Liubao Tea Extract Attenuates High-Fat Diet and Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetes in Mice by Remodeling Hepatic Metabolism and Gut Microbiota
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Preparation and Preliminary Chemometric Analysis of LBTE
2.3. Characterization of the Chemical Composition of LBTE
2.4. Network Pharmacology Analysis
2.4.1. Drug Target Prediction and Disease Target Identification
2.4.2. Molecular Docking
2.5. Identification of Potential Active Ingredients in LBTE
2.6. Quantitative Analysis of Potential Ingredients in LBTE
2.7. Experimental Verification
2.7.1. Animal Model and Treatment
2.7.2. Sample Collection
2.7.3. Biochemical Index Determination
2.7.4. Histopathological Analysis
2.8. Metabolomic Analysis of Serum Samples
2.9. Gut Microbiota Analysis
2.10. MetOrigin Analysis
2.11. SCFA Analysis
2.12. Determination of Gene Expression Using qPCR
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
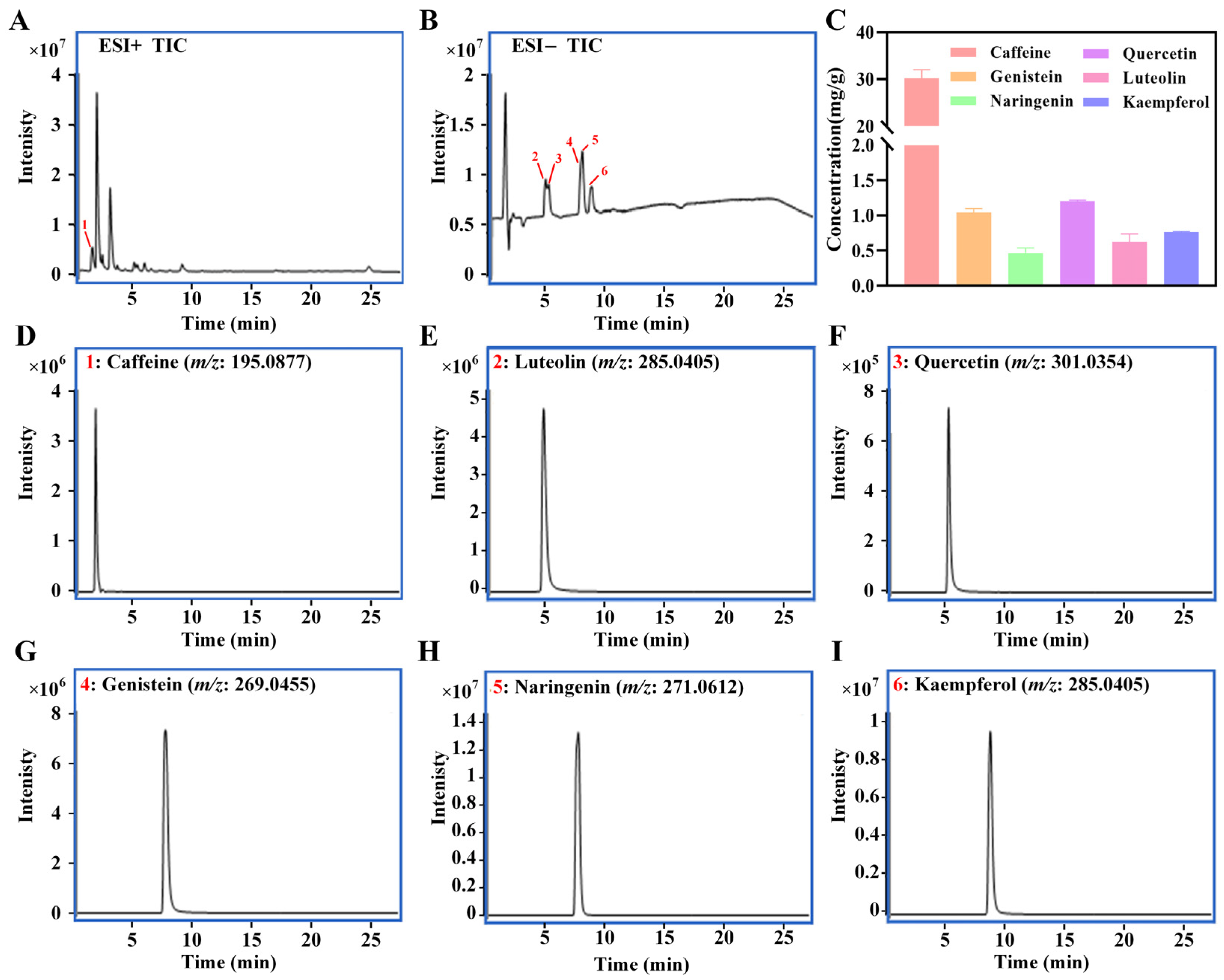
3.1. Chemical Composition Profiling of LBTE
3.2. Network Pharmacology Analysis and Potential Active Ingredients Identification
3.3. Quantification of Potential Ingredients in LBTE
3.4. Amelioration of LBTE on T2D Mice
3.5. Influence of LBTE Treatment on the Serum Metabolic Profiles of T2D Mice
3.6. Regulation of LBTE on Expression of Key Genes Involved in Inflammatory Response, Glucose and Lipid Metabolism Pathways
3.7. LBTE Administration Modulated the Gut Microbiota Profiles in T2D Mice
3.8. MetOrigin Tracing Analysis of Differential Metabolites
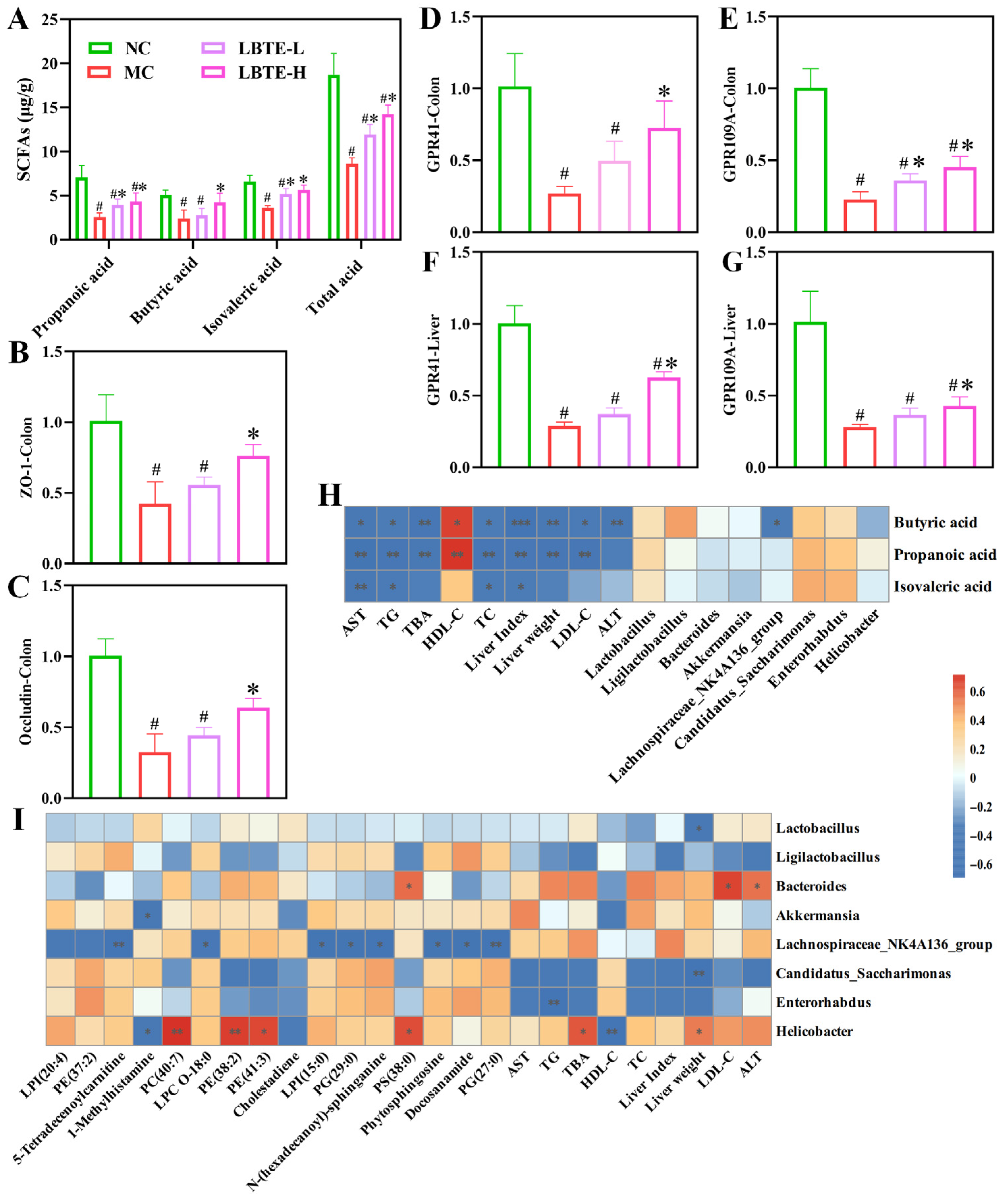
3.9. LBTE Enhanced the Intestinal Barrier Function by Promoting SCFA Production and Regulating GPCR Gene Expression
3.10. Correlation Analysis
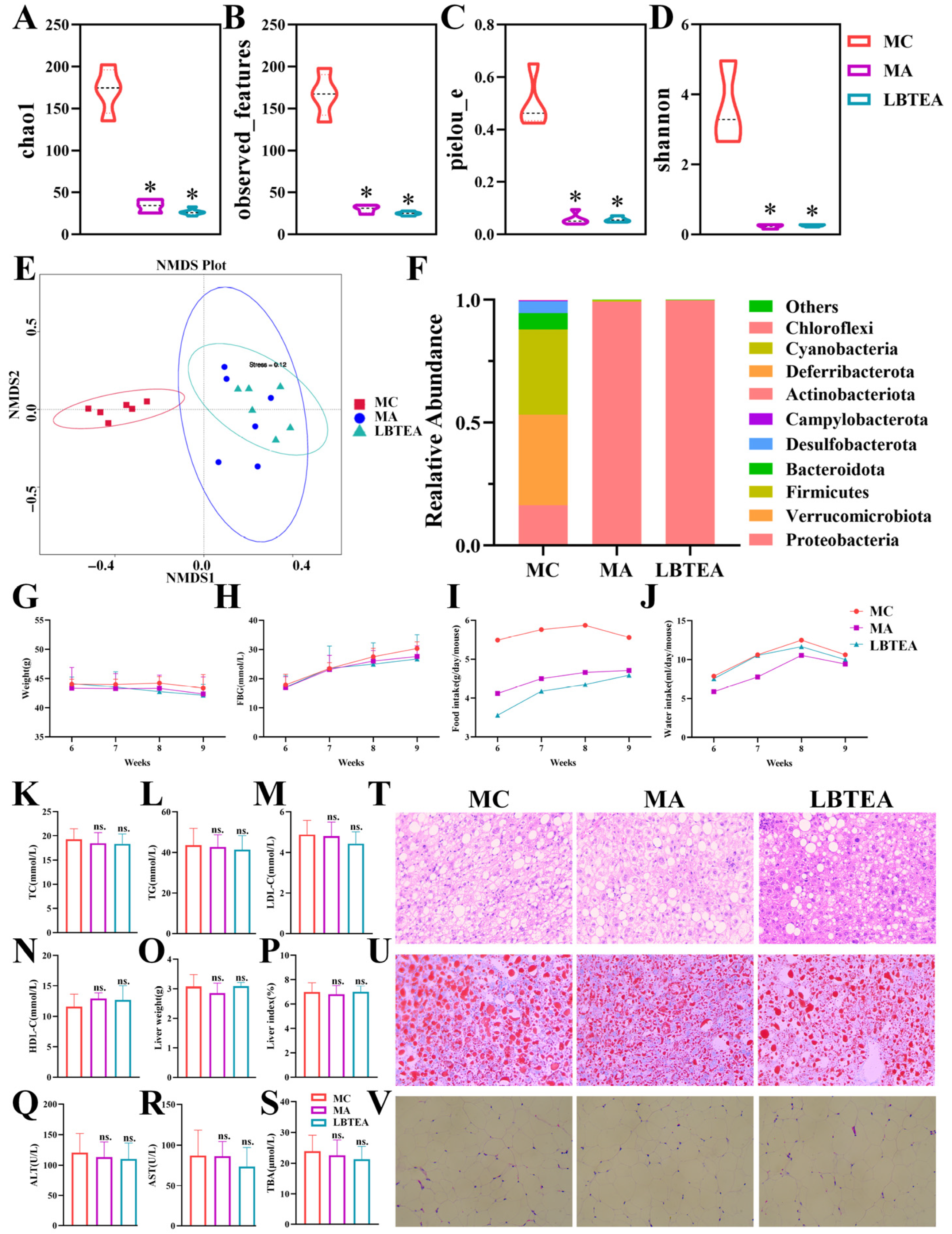
3.11. LBTE Alleviated T2D Pathology Depending on Gut Microbiota
