Extracellular Vesicles from Escherichia coli Strains of the Gut Microbiota Trigger Hepatic Antioxidant and Anti-Lipogenic Effects via the Gut-Liver Axis in Healthy Neonatal Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Isolation of Extracellular Vesicles (EVs)
2.2. Animals and Experimental Design
2.3. Cell Culture and Stimulation Conditions
2.4. Cell Viability Assays
2.5. Gene Expression Analysis by Reverse Transcription—Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.6. Quantification of Cytokines, LPS and Zonulin by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays (ELISA)
2.7. Dot Blot Assay
2.8. Lipid and Glucose Determination
2.9. Measurement of Enzyme Activities in Liver
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
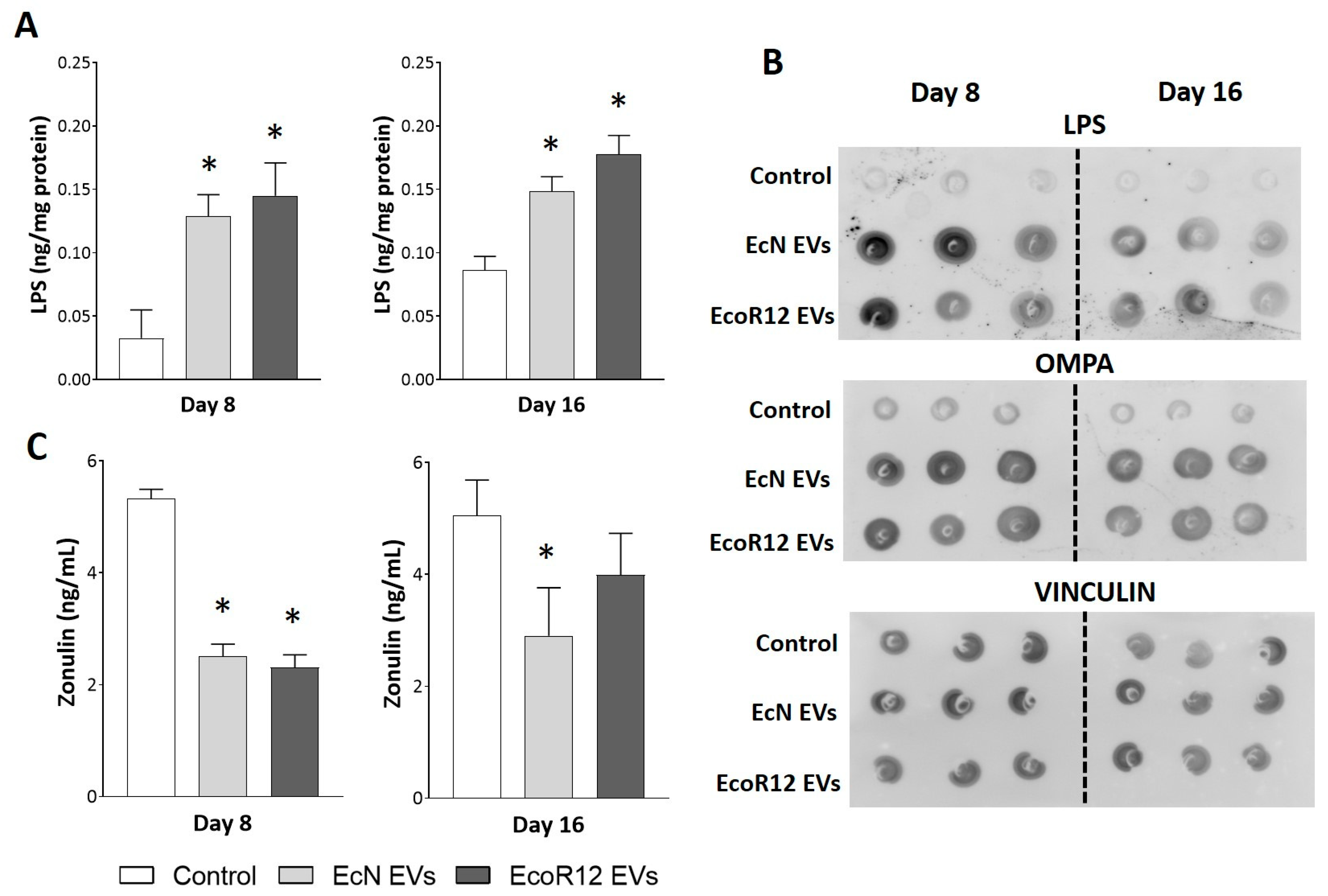
3.1. Orally Administered EVs Reach the Liver While Enhancing Gut Barrier Integrity
3.2. Interventions with EcN and EcoR12 EVs Reduce Liver Inflammation and Improve the Antioxidant Response in Neonatal Rats
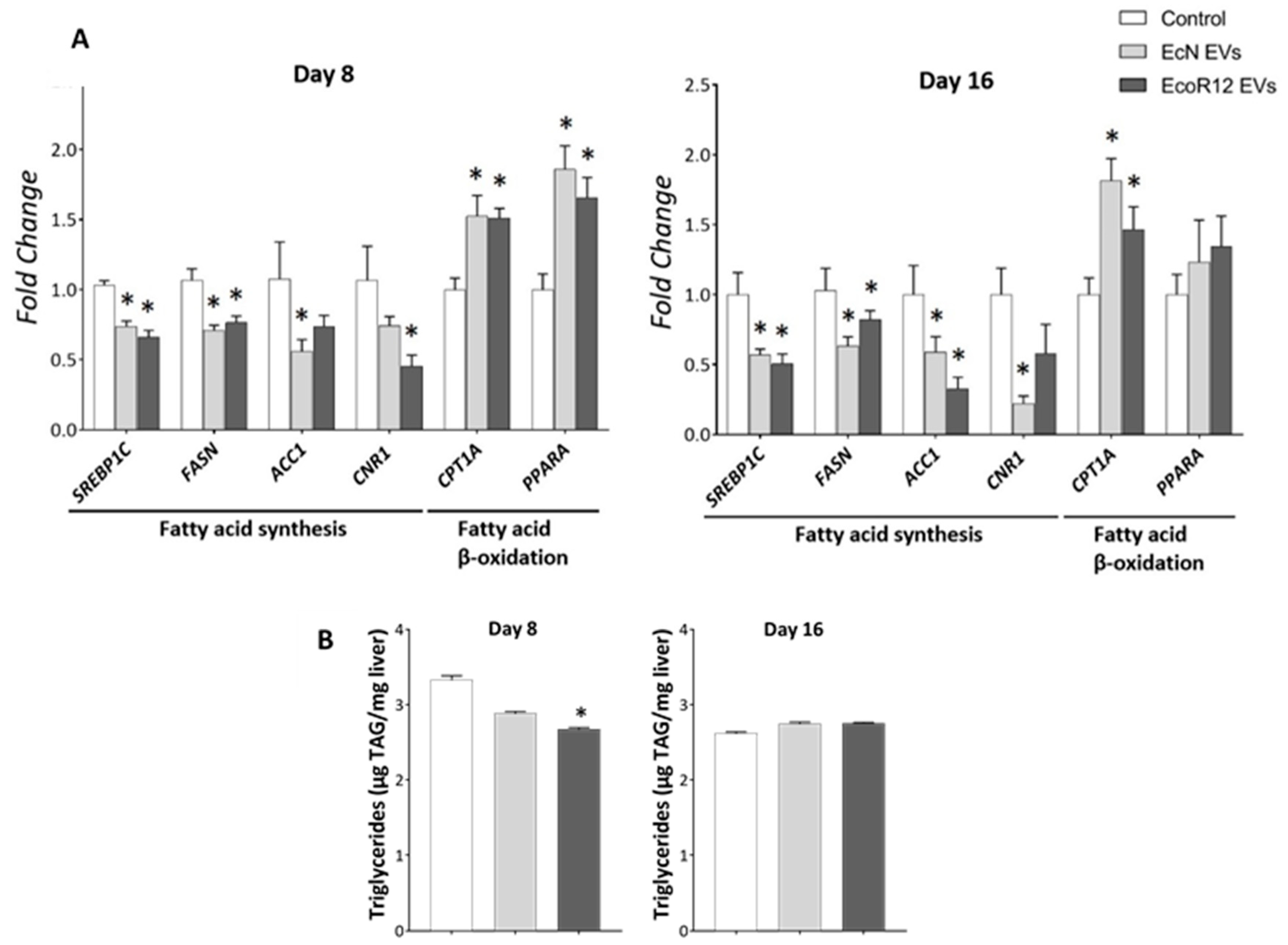
3.3. EcN and EcoR12 EVs Regulate Hepatic Lipid Metabolism via the Gut-Liver Axis by Promoting Lipid Oxidation and Inhibiting Lipid Synthesis
3.4. Influence of EcN and EcoR12 EVs on Hepatic Glucose Metabolism During Neonatal Development
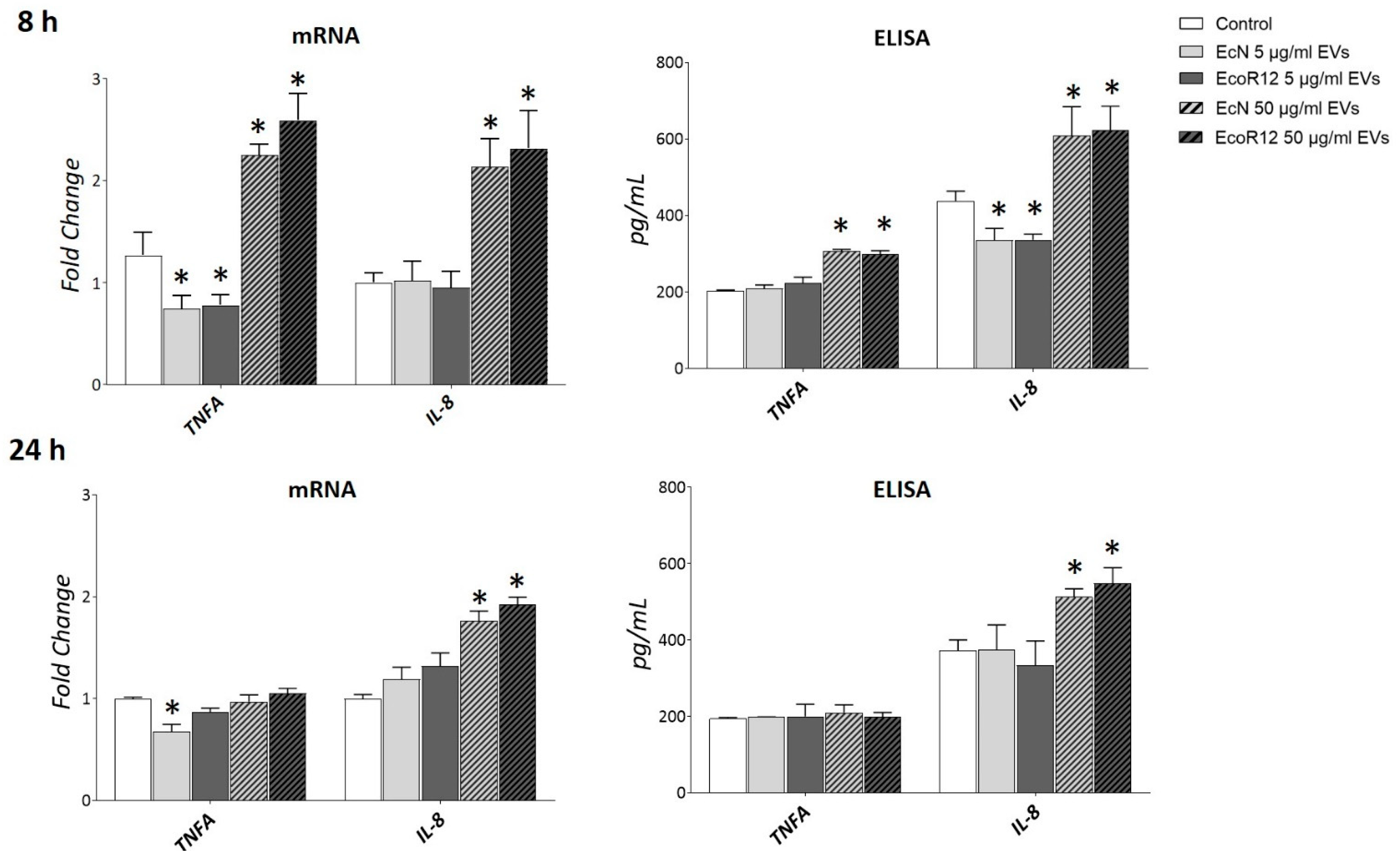
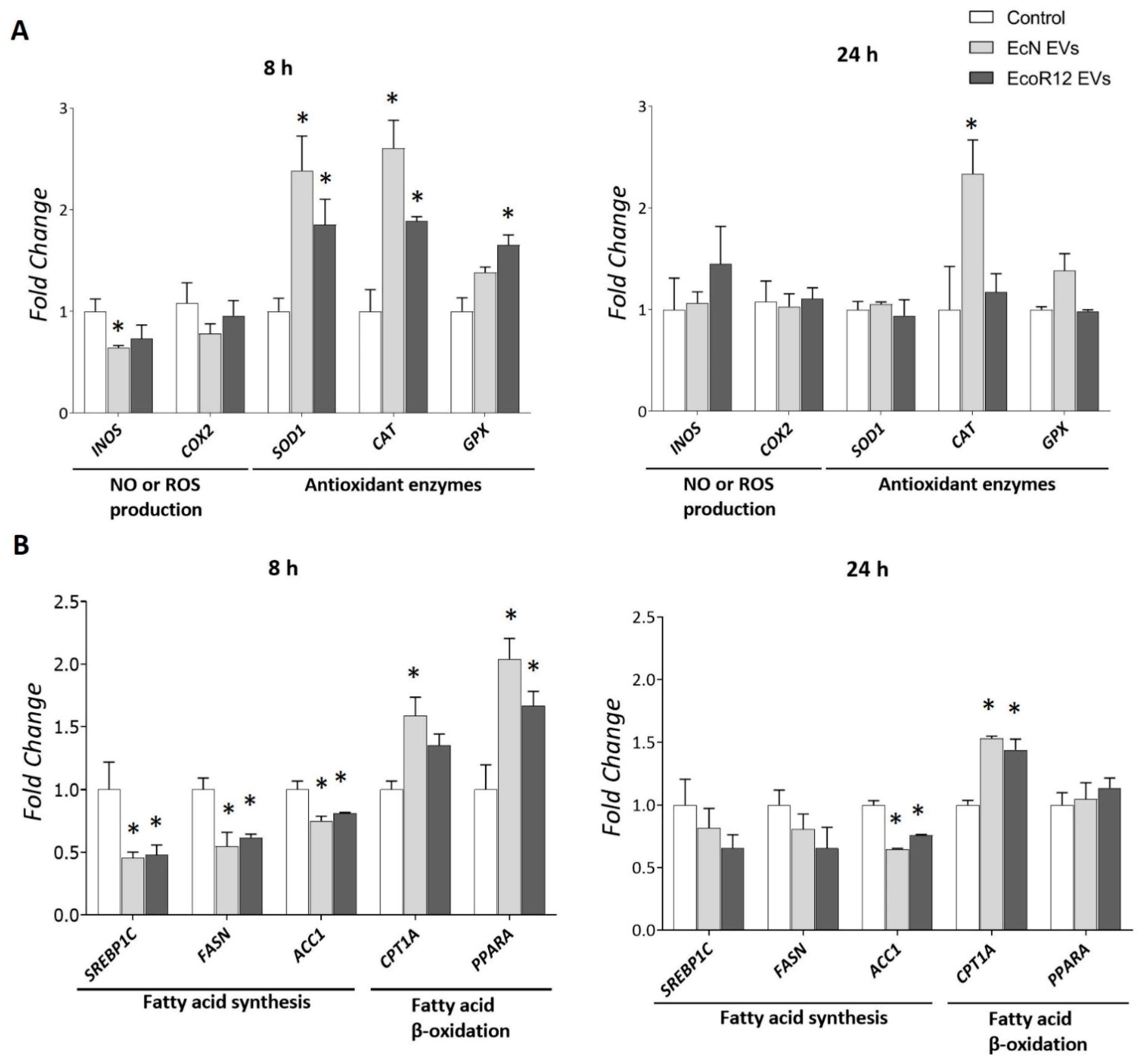
3.5. Gene Regulation by EcN or EcoR12 EVs in HepG2 Cells Improves Anti-Inflammatory, Antioxidative, and Lipid Oxidation Pathways
4. Discussion
5. Concluding Remarks
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jandhyala, S.M.; Talukdar, R.; Subramanyam, C.; Vuyyuru, H.; Sasikala, M.; Reddy, D.N. Role of the Normal Gut Microbiota. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 8836–8847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adak, A.; Khan, M.R. An Insight into Gut Microbiota and Its Functionalities. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 76, 473–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlawat, S.; Asha, N.; Sharma, K.K. Gut–Organ Axis: A Microbial Outreach and Networking. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 72, 636–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hul, M.; Cani, P.D.; Petifils, C.; De Vos, W.M.; Tilg, H.; El Omar, E.M. What Defines a Healthy Gut Microbiome? Gut 2024, 73, 1893–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzaal, M.; Saeed, F.; Shah, Y.A.; Hussain, M.; Rabail, R.; Socol, C.T.; Hassoun, A.; Pateiro, M.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Rusu, A.V.; et al. Human Gut Microbiota in Health and Disease: Unveiling the Relationship. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 999001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vos, W.M.; Tilg, H.; Van Hul, M.; Cani, P.D. Gut Microbiome and Health: Mechanistic Insights. Gut 2022, 71, 1020–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, M.E.V.; Sjövall, H.; Hansson, G.C. The Gastrointestinal Mucus System in Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadoni, I.; Zagato, E.; Bertocchi, A.; Paolinelli, R.; Hot, E.; Di Sabatino, A.; Caprioli, F.; Bottiglieri, L.; Oldani, A.; Viale, G.; et al. A Gut-Vascular Barrier Controls the Systemic Dissemination of Bacteria. Science 2015, 350, 830–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadoni, I.; Fornasa, G.; Rescigno, M. Organ-Specific Protection Mediated by Cooperation between Vascular and Epithelial Barriers. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Garrido, N.; Badia, J.; Baldomà, L. Microbiota-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Interkingdom Communication in the Gut. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Ali, S.A.; Yan, F. Interactions between the Gut Microbiota-Derived Functional Factors and Intestinal Epithelial Cells—Implication in the Microbiota-Host Mutualism. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1006081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyofuku, M.; Schild, S.; Kaparakis-Liaskos, M.; Eberl, L. Composition and Functions of Bacterial Membrane Vesicles. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stentz, R.; Carvalho, A.L.; Jones, E.J.; Carding, S.R. Fantastic Voyage: The Journey of Intestinal Microbiota-Derived Microvesicles through the Body. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2018, 46, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, E.J.; Booth, C.; Fonseca, S.; Parker, A.; Cross, K.; Miquel-Clopés, A.; Hautefort, I.; Mayer, U.; Wileman, T.; Stentz, R.; et al. The Uptake, Trafficking, and Biodistribution of Bacteroides Thetaiotaomicron Generated Outer Membrane Vesicles. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 509053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, H.; Kumar, A.; Almousa, S.; Mishra, S.; Langsten, K.L.; Kim, S.; Sharma, M.; Su, Y.; Singh, S.; Kerr, B.A.; et al. Characterisation of LPS+ Bacterial Extracellular Vesicles along the Gut-Hepatic Portal Vein-Liver Axis. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaack, B.; Hindré, T.; Quansah, N.; Hannani, D.; Mercier, C.; Laurin, D. Microbiota-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Detected in Human Blood from Healthy Donors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbunt, J.; Jocken, J.; Blaak, E.; Savelkoul, P.; Stassen, F. Gut-Bacteria Derived Membrane Vesicles and Host Metabolic Health: A Narrative Review. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2359515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margutti, P.; D’Ambrosio, A.; Zamboni, S. Microbiota-Derived Extracellular Vesicle as Emerging Actors in Host Interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabst, O.; Hornef, M.W.; Schaap, F.G.; Cerovic, V.; Clavel, T.; Bruns, T. Gut–Liver Axis: Barriers and Functional Circuits. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 447–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.; Debelius, J.; Brenner, D.A.; Karin, M.; Loomba, R.; Schnabl, B.; Knight, R. Publisher Correction: The Gut–Liver Axis and the Intersection with the Microbiome. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Mateos, R.; Albillos, A. The Role of the Gut-Liver Axis in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 660179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milosevic, I.; Vujovic, A.; Barac, A.; Djelic, M.; Korac, M.; Spurnic, A.R.; Gmizic, I.; Stevanovic, O.; Djordjevic, V.; Lekic, N.; et al. Gut-Liver Axis, Gut Microbiota, and Its Modulation in the Management of Liver Diseases: A Review of the Literature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albillos, A.; de Gottardi, A.; Rescigno, M. The Gut-Liver Axis in Liver Disease: Pathophysiological Basis for Therapy. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 558–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.; Kuang, Z.; Li, C.; Guo, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, D.; Hu, Y.; Song, B.; Jiang, Z.; Ge, Z.; et al. Gut Akkermansia Muciniphila Ameliorates Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease by Regulating the Metabolism of L-Aspartate via Gut-Liver Axis. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.L.; Schnabl, B. The Gut–Liver Axis and Gut Microbiota in Health and Liver Disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 719–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Li, F.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, L.; He, L.; Wilkey, D.W.; Merchant, M.; Zhang, X.; Deng, Z.B.; et al. Exosome-Like Nanoparticles From Lactobacillus Rhamnosus GG Protect Against Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease Through Intestinal Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor in Mice. Hepatol. Commun. 2021, 5, 846–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarz Azizi Raftar, S.; Ashrafian, F.; Yadegar, A.; Lari, A.; Moradi, H.R.; Shahriary, A.; Azimirad, M.; Alavifard, H.; Mohsenifar, Z.; Davari, M.; et al. The Protective Effects of Live and Pasteurized Akkermansia Muciniphila and Its Extracellular Vesicles against HFD/CCl4-Induced Liver Injury. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e0048421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivo-Martínez, Y.; Bosch, M.; Badia, J.; Baldomà, L. Modulation of the Intestinal Barrier Integrity and Repair by Microbiota Extracellular Vesicles through the Differential Regulation of Trefoil Factor 3 in LS174T Goblet Cells. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fábrega, M.J.; Rodríguez-Nogales, A.; Garrido-Mesa, J.; Algieri, F.; Badía, J.; Giménez, R.; Gálvez, J.; Baldomà, L. Intestinal Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Outer Membrane Vesicles from Escherichia Coli Nissle 1917 in DSS-Experimental Colitis in Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 275361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ruiz, S.; Olivo-Martínez, Y.; Cordero, C.; Rodríguez-Lagunas, M.J.; Pérez-Cano, F.J.; Badia, J.; Baldoma, L. Microbiota-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as a Postbiotic Strategy to Alleviate Diarrhea and Enhance Immunity in Rotavirus-Infected Neonatal Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ruiz, S.; Sáez-Fuertes, L.; Casanova-Crespo, S.; Rodríguez-Lagunas, M.J.; Pérez-Cano, F.J.; Badia, J.; Baldoma, L. Microbiota-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Promote Immunity and Intestinal Maturation in Suckling Rats. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochman, H.; Selander, R.K. Standard Reference Strains of Escherichia Coli from Natural Populations. J. Bacteriol. 1984, 157, 690–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Garrido, N.; Badia, J.; Baldomà, L. Modulation of Dendritic Cells by Microbiota Extracellular Vesicles Influences the Cytokine Profile and Exosome Cargo. Nutrients 2022, 14, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, P.G.; Nielsen, F.H.; Fahey, G.C. AIN-93 Purified Diets for Laboratory Rodents: Final Report of the American Institute of Nutrition Ad Hoc Writing Committee on the Reformulation of the AIN-76A Rodent Diet. J. Nutr. 1993, 123, 1939–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivo-Martínez, Y.; Martínez-Ruiz, S.; Cordero-Alday, C.; Bosch, M.; Badia, J.; Baldoma, L. Modulation of Serotonin-Related Genes by Extracellular Vesicles of the Probiotic Escherichia Coli Nissle 1917 in the Interleukin-1β-Induced Inflammation Model of Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, R.; Khanipov, K.; Radnaa, E.; Ganguly, E.; Bento, G.F.C.; Urrabaz-Garza, R.; Kammala, A.K.; Yaklic, J.; Pyles, R.; Golovko, G.; et al. Amplification of Microbial DNA from Bacterial Extracellular Vesicles from Human Placenta. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1213234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weström, B.; Arévalo Sureda, E.; Pierzynowska, K.; Pierzynowski, S.G.; Pérez-Cano, F.J. The Immature Gut Barrier and Its Importance in Establishing Immunity in Newborn Mammals. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 531569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulkens, J.; Vergauwen, G.; Van Deun, J.; Geeurickx, E.; Dhondt, B.; Lippens, L.; De Scheerder, M.A.; Miinalainen, I.; Rappu, P.; De Geest, B.G.; et al. Increased Levels of Systemic LPS-Positive Bacterial Extracellular Vesicles in Patients with Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction. Gut 2020, 69, 191–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakaroun, R.M.; Massier, L.; Kovacs, P. Gut Microbiome, Intestinal Permeability, and Tissue Bacteria in Metabolic Disease: Perpetrators or Bystanders? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Xiao, C.; Feng, S.; Bai, J. Artemisitene Alters LPS-Induced Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Ferroptosis in Liver Through Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-KB Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1177542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vincenzo, F.; Del Gaudio, A.; Petito, V.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Scaldaferri, F. Gut Microbiota, Intestinal Permeability, and Systemic Inflammation: A Narrative Review. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2024, 19, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Campo, J.A.; Gallego, P.; Grande, L. Role of Inflammatory Response in Liver Diseases: Therapeutic Strategies. World J. Hepatol. 2018, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Nogales, A.; Algieri, F.; Garrido-Mesa, J.; Vezza, T.; Utrilla, M.P.; Chueca, N.; Fernández-Caballero, J.A.; García, F.; Rodríguez-Cabezas, M.E.; Gálvez, J. The Administration of Escherichia Coli Nissle 1917 Ameliorates Development of DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 329841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, S.; Ma, H.W.; Park, I.S.; Son, M.; Kim, J.H.; Shin, Y.; Kim, S.W.; Cheon, J.H. Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Escherichia Coli Nissle 1917 in a Murine Colitis Model. Intest. Res. 2021, 19, 478–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Roh, Y.S.; Song, J.; Zhang, B.; Liu, C.; Loomba, R.; Seki, E. Transforming Growth Factor Beta Signaling in Hepatocytes Participates in Steatohepatitis through Regulation of Cell Death and Lipid Metabolism in Mice. Hepatology 2014, 59, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabregat, I.; Moreno-Càceres, J.; Sánchez, A.; Dooley, S.; Dewidar, B.; Giannelli, G.; ten Dijke, P. TGF-β Signalling and Liver Disease. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 2219–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gottardi, A.; Spahr, L.; Ravier-Dall’Antonia, F.; Hadengue, A. Cannabinoid Receptor 1 and 2 Agonists Increase Lipid Accumulation in Hepatocytes. Liver Int. 2010, 30, 1482–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, N.; Cuffe, J.S.M.; Hutchinson, D.S.; Headrick, J.P.; Perkins, A.V.; McAinch, A.J.; Hryciw, D.H. Peripheral Modulation of the Endocannabinoid System in Metabolic Disease. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 592–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazwinsky-Wutschke, I.; Zipprich, A.; Dehghani, F. Endocannabinoid System in Hepatic Glucose Metabolism, Fatty Liver Disease, and Cirrhosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatelain, F.; Pégorier, J.P.; Minassian, C.; Bruni, N.; Tarpin, S.; Girard, J.; Mithieux, G. Development and regulation of glucose-6-phosphatase gene expression in rat liver, intestine, and kidney: In vivo and in vitro studies in cultured fetal hepatocytes. Diabetes 1998, 47, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, D.G.; Holland, G. The development of hepatic glucokinase in the neonatal rat. Biochem. J. 1965, 97, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, D.G.; Eaton, S.W. Regulation of development of hepatic glucokinase in the neonatal rat by the diet. Biochem. J. 1967, 105, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Cederbaum, A.I. Ethanol and Arachidonic Acid Produce Toxicity in Hepatocytes from Pyrazole-Treated Rats with High Levels of CYP2E1. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2000, 204, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killingsworth, Z.K.; Misare, K.R.; Ryan, A.S.; Ampolini, E.A.; Mendenhall, T.T.; Engevik, M.A.; Hartman, J.H. Subcellular Expression of CYP2E1 in HepG2 Cells Impacts Response to Free Oleic and Palmitic Acid. Curr. Res. Toxicol. 2024, 7, 100195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Zhan, X.; Yu, X.; Jia, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, J.; Hu, X.; Bao, Z. Inhibiting CB1 Receptors Improves Lipogenesis in an in Vitro Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Model. Lipids Health Dis. 2014, 13, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, S.; Mande, S.S. Host-Microbiome Interactions: Gut-Liver Axis and Its Connection with Other Organs. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2022, 8, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Luo, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, T.; Sun, J.; Xi, Q.; Zhang, Y. Extracellular Vesicles: A Crucial Player in the Intestinal Microenvironment and Beyond. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Huang, W.H.; Luo, M.; Feng, X.; Zhang, H.; Qi, Q. Protective Effect of Enterococcus Faecium Against Alcohol-Induced Acute Liver Injury Via Extracellular Vesicles in Rats. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2025; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.J.; Meyerovich, G.; Blank, S.; Ovdat, E.; Loewenstein, S.; Kania-Almog, J.; Cohen, M.; Lahat, G.; Klausner, J.M.; Lubezky, N. Microbiota Transfer Following Liver Surgery Involves Microbial Extracellular Vesicle Migration That Affects Liver Immunity. Hepatol. Commun. 2023, 7, e0164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaparakis-Liaskos, M.; Ferrero, R.L. Immune Modulation by Bacterial Outer Membrane Vesicles. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.D.; Akbar, R.; Oliverio, A.; Thapa, K.; Wang, X.; Fan, G.C. Bacteria Extracellular Vesicles in the Regulation of Inflammatory Response and Host-Microbe Interactions. Shock 2024, 61, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massart, J.; Begriche, K.; Hartman, J.H.; Fromenty, B. Role of Mitochondrial Cytochrome P450 2E1 in Healthy and Diseased Liver. Cells 2022, 11, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgačević, B.; Vučević, D.; Samardžić, J.; Mladenović, D.; Vesković, M.; Vukićević, D.; Ješić, R.; Radosavljević, T. The Effect of CB1 Antagonism on Hepatic Oxidative/Nitrosative Stress and Inflammation in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pignatti, C.; D’Adamo, S.; Flamigni, F.; Cetrullo, S. Molecular Mechanisms Linking Nutrition to Metabolic Homeostasis: An Overview Picture of Current Understanding. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2020, 30, 543–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burchell, A.; Leakey, J.E. Development of the rat hepatic microsomal glucose-6-phosphatase system and its glucocorticoid inducibility. Biol. Neonate 1988, 54, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippis, F.; Esposito, A.; Ercolini, D. Outlook on Next-Generation Probiotics from the Human Gut. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaderi, F.; Sotoodehnejadnematalahi, F.; Hajebrahimi, Z.; Fateh, A.; Siadat, S.D. Effects of Active, Inactive, and Derivatives of Akkermansia Muciniphila on the Expression of the Endocannabinoid System and PPARs Genes. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; Cao, Y.Y.; Zheng, M.H. Current Status and Future Trends of the Global Burden of MASLD. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 35, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.Q.; Wong, V.W.S.; Rinella, M.E.; Boursier, J.; Lazarus, J.V.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; Loomba, R. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease in Adults. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2025, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, H.K.; Bataller, R.; Cortez-Pinto, H.; Gao, B.; Gual, A.; Lackner, C.; Mathurin, P.; Mueller, S.; Szabo, G.; Tsukamoto, H. Alcoholic Liver Disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salminen, S.; Collado, M.C.; Endo, A.; Hill, C.; Lebeer, S.; Quigley, E.M.M.; Sanders, M.E.; Shamir, R.; Swann, J.R.; Szajewska, H.; et al. The International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) Consensus Statement on the Definition and Scope of Postbiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 649–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegh, C.A.M.; Geerlings, S.Y.; Knol, J.; Roeselers, G.; Belzer, C. Postbiotics and Their Potential Applications in Early Life Nutrition and Beyond. Int. J.Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żółkiewicz, J.; Marzec, A.; Ruszczyński, M.; Feleszko, W. Postbiotics—A Step Beyond Pre- and Probiotics. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Tu, H.; Chen, T. Postbiotics in Human Health: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Li, Q.; Haesebrouck, F.; Van Hoecke, L.; Vandenbroucke, R.E. The Tremendous Biomedical Potential of Bacterial Extracellular Vesicles. Trends Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1173–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Li, Q.; Nie, S. Bacterial Extracellular Vesicles: An Emerging Postbiotic. Trends Food. Sci. Technol. 2024, 143, 104275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez-Ruiz, S.; Badia, J.; Baldoma, L. Extracellular Vesicles from Escherichia coli Strains of the Gut Microbiota Trigger Hepatic Antioxidant and Anti-Lipogenic Effects via the Gut-Liver Axis in Healthy Neonatal Rats. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3066. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193066
Martínez-Ruiz S, Badia J, Baldoma L. Extracellular Vesicles from Escherichia coli Strains of the Gut Microbiota Trigger Hepatic Antioxidant and Anti-Lipogenic Effects via the Gut-Liver Axis in Healthy Neonatal Rats. Nutrients. 2025; 17(19):3066. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193066
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez-Ruiz, Sergio, Josefa Badia, and Laura Baldoma. 2025. "Extracellular Vesicles from Escherichia coli Strains of the Gut Microbiota Trigger Hepatic Antioxidant and Anti-Lipogenic Effects via the Gut-Liver Axis in Healthy Neonatal Rats" Nutrients 17, no. 19: 3066. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193066
APA StyleMartínez-Ruiz, S., Badia, J., & Baldoma, L. (2025). Extracellular Vesicles from Escherichia coli Strains of the Gut Microbiota Trigger Hepatic Antioxidant and Anti-Lipogenic Effects via the Gut-Liver Axis in Healthy Neonatal Rats. Nutrients, 17(19), 3066. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193066





