Protocol for the Digital, Individualized, and Collaborative Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes in General Practice Based on Decision Aid (DICTA)—A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Population and Recruitment
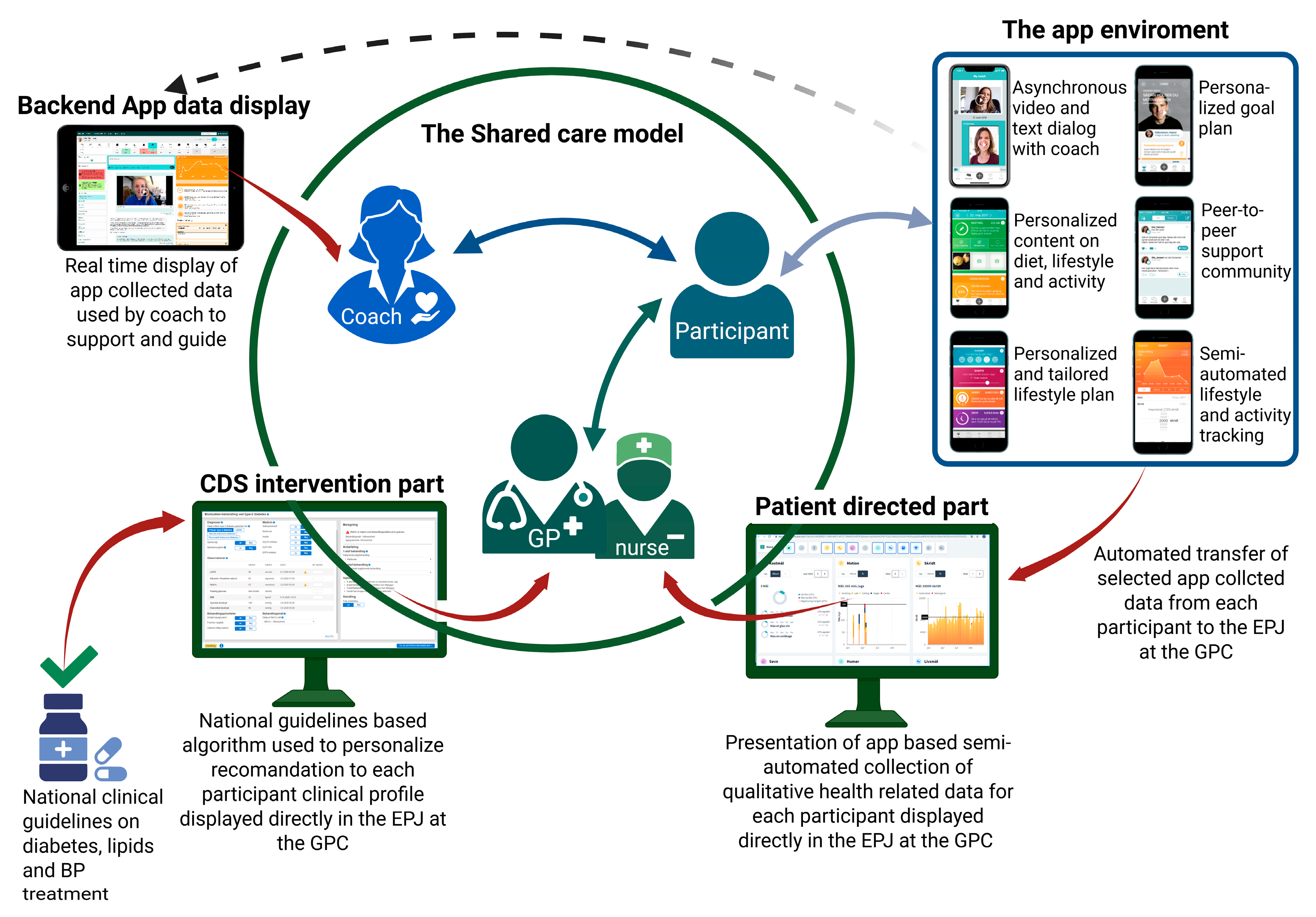
2.3. Study Intervention
- eHealth lifestyle coaching: Individuals with T2D in the intervention group will receive individualized digital coaching from a health coach through the LIVA application. PROs are shared with GPs and health staff via the EPJ, enabling tailored, data-driven lifestyle support.
