1–4, doses were taken morning (~9 a.m.) and evening (~9 p.m.); on day 5, both doses were taken together 2.5 h before exercise testing. | Chronic (2 × 5-days) |
| |
| 7 | Esen O. et al. [81] | 10 men and 6 women | Nitrate-rich (NIT) beetroot juice 2 × 70 mL/day (~12.8 mmol/day NO3−) for 4 days (morning & evening), plus 2 × 70 mL 2.5 h before trial; or PLA (nitrate-depleted beetroot juice). | Juice | Chronic (short term; 2 × 5-days separated by a washout period) |
|
| 8 | Huang X. et al. [32] | 44 men and 36 women | Concentrated beetroot juice (BRJ; 6.5 mmol NO3−/70 mL) or nitrate-free placebo (PL; 0.065 mmol NO3−/70 mL), 3 × 70 mL/day for 7 days. | Juice | Chronic (7-days) |
|
| 9 | Khosravi S. et al. [51] | 12 men | Beetroot juice (BRJ), 2 × 70 mL/day (~12.8 mmol NO3− per day) for 6 days; exercise testing on day 6, 2–2.5 h after the final dose; or PLA (blackcurrant juice). | Juice | Chronic; (6 days) |
|
| 10 | Kozłowska L. et al. [82] | 10 men and 10 women | Freeze-dried beetroot juice (BRJ), 26 g/day (~200 mL juice equivalent, ~2.1 mmol NO3−), taken once daily with a meal 2 h before VO2max testing; or PLA (ID- dietary recommendations without additional BRJ). | Freeze-dried juice | Chronic (4-weeks) |
|
| 11 | Liubertas T. et al. [83] | 13 men | Oat bar (60 g; 4 g standardized Amaranthus hypochondriacus concentrate; ≈400 mg NO3−), consumed 1 h before exercise during single-dose testing, and daily for 6 days before long-term testing; or PLA (60 g-oat bar with excluded Amaranthus hypochondriacus). | Oat bar | Chronic (6 days) and single-dose test performed 1 h after first ingestion |
|
| 12 | Nicholas C. et al. [84] | 10 men | 140 mL/day of NO3−−-rich (12.8 mmol·d−1; BRJ + lemon juice); 2.5 h before the trial; or PLA (nitrate-depleted BRJ + lemon juice for taste). | Juice | Chronic (6 days) |
|
| 13 | Rowland S.N. et al. [85] | 9 men | Beetroot powder—NO3−-rich (BR, 6% NO3−, 8 mmol NO3−). Participants consumed 8.4 g/day in ≥250 mL water for 6 days. On day 7, a pre-exercise dose 2 h before cycling and a top-up 8.4 g dose 1 h into the 2-h exercise. | Powder dissolved in water | Chronic (Two 7-day supplementation periods (BR or PL), cross-over, with experimental testing on day 7 including pre- and mid-exercise top-up doses) |
|
| 14 | Tan R. et al. [86] | 8 men and 4 women | Nitrate-rich beetroot juice (BR, ~6.2 mmol NO3−− per 70 mL, 2 × 70 mL/day) compared to NO3−-depleted beetroot juice placebo (PL, ~0.04 mmol NO3−− per 70 mL) and control water (CON); (Three separate 4-day supplementation periods (2 × 70 mL/day; days 1–2 one morning + one evening, days 3–4 both in morning ~2.5 h before exercise). | Juice | Chronic |
|
| 15 | Tirkey D. et al. [33] | 15 men and 15 women | Beetroot juice (BRJ) 250 mL/day in natura, providing ~5.00 mmol NO3− per day; or PLA (nitrate-depleted beverage). | Juice | Chronic (15 days) |
|
| 16 | Viribay A. et al. [87] | 20 men | Per day: (I) 5 capsules of placebo and 6 g of maltodextrin in powder; (II) 5 capsules (500 mg) of BR and 6 g of maltodextrin in powder; (III) 5 capsules of BR (500 mg) and 6 g of CIT in powder. | Capsules | Chronic (7-days) |
|
| Non-Significant/No Effects of Supplementation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Sample Size | Dose | Form | Duration | Results | |
| 1 | Berjisian, E. et al. [88] | 16 men | One 60-mL bottle of fluid containing either 6.4 mmol (NO3−), 500 mg L-Arginine, and L-Ornithine or NO3− depleted dried powder as placebo and ingested a capsule containing 5 mg/kg body mass of caffeine (CAF) or cellulose as PL 60 min before the start of the Stroop test. Four experimental trials: BJ + CAF, CAF + PL, BJ + PL, and PL + PL. | Juice | Acute |
|
| 2 | Berlanga L.A. et al. [89] | 10 men | 150 min before testing: 70-mL dose of BJ (6.4 mmol of NO3−); or PLA (nitrate-depleted BJ). | Juice | Acute |
|
| 3 | Burke L.M. et al. [38] | 21 men | Study 1: two evenings before the experimental trial (−36, and −12 h): 70 mL shot of NO3−-rich beetroot juice (BRJ; 6.45 mmol NO3−); Morning of the experimental trial: 140 mL (~12.9 mmol NO3−) of BRJ supplement with breakfast+ second treatment after 7 km exercise: 70 mL BRJ (6.45 mmol NO3−); after each treadmill 26-km protocol: 190 mL of allocated test drink Study 2: Carb Max | Juice | Acute |
|
| 4 | Collins S.M. et al. [90] | 15 men and 9 women | Subjects performed two counterbalanced trials, once with a control and another after consuming 70 mL (~4.2 mmol NO3−) of beetroot concentrate nitrate supplement 2 h prior to physical activity; or PLA (strongly flavored water). | Beetroot concentrate | Acute |
|
| 5 | Conger S.A. et al. [91] | 14 men | The supplement was provided to the participant 24 to 72 h preceding the trial. One dose of red beet juice powder containing ~8 mmol (496 mg) NO3− mixed with 237 mL of water (this dose is considered “high” (high > 7.5 mmol); or PLA (cherry-apple-cranberry juice blend). | Juice | Acute |
|
| 6 | Esen O. et al. [92] | 12 men | 140 mL NO3−-rich (BRJ; 2 × 70 mL; ~12.8 mmol NO3−) or NO3−-depleted (PLA) BRJ, 3 h before two experimental trials three. | Juice | Acute |
|
| 7 | Fernández-Elías V. et al. [45] | 9 men | 3 h prior to exercise: 70 mL of concentrated beetroot juice (6.4 mmol NO3−); or PLA (0.005 mmol of NO3−) prepared by dissolving 1 g of powdered beetroot and lemon juice in water. | Juice | Acute |
|
| 8 | Hennis P.J. et al. [93] | 21 men and 6 women | 3 days prior to exercise trials and continued throughout the exercise trials: 3 × 200 mL, daily nitrate consumption of ~0.18 [18.5 (±2.0) mmol]; or PLA (nitrate-depleted beetroot/fruit juice [1.4 (0.1) mmol]). | Juice | Chronic |
|
| 9 | López-Samanes Á. et al. [39] | 11 women | 3 h before each testing session: 70 mL dose of beetroot juice (6.4 mmol of NO3−); or PLA (nitrate-depleted beetroot juice). | Juice | Acute |
|
| 10 | López-Samanes Á. [94] | 13 men | Two separate occasions: 3 h before testing; 70 mL of either BJ (containing 6.4 mmol of NO3−) or PLA; (in each trial, 50% of participants ingested PLA and 50% ingested BJ beverages) with random assignment to each supplement. | Juice | Acute |
|
| 11 | Moreno B. et al. [95] | 6 women and 7 men | Beetroot juice (BJ, 70 mL, 6.4 mmol NO3−) or nitrate-depleted placebo (PLA, 70 mL), ingested 3 h before swimming test. Two sessions separated by 18-day washout. | Juice | Acute |
|
| 12 | Ortiz de Zevallos J. et al. [96] | 12 women and 14 men | 70 mL of beetroot juice (BRJ ~6.5 mmol NO3−) twice/day (~13 mmol total NO3−) for ~3 days or an identical NO3−-depleted placebo (PL). On testing days—the last two 70 mL shots 2 h before their laboratory arrival time. Female subjects were given additional bottles and were instructed to start consuming the juice the day before the estimated day of menses to consider any changes in the start of the menstrual cycle and guarantee consumption of at least 3 days of supplementation before experimental visits. | Juice | Acute (3-days) |
|
| 13 | Robinson G.P. et al. [47] | 8 men | 3 h prior to testing: 140 mL of beetroot juice (providing ~12.4 mmol NO3−) daily for 7 days. On nonexperimental days (days 1–2, 4, and 6)—1 × 70 mL in the morning (~09:00) and 1 × 70 mL in the evening (~19:00); or PLA (~0.08 mmol NO3−). | Juice | Chronic |
|
| 14 | Rokkedal-Lausch T. et al. [46] | 12 well-trained cyclists (gender not specified) | 140 mL of concentrated beetroot juice (~12.4 mmol nitrate) per day; one dose (70 mL) in the morning and one dose (70 mL) in the evening. On the days of the experimental trials: total dose 2-h before arriving at the laboratory; or PLA (nitrate-depleted BR). | Juice | Chronic (7 days) |
