Abstract
Background/Objectives: Caffeine is widely recognized as an ergogenic aid, yet evidence regarding its acute effects on repeated sprint ability (RSA) remains inconsistent. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the effects of acute caffeine ingestion on RSA across different populations, exercise modalities, and dosage levels. Methods: A comprehensive literature search was conducted in the PubMed, EBSCO, Cochrane Library, Web of science, and Scopus databases. Data were pooled using the weighted mean difference (WMD) with 95% confidence interval (CI). Results: Thirteen studies met the inclusion criteria. Acute caffeine ingestion significantly enhanced RSA peak power output (PPO) compared with placebo (WMD, 5.28; 95% CI, 2.49 to 8.07; p = 0.0002). Subgroup analyses revealed significant improvements in both males (WMD, 13.11; 95% CI, 5.63 to 20.59; p = 0.0006) and females (WMD, 4.03; 95% CI, 1.10 to 6.97; p = 0.007). A caffeine dose of ≥6 mg/kg body weight (BW) produced greater ergogenic benefits (WMD, 6.67; 95% CI, 3.32 to 10.02; p < 0.0001) than lower doses (WMD, 2.16; 95% CI, −2.87 to 7.19; p = 0.40). Moreover, a more pronounced enhancement was observed in cycling-based RSA (WMD, 8.77; 95% CI, 1.98 to 15.56; p = 0.01) compared with running-based protocols (WMD, 4.56; 95% CI, 1.58 to 7.55; p = 0.003). Conclusions: Acute caffeine ingestion significantly enhances RSA, particularly at doses ≥6 mg/kg BW. This effect is consistent across both male and female participants, with no statistically significant sex difference observed in the pooled analysis. These findings reinforce caffeine’s role as an effective ergogenic aid for optimizing high-intensity intermittent performance, with the strongest benefits evident in cycling exercise.
1. Introduction
Caffeine, the primary bioactive compound found in widely consumed beverages such as coffee, tea, and cocoa, acts as a central nervous system stimulant and adenosine receptor antagonist [1]. It is rapidly absorbed and exerts diverse physiological effects, including reducing fatigue, enhancing lipolysis, and increasing alertness [2,3,4]. Although generally considered safe at typical consumption levels, excessive intake may cause adverse effects such as anxiety, insomnia, and gastrointestinal discomfort [5,6,7]. Owing to its pronounced physiological actions, caffeine has long been a subject of extensive research in the context of performance enhancement and remains one of the most widely used legal psychoactive substances worldwide.
In the field of sports science, caffeine is recognized as a potent ergogenic aid capable of augmenting athletic performance through multiple mechanisms. Early studies demonstrated that caffeine enhances aerobic endurance primarily by promoting fat oxidation and conserving muscle glycogen stores [8,9]. Subsequent research extended these observations, indicating that caffeine may also improve anaerobic endurance and high-intensity exercise performance through multiple mechanisms, including reduced pain perception, enhanced muscle contractility, and improved neural drive [10,11]. Notably, caffeine was only removed from the World Anti-Doping Agency’s list of prohibited substances in 2004, thereby legitimizing its use as an ergogenic aid among elite athletes. Since then, caffeine-containing energy drinks have emerged as a popular vehicle for delivering this ergogenic aid. These beverages typically combine substantial amounts of caffeine with additional ingredients such as carbohydrates, B vitamins, and taurine, thereby providing an auxiliary energy source during exercise [12,13]. However, the primary ergogenic benefits are largely attributed to their high caffeine content, with nearly half of professional athletes reportedly using caffeine-based supplements to enhance performance [14]. According to the International Society of Sports Nutrition, caffeine consumption approximately 60 min prior to exercise can effectively improve various aspects of athletic performance, including endurance capacity, high-intensity effort, and muscular strength [15].
Repeated sprint ability (RSA) is a performance parameter that depends primarily on the adenosine triphosphate-creatine phosphate (ATP-CP) energy system and plays a crucial role in high-intensity intermittent sports such as basketball, soccer, and rugby [16,17,18,19]. However, the ergogenic potential of acute caffeine ingestion for improving RSA remains controversial. Several studies have reported that acute caffeine supplementation enhances RSA by increasing both peak power output (PPO) and mean power output (MPO) [20,21]. In contrast, other studies have failed to detect such benefits. For instance, Bernardo et al. [22] observed no significant differences in PPO or MPO between caffeine and placebo conditions in male participants. Similarly, Houda et al. [23] reported that an acute caffeine dose of 3 mg/kg body weight (BW) did not significantly influence RSA in young female athletes, whereas higher doses of 6 or 9 mg/kg BW improved performance by reducing both the fastest and mean sprint time, suggesting a potential dose–response effect. Conversely, another research demonstrated that even a 3 mg/kg BW caffeine dose was sufficient to enhance both PPO and MPO during repeated sprints [24]. Collectively, these inconsistent findings indicate that the ergogenic effects of caffeine on RSA remain equivocal and may be influenced by interindividual differences in caffeine sensitivity [25].
Existing meta-analyses examining the effects of acute caffeine ingestion on RSA have also produced divergent conclusions. For instance, Gomez-Bruton et al. [26] reported no significant effect of caffeine on RSA in females athletes, whereas López-Torres et al. [27] demonstrated a positive ergogenic effect. Similarly, Lopes-Silva et al. [28] found that acute caffeine ingestion did not significantly improve RSA, while another meta-analysis revealed that caffeine markedly enhanced high-intensity performance in elite athletes during both real or simulated competitions [29]. These discrepancies among meta-analytic findings may stem from methodological limitations, such as the inclusion of only female participants, the absence of dosage stratification, and inadequate control for habitual caffeine consumption.
Therefore, to address these inconsistencies and methodological gaps, the present systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to comprehensively evaluate the effects of acute caffeine ingestion on RSA.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
This systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Evaluation and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) guidelines [30]. The study protocol was prospectively registered in the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO; registration number CRD420251150247).
2.2. Search Strategy
A comprehensive literature search was performed in PubMed, EBSCO, Cochrane Library, Web of science, and Scopus databases from their inception to 6 September 2025. The search strategy employed the keywords and MESH terms “caffeine” and “repeated sprint ability” (Table S1). Additionally, reference lists of the identified systematic reviews and meta-analyses were manually searched to identify potential eligible studies. Article screening and selection were independently conducted by two authors (Y.W. and W.S.).
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
The inclusion criteria were established based on the Population, Intervention, Comparison, and Outcome (PICO) principle: (1) Population: human participants; (2) Intervention: administration of acute, rather than long-term, caffeine interventions; (3) Comparison: evaluation of acute effects between caffeine ingestion and placebo control groups; and (4) Outcome: the primary endpoint was PPO.
PPO was assessed using cycle ergometer, while fastest sprint time was measured during running-based tests. Where necessary, fastest sprint time data were converted to PPO using the following equation [31]:
Power output = (body mass (kg) × distance (m)2)/time (s)3
Exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) non-English publications; (2) conference papers; (3) review articles; and (4) animal or in vitro studies.
2.4. Data Extraction
Data extraction was independently conducted by two authors (Y.W. and W.S.) using a predefined template. The extracted information included: (1) study characteristics (first author, publication year, country); (2) subject characteristics (age, sex, sample size); (3) intervention characteristics (caffeine dosage and timing); and (4) outcome characteristics (exercise modality, PPO, fastest sprint time).
2.5. Methodological Quality Assessment
The methodological quality of the included studies was evaluated using the Cochrane risk of bias tool [1,32] and further evaluated with the Physiotherapy Evidence Database (PEDro) scale. The Cochrane risk of bias tool evaluates five domains of potential bias, including selection bias, performance bias, detection bias, attrition bias, and reporting bias. Each domain rated as having a low, unclear, or high risk of bias. The PEDro scale comprises 11 items, and studies scoring <4 points, 4–5 points, 6–8 points, and ≥9 points were categorized as poor, average, good, and excellent quality, respectively [33].
2.6. Certainty Assessment
The Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) approach was used to assess the certainty of evidence across outcomes, with ratings categorized as high, moderate, low, or very low. The GRADE assessment was conducted two independent authors (Y.W. and W.S.).
