Mixed Green Banana (Musa spp.) Pulp and Peel Flour Reduced Body Weight Gain and Adiposity and Improved Lipid Profile and Intestinal Morphology in Wistar Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials and Preparation of Banana Flours
2.2. Proximate Composition
2.3. Total Phenolic Content
2.4. Total Starch and Resistant Starch Contents
2.5. In Vivo Study
2.5.1. Experimental Model
2.5.2. Food Efficiency Ratio, Cecum Index, and Total Body Adiposity
2.5.3. Biochemical Analyzes
2.5.4. Cecum Histomorphometry Analysis
2.5.5. Fecal pH
2.5.6. Fecal Moisture Content
2.5.7. Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFA)
2.5.8. Extraction of mRNA from Intestinal Tissue and cDNA Synthesis
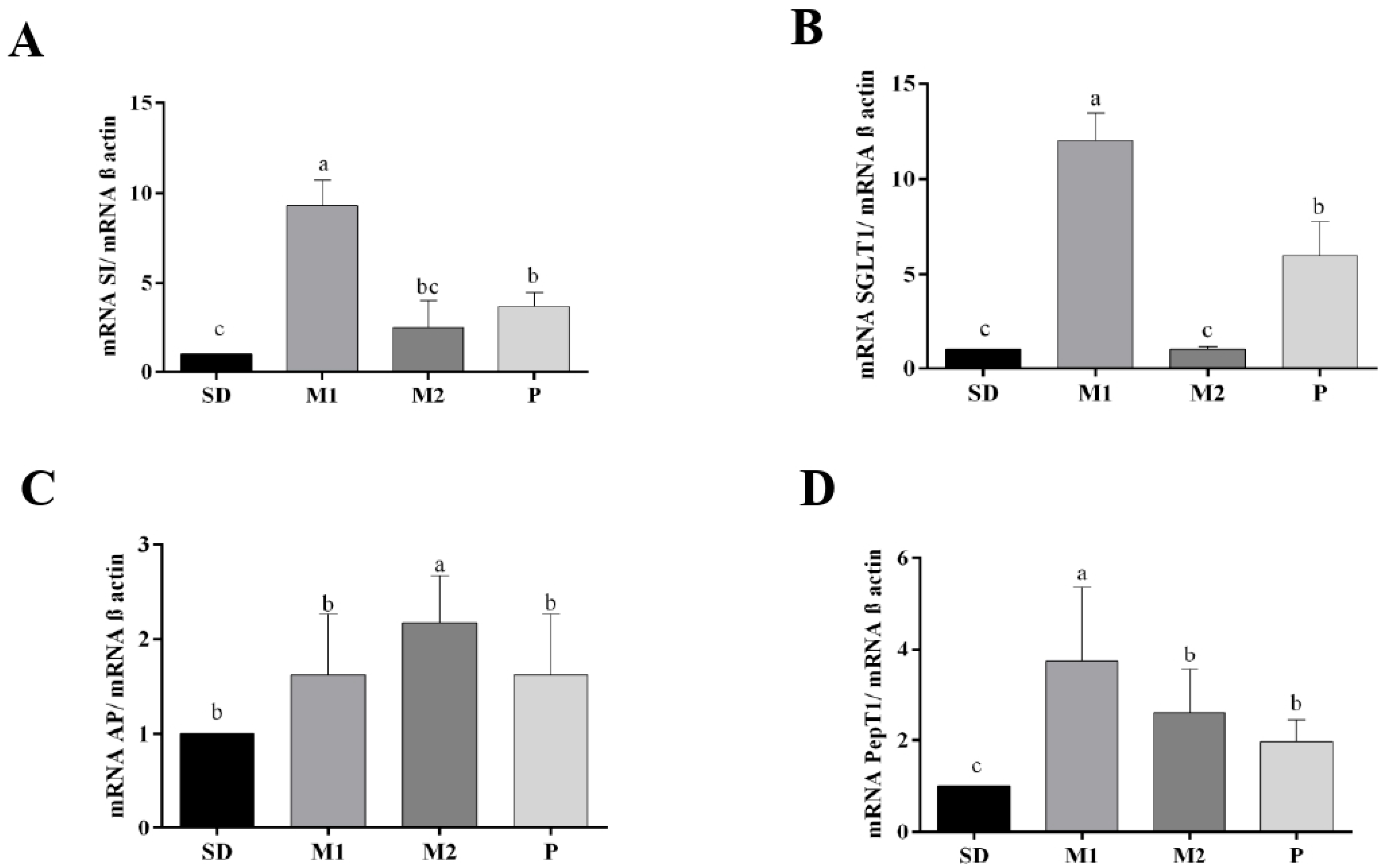
2.5.9. Determination of Gene Expression of Proteins Involved in Intestinal Health by Quantitative Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
2.5.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Characterization of the Green Banana Pulp and Peel Flours
3.2. In Vivo Study
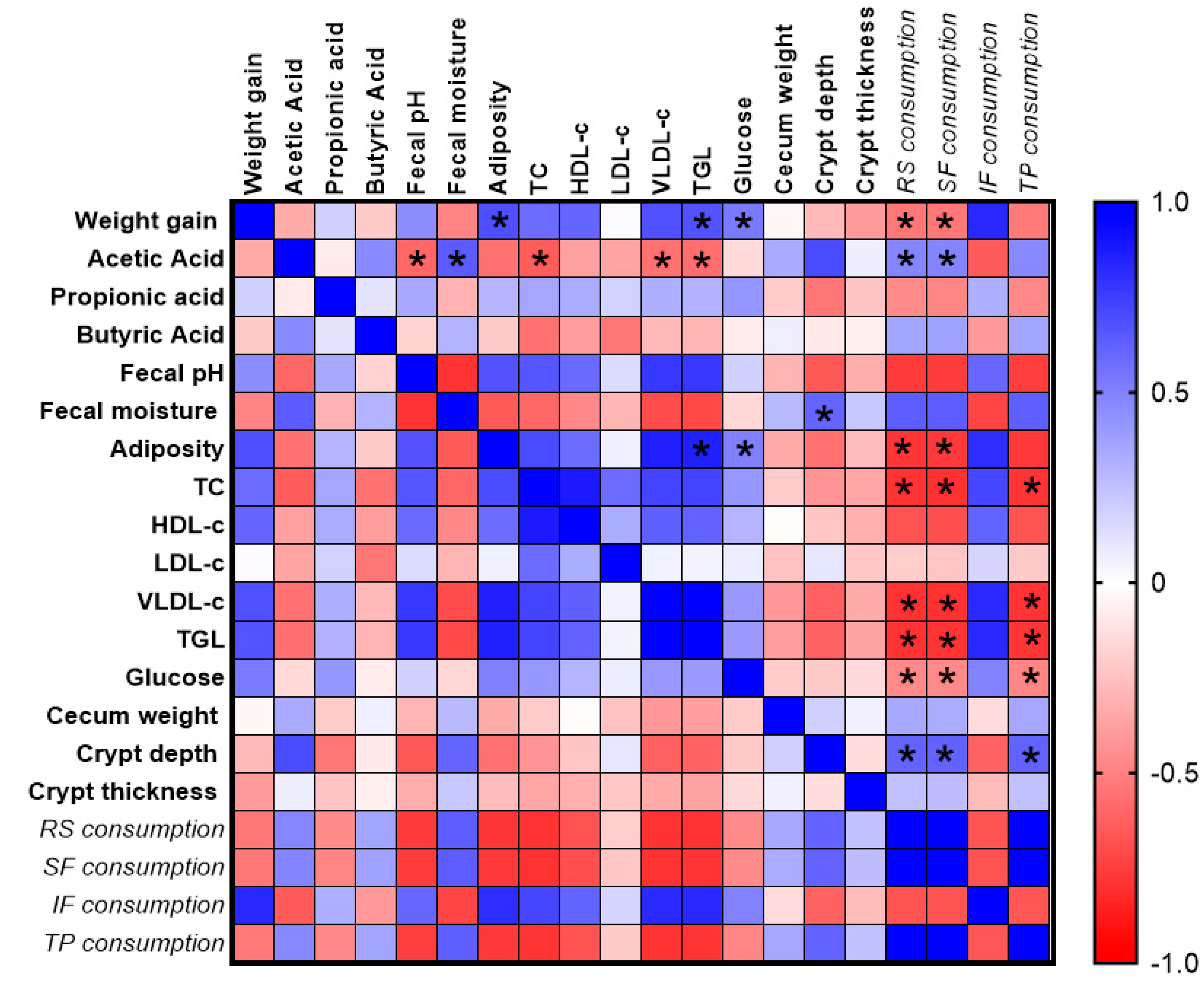
Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flores-Silva, P.C.; Tovar, J.; Reynoso-Camacho, R.; Bello-Pérez, L.A. Impact of Chickpea- and Raw Plantain-Based Gluten-Free Snacks on Weight Gain, Serum Lipid Profile, and Insulin Resistance of Rats Fed with a High-Fructose Diet. Cereal Chem. J. 2017, 94, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M.S.; Hui Yan, T.; Saari, N.; Sarbini, S.R. A Review: Resistant Starch, a Promising Prebiotic for Obesity and Weight Management. Food Biosci. 2022, 50, 101965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojarczuk, A.; Skąpska, S.; Mousavi Khaneghah, A.; Marszałek, K. Health Benefits of Resistant Starch: A Review of the Literature. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 93, 105094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini Khoozani, A.; Birch, J.; Bekhit, A.E.D.A. Production, Application and Health Effects of Banana Pulp and Peel Flour in the Food Industry. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Barros Mesquita, C.; Leonel, M.; Franco, C.M.L.; Leonel, S.; Garcia, E.L.; dos Santos, T.P.R. Characterization of Banana Starches Obtained from Cultivars Grown in Brazil. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 89, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosado, C.P.; Rosa, V.H.C.; Martins, B.C.; Soares, A.C.; Santos, I.B.; Monteiro, E.B.; Moura-Nunes, N.; da Costa, C.A.; Mulder, A.d.R.P.; Daleprane, J.B. Resistant Starch from Green Banana (Musa sp.) Attenuates Non-Alcoholic Fat Liver Accumulation and Increases Short-Chain Fatty Acids Production in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 145, 1066–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosado, C.; Rosa, V.; Martins, B.; Soares, A.; Almo, A.; Elisa, M.; Mulder, A.; Moura-Nunes, N.; Daleprane, J.B. Green Banana Flour Supplementation Improves Obesity-Associated Systemic Inflammation and Regulates Gut Microbiota Profile in High-Fat Diet–Fed Mice. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 46, 1469–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida-Junior, L.D.; Curimbaba, T.F.S.; Chagas, A.S.; Quaglio, A.E.V.; Di Stasi, L.C. Dietary Intervention with Green Dwarf Banana Flour (Musa sp. AAA) Modulates Oxidative Stress and Colonic SCFAs Production in the TNBS Model of Intestinal Inflammation. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 38, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, A.; Rocha-Gomes, A.; dos Reis, C.G.M.; Herrera, K.N.S.; Guedes, T.d.J.; da Silva, A.A.; Lessa, M.R.; Dessimoni-Pinto, N.A.V.; Riul, T.R. Unripe Banana Flour (Musa cavendishii) Promotes Decrease in Weight Gain and Elimination of Fecal Cholesterol in Wistar Rats. Nutr. Food Sci. 2020, 50, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis-Pereira, M.C.; Barcelos, M.d.F.P.; Pereira, R.C.; Pereira, J.d.A.R.; de Sousa, R.V. Chemical Composition of Unripe Banana Peels and Pulps Flours and Its Effects on Blood Glucose of Rats. Nutr. Food Sci. 2016, 46, 504–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, L.M.; Rodrigues, F.S.R.; Santos, M.C.B.; Lima, A.d.S.; Nabeshima, E.H.; Leite, M.d.O.; Martins, M.A.; de Carvalho, C.W.P.; Maltarollo, V.G.; Azevedo, L.; et al. Green Banana (Musa ssp.) Mixed Pulp and Peel Flour: A New Ingredient with Interesting Bioactive, Nutritional, and Technological Properties for Food Applications. Food Chem. 2024, 451, 139506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AOAC International. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International (AOAC); AOAC: Rockville, MD, USA, 2016; p. 3172. ISBN 9780935584875, 0935584870. [Google Scholar]
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A. Colorimetry of Total Phenolics with Phosphomolybdic-Phosphotungstic Acid Reagents. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AACC International. Approved Methods of Analysis, 11th ed.; AACC International: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Reeves, P.G.; Nielsen, F.H.; Fahey, G.C. AIN-93 Purified Diets for Laboratory Rodents: Final Report of the American Institute of Nutrition Ad Hoc Writing Committee on the Reformulation of the AIN-76A Rodent Diet. J. Nutr. 1993, 123, 1939–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sousa, A.R.; de Castro Moreira, M.E.; Toledo, R.C.L.; dos Anjos Benjamin, L.; Queiroz, V.A.V.; Veloso, M.P.; de Souza Reis, K.; Martino, H.S.D. Extruded Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.) Reduces Metabolic Risk of Hepatic Steatosis in Obese Rats Consuming a High Fat Diet. Food Res. Int. 2018, 112, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Hong, J.; Jeon, R.; Kim, H.S. Adzuki Bean Ameliorates Hepatic Lipogenesis and Proinflammatory Mediator Expression in Mice Fed a High-Cholesterol and High-Fat Diet to Induce Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutr. Res. 2016, 36, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, B.P.; Dias, D.M.; de Castro Moreira, M.E.; Toledo, R.C.L.; da Matta, S.L.P.; Della Lucia, C.M.; Martino, H.S.D.; Pinheiro-Sant’Ana, H.M. Chia Seed Shows Good Protein Quality, Hypoglycemic Effect and Improves the Lipid Profile and Liver and Intestinal Morphology of Wistar Rats. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2016, 71, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaliere, G.A. Parâmetros Histom$orfométricos do int$estino d$elgado em fra$ngos de Corte Alimentados Com Rações Contendo Diferentes Fontes de Sorgo e Concentrações de Tanino. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Federal de São Carlos, São Carlos, Brazil, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Grancieri, M.; Costa, N.M.B.; Vaz Tostes, M.d.G.; de Oliveira, D.S.; Nunes, L.d.C.; Marcon, L.d.N.; Veridiano, T.A.; Viana, M.L. Yacon Flour (Smallanthus sonchifolius) Attenuates Intestinal Morbidity in Rats with Colon Cancer. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 37, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegfried, V.R.; Ruckemmann, H.; Stumpf, G. Method for the Determination of Organic Acids in Silage by High Performance Liquid Chromatography. Landwirtsch. Forsch. 1984, 37, 298–304. [Google Scholar]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina Martinez, O.D.; Vieira Theodoro, J.M.; Grancieri, M.; Lopes Toledo, R.C.; Vieira Queiroz, V.A.; Ribeiro de Barros, F.A.; Duarte Martino, H.S. Dry Heated Whole Sorghum Flour (BRS 305) with High Tannin and Resistant Starch Improves Glucose Metabolism, Modulates Adiposity, and Reduces Liver Steatosis and Lipogenesis in Wistar Rats Fed with a High-Fat High-Fructose Diet. J. Cereal Sci. 2021, 99, 103201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishima, M.D.V.; da Silva, B.P.; Gomes, M.J.C.; Toledo, R.C.L.; Pereira, C.E.R.; Costa, N.M.B.; Martino, H.S.D. Effect of Chia Flour Associated with High Fat Diet on Intestinal Health in Female Ovariectomized Wistar Rats. Eur. J. Nutr. 2023, 62, 905–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishima, M.D.V.; Da Silva, B.P.; Gomes, M.J.C.; Toledo, R.C.L.; Mantovani, H.C.; José, V.P.B.d.S.; Costa, N.M.B.; Tako, E.; Martino, H.S.D. Effect of Chia (Salvia hispanica L.) Associated with High-Fat Diet on the Intestinal Health of Wistar Rats. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, O.D.M.; Gomes, M.J.C.; Grancieri, M.; de São José, V.P.B.; Toledo, R.C.L.; Queiroz, V.A.V.; da Silva, B.P.; Martino, H.S.D. Sorghum Flour BRS 305 Hybrid Has the Potential to Modulate the Intestinal Microbiota of Rats Fed with a High-Fat High-Fructose Diet. Eur. J. Nutr. 2023, 62, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrera-Quintanar, L.; Roa, R.I.L.; Quintero-Fabián, S.; Sánchez-Sánchez, M.A.; Vizmanos, B.; Ortuño-Sahagún, D. Phytochemicals That Influence Gut Microbiota as Prophylactics and for the Treatment of Obesity and Inflammatory Diseases. Mediators Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 9734845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.D.; Cao, Y.N.; Peng, L.X.; Yan, Z.Y.; Zhao, G. Coarse Cereals and Legume Grains Exert Beneficial Effects through Their Interaction with Gut Microbiota: A Review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 861–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, C.; Swanson, K.S.; Fahey, G.C.; Garleb, K.A. Perspective: Physiologic Importance of Short-Chain Fatty Acids from Nondigestible Carbohydrate Fermentation. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, 576–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oguma, T.; Nakayama, K.; Kuriyama, C.; Matsushita, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Hikida, K.; Obokata, N.; Tsuda-Tsukimoto, M.; Saito, A.; Arakawa, K.; et al. Intestinal Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 1 Inhibition Enhances Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Secretion in Normal and Diabetic Rodents. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2015, 354, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, H.S.D.; Kolba, N.; Tako, E. Yacon (Smallanthus sonchifolius) Flour Soluble Extract Improve Intestinal Bacterial Populations, Brush Border Membrane Functionality and Morphology In Vivo (Gallus gallus). Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacifici, S.; Song, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Q.; Glahn, R.P.; Kolba, N.; Tako, E. Intra Amniotic Administration of Raffinose and Stachyose Affects the Intestinal Brush Border Functionality and Alters Gut Microflora Populations. Nutrients 2017, 9, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, D.V.; Silva, L.M.A.; Alves Filho, E.G.; Santos, F.A.; De Lima, R.P.; Viana, A.F.S.C.; Nunes, P.I.G.; Fonseca, S.G.D.C.; De Melo, T.S.; Viana, D.D.A.; et al. Cashew Apple Fiber Prevents High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice: An NMR Metabolomic Evaluation. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 1671–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkandawire, N.L.; Kaufman, R.C.; Bean, S.R.; Weller, C.L.C.; Jackson, D.D.S.; Rose, D.J. Effects of Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench) Tannins on α-Amylase Activity and in Vitro Digestibility of Starch in Raw and Processed Flours. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 4448–4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, L.D.A.; Verneque, B.J.F.; Mota, A.P.L.; Duarte, C.K. Chia Seed (Salvia hispanica L.) Consumption and Lipid Profile: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 8835–8849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdes, D.S.; So, D.; Gill, P.A.; Kellow, N.J. Effect of Dietary Acetic Acid Supplementation on Plasma Glucose, Lipid Profiles, and Body Mass Index in Human Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2021, 121, 895–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Ingredients | Experimental Diets | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SD | M1 | M2 | P | |
| Casein * | 16.16 | 14.27 | 14.56 | 13.77 |
| Mixed PF + PeF (90:10) | - | 42.65 | - | - |
| Mixed PF + PeF (80:20) | - | - | 33.74 | - |
| Green banana pulp flour | - | - | - | 57.94 |
| Dextrinized starch | 13.20 | 13.20 | 13.20 | 6.59 |
| Sucrose | 10.00 | 10.00 | 10.00 | 10.00 |
| Soybean oil | 7.00 | 6.44 | 6.33 | 6.65 |
| Microcrystalline cellulose | 5.00 | - | - | - |
| Mineral mix | 3.50 | 3.50 | 3.50 | 3.50 |
| Vitamin mix | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| L-Cystine | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 |
| Choline bitartrate | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| Corn starch | 43.59 | 8.39 | 17.12 | - |
| Composition of diets (%) | ||||
| Protein | 16.40 | 16.70 | 16.60 | 16.70 |
| Carbohydrate | 67.70 | 66.70 | 66.90 | 66.50 |
| Lipid | 16.00 | 16.60 | 16.50 | 16.80 |