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, K.; Xiong, W.; Qiu, Y.; He, X.; Liu, B.; Zeng, F. Sanghuangporus vaninii mixture ameliorated type 2 diabetes mellitus and altered intestinal microbiota in mice. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 11758–11769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Pan, P.; Zhang, H.; Li, R.; Ren, D.; Jiang, B. Latilactobacillus sakei QC9 alleviates hyperglycaemia in high-fat diet and streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetes mellitus mice via the microbiota-gut-liver axis. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 8008–8029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.; Liu, T.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yin, X.; Huang, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhao, C.; Shao, R.; Xu, W. Fagopyrum tataricum ethanol extract ameliorates symptoms of hyperglycemia by regulating gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes mellitus mice. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 8487–8503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Luo, L.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Luo, H. Biological potential and mechanisms of Tea′ s bioactive compounds: An Updated review. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 65, 345–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.J.; Chen, X.X.; Wei, S.Y.; Lan, L.L.; Qiu, R.J.; Ling, Y.P.; Zhou, D.S.; Wu, Z.M.; Cao, Z.H.; Yu, C.P.; et al. Study on the mechanism of active components of Liupao tea on 3CL(pro) based on HPLC-DAD fingerprint and molecular docking technique. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Yang, Q.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wei, X. Distinct Changes of Metabolic Profile and Sensory Quality during Qingzhuan Tea Processing Revealed by LC-MS-Based Metabolomics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 