Relationship of Mediterranean Diet and Its Components with Parameters of Structure, Vascular Function, and Vascular Aging in Subjects Diagnosed with Long COVID: BioICOPER Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
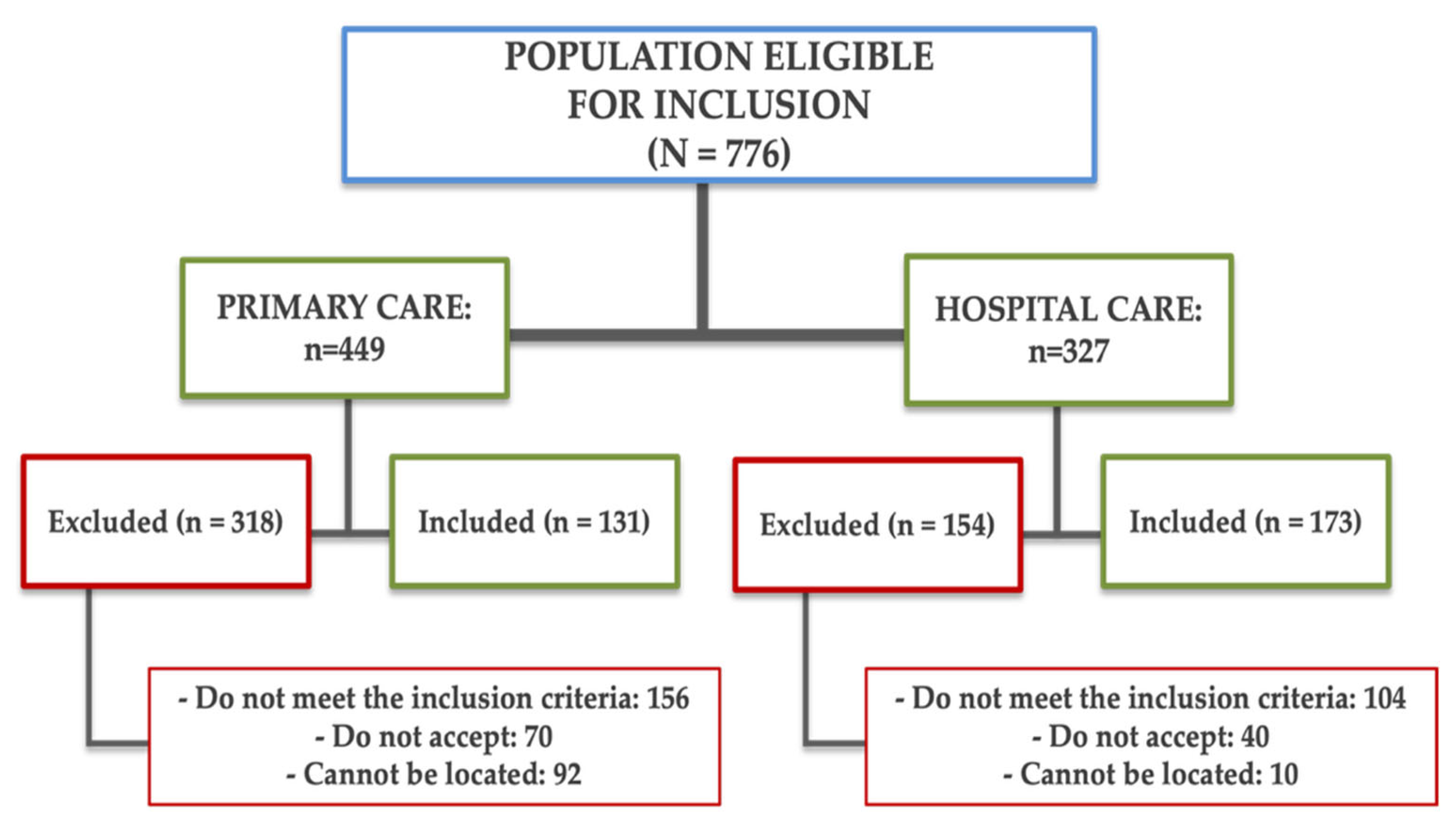
2.2. Population
2.3. Variables and Measurement Instruments
2.3.1. Sociodemographic Variables
2.3.2. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet
2.3.3. Vascular Structure, Vascular Function, and Vascular Aging
Vascular Structure
Vascular Function
Vascular Aging
2.3.4. Lifestyles
2.3.5. Cardiovascular Risk Factors
Blood Pressure Measurement
Analytical Parameters
Anthropometric Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethical Principles
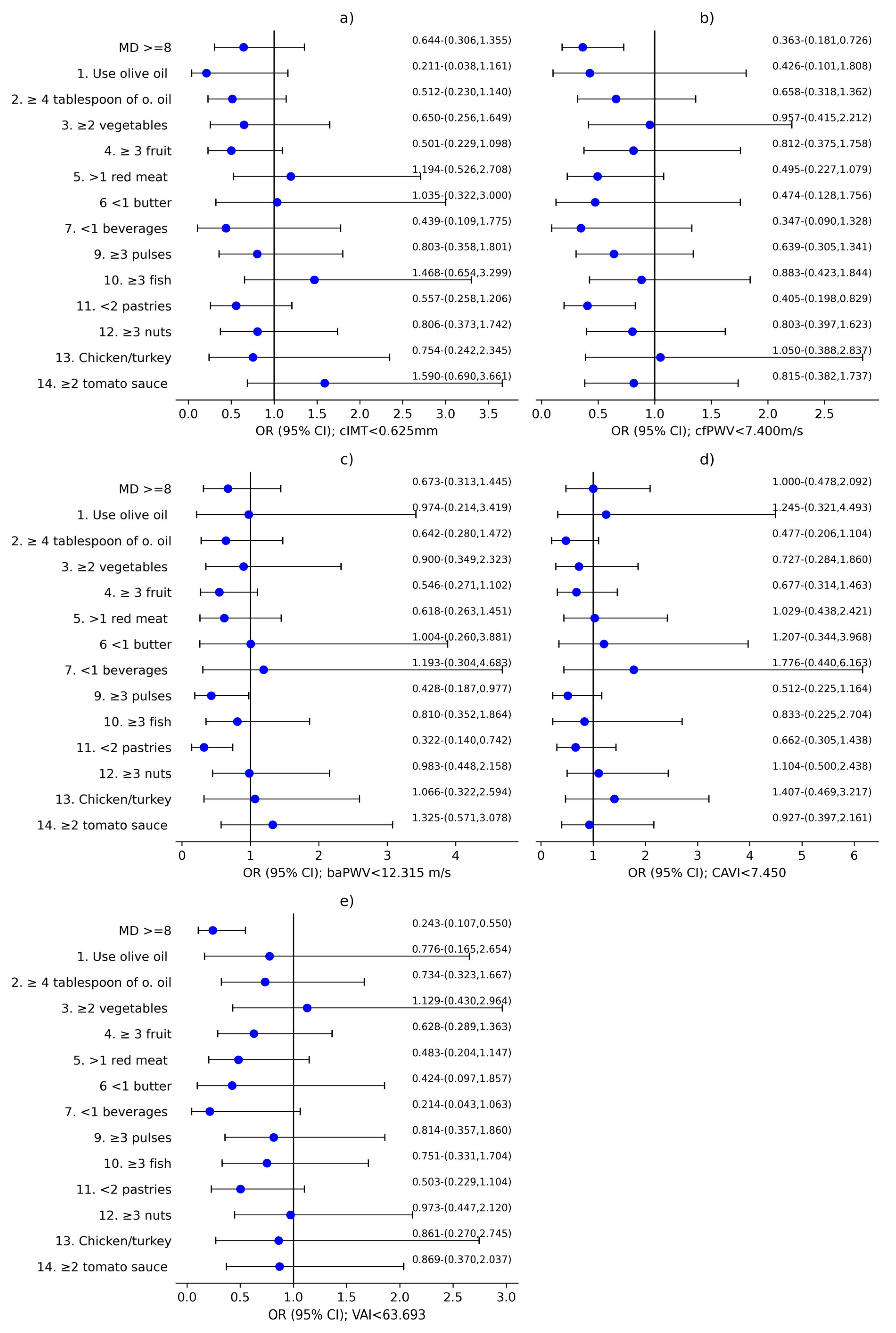
3. Results
3.1. Participants Characteristics
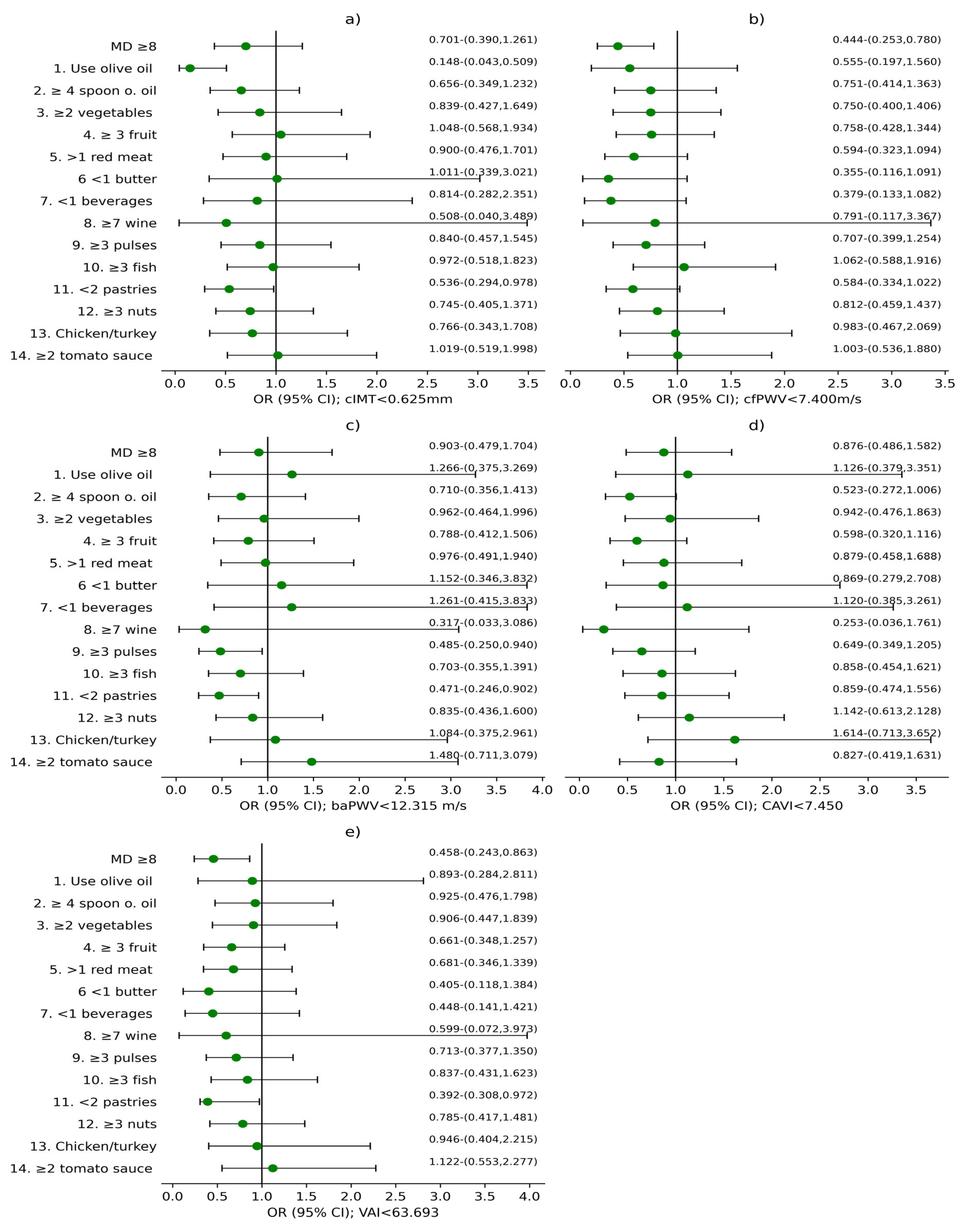
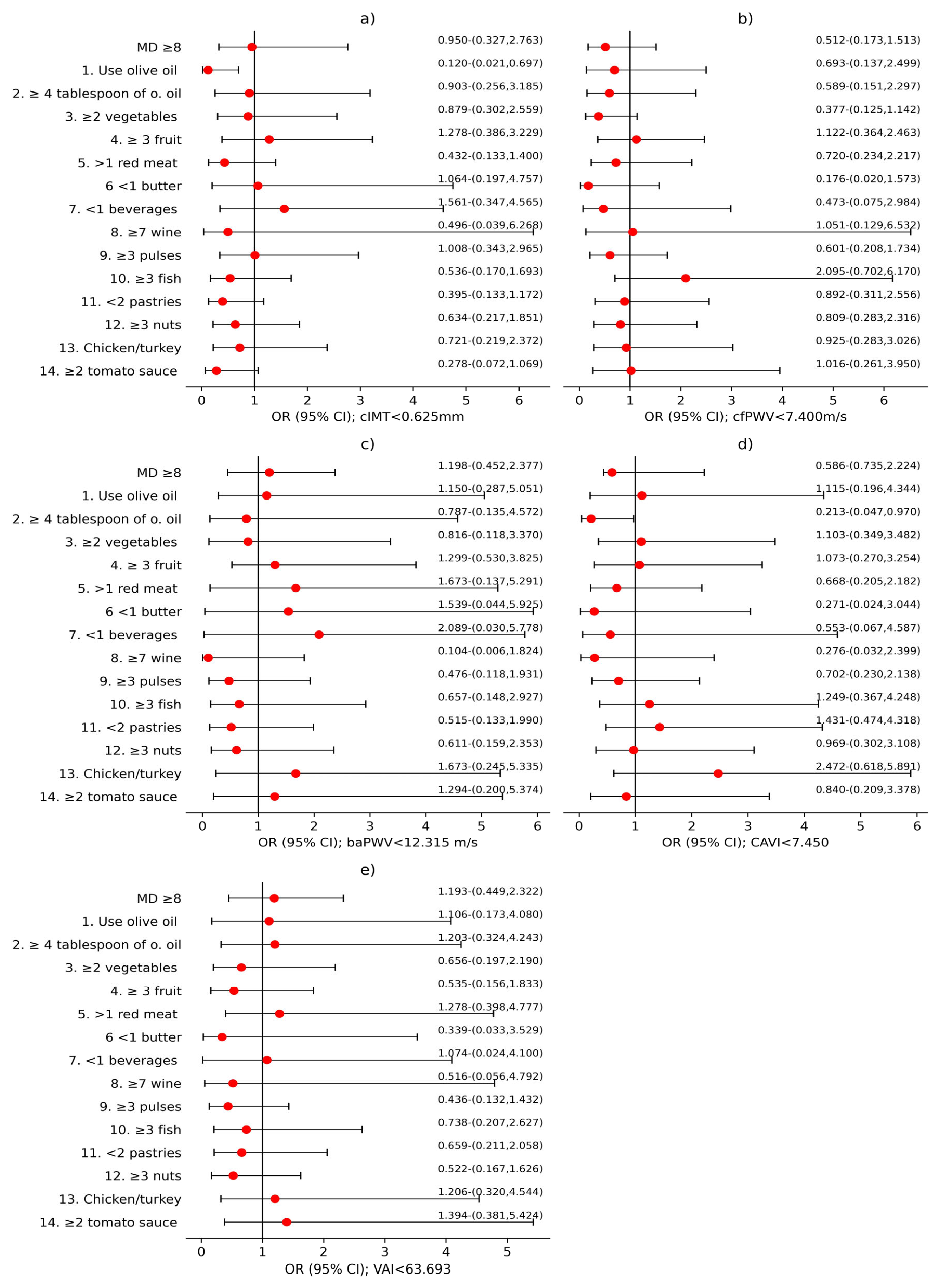
3.2. Analysis of the Association Between MD and Vascular Structure, Function, and Aging
4. Discussion
4.1. Relationship Between the MD and Vascular Parameters
4.2. Sex Differences in the Association Between Mediterranean Diet and Vascular Parameters
4.3. Relevance of Specific Dietary Components
4.4. Comparison with Other Studies in Patients with Long COVID
4.5. Strengths and Limitations of the Study
4.6. Clinical Implications and Future Lines of Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LC | Long COVID |
| MD | Mediterranean Diet |
| AS | Arterial stiffness |
| VA | Vascular aging |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| APISAL | Primary Care Research Unit of Salamanca |
| cIMT | Carotid intima-media thickness |
| CAVI | Cardio-ankle vascular index |
| baPWV | Brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity |
| cfPWV | Carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity |
| SBP | Systolic blood pressure |
| DBP | Diastolic blood pressure |
| ESH | European Society of Hypertension |
| LDL | Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| HDL | High-density protein cholesterol |
| FPG | Fasting plasma glucose |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| WC | Waste circumference |
| MetS | Metabolic Syndrome |
References
- Al-Aly, Z.; Davis, H.; McCorkell, L.; Soares, L.; Wulf-Hanson, S.; Iwasaki, A.; Topol, E.J. Long COVID Science, Research and Policy. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 2148–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigman, G.; Rusu, M.E.; Shelawala, N.; Sorkin, J.D.; Beamer, B.A.; Ryan, A.S. A Comprehensive Scoping Review on Diet and Nutrition in Relation to Long COVID-19 Symptoms and Recovery. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiyegbusi, O.L.; Hughes, S.E.; Turner, G.; Rivera, S.C.; McMullan, C.; Chandan, J.S.; Haroon, S.; Price, G.; Davies, E.H.; Nirantharakumar, K.; et al. Symptoms, Complications and Management of Long COVID: A Review. J. R. Soc. Med. 2021, 114, 428–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Peluso, M.J.; Luo, X.; Thomas, R.; Shin, M.G.; Neidleman, J.; Andrew, A.; Young, K.C.; Ma, T.; Hoh, R.; et al. Long COVID Manifests with T Cell Dysregulation, Inflammation and an Uncoordinated Adaptive Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Immunol. 