2.7. Statistical Analysis
From each included study, the mean and standard deviation (SD) of RSA-related variables were extracted for both caffeine and placebo conditions. Data were pooled using fixed-effects models to obtain the weighted mean difference (WMD) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). When studies reported standard errors (SEs) and 95% CIs instead of SDs, the corresponding SD was estimated [34,35].
Heterogeneity was assessed using the I2 statistic, in cases of substantial heterogeneity, subgroup analysis and sensitivity analysis were conducted to explore potential sources of variation [36,37]. Subgroup analyses examined the influence of (1) caffeine dosage (<6 vs. ≥6 mg/kg BW), (2) exercise modality (cycling vs. running), and (3) participant sex (male vs. female).
Forest plots were generated using RevMan software (Version 5.4), while sensitivity analysis, funnel plot, and meta-regression were performed using Stata software (Version 15.0). Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Studies Selection
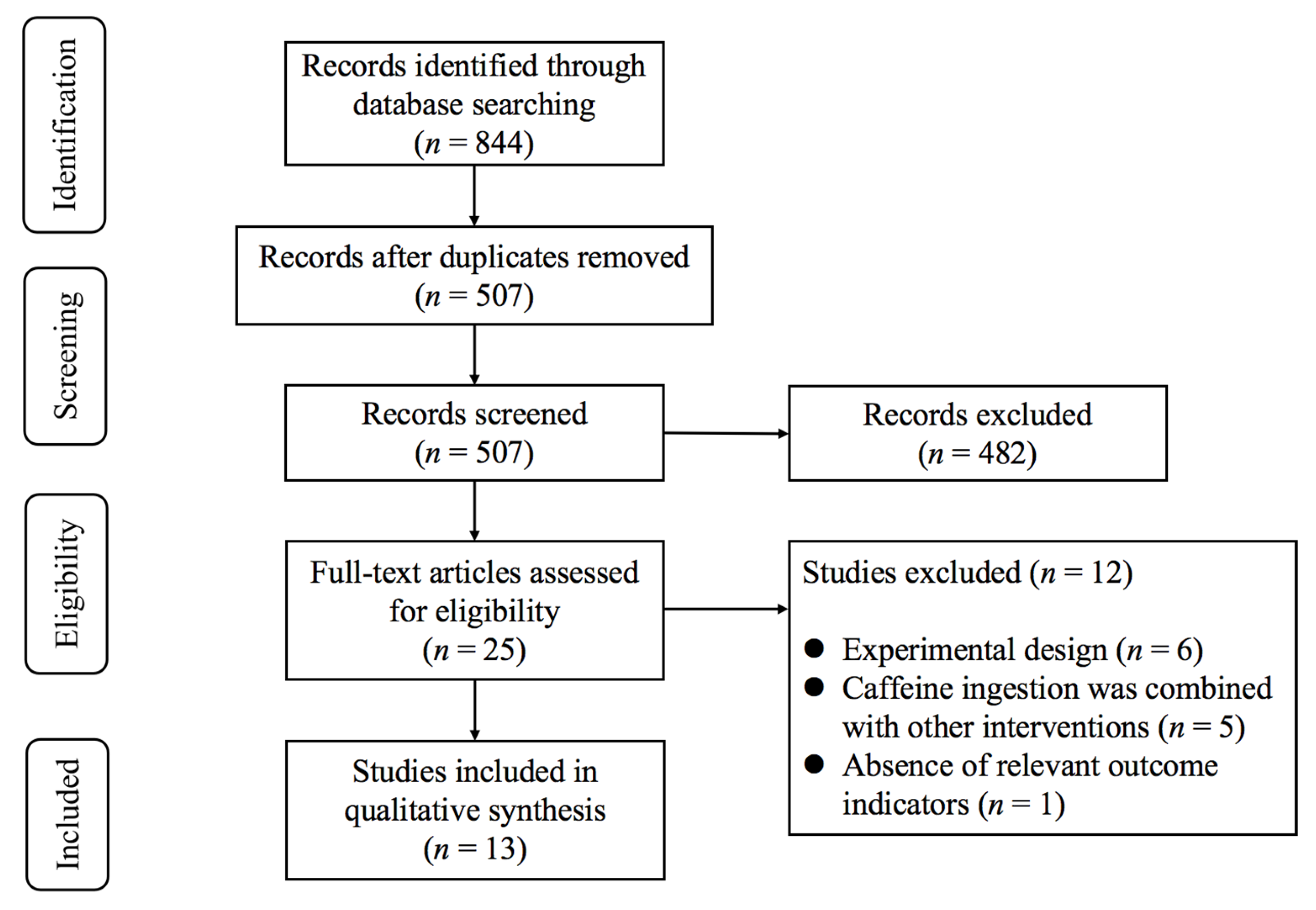
As illustrated in Figure 1, the initial database search identified 844 records. After removing duplicates, 507 studies remained for title and abstract screening. Following this process, 25 potentially eligible studies were retained for full-text evaluation. Upon detailed review, 12 studies were excluded for the following reasons: (1) experimental design (n = 6); (2) caffeine ingestion was combined with other interventions (n = 5); (3) absence of relevant outcome indicators (n = 1). Finally, 13 studies [10,11,12,13,14,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36] met the inclusion criteria.
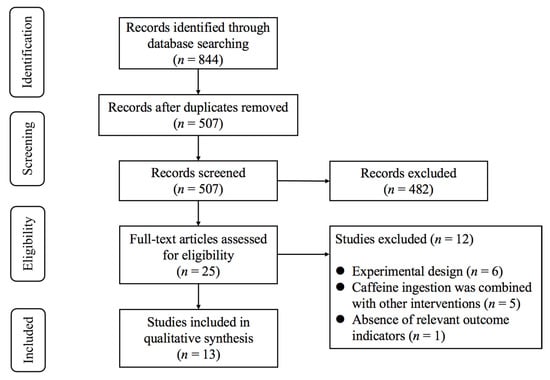
Figure 1.
PRISMA flowchart of study selection.
3.2. Characteristics of the Included Studies
The characteristics of the included studies and participants are summarized in Table 1. Among the 13 studies, 2 studies [38,39] employed a low caffeine dosage (<6 mg/kg BW), 7 studies [21,22,40,41,42,43,44] used a high caffeine dosage (≥6 mg/kg BW), and 4 studies [20,23,24,45] examined both low and high dosages. Regarding participant characteristics, six studies [21,22,24,38,42,44] involved only males, 6 studies [20,23,40,41,43,45] included only females, and 1 study [39] involved participants of both sexes. Eight studies [21,22,24,38,39,42,43,45] reported PPO data assessed via cycling tests, whereas 5 studies [20,23,40,41,44] provided data for fastest sprint time measured using running tests. Caffeine dosage ranged from 3 to 9 mg/kg BW, with ingestion typically occurring 60 min prior to testing.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the studies included in this meta-analysis.
3.3. Risk of Bias
The risk of bias assessment using the Cochrane risk of bias tool identified two studies as having a high risk of reporting bias, while the remaining studies were generally classified as low risk across the domains of selection, performance, detection, attrition, and reporting biases (Figure S1). Based on the PEDro scale, 13 studies [20,21,22,23,24,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45] were rated as excellent quality (Table S2).