4955–4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Huang, L.; Xia, N.; Teng, J.; Wei, B.; Lin, X.; Khan, M.R. Two Polysaccharides from Liupao Tea Exert Beneficial Effects in Simulated Digestion and Fermentation Model In Vitro. Foods 2022, 11, 2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Chen, M.; Song, H.; Ma, S.; Ou, C.; Li, Z.; Hu, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Pan, Y.; et al. A systemic review on Liubao tea: A time-honored dark tea with distinctive raw materials, process techniques, chemical profiles, and biological activities. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 5063–5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yu, W.; Ni, W.; Teng, C.; Ye, W.; Yu, C.; Zeng, Y. Improvement of obesity by Liupao tea is through the IRS-1/PI3K/AKT/GLUT4 signaling pathway according to network pharmacology and experimental verification. Phytomedicine 2023, 110, 154633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wei, Z.; Luo, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, G.; Guan, X.; She, Z.; Liu, W.; Tong, Y.; Liu, H.; et al. Integrated bioinformatics and multiomics reveal Liupao tea extract alleviating NAFLD via regulating hepatic lipid metabolism and gut microbiota. Phytomedicine 2024, 132, 155834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, X.; She, Z.; Huang, L.; Wei, H.; Yang, S.; Wei, Z.; Chen, H.; Yang, B.; Hu, Z.; et al. Combining bioinformatics and multiomics strategies to investigate the key microbiota and active components of Liupao tea ameliorating hyperlipidemia. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 333, 118438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Q.; Zhang, B.; Zheng, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Yan, R.; Zhang, T.; Yu, L.; Dong, Y.; Ma, B. Liupao tea extract alleviates diabetes mellitus and modulates gut microbiota in rats induced by streptozotocin and high-fat, high-sugar diet. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Wu, M.; Zhou, H.; Cheng, L.; Wei, X.; Wang, Y. Liubao brick tea activates the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway to lower blood glucose, metabolic disorders and insulin resistance via altering the intestinal flora. Food Res. Int. 2021, 148, 110594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Song, P.; Yin, S.; Fan, T.; Li, F.; Ge, X.; Liu, T.; Xu, W.; Xu, S.; Chen, L. Onchidium struma polysaccharides exhibit hypoglycemic activity and modulate the gut microbiota in mice with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 1937–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabst, O.; Hornef, M.W.; Schaap, F.G.; Cerovic, V.; Clavel, T.; Bruns, T. Gut-liver axis: Barriers and functional circuits. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 447–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Liu, C.; Wan, L.; Peng, L.; Wen, S.; Fang, W.; Chen, H.; Wang, K.; Yang, X.; Huang, J.; et al. (-)-Epicatechin ameliorates type 2 diabetes mellitus by reshaping the gut microbiota and Gut-Liver axis in GK rats. Food Chem. 2024, 447, 138916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Liu, A.; Ma, W.; Liu, X.; Luo, P.; Zhan, M.; Zhou, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, J. Lactobacillus gasseri CKCC1913 mediated modulation of the gut-liver axis alleviated insulin resistance and liver damage induced by type 2 diabetes. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 8504–8520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Hu, D.; Xu, J.; Zhao, S.; Song, Y.; Qin, G.; Liu, Y. Identification of hub genes associated with diabetic cardiomyopathy using integrated bioinformatics analysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 15324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Song, Q.; Shaw, P.C.; Zuo, Z. Dendrobium officinale regulate lipid metabolism in diabetic