2024, 25, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervia-Hasler, C.; Brüningk, S.C.; Hoch, T.; Fan, B.; Muzio, G.; Thompson, R.C.; Ceglarek, L.; Meledin, R.; Westermann, P.; Emmenegger, M.; et al. Persistent Complement Dysregulation with Signs of Thromboinflammation in Active Long Covid. Science 2024, 383, eadg7942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelman, B.; Charlton, B.T.; Goulding, R.P.; Kerkhoff, T.J.; Breedveld, E.A.; Noort, W.; Offringa, C.; Bloemers, F.W.; van Weeghel, M.; Schomakers, B.V.; et al. Muscle Abnormalities Worsen after Post-Exertional Malaise in Long COVID. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proal, A.D.; VanElzakker, M.B.; Aleman, S.; Bach, K.; Boribong, B.P.; Buggert, M.; Cherry, S.; Chertow, D.S.; Davies, H.E.; Dupont, C.L.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Reservoir in Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC). Nat. Immunol. 2023, 24, 1616–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarnieri, J.W.; Dybas, J.M.; Fazelinia, H.; Kim, M.S.; Frere, J.; Zhang, Y.; Soto Albrecht, Y.; Murdock, D.G.; Angelin, A.; Singh, L.N.; et al. Core Mitochondrial Genes Are Down-Regulated during SARS-CoV-2 Infection of Rodent and Human Hosts. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eabq1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhardt, N.; Noval, M.G.; Kaur, R.; Amadori, L.; Gildea, M.; Sajja, S.; Das, D.; Cilhoroz, B.; Stewart, O.J.; Fernandez, D.M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infection Triggers pro-Atherogenic Inflammatory Responses in Human Coronary Vessels. Nat. Cardiovasc. Res. 2023, 2, 899–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, A.; Ong, P. Endothelial Dysfunction in COVID-19: A Potential Predictor of Long-COVID? Int. J. Cardiol. 2022, 349, 155–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccatonda, A.; Campello, E.; Simion, C.; Simioni, P. Long-Term Hypercoagulability, Endotheliopathy and Inflammation Following Acute SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2023, 16, 1035–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.W.; Ilyas, I.; Weng, J.P. Endothelial Dysfunction in COVID-19: An Overview of Evidence, Biomarkers, Mechanisms and Potential Therapies. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2023, 44, 695–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfaro, E.; Díaz-García, E.; García-Tovar, S.; Galera, R.; Casitas, R.; Torres-Vargas, M.; López-Fernández, C.; Añón, J.M.; García-Río, F.; Cubillos-Zapata, C. Endothelial Dysfunction and Persistent Inflammation in Severe Post-COVID-19 Patients: Implications for Gas Exchange. BMC Med. 2024, 22, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untersmayr, E.; Venter, C.; Smith, P.; Rohrhofer, J.; Ndwandwe, C.; Schwarze, J.; Shannon, E.; Sokolowska, M.; Sadlier, C.; O’Mahony, L. Immune Mechanisms Underpinning Long COVID: Collegium Internationale Allergologicum Update 2024. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2024, 185, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Araluce, R.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Fernández-Lázaro, C.I.; Bes-Rastrollo, M.; Gea, A.; Carlos, S. Mediterranean Diet and the Risk of COVID-19 in the “Seguimiento Universidad de Navarra” Cohort. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 3061–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, G.; Pala, B.; Gualtieri, P.; Tocci, G.; La Placa, G.; Di Renzo, L. Adherence to Mediterranean Diet and Implications for Cardiovascular Risk Prevention. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visioli, F.; Galli, C. Biological Properties of Olive Oil Phytochemicals. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2002, 42, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuffaro, D.; Pinto, D.; Silva, A.M.; Bertolini, A.; Bertini, S.; Saba, A.; Macchia, M.; Rodrigues, F.; Digiacomo, M. Insights into the Antioxidant/Antiradical Effects and In Vitro Intestinal Permeation of Oleocanthal and Its Metabolites Tyrosol and Oleocanthalic Acid. Molecules 2023, 28, 5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuharu, T.; Setoh, K.; Kawaguchi, T.; Nakayama, T.; Matsuda, F. Brachial-Ankle Pulse Wave Velocity and Cardio-Ankle Vascular Index Are Associated with Future Cardiovascular Events in a General Population: The Nagahama Study. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2021, 23, 1390–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Hu, M.J.; Cui, Y.J.; Liang, L.; Zhou, M.M.; Yang, Y.W.; Huang, F. Carotid-Femoral Pulse Wave Velocity in the Prediction of Cardiovascular Events and Mortality: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Angiology 2018, 69, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, K.L.; Rossman, M.J.; Chonchol, M.; Seals, D.R. Strategies for Achieving Healthy Vascular Aging. Hypertension 2018, 71, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnaubelt, S.; Oppenauer, J.; Tihanyi, D.; Mueller, M.; Maldonado-Gonzalez, E.; Zejnilovic, S.; Haslacher, H.; Perkmann, T.; Strassl, R.; Anders, S.; et al. Arterial Stiffness in Acute COVID-19 and Potential Associations with Clinical Outcome. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 290, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, A.; Bhushan, D.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, A.; Singh, V.; Singh, P.K. The COSEVAST Study Outcome: Evidence of COVID-19 Severity Proportionate to Surge in Arterial Stiffness. Indian. J. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 25, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavraganis, G.; Dimopoulou, M.A.; Delialis, D.; Bampatsias, D.; Patras, R.; Sianis, A.; Maneta, E.; Stamatelopoulos, K.; Georgiopoulos, G. Clinical Implications of Vascular Dysfunction in Acute and Convalescent COVID-19: A Systematic Review. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 52, e13859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durieux, J.C.; Zisis, S.N.; Mouchati, C.; Labbato, D.; Abboud, M.; McComsey, G.A. Sex Modifies the Effect of COVID-19 on Arterial Elasticity. Viruses 2024, 16, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-Sierra, A.; de la O, V.; Higuera-Gómez, A.; Chero-Sandoval, L.; de Cuevillas, B.; Martínez-Urbistondo, M.; Moreno-Torres, V.; Pintos-Pascual, I.; Castejón, R.; Martínez, J.A. Mediterranean Diet and Olive Oil Redox Interactions on Lactate Dehydrogenase Mediated by Gut Oscillibacter in Patients with Long-COVID-19 Syndrome. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupo, R.; Castellana, F.; Lisco, G.; Corbo, F.; Crupi, P.; Sardone, R.; Catino, F.; Perna, S.; Gesualdo, L.; Lozupone, M.; et al. The Effect of a Mediterranean Diet on Arterial Stiffness: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Sánchez, L.; Tamayo-Morales, O.; Suárez-Moreno, N.; Bermejo-Martín, J.F.; Domínguez-Martín, A.; Martín-Oterino, J.A.; Martín-González, J.I.; González-Calle, D.; García-García, Á.; Lugones-Sánchez, C.; et al. Relationship between the Structure, Function and Endothelial Damage, and Vascular Ageing and the Biopsychological Situation in Adults Diagnosed with Persistent COVID (BioICOPER Study). A Research Protocol of a Cross-Sectional Study. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1236430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano, J.B.; Murthy, S.; Marshall, J.C.; Relan, P.; Diaz, J.V., on behalf of the WHO Clinical Case Definition Working Group on Post-COVID-19 Condition. A Clinical Case Definition of Post-COVID-19 Condition by a Delphi Consensus. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, e102–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, H.; Fitó, M.; Estruch, R.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Corella, D.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.; Ros, E.; Salaverría, I.; Fiol, M.; et al. A Short Screener Is Valid for Assessing Mediterranean Diet Adherence among Older Spanish Men and Women. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 135566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortier, C.; Agharazii, M. Arterial Stiffness Gradient. Pulse 2015, 3, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.M.; Torrado, J.; Sosa, C.; Diaz, A.; Bia, D.; Zócalo, Y. Center-To-Periphery Arterial Stiffness Gradient Is Attenuated and/or Reversed in Pregnancy-Associated Hypertension. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 766723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirai, K.; Hiruta, N.; Song, M.; Kurosu, T.; Suzuki, J.; Tomaru, T.; Miyashita, Y.; Saiki, A.; Takahashi, M.; Suzuki, K.; et al. Cardio-Ankle Vascular Index (CAVI) as a Novel Indicator of Arterial Stiffness: Theory, Evidence and Perspectives. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2011, 18, 924–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reference Values for Arterial Stiffness’ Collaboration. Determinants of Pulse Wave Velocity in Healthy People and in the Presence of Cardiovascular Risk Factors: ‘Establishing Normal and Reference Values’. Eur. Heart J. 2010, 31, 2338–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson Wadström, B.; Fatehali, A.H.; Engström, G.; Nilsson, P.M. A Vascular Aging Index as Independent Predictor of Cardiovascular Events and Total Mortality in an Elderly Urban Population. Angiology 2019, 70, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Agabiti Rosei, E.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.; Coca, A.; De Simone, G.; Dominiczak, A.; et al. 2018 Practice Guidelines for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension and the European Society of Cardiology: ESH/ESC Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2018, 36, 2284–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO MONICA Project Principal Investigators. The World Health Organization Monica Project (Monitoring Trends and Determinants in Cardiovascular Disease): A Major International Collaboration. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1988, 41, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steeves, J.A.; Tyo, B.M.; Connolly, C.P.; Gregory, D.A.; Stark, N.A.; Bassett, D.R. Validity and Reliability of the Omron HJ-303 Tri-Axial Accelerometer-Based Pedometer. J. Phys. Act. Health 2011, 8, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, K.G.M.M.; Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Cleeman, J.I.; Donato, K.A.; Fruchart, J.C.; James, W.P.T.; Loria, C.M.; Smith, S.C. Harmonizing the Metabolic Syndrome: A Joint Interim Statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; And International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation 2009, 120, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar]
