Sex-Specific Lifespan Extension and Anti-Obesogenic Effects of Salicornia europaea Extract Through Tor Signaling Modulation in Drosophila
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Extraction
2.2. Fly Husbandry
2.3. Lifespan Assay and Analysis
2.4. Body Fat Quantification
2.5. Glucose Measurement and Protein Content Analysis
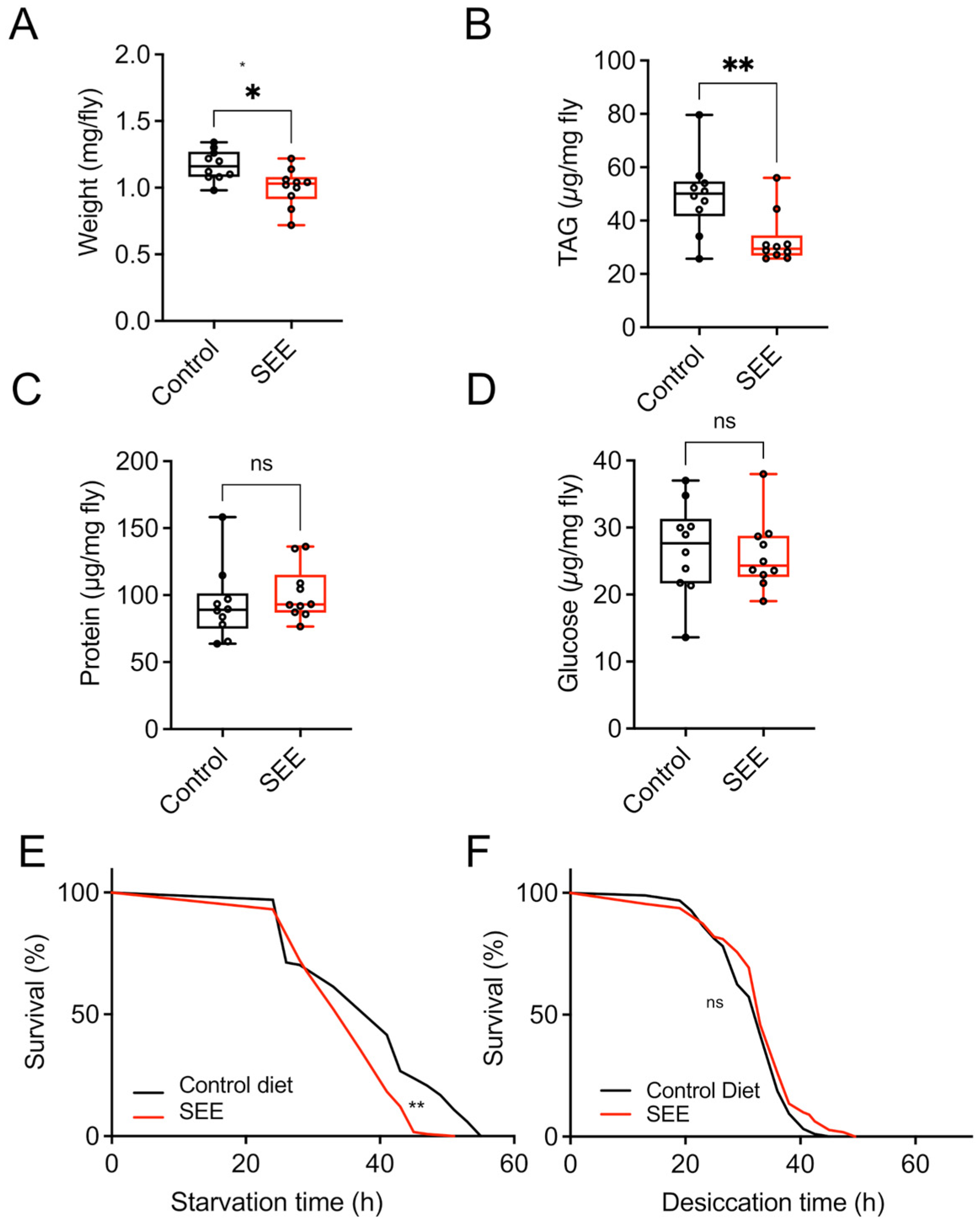
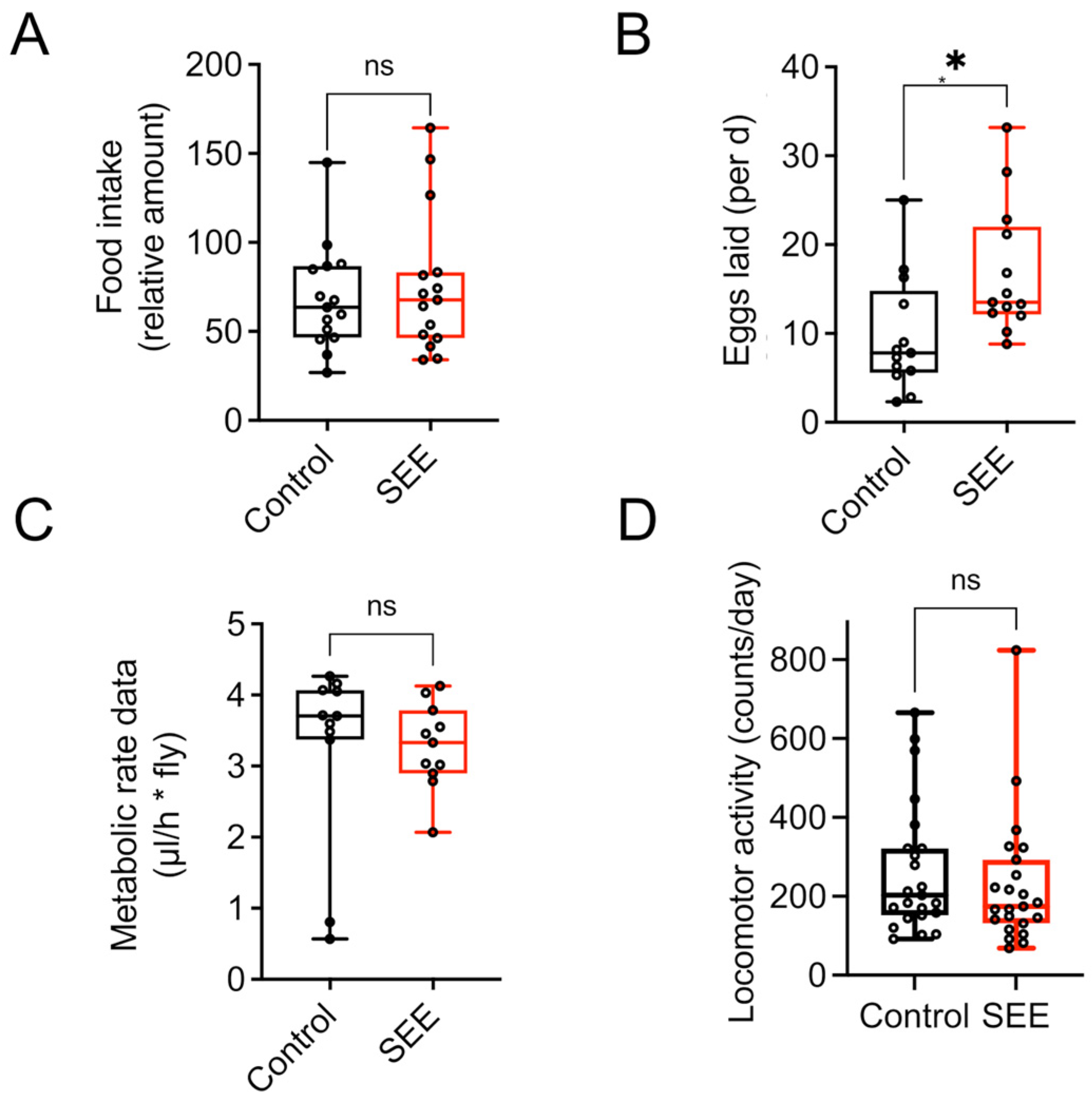
2.6. Starvation, Desiccation, Paraquat Resistance, and Fecundity Assays
2.7. Food Intake
2.8. Smurf Assay
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Salicornia Extracts Extend the Lifespan of Drosophila melanogaster in a Sex-Dependent Manner
3.2. Salicornia-Treated Fruit Flies Are Lighter and Have Reduced Triacylglyceride Levels
3.3. Effect of SEE Extract on Energy Metabolism
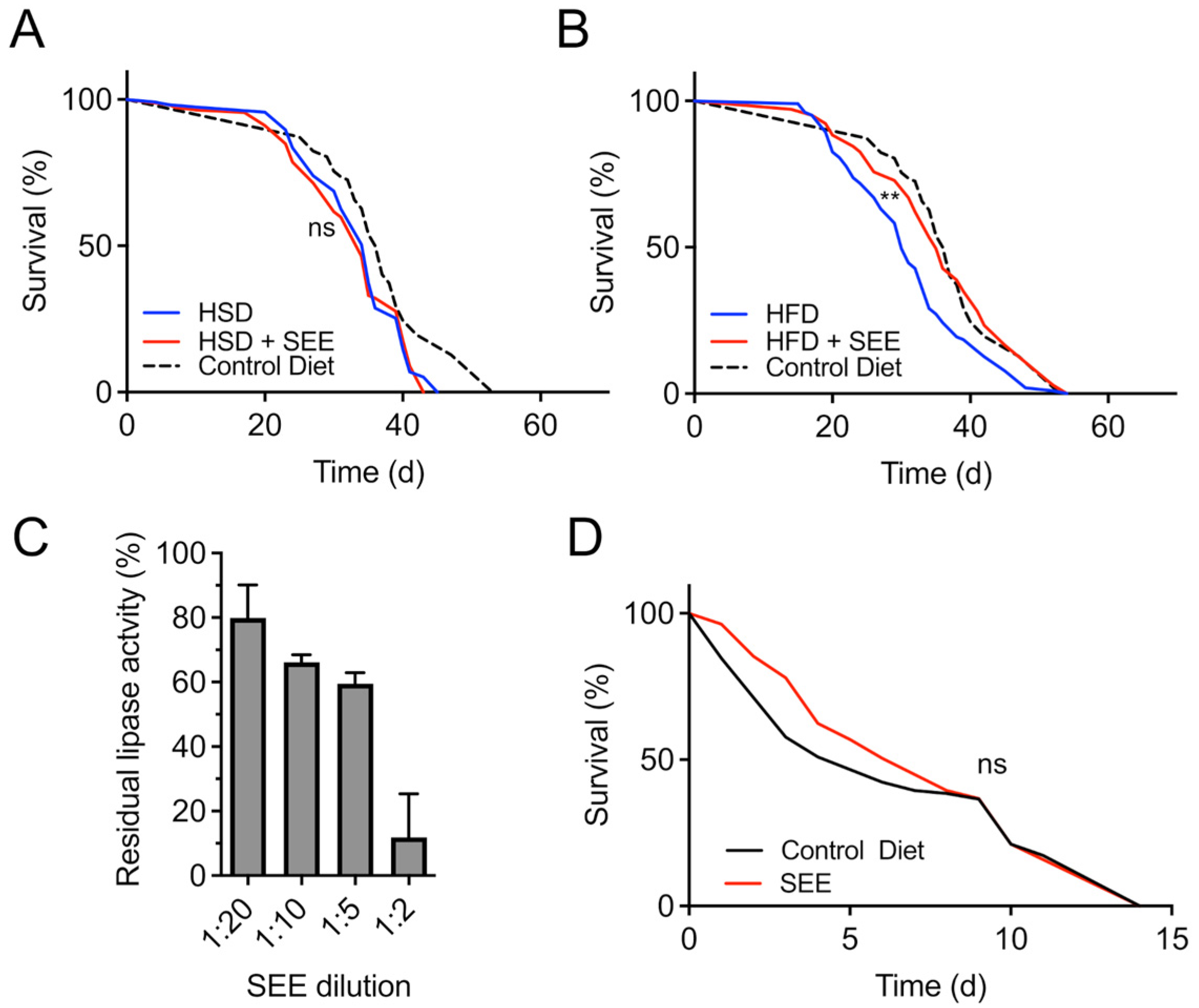
3.4. Stress Resistance to High-Fat Dieting Is Enhanced After SEE Treatment
3.5. Mode of Action of the Lifespan Prolonging Effects of Salicornia Extract
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SEE | Salicornia europaea extract |
| rpm | Rounds per minute |
| TAG | Triacylglycerol |
References
- Brown-Borg, H.M.; Buffenstein, R. Cutting back on the essentials: Can manipulating intake of specific amino acids modulate health and lifespan? Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 39, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, L.; Partridge, L. Promoting health and longevity through diet: From model organisms to humans. Cell 2015, 161, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapahi, P.; Kaeberlein, M.; Hansen, M. Dietary restriction and lifespan: Lessons from invertebrate models. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 39, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriella, T.; Fiorella, B.; Giuseppe, P.; Elena, C. Calorie Restriction and Dietary Restriction Mimetics: A Strategy for Improving Healthy Aging and Longevity. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 2950–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo-Quan, J.I.; Tain, L.S.; Kinghorn, K.J.; Li, L.; Gronke, S.; Hinze, Y.; Blackwell, T.K.; Bjedov, I.; Partridge, L. A triple drug combination targeting components of the nutrient-sensing network maximizes longevity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 