| Caloric density (Kcal/g) | 3.95 | 3.79 | 3.81 | 3.75 |
| Components | Flours | |
|---|---|---|
| PF | PeF | |
| Moisture (g/100 g) | 6.15 ± 0.15 b | 7.40 ± 0.13 a |
| Protein (g/100 g) | 3.33 ± 0.48 b | 5.80 ± 0.00 a |
| Lipids (g/100 g) | 0.61 ± 0.05 b | 7.53 ± 0.02 a |
| Ash (g/100 g) | 2.23 ± 0.04 b | 8.41 ± 0.11 a |
| Total starch (g/100 g) | 69.54 ± 0.75 a | 24.04 ± 0.00 b |
| Resistant starch (g/100 g) | 44.11 ± 0.66 a | 17.89 ± 0.40 b |
| Total dietary fiber (g/100 g) | 8.63 ± 0.62 b | 39.57 ± 1.23 a |
| Soluble fiber (g/100 g) | 2.39 ± 0.65 b | 4.89 ± 0.64 a |
| Insoluble fiber (g/100 g) | 6.24 ± 0.03 b | 34.68 ± 0.59 a |
| Total phenolics (mg GAE per g) | 3.80 ± 0.002 b | 7.60 ± 0.004 a |
| Parameters | Groups | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SD | M1 | M2 | P | |
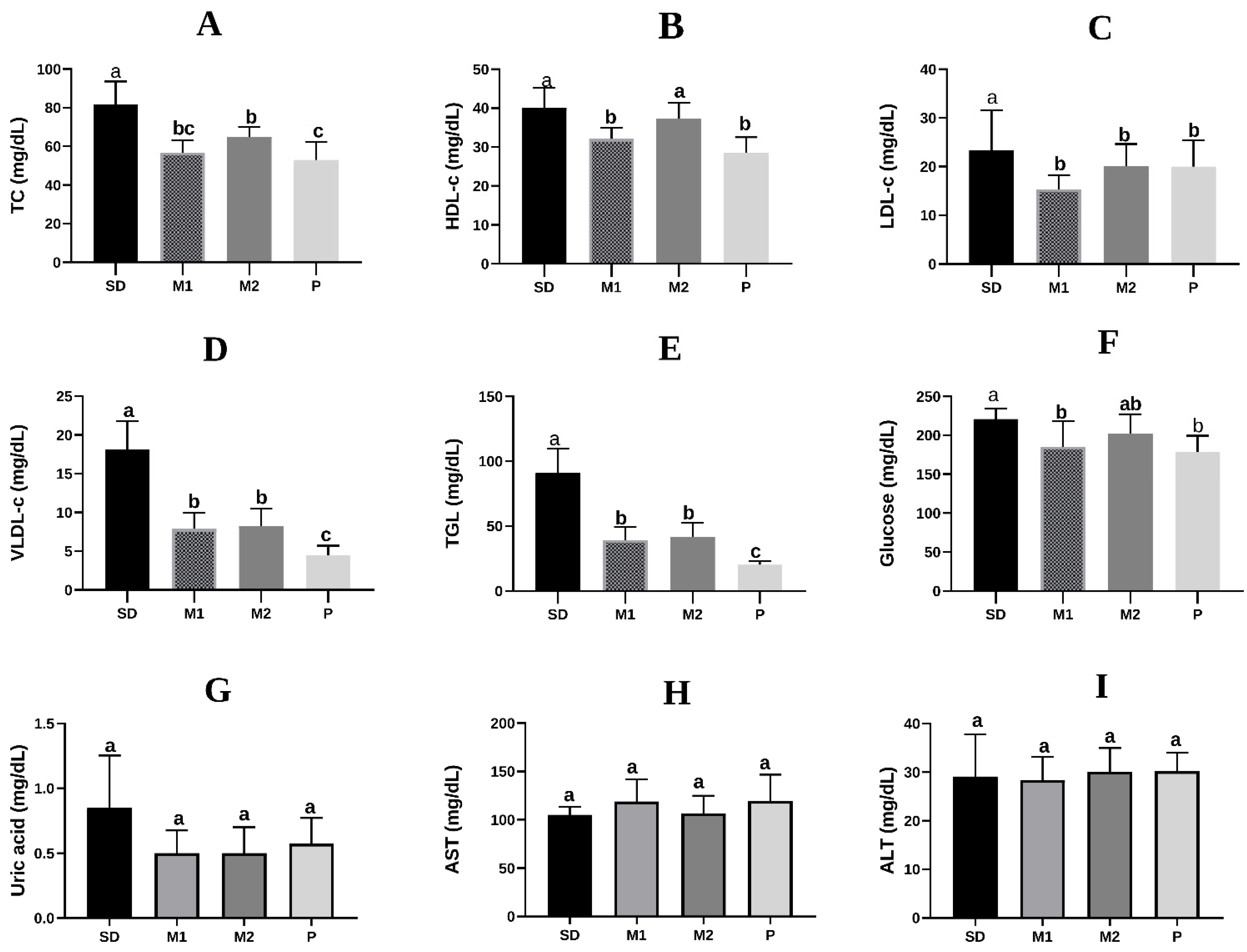
| Weight gain (g) | 168.57 ± 9.59 a | 153.84 ± 10.24 b | 154.02 ± 7.62 b | 146.95 ± 6.37 b |
| Adiposity (%) | 4.27 ± 0.77 a | 2.45 ± 0.41 b | 2.90 ± 0.39 b | 1.39 ± 0.21 c |
| Food intake (g/week) | 118.93 ± 7.50 a | 122.18 ± 6.35 a | 120.19 ± 8.04 a | 120.67 ± 7.70 a |
| FER | 35.47 ± 1.38 a | 31.48 ± 1.44 bc | 32.62 ± 1.31 b | 30.32 ±1.77 c |
| Total consumption (g/day) | ||||
| Resistant starch (g/day) | - | 3.09 ± 0.16 b | 2.25 ± 0.15 c | 4.41 ± 0.28 a |
| Soluble fiber (g/day) | - | 0.20 ± 0.01 b | 0.17 ± 0.01 c | 0.24 ± 0.02 a |
| Insoluble fiber (g/day) | 0.85 ± 0.05 a | 0.68 ± 0.04 b | 0.71 ± 0.05 b | 0.62 ± 0.04 c |
| Parameters | Groups | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SD | M1 | M2 | P | |
| Cecum weight (g) | 3.90 ± 0.39 c | 15.09 ± 2.10 a | 10.27 ± 2.97 b | 17.19 ± 3.85 a |
| Cecum index (%) | 2.33 ± 0.29 c | 10.16 ± 1.11 a | 6.55 ± 1.67 b | 13.30 ± 2.64 a |
| Fecal moisture (%) | 34.80 ± 7.31 c | 52.98 ± 4.95 b | 57.11 ± 4.33 b | 65.37 ± 7.12 a |
| Fecal pH | 8.32 ± 0.38 a | 6.80 ± 0.68 b | 6.29 ± 0.78 b | 5.17 ± 0.34 c |
| Short-chain Fatty Acids (mM) | ||||
| Acetic acid | 4.86 ± 0.93 b | 8.93 ± 3.196 a | 8.14 ± 0.96 a | 8.19 ± 1.71 a |
| Butyric acid | 1.33 ± 1.33 a | 2.17 ± 0.69 a | 2.12 ± 1.69 a | 2.02 ± 0.96 a |