- Association, W.M. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasalvia, P.; Gianfagna, F.; Veronesi, G.; Franchin, M.; Tozzi, M.; Castelli, P.; Grandi, A.M.; Zambon, A.; Iacoviello, L.; Ferrario, M.M. Identification of Dietary Patterns in a General Population of North Italian Adults and Their Association with Arterial Stiffness. The RoCAV Study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 31, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro Cáceres, A.; Navarro-Matías, E.; Gómez-Sánchez, M.; Tamayo-Morales, O.; Lugones-Sánchez, C.; González-Sánchez, S.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, E.; García-Ortiz, L.; Gómez-Sánchez, L.; Gómez-Marcos, M.A.; et al. Increase in Vascular Function Parameters According to Lifestyles in a Spanish Population without Previous Cardiovascular Disease-EVA Follow-Up Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Laar, R.J.; Stehouwer, C.D.; van Bussel, B.C.; Prins, M.H.; Twisk, J.W.; Ferreira, I. Adherence to a Mediterranean Dietary Pattern in Early Life Is Associated with Lower Arterial Stiffness in Adulthood: The Amsterdam Growth and Health Longitudinal Study. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 273, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Sánchez, L.; González-Falcon, D.; Llamas-Ramos, R.; Rodríguez, M.C.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, E.; García-Ortiz, L.; Llamas-Ramos, I.; Gómez-Sánchez, M.; Gómez-Marcos, M.A. The Relationship between Healthy Vascular Aging with the Mediterranean Diet and Other Lifestyles in the Spanish Population: The EVA Study. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GómezSánchez, M.; Gómez Sánchez, L.; Patino-Alonso, M.C.; Alonso-Domínguez, R.; Sánchez-Aguadero, N.; Lugones-Sánchez, C.; Rodríguez Sánchez, E.; García Ortiz, L.; Gómez-Marcos, M.A. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet in Spanish Population and Its Relationship with Early Vascular Aging According to Sex and Age: EVA Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baissary, J.; Koberssy, Z.; Durieux, J.C.; Atieh, O.; Daher, J.; Ailstock, K.; Labbato, D.; Foster, T.; Rodgers, M.A.; Merheb, A.; et al. The Effect of COVID-19 on Arterial Stiffness and Inflammation: A Longitudinal Prospective Study. Viruses 2025, 17, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrignani, M.G.; Lucà, F.; Favilli, S.; Benvenuto, M.; Rao, C.M.; Di Fusco, S.A.; Gabrielli, D.; Gulizia, M.M. Lifestyles and Cardiovascular Prevention in Childhood and Adolescence. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2019, 40, 1113–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, A.E.; Howlett, S.E. Differences in Cardiovascular Aging in Men and Women. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1065, 389–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theresa, C.; Katebe, B.; Shibao, C.A.; Kirabo, A. Arterial Stiffness in Adults with Long COVID in Sub-Saharan Africa. Physiol. Rep. 2024, 12, e70029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez-Moreno, N.; Gómez-Sánchez, L.; Navarro-Caceres, A.; Arroyo-Romero, S.; Domínguez-Martín, A.; Lugones-Sánchez, C.; Tamayo-Morales, O.; González-Sánchez, S.; Castro-Rivero, A.B.