3.4. Meta-Analysis
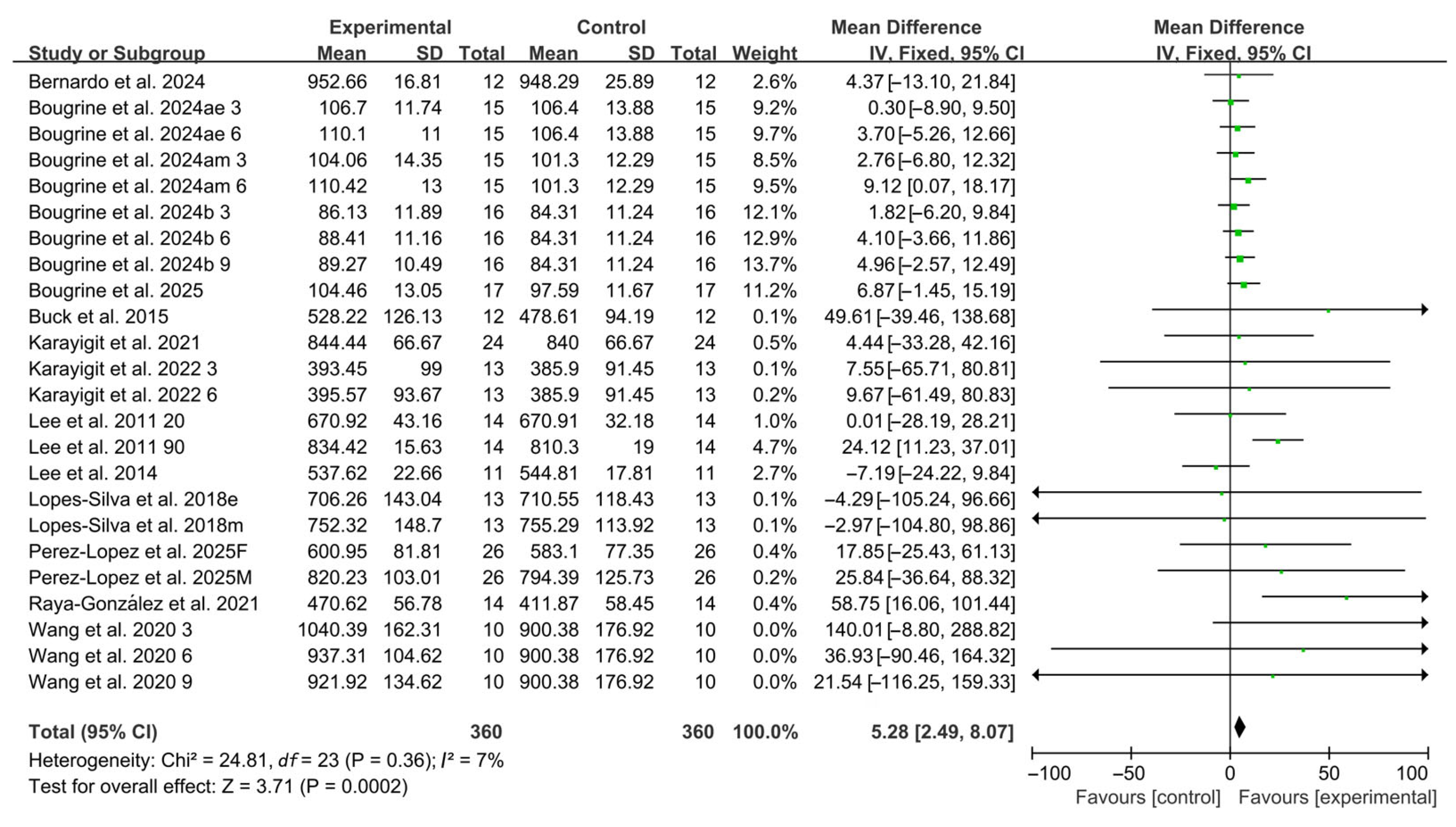
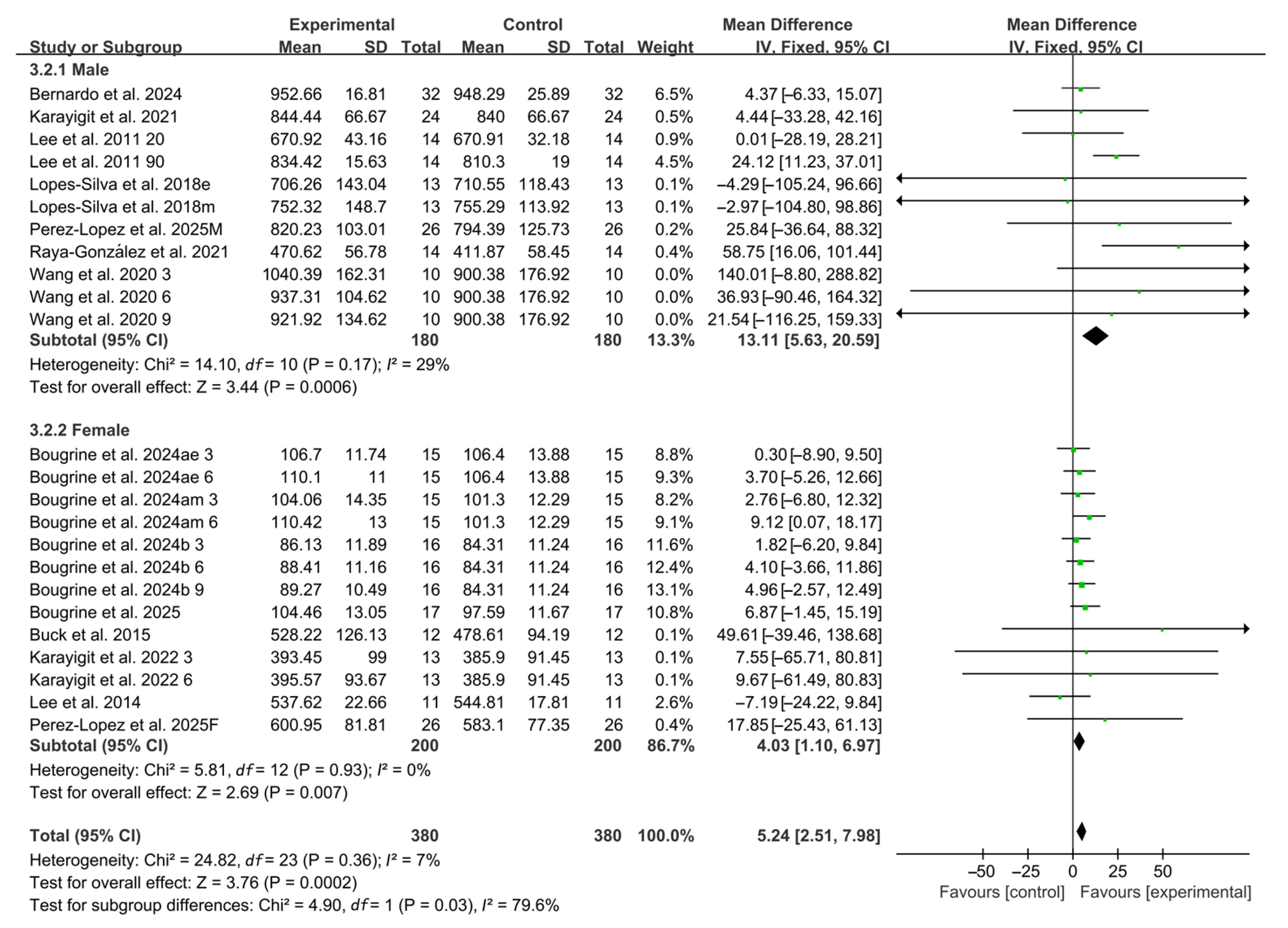
Compared with placebo, acute caffeine ingestion significantly enhanced RSA (WMD, 5.28, 95% CI, 2.49 to 8.07, p = 0.0002, I2 = 7%, Figure 2).
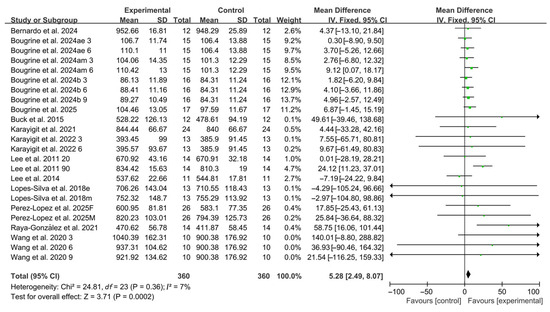
Figure 2.
Meta-analysis results of the effects of acute caffeine ingestion on RSA [20,21,22,23,24,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45]. Articles by the same author are distinguished by the suffixes “a” and “b”. Morning and evening sessions are denoted by “m” and “e”, respectively; participant sex by “M” (male) and “F” (female); caffeine dose by “3”, “6”, or “9” (mg/kg body weight); and inter-interval rest duration by “20” or “90” (min).