|
| 15 | Sousa A. et al. [97] | 30 men | Three experimental groups: (I) HNO: high-intensity exercise training sessions in normobaric hypoxia with NO3− supplement; (II) HPL: high-intensity exercise training sessions in normobaric hypoxia with placebo and (III) CON: high-intensity exercise training sessions in normoxia with placebo. Supplements given 2.5–3 h prior to each session. ((NO3− beetroot juice; 400 mg of a powdered standardized beetroot extract (2% of NO3−, ~8.4 mmol)) | Juice | Chronic |
|
| 16 | Tan R. et al. [98] | 16 men | Four supplementation conditions: (1) PL with MAL (PL + MAL), (2) PL with NAC (PL + NAC), (3) BR with MAL (BR + MAL) (4) BR with NAC (BR + NAC); 2 × 70 mL doses per day of either BR (~6.2 mmol of NO3−per 70 mL) or PL. On day 1–5: one 70 mL beverage in the morning and one in the evening. On the experimental day: 2 × 70 mL of allocated beverage 2.5 h prior to exercise and 70 mg/kg of NAC (N-acetylcysteine; 600 mg NAC per capsule)) or maltodextrin (MAL; 600 mg per capsule) 1 h prior to exercise. | Juice | Chronic (6 days) |
|
| 17 | Tan R. et al. [99] | 15 men | (1) PL; (2) NO3−-rich beetroot juice (BR: ~12 mmol of NO3−) with 2 empty gelatin capsules; (3) BR with 2 capsules with pomegranate powder (POM: 1000 mg; BR + POM; On experimental: 2 × 70 mL of allocated beverage and capsules 2.5 h before exercise + on a separate visit: two capsules containing 1000 mg of POM 2.5 h prior to a blood draw | Juice + Capsules | Acute |
|
| 18 | Tan R. et al. [44] | 15 women | 2 × 70 mL of concentrated NO3−-depleted placebo (PL; 0.10 mmol NO3− total) or NO3−-rich beetroot juice (BR; ~ 12.0 mmol NO3− total) with a washout-out period of at least 5 days separating the two supplementation periods. | Juice | Acute |
|
| 19 | Trexler E.T. et al. [40] | 27 men | 2 h before exercise: (1) 70-mL beetroot juice beverage (400 mg dietary nitrate); (2) placebo (PLA); (3) 8 g of unflavored citrulline malate (CitMal) | Juice | Acute |
|
| 20 | Viribay A. [100] | 20 men | (I) Placebo group (PLAG); (II) Beetroot extract group (BRG); and (III) BR supplemented with L-citrulline group (BR-CITG). The intervention spanned 3 consecutive weeks, with each week corresponding to a distinct supplement-intake condition. Daily dosages for 7 days: (I) five placebo capsules per, alongside 6 g of maltodextrin powder; (II) five capsules (each containing 500 mg) per day of BR accompanied by 6 g of maltodextrin powder; or (III) 5 capsules per day (each containing 500 mg) of BR alongside 6 g of L-citrulline powder. | Capsules | Chronic (7-days) |
|
| Review Articles | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Included Articles | Conclusions | |
| 1 | Abreu R. et al. [101] |
| Performance decreased after exercise in both groups, but the reduction was smaller with beetroot juice, suggesting possible benefits during long-term recovery. |
| 2 | Alsharif N. et al. [102] |
| It was noted that supplementation contributed to the improvement of: total distance covered, peak power, mean power output, total work done. The results from this review and meta-analysis confirm the ergogenic potential of dietary NO3 supplementation in some aspects of high-intensity exercise capacity |
| 3 | Antonio J. et al. [103] |
| All five studies in the review reported benefits of beetroot supplementation, including increased time to exhaustion, reduced oxygen consumption, and improved training load. Beetroot juice supplementation by athletes may have a positive impact on their performance and physical endurance during training |
| 4 | Apte M. et al. [3] |
| Beetroot juice supplementation consistently improved time-trial performance across studies, with some evidence of cognitive benefits in young adults (18–30 years), though results were mixed. Natural dietary nitrates appear to be an accessible and low-cost ergogenic aid. |
| 5 | Calvo J. et al. [104] |
| Supplementation reduced VO2, improved pain threshold, and enhanced performance in sprint interval training, but heterogeneity requires more trials. |
| 6 | Chen L. et al. [105] |
| Some studies showed gains in kayaking, resistance, and mountaineering performance, confirming the ergogenic potential of beetroot, though results remain varied. |
| 7 | Delleli S. et al. [106] |
| In combat sports, six studies reported improved performance with beetroot supplementation, while three found no benefit or deterioration. Effectiveness may depend on training level, and further confirmation is required. |
| 8 | Domínguez R. et al. [107] |
| Beetroot juice supplementation improved agility and handgrip strength in tennis players and improved performance in endurance, high-intensity sports and resistance training. |
| 9 | d’Unienville N.M.A. et al. [48] |
| Nitrate supplementation showed benefits only when derived from beetroot, especially in less trained individuals, while no clear effects were observed in women. Sex differences and limited data in female athletes highlight the need for more targeted research. |
| 10 | Esen O. et al. [108] |
| Beetroot juice slightly enhanced peak and mean power and time to peak power but showed no effect on isometric strength. Wide variability among studies limits practical interpretation. |
| 11 | Gamonales J.M. et al. [109] |
| Some studies reported benefits in jump performance, pain threshold, and VO2 recovery, while five found no differences. Effects appear small, inconsistent, and require further exploration. Over 60% indicated positive effects on regeneration, but evidence remains heterogeneous. |
| 12 | Gilsanz L. et al. [110] |
| No studies demonstrated improvements in physical performance parameters with beetroot juice compared to placebo. |
| 13 | Harlow J. et al. [111] |
| Beetroot juice improved exercise performance compared with placebo and promoted faster post-exercise heart rate recovery. Beetroot juice may have a positive effect on performance during high-intensity, moderate-duration workouts. |
| 14 | Hogwood A. et al. [112] |
| A small, non-significant trend toward improved VO2peak was observed, but overall effects were inconsistent. Adding beetroot juice to training did not enhance outcomes beyond exercise alone. |
| 15 | Jones L. et al. [113] |
| Beetroot juice improved recovery of isometric strength and jumping ability but had no effect on oxidative stress markers. Benefits may depend on training modality. |
| 16 | Kiani A. et al. [114] |
| Beetroot supplementation significantly improved completion time, average power output, and time to exhaustion in cycle ergometer time trials compared with placebo. These findings suggest benefits for high-intensity endurance exercise, though further studies are needed to define optimal supplementation strategies. |
| 17 | Kim J. et al. [115] |
| Rowing studies demonstrated improved repetitions and 2000-m performance, particularly in moderately trained athletes, alongside rises in plasma nitrite levels. |
| 18 | Lago-Rodríguez Á. et al. [116] |
| Studies on healthy individuals found no effect on isokinetic torque but suggested potential benefits in less trained or short-term contexts. Evidence remains limited. |
| 19 | López-Laval I. et al. [117] |
| Supplementation improved muscle oxygen saturation, recovery of strength, and reduced exercise-induced strength loss, though variability limits firm conclusions. |
| 20 | López-Torres O. et al. [118] |