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, E.; et al. Association of Mediterranean Diet with Cardiovascular Risk Factors and with Metabolic Syndrome in Subjects with Long COVID: BioICOPER Study. Nutrients 2025, 17, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Y.; Ma, W.; Accorsi, E.K.; Ding, M.; Hu, F.; Willett, W.C.; Chan, A.T.; Sun, Q.; Rich-Edwards, J.; Smith-Warner, S.A.; et al. Long-Term Diet and Risk of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Infection and Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Severity. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 116, 1672–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlidou, E.; Poulios, E.; Papadopoulou, S.K.; Fasoulas, A.; Dakanalis, A.; Giaginis, C. Clinical Evidence on the Potential Beneficial Effects of Diet and Dietary Supplements against COVID-19 Infection Risk and Symptoms’ Severity. Med. Sci. 2024, 12, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, S.J. COVID-19 Accelerates Endothelial Dysfunction and Nitric Oxide Deficiency. Microbes Infect. 2020, 22, 149–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | Global (n = 304) | Men (n = 97) | Women (n = 207) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 52.71 ± 11.94 | 55.70 ± 12.28 | 51.32 ± 11.54 | 0.001 |
| Time with COVID-19 (months) | 38.66 ± 9.58 | 38.74 ± 9.41 | 38.50 ± 9.96 | 0.990 |
| Lifestyles | ||||
| MD (total score) | 7.80 ± 2.33 | 7.71 ± 2.23 | 7.84 ± 2.39 | 0.487 |
| Adherence to the MD ≥ 8, n (%) | 123 (40.5) | 38 (39.2) | 85 (41.1) | 0.427 |
| Alcohol (g/w) | 29.35 ± 52.87 | 60.39 ± 76.35 | 14.88 ± 27.19 | <0.001 |
| Steps per day | 7447 ± 3633 | 7069 ± 3302 | 7624 ± 3773 | 0.194 |
| CVRF | ||||
| Years of smoking | 22.90 ±11.62 | 24.96 ± 12.01 | 21.51 ± 11.22 | 0.106 |
| Active smoker, n (%) | 17 (5.7) | 8 (8.4) | 9 (4.5) | 0.065 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 119.95 ± 16.75 | 129.45 ± 14.37 | 115.52 ± 15.94 | <0.001 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 76.85 ± 11.11 | 82.34 ± 11.04 | 74.30 ± 10.20 | <0.001 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 110 (36.2) | 53 (54.6) | 57 (27.5) | <0.001 |
| Antihypertensives, mean ± SD | 0.36 ± 0.70 | 0.30 ± 0.66 | 0.49 ± 0.78 | 0.024 |
| Antihypertensives, n (%) | 79 (25.9%) | 45 (21.6%) | 34 (35.1%) | 0.013 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 187.45 ± 34.30 | 182.11 ± 32.94 | 189.95 ± 34.71 | 0.029 |
| LDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 113.03 ± 31.76 | 113.59 ± 32.12 | 112.77 ± 31.67 | 0.417 |
| HDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 56.92 ± 13.58 | 48.78 ± 10.86 | 60.73 ± 13.06 | <0.001 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 102.23 ± 50.81 | 117.47 ± 54.39 | 95.09 ± 47.52 | <0.001 |
| Dyslipidaemia, n (%) | 172 (57.0) | 67 (69.1) | 105 (69.1) | 0.003 |
| Antihyperlipidemic, mean ± SD | 0.29 ± 0.56 | 0.20 ± 0.48 | 0.47 ± 0.66 | <0.001 |
| Antihyperlipidemic, n (%) | 75 (24.6%) | 35 (16.8%) | 40 (41.2%) | <0.001 |
| FPG (mg/dL) | 87.88 ± 17.67 | 94.37 ± 19.78 | 84.84 ± 15.74 | <0.001 |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 37 (12.2) | 22 (22.7) | 15 (7.3) | <0.001 |
| Hypoglycaemics, mean ± SD | 0.11 ± 0.31 | 0.07 ± 0.25 | 0.19 ± 0.39 | 0.004 |
| Hypoglycaemics, n (%) | 32 (10.5%) | 14 (6.7%) | 18 (18.6%) | 0.002 |
| Weight (kg) | 75.95 ± 17.39 | 88.09 ± 14.95 | 70.29 ± 15.46 | <0.001 |