20817–20819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitto, A.; Ito, T.K.; Pineda, V.V.; LeTexier, N.J.; Huang, H.Z.; Sutlief, E.; Tung, H.; Vizzini, N.; Chen, B.; Smith, K.; et al. Transient rapamycin treatment can increase lifespan and healthspan in middle-aged mice. eLife 2016, 5, e16351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjedov, I.; Toivonen, J.M.; Kerr, F.; Slack, C.; Jacobson, J.; Foley, A.; Partridge, L. Mechanisms of life span extension by rapamycin in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. Cell Metab. 2010, 11, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulain, M.; Pes, G.M.; Grasland, C.; Carru, C.; Ferrucci, L.; Baggio, G.; Franceschi, C.; Deiana, L. Identification of a geographic area characterized by extreme longevity in the Sardinia island: The AKEA study. Exp. Gerontol. 2004, 39, 1423–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willcox, D.C.; Scapagnini, G.; Willcox, B.J. Healthy aging diets other than the Mediterranean: A focus on the Okinawan diet. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2014, 136–137, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willcox, D.C.; Willcox, B.J.; Todoriki, H.; Suzuki, M. The Okinawan diet: Health implications of a low-calorie, nutrient-dense, antioxidant-rich dietary pattern low in glycemic load. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2009, 28 (Suppl. 4), 500S–516S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onur, S.; Stöckmann, H.; Zenthoefer, M.; Piker, L.; Döring, F. The Plant Extract Collection Kiel in Schleswig-Holstein (PECKISH) Is an Open Access Screening Library. J. Food Res. 2013, 2, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, T.S. The use of Drosophila melanogaster as a screening agent for longevity factors; the effects of biotin, pyridoxine, sodium yeast nucleate, and pantothenic acid on the life span of the fruit fly. J. Gerontol. 1948, 3, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linford, N.J.; Bilgir, C.; Ro, J.; Pletcher, S.D. Measurement of lifespan in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 71, 50068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staats, S.; Luersen, K.; Wagner, A.E.; Rimbach, G. Drosophila melanogaster as a Versatile Model Organism in Food and Nutrition Research. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 3737–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, U.B.; Nichols, C.D. Human disease models in Drosophila melanogaster and the role of the fly in therapeutic drug discovery. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 411–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Romey-Glusing, R.; Tahan Zadeh, N.; von Frieling, J.; Hoffmann, J.; Huebbe, P.; Bruchhaus, I.; Rimbach, G.; Fink, C.; Roeder, T. Furbellow (Brown Algae) Extract Increases Lifespan in Drosophila by Interfering with TOR-Signaling. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahanzadeh, N.; Knop, M.; Seidler, Y.; Dirndorfer, S.; Lursen, K.; Bruchhaus, I.; Lang, R.; Rimbach, G.; Roeder, T. An aqueous extract of the brown alga Eisenia bicyclis extends lifespan in a sex-specific manner by interfering with the Tor-FoxO axis. Aging 2022, 14, 6427–6448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huebbe, P.; Nikolai, S.; Schloesser, A.; Herebian, D.; Campbell, G.; Gluer, C.C.; Zeyner, A.; Demetrowitsch, T.; Schwarz, K.; Metges, C.C.; et al. An extract from the Atlantic brown algae Saccorhiza polyschides counteracts diet-induced obesity in mice via a gut related multi-factorial mechanisms. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 73501–73515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S. Salicornia: Evaluating the halophytic extremophile as a food and a pharmaceutical candidate. 3 Biotech 2016, 6, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Go, H.K.; Kweon, M.H.; Kim, D.H. Desalted Salicornia europaea powder and its active constituent, trans-ferulic acid, exert anti-obesity effects by suppressing adipogenic-related factors. Pharm. Biol. 2018, 56, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limongelli, F.; Crupi, P.; Clodoveo, M.L.; Corbo, F.; Muraglia, M. Overview of the Polyphenols in Salicornia: From Recovery to Health-Promoting Effect. Molecules 2022, 27, 7954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, H.-Y.; Kim, M.-S.; Kim, D. Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, and Anticoagulation Activities of Salicornia europaea seeds. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Lett. 2016, 44, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, R.; Arbi, K.E.; Aydi, S.S.; Hzami, A.; Tlahig, S.; Najar, R.; Aydi, S.; Debouba, M. Biochemical composition and biological activities of Salicornia europaea L. from southern Tunisia. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2022, 16, 4833–4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira-Alves, S.C.; Andrade, F.; Prazeres, I.; Silva, A.B.; Capelo, J.; Duarte, B.; Caçador, I.; Coelho, J.; Serra, A.T.; Bronze, M.R. Impact of Drying Processes on the Nutritional Composition, Volatile Profile, Phytochemical Content and Bioactivity of Salicornia ramosissima J. Woods. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romey-Glusing, R.; Li, Y.; Hoffmann, J.; von Frieling, J.; Knop, M.; Pfefferkorn, R.; Bruchhaus, I.; Fink, C.; Roeder, T. Nutritional regimens with periodically recurring phases of dietary restriction extend lifespan in Drosophila. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 1993–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Frieling, J.; Faisal, M.N.; Sporn, F.; Pfefferkorn, R.; Nolte, S.S.; Sommer, F.; Rosenstiel, P.; Roeder, T. A high-fat diet induces a microbiota-dependent increase in stem cell activity in the Drosophila intestine. PLoS Genet. 2020, 16, e1008789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Hoffmann, J.; Li, Y.; Stephano, F.; Bruchhaus, I.; Fink, C.; Roeder, T. Octopamine controls starvation resistance, life span and metabolic traits in Drosophila. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shell, B.C.; Schmitt, R.E.; Lee, K.M.; Johnson, J.C.; Chung, B.Y.; Pletcher, S.D.; Grotewiel, M. Measurement of solid food intake in Drosophila via consumption-excretion of a dye tracer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rera, M.; Clark, R.I.; Walker, D.W. Intestinal barrier dysfunction links metabolic and inflammatory markers of aging to death in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 21528–21533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canic, T.; Lopez, J.; Ortiz-Vega, N.; Zhai, R.G.; Syed, S. High-resolution, high-throughput analysis of Drosophila geotactic behavior. bioRxiv 2024, 228, JEB248029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, J.; Romey, R.; Fink, C.; Yong, L.; Roeder, T. Overexpression of Sir2 in the adult fat body is sufficient to extend lifespan of male and female Drosophila. Aging 2013, 5, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katewa, S.D.; Kapahi, P. Dietary restriction and aging, 2009. Aging Cell 2010, 9, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katewa, S.D.; Kapahi, P. Role of TOR signaling in aging and related biological processes in Drosophila melanogaster. Exp. Gerontol. 