Investigating the Digestibility, Bioavailability and Utilization of Protein Blends in Older Adults Using a Dual Stable Isotope Tracer Technique
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Measurement of MPS
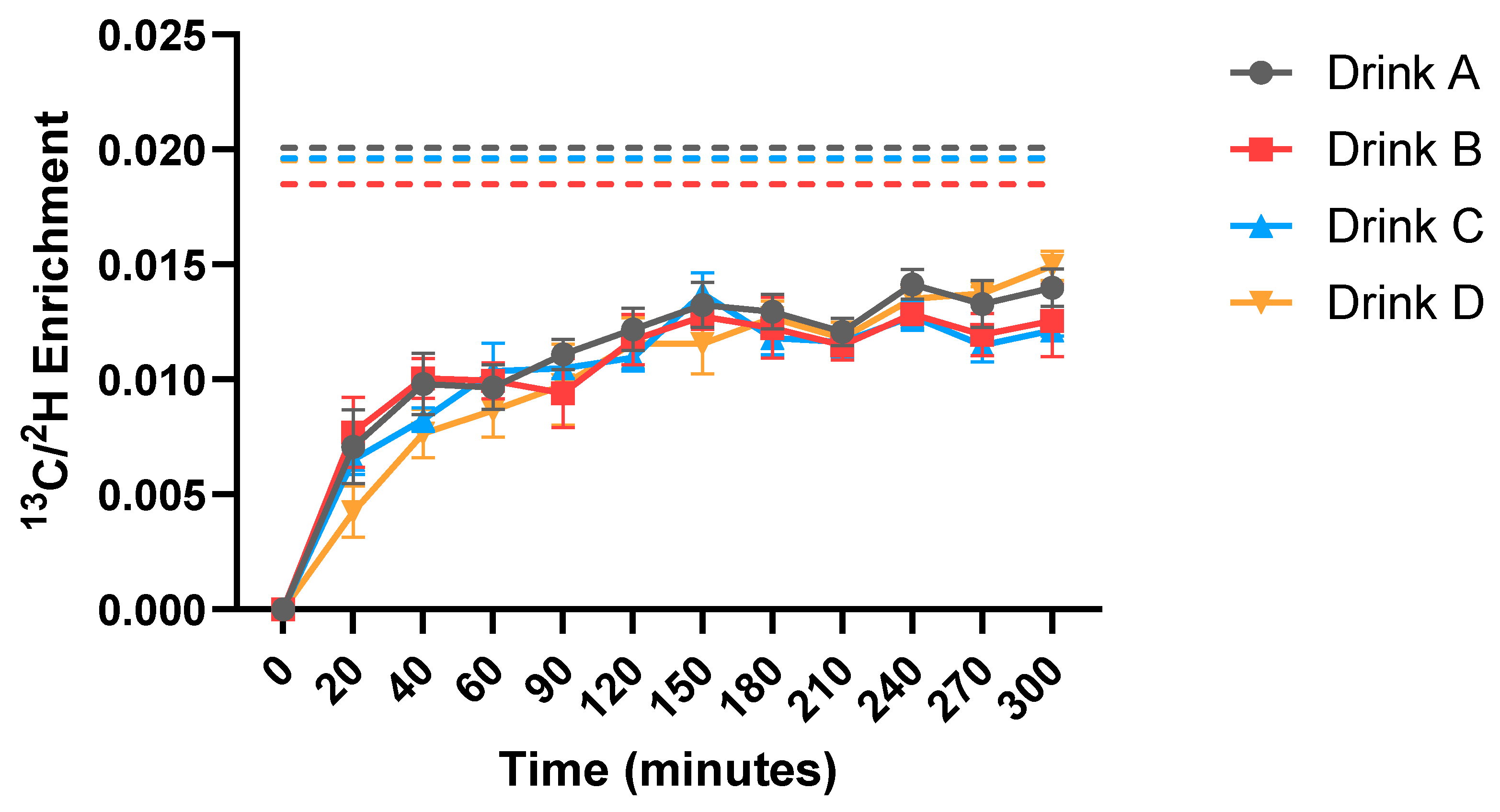
2.4. Measurement of Protein Digestibility
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Plasma Amino Acid Concentrations
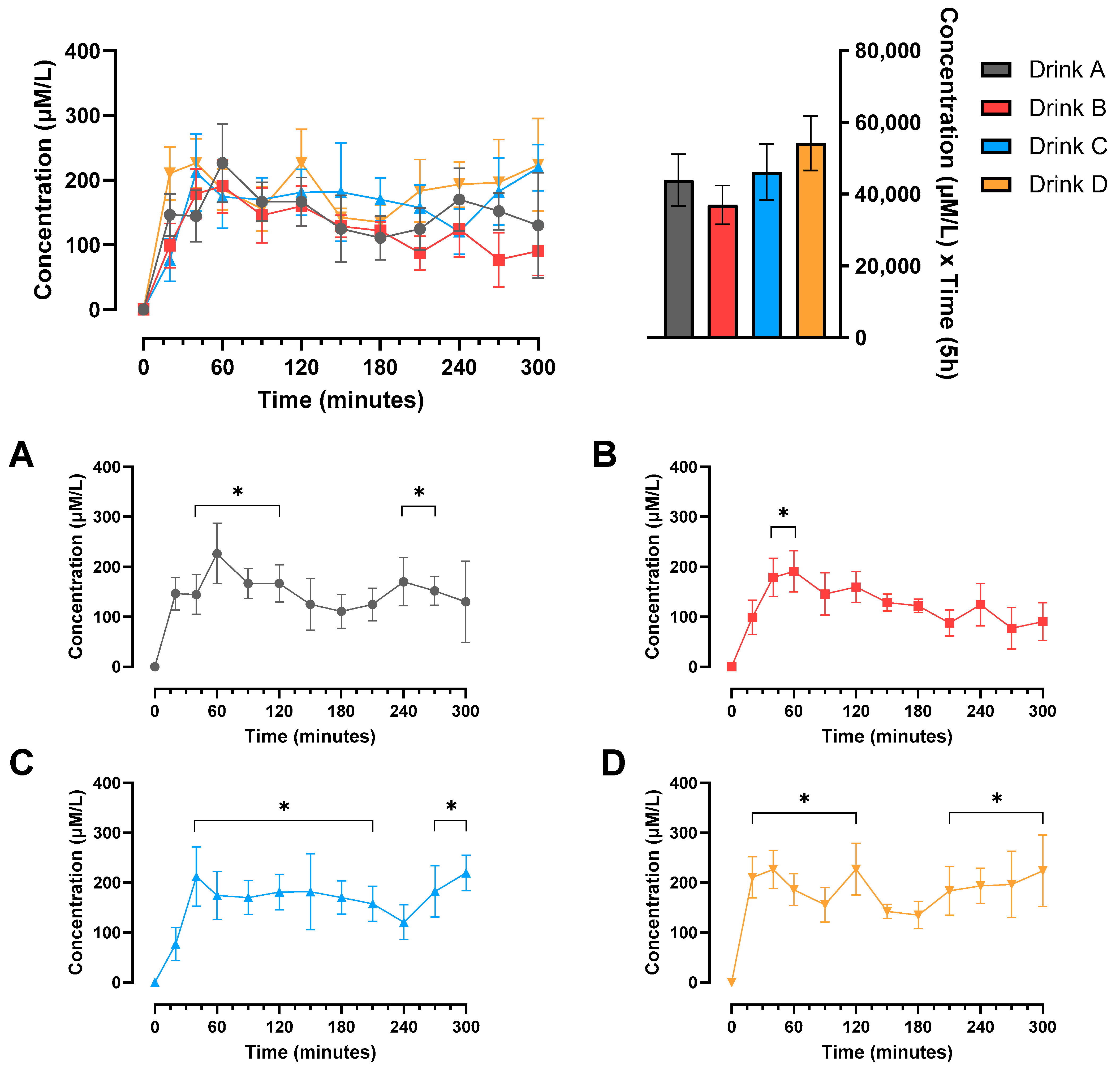
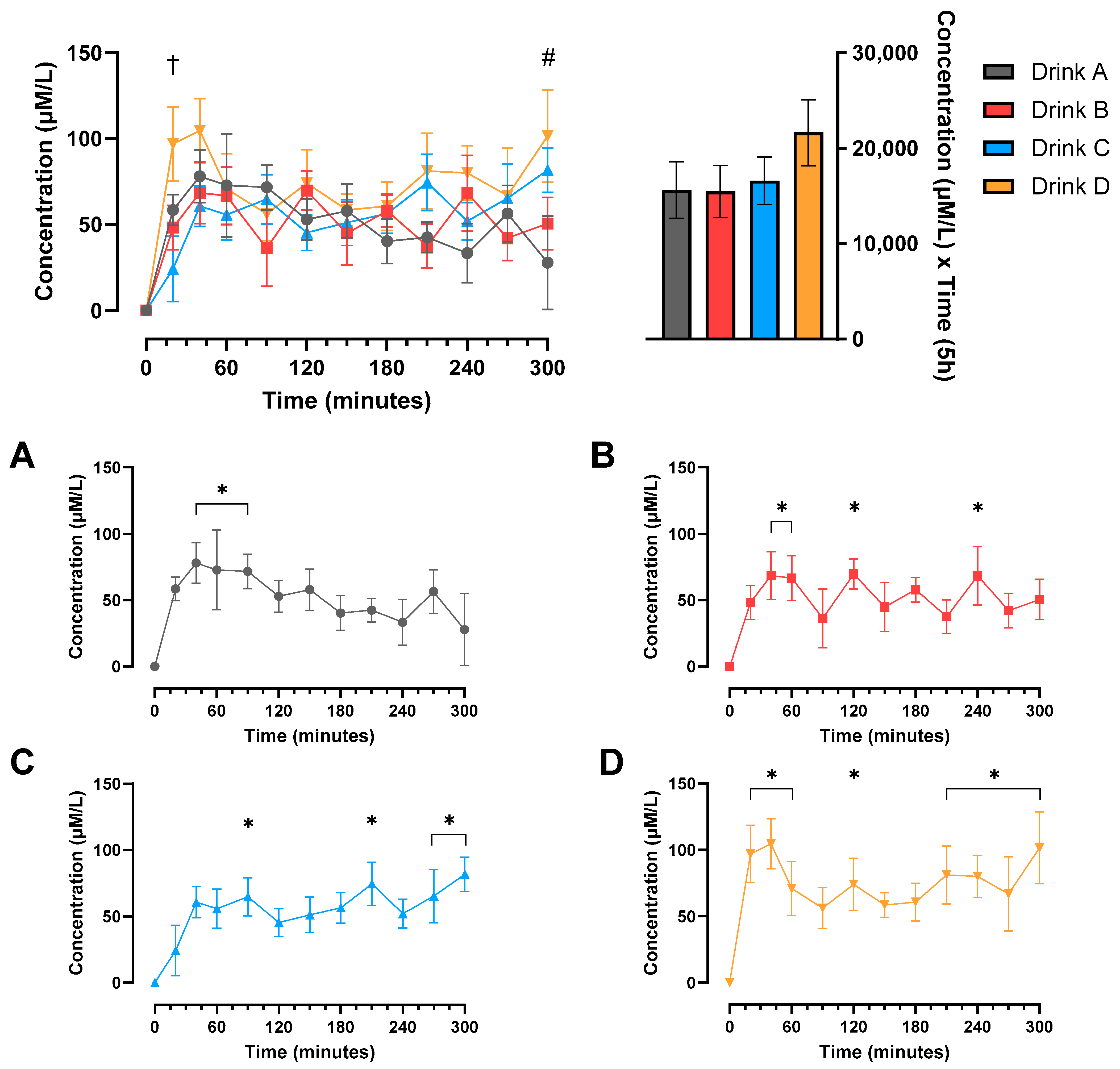
3.2. Protein Digestibility
3.3. Myofibrillar FSR Response
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Phillips, S.M.; Glover, E.I.; Rennie, M.J. Alterations of protein turnover underlying disuse atrophy in human skeletal muscle. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 107, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpi, E.; Ferrando, A.A.; Yeckel, C.W.; Tipton, K.D.; Wolfe, R.R. Exogenous amino acids stimulate net muscle protein synthesis in the elderly. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 101, 2000–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tipton, K.D.; Borsheim, E.; Wolf, S.E.; Sanford, A.P.; Wolfe, R.R. Acute response of net muscle protein balance reflects 24-h balance after exercise and amino acid ingestion. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 284, E76–E89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atherton, P.J.; Etheridge, T.; Watt, P.W.; Wilkinson, D.; Selby, A.; Rankin, D.; Smith, K.; Rennie, M.J. Muscle full effect after oral protein: Time-dependent concordance and discordance between human muscle protein synthesis and mTORC1 signaling. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 92, 1080–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukhari, S.S.; Phillips, B.E.; Wilkinson, D.J.; Limb, M.C.; Rankin, D.; Mitchell, W.K.; Kobayashi, H.; Greenhaff, P.L.; Smith, K.; Atherton, P.J. Intake of low-dose leucine-rich essential amino acids stimulates muscle anabolism equivalently to bolus whey protein in older women at rest and after exercise. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 308, E1056–E1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryawan, A.; Jeyapalan, A.S.; Orellana, R.A.; Wilson, F.A.; Nguyen, H.V.; Davis, T.A. Leucine stimulates protein synthesis in skeletal muscle of neonatal pigs by enhancing mTORC1 activation. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 295, E868–E875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, I.H. Sarcopenia: Origins and clinical relevance. J. Nutr. 1997, 127, 990S–991S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Selby, A.; Rankin, D.; Patel, R.; Atherton, P.; Hildebrandt, W.; Williams, J.; Smith, K.; Seynnes, O.; Hiscock, N.; et al. Age-related differences in the dose–response relationship of muscle protein synthesis to resistance exercise in young and old men. J. Physiol. 