Dietary Management of Eosinophilic Esophagitis in the Era of Molecular Diagnostics: The Role and Limitations of Component-Resolved Diagnostics—A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis
2.1. Standard Dietary Comparators
2.2. IgE-Centric and Combined Allergy Testing
2.3. Age and Geographic Differences
2.4. Step-Up and Step-Down Dietary Frameworks
2.5. Combined Modalities and Adjunctive Pharmacotherapy
2.6. Summary and Transition to Molecular Approaches
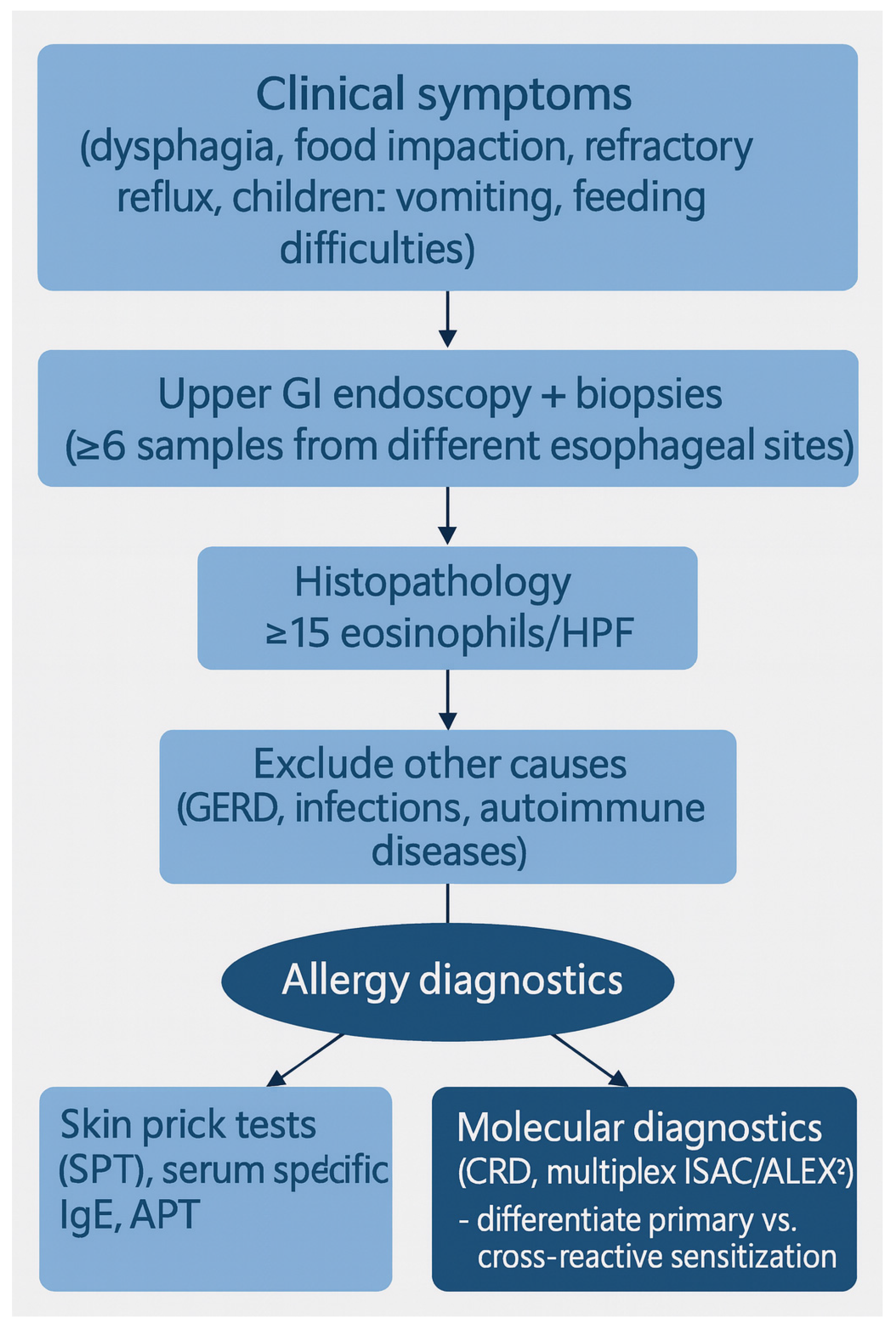
3. Component-Resolved Diagnostics and Molecular Approaches in Eosinophilic Esophagitis
3.1. Diagnostic Accuracy and Clinical Relevance of CRD
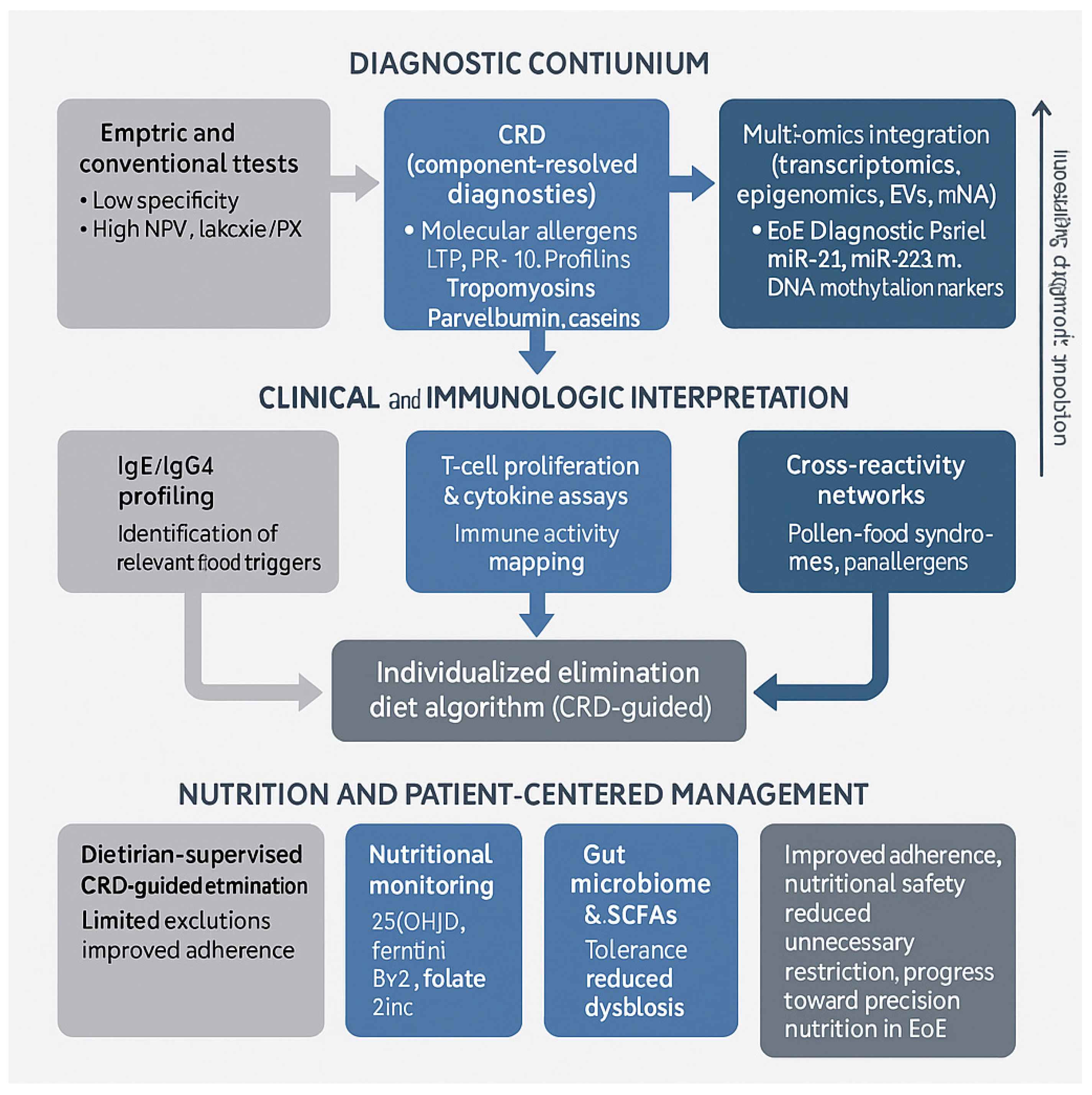
3.2. CRD-Guided Elimination Diet Strategies
3.3. Clinical Advantages and Limitations of CRD
3.4. Future Directions and Research Gaps for CRD in EoE
3.5. Nutrition Considerations and Practical Implementation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arias, Á.; González-Cervera, J.; Tenías, J.; Lucendo, A.J. Efficacy of dietary interventions for inducing histologic remission in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1639–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, C.J.; Abonia, J.P.; King, E.C.; Putnam, P.E.; Collins, M.H.; Franciosi, J.P.; Rothenberg, M.E. Comparative dietary therapy effectiveness in remission of pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 1570–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitsios, C.; Vassilopoulou, E.; Pantavou, K.; Terreehorst, I.; Nowak-Wegzryn, A.; Cianferoni, A.; Tsigkrelis, G.P.; Papachristodoulou, M.; Bonovas, S.; Nikolopoulos, G.K. Allergy-test-based elimination diets for the treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis: A systematic review of their efficacy. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, Á.; Tejera-Muñoz, A.; Gutiérrez-Ramírez, L.; Molina-Infante, J.; Lucendo, A.J. Efficacy of dietary therapy for eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adults: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armentia, A.; Martín-Armentia, S.; Martín-Armentia, B.; Santos-Fernández, J.; Álvarez, R.; Madrigal, B.; Fernández-González, D.; Gayoso, S.; Gayoso, M. Is eosinophilic esophagitis an equivalent of pollen-allergic asthma? Analysis of biopsies and therapy guided by component-resolved diagnosis. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2018, 46, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyane-Yeboa, A.; Wang, W.; Kavitt, R.T. The Role of Allergy Testing in Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 14, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhernov, Y.V.; Vysochanskaya, S.O.; Sukhov, V.A.; Zaostrovtseva, O.K.; Gorshenin, D.S.; Sidorova, E.A.; Mitrokhin, O.V. Molecular Mechanisms of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, J.; Mehrzad, R.; Hundal, N.V.; Alejos, A.; Hesterberg, P.E.; Katz, A.J.; Yuan, Q.; Shreffler, W.G. Longitudinal perspective on managing refractory eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2015, 3, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuyttens, L.; Dominicus, T.; Keppens, C.; Alliet, T.; Verelst, S.; Diels, M.; Bosmans, T.; Schrijvers, R.; Hoffman, I.; Bullens, D.M.A. IgE-mediated food sensitization, management strategies, and quality of life in pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis: A prospective observational study. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliewer, K.L.; Gonsalves, N.; Dellon, E.S.; Katzka, D.A.; Abonia, J.P.; Aceves, S.S.; Arva, N.C.; Besse, J.A.; Bonis, P.A.; Caldwell, J.M.; et al. One-food versus six-food elimination diet therapy for the treatment of eosinophilic oesophagitis: A multicentre, randomised, open-label trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 408–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagalwalla, A.F.; Amsden, K.; Shah, A.; Ritz, S.; Manuel-Rubio, M.; Dunne, K.; Nelson, S.P.; Wershil, B.K.; Melin-Aldana, H. Cow’s milk elimination: A novel dietary approach to treat eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2012, 55, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayerhofer, C.; Kavallar, A.; Aldrian, D.; Lindner, A.K.; Müller, T. Efficacy of elimination diets in eosinophilic esophagitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 21, 2197–2210.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, C.C.; Eluri, S.; Wolf, W.A.; Dellon, E.S. Six-food elimination diet and topical steroids are effective for eosinophilic esophagitis: A meta-regression. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 2408–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowitz, J.E.; Spergel, J.M.; Ruchelli, E.; Liacouras, C.A. Elemental diet is an effective treatment for eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adolescents. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 98, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, K.A.; Byrne, K.R.; Vinson, L.A.; Ying, J.; Boynton, K.K.; Fang, J.C.; Gleich, G.J.; Adler, D.G.; Clayton, F. Elemental diet induces histologic response in adult eosinophilic esophagitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucendo, A.J.; Arias, Á.; González-Cervera, J.; Yagüe-Compadre, J.L.; Guagnozzi, D.; Angueira, T.; Jiménez-Contreras, S.; González-Castillo, S.; Rodríguez-Domíngez, B.; De Rezende, L.C.; et al. Empiric six-food elimination diet induced and maintained prolonged remission in adults with eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonsalves, N.; Yang, G.Y.; Doerfler, B.; Ritz, S.; Ditto, A.M.; Hirano, I. Elimination diet effectively treats eosinophilic esophagitis in adults; food reintroduction identifies causative factors. Gastroenterology. 2012, 142, 1451–1459.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagalwalla, A.F.; Sentongo, T.A.; Ritz, S.; Hess, T.; Nelson, S.P.; Emerick, K.M.; Melin–Aldana, H.; Li, B. Effect of six-food elimination diet on clinical and histologic outcomes in eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 4, 1097–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Infante, J.; Arias, A.; Barrio, J.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, J.; Sanchez-Cazalilla, M.; Lucendo, A.J. Four-food group elimination diet for adult eosinophilic esophagitis: A prospective multicenter study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 1093–1099.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Infante, J.; Arias, Á.; Alcedo, J.; Garcia-Romero, R.; Casabona-Frances, S.; Prieto-Garcia, A.; Modolell, I.; Gonzalez-Cordero, P.L.; Perez-Martinez, I.; Martin-Lorente, J.L.; et al. Step-up empiric elimination diet for eosinophilic esophagitis: The 2-4-6 study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 141, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechsler, J.B.; Schwartz, S.; Arva, N.C.; Kim, K.