| Results were mixed in women and elite athletes, with no benefits reported in some groups, while kayakers and runners showed significant improvements. More research in women is particularly needed. |
| 21 | Mohd Daud S.M. et al. [119] |
| Supplementation improved muscle recovery in volunteers and also reduces post-exercise muscle pain. Fruit juices may be the best natural-based dietary supplements, replacing other supplement products in supporting muscle recovery and improving athletic performance in trained athletes. Future research, focusing on optimal dose, timing, and frequency of consumption, is needed. |
| 22 | O’Connor E. et al. [120] |
| Supplementation reduced post-exercise muscle soreness in soccer players and sprinters, but not in endurance athletes. Blood markers of damage, oxidative stress, and inflammation were unaffected. |
| 23 | Poulios A. et al. [121] |
| Supplementation enhanced jump height, strength, speed, and reduced muscle soreness, but did not alter biochemical markers of muscle damage. |
| 24 | Rojano-Ortega D. et al. [122] |
| Four of these studies demonstrated improvement in these variables, four studies also demonstrated improvement in muscle soreness, and only one study demonstrated a significant difference in creatine kinase levels after beetroot supplementation versus placebo. However, no effect of supplementation on inflammatory markers was demonstrated. |
| 25 | San Juan A. et al. [123] |
| All included studies showed gains in resistance training outcomes like repetitions, bench press power, and VO2 reduction. Beetroot may benefit both racquet sports and weightlifting, though mechanisms remain unclear. |
| 26 | Silva K. et al. [124] |
| A meta-analysis concluded that beetroot juice is more effective than other nitrate sources, particularly for exercise lasting 2–10 min. |
| 27 | Tan R. et al. [125] |
| Supplementation positively influenced time to peak power during short sprints, but had no effect on average or peak power. Findings are promising but limited, requiring further research. |
| 28 | Tan R. et al. [126] |
| Supplementation improved repetitions to failure, average power, and velocity in resistance exercise. However, study heterogeneity limits the strength of conclusions. |
| 29 | Tan R. et al. [127] |
| Positive effects were observed in squat, knee strength, and bench press velocity, but further standardized studies are needed to confirm findings. |
| 30 | Tanabe Y. et al. [128] |
| Some studies reported improvements in creatine kinase and faster recovery in strength and VO2, but no reductions in blood markers of muscle damage. |
| 31 | Vicente-Salar N. et al. [129] |
| In combat sports, several studies found improved physical performance and reduced soreness, though no effects were seen on inflammation markers (only one study demonstrated a significant difference in creatine kinase levels). A supplement such as beetroot juice needs further research to strengthen the evidence of its positive effect in improving performance in combat sports and other disciplines. |
| 32 | Vicente-Salar N. et al. [130] |
| In elite tennis players, supplementation did not improve explosive movements or perceptual effort. Further research is needed to assess strength-related outcomes. |
| 33 | Wong T.H. et al. [131] |
| Evidence was mixed: some studies showed improvements in power and performance whereas others showed no change or declines. Supplementation may help alleviate muscle soreness, but variability remains high. |
| 34 | Wong T.H. et al. [132] |
| Time trial performance improved in cycling trials (4–5 km), with slightly faster completion after beetroot versus placebo. |
| 35 | Zamani H. et al. [133] |
| A single dose improved blood flow, sprint and interval performance, time to exhaustion, and post-exercise recovery, particularly in less trained athletes. |
| 36 | Zoughaib W.S. et al. [134] |
| Beetroot improved distance, power, and work done, and may be more effective than nitrate salts, though study numbers are small. |
4. Discussion
5. Summary and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stein, L.Y.; Klotz, M.G. The Nitrogen Cycle. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, R94–R98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E. Biology of Nitrogen Oxides in the Gastrointestinal Tract. Gut 2013, 62, 616–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apte, M.; Nadavade, N.; Sheikh, S.S. A Review on Nitrates’ Health Benefits and Disease Prevention. Nitric Oxide 2024, 142, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E.; Gladwin, M.T. The Nitrate-Nitrite-Nitric Oxide Pathway in Physiology and Therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Hu, L.; Feng, X.; Wang, S. Nitrate and Nitrite in Health and Disease. Aging Dis. 2018, 9, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, S.-S.; Chung, J.-C.; Hwang, D.-F.; Chou, S.-S.; Chung, J.-C.; Hwang, D.-F. A High Performance Liquid Chromatography Method for Determining Nitrate and Nitrite Levels in Vegetables. Available J. Food Drug Anal. 2003, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, I.; Mignogna, C.; Del Rio, D.; Mena, P. Health Effects of 100% Fruit and Vegetable Juices: Evidence from Human Subject Intervention Studies. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2024, 37, 194–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Nitrate and Nitrite in Drinking-Water Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA. Confirms Safe Levels for Nitrites and Nitrates Added to Food; EFSA: Parma, Italy, 2025; Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/press/news/170615 (accessed on 31 August 2025).
- Regulation–EU–2023/2108–EN–EUR-Lex. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2023/2108/oj/eng (accessed on 31 August 2025).
- Bryan, N.S.; van Grinsven, H. The Role of Nitrate in Human Health. Adv. Agron. 2013, 119, 153–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehzadeh, H.; Maleki, A.; Rezaee, R.; Shahmoradi, B.; Ponnet, K. The Nitrate Content of Fresh and Cooked Vegetables and Their Health-Related Risks. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, B.C.; Soto, K.O.; González, D.R.; Gonzalez Reinoso, D. El Consumo de Nitrato y Su Potencial Efecto Benéfi Co Sobre La Salud Cardiovascular Nitrate Consumption and Potential Benefi Cial Effect on Cardiovascular Health. Rev. Chil. Nutr. 2015, 42, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, E.J.; Coggan, A.R. What Is in Your Beet Juice? Nitrate and Nitrite Content of Beet Juice Products Marketed to Athletes. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2019, 29, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bescos, R.; Rollason, M.L.; Davies, T.S.; Casas-Agustench, P. Content of Nitrate and Nitrite in Commercial and Self-made Beetroot Juices and the Effect of Storage Temperature. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 6376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wylie, L.J.; Kelly, J.; Bailey, S.J.; Blackwell, J.R.; Skiba, P.F.; Winyard, P.G.; Jeukendrup, A.E.; Vanhatalo, A.; Jones, A.M. Beetroot Juice and Exercise: Pharmacodynamic and Dose-Response Relationships. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 115, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietary Nitrate/Beetroot Juice|Australian Sports Commission. Available online: https://www.ausport.gov.au/ais/nutrition/supplements/group_a/performance-supplements2/beetroot-juicenitrate (accessed on 2 September 2025).
