Influence of Tempeh, Daidzein, Probiotics, and Their Combination on Magnesium Status and Hematological Ratios in a Postmenopausal Osteoporotic Animal Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Ethical Considerations in Animal Research
2.3. Preparing the Animal Laboratory Environment
2.4. Bilateral Ovariectomy Procedure
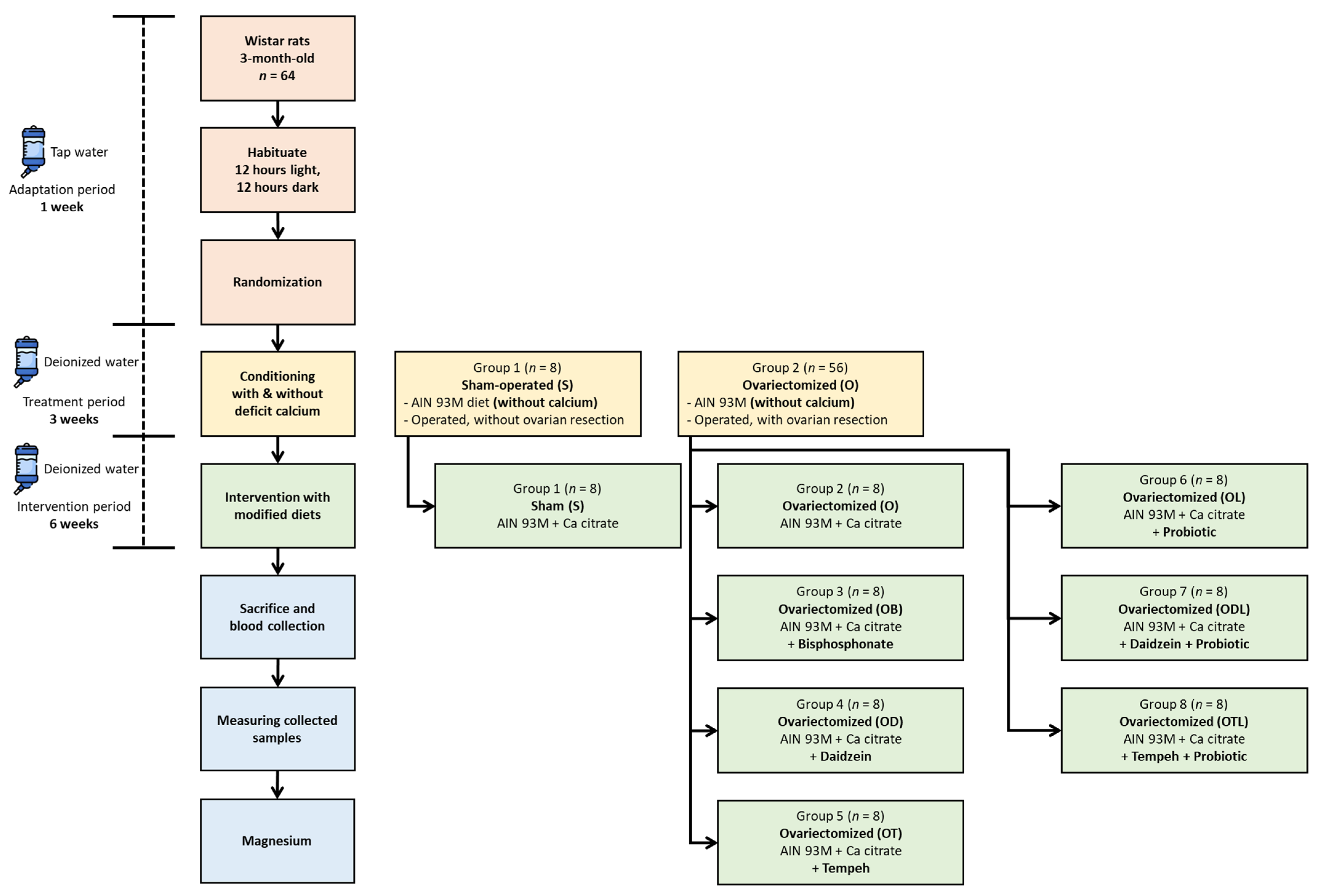
2.5. Assigning Rats to Experimental Groups
2.6. Establishing Calcium Deficiency
2.7. Dietary Intervention Strategy
2.8. Tracking Dietary Intake
2.9. Euthanizing the Rats
2.10. Measurement of Magnesium Levels in Diets, Tissues, and Feces
2.11. Measurement of Hematological Ratios
- NLR = Neutrophil count (G/L)/Lymphocyte count (G/L)
- MLR = Monocyte count (G/L)/Lymphocyte count (G/L)
- PLR = Platelet count (G/L)/Lymphocyte count (G/L)
- TyG = ln [Triglyceride level (mg/dL) × Glucose level (mg/dL)/2]
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
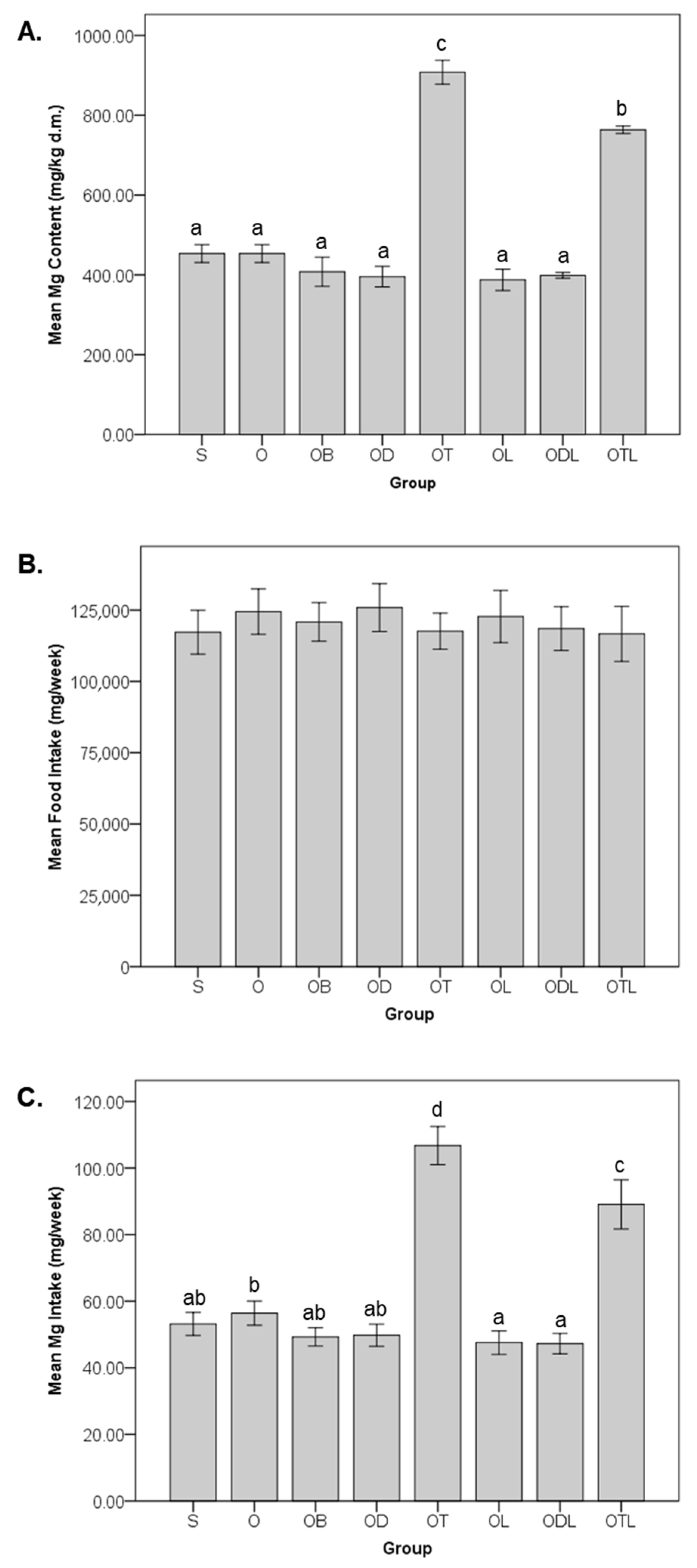
3.1. Magnesium Content, Food Intake, and Dietary Magnesium Intake
3.2. Impact on Magnesium Levels in Tissues and Feces
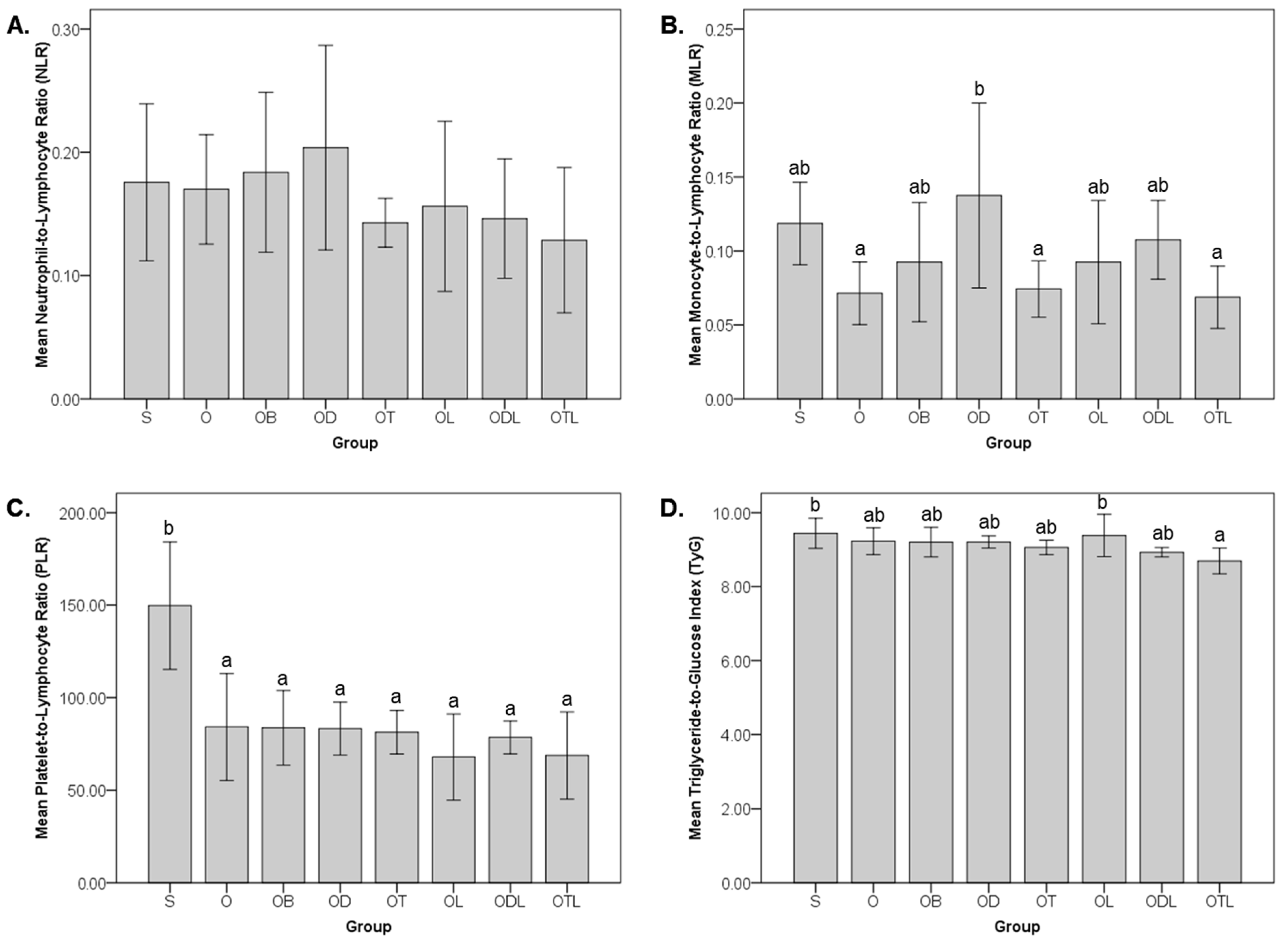
3.3. Impact on Hematological Ratios
3.4. Correlation Between Magnesium Levels and Hematological Ratios
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMPK | Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase |
| BMD | Bone mineral density |
| IL-1 | Interleukin-1 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| hsCRP | High-sensitivity C-reactive protein |
| LDL | Low-density lipoprotein |
| MLR | Monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| NAFLD | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa B |
| NLR | Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| PGC-1α | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator (PGC)-1alpha |
| PLR | Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| PPARα | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| TLR4 | Toll-like receptor 4 |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| TyG | Triglyceride-to-glucose index |
References
- Bloom, D.E.; Luca, D.L. The Global Demography of Aging. In Handbook of the Economics of Population Aging; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 1, pp. 3–56. [Google Scholar]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Anastasilakis, A.D.; Efstathiadou, Z.A.; Yavropoulou, M.P.; Makras, P. Postmenopausal osteoporosis coexisting with other metabolic diseases: Treatment considerations. Maturitas 2021, 147, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hu, W.; Zou, Z.; Li, Y.; Kang, F.; Li, J.; Dong, S. The role of lipid metabolism in osteoporosis: Clinical implication and cellular mechanism. Genes Dis. 2024, 11, 101122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Huang, X.; Wu, J.; Lin, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, Z.; Pan, X.; Xu, J.; Qiao, J.; Zhang, T.; et al. The Global Burden of Osteoporosis, Low Bone Mass, and Its Related Fracture in 204 Countries and Territories, 1990–2019. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 882241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteleone, P.; Mascagni, G.; Giannini, A.; Genazzani, A.R.; Simoncini, T. Symptoms of menopause—Global prevalence, physiology and implications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, V.; Morgan, E.F. Estrogen and estrogen receptors mediate the mechanobiology of bone disease and repair. Bone 2024, 188, 117220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Cai, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, C. Estrogen deficiency-mediated osteoimmunity in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Med. Res. Rev. 2024, 45, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNamara, L.M. Osteocytes and Estrogen Deficiency. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2021, 19, 592–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.B.; Worthley, L.I.G. The Essentials of Calcium, Magnesium and Phosphate Metabolism: Part I. Physiology. Crit. Care Resusc. 2002, 4, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Mao, X.; Ling, J.; He, Q.; Quan, J.; Jiang, H. Association between serum level of magnesium and postmenopausal osteoporosis: A meta-analysis. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2014, 159, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazza, M.G.; Lucchi, S.; Rossetti, A.; Clerici, M. Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, monocyte-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-lymphocyte ratio in non-affective psychosis: A meta-analysis and systematic review. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 21, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Yang, Y.; Lee, E.Y.; Yang, H.K.; Kim, H.S.; Lim, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.S.; Suh, B.K.; Yoon, K.H. Triglycerides/glucose index is a useful surrogate marker of insulin resistance among adolescents. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 789–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greere, D.I.I.; Grigorescu, F.; Manda, D.; Lautier, C.; Poianã, C. Insulin Resistance and Pathogenesis of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Acta Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korpe, B.; Kose, C.; Mermi, S.; Ergorun, S.K.; Keskin, H.L. Investigating the triglyceride–glucose index in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Climacteric 2025, 28, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukasaki, M.; Takayanagi, H. Osteoimmunology: Evolving concepts in bone–immune interactions in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 626–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dermience, M.; Lognay, G.; Mathieu, F.; Goyens, P. Effects of thirty elements on bone metabolism. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2015, 32, 86–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwalfenberg, G.K.; Genuis, S.J. The Importance of Magnesium in Clinical Healthcare. Scientifica 2017, 2017, 4179326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Mai, C.L.; Xiong, Y.; Lin, Z.J.; Jie, Y.T.; Mai, J.Z.; Liu, C.; Xie, M.X.; Zhou, X.; Liu, X.G. The causal role of magnesium deficiency in the neuroinflammation, pain hypersensitivity and memory/emotional deficits in ovariectomized and aged female mice. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 6633–6656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, F.H. Magnesium deficiency and increased inflammation: Current perspectives. J. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 11, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harahap, I.A.; Suliburska, J. Probiotics and Isoflavones as a Promising Therapeutic for Calcium Status and Bone Health: A Narrative Review. Foods 2021, 10, 2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccarelli, I.; Bioletti, L.; Peparini, S.; Solomita, E.; Ricci, C.; Casini, I.; Miceli, E.; Aloisi, A.M. Estrogens and phytoestrogens in body functions. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 132, 648–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Cai, H.; Zheng, W.; Shu, X.O. Associations of Dietary Intakes of Calcium, Magnesium, and Soy Isoflavones With Bone Fracture Risk in Men: A Prospective Study. JBMR Plus 2022, 6, e10563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Cai, H.; Gao, Y.; Dai, Q.; Yang, G.; Zheng, W.; Shu, X.O. Associations of dietary intakes of calcium, magnesium and soy isoflavones with osteoporotic fracture risk in postmenopausal women: A prospective study. J. Nutr. Sci. 2022, 11, e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadadi, N.; Berweiler, V.; Wang, H.; Trajkovski, M. Intestinal microbiota as a route for micronutrient bioavailability. Curr. Opin. Endocr. Metab. Res. 2021, 20, 100285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Cheng, J.; Liu, L.; Luo, J.; Peng, X. Lactobacillus acidophilus (LA) Fermenting Astragalus Polysaccharides (APS) Improves Calcium Absorption and Osteoporosis by Altering Gut Microbiota. Foods 2023, 12, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harahap, I.A.; Kuligowski, M.; Schmidt, M.; Kurzawa, P.; Suliburska, J. Influence of Isoflavones and Probiotics on Magnesium Status in Healthy Female Rats. Foods 2023, 12, 3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harahap, I.A.; Kuligowski, M.; Schmidt, M.; Suliburska, J. The impact of soybean products and probiotics on calcium bioaccessibility from organic and inorganic calcium salts in an in vitro digestion model. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 2, 100269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harahap, I.A.; Schmidt, M.; Pruszyńska-Oszmałek, E.; Sassek, M.; Suliburska, J. Impact of Lactobacillus acidophilus and Its Combination with Isoflavone Products on Calcium Status, Calcium Transporters, and Bone Metabolism Biomarkers in a Post-Menopausal Osteoporotic Rat Model. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harahap, I.A.; Kuligowski, M.; Cieslak, A.; Kołodziejski, P.A.; Suliburska, J. Effect of Tempeh and Daidzein on Calcium Status, Calcium Transporters, and Bone Metabolism Biomarkers in Ovariectomized Rats. Nutrients 2024, 16, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharode, Y.P.; Sharp, M.C.; Bodine, P.V.N. Utility of the Ovariectomized Rat as a Model for Human Osteoporosis in Drug Discovery. In Osteoporosis: Methods and Protocols; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 111–124. ISBN 9781588298287. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, X.; Wang, P. Are there differences between Sprague-Dawley and Wistar rats in long-term effects of ovariectomy as a model for postmenopausal osteoporosis? Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 1491–1502. [Google Scholar]