2011, 46, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juricic, P.; Lu, Y.X.; Leech, T.; Drews, L.F.; Paulitz, J.; Lu, J.; Nespital, T.; Azami, S.; Regan, J.C.; Funk, E.; et al. Long-lasting geroprotection from brief rapamycin treatment in early adulthood by persistently increased intestinal autophagy. Nat. Aging 2022, 2, 824–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garratt, M.; Try, H.; Smiley, K.O.; Grattan, D.R.; Brooks, R.C. Mating in the absence of fertilization promotes a growth-reproduction versus lifespan trade-off in female mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 15748–15754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lushchak, O.; Strilbytska, O.; Storey, K.B. Gender-specific effects of pro-longevity interventions in Drosophila. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2023, 209, 111754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, S.; Lagisz, M.; Hector, K.L.; Spencer, H.G. Comparative and meta-analytic insights into life extension via dietary restriction. Aging Cell 2012, 11, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dähn, S.; Wagner, A.E. Drosophila melanogaster as a model organism to investigate sex specific differences. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 19648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wat, L.W.; Chowdhury, Z.S.; Millington, J.W.; Biswas, P.; Rideout, E.J. Sex determination gene transformer regulates the male-female difference in Drosophila fat storage via the adipokinetic hormone pathway. eLife 2021, 10, e72350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wat, L.W.; Chao, C.; Bartlett, R.; Buchanan, J.L.; Millington, J.W.; Chih, H.J.; Chowdhury, Z.S.; Biswas, P.; Huang, V.; Shin, L.J.; et al. A role for triglyceride lipase brummer in the regulation of sex differences in Drosophila fat storage and breakdown. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiello, G.; Sabino, C.; Pernici, D.; Audano, M.; Antonica, F.; Gianesello, M.; Ballabio, C.; Quattrone, A.; Mitro, N.; Romanel, A.; et al. Transient rapamycin treatment during developmental stage extends lifespan in Mus musculus and Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO Rep. 2022, 23, e55299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoli, D.; Boulay, K.; Kazak, L.; Pollak, M.; Mallette, F.A.; Topisirovic, I.; Hulea, L. mTOR as a central regulator of lifespan and aging. F1000Research 2019, 8, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partridge, L.; Alic, N.; Bjedov, I.; Piper, M.D. Ageing in Drosophila: The role of the insulin/Igf and TOR signalling network. Exp. Gerontol. 