- Senefeld, J.W.; Wiggins, C.C.; Regimbal, R.J.; Dominelli, P.B.; Baker, S.E.; Joyner, M.J. Ergogenic Effect of Nitrate Supplementation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2020, 52, 2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siervo, M.; Babateen, A.; Alharbi, M.; Stephan, B.; Shannon, O. Dietary Nitrate and Brain Health. Too Much Ado about Nothing or a Solution for Dementia Prevention? Br. J. Nutr. 2022, 128, 1130–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gareau, M.G. Cognitive Function and the Microbiome. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2016, 131, 227–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.M.; Thompson, C.; Wylie, L.J.; Vanhatalo, A. Dietary Nitrate and Physical Performance. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2018, 38, 303–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peth-Nui, T.; Wattanathorn, J.; Muchimapura, S.; Tong-Un, T.; Piyavhatkul, N.; Rangseekajee, P.; Ingkaninan, K.; Vittaya-Areekul, S. Effects of 12-Week Bacopa Monnieri Consumption on Attention, Cognitive Processing, Working Memory, and Functions of Both Cholinergic and Monoaminergic Systems in Healthy Elderly Volunteers. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 606424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.C.; Choe, Y.M.; Suh, G.H.; Choi, I.G.; Kim, H.S.; Hwang, J.; Yi, D.; Jhoo, J.H.; Kim, J.W. Ginseng Intake and Alzheimer Disease-Specific Cognition in Older Adults According to Apolipoprotein Ε4 Allele Status. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1152626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojcheva, E.I.; Quintela, J.C. The Effectiveness of Rhodiola Rosea L. Preparations in Alleviating Various Aspects of Life-Stress Symptoms and Stress-Induced Conditions—Encouraging Clinical Evidence. Molecules 2022, 27, 3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopukumar, K.; Thanawala, S.; Somepalli, V.; Rao, T.S.S.; Thamatam, V.B.; Chauhan, S. Efficacy and Safety of Ashwagandha Root Extract on Cognitive Functions in Healthy, Stressed Adults: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 8254344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiland, E.G.; Lindh, F.; Regan, C.; Ekblom, Ö.; Kjellenberg, K.; Larsen, F.J.; Fernström, M.; Nyberg, G.; Ekblom, M.M.; Helgadóttir, B. A Randomised Crossover Trial of Nitrate and Breakfast on Prefrontal Cognitive and Haemodynamic Response Functions. npj Sci. Food 2024, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilchrist, M.; Winyard, P.G.; Fulford, J.; Anning, C.; Shore, A.C.; Benjamin, N. Dietary Nitrate Supplementation Improves Reaction Time in Type 2 Diabetes: Development and Application of a Novel Nitrate-Depleted Beetroot Juice Placebo. Nitric Oxide 2014, 40, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaccaro, M.G.; Innocenti, B.; Cione, E.; Gallelli, L.; De Sarro, G.; Bonilla, D.A.; Cannataro, R. Acute Effects of a Chewable Beetroot-Based Supplement on Cognitive Performance: A Double-Blind Randomized Placebo-Controlled Crossover Clinical Trial. Eur. J. Nutr. 2024, 63, 303–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.; Bennett, H.; Miatke, A.; Dumuid, D.; Curtis, R.; Ferguson, T.; Brinsley, J.; Szeto, K.; Petersen, J.M.; Gough, C.; et al. Effectiveness of Exercise for Improving Cognition, Memory and Executive Function: A Systematic Umbrella Review and Meta-Meta-Analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2025, 59, e108589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trecroci, A.; Duca, M.; Cavaggioni, L.; Rossi, A.; Scurati, R.; Longo, S.; Merati, G.; Alberti, G.; Formenti, D. Relationship between Cognitive Functions and Sport-Specific Physical Performance in Youth Volleyball Players. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks-Wilson, A.R. Genetics of Healthy Aging and Longevity. Hum. Genet. 2013, 132, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Tang, K.; Gao, B. Influence of Chronic Nitrate-Rich Beetroot Juice Supplementation on the Endurance Performance of Active Winter Triathletes: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Am. Nutr. Assoc. 2023, 42, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirkey, D.; Anant, S.K.; Venugopal, R. Effect of Beetroot Supplementation on 10 Km Time Trial Performance of Distance Runners. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2021, 14, 6423–6429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Fernández, A.; Castillo, D.; Raya-González, J.; Domínguez, R.; Bailey, S.J. Beetroot Juice Supplementation Increases Concentric and Eccentric Muscle Power Output. Original Investigation. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2021, 24, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado-Castro, J.M.; Campos-Perez, J.; Ranchal-Sanchez, A.; Durán-López, N.; Domínguez, R. Acute Effects of Beetroot Juice Supplements on Lower-Body Strength in Female Athletes: Double-Blind Crossover Randomized Trial. Sports Health 2022, 14, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daab, W.; Bouzid, M.A.; Lajri, M.; Bouchiba, M.; Saafi, M.A.; Rebai, H. Chronic Beetroot Juice Supplementation Accelerates Recovery Kinetics Following Simulated Match Play in Soccer Players. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2021, 40, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamim, C.J.R.; de Sousa Júnior, F.W.; Porto, A.A.; Andrade, C.V.G.; de Figueiredo, M.Í.L.S.; Benjamim, C.J.R.; da Silva Rodrigues, G.; Rocha, E.M.B.; Cavalcante, T.F.; Garner, D.M.; et al. Negligible Effects of Nutraceuticals from Beetroot Extract on Cardiovascular and Autonomic Recovery Response Following Submaximal Aerobic Exercise in Physically Active Healthy Males: A Randomized Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, L.M.; Hall, R.; Heikura, I.A.; Ross, M.L.; Tee, N.; Kent, G.L.; Whitfield, J.; Forbes, S.F.; Sharma, A.P.; Jones, A.M.; et al. Neither Beetroot Juice Supplementation nor Increased Carbohydrate Oxidation Enhance Economy of Prolonged Exercise in Elite Race Walkers. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Samanes, Á.; Pérez-Lopez, A.; Morencos, E.; Muñoz, A.; Kühn, A.; Sánchez-Migallón, V.; Moreno-Pérez, V.; González-Frutos, P.; Bach-Faig, A.; Roberts, J.; et al. Beetroot Juice Ingestion Does Not Improve Neuromuscular Performance and Match-Play Demands in Elite Female Hockey Players: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2023, 62, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trexler, E.T.; Keith, D.S.; Lucero, A.A.; Stoner, L.; Schwartz, T.A.; Persky, A.M.; Ryan, E.D.; Smith-Ryan, A.E. Effects of Citrulline Malate and Beetroot Juice Supplementation on Energy Metabolism and Blood Flow During Submaximal Resistance Exercise. J. Diet. Suppl. 2020, 17, 698–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miraftabi, H.; Avazpoor, Z.; Berjisian, E.; Sarshin, A.; Rezaei, S.; Domínguez, R.; Reale, R.; Franchini, E.; Samanipour, M.H.; Koozehchian, M.S.; et al. Effects of Beetroot Juice Supplementation on Cognitive Function, Aerobic and Anaerobic Performances of Trained Male Taekwondo Athletes: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neteca, J.; Veseta, U.; Liepina, I.; Volgemute, K.; Dzintare, M.; Babarykin, D. Effect of Beetroot Juice Supplementation on Aerobic Capacity in Female Athletes: A Randomized Controlled Study. Nutrients 2024, 17, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnacho-Castaño, M.V.; Sánchez-Nuño, S.; Molina-Raya, L.; Carbonell, T.; Maté-Muñoz, J.L.; Pleguezuelos-Cobo, E.; Serra-Payá, N. Circulating Nitrate-Nitrite Reduces Oxygen Uptake for Improving Resistance Exercise Performance after Rest Time in Well-Trained CrossFit Athletes. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.; Merrill, C.; Riley, C.F.; Hammer, M.A.; Kenney, R.T.; Riley, A.A.; Li, J.; Zink, A.C.; Karl, S.T.; Price, K.M.; et al. Acute Inorganic Nitrate Ingestion Does Not Impact Oral Microbial Composition, Cognitive Function, or High-Intensity Exercise Performance in Female Team-Sport Athletes. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2024, 124, 3511–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Elias, V.; Courel-Ibanez, J.; Perez-Lopez, A.; Jodra, P.; Moreno-Perez, V.; Coso, J.D.; Lopez-Samanes, A. Acute Beetroot Juice Supplementation Does Not Improve Match-Play Activity in Professional Tennis Players. J. Am. Nutr. Assoc. 2022, 41, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rokkedal-Lausch, T.; Franch, J.; Poulsen, M.K.; Thomsen, L.P.; Weitzberg, E.; Kamavuako, E.N.; Karbing, D.S.; Larsen, R.G. Multiple-Day High-Dose Beetroot Juice Supplementation Does Not Improve Pulmonary or Muscle Deoxygenation Kinetics of Well-Trained Cyclists in Normoxia and Hypoxia. Nitric Oxide 2021, 111–112, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, G.P.; Killer, S.C.; Stoyanov, Z.; Stephens, H.; Read, L.; James, L.J.; Bailey, S.J. Influence of Dietary Nitrate Supplementation on High-Intensity Intermittent Running Performance at Different Doses of Normobaric Hypoxia in Endurance-Trained Males. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2020, 31, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- d’Unienville, N.M.A.; Blake, H.T.; Coates, A.M.; Hill, A.M.; Nelson, M.J.; Buckley, J.D. Effect of Food Sources of Nitrate, Polyphenols, L-Arginine and L-Citrulline on Endurance Exercise Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2021, 18, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T.D.; Martin, M.P.; Mintz, J.A.; Rogers, R.R.; Ballmann, C.G. Effect of Acute Beetroot Juice Supplementation on Bench Press Power, Velocity, and Repetition Volume. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2020, 34, 924–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Vanhatalo, A.; Black, M.I.; Rajaram, R.; Massey, G.; Jones, A.M. Dose-Response Relationship between Dietary Nitrate Intake and Nitric Oxide Congeners in Various Blood Compartments and Skeletal Muscle: Differential Effects on Skeletal Muscle Torque and Velocity. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2025, 229, 520–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, S.; Ahmadizad, S.; Yekaninejad, M.S.; Karami, M.R.; Djafarian, K. The Effect of Beetroot Juice Supplementation on Muscle Performance during Isokinetic Knee Extensions in Male Taekwondo Athletes. Sci. Sports 2021, 36, 483.e1–483.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiaqi, Z.; Zihan, D.; Wong, S.H.-S.; Chen, Z.; Poon, E.T.-C. Acute Effects of Various Doses of Nitrate-Rich Beetroot Juice on High-Intensity Interval Exercise Responses in Women: A Randomized, Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Trial. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2024, 21, 2334680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadpour, A.; Fashi, M.; Hemmatinafar, M. Consuming Beetroot Juice Improves Slalom Performance and Reduces Muscle Soreness in Alpine Skiers under Hypoxic Conditions. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2024, 8, 104408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, M.I.; Wylie, L.J.; Kadach, S.; Piknova, B.; Park, J.W.; Stoyanov, Z.; L’Heureux, J.E.; Schechter, A.N.; Vanhatalo, A.; Jones, A.M. Effects of Low and High Dietary Nitrate Intake on Human Saliva, Plasma and Skeletal Muscle Nitrate and Nitrite Concentrations and Their Functional Consequences. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2024, 225, 881–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomer, R.J.; Butawan, M.; Pigg, B.; Martin, K.R. Acute Ingestion of a Novel Nitrate-Rich Dietary Supplement Significantly Increases Plasma Nitrate/Nitrite in Physically Active Men and Women. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocksedge, S.P.; Breese, B.C.; Morgan, P.T.; Nogueira, L.; Thompson, C.; Wylie, L.J.; Jones, A.M.; Bailey, S.J. Influence of Muscle Oxygenation and Nitrate-Rich Beetroot Juice Supplementation on O2 Uptake Kinetics and Exercise Tolerance. Nitric Oxide 2020, 99, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DE SOUZA, D.B.; Ribeiro, J.N.; Simão, A.N.C.; Aguilar-Navarro, M.; Polito, M.D. The Acute Effect of In Natura Beetroot Juice Intake on Intra-Session Exercise Sequences During Concurrent Training. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2022, 15, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumar, A.M.; Huntington, A.F.; Rogers, R.R.; Kopec, T.J.; Ballmann, C.G. Acute Beetroot Juice Supplementation Attenuates Morning-Associated Decrements in Supramaximal Exercise Performance in Trained Sprinters. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esen, O.; Domínguez, R.; Karayigit, R. Acute Beetroot Juice Supplementation Enhances Intermittent Running Performance but Does Not Reduce Oxygen Cost of Exercise among Recreational Adults. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, S.P.A.; Spriet, L.L. Potential Effect of Beetroot Juice Supplementation on Exercise Economy in Well-Trained Females. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2022, 47, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnacho-Castaño, M.V.; Pleguezuelos-Cobo, E.; Berbel, M.; Irurtia, A.; Carrasco-Marginet, M.; Castizo-Olier, J.; Veiga-Herreros, P.; Faundez-Zanuy, M.; Serra-Payá, N. Effects of Acute Beetroot Juice Intake on Performance, Maximal Oxygen Uptake, and Ventilatory Efficiency in Well-Trained Master Rowers: A Randomized, Double-Blinded Crossover Study. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2024, 21, 2373170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnacho-Castaño, M.V.; Palau-Salvà, G.; Serra-Payá, N.; Ruiz-Hermosel, M.; Berbell, M.; Viñals, X.; Bataller, M.G.; Carbonell, T.; Vilches-Saez, S.; Cobo, E.P.; et al. Understanding the Effects of Beetroot Juice Intake on CrossFit Performance by Assessing Hormonal, Metabolic and Mechanical Response: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Crossover Design. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2020, 17, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmatinafar, M.; Zaremoayedi, L.; Koushkie Jahromi, M.; Alvarez-Alvarado, S.; Wong, A.; Niknam, A.; Suzuki, K.; Imanian, B.; Bagheri, R. Effect of Beetroot Juice Supplementation on Muscle Soreness and Performance Recovery after Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage in Female Volleyball Players. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado-Castro, J.M.; Casanova-Rodriguez, D.; Campos-Perez, J.; Llorente-Cantarero, F.J.; De La Florida-Villagran, C.A.; Diaz-Bernier, V.M.; Ranchal-Sanchez, A. Beetroot Juice Produces Changes in Heart Rate Variability and Reduces Internal Load during Resistance Training in Men: A Randomized Double-Blind Crossover. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macuh, M.; Kojić, N.; Knap, B. The Effects of Nitrate Supplementation on Performance as a Function of Habitual Dietary Intake of Nitrates: A Randomized Controlled Trial of Elite Football Players. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranchal-Sanchez, A.; Diaz-Bernier, V.M.; De La Florida-Villagran, C.A.; Llorente-Cantarero, F.J.; Campos-Perez, J.; Jurado-Castro, J.M. Acute Effects of Beetroot Juice Supplements on Resistance Training: A Randomized Double-Blind Crossover. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowland, S.N.; James, L.J.; O’Donnell, E.; Bailey, S.J. Influence of Acute Dietary Nitrate Supplementation Timing on Nitrate Metabolism, Central and Peripheral Blood Pressure and Exercise Tolerance in Young Men. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2023, 124, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra-Payá, N.; Garnacho-Castaño, M.V.; Sánchez-Nuño, S.; Albesa-Albiol, L.; Girabent-Farrés, M.; Arcone, L.M.; Fernández, A.P.; García-Fresneda, A.; Castizo-Olier, J.; Viñals, X.; et al. The Relationship between Resistance Exercise Performance and Ventilatory Efficiency after Beetroot Juice Intake in Well-Trained Athletes. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.; Pennell, A.; Price, K.M.; Karl, S.T.; Seekamp-Hicks, N.G.; Paniagua, K.K.; Weiderman, G.D.; Powell, J.P.; Sharabidze, L.K.; Lincoln, I.G.; et al. Effects of Dietary Nitrate Supplementation on Performance and Muscle Oxygenation during Resistance Exercise in Men. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatlici, A.; Lima, Y.; Yilmaz, S.; Ekin, A.; Okut, S.; Ceviz, E. The Effects of Beetroot Juice Supplementation on Balance Performance of Wrestlers. Arch. Razi Inst. 2021, 15, pjmhs211572234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatlici, A. The Effects of Acute Beetroot Juice Supplementation on Lower and Upper Body Isokinetic Strength of the Wrestlers. J. Mens. Health 2021, 17, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurston, T.S.; Weavil, J.C.; Hureau, T.J.; Gifford, J.R.; Georgescu, V.P.; Wan, H.Y.; la Salle, D.T.; Richardson, R.S.; Amann, M. On the Implication of Dietary Nitrate Supplementation for the Hemodynamic and Fatigue Response to Cycling Exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2021, 131, 1691–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volino-Souza, M.; de Oliveira, G.V.; Barros-Santos, E.; Conte-Junior, C.A.; Alvares, T.S. The Impact of Beetroot Juice Intake on Muscle Oxygenation and Performance during Rhythmic Handgrip Exercise. PharmaNutrition 2020, 14, 100215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.H.; Sim, R.; Sim, A.; Burns, S.F. Effects of an Isotonic Beetroot Drink on Power Output During Sprint Exercise and Jump Performance in Physically Active Individuals: A Randomized Crossover Trial. J. Diet. Suppl. 2024, 21, 808–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuschen, X.; Choi, J.H.; Seo, J.; Sun, Y.; Lee, E.; Kim, S.W.; Park, H.Y. Effects of Acute Beetroot Juice Supplementation and Exercise on Cardiovascular Function in Healthy Men in Preliminary Study: A Randomized, Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled, and Crossover Trial. Healthcare 2024, 12, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgos, J.; Viribay, A.; Calleja-gonzález, J.; Fernández-lázaro, D.; Olasagasti-ibargoien, J.; Seco-calvo, J.; Mielgo-ayuso, J. Long-Term Combined Effects of Citrulline and Nitrate-Rich Beetroot Extract Supplementation on Recovery Status in Trained Male Triathletes: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Biology 2022, 11, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos, J.; Viribay, A.; Fernández-Lázaro, D.; Calleja-González, J.; González-Santos, J.; Mielgo-Ayuso, J. Combined Effects of Citrulline Plus Nitrate-Rich Beetroot Extract Co-Supplementation on Maximal and Endurance-Strength and Aerobic Power in Trained Male Triathletes: A Randomized Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2021, 14, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, G.V.; Do Nascimento, L.A.D.; Volino-Souza, M.; Do Couto Vellozo, O.; Alvares, T.S. A Single Oral Dose of Beetroot-Based Gel Does Not Improve Muscle Oxygenation Parameters, but Speeds up Handgrip Isometric Strength Recovery in Recreational Combat Sports Athletes. Biol. Sport 2020, 37, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esen, O.; Bailey, S.J.; Stashuk, D.W.; Howatson, G.; Goodall, S. Influence of Nitrate Supplementation on Motor Unit Activity during Recovery Following a Sustained Ischemic Contraction in Recreationally Active Young Males. Eur. J. Nutr. 2024, 63, 2379–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esen, O.; Cepicka, L.; Gabrys, T.; Karayigit, R. High-Dose Nitrate Supplementation Attenuates the Increased Blood Pressure Responses to Isometric Blood Flow Restriction Exercise in Healthy Males. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esen, O.; Faisal, A.; Zambolin, F.; Bailey, S.J.; Callaghan, M.J. Effect of Nitrate Supplementation on Skeletal Muscle Motor Unit Activity during Isometric Blood Flow Restriction Exercise. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2022, 122, 1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozłowska, L.; Mizera, O.; Gromadzińska, J.; Janasik, B.; Mikołajewska, K.; Mróz, A.; Wąsowicz, W. Changes in Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Muscle Damage Markers Following Diet and Beetroot Juice Supplementation in Elite Fencers. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liubertas, T.; Kairaitis, R.; Stasiule, L.; Capkauskiene, S.; Stasiulis, A.; Viskelis, P.; Viškelis, J.; Urbonaviciene, D. The Influence of Amaranth (Amaranthus Hypochondriacus) Dietary Nitrates on the Aerobic Capacity of Physically Active Young Persons. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2020, 17, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordonie, N.C.; Saunders, M.J.; de Zevallos, J.O.; Kurti, S.P.; Luden, N.D.; Crance, J.H.; Baur, D.A. Dietary Nitrate Supplementation Enhances Heavy Load Carriage Performance in Military Cadets. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2023, 123, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, S.N.; Da Boit, M.; Tan, R.; Robinson, G.P.; O’Donnell, E.; James, L.J.; Bailey, S.J. Dietary Nitrate Supplementation Enhances Performance and Speeds Muscle Deoxyhaemoglobin Kinetics during an End-Sprint after Prolonged Moderate-Intensity Exercise. Antioxidants 2022, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, R.; Wylie, L.J.; Wilkerson, D.P.; Vanhatalo, A.; Jones, A.M. Effects of Dietary Nitrate on the O2 Cost of Submaximal Exercise: Accounting for “Noise” in Pulmonary Gas Exchange Measurements. J. Sports Sci. 2022, 40, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viribay, A.; Alcantara, J.M.A.; López, I.; Mielgo-Ayuso, J.; Castañeda-Babarro, A. Impact of a Short-Term Nitrate and Citrulline Co-Supplementation on Sport Performance in Elite Rowers: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Crossover Trial. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2024, 124, 1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berjisian, E.; McGawley, K.; Saunders, B.; Domínguez, R.; Koozehchian, M.S.; de Oliveira, C.V.C.; Rafiei, R.; Miraftabi, H.; Sarshin, A.; Naderi, A. Acute Effects of Beetroot Juice and Caffeine Co-Ingestion during a Team-Sport-Specific Intermittent Exercise Test in Semi-Professional Soccer Players: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2022, 14, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlanga, L.A.; Lopez-Samanes, A.; Martin-Lopez, J.; de la Cruz, R.M.; Garces-Rimon, M.; Roberts, J.; Bertotti, G. Dietary Nitrate Ingestion Does Not Improve Neuromuscular Performance in Male Sport Climbers. J. Hum. Kinet. 2023, 87, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, S.M.; Kearns, D. The Effect of Beetroot Supplementation on High-Intensity Functional Training Performance. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2020, 13, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conger, S.A.; Zamzow, C.M.; Darnell, M.E. Acute Beet Juice Supplementation Does Not Improve 30- or 60-Second Maximal Intensity Performance in Anaerobically Trained Athletes. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2021, 14, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esen, O.; Karayigit, R.; Peart, D.J. Acute Beetroot Juice Supplementation Did Not Enhance Intermittent Running Performance in Trained Rugby Players. Eur. J. Sport. Sci. 2023, 23, 2321–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennis, P.J.; Cumpstey, A.F.; O’Doherty, A.F.; Fernandez, B.O.; Gilbert-Kawai, E.T.; Mitchell, K.; Moyses, H.; Cobb, A.; Meale, P.; Pöhnl, H.; et al. Dietary Nitrate Supplementation Does Not Alter Exercise Efficiency at High Altitude–Further Results From the Xtreme Alps Study. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 827235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Samanes, Á.; Pérez-López, A.; Moreno-Pérez, V.; Nakamura, F.Y.; Acebes-Sánchez, J.; Quintana-Milla, I.; Sánchez-Oliver, A.J.; Moreno-Pérez, D.; Fernández-Elías, V.E.; Domínguez, R. Effects of Beetroot Juice Ingestion on Physical Performance in Highly Competitive Tennis Players. Nutrients 2020, 12, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, B.; Morencos, E.; Vicente-Campos, D.; Muñoz, A.; González-García, J.; Veiga, S. Effects of Beetroot Juice Intake on Repeated Performance of Competitive Swimmers. Front. Physiol. 2023, 13, 1076295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Zevallos, J.O.; Hogwood, A.C.; Kruse, K.; De Guzman, J.; Buckley, M.; Weltman, A.L.; Allen, J.D. Sex Differences in the Effects of Inorganic Nitrate Supplementation on Exercise Economy and Endurance Capacity in Healthy Young Adults. J. Appl. Physiol. 