- CDS: GPs receive real-time, individualized, algorithm-based pharmacological treatment recommendations for managing T2D, hypertension, and hypercholesterolemia, as appropriate.
2.4. eHealth Lifestyle Coaching
2.5. Clinical Decision Support for GPCs
2.6. Control Group
2.7. Patient Examination and Data Sampling
3. Outcomes
- Quality of life, measured by EQ-5D-5L;
- HbA1c, blood pressure, LDL cholesterol, smoking, and UACR;
- Use of glucose-lowering, antihypertensive, and lipid-lowering medications;
- Weight and abdominal circumference;
- Daily physical activity level, measured with AX3 accelerometers.
4. Statistics
4.1. Power Calculations
4.2. Analysis
5. Prospects and Potential for Upscaling
6. Ethics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lean, M.E.; Leslie, W.S.; Barnes, A.C.; Brosnahan, N.; Thom, G.; McCombie, L.; Peters, C.; Zhyzhneuskaya, S.; Al-Mrabeh, A.; Hollingsworth, K.G.; et al. Primary care-led weight management for remission of type 2 diabetes (DiRECT): An open-label, cluster-randomised trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansen, M.Y.; MacDonald, C.S.; Hansen, K.B.; Karstoft, K.; Christensen, R.; Pedersen, M.; Hansen, L.S.; Zacho, M.; Wedell-Neergaard, A.S.; Nielsen, S.T.; et al. Effect of an Intensive Lifestyle Intervention on Glycemic Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2017, 318, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, J.R.; Laursen, D.H.; Lauridsen, J.T.; Hesseldal, L.; Jakobsen, P.R.; Nielsen, J.B.; Søndergaard, J.; Brandt, C.J. Reversing Type 2 Diabetes in a Primary Care-Anchored eHealth Lifestyle Coaching Programme in Denmark: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP) Research group; Hamman, R.F.; Horton, E.; Barrett-Connor, E.; Bray, G.A.; Christophi, C.A.; Crandall, J.; Florez, J.C.; Fowler, S.; Goldberg, R.; et al. Factors affecting the decline in incidence of diabetes in the Diabetes Prevention Program Outcomes Study (DPPOS). Diabetes 2015, 64, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckman, J.A.; Creager, M.A. Vascular Complications of Diabetes. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 1771–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tancredi, M.; Rosengren, A.; Svensson, A.-M.; Kosiborod, M.; Pivodic, A.; Gudbjörnsdottir, S.; Wedel, H.; Clements, M.; Dahlqvist, S.; Lind, M. Excess Mortality among Persons with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1720–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, M.; Garcia-Rodriguez, L.A.; Booth, G.L.; Cea-Soriano, L.; Shah, B.R.; Ekeroth, G.; Lipscombe, L.L. Mortality trends in patients with and without diabetes in Ontario, Canada and the UK from 1996 to 2009: A population-based study. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 2601–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, M.E.; Kolding, J.; Husted, G.R.; Cerqueira, C.S.; Rossing, P.; Kristensen, J.K. The Danish Adult Diabetes Registry. Clin. Epidemiol 2016, 8, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowler, W.C.; Barrett-Connor, E.; Fowler, S.E.; Hamman, R.F.; Lachin, J.M.; Walker, E.A.; Nathan, D.M. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- du Pon, E.; Kleefstra, N.; Cleveringa, F.; van Dooren, A.; Heerdink, E.R.; van Dulmen, S. Effects of the Proactive interdisciplinary self-management (PRISMA) program on self-reported and clinical outcomes in type 2 diabetes: A pragmatic randomized controlled trial. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2019, 19, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, A.; Thomsen, R.; Nielsen, J.; Nicolaisen, S.; Beck-Nielsen, H.; Rungby, J.; Sørensen, H.; Hansen, T.; Søndergaard, J.; Friborg, S.; et al. Early-onset type 2 diabetes: Age gradient in clinical and behavioural risk factors in 5115 persons with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes-Results from the DD2 study. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2018, 34, e2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, S.E.; Speroff, T.; Dittus, R.S.; Brown, A.; Pichert, J.W.; A Elasy, T. Diabetes patient education: A meta-analysis and meta-regression. Patient. Educ. Couns. 2004, 52, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, M. Diabetes self-management education: A review of published studies. Prim. Care Diabetes 2008, 2, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Zhang, P.; Wang, J.; Ma, J.; An, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, B.; Feng, X.; Li, H.; Chen, X.; et al. Morbidity and mortality after lifestyle intervention for people with impaired glucose tolerance: 30-year results of the Da Qing Diabetes Prevention Outcome Study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avogaro, A.; Fadini, G.P. Microvascular complications in diabetes: A growing concern for cardiologists. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 291, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshin, A.; Babalola, D.; Mclean, M.; Yu, Z.; Ma, W.; Chen, C.-Y.; Arabi, M.; Mozaffarian, D. Information Technology and Lifestyle: A Systematic Evaluation of Internet and Mobile Interventions for Improving Diet, Physical Activity, Obesity, Tobacco, and Alcohol Use. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e003058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haste, A.; Adamson, A.J.; McColl, E.; Araujo-Soares, V.; Bell, R. Web-Based Weight Loss Intervention for Men with Type 2 Diabetes: Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. JMIR Diabetes 2017, 2, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, D.M.; Savarimuthu, S.; Squires, A.; Nicholson, J.; Jay, M. Technology-assisted weight loss interventions in primary care: A systematic review. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2015, 30, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limaye, T.; Kumaran, K.; Joglekar, C.; Bhat, D.; Kulkarni, R.; Nanivadekar, A.; Yajnik, C. Efficacy of a virtual assistance-based lifestyle intervention in reducing risk factors for Type 2 diabetes in young employees in the information technology industry in India: LIMIT, a randomized controlled trial. Diabet. Med. 2017, 34, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, C.J.; Søgaard, G.I.; Clemensen, J.; Sndergaard, J.; Nielsen, J.B. General Practitioners′ Perspective on eHealth and Lifestyle Change: Qualitative Interview Study. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2018, 6, e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesseldal, L.; Christensen, J.R.; Olesen, T.B.; Olsen, M.H.; Jakobsen, P.R.; Laursen, D.H.; Lauridsen, J.T.; Nielsen, J.B.; Søndergaard, J.; Brandt, C.J. Long-term Weight Loss in a Primary Care-Anchored eHealth Lifestyle Coaching Program: Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Med. Internet Res. 2022, 24, e39741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, C.J.; Søgaard, G.I.; Clemensen, J.; Søndergaard, J.; Nielsen, J.B. Determinants of Successful eHealth Coaching for Consumer Lifestyle Changes: Qualitative Interview Study Among Health Care Professionals. J. Med. Internet Res. 2018, 20, e237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, C.J.; Clemensen, J.; Nielsen, J.B.; Søndergaard, J. Drivers for successful long-term lifestyle change, the role of e-health: A qualitative interview study. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e017466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, V.; Brandt, C.J.; Glintborg, D.; Arendal, C.; Toubro, S.; Brandt, K. Sustained Weight Loss during 20 Months using a Personalized Interactive Internet Based Dietician Advice Program in a General Practice Setting. Int. J. Adv. Life Sci. 2011, 3, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Stidsen, J.V.; Nielsen, J.S.; Henriksen, J.E.; Friborg, S.G.; Thomsen, R.W.; Olesen, T.B.; Olsen, M.H.; Beck-Nielsen, H. Protocol for the specialist supervised individualised multifactorial treatment of new clinically diagnosed type 2 diabetes in general practice (IDA): A prospective controlled multicentre open-label intervention study. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e017493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, C.J.; Christensen, J.R.; Lauridsen, J.T.; Nielsen, J.B.; Søndergaard, J.; Sortsø, C. Evaluation of the Clinical and Economic Effects of a Primary Care Anchored, Collaborative, Electronic Health Lifestyle Coaching Program in Denmark: Protocol for a Two-Year Randomized Controlled Trial. JMIR Res. Protoc. 2020, 9, e19172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ried-Larsen, M.; Thomsen, R.W.; Berencsi, K.; Brinkløv, C.F.; Brøns, C.; Valentiner, L.S.; Karstoft, K.; Langberg, H.; Vaag, A.; Pedersen, B.K.; et al. Implementation of interval walking training in patients with type 2 diabetes in Denmark: Rationale, design, and baseline characteristics. Clin. Epidemiol. 2016, 8, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, M.C.; Zbrozek, A.S.; Dukes, E.M. The Validity and Reproducibility of a Work Productivity and Activity Impairment Instrument. Pharmacoeconomics 1993, 4, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herdman, M.; Gudex, C.; Lloyd, A.; Janssen, M.; Kind, P.; Parkin, D.; Bonsel, G.; Badia, X. Development and preliminary testing of the new five-level version of EQ-5D (EQ-5D-5L). Qual. Life Res. 2011, 20, 1727–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koushede, V.; Lasgaard, M.; Hinrichsen, C.; Meilstrup, C.; Nielsen, L.; Rayce, S.B.; Torres-Sahli, M.; Gudmundsdottir, D.G.; Stewart-Brown, S.; Santini, Z.I. Measuring mental well-being in Denmark: Validation of the original and short version of the Warwick-Edinburgh mental well-being scale (WEMWBS and SWEMWBS) and cross-cultural comparison across four European settings. Psychiatry Res. 2019, 271, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart-Brown, S.; Tennant, A.; Tennant, R.; Platt, S.; Parkinson, J.; Weich, S. Internal construct validity of the Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-being Scale (WEMWBS): A Rasch analysis using data from the Scottish Health Education Population Survey. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2009, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayser, L.; Karnoe, A.; Furstrand, D.; Batterham, R.; Christensen, K.B.; Elsworth, G.; Osborne, R.H. A Multidimensional Tool Based on the eHealth Literacy Framework: Development and Initial Validity Testing of the eHealth Literacy Questionnaire (eHLQ). J. Med. Internet Res. 2018, 20, e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SCORE2-Diabetes Working Group and the ESC Cardiovascular Risk Collaboration. SCORE2-Diabetes: 10-year cardiovascular risk estimation in type 2 diabetes in Europe. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 2544–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawshani, A.; Rawshani, A.; Franzén, S.; Sattar, N.; Eliasson, B.; Svensson, A.M.; Zethelius, B.; Miftaraj, M.; McGuire, D.K.; Rosengren, A.; et al. Risk Factors, Mortality, and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, F.P.B.; Nicolaisen, S.K.; Nielsen, J.S.; Christensen, D.H.; Højlund, K.; Beck-Nielsen, H.; Rungby, J.; Friborg, S.G.; Brandslund, I.; Christiansen, J.S.; et al. The Danish Centre for Strategic Research in Type 2 Diabetes (DD2) Project Cohort and Biobank from 2010 Through 2023-A Cohort Profile Update. Clin. Epidemiol. 2024, 16, 641–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