mouse liver via PPAR-RXR signaling pathway: Evidence from an integrated multi-omics analysis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 173, 116395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, F.; Yu, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liang, S.; Zhang, F. Deciphering the pharmacological mechanisms of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi on oral leukoplakia by combining network pharmacology, molecular docking and experimental evaluations. Phytomedicine 2022, 103, 154195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Bai, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, S.; Hu, J.; Gao, J.; Guo, S.; Ho, C.T.; Bai, N. Gut Microbiota Combined with Serum Metabolomics to Investigate the Hypoglycemic Effect of Actinidia arguta Leaves. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wu, X.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Jian, C.; Li, M.; Qin, X. Microbiome and metabolome integrally reveal the anti-depression effects of Cistanche deserticola polysaccharides from the perspective of gut homeostasis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 245, 125542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB/T 32719.4-2016; Dark Tea. Part 4: Liupao Tea. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Wu, Y.; Sun, H.; Yi, R.; Tan, F.; Zhao, X. Anti-obesity effect of Liupao tea extract by modulating lipid metabolism and oxidative stress in high-fat-diet-induced obese mice. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB/T 8313-2018; Determination of Total Polyphenols and Catechins Content in Tea. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- SN/T 4592-2016; Determination of Total Flavonoids in Export Food. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB/T 8314–2013; Tea-Determination of Free Amino Acids Content. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2013.