2023, 135, 1157–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, A.; Viana, J.L.; Milheiro, J.; Reis, V.M.; Millet, G.P. Dietary Nitrate Supplementation Is Not Helpful for Endurance Performance at Simulated Altitude Even When Combined With Intermittent Normobaric Hypoxic Training. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 839996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, R.; Black, M.; Home, J.; Blackwell, J.; Clark, I.; Wylie, L.; Vanhatalo, A.; Jones, A.M. Physiological and Performance Effects of Dietary Nitrate and N-Acetylcysteine Supplementation during Prolonged Heavy-Intensity Cycling. J. Sports Sci. 2023, 40, 2585–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.; Price, K.M.; Wideen, L.E.; Lincoln, I.G.; Karl, S.T.; Seals, J.P.; Paniagua, K.K.; Hagen, D.W.; Tchaprazian, I.; Bailey, S.J.; et al. Dietary Nitrate Ingested with and without Pomegranate Supplementation Does Not Improve Resistance Exercise Performance. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1217192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viribay, A.; Alcantara, J.M.A.; López, I.; Mielgo-Ayuso, J.; Castañeda-Babarro, A. No Evidence of Improvements in Energy Metabolism after 1 Week of Nitrate and Citrulline Co-Supplementation in Elite Rowers. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2025, 125, 715–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, R.; Oliveira, C.B.; Costa, J.A.; Brito, J.; Teixeira, V.H. Effects of Dietary Supplements on Athletic Performance in Elite Soccer Players: A Systematic Review. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2023, 20, 2236060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsharif, N.S.; Clifford, T.; Alhebshi, A.; Rowland, S.N.; Bailey, S.J. Effects of Dietary Nitrate Supplementation on Performance during Single and Repeated Bouts of Short-Duration High-Intensity Exercise: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonio, J.; Pereira, F.; Curtis, J.; Rojas, J.; Evans, C. The Top 5 Can’t-Miss Sport Supplements. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, J.L.; Alorda-Capo, F.; Pareja-Galeano, H.; Jiménez, S.L. Influence of Nitrate Supplementation on Endurance Cyclic Sports Performance: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Wu, S.; Jin, C. Beetroot as a Functional Food with Huge Health Benefits: Antioxidant, Antitumor, Physical Function, and Chronic Metabolomics Activity. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 6406–6420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delleli, S.; Ouergui, I.; Messaoudi, H.; Trabelsi, K.; Glenn, J.M.; Ammar, A.; Chtourou, H. Does Beetroot Supplementation Improve Performance in Combat Sports Athletes? A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2023, 15, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez, R.; Oliver, A.J.S.; Da Silva, S.F.; López-Samanes, A.; Martínez-Sanz, J.M.; Mata, F. Dietary-Nutritional Needs in Tennis: A Narrative Review Necesidades Dietético-Nutricionales En El Tenis: Una Revisión Narrativa. Rev. Esp. Nutr. Humana Diet. 2021, 25, e1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esen, O.; Dobbin, N.; Callaghan, M.J. The Effect of Dietary Nitrate on the Contractile Properties of Human Skeletal Muscle: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Nutr. Assoc. 2023, 42, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamonales, J.M.; Rojas-Valverde, D.; Muñoz-Jiménez, J.; Serrano-Moreno, W.; Ibáñez, S.J. Effectiveness of Nitrate Intake on Recovery from Exercise-Related Fatigue: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilsanz, L.; Del Coso, J.; Jiménez-Saiz, S.L.; Pareja-Galeano, H. Effect of Caffeine and Nitrates Combination on Exercise Performance, Heart Rate and Oxygen Uptake: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlow, J.; Blodgett, K.; Stedman, J.; Pojednic, R. Dietary Supplementation on Physical Performance and Recovery in Active-Duty Military Personnel: A Systematic Review of Randomized and Quasi-Experimental Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogwood, A.C.; Anderson, K.C.; Ortiz de Zevallos, J.; Paterson, C.; Weltman, A.; Allen, J.D. Limited Effects of Inorganic Nitrate Supplementation on Exercise Training Responses: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. Open 2023, 9, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.; Bailey, S.J.; Rowland, S.N.; Alsharif, N.; Shannon, O.M.; Clifford, T. The Effect of Nitrate-Rich Beetroot Juice on Markers of Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Human Intervention Trials. J. Diet. Suppl. 2022, 19, 749–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, A.K.; Bonetti, G.; Medori, M.C.; Caruso, P.; Manganotti, P.; Fioretti, F.; Nodari, S.; Connelly, S.T.; Bertelli, M. Dietary Supplements for Improving Nitric-Oxide Synthesis. J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 2022, 63, E239–E245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, E.K. Nutritional Strategies to Optimize Performance and Recovery in Rowing Athletes. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lago-Rodríguez, Á.; Domínguez, R.; Ramos-álvarez, J.J.; Tobal, F.M.; Jodra, P.; Tan, R.; Bailey, S.J. The Effect of Dietary Nitrate Supplementation on Isokinetic Torque in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Laval, I.; Mielgo-Ayuso, J.; Terrados, N.; Calleja-González, J. Evidence-Based Post Exercise Recovery in Combat Sports: A Narrative Review. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2021, 61, 386–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Torres, O.; Rodríguez-Longobardo, C.; Capel-Escoriza, R.; Fernández-Elías, V.E. Ergogenic Aids to Improve Physical Performance in Female Athletes: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2022, 15, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, S.M.M.; Sukri, N.M.; Johari, M.H.; Gnanou, J.; Manaf, F.A. Pure Juice Supplementation: Its Effect on Muscle Recovery and Sports Performance. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 30, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, E.; Mündel, T.; Barnes, M.J. Nutritional Compounds to Improve Post-Exercise Recovery. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulios, A.; Papanikolaou, K.; Draganidis, D.; Tsimeas, P.; Chatzinikolaou, A.; Tsiokanos, A.; Jamurtas, A.Z.; Fatouros, I.G. The Effects of Antioxidant Supplementation on Soccer Performance and Recovery: A Critical Review of the Available Evidence. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojano-Ortega, D.; Peña Amaro, J.; Berral-Aguilar, A.J.; Berral-de la Rosa, F.J. Effects of Beetroot Supplementation on Recovery After Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage: A Systematic Review. Sports Health 2022, 14, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Juan, A.F.; Dominguez, R.; Lago-Rodríguez, Á.; Montoya, J.J.; Tan, R.; Bailey, S.J. Effects of Dietary Nitrate Supplementation on Weightlifting Exercise Performance in Healthy Adults: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, K.V.C.; Costa, B.D.; Gomes, A.C.; Saunders, B.; Mota, J.F. Factors That Moderate the Effect of Nitrate Ingestion on Exercise Performance in Adults: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analyses and Meta-Regressions. Adv. Nutr. 2022, 13, 1866–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.; Cass, J.K.; Lincoln, I.G.; Wideen, L.E.; Nicholl, M.J.; Molnar, T.J.; Gough, L.A.; Bailey, S.J.; Pennell, A. Effects of Dietary Nitrate Supplementation on High-Intensity Cycling Sprint Performance in Recreationally Active Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, R.; Pennell, A.; Karl, S.T.; Cass, J.K.; Go, K.; Clifford, T.; Bailey, S.J.; Perkins Storm, C. Effects of Dietary Nitrate Supplementation on Back Squat and Bench Press Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, R.; Cano, L.; Lago-Rodríguez, Á.; Domínguez, R. The Effects of Dietary Nitrate Supplementation on Explosive Exercise Performance: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, Y.; Fujii, N.; Suzuki, K. Dietary Supplementation for Attenuating Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage and Delayed-Onset Muscle Soreness in Humans. Nutrients 2021, 14, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Salar, N.; Fuster-Muñoz, E.; Martínez-Rodríguez, A. Nutritional Ergogenic Aids in Combat Sports: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Salar, N.; Santos-Sánchez, G.; Roche, E. Nutritional Ergogenic Aids in Racquet Sports: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.H.; Sim, A.; Burns, S.F. The Effect of Beetroot Ingestion on High-Intensity Interval Training: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.H.; Sim, A.; Burns, S.F. The Effects of Nitrate Ingestion on High-Intensity Endurance Time-Trial Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Exerc. Sci. Fit. 2022, 20, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, H.; de Joode, M.E.J.R.; Hossein, I.J.; Henckens, N.F.T.; Guggeis, M.A.; Berends, J.E.; de Kok, T.M.C.M.; van Breda, S.G.J. The Benefits and Risks of Beetroot Juice Consumption: A Systematic Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 788–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoughaib, W.S.; Fry, M.J.; Singhal, A.; Coggan, A.R. Beetroot Juice Supplementation and Exercise Performance: Is There More to the Story than Just Nitrate? Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1347242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelwarne, B.; Halagur, S.B. Red Beet: An Overview. Red. Beet Biotechnol. Food Pharm. Appl. 2013, 11, 1347242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, A.; Moffett, J. Saltpetre in Early and Medieval Chinese Medicine. Asian Med. 2009, 5, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, F.J.; Weitzberg, E.; Lundberg, J.O.; Ekblom, B. Effects of Dietary Nitrate on Oxygen Cost during Exercise. Acta Physiol. 2007, 191, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moncada, S.; Palmer, R.M.J.; Higgs, E.A. The Discovery of Nitric Oxide as the Endogenous Nitrovasodilator. Hypertension 1988, 12, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidder, S.; Webb, A.J. Vascular Effects of Dietary Nitrate (as Found in Green Leafy Vegetables and Beetroot) via the Nitrate-nitrite-nitric Oxide Pathway. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 75, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapil, V.; Khambata, R.S.; Jones, D.A.; Rathod, K.; Primus, C.; Massimo, G.; Fukuto, J.M.; Ahluwalia, A. The Noncanonical Pathway for in Vivo Nitric Oxide Generation: The Nitrate-Nitrite-Nitric Oxide Pathway. Pharmacol. Rev. 2020, 72, 692–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.M. Dietary Nitrate Supplementation and Exercise Performance. Sports Med. 2014, 44, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyner, M.J.; Casey, D.P. Regulation of Increased Blood Flow (Hyperemia) to Muscles during Exercise: A Hierarchy of Competing Physiological Needs. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 549–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, F.J.; Schiffer, T.A.; Borniquel, S.; Sahlin, K.; rn Ekblom, B.; Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E. Dietary Inorganic Nitrate Improves Mitochondrial Efficiency in Humans. Cell Metab. 2011, 13, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Coggan, A.R.; Ferreira, L.F. Nitric Oxide and Skeletal Muscle Contractile Function. Nitric Oxide 2022, 122–123, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Syed, B.; Abed, I.; Manguerra, D.; Shehabat, M.; Razick, D.I.; Nadora, D.; Nadora, D.; Akhtar, M.; Pai, D. Improved Effect of Spinach Extract on Physical Performance: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Cureus 2025, 17, e77840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, J.T.; Townsend, J.R.; Aziz, M.A.; Jones, M.D.; Littlefield, L.A.; Ruiz, M.D.; Johnson, K.D.; Gonzalez, A.M. Impact of Red Spinach Extract Supplementation on Bench Press Performance, Muscle Oxygenation, and Cognitive Function in Resistance-Trained Males. Sports 2021, 9, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, E.M.R.; Stegen, J.H.C.H.; Brouns, F. Effect of Caffeinated Drinks on Substrate Metabolism, Caffeine Excretion, and Performance. J. Appl. Physiol. 1998, 85, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, M. Dietary Supplements and Sports Performance: Herbals. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2006, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellami, M.; Slimeni, O.; Pokrywka, A.; Kuvačić, G.; Hayes, L.D.; Milic, M.; Padulo, J. Herbal Medicine for Sports: A Review. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2018, 15, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymańska, A.; Nowak, A.; Lipert, A.; Kochan, E. Effect of Ginseng Supplementation on Exercise Endurance as a Support for Cardiovascular Disease Management: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla, D.A.; Moreno, Y.; Gho, C.; Petro, J.L.; Odriozola-Martínez, A.; Kreider, R.B. Effects of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) on Physical Performance: Systematic Review and Bayesian Meta-Analysis. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2021, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Database | Terms Combination |
|---|---|
| PubMed | ((“Beetroot*”[Text Word] OR “beta vulgaris”[MeSH Terms] OR “beta vulgaris”[tw]) AND (“physical activit*”[Title/Abstract] OR physical[tw] OR “sport*”[Title/Abstract] OR “Athletic Performance”[MeSH Terms] OR “athletic performance*”[Title/Abstract] OR “exercise*”[Title/Abstract] OR “aerobic”[Text Word] OR “gymnastic*”[Text Word] OR “training”[Text Word]) AND “cognit*”[Text Word]) NOT (animals[mh] NOT humans[mh]) |
| ((“Beetroot*”[Text Word] OR “beta vulgaris”[MeSH Terms] OR “beta vulgaris”[tw]) AND (“physical activit*”[Title/Abstract] OR “sport*”[Title/Abstract] OR “Athletic Performance”[MeSH Terms] OR “athletic performance*”[Title/Abstract] OR “exercise*”[Title/Abstract] OR “aerobic”[Text Word] OR “gymnastic*”[Text Word] OR “training”[Text Word])) NOT (animals[mh] NOT humans[mh]) | |
| Embase | (‘beetroot*’:ti,ab,kw,de,dn,df,mn,tn OR ‘beet’/exp OR ‘beet’ OR ‘beta vulgaris’:ti,ab,kw,de,dn,df,mn,tn) AND (‘physical activit*’:ti,ab,kw OR ‘physical’:ti,ab,kw,de,dn,df,mn,tn OR ‘sport*’:ti,ab,kw OR ‘athletic performance’/exp OR ‘athletic performance’ OR ‘athletic performance*’:ti,ab,kw OR ‘exercise*’:ti,ab,kw OR ‘aerobic’:ti,ab,kw,de,dn,df,mn,tn OR ‘gymnastic*’:ti,ab,kw,de,dn,df,mn,tn OR ‘training’:ti,ab,kw,de,dn,df,mn,tn) AND ‘cognit*’:ti,ab,kw,de,dn,df,mn,tn NOT ((‘animal’/exp OR ‘animal’) NOT (‘human’/exp OR ‘human’)) |
| ‘beetroot*’:ti,ab,kw,de,dn,df,mn,tn OR ‘beet’/exp OR ‘beet’ OR ‘beta vulgaris’:ti,ab,kw,de,dn,df,mn,tn) AND (‘physical activit*’:ti,ab,kw OR ‘sport*’:ti,ab,kw OR ‘athletic performance’/exp OR ‘athletic performance’ OR ‘athletic performance*’:ti,ab,kw OR ‘exercise*’:ti,ab,kw OR ‘aerobic’:ti,ab,kw,de,dn,df,mn,tn OR ‘gymnastic*’:ti,ab,kw,de,dn,df,mn,tn OR ‘training’:ti,ab,kw,de,dn,df,mn,tn) NOT ((‘animal’/exp OR ‘animal’) NOT (‘human’/exp OR ‘human’)) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nowak, A.; Szymańska, A.; Kwaśniewska, M.; Kochan, E.; Lipert, A. Beetroot Juice Supplementation as a Healthy Aging Strategy Through Improving Physical Performance and Cognitive Functions: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3954. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17243954
Nowak A, Szymańska A, Kwaśniewska M, Kochan E, Lipert A. Beetroot Juice Supplementation as a Healthy Aging Strategy Through Improving Physical Performance and Cognitive Functions: A Systematic Review. Nutrients. 2025; 17(24):3954. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17243954
Chicago/Turabian StyleNowak, Anna, Angelika Szymańska, Magdalena Kwaśniewska, Ewa Kochan, and Anna Lipert. 2025. "Beetroot Juice Supplementation as a Healthy Aging Strategy Through Improving Physical Performance and Cognitive Functions: A Systematic Review" Nutrients 17, no. 24: 3954. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17243954
APA StyleNowak, A., Szymańska, A., Kwaśniewska, M., Kochan, E., & Lipert, A. (2025). Beetroot Juice Supplementation as a Healthy Aging Strategy Through Improving Physical Performance and Cognitive Functions: A Systematic Review. Nutrients, 17(24), 3954. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17243954