-Y.A.; Chen, L.; Makhija, M.; Amsden, K.; Keeley, K.; Mohammed, S.; Dellon, E.S.; et al. A single food milk elimination diet is effective for treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis in children. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 20, 1748–1756.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalewski, A.; Doerfler, B.; Krause, A.J.; Hirano, I.; Gonsalves, N. Long-term outcomes of the six-food elimination diet and food reintroduction in adults with eosinophilic esophagitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 117, 1963–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Sánchez, J.; Torrijos, E.G.; Viedma, B.L.; Belda, E.d.l.S.; Dávila, F.M.; Rodríguez, C.G.; Brito, F.F.; Camacho, J.O.; Figueroa, P.R.; Molina-Infante, J. Efficacy of IgE-targeted vs empiric six-food elimination diets for adult eosinophilic oesophagitis. Allergy 2014, 69, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellon, E.S.; Guo, R.; McGee, S.J.; Hamilton, D.K.; Nicolai, E.; Covington, J.; Moist, S.E.; Arrington, A.; Wright, B.L.; Burks, A.W.; et al. A novel allergen-specific immune signature-directed approach to dietary elimination in eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2019, 10, e00099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, W.A.; Jerath, M.; Sperry, S.L.; Shaheen, N.J.; Dellon, E.S. Dietary elimination therapy is an effective option for adults with eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 1272–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Spergel, J.M.; Brown-Whitehorn, T.F.; Cianferoni, A.; Shuker, M.; Wang, M.-L.; Verma, R.; Liacouras, C.A. Identification of causative foods in children with eosinophilic esophagitis treated with an elimination diet. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 461–467.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesek, R.D.; Rettiganti, M.; O’BRien, E.; Beckwith, S.; Daniel, C.; Luo, C.; Scurlock, A.M.; Chandler, P.; Levy, R.A.; Perry, T.T.; et al. Effects of allergen sensitization on response to therapy in children with eosinophilic esophagitis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017, 119, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Cervera, J.; Lucendo, A.J. Eosinophilic esophagitis: An evidence-based approach to therapy. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 26, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, P.; Shah-Riar, P.; Bushra, S.S.; Haque, S.N.; Rafa, Z.I.; Hawa, F.; Chakrabarty, S.; Nath, S.D.; Afrin, H.; Shama, N.; et al. Recent trends in the management of eosinophilic esophagitis: A systematic review. Cureus 2023, 15, e43221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantine, G.; Seth, N.; Chokshi, N.; Minard, C.G.; Guffey, D.; Olive, A.P.; Davis, C.M. Combination steroid and test-based food elimination for eosinophilic esophagitis: A retrospective analysis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 64, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, C.C.; Safta, A.M.; Qasem, S.; Almond, M.A.; Dellon, E.S.; Jensen, E.T. Combined and alternating topical steroids and food elimination diet for the treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2018, 63, 2381–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spergel, B.L.; Ruffner, M.A.; Godwin, B.C.; Liacouras, C.A.; Cianferoni, A.; Gober, L.; Hill, D.A.; Brown-Whitehorn, T.F.; Chaiboonma, K.; Aceves, S.A.; et al. Improvement in eosinophilic esophagitis when using dupilumab for other indications or compassionate use. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2022, 128, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucendo, A.; Molina-Infante, J. Current treatment options and long-term outcomes in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 18, 859–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nhu, Q.; Aceves, S. Medical and dietary management of eosinophilic esophagitis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018, 121, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muir, A.; Falk, G. Eosinophilic esophagitis: A review. JAMA 2021, 326, 1310–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitt, R.; Hirano, I.; Vaezi, M. Diagnosis and treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis in adults. Am. J. Med. 2016, 129, 924–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feo-Ortega, S.; Lucendo, A. Evidence-based treatments for eosinophilic esophagitis: Insights for the clinician. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2022, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.W.; Kao, J. Eosinophilic esophagitis: Update on management and controversies. BMJ 2017, 359, j4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Infante, J. Nutritional and psychological considerations for dietary therapy in eosinophilic esophagitis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visaggi, P.; Baiano Svizzero, F.; Savarino, E. Food elimination diets in eosinophilic esophagitis: Practical tips in current management and future directions. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2023, 64, 101825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Infante, J.; Lucendo, A.J. Dietary therapy for eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, D.; Straumann, A.; Schoepfer, A.M.; Simon, H.-U. Current concepts in eosinophilic esophagitis. Allergo J. Int. 2017, 26, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, A.H.W.; Ngoi, B.; Perkins, G.B.; Wong, S.; Whitelock, G.; Hurtado, P.; Ruszkiewicz, A.; Le, T.-T.A.; Hissaria, P.; Nguyen, N.Q. Outcomes of serum food-specific immunoglobulin G4 to guide elimination diet in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 119, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawrzeńczyk, A.; Rawicka, E.; Napiórkowska-Baran, K.; Alska, E.; Bartuzi, Z. Cross-reactive aeroallergens—The main cause of food allergy. Food Agric. Immunol. 2022, 34, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckmann, J.D.; Ravi, K.; Katzka, D.A.; Davis, D.R.; See, J.A.; Geno, D.R.; Kryzer, L.A.; Alexander, J.A. Efficacy of atopy patch testing in directed dietary therapy of eosinophilic esophagitis: A pilot study. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2018, 63, 1168–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spergel, J.M.; Andrews, T.; Brown-Whitehorn, T.F.; Beausoleil, J.L.; Liacouras, C.A. Treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis with specific food elimination diet directed by a combination of skin prick and patch tests. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2005, 95, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucendo, A.J.; Molina-Infante, J. Treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis with diets. Minerva Gastroenterol. Dietol. 