- Reeves, P.G.; Nielsen, F.H.; Fahey, G.C. AIN-93 Purified Diets for Laboratory Rodents: Final Report of the American Institute of Nutrition Ad Hoc Writing Committee on the Reformulation of the AIN-76A Rodent Diet. J. Nutr. 1993, 123, 1939–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, R.B.M.; Wever, K.E.; Avey, M.T.; Stephens, M.L.; Sena, E.S.; Leenaars, M. The Usefulness of Systematic Reviews of Animal Experiments for the Design of Preclinical and Clinical Studies. ILAR J. 2014, 55, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveri, R.S.; Bello, S.; Biering-Sørensen, F. Mesenchymal stem cells improve locomotor recovery in traumatic spinal cord injury: Systematic review with meta-analyses of rat models. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 62, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotani, M.; Kim, K.H.; Ishizaki, N.; Funaba, M.; Matsui, T. Magnesium and calcium deficiencies additively increase zinc concentrations and metallothionein expression in the rat liver. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 109, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.J.; Tang, T.T.; Hao, Y.Q.; Dai, K.R. Long-term effects of alendronate on fracture healing and bone remodeling of femoral shaft in ovariectomized rats. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2013, 34, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Chiba, H.; Higuchi, M.; Nakatani, T.; Ezaki, O.; Cui, H.; Yamada, K.; Ishimi, Y. Combined intervention of soy isoflavone and moderate exercise prevents body fat elevation and bone loss in ovariectomized mice. Metabolism 2004, 53, 942–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Lee, S.-K.; Chun, O.K. Soy isoflavones and osteoporotic bone loss: A review with an emphasis on modulation of bone remodeling. J. Med. Food 2016, 19, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villares, A.; Rostagno, M.A.; García-Lafuente, A.; Guillamón, E.; Martínez, J.A. Content and Profile of Isoflavones in Soy-Based Foods as a Function of the Production Process. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2011, 4, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, K.; Tyagi, A.M.; Khan, K.; Dixit, M.; Lahiri, S.; Kumar, A.; Changkija, B.; Khan, M.P.; Nagar, G.K.; Yadav, D.K.; et al. Isoformononetin, a methoxydaidzein present in medicinal plants, reverses bone loss in osteopenic rats and exerts bone anabolic action by preventing osteoblast apoptosis. Phytomedicine 2013, 20, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.; Park, Y.K. Soy isoflavone supplementation improves longitudinal bone growth and bone quality in growing female rats. Nutrition 2017, 37, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dar, H.Y.; Shukla, P.; Mishra, P.K.; Anupam, R.; Mondal, R.K.; Tomar, G.B.; Sharma, V.; Srivastava, R.K. Lactobacillus acidophilus inhibits bone loss and increases bone heterogeneity in osteoporotic mice via modulating Treg-Th17 cell balance. Bone Rep. 2018, 8, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szulińska, M.; Łoniewski, I.; Skrypnik, K.; Sobieska, M.; Korybalska, K.; Suliburska, J.; Bogdański, P. Multispecies probiotic supplementation favorably affects vascular function and reduces arterial stiffness in obese postmenopausal women—A 12-week placebo-controlled and randomized clinical study. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, N.E. Food or fluid restriction in common laboratory animals: Balancing welfare considerations with scientific inquiry. Comp. Med. 2007, 57, 149–160. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Íñigo, L.; Navarro-González, D.; Fernández-Montero, A.; Pastrana-Delgado, J.; Martínez, J.A. The TyG index may predict the development of cardiovascular events. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 46, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, R. Magnesium metabolism and its disorders. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2003, 24, 47–66. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scholz-Ahrens, K.E.; Adolphi, B.; Rochat, F.; Barclay, D.V.; de Vrese, M.; Açil, Y.; Schrezenmeir, J. Effects of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics on mineral metabolism in ovariectomized rats—Impact of bacterial mass, intestinal absorptive area and reduction of bone turn-over. NFS J. 2016, 3, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Kong, X.; Wang, K.; Chen, Y.; Du, M.; Xu, B.; Xu, J.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Yu, T. Effect of fermentation using different lactic acid bacteria strains on the nutrient components and mineral bioavailability of soybean yogurt alternative. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1198456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenorio, M.D.; Espinosa-Martos, I.; Préstamo, G.; Rupérez, P. Soybean whey enhance mineral balance and caecal fermentation in rats. Eur. J. Nutr. 2010, 49, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashique, S.; Kumar, S.; Hussain, A.; Mishra, N.; Garg, A.; Gowda, B.H.J.; Farid, A.; Gupta, G.; Dua, K.; Taghizadeh-Hesary, F. Correction: A narrative review on the role of magnesium in immune regulation, inflammation, infectious diseases, and cancer. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2023, 42, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.W.; Park, T.J. Magnesium metabolism. Electrolyte Blood Press. 2008, 6, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, J.A.; Castiglioni, S.; Locatelli, L.; Zocchi, M.; Mazur, A. Magnesium and inflammation: Advances and perspectives. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 115, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Ketteler, M. Magnesium basics. Clin. Kidney J. 2012, 5, i3–i14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Xiong, P.; Chen, N.; He, J.; Lin, G.; Xue, Y.; Li, W.; Yu, D. Effects of Replacing of Inorganic Trace Minerals by Organically Bound Trace Minerals on Growth Performance, Tissue Mineral Status, and Fecal Mineral Excretion in Commercial Grower-Finisher Pigs. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 173, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jutha, N.; Jardine, C.; Schwantje, H.; Mosbacher, J.; Kinniburgh, D.; Kutz, S. Evaluating the use of hair as a non-invasive indicator of trace mineral status in woodland caribou (Rangifer tarandus caribou). PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.H.; Barrett-Connor, E.; Chung, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, K.S. Associations of Calcium and Magnesium in Serum and Hair with Bone Mineral Density in Premenopausal Women. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2007, 118, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Daghri, N.M.; Aziz, I.; Yakout, S.; Aljohani, N.J.; Al-Saleh, Y.; Amer, O.E.; Sheshah, E.; Younis, G.Z.; Al-Badr, F.B.M. Inflammation as a contributing factor among postmenopausal Saudi women with osteoporosis. Medicine 2017, 96, e5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Liao, R.; Zhou, L.; Yi, T.; Ran, M.; Luo, J.; Huang, F.; Wu, A.; Mei, Q.; Wang, L.; et al. Genistin: A Novel Estrogen Analogue Targeting ERβ to Alleviate Thrombocytopenia. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2024, 20, 2236–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaoka, O.; Mori, T.; Ito, F.; Okimura, H.; Kataoka, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Koshiba, A.; Kusuki, I.; Shigehiro, S.; Amami, T.; et al. Daidzein-rich isoflavone aglycones inhibit cell growth and inflammation in endometriosis. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 181, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danciu, C.; Avram, S.; Pavel, I.Z.; Ghiulai, R.; Dehelean, C.A.; Ersilia, A.; Minda, D.; Petrescu, C.; Moaca, E.-A.; Soica, C. Main Isoflavones Found in Dietary Sources as Natural Anti-inflammatory Agents. Curr. Drug Targets 2018, 19, 841–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ho, S.C.; Chen, Y.; Ho, S.; To, K.; Tomlinson, B.; Woo, J. Whole soy, but not purified daidzein, had a favorable effect on improvement of cardiovascular risks: A 6-month randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled trial in equol-producing postmenopausal women. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.H.; Sobia, F.; Niazi, N.K.; Manzoor, S.M.; Fazal, N.; Ahmad, F. Metabolic clustering of risk factors: Evaluation of Triglyceride-glucose index (TyG index) for evaluation of insulin resistance. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2018, 10, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; He, X.; Feng, E.; Wei, J.; Tu, H.; Chen, T. Lactobacillus acidophilus JYLA-126 Ameliorates Obesity-Associated Metabolic Disorders by Positively Regulating the AMPK Signaling Pathway Through the Gut-Liver Axis. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2023, 17, 62–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, H.M.; Ali, N.M.; Yeap, S.K.; Ho, W.Y.; Beh, B.K.; Koh, S.P.; Long, K.; Alitheen, N.B. Anti-inflammatory, analgesic and acute toxicity effects of fermented soybean. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harahap, I.A.; Moszak, M.; Czlapka-Matyasik, M.; Skrypnik, K.; Bogdański, P.; Suliburska, J. Effects of daily probiotic supplementation with Lactobacillus acidophilus on calcium status, bone metabolism biomarkers, and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women: A controlled and randomized clinical study. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1401920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcinelli, S.; Rodiles, A.; Hatef, A.; Picchietti, S.; Cossignani, L.; Merrifield, D.L.; Unniappan, S.; Carnevali, O. Influence of Probiotics Administration on Gut Microbiota Core. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2018, 52, S50–S56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champagne, C.P.; Gomes da Cruz, A.; Daga, M. Strategies to improve the functionality of probiotics in supplements and foods. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2018, 22, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, A.; Maier, J.A.M.; Rock, E.; Gueux, E.; Nowacki, W.; Rayssiguier, Y. Magnesium and the inflammatory response: Potential physiopathological implications. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 458, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arancibia-Hernández, Y.L.; Hernández-Cruz, E.Y.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J. Magnesium (Mg2+) Deficiency, Not Well-Recognized Non-Infectious Pandemic: Origin and Consequence of Chronic Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress-Associated Diseases. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 57, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavani, N.G.; Saneei, P.; Hassanzadeh Keshteli, A.; Yazdannik, A.; Falahi, E.; Sadeghi, O.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Magnesium intake, insulin resistance and markers of endothelial function among women. Public Health Nutr. 2021, 24, 5777–5785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Xu, S.; Guo, H.; Lu, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, G.; Hao, K. Magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate prevents the nonalcoholic hepatic steatosis via regulating energy homeostasis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 7201–7213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Yeon, A.; Parker, S.J.; Shahid, M.; Thiombane, A.; Cho, E.; You, S.; Emam, H.; Kim, D.G.; Kim, M. Alendronate-induced perturbation of the bone proteome and microenvironmental pathophysiology. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 3261–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budzinska, A.; Galganski, L.; Jarmuszkiewicz, W. The bisphosphonates alendronate and zoledronate induce adaptations of aerobic metabolism in permanent human endothelial cells. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Y.; Lu, L. Systemic immune-inflammation index acts as a novel diagnostic biomarker for postmenopausal osteoporosis and could predict the risk of osteoporotic fracture. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilesanmi-Oyelere, B.L.; Schollum, L.; Kuhn-Sherlock, B.; McConnell, M.; Mros, S.; Coad, J.; Roy, N.C.; Kruger, M.C. Inflammatory markers and bone health in postmenopausal women: A cross-sectional overview. Immun. Ageing 2019, 16, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäffers, O.J.M.; Hoenderop, J.G.J.; Bindels, R.J.M.; de Baaij, J.H.F. The rise and fall of novel renal magnesium transporters. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2018, 314, F1027–F1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrypnik, K.; Suliburska, J. Association between the gut microbiota and mineral metabolism. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 2449–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Group | Tissues | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faeces (mg/g) | Spleen (μg/g) | Femur (mg/g) | Heart (μg/g) | Liver (μg/g) | Kidney (μg/g) | Hair (μg/g) | |