3.5. Subgroup Analysis
3.5.1. Caffeine Dosage
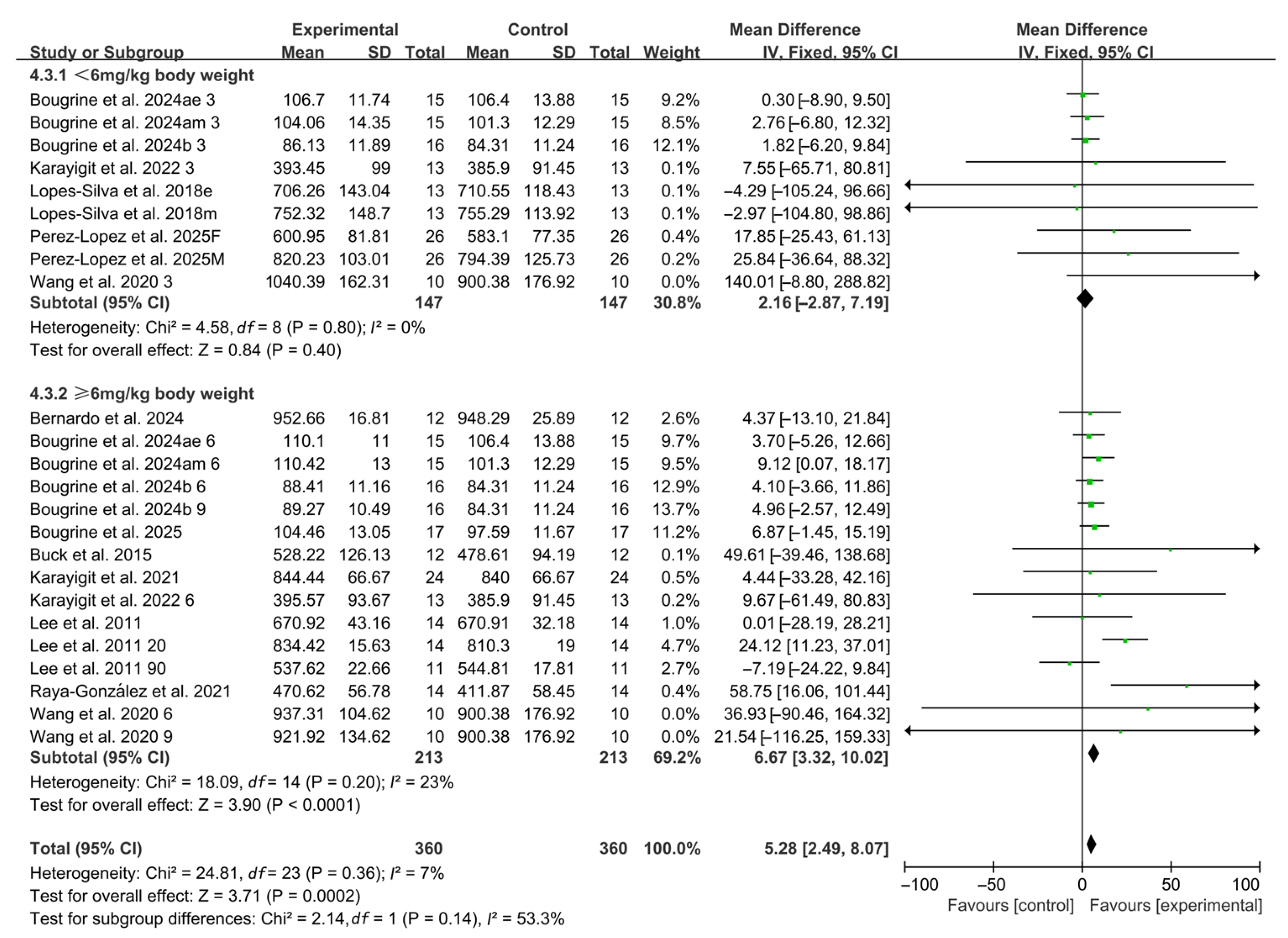
When stratified by caffeine dosage, 9 studies investigated low doses (<6 mg/kg BW), including 7 studies using 3 mg/kg BW and 2 studies using 5 mg/kg BW. No significant improvements in RSA were observed within this subgroup (WMD, 2.16, 95% CI, −2.87 to 7.19, p = 0.40, I2 = 0%, Figure 3). In contrast, 15 studies assessed high doses, with 13 studies using 6 mg/kg BW and 2 studies using 9 mg/kg BW. In this subgroup, caffeine ingestion produced a significant improvement in RSA (WMD, 6.67, 95% CI, 3.32 to 10.02, p < 0.0001, I2 = 23%, Figure 3).
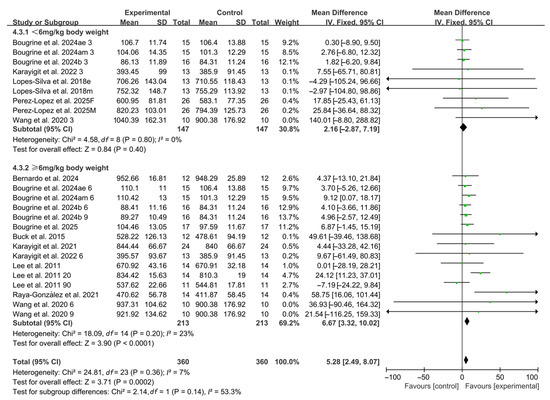
Figure 3.
Meta-analysis results of the effects of caffeine dosage on RSA [20,21,22,23,24,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45]. Articles by the same author are distinguished by the suffixes “a” and “b”. Morning and evening sessions are denoted by “m” and “e”, respectively; participant sex by “M” (male) and “F” (female); caffeine dose by “3”, “6”, or “9” (mg/kg body weight); and inter-interval rest duration by “20” or “90” (min).
3.5.2. Exercise Modality
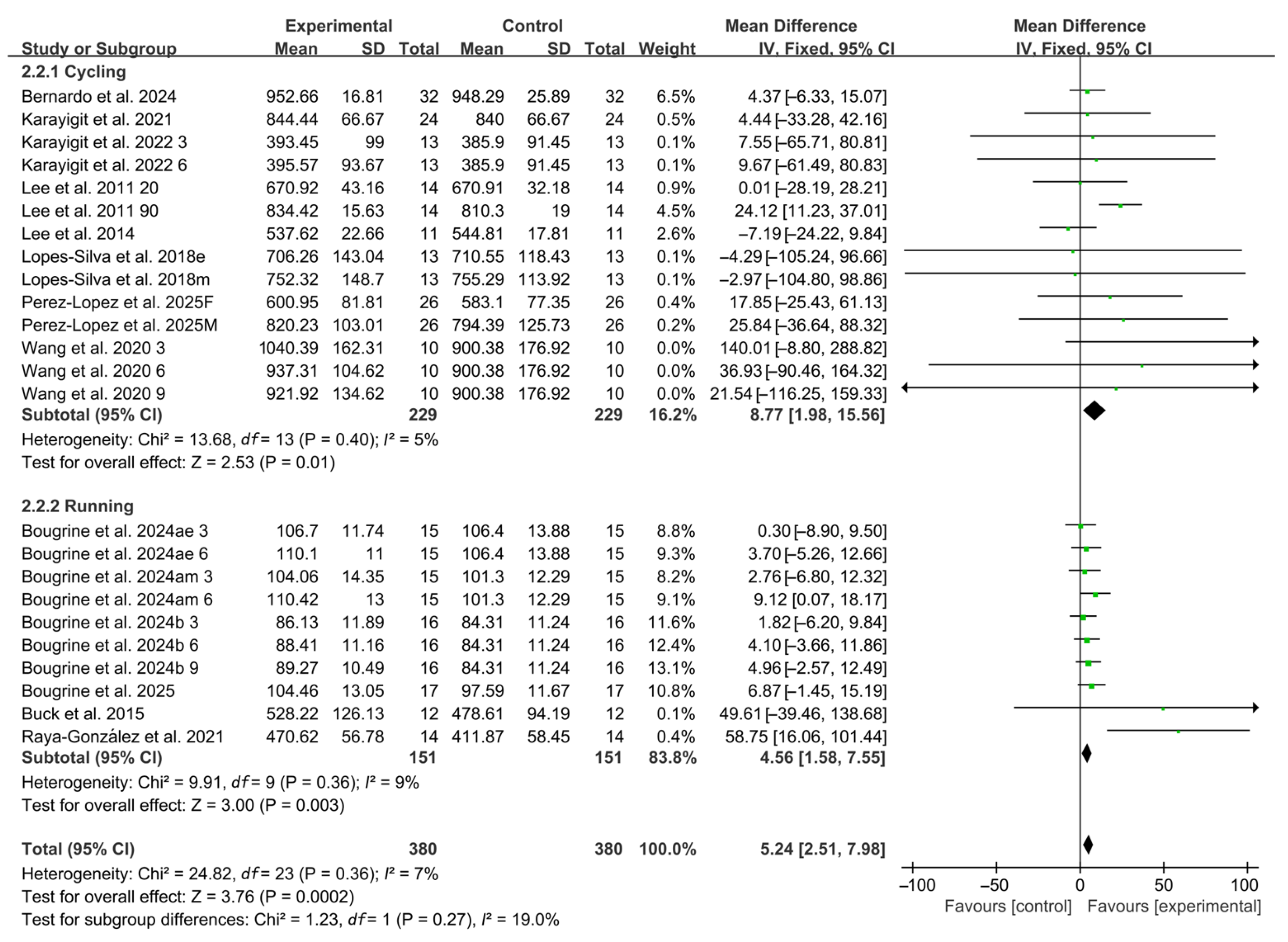
When stratified by exercise modality, 14 studies employed cycling protocols and 10 studies used running-based tests. Significant improvements in RSA were observed for both modalities (cycling: WMD, 8.77, 95% CI, 1.98 to 15.56, p = 0.01, I2 = 5%; running: WMD, 4.56, 95% CI, 1.58 to 7.55, p = 0.003, I2 = 9%, Figure 4), with running-based RSA exhibiting a more pronounced effect.
