Effects of Soy Protein on Liver and Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Gut Microbiota in Mice Fed with Ketogenic Diets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Blood Analysis
2.3. Liver Sample Analysis
2.4. Adipose Tissue Analysis
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. Fecal Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Energy Intake and Body and Tissue Weight
3.2. Effects of Ketogenic Diets on Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolism
3.3. Effects of Ketogenic Diets on Inflammatory Responses
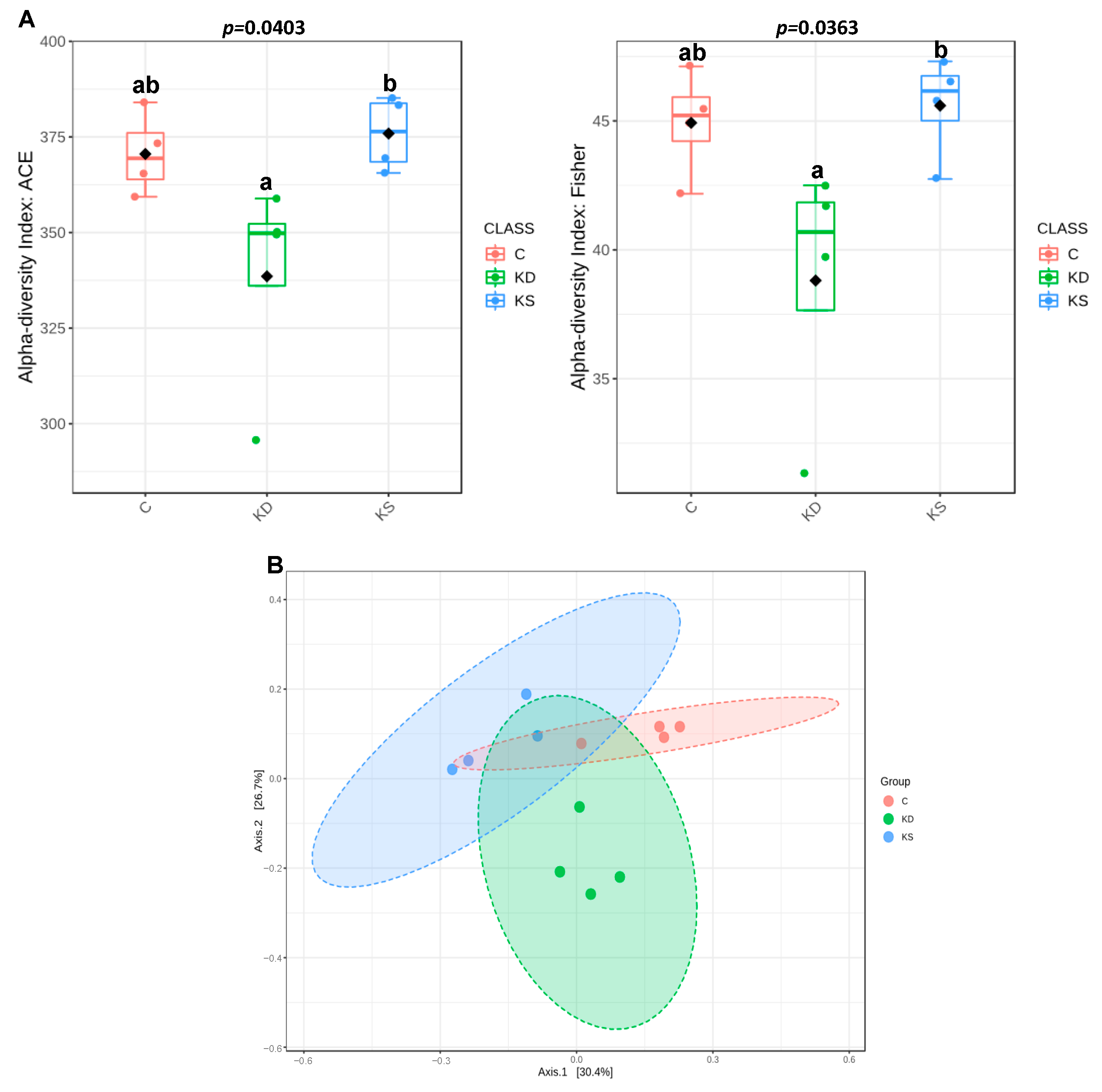
3.4. Effects of Ketogenic Diets on Gut Microbiota
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration. Trends in adult body-mass index in 200 countries from 1975 to 2014: A pooled analysis of 1698 population-based measurement studies with 19.2 million participants. Lancet 2016, 387, 1377–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiechert, M.; Holzapfel, C. Nutrition Concepts for the Treatment of Obesity in Adults. Nutrients 2021, 14, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koliaki, C.; Spinos, T.; Spinou, M.; Brinia Mu, E.; Mitsopoulou, D.; Katsilambros, N. Defining the Optimal Dietary Approach for Safe, Effective and Sustainable Weight Loss in Overweight and Obese Adults. Healthcare 2018, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosinski, C.; Jornayvaz, F.R. Effects of Ketogenic Diets on Cardiovascular Risk Factors: Evidence from Animal and Human Studies. Nutrients 2017, 9, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, B.; Raggi, P. The ketogenic diet: Pros and cons. Atherosclerosis 2020, 292, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, E.A.; Velazquez, K.T.; Herbert, K.M. Influence of high-fat diet on gut microbiota: A driving force for chronic disease risk. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2015, 18, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezhilarasan, D.; Langeswaran, K. Hepatocellular Interactions of Potential Nutraceuticals in the Management of Inflammatory NAFLD. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2024, 42, e4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, C.A.; Kjeldsen, E.W.; Frikke-Schmidt, R. Vegetarian or vegan diets and blood lipids: A meta-analysis of randomized trials. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 2609–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, C.; Gleddie, S.; Xiao, C.W. Soybean Bioactive Peptides and Their Functional Properties. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Krishnan, H.B.; Pham, Q.; Yu, L.L.; Wang, T.T. Soy and Gut Microbiota: Interaction and Implication for Human Health. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 8695–8709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butteiger, D.N.; Hibberd, A.A.; McGraw, N.J.; Napawan, N.; Hall-Porter, J.M.; Krul, E.S. Soy Protein Compared with Milk Protein in a Western Diet Increases Gut Microbial Diversity and Reduces Serum Lipids in Golden Syrian Hamsters. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firman, C.H.; Mellor, D.D.; Unwin, D.; Brown, A. Does a Ketogenic Diet Have a Place Within Diabetes Clinical Practice? Review of Current Evidence and Controversies. Diabetes Ther. 2024, 15, 77–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lidster, K.; Owen, K.; Browne, W.J.; Prescott, M.J. Cage aggression in group-housed laboratory male mice: An international data crowdsourcing project. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jornayvaz, F.R.; Jurczak, M.J.; Lee, H.Y.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Frederick, D.W.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, X.M.; Samuel, V.T.; Shulman, G.I. A high-fat, ketogenic diet causes hepatic insulin resistance in mice, despite increasing energy expenditure and preventing weight gain. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 299, E808–E815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagi, K. Simple assay for the level of total lipid peroxides in serum or plasma. Methods Mol. Biol. 1998, 108, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane Stanley, G.H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godon, J.J.; Zumstein, E.; Dabert, P.; Habouzit, F.; Moletta, R. Molecular microbial diversity of an anaerobic digestor as determined by small-subunit rDNA sequence analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 2802–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Diao, Y.; Strappe, P.; Prenzler, P.; Ayton, J.; Blanchard, C. Deep-fried oil consumption in rats impairs glycerolipid metabolism, gut histology and microbiota structure. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzaccara, C.; Labruna, G.; Cito, G.; Scarfo, M.; De Felice, M.; Pastore, L.; Sacchetti, L. Age-Related Reference Intervals of the Main Biochemical and Hematological Parameters in C57BL/6J, 129SV/EV and C3H/HeJ Mouse Strains. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youm, Y.H.; Nguyen, K.Y.; Grant, R.W.; Goldberg, E.L.; Bodogai, M.; Kim, D.; D’Agostino, D.; Planavsky, N.; Lupfer, C.; Kanneganti, T.D.; et al. The ketone metabolite beta-hydroxybutyrate blocks NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammatory disease. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mochizuki, Y.; Maebuchi, M.; Kohno, M.; Hirotsuka, M.; Wadahama, H.; Moriyama, T.; Kawada, T.; Urade, R. Changes in lipid metabolism by soy beta-conglycinin-derived peptides in HepG2 cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, W.J.; Yang, H.Y.; Chen, J.R. Soy β-conglycinin retards progression of diabetic nephropathy via modulating the insulin sensitivity and angiotensin-converting enzyme activity in rats fed with high salt diet. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 2898–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasser, S.; Solé, T.; Vega, N.; Thomas, T.; Balcerczyk, A.; Strigini, M.; Pirola, L. Ketogenic diet administration to mice after a high-fat-diet regimen promotes weight loss, glycemic normalization and induces adaptations of ketogenic pathways in liver and kidney. Mol. Metab. 2022, 65, 101578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.Y.; Linden, M.A.; Fuller, S.E.; Goldsmith, F.R.; Simon, J.; Batdorf, H.M.; Scott, M.C.; Essajee, N.M.; Brown, J.M.; Noland, R.C. Combined effects of a ketogenic diet and exercise training alter mitochondrial and peroxisomal substrate oxidative capacity in skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 320, E1053–E1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Mi, J.; Wang, Y.; Xue, L.; Liu, J.; Fan, M.; Zhang, D.; Wang, L.; Qian, H.; Li, Y. Effects of low-carbohydrate diet and ketogenic diet on glucose and lipid metabolism in type 2 diabetic mice. Nutrition 2021, 89, 111230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, C.S.; Tjonn, S.L.; Swan, P.D.; White, A.; Hutchins, H.; Sears, B. Ketogenic low-carbohydrate diets have no metabolic advantage over nonketogenic low-carbohydrate diets. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, S.; Noda, K.; Maeda, A.; Matsuoka, M.; Yamasaki, M.; Fukui, T. Acetoacetyl-CoA synthetase, a ketone body-utilizing enzyme, is controlled by SREBP-2 and affects serum cholesterol levels. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2012, 107, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielohuby, M.; Menhofer, D.; Kirchner, H.; Stoehr, B.J.; Muller, T.D.; Stock, P.; Hempel, M.; Stemmer, K.; Pfluger, P.T.; Kienzle, E.; et al. Induction of ketosis in rats fed low-carbohydrate, high-fat diets depends on the relative abundance of dietary fat and protein. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 300, E65–E76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Sarna, L.K.; Hwang, S.Y.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, P.; Siow, Y.L.; O, K. Activation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase during high fat diet feeding. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1832, 1560–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.C.; Liu, S.M.; Yang, H.Y.; Lin, Y.H.; Chen, J.R. Soybean protein hydrolysate improves plasma and liver lipid profiles in rats fed high-cholesterol diet. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2007, 26, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flier, J.S. Hormone resistance in diabetes and obesity: Insulin, leptin, and FGF21. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2012, 85, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luukkonen, P.K.; Dufour, S.; Lyu, K.; Zhang, X.M.; Hakkarainen, A.; Lehtimäki, T.E.; Cline, G.W.; Petersen, K.F.; Shulman, G.I.; Yki-Järvinen, H. Effect of a ketogenic diet on hepatic steatosis and hepatic mitochondrial metabolism in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 7347–7354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thio, L.L.; Erbayat-Altay, E.; Rensing, N.; Yamada, K.A. Leptin Contributes to Slower Weight Gain in Juvenile Rodents on a Ketogenic Diet. Pediatr. Res. 2006, 60, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Tan, W.; Liu, X.; Deng, L.; Huang, L.; Wang, X.; Gao, X. New insight and potential therapy for NAFLD: CYP2E1 and flavonoids. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 137, 111326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, E.; Hu, H. Role of Ferroptosis in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Its Implications for Therapeutic Strategies. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaker, M.E. The contribution of sterile inflammation to the fatty liver disease and the potential therapies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 148, 112789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, A.; Bonucci, A.; Maggi, E.; Corsi, M.; Businaro, R. Anti-Oxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Ketogenic Diet: New Perspectives for Neuroprotection in Alzheimer’s Disease. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asrih, M.; Altirriba, J.; Rohner-Jeanrenaud, F.; Jornayvaz, F.R. Ketogenic Diet Impairs FGF21 Signaling and Promotes Differential Inflammatory Responses in the Liver and White Adipose Tissue. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandivada, P.; Fell, G.L.; Pan, A.H.; Nose, V.; Ling, P.R.; Bistrian, B.R.; Puder, M. Eucaloric Ketogenic Diet Reduces Hypoglycemia and Inflammation in Mice with Endotoxemia. Lipids 2016, 51, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, F.M.; Maratos-Flier, E. Understanding the Physiology of FGF21. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2016, 78, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. TLR signaling. Semin. Immunol. 2007, 19, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen-Sfady, M.; Nussbaum, G.; Pevsner-Fischer, M.; Mor, F.; Carmi, P.; Zanin-Zhorov, A.; Lider, O.; Cohen, I.R. Heat shock protein 60 activates B cells via the TLR4-MyD88 pathway. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 3594–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Li, X.; Jia, H.; Loor, J.J.; Bucktrout, R.; Xu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Shu, X.; Dong, J.; Zuo, R.; et al. Effect of heat-shock protein B7 on oxidative stress in adipocytes from preruminant calves. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 5673–5685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Q.; Ding, H.; Dong, Q.; Chen, X.; Cui, M. Ketogenic Diet Improves Brain Ischemic Tolerance and Inhibits NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation by Preventing Drp1-Mediated Mitochondrial Fission and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malesza, I.J.; Malesza, M.; Walkowiak, J.; Mussin, N.; Walkowiak, D.; Aringazina, R.; Bartkowiak-Wieczorek, J.; Madry, E. High-Fat, Western-Style Diet, Systemic Inflammation, and Gut Microbiota: A Narrative Review. Cells 2021, 10, 3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowis, K.; Banga, S. The Potential Health Benefits of the Ketogenic Diet: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, K.; Igarashi, M.; Li, X.; Nakatani, A.; Miyamoto, J.; Inaba, Y.; Sutou, A.; Saito, T.; Sato, T.; Tachibana, N.; et al. Dietary soybean protein ameliorates high-fat diet-induced obesity by modifying the gut microbiota-dependent biotransformation of bile acids. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, W.; Tian, F.; Shen, H.; Zhou, M. A combination of quercetin and resveratrol reduces obesity in high-fat diet-fed rats by modulation of gut microbiota. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 4644–4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakata, T.; Kyoui, D.; Takahashi, H.; Kimura, B.; Kuda, T. Inhibitory effects of soybean oligosaccharides and water-soluble soybean fibre on formation of putrefactive compounds from soy protein by gut microbiota. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 97, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagpal, R.; Neth, B.J.; Wang, S.; Craft, S.; Yadav, H. Modified Mediterranean-ketogenic diet modulates gut microbiome and short-chain fatty acids in association with Alzheimer’s disease markers in subjects with mild cognitive impairment. EBioMedicine 2019, 47, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| C | KD | KS | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Body weight (g) | |||