| Height (cm) | 164.50 ± 8.71 | 172.51 ± 7.35 | 160.77 ± 6.52 | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.97 ± 5.55 | 29.60 ± 4.64 | 27.21 ± 5.78 | <0.001 |
| WC (cm) | 93.92 ± 15.39 | 104.34 ± 12.52 | 89.04 ± 14.31 | <0.001 |
| Obesity, n (%) | 99 (32.5) | 55 (26.4) | 44 (45.4) | <0.001 |
| Number of components MetS | 1.53 ± 1.34 | 2.04 ± 1.38 | 1.30 ± 1.26 | <0.001 |
| MetS, n (%) | 72 (23.7) | 39 (40.2) | 33 (15.9) | <0.001 |
| Variable | Global (n = 304) | Men (n = 97) | Women (n = 207) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cIMT, mean ± SD mm | 0.638 ± 0.092 | 0.679 ± 0.116 | 0.619 ± 0.072 | <0.001 |
| cfPWV, mean ± SD m/s | 7.797 ± 2.548 | 7.895 ± 1.360 | 7.307 ± 2.055 | <0.001 |
| baPWV, mean ± SD m/s | 7.509 ± 1.261 | 8.854 ± 3.134 | 7.328 ± 1.171 | <0.001 |
| CAVI, mean ± SD | 12.794 ± 2.380 | 13.632 ± 2.403 | 12.396 ± 2.268 | <0.001 |
| VAI, mean ± SD | 30.871 ± 19.417 | 72.921 ± 17.607 | 63.066 ± 11.867 | <0.001 |
| cIMT ≤ 0.625, n (%) | 152 (50.0) | 33 (34.0) | 119 (57.5) | <0.001 |
| cfPWV ≤ 7.410, n (%), | 156 (51.3) | 36 (37.1) | 120 (58.0) | 0.001 |
| baPWV ≤ 12.315, n (%), | 151 (49.7) | 30 (30.9) | 121 (58.5) | <0.001 |
| CAVI ≤ 7.400, n (%) | 151 (48,7) | 39 (40.2) | 112 (54.1) | 0.016 |
| VAI ≤ 63.692, n (%) | 151 (49.7) | 29 (29.9) | 122 (58.9) | <0.001 |
| Variable | Low-Adherence MD, <8 Points (n = 181) | High-Adherence MD, ≥8 Points (n = 123) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 51.71 ±12.44 | 54.35 ± 10.95 | 0.026 |
| Time with COVID-19 (months) | 29.56 ± 51.33 | 28.96 ± 55.42 | 0.462 |
| Lifestyles | |||
| Alcohol consumption (g/w) | 23.94 ± 11.56 | 21.91 ± 11.15 | 0.354 |
| Steps per day | 7422 ± 3743 | 7483 ± 3480 | 0.443 |
| CVRF | |||
| Years of smoking | 23.94 ± 11.56 | 21.91 ± 11.15 | 0.341 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 118.52 ± 16.14 | 122.11 ± 17.50 | 0.171 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 76.67 ± 11.20 | 77.19 ± 11.03 | 0.036 * |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 188.49 ± 33.96 | 185.86 ± 35.00 | 0.346 |
| LDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 113.93 ± 32.31 | 111.86 ± 31.12 | 0.258 |
| HDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 55.81 ± 13.14 | 58.36 ± 14.00 | 0.258 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 103.46 ± 49.35 | 100.54 ± 53.22 | 0.050 * |
| FPG (mg/dL) | 86.83 ± 13.51 | 89.50 ± 22.42 | 0.315 |
| Weight (kg) | 77.30 ± 17.20 | 74.13 ± 1.00 | 0.191 |
| Height (cm) | 164.70 ± 8.30 | 164.27 ± 9.33 | 0.682 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 28.42 ± 5.66 | 27.35 ± 5.36 | 0.096 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 94.97 ± 15.91 | 92.37 ± 14.76 | 0.145 |
| Number of components MetS | 1.59 ± 1.37 | 1.46 ± 1.29 | 0.431 |
| cIMT, mean ± SD (mm) | 0.63 ± 0.10 | 0.65 ± 0.08 | 0.194 |
| cfPWV, mean ± SD (m/s) | 7.64 ± 2.53 | 8.03 ± 2.56 | 0.193 |
| baPWV, mean ± SD (m/s) | 7.50 ± 1.25 | 7.60 ± 1.28 | 0.322 |
| CAVI, mean ± SD | 12.66 ± 2.30 | 12.99 ± 2.48 | 0.248 |
| VAI, mean ± SD | 65.18 ± 14.51 | 67.57 ± 14.73 | 0.166 |
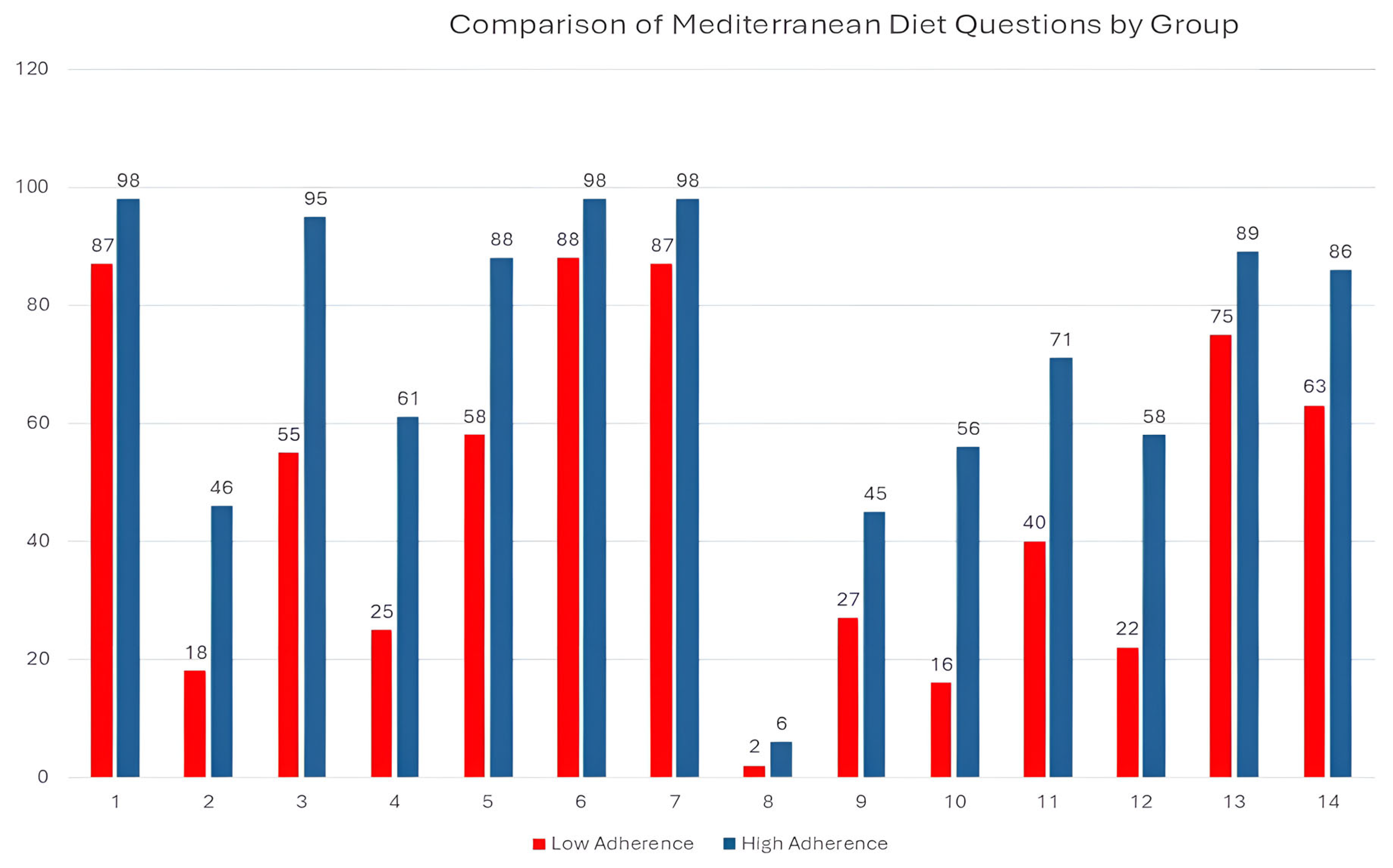
| MD Components | Global (n %) | Men (n %) | Women (n %) | p Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. USE OF OLIVE OIL AS THE PRINCIPAL SOURCE OF FAT FOR COOKING | 272 | (91.6%) | 85 | (89.5%) | 187 | (92.6%) | 0.247 |
| 2. ≥4 TABLESPOONS OF OLIVE OIL PER DAY | 88 | (29.8%) | 25 | (26.3%) | 63 | (31.5%) | 0.221 |
| 3. ≥2 SERVINGS OF VEGETABLES PER DAY | 212 | (71.6%) | 58 | (61.1%) | 154 | (76.6%) | 0.005 * |