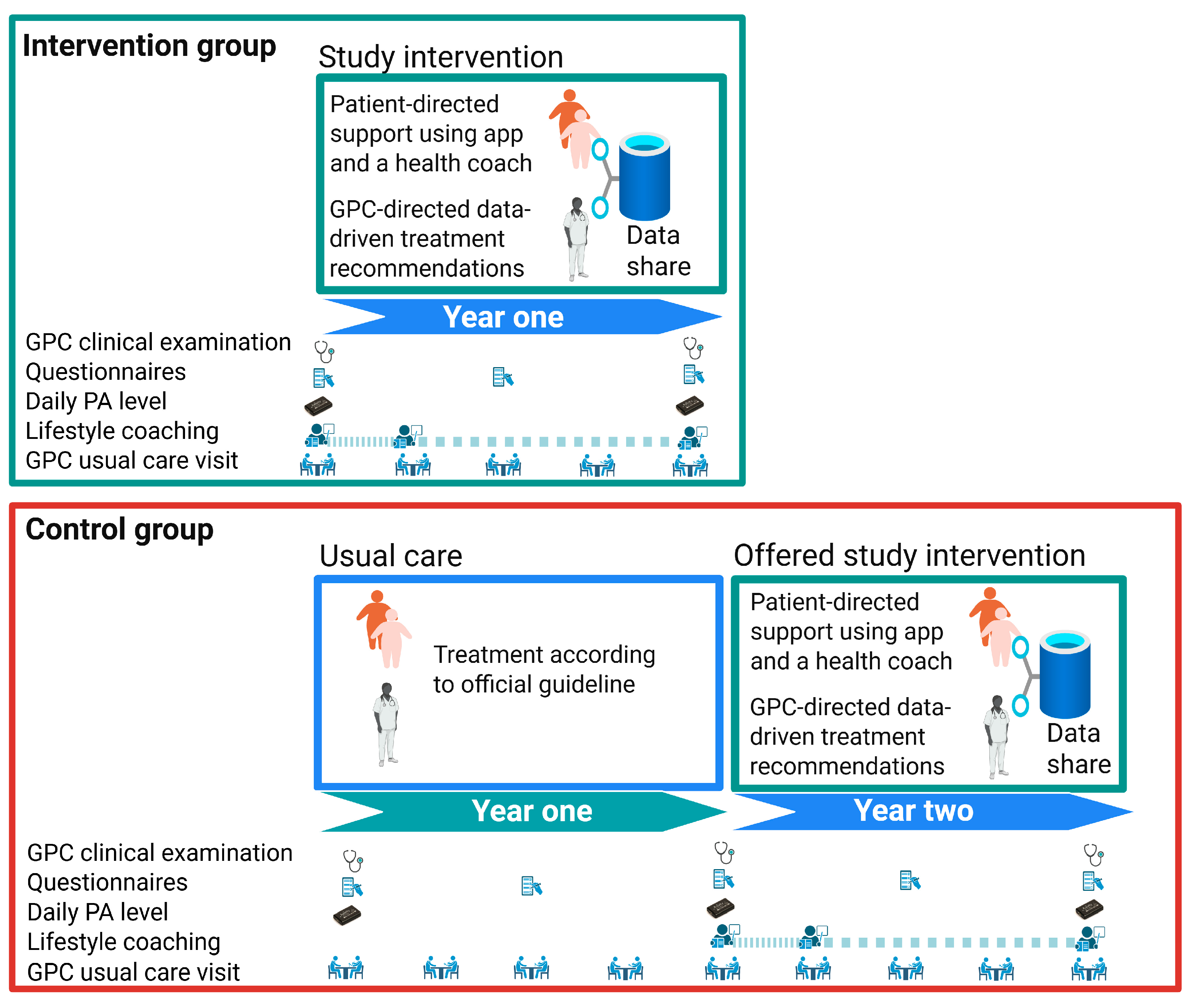

| Time Point | Study Component | Intervention Group | Control Group |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recruitment | Information and consent | Oral and written information provided by the GP | Oral and written information provided by the GP |
| Baseline visit | Written informed consent | Written informed consent signed by the participant | Written informed consent signed by the participant |
| DICTA examination 1 | Full clinical examination: blood/urine sampling, home BP, height (baseline only), weight, waist/hip circumference Accelerometer setup | Full clinical examination: blood/urine sampling, home BP, height (baseline only), weight, waist/hip circumference Accelerometer setup | |
| DICTA questionnaire 2 | Questionnaire on lifestyle, quality of life, and eHealth literacy | Questionnaire on lifestyle, quality of life, and eHealth literacy | |
| DD2 enrollment (if not enrolled already) | DD2 Blood and urine samples + DD2 online questionnaire | DD2 Blood and urine samples + DD2 online questionnaire | |
| Week 1–2 post baseline | eHealth lifestyle coaching onboarding | Digital motivational interview, app installation support, goal setting with health coach (via LIVA app version 4.19.0 or older for IOS and version 4.10.83 or older for Android) | NA |
| Every 1–3 months | Follow-up visits 3 (if risk factors unmet) | CDS-supported medical review (hyperglycemia, hypertension, and hypercholesterolemia) Lifestyle check-in via LIVA, review of PRO | NA |
| 12-month visit | DICTA examination 1 | Full clinical examination: blood/urine sampling, home BP, weight, waist/hip circumference Accelerometer setup | Full clinical examination: blood/urine sampling, home BP, weight, waist/hip circumference Accelerometer setup |
| DICTA questionnaire 2 | Questionnaire on lifestyle, quality of life (EQ-5D-5L), and eHealth literacy | Questionnaire on lifestyle, quality of life, and eHealth literacy | |
| CDS medication adjustment | Based on updated PRO and guideline-based CDS recommendations via EPJ | NA |
| Category | Variable | Definition/Measurement | Type | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Measurements | Height | Measured without shoes (cm) | Continuous | DICTA GP Questionnaire (REDCap) |
| Weight | Measured with clothes but without shoes, (−1 kg adjustment) (kg) | Continuous | DICTA GP Questionnaire (REDCap) | |
| Waist Circumference | Horizontal circumference at midpoint between the lowest rib and upper point of iliac crest (cm) If the ribs and the iliac crest are not accessible, the horizontal circumference just above the navel | Continuous | DICTA GP Questionnaire (REDCap) | |
| Hip Circumference | Horizontal circumference at iliac crest or one handbreadth above inguen (cm) If the ribs and the iliac crest are not accessible: horizontal circumference at the level of a handbreadth above the inguen | Continuous | DICTA GP Questionnaire (REDCap) | |
| Blood Pressure | Systolic and diastolic home BP using calibrated monitor (mmHg) | Continuous | DICTA GP Questionnaire (REDCap) | |
| Biochemical Measurements | HbA1c | Fasting venous blood sample from the arm. Analyzed by the clinical biochemistry department associated with the GP (mmol/mole) | Continuous | EPJ |