2011, 46, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, M.C.; Zhou, J.; Boutros, M. Ageing, metabolism and the intestine. EMBO Rep. 2020, 21, e50047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasper, H. Intestinal Stem Cell Aging: Origins and Interventions. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2020, 82, 203–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.Z.; Lin, C.S.; Wei, Y.W.; Yeh, S.R.; Tsai, Y.H.; Lee, A.C.; Lin, W.S.; Wang, P.Y. Dietary citrate supplementation enhances longevity, metabolic health, and memory performance through promoting ketogenesis. Aging Cell 2021, 20, e13510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.S.; Seo, H.; Ryu, S.; Kwon, T.D. The effect of swimming exercise and powdered-Salicornia herbacea L. ingestion on glucose metabolism in STZ-induced diabetic rats. J. Exerc. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 19, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Im, S.A.; Lee, Y.R.; Lee, Y.H.; Oh, S.T.; Gerelchuluun, T.; Kim, B.H.; Kim, Y.; Yun, Y.P.; Song, S.; Lee, C.K. Synergistic activation of monocytes by polysaccharides isolated from Salicornia herbacea and interferon-gamma. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 111, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souid, A.; Giambastiani, L.; Castagna, A.; Santin, M.; Vivarelli, F.; Canistro, D.; Morosini, C.; Paolini, M.; Franchi, P.; Lucarini, M.; et al. Assessment of the Antioxidant and Hypolipidemic Properties of Salicornia europaea for the Prevention of TAFLD in Rats. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofacker, A.C.; Knop, M.; Krauss-Etschmann, S.; Roeder, T. Time-Restricted Feeding Promotes Longevity and Gut Health Without Fitness Trade-Offs. FASEB J. 2025, 39, e70627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel, J.; Ojcius, D.M.; Chang, C.J.; Lin, C.S.; Lu, C.C.; Ko, Y.F.; Tseng, S.F.; Lai, H.C.; Young, J.D. Anti-obesogenic and antidiabetic effects of plants and mushrooms. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, B.; Friar, E.P.; Vohra, M.S.; Garrett, M.D.; Serpell, C.J.; Fong, I.L.; Wong, E.H. Mechanisms of action for the anti-obesogenic activities of phytochemicals. Phytochemistry 2020, 180, 112513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.T.; Liu, X.T.; Chen, Q.X.; Shi, Y. Lipase Inhibitors for Obesity: A Review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 128, 110314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, E.Y.; Hillman, P.F.; Ko, J.; Yang, I.; Nam, S.J. Chemical Structure and Biological Activities of Secondary Metabolites from Salicornia europaea L. Molecules 2021, 26, 2252. Molecules 2021, 26, 2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Fang, C.; Liu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Li, G.; Li, M.; Zhang, M.; Huang, Y. Chemical composition and cytotoxicity of Salicornia europaea L. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2023, 110, 104714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthivashan, G.; Park, S.Y.; Kweon, M.H.; Kim, J.; Haque, M.E.; Cho, D.Y.; Kim, I.S.; Cho, E.A.; Ganesan, P.; Choi, D.K. Ameliorative potential of desalted Salicornia europaea L. extract in multifaceted Alzheimer’s-like scopolamine-induced amnesic mice model. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siswanto, F.M.; Sakuma, R.; Oguro, A.; Imaoka, S. Chlorogenic Acid Activates Nrf2/SKN-1 and Prolongs the Lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans via the Akt-FOXO3/DAF16a-DDB1 Pathway and Activation of DAF16f. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2022, 77, 1503–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.Q.; Huang, X.B.; Xing, T.K.; Ding, A.J.; Wu, G.S.; Luo, H.R. Chlorogenic Acid Extends the Lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans via Insulin/IGF-1 Signaling Pathway. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2017, 72, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surco-Laos, F.; Cabello, J.; Gomez-Orte, E.; Gonzalez-Manzano, S.; Gonzalez-Paramas, A.M.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Duenas, M. Effects of O-methylated metabolites of quercetin on oxidative stress, thermotolerance, lifespan and bioavailability on Caenorhabditis elegans. Food Funct. 2011, 2, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tungmunnithum, D.; Drouet, S.; Hano, C. Flavonoids from Sacred Lotus Stamen Extract Slows Chronological Aging in Yeast Model by Reducing Oxidative Stress and Maintaining Cellular Metabolism. Cells 2022, 11, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallauf, K.; Duckstein, N.; Rimbach, G. A literature review of flavonoids and lifespan in model organisms. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2017, 76, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