2020, 66, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vlieger, L.; Smolders, L.; Nuyttens, L.; Verelst, S.; Breynaert, C.; Vanuytsel, T.; Hoffman, I.; Bullens, D.M. A clinical perspective on the dietary therapies for pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis: The gap between research and daily practice. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 677859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ÁlvarezHodel, A. Utilidad del Estudio ALERGOLÓGICO por microarrays en el Diagnóstico y Tratamiento de la Esofagitis Eosinofílica. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Valladolid, Valladolid, Spain, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.W.; Haller, E.; Dellon, E.S. Dietary management of eosinophilic esophagitis: Man versus food or food versus man? Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 50, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armentia, A.; Martín, S.; Barrio, J.; Martín, B.; García, J.; Vega, J.; Sánchez, A.; Fernández, P.; Corell, A. Value of microarray allergen assay in the management of eosinophilic oesophagitis. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2015, 43, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rhijn, B.D.; van Ree, R.; Versteeg, S.A.; Vlieg-Boerstra, B.J.; Sprikkelman, A.B.; Terreehorst, I.; Smout, A.J.P.M.; Bredenoord, A.J. Birch pollen sensitization with cross-reactivity to food allergens predominates in adults with eosinophilic esophagitis. Allergy 2013, 68, 1475–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawrzeńczyk, A.; Napiórkowska-Baran, K.; Wawrzeńczyk, A.; Alska, E.; Bartuzi, Z. Panalergeny-źródło alergii pokarmowej. Alerg. Astma Immunol.-Przegląd Klin. 2019, 24, 164–169. [Google Scholar]
- Lluncor, M.; Pedrosa, M.; Cancelliere, N.; Rivero-Paparoni, D.; Burgos, A.; Fiandor, A.; Pagola, M.; Quirce, S.; Caballero, T. Molecular sensitization profile according to proton pump inhibitor response in patients with esophageal eosinophilia. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 28, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.; Shoda, T.; Wen, T.; Rothenberg, M.E. Diagnostic merits of the Eosinophilic Esophagitis Diagnostic Panel from a single esophageal biopsy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 1401–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rank, M.A.; Sharaf, R.N.; Furuta, G.T.; Aceves, S.S.; Greenhawt, M.; Spergel, J.M.; Falck-Ytter, Y.T.; Dellon, E.S.; Chachu, K.A.; Day, L.; et al. Technical review on the management of eosinophilic esophagitis: A report from the AGA Institute and the Joint Task Force on Allergy-Immunology Practice Parameters. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020, 158, 1789–1810.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilollo, J.; Rodríguez-López, E.M.; Wilkey, L.; Martin, E.K.; Spergel, J.M.; Hill, D.A. Peripheral markers of allergen-specific immune activation predict clinical allergy in eosinophilic esophagitis. Allergy 2021, 76, 3470–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slack, I.; Schwartz, J.T.; Mukkada, V.; Hottinger, S.; Abonia, J.P. Eosinophilic esophagitis: Existing and upcoming therapies in an age of emerging molecular and personalized medicine. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2020, 20, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Stucke, E.M.; Grotjan, T.M.; Kemme, K.A.; Abonia, J.P.; Putnam, P.E.; Franciosi, J.P.; Garza, J.M.; Kaul, A.; King, E.C.; et al. Molecular diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis by gene expression profiling. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 1289–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rhijn, B.D.; Vlieg-Boerstra, B.J.; Versteeg, S.A.; Akkerdaas, J.H.; van Ree, R.; Terreehorst, I.; Sprikkelman, A.B.; Verheij, J.; Smout, A.J.; Bredenoord, A.J. Evaluation of allergen-microarray-guided dietary intervention as treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 1479–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.X.; Sherrill, J.D.; Wen, T.; Plassard, A.J.; Besse, J.A.; Abonia, J.P.; Franciosi, J.P.; Putnam, P.E.; Eby, M.; Martin, L.J.; et al. MicroRNA signature in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis, reversibility with glucocorticoids, and assessment as disease biomarkers. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 1064–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, E.; Langefeld, C.; Howard, T.; Dellon, E.S. Validation of epigenetic markers for the prediction of response to topical corticosteroid treatment in eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2023, 14, e00500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markey, G.E.; Ryan, S.; Furuta, G.T.; Menard-Katcher, C.; McNamee, E. Hypoxia-inducible microRNA-155 negatively regulates epithelial barrier in eosinophilic esophagitis by suppressing tight junction claudin-7. FASEB J. 2023, 37, e23025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherrill, J.D.; Blanchard, C. Genetics of eosinophilic esophagitis. Dig Dis. 2014, 32, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucendo, A.J.; Serrano-Montalbán, B.; Arias, Á.; Redondo, O.; Tenias, J.M. Efficacy of Dietary Treatment for Inducing Disease Remission in Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 61, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, K.; Yamada, S.; Sato, H.; Zhan, J.; Shoda, T. Advances in omics data for eosinophilic esophagitis: Moving towards multi-omics analyses. J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 59, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Ghaffari, G. Biomarkers for eosinophilic esophagitis: A review. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2012, 108, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffner, M.A.; Cianferoni, A. Phenotypes and endotypes in eosinophilic esophagitis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019, 123, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherrill, J.D.; Kc, K.; Blanchard, C.; Stucke, E.M.; Kemme, K.A.; Collins, M.H.; Abonia, J.P.; Putnam, P.E.; Mukkada, V.A.; Kaul, A.; et al. Analysis and expansion of the eosinophilic esophagitis transcriptome by RNA sequencing. Genes Immun. 2014, 15, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adel-Patient, K.; Campeotto, F.; Grauso, M.; Guillon, B.; Moroldo, M.; Venot, E.; Dietrich, C.; Machavoine, F.; Castelli, F.A.; Fenaille, F.; et al. Assessment of local and systemic signature of eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) in children through multi-omics approaches. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1108895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busing, J.D.; Buendia, M.A.; Choksi, Y.; Hiremath, G.; Das, S.R. Microbiome in eosinophilic esophagitis—Metagenomic, metatranscriptomic, and metabolomic changes: A systematic review. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 731034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.J.; Marsland, B.J.; Bunyavanich, S.; O’Mahony, L.; Leung, D.Y.M.; Muraro, A.; Fleisher, T.A. The microbiome in allergic disease: Current understanding and future opportunities—2017 PRACTALL document of the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology and the European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study | Population/Design | Dietary Approach | Histologic Remission (%) | Key Findings/Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Markowitz et al., 2003 [14] | Pediatric, prospective | Elemental diet | 96 | Highest efficacy; limited by adherence and palatability. |
| Peterson et al., 2013 [15] | Adult, prospective | Elemental diet | 94 | Effective in adults; confirms antigen-driven mechanism. |
| Arias et al., 2014 [1] | Mixed, meta-analysis | Elemental vs. empiric vs. test-based | 90.8 (elemental), 72.1 (SFED), 45.5 (test-based) | Established efficacy gradient. |
| Arias et al., 2024 [4] | Mixed, meta-analysis | Elemental, SFED, 4FED, 2FED, 1FED | 94.5, 63.9, 54.7, 44.3, 46.4 respectively | Updated pooled remission rates across diets. |
| Lucendo et al., 2013 [16] | Adult, prospective | SFED | 73 | Durable remission; supports empiric diet as first-line. |
| Gonsalves et al., 2012 [17] | Adult, prospective | SFED | 64 (≤5 eos/hpf) | Significant symptom and histologic response. |
| Wolf et al., 2014 [25] | Adult, retrospective | SFED vs. targeted | 56 (SFED), 32 (targeted) | Empiric diet more effective than test-based. |
| Kagalwalla et al., 2006 [18] | Pediatric, prospective | SFED | 81 | Validated efficacy in children; feasible approach. |
| Molina-Infante et al., 2014 [19] | Adult, multicenter, prospective | 4FED | 54 | Simplified diet with moderate remission and improved adherence. |
| Molina-Infante et al., 2017 [20] | Mixed, prospective | Step-up (2 → 4 → 6 foods) | 43–79 (cumulative) | Effective while reducing unnecessary restriction. |
| Kliewer et al., 2023 [10] | Pediatric, RCT | 1-food vs. 6-food elimination | 34 (1FED), 40 (SFED) | 1FED non-inferior; better adherence and tolerability. |
| Wechsler et al., 2021 [21] | Pediatric, prospective | 1-food (milk-only) | 64 | Supports milk-driven phenotype; high compliance. |
| Kagalwalla et al., 2012 [11] | Pediatric, prospective | Milk elimination | 77 | Confirms milk as predominant trigger in EoE. |
| Zalewski et al., 2022 [22] | Adult, retrospective | SFED, long-term follow-up | 54–58 | Sustained remission; defines chronic dietary outcomes. |
| Henderson et al., 2012 [2] | Pediatric, retrospective | Elemental, SFED, test-based | 96, 81, 65 | Elemental > empiric > test-based; consistent hierarchy. |
| Cotton et al., 2017 [13] | Mixed, meta-regression | SFED ± steroids | 72 (diet), 84 (combination) | Combined approach yields higher remission. |
| Mayerhofer et al., 2023 [12] | Mixed, meta-analysis | Elemental vs. empiric vs. targeted | 90 vs. 70 vs. 45 | Confirms elemental superiority; empiric remains standard. |
| Study | Population | Testing Method(s) | Dietary Strategy | Histologic Remission (%) | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Henderson et al., 2012 [2] | Pediatric | SPT, APT | Test-directed vs. SFED | 65 (test) vs. 81 (SFED) | Empiric superior to test-directed elimination. |
| Spergel et al., 2012 [26] | Pediatric | SPT, APT | Combined testing-guided | 53–77 | Partial remission; high variability. |