| Initial | 21.3 ± 0.2 | 21.2 ± 0.3 | 21.3 ± 0.3 |
| Final | 32.1 ± 0.8 | 29.9 ± 0.7 | 32.3 ± 1.0 |
| Liver weight (g) | 1.5 ± 0.1 a | 1.1 ± 0.1 b | 1.2 ± 0.0 b |
| Mesenteric fat (g) | 0.6 ± 0.1 a | 0.4 ± 0.0 b | 0.4 ± 0.0 b |
| Retroperitoneal fat (g) | 0.4 ± 0.0 | 0.4 ± 0.0 | 0.5 ± 0.1 |
| Epididymal fat (g) | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 1.2 ± 0.1 |
| C | KD | KS | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blood: | |||
| glucose (mg/dL) | 230.4 ± 14.1 a | 167.9 ± 7.9 b | 190.9 ± 10.0 b |
| β-hydroxybutyrate (mmol/L) | 1.2 ± 0.2 b | 3.2 ± 0.4 a | 2.6 ± 0.5 ab |
| insulin (µg/L) | 1.8 ± 0.4 a | 0.4 ± 0.0 b | 0.4 ± 0.0 b |
| FFA (µmol/mL) | 260.4 ± 27.7 | 365.4 ± 54.4 | 355.3 ± 68.7 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 59.7 ± 6.1 | 77.0 ± 11.3 | 57.8 ± 6.4 |
| TC (mg/dL) | 74.9 ± 5.0 c | 92.2 ± 2.7 b | 111.4 ± 3.2 a |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 67.9 ± 4.7 c | 85.7 ± 3.3 b | 103.7 ± 3.0 a |
| LDL-C(mg/dL) | 5.9 ± 0.6 b | 7.3 ± 0.3 b | 15.4 ± 1.0 a |
| LDL-C/HDL-C (%) | 8.6 ± 0.4 b | 8.6 ± 0.3 b | 14.8 ± 0.7 a |
| AST (U/L) | 73.9 ± 7.6 a | 49.9 ± 2.5 b | 43.4 ± 2.2 b |
| ALT (U/L) | 56.0 ± 10.3 a | 27.8 ± 2.0 b | 27.9 ± 1.4 b |
| FGF21 (µg/mL) | 3.2 ± 0.4 b | 5.5 ± 0.1 a | 5.9 ± 0.1 a |
| Liver: | |||
| FFA (mmol/g liver) | 2.3 ± 1.2 | 3.4 ± 0.4 | 4.4 ± 0.6 |
| TG (μmol/g liver) | 9.8 ± 1.8 | 9.1 ± 1.2 | 6.7 ± 0.7 |
| TC (μmol/g liver) | 13.9 ± 2.1 | 14.0 ± 2.0 | 11.6 ± 1.3 |
| C | KD | KS | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma | |||
| Adiponectin (ng/mL) | 506.6 ± 16.7 | 492.9 ± 12.8 | 486.9 ± 14.7 |
| Leptin (ng/mL) | 4.1 ± 0.9 | 2.5 ± 0.5 | 4.5 ± 0.9 |
| A/L (%) | 178.1 ± 38.8 | 307.8 ± 76.0 | 156.0 ± 37.7 |
| WAT | |||
| Adiponectin (ng/mg PT) | 20.6 ± 0.9 | 20.6 ± 1.1 | 17.8 ± 0.4 |
| Leptin (ng/mg PT) | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.1 |
| A/L (%) | 28.4 ± 2.4 b | 40.4 ± 4.3 a | 33.8 ± 3.2 ab |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.-K.; Wu, I.-T.; Yeh, W.-J.; Huang, W.-C.; Yang, H.-Y. Effects of Soy Protein on Liver and Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Gut Microbiota in Mice Fed with Ketogenic Diets. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2428. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152428
Li W-K, Wu I-T, Yeh W-J, Huang W-C, Yang H-Y. Effects of Soy Protein on Liver and Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Gut Microbiota in Mice Fed with Ketogenic Diets. Nutrients. 2025; 17(15):2428. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152428
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wen-Keng, I-Ting Wu, Wan-Ju Yeh, Wen-Chih Huang, and Hsin-Yi Yang. 2025. "Effects of Soy Protein on Liver and Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Gut Microbiota in Mice Fed with Ketogenic Diets" Nutrients 17, no. 15: 2428. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152428
APA StyleLi, W.-K., Wu, I.-T., Yeh, W.-J., Huang, W.-C., & Yang, H.-Y. (2025). Effects of Soy Protein on Liver and Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Gut Microbiota in Mice Fed with Ketogenic Diets. Nutrients, 17(15), 2428. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152428