2009, 587, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, D.R.; Churchward-Venne, T.A.; Witard, O.; Breen, L.; Burd, N.A.; Tipton, K.D.; Phillips, S.M. Protein ingestion to stimulate myofibrillar protein synthesis requires greater relative protein intakes in healthy older versus younger men. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biomed. Sci. Med. Sci. 2015, 70, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, R.R.; Miller, S.L.; Miller, K.B. Optimal protein intake in the elderly. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 27, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breen, L.; Phillips, S.M. Skeletal muscle protein metabolism in the elderly: Interventions to counteract the ’anabolic resistance’ of ageing. Nutr. Metab. 2011, 8, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Areta, J.L.; Burke, L.M.; Ross, M.L.; Camera, D.M.; West, D.W.D.; Broad, E.M.; Jeacocke, N.A.; Moore, D.R.; Stellingwerff, T.; Phillips, S.M.; et al. Timing and distribution of protein ingestion during prolonged recovery from resistance exercise alters myofibrillar protein synthesis. J. Physiol. 2013, 591, 2319–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutz, N.E.; Bauer, J.M.; Barazzoni, R.; Biolo, G.; Boirie, Y.; Bosy-Westphal, A.; Cederholm, T.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.; Krznariç, Z.; Nair, K.S.; et al. Protein intake and exercise for optimal muscle function with aging: Recommendations from the ESPEN Expert Group. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baum, J.I.; Kim, I.-Y.; Wolfe, R.R. Protein consumption and the elderly: What is the optimal level of intake? Nutrients 2016, 8, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isanejad, M.; Mursu, J.; Sirola, J.; Kröger, H.; Rikkonen, T.; Tuppurainen, M.; Erkkilä, A.T. Dietary protein intake is associated with better physical function and muscle strength among elderly women. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 115, 1281–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpi, E.; Campbell, W.W.; Dwyer, J.T.; Johnson, M.A.; Jensen, G.L.; Morley, J.E.; Wolfe, R.R. Is the optimal level of protein intake for older adults greater than the recommended dietary allowance? J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biomed. Sci. Med. Sci. 2013, 68, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamerow, M.M.; Mettler, J.A.; English, K.L.; Casperson, S.L.; Arentson-Lantz, E.; Sheffield-Moore, M.; Layman, D.K.; Paddon-Jones, D. Dietary protein distribution positively influences 24-h muscle protein synthesis in healthy adults. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.M. The impact of protein quality on the promotion of resistance exercise-induced changes in muscle mass. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 13, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, P.T.; Harris, D.O.; Marshall, R.N.; Quinlan, J.; Edwards, S.J.; Allen, S.L.; Breen, L. Protein source and quality for skeletal muscle anabolism in young and older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 1901–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, B.F.; Olesen, J.L.; Hansen, M.; Døssing, S.; Crameri, R.M.; Welling, R.J.; Langberg, H.; Flyvbjerg, A.; Kjaer, M.; Babraj, J.A.; et al. Coordinated collagen and muscle protein synthesis in human patella tendon and quadriceps muscle after exercise. J. Physiol. 2005, 567, 1021–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atherton, P.; Smith, K. Muscle protein synthesis in response to nutrition and exercise. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, B.S.; Kelleher, A.R.; Kimball, S.R. Regulation of muscle protein synthesis and the effects of catabolic states. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 2147–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deane, C.S.; Cox, J.; Atherton, P.J. Critical Variables Regulating Age-related Anabolic Responses to Protein Nutrition in Skeletal Muscle. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1419229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgkinson, S.M. Protein and amino acid digestibility: Definitions and conventional oro-ileal determination in humans. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1407604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, J.; Wilkinson, D.J.; Atherton, P.J.; Smith, K. Dietary protein splanchnic uptake and digestibility via stable isotope tracers. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2024, 27, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tessier, R.; Calvez, J.; Airinei, G.; Khodorova, N.; Kapel, R.; Quinsac, A.; Galet, O.; Piedcoq, J.; Benamouzig, R.; Tomé, D.; et al. The true amino acid digestibility of 15N-labelled sunflower biscuits determined with ileal balance and dual isotope methods in healthy humans. J. Nutr. 2022, 152, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillin, F.M.; Gaudichon, C.; Guérin-Deremaux, L.; Lefranc-Millot, C.; Airinei, G.; Khodorova, N.; Benamouzig, R.; Pomport, P.-H.; Martin, J.; Calvez, J. Values for the Digestibility of Pea Protein Isolate or Casein Amino Acids Determined using the Dual Isotope Method Are Not Similar to Those Derived with the Standard Ileal Balance Method in Healthy Volunteers. J. Nutr. 2024, 154, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, S.; Varkey, A.; Shivakumar, N.; Devi, S.; Reddy B H, R.; Thomas, T.; Preston, T.; Sreeman, S.; Kurpad, A.V. True ileal digestibility of legumes determined by dual-isotope tracer method in Indian adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 110, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, S.; Varkey, A.; Dharmar, M.; Holt, R.R.; Allen, L.H.; Sheshshayee, M.S.; Preston, T.; Keen, C.L.; Kurpad, A.V. Amino acid digestibility of extruded chickpea and yellow pea protein is high and comparable in moderately stunted South Indian children with use of a dual stable isotope tracer method. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, S.; Shivakumar, N.; Varkey, A.; Duraisamy, R.; Thomas, T.; Preston, T.; Devi, S.; Kurpad, A.V. Ileal digestibility of intrinsically labeled hen’s egg and meat protein determined with the dual stable isotope tracer method in Indian adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 108, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Barca, A.M.C.; Martínez-Díaz, G.; Ibarra-Pastrana, É.N.; Devi, S.; Kurpad, A.V.; Valencia, M.E. Pinto bean amino acid digestibility and score in a Mexican dish with corn tortilla and guacamole, evaluated in adults using a dual-tracer isotopic method. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 3151–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, S.; Shivakumar, N.; Sejian, V.; Deutz, N.E.P.; Preston, T.; Sreeman, S.; Devi, S.; Kurpad, A.V. Goat milk protein digestibility in relation to intestinal function. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 113, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayour, M.; Benmhimdane, A.; Calvez, J.; Saeid, N.; Khodorova, N.; Belghiti, H.; El Hamdouchi, A.; El Kari, K.; Owino, V.; Tomé, D.; et al. Indispensable Amino Acid Digestibility of Moroccan Fava Bean Using the Dual Isotope Method in Healthy Adults. J. Nutr. 2023, 153, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.J.; Riley, C.; Devi, S.; Kurpad, A.V.; Preston, T.; Francis, R.; Chambers, B.; Brown, O.; Badaloo, A.V. Determination of Indispensable Amino Acid Digestibility of the Red Kidney Bean in Humans Using a Dual Stable Isotope Tracer Method. J. Nutr. 2023, 153, 2979–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, S.; Devi, S.; Pasanna, R.M.; Preston, T.; Kurpad, A.V. True digestibility of tryptophan in plant and animal protein. J. Nutr. 2024, 154, 3203–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelen, M.; Com, G.; Anderson, P.; Deutz, N. New stable isotope method to measure protein digestibility and response to pancreatic enzyme intake in cystic fibrosis. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrichson, P.; Coakley, J.; Smith, P.; Griffiths, R.D.; Helliwell, T.R.; Edwards, R.H. Conchotome and needle percutaneous biopsy of skeletal muscle. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1987, 50, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, D.J.; Hossain, T.; Hill, D.S.; Phillips, B.E.; Crossland, H.; Williams, J.; Loughna, P.; Churchward-Venne, T.A.; Breen, L.; Phillips, S.M.; et al. Effects of leucine and its metabolite β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate on human skeletal muscle protein metabolism. J. Physiol. 2013, 591, 2911–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watt, P.W.; Lindsay, Y.; Scrimgeour, C.M.; Chien, P.A.; Gibson, J.N.; Taylor, D.J.; Rennie, M.J. Isolation of aminoacyl-tRNA and its labeling with stable-isotope tracers: Use in studies of human tissue protein synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 5892–5896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathai, J.K.; Liu, Y.; Stein, H.H. Values for digestible indispensable amino acid scores (DIAAS) for some dairy and plant proteins may better describe protein quality than values calculated using the concept for protein digestibility-corrected amino acid scores (PDCAAS). Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillin, F.M.; Gaudichon, C.; Guérin-Deremaux, L.; Lefranc-Millot, C.; Airinei, G.; Khodorova, N.; Benamouzig, R.; Pomport, P.-H.; Martin, J.; Calvez, J. Real ileal amino acid digestibility of pea protein compared to casein in healthy humans: A randomized trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 115, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, S.; Varkey, A.; Sheshshayee, M.; Preston, T.; Kurpad, A.V. Measurement of protein digestibility in humans by a dual-tracer method. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 107, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennings, B.; Boirie, Y.; Senden, J.M.; Gijsen, A.P.; Kuipers, H.; van Loon, L.J. Whey protein stimulates postprandial muscle protein accretion more effectively than do casein and casein hydrolysate in older men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorissen, S.H.; Crombag, J.J.; Senden, J.M.; Waterval, W.A.H.; Bierau, J.; Verdijk, L.B.; van Loon, L.J.C. Protein content and amino acid composition of commercially available plant-based protein isolates. Amino Acids 2018, 50, 1685–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Klebach, M.; Visser, M.; Hofman, Z. Amino acid availability of a dairy and vegetable protein blend compared to single casein, whey, soy, and pea proteins: A double-blind, cross-over trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, B.T.; Gorissen, S.H.; Pennings, B.; Koopman, R.; Groen, B.B.L.; Verdijk, L.B.; Van Loon, L.J.C. Aging is accompanied by a blunted muscle protein synthetic response to protein ingestion. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brook, M.S.; Wilkinson, D.J.; Mitchell, W.K.; Lund, J.N.; Phillips, B.E.; Szewczyk, N.J.; Greenhaff, P.L.; Smith, K.; Atherton, P.J. Synchronous deficits in cumulative muscle protein synthesis and ribosomal biogenesis underlie age-related anabolic resistance to exercise in humans. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 7399–7417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinckaers, P.J.; Kouw, I.W.; Hendriks, F.K.; van Kranenburg, J.M.; de Groot, L.C.; Verdijk, L.B.; Snijders, T.; van Loon, L.J. No differences in muscle protein synthesis rates following ingestion of wheat protein, milk protein, and their protein blend in healthy, young males. Br. J. Nutr. 2021, 126, 1832–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shur, N.; Creedon, L.; Skirrow, S.; Atherton, P.; MacDonald, I.; Lund, J.; Greenhaff, P. Age-related changes in muscle architecture and metabolism in humans: The likely contribution of physical inactivity to age-related functional decline. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 68, 101344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, J.; Biolo, G.; Cederholm, T.; Cesari, M.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Morley, J.E.; Phillips, S.; Sieber, C.; Stehle, P.; Teta, D.; et al. Evidence-based recommendations for optimal dietary protein intake in older people: A position paper from the PROT-AGE Study Group. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2013, 14, 542–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cox, J.; Phillips, B.E.; Bunce, J.; Smart, T.; Wall, J.; Crossland, H.; Wilkinson, D.J.; Smith, K.; Atherton, P.J. Investigating the Digestibility, Bioavailability and Utilization of Protein Blends in Older Adults Using a Dual Stable Isotope Tracer Technique. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3328. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17213328
Cox J, Phillips BE, Bunce J, Smart T, Wall J, Crossland H, Wilkinson DJ, Smith K, Atherton PJ. Investigating the Digestibility, Bioavailability and Utilization of Protein Blends in Older Adults Using a Dual Stable Isotope Tracer Technique. Nutrients. 2025; 17(21):3328. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17213328
Chicago/Turabian StyleCox, Jake, Bethan E. Phillips, James Bunce, Thomas Smart, Joshua Wall, Hannah Crossland, Daniel J. Wilkinson, Kenneth Smith, and Philip J. Atherton. 2025. "Investigating the Digestibility, Bioavailability and Utilization of Protein Blends in Older Adults Using a Dual Stable Isotope Tracer Technique" Nutrients 17, no. 21: 3328. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17213328
APA StyleCox, J., Phillips, B. E., Bunce, J., Smart, T., Wall, J., Crossland, H., Wilkinson, D. J., Smith, K., & Atherton, P. J. (2025). Investigating the Digestibility, Bioavailability and Utilization of Protein Blends in Older Adults Using a Dual Stable Isotope Tracer Technique. Nutrients, 17(21), 3328. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17213328






