Impact of Diet and Maternal Obesity on Human Milk Hyaluronan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
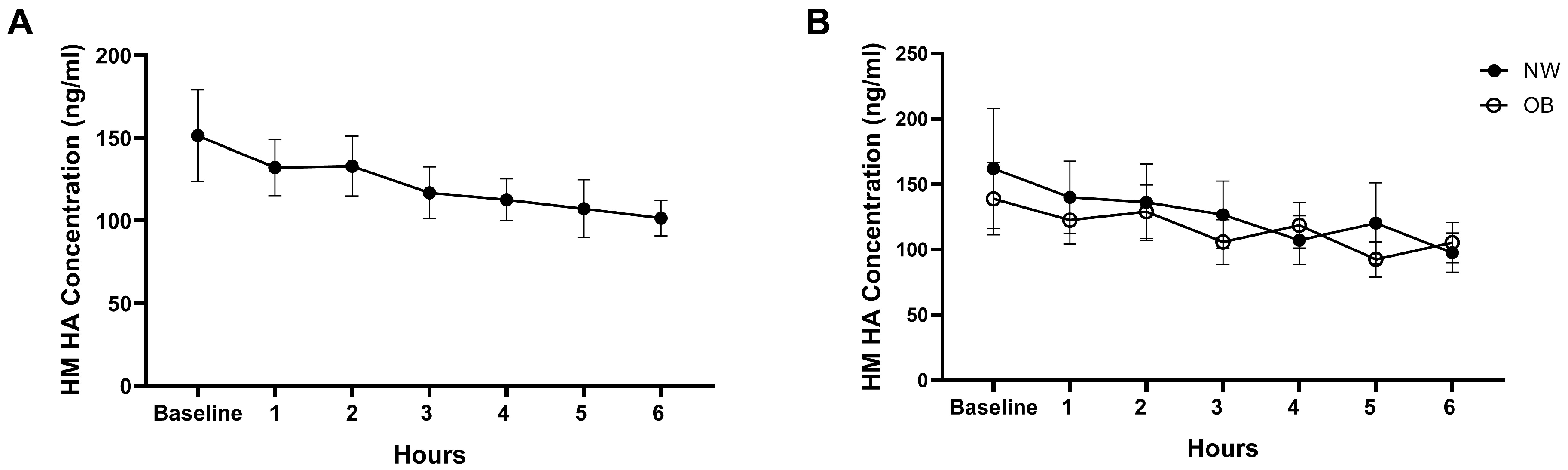
3.2. Effect of Acute Maternal Diet on HM HA Concentrations
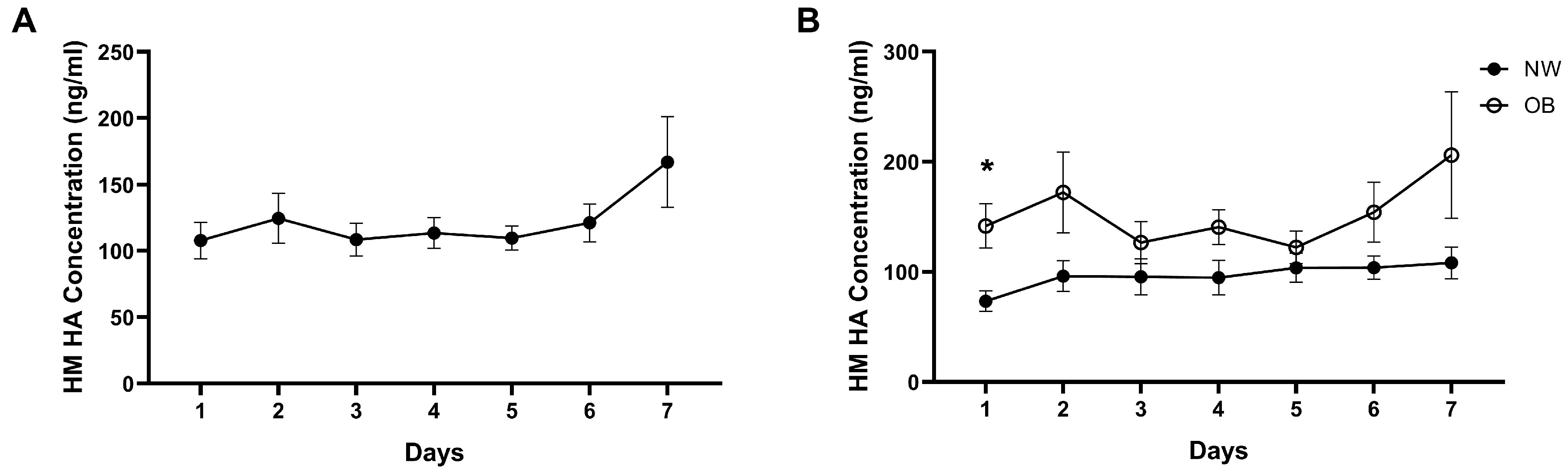
3.3. Temporal Stability of HM HA Concentrations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HA | Hyaluronan |
| SEM | Standard error of mean |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| OB | Obese |
| NW | Normal weight |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| HM | Human milk |
| HMO | Human milk oligosaccharide |
| NEC | Necrotizing enterocolitis |
| OUHSC | University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| IL | Interleukin |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa beta |
| HAS | Hyaluronan synthase |
| UDP-GlcNAc | Uridine diphosphate N-acetylglucosamine |
| HYAL | Hyaluronidase |
| CEMIP | Cell migration-inducing hyaluronidase |
| TMEM2 | Transmembrane protein 2 |
| TLR4 | Toll-like receptor 4 |
| ZO-1 | Zonula occludens 1 |
References
- Donovan, S.M.; Aghaeepour, N.; Andres, A.; Azad, M.B.; Becker, M.; Carlson, S.E.; Järvinen, K.M.; Lin, W.; Lönnerdal, B.; Slupsky, C.M.; et al. Evidence for human milk as a biological system and recommendations for study design-a report from “Breastmilk Ecology: Genesis of Infant Nutrition (BEGIN)” Working Group 4. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 117 (Suppl. S1), S61–S86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwaydi, M.A.; Lai, C.T.; Warden, A.H.; Perrella, S.L.; McEachran, J.L.; Wlodek, M.E.; Geddes, D.T.; Gridneva, Z. Investigation of Relationships between Intakes of Human Milk Total Lipids and Metabolic Hormones and Infant Sex and Body Composition. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, E.; Yang, N.; Muhlhausler, B.S.; Leghi, G.E.; Netting, M.J.; Elmes, M.J.; Langley-Evans, S.C. Acute changes to breast milk composition following consumption of high-fat and high-sugar meals. Matern. Child. Nutr. 2021, 17, e13168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallam, M.C.; Barile, D.; Meyrand, M.; German, J.B.; Reimer, R.A. Maternal high-protein or high-prebiotic-fiber diets affect maternal milk composition and gut microbiota in rat dams and their offspring. Obesity 2014, 22, 2344–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fields, D.A.; Demerath, E.W. Relationship of insulin, glucose, leptin, IL-6 and TNF-α in human breast milk with infant growth and body composition. Pediatr. Obes. 2012, 7, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, P.K.; Hampson, H.E.; Schmidt, K.A.; Alderete, T.L.; Furst, A.; Yonemitsu, C.; Demerath, E.; Goran, M.I.; Fields, D.A.; Bode, L. Stability of Human-Milk Oligosaccharide Concentrations Over 1 Week of Lactation and Over 6 Hours Following a Standard Meal. J. Nutr. 2022, 152, 2727–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Siqueira, C.D.; Borges, L.; Dal Mora, T.; Saleh, N.A.; Alves, E.S.; Wopereis, S.; Mendes, B.G.; de Moraes, A.C.R.; Hatanaka, E.; Filippin-Monteiro, F.B. Early postnatal effects of maternal obesity on breast milk composition and breastfeeding outcomes. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2025, 65, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isganaitis, E.; Venditti, S.; Matthews, T.J.; Lerin, C.; Demerath, E.W.; Fields, D.A. Maternal obesity and the human milk metabolome: Associations with infant body composition and postnatal weight gain. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 110, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saben, J.L.; Sims, C.R.; Piccolo, B.D.; Andres, A. Maternal adiposity alters the human milk metabolome: Associations between nonglucose monosaccharides and infant adiposity. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 112, 1228–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinska-Pukos, M.A.; Kopiasz, Ł.; Hamulka, J. The Effect of Maternal Overweight/Obesity on Serum and Breastmilk Leptin, and Its Associations with Body Composition, Cardiometabolic Health Indices, and Maternal Diet: The BLOOM Study. Metabolites 2024, 14, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, P.K.; Plows, J.F.; Demerath, E.W.; Fields, D.A. Carbohydrate composition in breast milk and its effect on infant health. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2020, 23, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadr Dadres, G.; Whitaker, K.M.; Haapala, J.L.; Foster, L.; Smith, K.D.; Teague, A.M.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; Kharbanda, E.O.; McGovern, P.M.; Schoenfuss, T.C.; et al. Relationship of Maternal Weight Status Before, During, and After Pregnancy with Breast Milk Hormone Concentrations. Obesity 2019, 27, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenna, J.T.; Varamini, B.; Jensen, R.G.; Diersen-Schade, D.A.; Boettcher, J.A.; Arterburn, L.M. Docosahexaenoic and arachidonic acid concentrations in human breast milk worldwide. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 1457–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravi, F.; Wiens, F.; Decarli, A.; Dal Pont, A.; Agostoni, C.; Ferraroni, M. Impact of maternal nutrition on breast-milk composition: A systematic review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 646–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouhse, J.M.; Yang, K.; More-Bayona, J.; Gao, Y.; Goruk, S.; Plastow, G.; Field, C.J.; Barreda, D.R.; Willing, B.P. Neonatal Exposure to Amoxicillin Alters Long-Term Immune Response Despite Transient Effects on Gut-Microbiota in Piglets. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockway, M.M.; Daniel, A.I.; Reyes, S.M.; Gauglitz, J.M.; Granger, M.; McDermid, J.M.; Chan, D.; Refvik, R.; Sidhu, K.K.; Musse, S.; et al. Human Milk Bioactive Components and Child Growth and Body Composition in the First 2 Years: A Systematic Review. Adv. Nutr. 2024, 15, 100127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; de la Motte, C.A. The Role of Hyaluronan Treatment in Intestinal Innate Host Defense. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burge, K.; Bergner, E.; Gunasekaran, A.; Eckert, J.; Chaaban, H. The Role of Glycosaminoglycans in Protection from Neonatal Necrotizing Enterocolitis: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.; Huang, E.; West, G.A.; Mrdjen, M.; McMullen, M.R.; de la Motte, C.; Nagy, L.E. 35kDa hyaluronan ameliorates ethanol driven loss of anti-microbial defense and intestinal barrier integrity in a TLR4-dependent manner. Matrix Biol. 2023, 115, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, S.P.; Obery, D.R.; Nickerson, K.P.; Petrey, A.C.; McDonald, C.; de la Motte, C.A. Multifunctional Role of 35 Kilodalton Hyaluronan in Promoting Defense of the Intestinal Epithelium. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2018, 66, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, D.R.; Kessler, S.P.; Rho, H.K.; Cowman, M.K.; de la Motte, C.A. Specific-sized hyaluronan fragments promote expression of human β-defensin 2 in intestinal epithelium. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 30610–30624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, D.R.; Rho, H.K.; Kessler, S.P.; Amin, R.; Homer, C.R.; McDonald, C.; Cowman, M.K.; de la Motte, C.A. Human milk hyaluronan enhances innate defense of the intestinal epithelium. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 29090–29104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigetti, D.; Genasetti, A.; Karousou, E.; Viola, M.; Moretto, P.; Clerici, M.; Deleonibus, S.; De Luca, G.; Hascall, V.C.; Passi, A. Proinflammatory cytokines induce hyaluronan synthesis and monocyte adhesion in human endothelial cells through hyaluronan synthase 2 (HAS2) and the nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 24639–24645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigetti, D.; Deleonibus, S.; Moretto, P.; Karousou, E.; Viola, M.; Bartolini, B.; Hascall, V.C.; Tammi, M.; De Luca, G.; Passi, A. Role of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) and O-GlcNAcylation of hyaluronan synthase 2 in the control of chondroitin sulfate and hyaluronan synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 35544–35555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckart, E.K.; Peck, J.D.; Kharbanda, E.O.; Nagel, E.M.; Fields, D.A.; Demerath, E.W. Infant sex differences in human milk intake and composition from 1- to 3-month post-delivery in a healthy United States cohort. Ann. Hum. Biol. 2021, 48, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, P.K.; Fields, D.A.; Demerath, E.W.; Fujiwara, H.; Goran, M.I. High-Fructose Corn-Syrup-Sweetened Beverage Intake Increases 5-Hour Breast Milk Fructose Concentrations in Lactating Women. Nutrients 2018, 10, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racette, S.B.; Weiss, E.P.; Schechtman, K.B.; Steger-May, K.; Villareal, D.T.; Obert, K.A.; Holloszy, J.O.; Washington University School of Medicine CALERIE Team. Influence of Weekend Lifestyle Patterns on Body Weight. Obesity 2008, 16, 1826–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, R. Weekend-weekday differences in diet among U.S. adults, 2003–2012. Ann. Epidemiol. 2016, 26, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turicchi, J.; O’Driscoll, R.; Horgan, G.; Duarte, C.; Palmeira, A.L.; Larsen, S.C.; Heitmann, B.L.; Stubbs, J. Weekly, seasonal and holiday body weight fluctuation patterns among individuals engaged in a European multi-centre behavioural weight loss maintenance intervention. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romo, M.; López-Vicario, C.; Pérez-Romero, N.; Casulleras, M.; Martínez-Puchol, A.I.; Sánchez, B.; Flores-Costa, R.; Alcaraz-Quiles, J.; Duran-Güell, M.; Ibarzábal, A.; et al. Small fragments of hyaluronan are increased in individuals with obesity and contribute to low-grade inflammation through TLR-mediated activation of innate immune cells. Int. J. Obes. 2022, 46, 1960–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witschen, P.M.; Elfstrum, A.K.; Nelson, A.C.; Schwertfeger, K.L. Characterization of Hyaluronan Localization in the Developing Mammary Gland and Mammary Tumors. J. Mammary Gland. Biol. Neoplasia 2023, 28, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, K.M. Association of maternal obesity before conception with poor lactation performance. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2007, 27, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacaru, S.V.; Brett, B.E.; Eckermann, H.; de Weerth, C. Determinants of maternal breast milk cortisol increase: Examining dispositional and situational factors. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2023, 158, 106385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammarco, G.; Shalaby, M.; Elangovan, S.; Petti, L.; Roda, G.; Restelli, S.; Arena, V.; Ungaro, F.; Fiorino, G.; Day, A.J.; et al. Hyaluronan Accelerates Intestinal Mucosal Healing through Interaction with TSG-6. Cells 2019, 8, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowman, M.K.; Lee, H.G.; Schwertfeger, K.L.; McCarthy, J.B.; Turley, E.A. The Content and Size of Hyaluronan in Biological Fluids and Tissues. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valachová, K.; Hassan, M.E.; Šoltés, L. Hyaluronan: Sources, Structure, Features and Applications. Molecules 2024, 29, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Amin, R.; Ye, X.; de la Motte, C.A.; Cowman, M.K. Determination of hyaluronan molecular mass distribution in human breast milk. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 474, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patient Demographics | NW (n = 19) | OB (n = 16) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, y (range) | 30.0 ± 3.3 (22–34) | 30.9 ± 4.0 (25–38) | 0.41 |
| Parity | 2.29 ± 0.8 | 1.92 ± 1.08 | 0.35 |
| Pre-pregnancy Weight (kg) | 59.3 ± 5.9 | 86.5 ± 19.8 | <0.0001 |
| Pre-pregnancy Height (cm) | 163 ± 6.3 | 157 ± 9.8 | 0.03 |
| Pre-pregnancy BMI (kg/m2) | 22.1 ± 1.4 | 34.3 ± 4.6 | <0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hoover, C.; Moshal, K.S.; Eckert, J.V.; Wilson, A.P.; Burge, K.Y.; Fields, D.A.; Chaaban, H. Impact of Diet and Maternal Obesity on Human Milk Hyaluronan. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3560. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17223560
Hoover C, Moshal KS, Eckert JV, Wilson AP, Burge KY, Fields DA, Chaaban H. Impact of Diet and Maternal Obesity on Human Milk Hyaluronan. Nutrients. 2025; 17(22):3560. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17223560
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoover, Christopher, Karni S. Moshal, Jeffrey V. Eckert, Adam P. Wilson, Kathryn Y. Burge, David A. Fields, and Hala Chaaban. 2025. "Impact of Diet and Maternal Obesity on Human Milk Hyaluronan" Nutrients 17, no. 22: 3560. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17223560
APA StyleHoover, C., Moshal, K. S., Eckert, J. V., Wilson, A. P., Burge, K. Y., Fields, D. A., & Chaaban, H. (2025). Impact of Diet and Maternal Obesity on Human Milk Hyaluronan. Nutrients, 17(22), 3560. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17223560