| Propionic acid | 1.90 ± 0.34 a | 1.87 ± 0.09 a | 1.80 ± 0.44 a | 1.37 ± 0.59 a |
| Crypt depth (μm) | 130.50 ± 15.30 b | 166.10 ± 22.13 a | 176.50 ± 14.77 a | 192.80 ± 29.54 a |
| Crypt thickness (μm) | 37.98 ± 2.12 b | 38.50 ± 3.70 b | 38.59 ± 2.07 b | 46.52 ± 8.99 a |
| Number of goblet cells | 19.82 ± 2.70 a | 20.11 ± 2.56 a | 21.82 ± 2.98 a | 21.28 ± 3.00 a |
| CML (μm) | 58.67 ± 11.86 a | 73.29 ± 6.62 a | 69.66 ± 13.57 a | 69.44 ± 5.51 a |
| LML (μm) | 28.50 ± 4.52 a | 30.88 ± 3.03 a | 30.27 ± 2.71 a | 29.41 ± 6.81 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Viana, L.M.; da Silva, B.P.; Rodrigues, F.S.R.; Paes, L.T.; Mishima, M.D.V.; Toledo, R.C.L.; Tako, E.; Martino, H.S.D.; Barros, F. Mixed Green Banana (Musa spp.) Pulp and Peel Flour Reduced Body Weight Gain and Adiposity and Improved Lipid Profile and Intestinal Morphology in Wistar Rats. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152493
Viana LM, da Silva BP, Rodrigues FSR, Paes LT, Mishima MDV, Toledo RCL, Tako E, Martino HSD, Barros F. Mixed Green Banana (Musa spp.) Pulp and Peel Flour Reduced Body Weight Gain and Adiposity and Improved Lipid Profile and Intestinal Morphology in Wistar Rats. Nutrients. 2025; 17(15):2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152493
Chicago/Turabian StyleViana, Leonara Martins, Bárbara Pereira da Silva, Fabiana Silva Rocha Rodrigues, Laise Trindade Paes, Marcella Duarte Villas Mishima, Renata Celi Lopes Toledo, Elad Tako, Hércia Stampini Duarte Martino, and Frederico Barros. 2025. "Mixed Green Banana (Musa spp.) Pulp and Peel Flour Reduced Body Weight Gain and Adiposity and Improved Lipid Profile and Intestinal Morphology in Wistar Rats" Nutrients 17, no. 15: 2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152493
APA StyleViana, L. M., da Silva, B. P., Rodrigues, F. S. R., Paes, L. T., Mishima, M. D. V., Toledo, R. C. L., Tako, E., Martino, H. S. D., & Barros, F. (2025). Mixed Green Banana (Musa spp.) Pulp and Peel Flour Reduced Body Weight Gain and Adiposity and Improved Lipid Profile and Intestinal Morphology in Wistar Rats. Nutrients, 17(15), 2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152493