| S | 12.41 ± 1.53 ab | 360.19 ± 113.13 a | 5.61 ± 0.74 | 774.17 ± 20.05 | 658.84 ± 52.26 b | 627.80 ± 125.12 | 81.33 ± 28.16 b |
| O | 10.51 ± 2.18 a | 747.66 ± 106.82 b | 5.05 ± 1.24 | 712.89 ± 58.96 | 647.00 ± 59.36 ab | 625.61 ± 90.68 | 50.69 ± 5.41 a |
| OB | 12.42 ± 1.58 ab | 689.54 ± 125.27 b | 5.95 ± 0.14 | 686.80 ± 35.28 | 619.21 ± 59.78 ab | 630.24 ± 87.14 | 47.61 ± 9.77 a |
| OD | 14.40 ± 2.82 abc | 683.80 ± 39.96 b | 5.93 ± 0.24 | 736.17 ± 115.00 | 613.99 ± 16.64 ab | 593.00 ± 39.84 | 43.78 ± 4.60 a |
| OT | 17.36 ± 1.46 bc | 691.17 ± 42.83 b | 5.88 ± 0.30 | 682.72 ± 21.42 | 570.57 ± 42.19 a | 599.04 ± 32.16 | 46.24 ± 10.06 a |
| OL | 11.83 ± 3.13 a | 683.93 ± 105.86 b | 5.77 ± 0.41 | 699.89 ± 69.74 | 649.40 ± 84.22 ab | 589.13 ± 26.37 | 65.14 ± 18.63 ab |
| ODL | 11.85 ± 2.24 a | 652.11 ± 41.96 b | 5.37 ± 0.19 | 720.30 ± 24.65 | 584.39 ± 24.67 ab | 704.70 ± 26.65 | 76.94 ± 12.22 b |
| OTL | 19.32 ± 2.26 c | 752.28 ± 60.14 b | 5.45 ± 0.25 | 721.36 ± 45.72 | 570.36 ± 30.79 a | 624.90 ± 40.58 | 82.08 ± 10.92 b |
| Correlation | Correlation Coefficients (r) | Significant Values (p) |
|---|---|---|
| Mg Spleen—MLR | −0.297 | 0.025 * |
| Mg Spleen—TyG | −0.289 | 0.034 * |
| Mg Spleen—PLR | −0.626 | 0.000 ** |
| Mg Liver—NLR | 0.294 | 0.024 * |
| Mg Liver—MLR | 0.318 | 0.015 * |
| Mg Liver—PLR | 0.323 | 0.014 * |
| Mg Liver—TyG | 0.422 | 0.001 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Harahap, I.A.; Salem, O.; Fahmi, R.L.; Ahmed, N.; Leciejewska, N.; Suliburska, J. Influence of Tempeh, Daidzein, Probiotics, and Their Combination on Magnesium Status and Hematological Ratios in a Postmenopausal Osteoporotic Animal Model. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2917. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17182917
Harahap IA, Salem O, Fahmi RL, Ahmed N, Leciejewska N, Suliburska J. Influence of Tempeh, Daidzein, Probiotics, and Their Combination on Magnesium Status and Hematological Ratios in a Postmenopausal Osteoporotic Animal Model. Nutrients. 2025; 17(18):2917. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17182917
Chicago/Turabian StyleHarahap, Iskandar Azmy, Omar Salem, Rifaldi Lutfi Fahmi, Naglaa Ahmed, Natalia Leciejewska, and Joanna Suliburska. 2025. "Influence of Tempeh, Daidzein, Probiotics, and Their Combination on Magnesium Status and Hematological Ratios in a Postmenopausal Osteoporotic Animal Model" Nutrients 17, no. 18: 2917. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17182917
APA StyleHarahap, I. A., Salem, O., Fahmi, R. L., Ahmed, N., Leciejewska, N., & Suliburska, J. (2025). Influence of Tempeh, Daidzein, Probiotics, and Their Combination on Magnesium Status and Hematological Ratios in a Postmenopausal Osteoporotic Animal Model. Nutrients, 17(18), 2917. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17182917