| LDL Cholesterol | Fasting venous blood sample from the arm. Analyzed by the clinical biochemistry department associated with the GP (mmol/L) | Continuous | EPJ | |
| Urine Albumin/Creatinine Ratio (UACR) | Fasting urine sample (mg/g) | Continuous | EPJ | |
| Lifestyle Indicators | Smoking, Physical Activity, Alcohol, Diet | Self-reported via questionnaire | Categorical | DICTA Questionnaire (Table S2) |
| Quality of Life | EQ-5D-5L | Standardized measure of health-related quality of life | Categorical | DICTA Patient Questionnaire (Table S2) |
| Mental health | SWEMWBS | Standardized measure of mental well-being | Categorical | DICTA Patient Questionnaire (Table S2) |
| Work ability | WPAI | Standardized measure of work ability | Categorical | DICTA Patient Questionnaire (Table S2) |
| Technology | eHLQ | Standardized measure of e-health literacy | Categorical | DICTA Patient Questionnaire (Table S2) |
| Physical Activity Patterns | Daily Physical Activity
| Measured by accelerometers (Axivity AX3, NewCastle) | Continuous | Accelerometers AX3 and data downloaded by a software program called OmGui (version 1.0.0.45) |
| Daily Step Count | Number of steps via smartphone integration | Continuous | LIVA App | |
| Health Indicators | Medications | Prescribed pharmaceuticals dispensed for each patient in relation to the use of hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and glucose-lowering drugs, T2D, and hypertension, cholesterol | Continuous | Danish National Prescription Registry |
| Healthcare Utilization | Frequency of medical visits, hospitalizations | Categorical/Count | Danish National Patient Register |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kristoffersen, S.F.; Christensen, J.R.; Jeremiassen, L.M.R.; Kylkjær, L.B.; Christensen, N.R.; Jørgensen, S.W.; Kristensen, J.K.; Wehberg, S.; Raymond, I.E.; Jarbøl, D.E.; et al. Protocol for the Digital, Individualized, and Collaborative Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes in General Practice Based on Decision Aid (DICTA)—A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2494. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152494
Kristoffersen SF, Christensen JR, Jeremiassen LMR, Kylkjær LB, Christensen NR, Jørgensen SW, Kristensen JK, Wehberg S, Raymond IE, Jarbøl DE, et al. Protocol for the Digital, Individualized, and Collaborative Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes in General Practice Based on Decision Aid (DICTA)—A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients. 2025; 17(15):2494. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152494
Chicago/Turabian StyleKristoffersen, Sofie Frigaard, Jeanette Reffstrup Christensen, Louise Munk Ramo Jeremiassen, Lea Bolette Kylkjær, Nanna Reffstrup Christensen, Sally Wullf Jørgensen, Jette Kolding Kristensen, Sonja Wehberg, Ilan Esra Raymond, Dorte E. Jarbøl, and et al. 2025. "Protocol for the Digital, Individualized, and Collaborative Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes in General Practice Based on Decision Aid (DICTA)—A Randomized Controlled Trial" Nutrients 17, no. 15: 2494. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152494
APA StyleKristoffersen, S. F., Christensen, J. R., Jeremiassen, L. M. R., Kylkjær, L. B., Christensen, N. R., Jørgensen, S. W., Kristensen, J. K., Wehberg, S., Raymond, I. E., Jarbøl, D. E., Nielsen, J. B., Søndergaard, J., Olsen, M. H., Nielsen, J. S., & Brandt, C. J. (2025). Protocol for the Digital, Individualized, and Collaborative Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes in General Practice Based on Decision Aid (DICTA)—A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients, 17(15), 2494. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152494