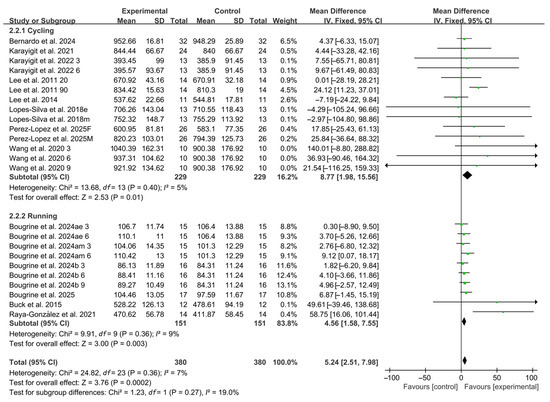
Figure 4.
Meta-analysis results of the effects of exercise modality on RSA [20,21,22,23,24,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45]. Articles by the same author are distinguished by the suffixes “a” and “b”. Morning and evening sessions are denoted by “m” and “e”, respectively; participant sex by “M” (male) and “F” (female); caffeine dose by “3”, “6”, or “9” (mg/kg body weight); and inter-interval rest duration by “20” or “90” (min).
3.5.3. Participant Sex
Subgroup analyses by participant sex revealed that caffeine ingestion significantly enhanced RSA in both male and female (male: WMD, 13.11, 95% CI, 5.63 to 20.59, p = 0.0006, I2 = 29%; female: WMD, 4.03, 95% CI, 1.10 to 6.97, p = 0.007, I2 = 0%, Figure 5), with male participants exhibiting a more pronounced effect.
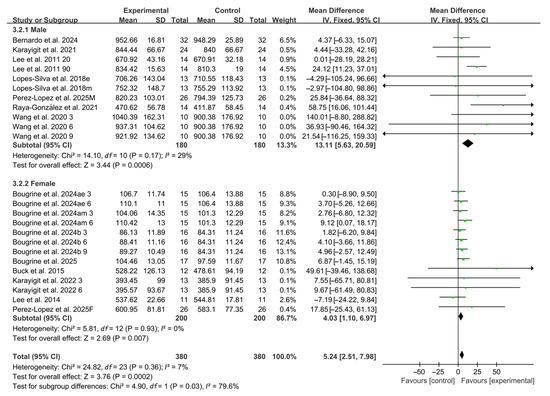
Figure 5.
Meta-analysis results of the effects of participant sex on RSA [20,21,22,23,24,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45]. Articles by the same author are distinguished by the suffixes “a” and “b”. Morning and evening sessions are denoted by “m” and “e”, respectively; participant sex by “M” (male) and “F” (female); caffeine dose by “3”, “6”, or “9” (mg/kg body weight); and inter-interval rest duration by “20” or “90” (min).
3.6. Publication Bias
Possible publication bias was assessed using funnel plot analysis (Figure S2). Visual inspection indicated a substantial asymmetry, suggesting a likelihood of publication bias. However, application of the Duval and Tweedie trim-and-fill method did not alter the overall effect size, confirming the robustness of the pooled estimates. This finding was supported by Egger’s test (p = 0.328, Table S3).
3.7. Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity analysis demonstrated that the overall effect of acute caffeine ingestion on RSA remained stable in both magnitude and direction after sequential exclusion of individual studies (Figure S3). These results confirm the robustness and reliability of the meta-analytic findings.
3.8. GRADE Summary
The certainty of the evidence underpinning our findings was systematically assessed using the GRADE framework. Following this rigorous appraisal, the overall certainty of the evidence was rated as high, indicating strong confidence in the reliability and generalizability of our conclusions (Table S4).
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Findings
The primary objective of this study was to systematically synthesize and quantify the effects of acute caffeine ingestion on RSA across diverse study populations, exercise modalities, and caffeine dosages. A total of 13 studies were included in the final analysis, and the pooled results revealed that acute caffeine ingestion exerted a statistically significant ergogenic effect on RSA in both male and female participants. Subgroup analyses further indicated that this performance-enhancing effect was consistent across two common exercise modalities—cycling and running. Notably, a dosage-dependent response was observed, with caffeine ingestion at a dose of ≥6 mg/kg BW yielding a more pronounced ergogenic impact on RSA compared to lower doses.
4.2. Effects of Acute Caffeine Ingestion on Repeated Sprint Ability
The findings of the present study demonstrated that acute caffeine ingestion significantly improved RSA, which is congruent with the results of prior studies [27,29]. Beyond oral ingestion, alternative routes of caffeine administration have also been explored for their effects on anaerobic performance. For instance, caffeine mouth rinse (without swallowing) has been shown to enhance maximal power production during short-duration, high-intensity exercise. This effect is thought to be mediated by caffeine’s activation of oral cavity adenosine receptors, which transmit sensory signals to the central nervous system to augment motor unit recruitment, a mechanism that may also contribute to improvements in RSA, given the sport-specific demand for repeated maximal power outputs [46].
Previous research has posited that ergogenic efficacy of caffeine may be attenuated under conditions of cumulative fatigue, a physiological challenge inherently associated with RSA protocols [38]. Mechanistically, caffeine exerts its central and peripheral effects primarily as a non-selective adenosine receptor antagonist, specifically targeting A1 and A2A receptors [1]. By competitively binding to these receptors, caffeine inhibits the action of adenosine, a key neuromodulator of fatigue, sleep, and arousal, thereby delaying the onset of perceived fatigue and enhancing central drive [47]. It is important to distinguish between caffeine’s effects on alertness and its capacity to reverse physiological fatigue: while caffeine has been shown to transiently improve subjective ratings of alertness in sleep-deprived individuals, it cannot mitigate the underlying physiological deficits (e.g., reduced glycogen stores, impaired neuromuscular function) induced by prolonged sleep deprivation [48]. Extending this to exercise contexts, caffeine ingestion has been shown to reduce time to exhaustion during endurance exercise; however, this effect was attributed to improvements in mood and perceived exertion rather than a direct attenuation of neuromuscular fatigue [49]. Consistent with these findings, further research has indicated that the efficacy of caffeine in enhance RSA diminishes as exercise-induced fatigue accumulates over successive sprints [50]. To address this potential attenuation and ensure sensitivity to caffeine’s true ergogenic potential, the present study focused on two key RSA outcomes: PPO (a measure of maximal anaerobic capacity) and fastest sprint time (a marker of optimal sprint performance) rather than MPO and mean sprint time, which are more susceptible to the confounding effects of cumulative fatigue.