| Rodríguez-Sánchez et al., 2014 [23] | Adult | sIgE, SPT, APT | sIgE-directed vs. SFED | 73 vs. 53 | No significant difference (p = 0.17). |
| Dellon et al., 2019 [24] | Adult | SPT, IgG4, CD4+ T-cell | Test-directed | <50 | Poor predictive value; limited accuracy. |
| Pesek et al., 2017 [27] | Pediatric | SPT, sIgE | Test-directed | – | Low predictive value; poor correlation with triggers. |
| Arias et al., 2014 [1] | Mixed | SPT, sIgE | Test-directed vs. SFED | 45.5 vs. 72.1 | Meta-analysis; empiric superior. |
| Pitsios et al., 2022 [3] | Mixed | SPT, APT, sIgE | Test-directed vs. empiric | 39–66 | Systematic review; low predictive accuracy. |
| Arias et al., 2024 [4] | Mixed | SPT, sIgE | Test-directed vs. empiric | 39.5 vs. 63.9 | Large meta-analysis; empiric consistently superior. |
| Framework | Approach | Example Protocol | Strengths | Limitations | Best Suited For | Key References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step-down | Begin broad, then liberalize | Start with SFED → sequential reintroduction | High initial remission; systematic | Burdensome initially; risk of over-restriction | Adults; severe phenotypes | [4] |
| Step-up | Begin narrow, then escalate | Start with 1–2 foods (milk ± wheat) → add if no remission | Minimizes unnecessary restriction; child-friendly | May require multiple endoscopies; slower trigger identification | Pediatrics; nutritionally vulnerable | [9,24,26] |
| Intervention Type | No. of Studies | Reported Remission Rate (%) | Diagnostic Accuracy (vs. Known Triggers) | Key References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRD/test-directed diet | 4 | 39.5–64 | 53–75 | [5,25,28,30,32] |
| Empiric six-food elimination (SFED) | 3 | 63.9–73 | Not applicable | [1,4,29] |
| Elemental diet | 4 | 90.8–96 | Not applicable | [4,29,30] |
| Combination or immune-guided (T-cell/IgG4) | 2 | 45–81.8 | 53–100 | [25,31,32] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wawrzeńczyk, A.; Napiórkowska-Baran, K.; Szota, M.; Treichel, P.; Durślewicz, J.; Bartuzi, Z. Dietary Management of Eosinophilic Esophagitis in the Era of Molecular Diagnostics: The Role and Limitations of Component-Resolved Diagnostics—A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3588. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17223588
Wawrzeńczyk A, Napiórkowska-Baran K, Szota M, Treichel P, Durślewicz J, Bartuzi Z. Dietary Management of Eosinophilic Esophagitis in the Era of Molecular Diagnostics: The Role and Limitations of Component-Resolved Diagnostics—A Narrative Review. Nutrients. 2025; 17(22):3588. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17223588
Chicago/Turabian StyleWawrzeńczyk, Adam, Katarzyna Napiórkowska-Baran, Maciej Szota, Paweł Treichel, Justyna Durślewicz, and Zbigniew Bartuzi. 2025. "Dietary Management of Eosinophilic Esophagitis in the Era of Molecular Diagnostics: The Role and Limitations of Component-Resolved Diagnostics—A Narrative Review" Nutrients 17, no. 22: 3588. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17223588
APA StyleWawrzeńczyk, A., Napiórkowska-Baran, K., Szota, M., Treichel, P., Durślewicz, J., & Bartuzi, Z. (2025). Dietary Management of Eosinophilic Esophagitis in the Era of Molecular Diagnostics: The Role and Limitations of Component-Resolved Diagnostics—A Narrative Review. Nutrients, 17(22), 3588. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17223588