| 4. ≥3 PIECES OF FRUIT PER DAY | 118 | (39.6%) | 38 | (39.6%) | 80 | (39.6%) | 0.550 |
| 5. <1 SERVING OF RED MEAT, HAMBURGER, OR SAUSAGE PER DAY | 208 | (70.3%) | 61 | (63.5%) | 147 | (73.5%) | 0.054 |
| 6. <1 SERVING OF BUTTER, MARGARINE, OR CREAM PER DAY | 271 | (91.9%) | 90 | (94.7%) | 181 | (90.5%) | 0.155 |
| 7. <1 CARBONATED AND/OR SUGAR-SWEETENED BEVERAGE PER DAY | 272 | (91.3%) | 88 | (91.7%) | 184 | (91.1%) | 0.530 |
| 8. ≥7 CUPS OF WINE PER WEEK | 10 | (3.4%) | 9 | (3.1%) | 1 | (0.3%) | <0.001 * |
| 9. ≥3 SERVINGS OF PULSES PER WEEK | 102 | (34.3%) | 40 | (42.1%) | 62 | (30.7%) | 0.037 * |
| 10. ≥3 SERVINGS OF FISH/SEAFOOD PER WEEK | 96 | (32.4%) | 28 | (29.5%) | 68 | (33.8%) | 0.271 |
| 11. <2 COMMERCIAL PASTRIES SUCH AS COOKIES OR CAKES PER WEEK | 156 | (52.7%) | 44 | (45.8%) | 112 | (56.0%) | 0.065 |
| 12. ≥3 SERVINGS OF NUTS PER WEEK | 110 | (36.9%) | 39 | (40.6%) | 71 | (35.1%) | 0.215 |
| 13. PREFERRING TO EAT CHICKEN, TURKEY, OR RABBIT INSTEAD OF BEEF, PORK, HAMBURGERS, OR SAUSAGES | 242 | (81.2%) | 68 | (70.8%) | 174 | (86.1%) | 0.002 * |
| 14. BOILED VEGETABLES, PASTA, RICE, OR OTHER DISHES WITH A SAUCE OF TOMATO, GARLIC, ONION, OR LEEKS SAUTÉED IN OLIVE OIL ≥2 TIMES PER WEEK | 214 | (72.1%) | 75 | (78.9%) | 139 | (68.8%) | 0.045 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Navarro-Cáceres, A.; Gómez-Sánchez, L.; Arroyo-Romero, S.; Suárez-Moreno, N.; Domínguez-Martín, A.; Lugones-Sánchez, C.; González-Sánchez, S.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, E.; García-Ortiz, L.; Gómez-Sánchez, M.; et al. Relationship of Mediterranean Diet and Its Components with Parameters of Structure, Vascular Function, and Vascular Aging in Subjects Diagnosed with Long COVID: BioICOPER Study. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3226. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17203226
Navarro-Cáceres A, Gómez-Sánchez L, Arroyo-Romero S, Suárez-Moreno N, Domínguez-Martín A, Lugones-Sánchez C, González-Sánchez S, Rodríguez-Sánchez E, García-Ortiz L, Gómez-Sánchez M, et al. Relationship of Mediterranean Diet and Its Components with Parameters of Structure, Vascular Function, and Vascular Aging in Subjects Diagnosed with Long COVID: BioICOPER Study. Nutrients. 2025; 17(20):3226. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17203226
Chicago/Turabian StyleNavarro-Cáceres, Alicia, Leticia Gómez-Sánchez, Silvia Arroyo-Romero, Nuria Suárez-Moreno, Andrea Domínguez-Martín, Cristina Lugones-Sánchez, Susana González-Sánchez, Emiliano Rodríguez-Sánchez, Luis García-Ortiz, Marta Gómez-Sánchez, and et al. 2025. "Relationship of Mediterranean Diet and Its Components with Parameters of Structure, Vascular Function, and Vascular Aging in Subjects Diagnosed with Long COVID: BioICOPER Study" Nutrients 17, no. 20: 3226. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17203226
APA StyleNavarro-Cáceres, A., Gómez-Sánchez, L., Arroyo-Romero, S., Suárez-Moreno, N., Domínguez-Martín, A., Lugones-Sánchez, C., González-Sánchez, S., Rodríguez-Sánchez, E., García-Ortiz, L., Gómez-Sánchez, M., Navarro-Matias, E., & Gómez-Marcos, M. A. (2025). Relationship of Mediterranean Diet and Its Components with Parameters of Structure, Vascular Function, and Vascular Aging in Subjects Diagnosed with Long COVID: BioICOPER Study. Nutrients, 17(20), 3226. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17203226