A critical methodological consideration in caffeine research is the timing of RSA assessment relative to ingestion, as plasma caffeine concentration reaches its peak approximately 60 min post-ingestion in healthy adults [51]. To minimize variability in caffeine bioavailability across studies, all 13 included investigations consistently administered caffeine 60 min prior to RSA testing, a methodological consistency that strengthens the internal validity of the present meta-analysis.
4.3. Effects of Caffeine Dosage on Repeated Sprint Ability
Caffeine dosage is a critical moderator of its ergogenic effect on RSA, and the present subgroup analysis confirmed a dose–response relationship. Specifically, acute caffeine ingestion at a dose of ≥6 mg/kg BW (high-dose) significantly enhanced RSA, while acute caffeine ingestion of <6 mg/kg BW (low-dose) did not elicit a statistically significant effect. This observation aligns with previous studies that high-dose caffeine confers a robust ergogenic benefit for RSA [23,52]. Interestingly, existing literature suggests that doses exceeding 6 mg/kg BW (e.g., 9 mg/kg BW) do not further amplify RSA improvements; studies comparing 6 mg/kg BW and 9 mg/kg BW have found no significant differences in RSA outcomes, indicating a potential ceiling effect for caffeine’s ergogenic action on repeated sprints [23,52].
A notable discrepancy emerged between the present findings and a study by Wang et al. [24], which reported that low-dose (rather than high-dose) caffeine improved RSA. This inconsistency may be attributed to the unique characteristics of the participant sample in Wang et al.’s study: the authors recruited individuals with low habitual caffeine consumption (defined as <60 mg/day). This may Population-based research has established that habitual caffeine intake modulates sensitivity to acute caffeine ingestion—low consumers typically exhibit greater physiological and performance responses to lower doses, whereas high consumers may develop tolerance, requiring higher doses to achieve similar effects [53]. Thus, the low habitual intake of Wang et al.’s participants likely enhanced their responsiveness to low-dose caffeine, accounting for the divergent results.
4.4. Effects of Exercise Modality on Repeated Sprint Ability
Cycling and running are the two most prevalent exercise modalities used to assess RSA in experimental research, as they allow for precise measurement of power output (cycling) and sprint time (running) while controlling for external variables (e.g., terrain, technique). The present subgroup analysis confirmed that acute caffeine ingestion improved RSA across both modalities, with running-based RSA exhibiting a more pronounced effect, a finding that is supported by multiple previous studies [46,54,55]. In cycling-based RSA protocols, Schneiker et al. [54] reported that participants who ingested caffeine (6 mg/kg BW) exhibited significantly higher PPO across repeated sprints compared to those in the placebo group, a result that was later replicated by Beaven et al. [46], who observed a significant increase in PPO following caffeine ingestion in trained males. In running-based RSA tests, Glaister et al. [55] demonstrated that acute caffeine ingestion (5 mg/kg BW) significantly reduced fastest sprint time in physically active males.
An important practical consideration is the ecological validity of exercise modalities for specific sports. Running-based RSA tests entail greater total energy expenditure and neuromuscular demand (e.g., activation of lower-body muscles, balance control) compared to cycling tests, which are constrained by fixed pedaling mechanics [56]. This difference suggests that cycling may not be the optimal modality for assessing RSA in running-based sports (e.g., basketball, volleyball, soccer), as it fails to replicate the movement patterns and physiological stressors inherent to these sports. This potential lack of ecological validity may explain why some studies utilizing cycling tests to assess RSA in running-based sports athletes found no significant effect of acute caffeine ingestion on PPO [57,58]. These findings highlight the importance of selecting exercise modalities that align with the sport-specific demands of the participant population when investigating caffeine’s effects on RSA.
4.5. Effects of Participant Sex on Repeated Sprint Ability
While the present meta-analysis confirmed that acute caffeine ingestion significantly improved RSA in both males and females, subgroup analysis and a synthesis of existing literature revealed substantial heterogeneous in the magnitude and consistency of this effect across sexes.
In the male group, the pooled results indicated a significant ergogenic effect of caffeine on RSA; however, this finding contrasts with a study by Kopec et al. [59], which reported no differences in RSA between caffeine (6 mg/kg BW) and placebo groups in male team-sport athletes. The discrepancy may be attributed to the low sample size (n = 11) and moderate training status of participants in Kopec et al.’s study, which may have reduced statistical power to detect small-to-moderate effect sizes. In the female subgroup, our findings align with previous studies [23,60]. Bougrine et al. [23] demonstrated that acute caffeine ingestion at 6 mg/kg BW significantly improved RSA in female team-sport athletes, while another study by Lara et al. [60] reported that even a low dose of caffeine (3 mg/kg BW) enhanced RSA in female soccer players. Conversely, a previous meta-analysis by Gomez-Bruton et al. [26] found no significant effect of acute caffeine ingestion on RSA in female team-sport athletes. This null finding may be attributable to methodological heterogeneity, particularly the restriction of their analytical sample to participants aged ≥ 18 years, thereby limiting direct comparability with investigations incorporating younger cohorts.
A key physiological mechanism underlying potential sex differences in caffeine responsiveness is the rate of caffeine metabolism. Females have been shown to metabolize caffeine more slowly than males, primarily due to the inhibitory effect of estrogen on CYP1A2, the primary hepatic enzyme responsible for caffeine degradation [61]. This slower metabolism results in prolonged plasma caffeine concentrations in females, which may alter the timing and magnitude of caffeine’s ergogenic effect on RSA. Pérez-López et al. [39] provided empirical support for this mechanism, reporting that following acute caffeine ingestion, males exhibited higher PPO in the first two sprints of an RSA protocol, whereas females demonstrated superior PPO in the final two sprints. This temporal difference likely reflects the prolonged caffeine availability in females, which mitigates fatigue during later sprints.
Given the equivocal nature of existing evidence, with some studies reporting sex-specific effects and others finding no differences, further research is warranted to explicitly investigate sex as a moderator of caffeine’s effects on RSA. Future studies should control for variables such as menstrual cycle phase (in females), habitual caffeine intake, and training status to reduce heterogeneity and clarify the role of sex.
4.6. Practical Implications
These findings have practical implications for athletes and coaches seeking to optimize RSA performance: acute caffeine ingestion at 6 mg/kg BW, administered 60 min pre-exercise, represents an evidence-based strategy to enhance repeated sprint outcomes. Future research should address the limitations of the present study by explicitly investigating the moderating effects of training status, habitual caffeine intake, and participant age on caffeine’s ergogenic effect on RSA. Additionally, studies utilizing sport-specific RSA protocols (e.g., soccer-specific running drills, basketball agility sprints) are needed to further enhance the ecological validity and translational utility of caffeine research in applied sports settings.
4.7. Limitations
This study has several limitations. First, previous studies have employed diverse forms of caffeine administration (e.g., powder, capsules, mouth rinse, caffeinated beverages) [39,41,62,63]. Due to the limited number of eligible studies, the present analysis included only powder and capsule forms without distinguishing their effects separately. Second, substantial variability in the athletic capabilities of participants may have influenced RSA outcomes following acute caffeine ingestion. Differences in training status, habitual caffeine use, and sport-specific demands can substantially modulate the ergogenic response to caffeine [64,65]. As previously noted, cycling may not represent the most appropriate testing modality for RSA in running-based sports [56]. Therefore, future research should further delineate the effects of acute caffeine ingestion on RSA across various sport types and performance contexts.
Finally, although several studies have reported adverse effects associated with acute caffeine ingestion (e.g., such as ventricular fibrillation, irritability, and nervousness) [23,66], these outcomes were not analyzed in the current study. For example, Bougrine et al. [23] observed a higher incidence of side effects following caffeine ingestion at a dose of 9 mg/kg BW. Consequently, future investigations should consider not only the ergogenic potential but also the safety profile of different caffeine dosages to optimize performance benefits while minimizing potential risks. In line with recommendations from the International Society of Sports Nutrition (ISSN), caffeine doses of 3–6 mg/kg BW can enhance exercise performance, whereas doses of 9 mg/kg are associated with a higher incidence of adverse effects [15].