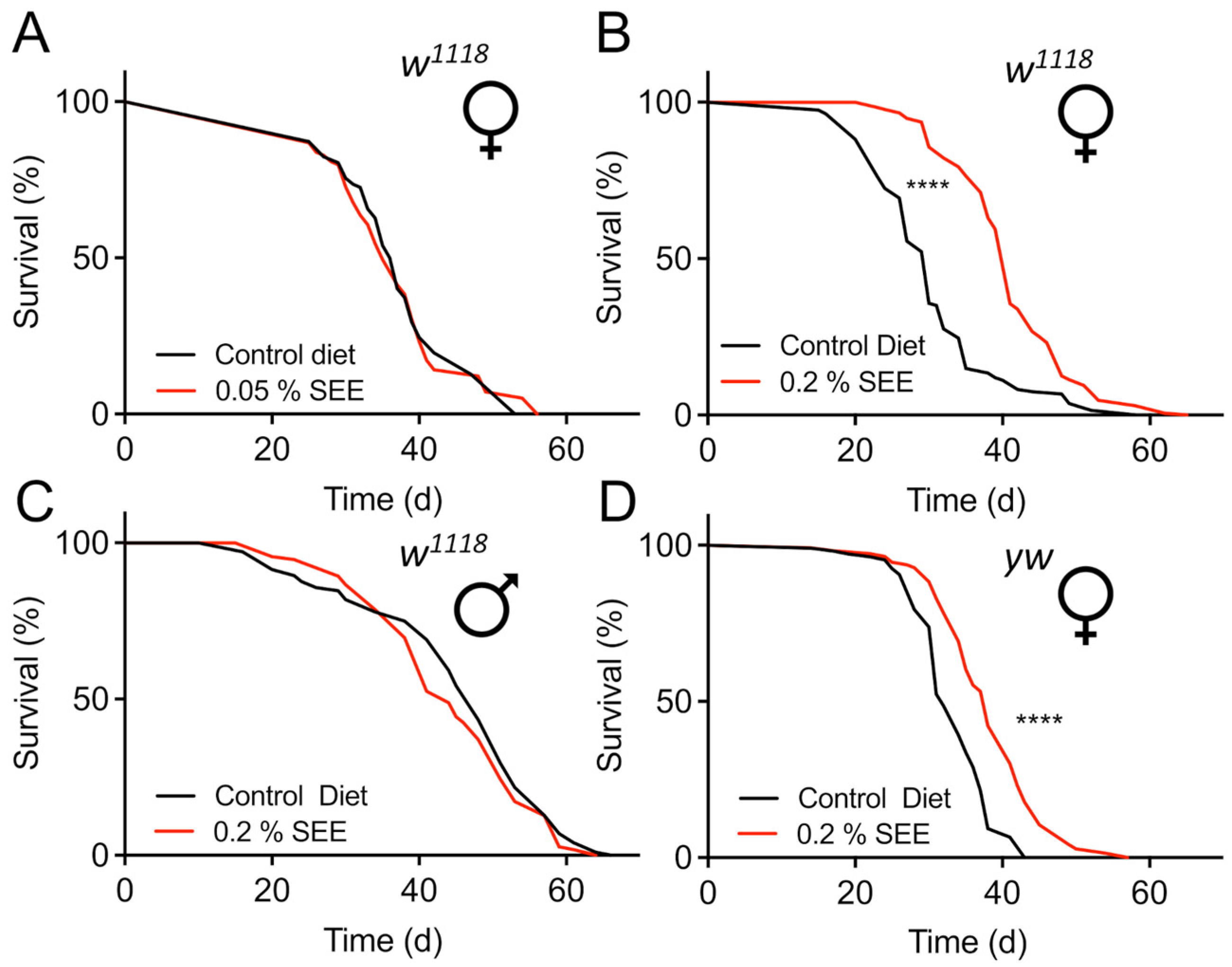
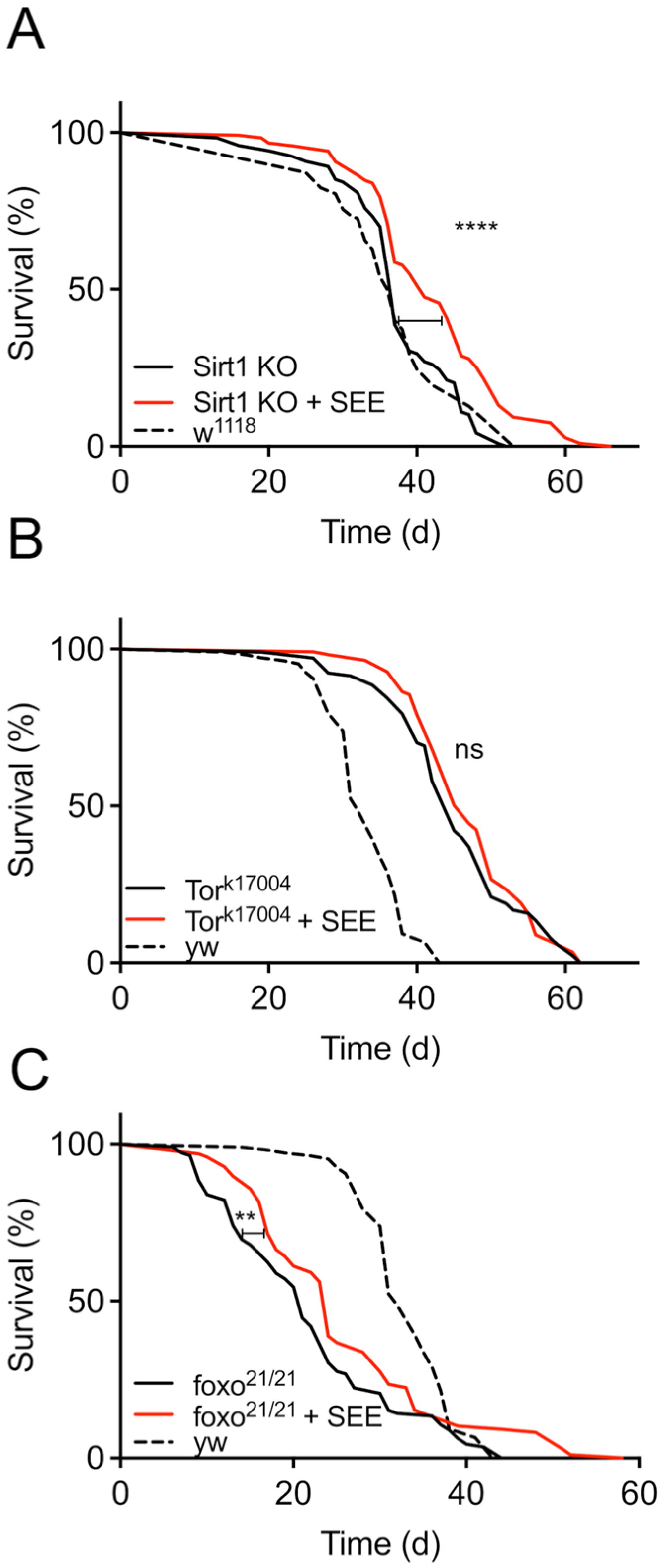
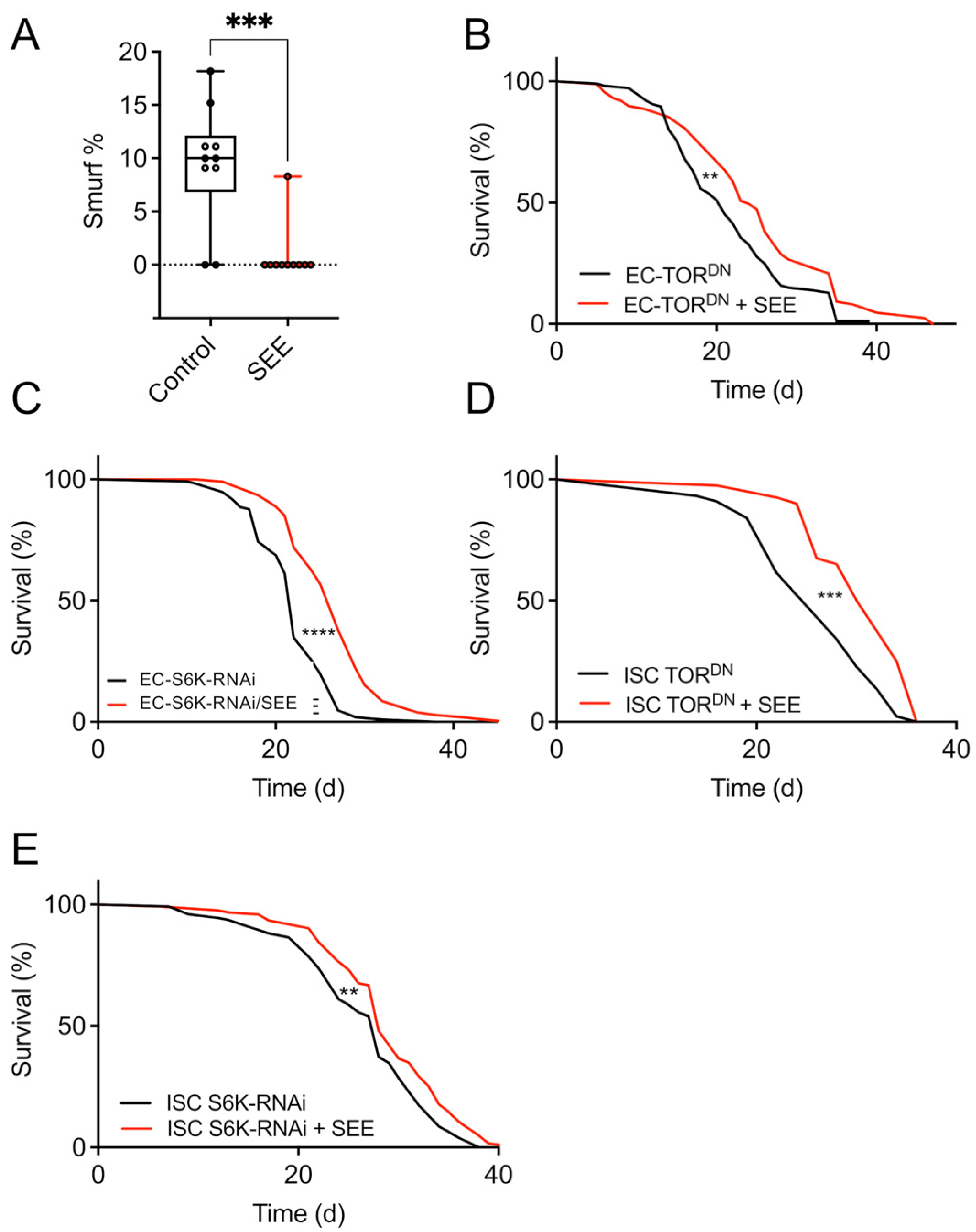
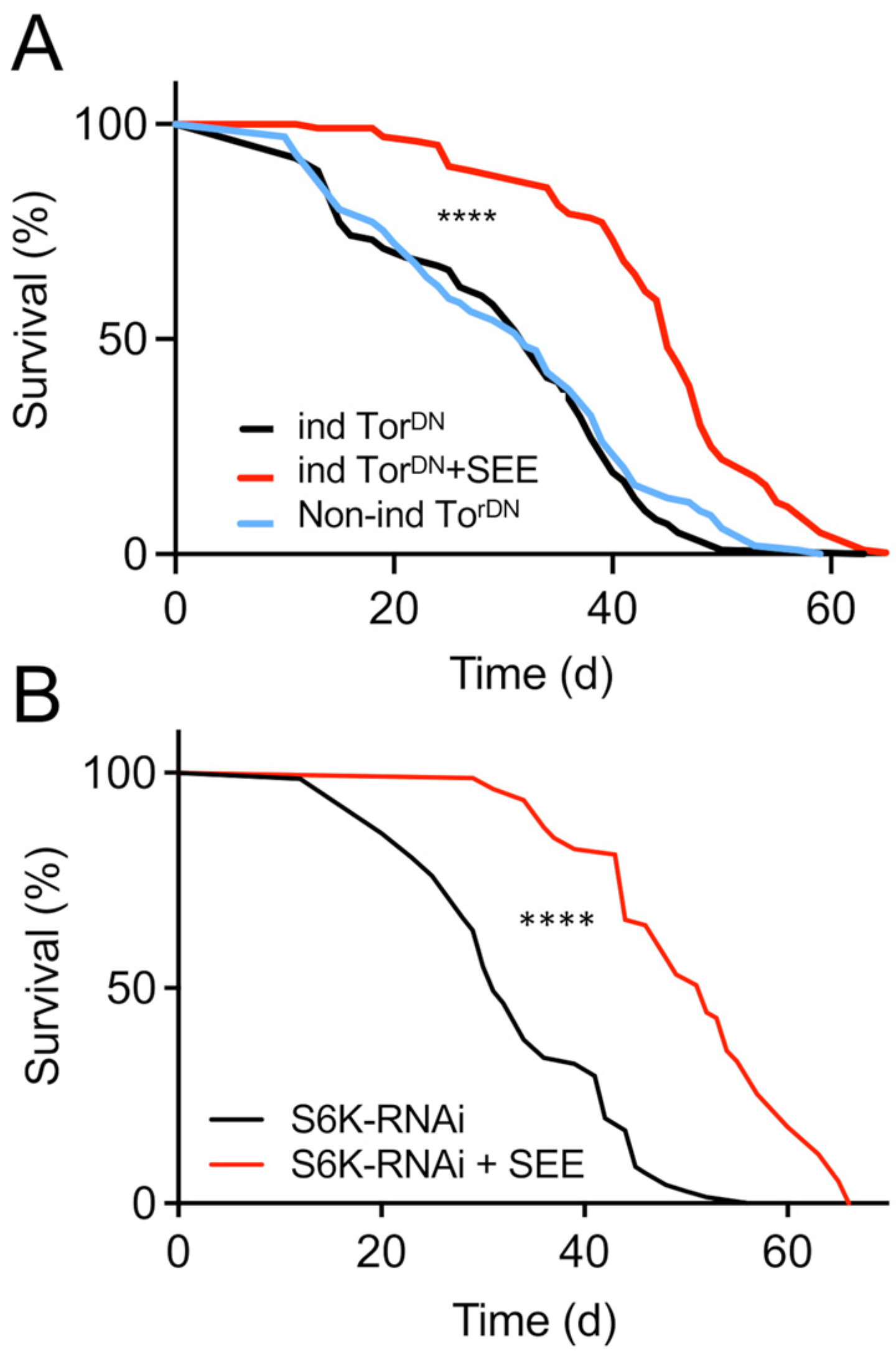
| Fly | Lifespan Extension (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| w1118 male 0.2% | - | 0.15 |
| w1118 female 0.05% | - | 0.90 |
| w1118 female 0.2% | 36.1 | <0.0001 |
| yw female 0.2% | 16.1 | <0.0001 |
| Algal Extract | Lifespan-Extension | Sex-Specificity | Tor-Dependent | Foxo-Dependent | Starvation | Body Fat Reduction | HF | HS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saliconia | +++ | ++ | +++ | + | − | ++ | ++ | − |
| Eisenia | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | − | − | − | ++ |
| Sacchoriza | + | − | +++ | ? | + − | ++ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tahan Zadeh, N.; Knop, M.; Ulrich, L.M.; Bruchhaus, I.; Lang, R.; Lüersen, K.; Rimbach, G.; Roeder, T. Sex-Specific Lifespan Extension and Anti-Obesogenic Effects of Salicornia europaea Extract Through Tor Signaling Modulation in Drosophila. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3065. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193065
Tahan Zadeh N, Knop M, Ulrich LM, Bruchhaus I, Lang R, Lüersen K, Rimbach G, Roeder T. Sex-Specific Lifespan Extension and Anti-Obesogenic Effects of Salicornia europaea Extract Through Tor Signaling Modulation in Drosophila. Nutrients. 2025; 17(19):3065. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193065
Chicago/Turabian StyleTahan Zadeh, Navid, Mirjam Knop, Lisa Marie Ulrich, Iris Bruchhaus, Roman Lang, Kai Lüersen, Gerald Rimbach, and Thomas Roeder. 2025. "Sex-Specific Lifespan Extension and Anti-Obesogenic Effects of Salicornia europaea Extract Through Tor Signaling Modulation in Drosophila" Nutrients 17, no. 19: 3065. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193065
APA StyleTahan Zadeh, N., Knop, M., Ulrich, L. M., Bruchhaus, I., Lang, R., Lüersen, K., Rimbach, G., & Roeder, T. (2025). Sex-Specific Lifespan Extension and Anti-Obesogenic Effects of Salicornia europaea Extract Through Tor Signaling Modulation in Drosophila. Nutrients, 17(19), 3065. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193065