- NY/T 1676-2008; Determination of Crude Mushroom Polysaccharides. China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2003.
- Liao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, Y.; Zou, K. Flavonoids Derived from Opuntia ficus-indica Fruit Alleviate Renal Injury in Diabetic Nephropathy Mice by Altering Gut Microbiota and Promoting the Production of SCFAs. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lai, J.; Fan, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, H. Extraction of polysaccharides from Polygonum cuspidatum with activity against Type 2 Diabetes via alterations in gut microbiota. Food Chem. 2025, 470, 140047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, L.; Hu, W.; Wang, Y.; Wen, X.; Yang, J. Simiao Wan modulates the gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism during improving type 2 diabetes mellitus in mice. Phytomedicine 2022, 104, 154264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fu, X.; Yi, R.; Sun, P.; Zou, M.; Long, X.; Zhao, X. Preventive Effect of Raw Liubao Tea Polyphenols on Mouse Gastric Injuries Induced by HCl/Ethanol via Anti-Oxidative Stress. Molecules 2018, 23, 2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Xie, M.; Wan, P.; Chen, D.; Dai, Z.; Ye, H.; Hu, B.; Zeng, X.; Liu, Z. Fuzhuan Brick Tea Polysaccharides Attenuate Metabolic Syndrome in High-Fat Diet Induced Mice in Association with Modulation in the Gut Microbiota. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 2783–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Qin, Z.; Liu, A.; Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Xie, X.; Huang, X.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Sulfonation metabolism in the gut microbiota is the main metabolic pathway of cholesterol in hypercholesterolemic mice. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 9750–9765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Wang, R.; Han, B.; Sun, C.; Chen, R.; Wei, H.; Chen, L.; Du, H.; Li, G.; Yang, Y.; et al. Functional and metabolic alterations of gut microbiota in children with new-onset type 1 diabetes. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Xu, C.; Zhang, D.; Ju, F.; Ni, Y. MetOrigin: Discriminating the origins of microbial metabolites for integrative analysis of the gut microbiome and metabolome. Imeta 2022, 1, e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Zhu, M.J. A sensitive GC/MS detection method for analyzing microbial metabolites short chain fatty acids in fecal and serum samples. Talanta 2019, 196, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, G.G.; Punt, J.; Arora, M.; Day, R.O.; Doogue, M.P.; Duong, J.K.; Furlong, T.J.; Greenfield, J.R.; Greenup, L.C.; Kirkpatrick, C.M.; et al. Clinical pharmacokinetics of metformin. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2011, 50, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zeng, M.; Wang, Z.; Qin, F.; Chen, J.; He, Z. Dietary Luteolin: A Narrative Review Focusing on Its Pharmacokinetic Properties and Effects on Glycolipid Metabolism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 1441–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Vaghari-Tabari, M.; Malakoti, F.; Moein, S.; Qujeq, D.; Yousefi, B.; Asemi, Z. Quercetin: An effective polyphenol in alleviating diabetes and diabetic complications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 9163–9186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.X.; Yu, Y.J.; Dai, S.; Zhang, C.Y.; Xue, X.Y.; Zhou, M.L.; Yao, C.H.; Li, Y.X. Kaempferol efficacy in metabolic diseases: Molecular mechanisms of action in diabetes mellitus, obesity, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, steatohepatitis, and atherosclerosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 175, 116694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Huang, X.; Wu, G.; Zhou, Y.; Deng, X.; Yang, J.; Yin, J.; Nie, S. Hepatic metabolism-related effects of polysaccharides from red kidney bean and small black soybean on type 2 diabetes. Food Chem. 2023, 403, 134334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Guo, X.; Jiang, K.; Shi, B.; Liu, L.; Hou, R.; Chen, G.; Farag, M.A.; Yan, N.; Liu, L. Dietary polyphenols regulate appetite mechanism via gut-brain axis and gut homeostasis. Food Chem. 2024, 446, 138739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panickar, K.S. Effects of dietary polyphenols on neuroregulatory factors and pathways that mediate food intake and energy regulation in obesity. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blachnio-Zabielska, A.; Hajduch, E.; Le Stunff, H. Editorial: The Role of Sphingolipid Metabolism in the Development of Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 835751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Ren, Y.; Ma, Y.; Liu, J.; Jiang, H.; Liu, C. Artesunate improves glucose and lipid metabolism in db/db mice by regulating the metabolic profile and the MAPK/PI3K/Akt signalling pathway. Phytomedicine 2024, 126, 155382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Tang, Z.; Song, Z.; Liu, C.; Wang, C. Total flavonoids of Hippophae rhamnoides L. improves type 2 diabetes symptoms in rats through down-regulating of the DAG/PRKCA/MAPK10/p65/TNF-α signalling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 318, 116962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Sarli Gutiérrez, L.; Castro, M.C.; Farromeque Vásquez, S.; Villagarcía, H.G.; González Arbeláez, L.; Rojano, B.; Schinella, G.; Maiztegui, B.; Francini, F. Protective Effect of Monoterpene Isoespintanol in a Rat Model of Prediabetes Induced by Fructose. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 17, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comba, S.; Menendez-Bravo, S.; Arabolaza, A.; Gramajo, H. Identification and physiological characterization of phosphatidic acid phosphatase enzymes involved in triacylglycerol biosynthesis in Streptomyces coelicolor. Microb. Cell Fact. 2013, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; Zhang, K.; Li, S.; Weng, S. Trichosanthes kirilowii Maxim. Polysaccharide attenuates diabetes through the synergistic impact of lipid metabolism and modulating gut microbiota. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2025, 10, 100977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xu, S.J.; Ye, F.; Zhang, B.; Sun, X.B. Integration of Transcriptomics and Lipidomics Profiling to Reveal the Therapeutic Mechanism Underlying Ramulus mori (Sangzhi) Alkaloids for the Treatment of Liver Lipid Metabolic Disturbance in High-Fat-Diet/Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Xue, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, A.; Zhang, J.; Luo, P.; Zhan, M.; Zhou, X.; Chen, L.; et al. Amelioration of Type 2 Diabetes Using Four Strains of Lactobacillus Probiotics: Effects on Gut Microbiota Reconstitution-Mediated Regulation of Glucose Homeostasis, Inflammation, and Oxidative Stress in Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 20801–20814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Chen, J.; Hu, X.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J.; Ao, T.; Wang, H.; Xie, J.; Yu, Q. Elucidation of the interaction effect between dietary fiber and bound polyphenol components on the anti-hyperglycemic activity of tea residue dietary fiber. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 2710–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Li, Y.; Cai, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, F.; Liang, S.; Zhang, W.; Guan, Y.; Shen, D.; et al. A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature 2012, 490, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Ma, J.; Rozi, P.; Kong, L.; Zhou, J.; Luo, Y.; Yang, H. The polysaccharides from seeds of Glycyrrhiza uralensis ameliorate metabolic disorders and restructure gut microbiota in type 2 diabetic mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 264, 130622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, Z.; Sarikaya, M.; Ergul, B.; Filik, L. The effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on insulin resistance and HbA1c level in people with normal glucose levels: A prospective study. Biomed. Pap. Med. Fac. Univ. Palacky. Olomouc Czech Repub. 2015, 159, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Sun, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Pan, B.; Su, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Lv, S.; Wang, H. Integrated 16S rRNA sequencing and nontargeted metabolomics analysis to reveal the mechanisms of Yu-Ye Tang on type 2 diabetes mellitus rats. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1159707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Hu, R.; Tang, T.; Tang, W.; Huang, C. Review of the correlation between Chinese medicine and intestinal microbiota on the efficacy of diabetes mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1085092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manilla, V.; Santopaolo, F.; Gasbarrini, A.; Ponziani, F.R. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Liver Disease: Across the Gut-Liver Axis from Fibrosis to Cancer. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Ge, W.; Song, Y.; He, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, L. Camel milk peptides alleviate hyperglycemia by regulating gut microbiota and metabolites in type 2 diabetic mice. Food Res. Int. 2023, 173, 113278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, Z.; Pang, W.; Sun, W.; Lu, B.; Zou, L.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y. Metallothionein-Kidney Bean Polyphenol Complexes Showed Antidiabetic Activity in Type 2 Diabetic Rats by Improving Insulin Resistance and Regulating Gut Microbiota. Foods 2023, 12, 3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Q.; Wang, Y.; Jin, T.; Zhu, L.; Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, N. Analysis of Intestinal Short-Chain Fatty Acid Metabolism Profile After Probiotics and GLP-1 Treatment for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 892127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, M.J.; Santos, A.; Prada, P.O. Linking Gut Microbiota and Inflammation to Obesity and Insulin Resistance. Physiology 2016, 31, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Xiaoyue, D.; Longkun, D.; Yue, X.; Man, Y.; Min, Z.; Liang, W.; Chengxue, Y.; Huaxi, X. Three main short-chain fatty acids inhibit the activation of THP-1 cells by Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2021, 85, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Wang, X.; Ke, J.; Hou, X.; Shen, G.; Li, S.; Chen, H.; Cui, Q.; Yu, J.; Luo, Q.; et al. Chayote pectin regulates blood glucose through the gut-liver axis: Gut microbes/SCFAs/FoxO1 signaling pathways. Food Res. Int. 2025, 202, 115706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Dai, H.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, F.; Bu, C.; Chen, S. Hydroxytyrosol Alleviates Acute Liver Injury by Inhibiting the TNF-α/PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway via Targeting TNF-α Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, N.T.; Zhang, M.; Juraschek, S.P.; Miller, E.R.; Appel, L.J. Effects of high-fiber diets enriched with carbohydrate, protein, or unsaturated fat on circulating short chain fatty acids: Results from the OmniHeart randomized trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 111, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, J.; Wei, Z.; Tan, Y.; Tong, Y.; Yang, B.; Wen, M.; Guan, X.; Zhu, P.; Xu, S.; Lin, X.; et al. Liubao Tea Extract Attenuates High-Fat Diet and Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetes in Mice by Remodeling Hepatic Metabolism and Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2665. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162665
Luo J, Wei Z, Tan Y, Tong Y, Yang B, Wen M, Guan X, Zhu P, Xu S, Lin X, et al. Liubao Tea Extract Attenuates High-Fat Diet and Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetes in Mice by Remodeling Hepatic Metabolism and Gut Microbiota. Nutrients. 2025; 17(16):2665. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162665
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Jichu, Zhijuan Wei, Yuru Tan, Ying Tong, Bao Yang, Mingsen Wen, Xuan Guan, Pingchuan Zhu, Song Xu, Xueting Lin, and et al. 2025. "Liubao Tea Extract Attenuates High-Fat Diet and Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetes in Mice by Remodeling Hepatic Metabolism and Gut Microbiota" Nutrients 17, no. 16: 2665. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162665
APA StyleLuo, J., Wei, Z., Tan, Y., Tong, Y., Yang, B., Wen, M., Guan, X., Zhu, P., Xu, S., Lin, X., & Zhang, Q. (2025). Liubao Tea Extract Attenuates High-Fat Diet and Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetes in Mice by Remodeling Hepatic Metabolism and Gut Microbiota. Nutrients, 17(16), 2665. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162665