5. Conclusions
The present systematic review and meta-analysis provide robust evidence that acute caffeine ingestion (administered 60 min prior to exercise) exerts a significant ergogenic effect on RSA in healthy adults. This effect is consistent across both male and female participants, with no statistically significant sex difference observed in the pooled analysis. Furthermore, acute caffeine ingestion enhances RSA in both cycling and running exercise modalities, though the ecological validity of cycling for running-based sports should be considered when interpreting these results. Moreover, caffeine ingestion at ≥6 mg/kg BW yields a more pronounced ergogenic impact on RSA, whereas doses < 6 mg/kg BW do not elicit significant performance improvements.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/nu17213475/s1, Figure S1: Results of Cochrane risk of bias tool; Figure S2: Funnel plot; Figure S3: Sensitivity analysis results; Table S1: Search strategies; Table S2: Characteristics of the studies included in this meta-analysis; Table S3: Methodological assessment of randomized controlled trials included in the systematic review using the PEDro scale; Table S4: Results of Egger’s test; PRISMA 2020 checklist.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.W. and W.S.; methodology, Y.W., W.S. and B.G.; software, Y.W. and W.S.; validation, S.Z. and Y.L.; formal analysis, Y.W. and W.S.; investigation, Y.W., W.S., S.Z., L.Z., Y.L. and B.G.; resources, L.Y.; data curation, S.Z. and L.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.W. and W.S.; writing—review and editing, Y.W., W.S., S.Z., L.Z., Y.L., B.G. and L.Y.; visualization, Y.W. and W.S.; supervision, L.Y.; project administration, L.Y.; funding acquisition, L.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Humanities and Social Science Fund of Ministry of Education of China, grant number 24YJC890065.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| RSA | Repeated sprint ability |
| ATP-CP | Adenosine triphosphate-creatine phosphate system |
| PPO | Peak power output |
| MPO | Mean power output |
| BW | Body weight |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Evaluation and Meta-Analysis |
| PROSPERO | International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| WMD | Weighted mean difference |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| SE | Standard error |
References
- Li, C.; Wu, S.; Lei, B.; Zang, W.; Tao, X.; Yu, L. Effect of aerobic exercise on endothelial function in hypertensive and prehypertensive patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Hypertens. 2025, 43, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.C.; Hsieh, M.H.; Ho, C.C.; Chang, Y.H.; Shiu, Y.J. Effects of Caffeinated Chewing Gum on Exercise Performance and Physiological Responses: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starling-Soares, B.; Pereira, M.; Renke, G. Extrapolating the Coffee and Caffeine (1,3,7-Trimethylxanthine) Effects on Exercise and Metabolism—A Concise Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonio, J.; Pereira, F.; Curtis, J.; Rojas, J.; Evans, C. The Top 5 Can’t-Miss Sport Supplements. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Hu, Z.; Tang, J.; Xue, J.; Lu, W. Caffeine intake and anxiety: A meta-analysis. Front. Psychol. 2024, 15, 1270246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saimaiti, A.; Zhou, D.D.; Li, J.; Xiong, R.G.; Gan, R.Y.; Huang, S.Y.; Shang, A.; Zhao, C.N.; Li, H.Y.; Li, H.B. Dietary sources, health benefits, and risks of caffeine. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 9648–9666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brower, J.O.; Swatek, J.L. Beyond the buzz: The fatal consequences of caffeine overconsumption. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2024, 48, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, C.R.; Anderson, M.E.; Fraser, S.F.; Stepto, N.K.; Klein, R.; Hopkins, W.G.; Hawley, J.A. Enhancement of 2000-m rowing performance after caffeine ingestion. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2000, 32, 1958–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, H.; Del Coso, J.; Pickering, C. Caffeine and Sports Performance: The Conflict between Caffeine Intake to Enhance Performance and Avoiding Caffeine to Ensure Sleep Quality. Sports Med. 2025, 55, 1579–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.K.; Green, J.M. Caffeine and anaerobic performance: Ergogenic value and mechanisms of action. Sports Med. 2009, 39, 813–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spriet, L.L. Exercise and sport performance with low doses of caffeine. Sports Med. 2014, 44 (Suppl. S2), S175–S184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantino, A.; Maiese, A.; Lazzari, J.; Casula, C.; Turillazzi, E.; Frati, P.; Fineschi, V. The Dark Side of Energy Drinks: A Comprehensive Review of Their Impact on the Human Body. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivy, J.L.; Kammer, L.; Ding, Z.; Wang, B.; Bernard, J.R.; Liao, Y.H.; Hwang, J. Improved cycling time-trial performance after ingestion of a caffeine energy drink. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2009, 19, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreutzer, A.; Graybeal, A.J.; Moss, K.; Braun-Trocchio, R.; Shah, M. Caffeine Supplementation Strategies Among Endurance Athletes. Front. Sports Act. Living 2022, 4, 821750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guest, N.S.; VanDusseldorp, T.A.; Nelson, M.T.; Grgic, J.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Jenkins, N.D.M.; Arent, S.M.; Antonio, J.; Stout, J.R.; Trexler, E.T.; et al. International society of sports nutrition position stand: Caffeine and exercise performance. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2021, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, O.; Mendez-Villanueva, A.; Bishop, D. Repeated-sprint ability—Part I: Factors contributing to fatigue. Sports Med. 2011, 41, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagna, C.; Manzi, V.; D’Ottavio, S.; Annino, G.; Padua, E.; Bishop, D. Relation between maximal aerobic power and the ability to repeat sprints in young basketball players. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2007, 21, 1172–1176. [Google Scholar]
- Stolen, T.; Chamari, K.; Castagna, C.; Wisloff, U. Physiology of soccer: An update. Sports Med. 2005, 35, 501–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, D.J.; Kelly, S.J. Positional differences in professional rugby league match play through the use of global positioning systems. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougrine, H.; Ammar, A.; Salem, A.; Trabelsi, K.; Zmijewski, P.; Jahrami, H.; Cthourou, H.; Souissi, N. Effects of Different Caffeine Dosages on Maximal Physical Performance and Potential Side Effects in Low-Consumer Female Athletes: Morning vs. Evening Administration. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-L.; Cheng, C.-F.; Lin, J.-C.; Huang, H.-W. Caffeine’s effect on intermittent sprint cycling performance with different rest intervals. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 112, 2107–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardo, M.F.; Enes, A.; Rezende, E.F.; Okuyama, A.R.; Alves, C.R.; Andrade, M.; Macedo, A.C.G.; Barros, M.P.; Candow, D.G.; Forbes, S.C.; et al. Caffeine Does Not Alter Performance, Perceptual Responses, and Oxidative Stress After Short Sprint Interval Training. Nutrients 2024, 34, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bougrine, H.; Ammar, A.; Salem, A.; Trabelsi, K.; Jahrami, H.; Cthourou, H.; Souissi, N. Optimizing Short-Term Maximal Exercise Performance: The Superior Efficacy of a 6 mg/kg Caffeine Dose over 3 or 9 mg/kg in Young Female Team-Sports Athletes. Nutrients 2024, 16, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Dong, C.; Zhou, Z.; Zheng, X. Effects of Various Doses of Caffeine Ingestion on Intermittent Exercise Performance and Cognition. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, A.; Lopez-Samanes, A.; Aguilar-Navarro, M.; Varillas-Delgado, D.; Rivilla-Garcia, J.; Moreno-Perez, V.; Del Coso, J. Effects of CYP1A2 and ADORA2A Genotypes on the Ergogenic Response to Caffeine in Professional Handball Players. Genes 2020, 11, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Bruton, A.; Marin-Puyalto, J.; Muiz-Pardos, B.; Matute-Llorente, A.; Coso, J.D.; Gomez-Cabello, A.; Vicente-Rodriguez, G.; Casajus, J.A.; Lozano-Berges, G. Does Acute Caffeine Supplementation Improve Physical Performance in Female Team-Sport Athletes? Evidence from a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Torres, O.; Rodriguez-Longobardo, C.; Capel-Escoriza, R.; Fernandez-Elias, V.E. Ergogenic Aids to Improve Physical Performance in Female Athletes: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2022, 15, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes-Silva, J.P.; Choo, H.C.; Franchini, E.; Abbiss, C.R. Isolated ingestion of caffeine and sodium bicarbonate on repeated sprint performance: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2019, 22, 962–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Lara, J.; Nieto-Acevedo, R.; Abian-Vicen, J.; Coso, J.D. Can Caffeine Change the Game? Effects of Acute Caffeine Intake on Specific Performance in Intermittent Sports During Competition: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2024, 19, 1180–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagatto, A.M.; Beck, W.R.; Gobatto, C.A. Validity of the running anaerobic sprint test for assessing anaerobic power and predicting short-distance performances. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2009, 23, 1820–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhou, R.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Lv, Y.; Yu, L. Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Blood Lipids in People with Overweight or Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Life 2025, 15, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhen, K.; Su, Q.; Chen, Y.; Lv, Y.; Yu, L. The Effect of Aerobic Exercise on Cognitive Function in People with Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Lv, Y.; Feng, L.; Yu, L. Effects of Exercise on Depression and Anxiety in Breast Cancer Survivors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Cancer Med. 2025, 14, e70671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, G.; Su, H.; Liang, Y.; Lv, Y.; Yu, L. Effects of exercise on balance function in people with multiple sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Neurol. 2025, 272, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Lv, Y.; Yu, L. Effects of Exercise on Cancer-Related Fatigue in Breast Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Life 2024, 14, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ren, H.; Hou, X.; Dong, X.; Zhang, S.; Lv, Y.; Li, C.; Yu, L. The effect of exercise on balance function in stroke patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Neurol. 2024, 271, 4751–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes-Silva, J.P.; Santos, J.F.D.S.; Franchini, E. Can caffeine supplementation reverse the effect of time of day on repeated-sprint exercise performance? Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2018, 44, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Lopez, A.; Garriga-Alonso, L.; Montalvo-Alonso, J.J.; del Val-Manzano, M.; Valades, D.; Vila, H.; Ferragut, C. Sex differences in the acute effect of caffeine on repeated sprint performance: A randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2025, 25, e12233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougrine, H.; Paillard, T.; Jebabli, N.; Ceylan, H.İ.; Maitre, J.; Dergaa, I.; Stefanica, V.; Ben Abderrahman, A.B. Ergogenic Effects of Combined Caffeine Supplementation and Motivational Music on Anaerobic Performance in Female Handball Players: A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, C.; Guelfi, K.; Dawson, B.; McNaughton, L.; Wallman, K. Effects of sodium phosphate and caffeine loading on repeated-sprint ability. J. Sports Sci. 2015, 33, 1971–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karayigit, R.; Aras, D. One Week of Low or Moderate Doses of Caffeinated Coffee Consumption Does Not Induce Tolerance to The Acute Effects of Caffeine on Sprint Performance. Eur. J. Human. Mov. 2021, 47, 49–60. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.-L.; Cheng, C.-F.; Astorino, T.A.; Lee, C.-J.; Huang, H.-W.; Chang, W.-D. Effects of carbohydrate combined with caffeine on repeated sprint cycling and agility performance in female athletes. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2014, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raya-González, J.; Scanlan, A.T.; Soto-Célix, M.; Rodríguez Fernández, A.; Castillo Alvira, D. Caffeine ingestion improves performance during fitness tests but does not alter activity during simulated games in professional basketball players. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2021, 16, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karayigit, R.; Forbes, S.C.; Osmanov, Z.; Yılmaz, C.; Yasli, B.C.; Naderi, A.; Buyukcelebi, H.; Benesova, D.; Gabrys, T.; Esen, O. Low and Moderate Doses of Caffeinated Coffee Improve Repeated Sprint Performance in Female Team Sport Athletes. Biology 2022, 11, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaven, C.M.; Maulder, P.; Pooley, A.; Kilduff, L.; Cook, C. Effects of caffeine and carbohydrate mouth rinses on repeated sprint performance. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2013, 38, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredholm, B.B.; Battig, K.; Holmen, J.; Nehlig, A.; Zvartau, E.E. Actions of caffeine in the brain with special reference to factors that contribute to its widespread use. Pharmacol. Rev. 1999, 51, 83–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.P. Effects of caffeine in chewing gum on mood and performance at different times of day. World J. Pharm. Med. Res. 2021, 8, 114–118. [Google Scholar]
- Smirmaul, B.P.; de Moraes, A.C.; Angius, L.; Marcora, S.M. Effects of caffeine on neuromuscular fatigue and performance during high-intensity cycling exercise in moderate hypoxia. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2017, 117, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romdhani, M.; Souissi, N.; Moussa-Chamari, I.; Chaabouni, Y.; Mahdouani, K.; Sahnoun, Z.; Driss, T.; Chamari, K.; Hammouda, O. Caffeine Use or Napping to Enhance Repeated Sprint Performance After Partial Sleep Deprivation: Why Not Both? Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2021, 16, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, T.E. Caffeine and exercise: Metabolism, endurance and performance. Sports Med. 2001, 31, 785–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; He, W.; Ding, L.; Lei, T.H.; Schlader, Z.; Mundel, T.; Wang, R.; Guo, L.; Liu, J.; Girard, O. Dose-response effects of caffeine during repeated cycling sprints in normobaric hypoxia to exhaustion. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2025, 125, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.; Tierney, P.; Gray, N.; Hawe, G.; Macken, M.; Egan, B. Acute Ingestion of Caffeinated Chewing Gum Improves Repeated Sprint Performance of Team Sport Athletes with Low Habitual Caffeine Consumption. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2018, 28, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneiker, K.T.; Bishop, D.; Dawson, B.; Hackett, L.P. Effects of caffeine on prolonged intermittent-sprint ability in team-sport athletes. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2006, 38, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaister, M.; Howatson, G.; Abraham, C.S.; Lockey, R.A.; Goodwin, J.E.; Foley, P.; McInnes, G. Caffeine supplementation and multiple sprint running performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2008, 40, 1835–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deliceoglu, G. Comparative Analysis of Energy System Demands and Performance Metrics in Professional Soccer Players: Running vs. Cycling Repeated Sprint Tests. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, R.; Daneghian, S.; Jafari, A.; Homayouni, A. Effect of Acute Caffeine Supplementation on Anaerobic Power and Blood Lactate Levels in Female Athletes. J. Caffeine Res. 2015, 5, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Campos, C.; Dengo, A.L.; Moncada-Jiménez, J. Acute Consumption of an Energy Drink Does Not Improve Physical Performance of Female Volleyball Players. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2015, 25, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopec, B.J.; Dawson, B.T.; Buck, C.; Wallman, K.E. Effects of sodium phosphate and caffeine ingestion on repeated-sprint ability in male athletes. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2016, 19, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, B.; Gonzalez-Millan, C.; Salinero, J.J.; Abian-Vicen, J.; Areces, F.; Barbero-Alvarez, J.C.; Munoz, V.; Portillo, L.J.; Gonzalez-Rave, J.M.; Del Coso, J. Caffeine-containing energy drink improves physical performance in female soccer players. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 1385–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollock, B.G.; Wylie, M.; Stack, J.A.; Sorisio, D.A.; Thompson, D.S.; Kirshner, M.A.; Folan, M.M.; Condifer, K.A. Inhibition of caffeine metabolism by estrogen replacement therapy in postmenopausal women. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1999, 39, 936–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabuco, L.L.; Saunders, B.; Sousa da Silva, R.A.; Molina, G.E.; Reis, C.E.G. Caffeine Mouth Rinse Does Not Improve Time to Exhaustion in Male Trained Cyclists. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2021, 31, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, S.L.; Díaz-Lara, J.; Pareja-Galeano, H.; Del Coso, J. Caffeinated Drinks and Physical Performance in Sport: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, N.; Baxter, H.; Fajemilua, E.; Jones, V.; Mundy, P. Coffee and Caffeine Ingestion Have Little Effect on Repeated Sprint Cycling in Relatively Untrained Males. Sports 2016, 4, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolf, K.; Bidwell, W.K.; Carlson, A.G. The Effect of Caffeine as an Ergogenic Aid in Anaerobic Exercise. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2008, 18, 412–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willson, C. The clinical toxicology of caffeine: A review and case study. Toxicol. Rep. 2018, 5, 1140–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).