Phthalate Metabolites and Their Relationship with Abdominal and General Obesity: Evidence from the Aragon Workers’ Health Study (AWHS)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Endpoints
2.3. Urinary Phthalate Metabolite Measurements
2.4. Creatinine Correction
2.5. Data Collection and Covariates
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Ethics and Consent
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.2. Urinary Phthalate Metabolites
3.3. Phthalate Metabolites and Abdominal Obesity
3.4. Phthalate Metabolites and General Obesity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AWHS | Aragon Workers’ Health Study |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| cx-MiDP | Mono-carboxy isononyl phthalate |
| DEHP | Di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate |
| DIBP | Diisobutyl phthalate |
| MBzP | Monobenzyl phthalate |
| MCMHP | Mono(2-carboxymethylhexyl) phthalate |
| MECPP | Mono-(2-ethyl-5-carboxypentyl) phthalate |
| MEHHP | Mono-(2-ethyl-5-hydroxyhexyl) phthalate |
| MEOHP | Mono-(2-ethyl-5-oxohexyl) phthalate |
| MEP | Monoethyl phthalate |
| MiBP | Mono-isobutyl phthalate |
| MnBP | Mono-n-butyl phthalate |
| NHANES | National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey |
| OH-MiDP | Mono-hydroxy-isodecyl phthalate |
| OH-MiNP | Mono-hydroxy-isononyl phthalate |
| WC | Waist circumference |
References
- Berrington De Gonzalez, A.; Hartge, P.; Cerhan, J.R.; Flint, A.J.; Hannan, L.; MacInnis, R.J.; Moore, S.C.; Tobias, G.S.; Anton-Culver, H.; Freeman, L.B.; et al. Body-Mass Index and Mortality among 1.46 Million White Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 2211–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierens, T.; Servaes, K.; Van Holderbeke, M.; Geerts, L.; De Henauw, S.; Sioen, I.; Vanermen, G. Analysis of phthalates in food products and packaging materials sold on the Belgian market. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 2575–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Xu, Y. Emission of Phthalates and Phthalate Alternatives from Vinyl Flooring and Crib Mattress Covers: The Influence of Temperature. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 14228–14237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huygh, J.; Clotman, K.; Malarvannan, G.; Covaci, A.; Schepens, T.; Verbrugghe, W.; Dirinck, E.; Van Gaal, L.; Jorens, P.G. Considerable exposure to the endocrine disrupting chemicals phthalates and bisphenol-A in intensive care unit (ICU) patients. Environ. Int. 2015, 81, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Liu, Z.H.; Yin, H.; Dang, Z.; Wu, P.X.; Zhu, N.W.; Lin, Z.; Liu, Y. Migration and potential risk of trace phthalates in bottled water: A global situation. Water Res. 2018, 147, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Kannan, K. A Survey of Phthalates and Parabens in Personal Care Products from the United States and Its Implications for Human Exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 14442–14449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewalque, L.; Charlier, C.; Pirard, C. Estimated daily intake and cumulative risk assessment of phthalate diesters in a Belgian general population. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 231, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, T.P.; Kumar, M.A. Remediation of phthalate acid esters from contaminated environment—Insights on the bioremedial approaches and future perspectives. Heliyon 2023, 9, 14945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Cornelis, M.C.; Townsend, M.K.; Tobias, D.K.; Eliassen, A.H.; Franke, A.A.; Hauser, R.; Hu, F.B. Association of Urinary Concentrations of Bisphenol A and Phthalate Metabolites with Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: A Prospective Investigation in the Nurses’ Health Study (NHS) and NHSII Cohorts. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mérida, D.M.; Moreno-Franco, B.; Marquès, M.; León-Latre, M.; Laclaustra, M.; Guallar-Castillón, P. Phthalate exposure and the metabolic syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 333, 121957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.B.; Pan, W.H.; Chang, J.W.; Chiang, H.C.; Guo, Y.L.; Jaakkola, J.J.K.; Huang, P.-C. Does exposure to phthalates influence thyroid function and growth hormone homeostasis? The Taiwan Environmental Survey for Toxicants (TEST) 2013. Environ. Res. 2017, 153, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Cui, S.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X. Associations between prenatal exposure to phthalates and birth weight: A meta-analysis study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 262, 115207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Kim, K.; Kannan, K.; Parsons, P.J.; Mlodnicka, A.; Schmidt, R.J.; Schweitzer, J.B.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Bennett, D.H. Early childhood exposure to environmental phenols and parabens, phthalates, organophosphate pesticides, and trace elements in association with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) symptoms in the CHARGE study. Environ. Health 2024, 23, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Wu, H.; Zhu, W.; Lin, Q.; Zhao, X.; Lin, R.; Luo, Y.; Wu, L.; Lin, D. Phthalate exposure and risk of ovarian dysfunction in endometriosis: Human and animal data. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1154923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.H.; Li, S.S.; Wu, M.H.; Pan, H.A.; Lee, C.C. Phthalates might interfere with testicular function by reducing testosterone and insulin-like factor 3 levels. Hum. Reprod. 2015, 30, 2658–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustamante-Montes, L.P.; Hernández-Valero, M.A.; Flores-Pimentel, D.; García-Fábila, M.; Amaya-Chávez, A.; Barr, D.B.; Borja-Aburto, V.H. Prenatal exposure to phthalates is associated with decreased anogenital distance and penile size in male newborns. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2013, 4, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiue, I. Urinary heavy metals, phthalates, perchlorate, nitrate, thiocyanate, hydrocarbons, and polyfluorinated compounds are associated with adult hearing disturbance: USA NHANES, 2011–2012. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 20306–20311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, Y.Y.; Huang, P.C.; Lee, C.C.; Wu, M.H.; Lin, S.J. Phthalate Exposure in Girls During Early Puberty. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 22, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Gao, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, M.; Li, S.; Chen, B. The concentrations and cumulative risk assessment of phthalates in general population from Shanghai: The comparison between groups with different ages. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637–638, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qian, H. Phthalates and Their Impacts on Human Health. Healthcare 2021, 9, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, F.; Tan, Y. Analysis of global commonly-used phthalates and non-dietary exposure assessment in indoor environment. Build. Environ. 2020, 177, 106853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatch, E.E.; Nelson, J.W.; Stahlhut, R.W.; Webster, T.F. Association of endocrine disruptors and obesity: Perspectives from epidemiological studies. Int. J. Androl. 2010, 33, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, R.; Zhou, T.; Chen, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.; Wu, M.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Chen, B. Gender- and Age-Specific Relationships Between Phthalate Exposures and Obesity in Shanghai Adults. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 73, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahlhut, R.W.; Van Wijngaarden, E.; Dye, T.D.; Cook, S.; Swan, S.H. Concentrations of Urinary Phthalate Metabolites Are Associated with Increased Waist Circumference and Insulin Resistance in Adult U.S. Males. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 876–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buser, M.C.; Murray, H.E.; Scinicariello, F. Age and sex differences in childhood and adulthood obesity association with phthalates: Analyses of NHANES 2007–2010. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2014, 217, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, T.; Hu, W.; Wang, X.; Xu, B.; Lin, Z.; Hofer, T.; Stefanoff, P.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Association between exposure to a mixture of phenols, pesticides, and phthalates and obesity: Comparison of three statistical models. Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Diaz, C.; Uriz-Martínez, M.; Ortega-Rico, C.; Leno-Duran, E.; Barrios-Rodríguez, R.; Salcedo-Bellido, I.; Arrebola, J.P.; Requena, P. Phthalate exposure and risk of metabolic syndrome components: A systematic review. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 340, 122714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golestanzadeh, M.; Riahi, R.; Kelishadi, R. Association of exposure to phthalates with cardiometabolic risk factors in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 35670–35686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarean, M.; Poursafa, P.; Amin, M.M.; Kelishadi, R. Association of Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals, Bisphenol A and Phthalates, with Childhood Obesity: A Systematic Review. J. Pediatr. Rev. 2017, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatch, E.E.; Nelson, J.W.; Qureshi, M.M.; Weinberg, J.; Moore, L.L.; Singer, M.; Webster, T.F. Association of urinary phthalate metabolite concentrations with body mass index and waist circumference: A cross-sectional study of NHANES data, 1999–2002. Environ. Health 2008, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Park, J.; Youn, K. Association between urinary phthalate metabolites and obesity in adult Korean population: Korean National Environmental Health Survey (KoNEHS), 2012–2014. Ann. Occup. Environ. Med. 2019, 31, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz Santana, M.V.; Hankinson, S.E.; Bigelow, C.; Sturgeon, S.R.; Zoeller, R.T.; Tinker, L.; Manson, J.A.E.; Calafat, A.M.; Meliker, J.R.; Reeves, K.W. Urinary concentrations of phthalate biomarkers and weight change among postmenopausal women: A prospective cohort study. Environ. Health 2019, 18, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haggerty, D.K.; Flaws, J.A.; Li, Z.; Strakovsky, R.S. Phthalate exposures and one-year change in body mass index across the menopausal transition. Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Razo, L.D.; Martínez-Ibarra, A.; Vázquez-Martínez, E.R.; Cerbón, M. The impact of Di-(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate and Mono(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate in placental development, function, and pathophysiology. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heindel, J.J.; Howard, S.; Agay-Shay, K.; Arrebola, J.P.; Audouze, K.; Babin, P.J.; Barouki, R.; Bansal, A.; Blanc, E.; Cave, M.C.; et al. Obesity II: Establishing causal links between chemical exposures and obesity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 199, 115015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casasnovas, J.A.; Alcaide, V.; Civeira, F.; Guallar, E.; Ibañez, B.; Borreguero, J.J.; Laclaustra, M.; León, M.; Peñalvo, J.L.; Ordovás, J.M.; et al. Aragon workers’ health study—Design and cohort description. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2012, 12, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Lancet 2007, 370, 1453–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, B.; Charlton, K.E.; Derman, W.; Jones, E. Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology, 4th ed.; Johnson, R.J., Feehally, J., Floege, J., Eds.; Saunders Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2010; pp. 428–435. [Google Scholar]
- Nuttall, F.Q. Body Mass Index: Obesity, BMI, and Health A Critical Review. Nutr. Today 2015, 50, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornung, R.W.; Reed, L.D. Estimation of Average Concentration in the Presence of Nondetectable Values. Appl. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 1990, 5, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, K.K.; Loch-Caruso, R.; Meeker, J.D. Exploration of Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Markers in Relation to Urinary Phthalate Metabolites: NHANES 1999–2006. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Fuente-Arrillaga, C.; Vázquez Ruiz, Z.; Bes-Rastrollo, M.; Sampson, L.; Martinez-González, M.A. Reproducibility of an FFQ validated in Spain. Public Health Nutr. 2010, 13, 1364–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-González, M.A.; López-Fontana, C.; Varo, J.J.; Sánchez-Villegas, A.; Martinez, J.A. Validation of the Spanish version of the physical activity questionnaire used in the Nurses’ Health Study and the Health Professionals’ Follow-up Study. Public Health Nutr. 2005, 8, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, T.A.; Palaniappan, L.P.; Artinian, N.T.; Carnethon, M.R.; Criqui, M.H.; Daniels, S.R.; Fonarow, G.C.; Fortmann, S.P.; Franklin, B.A.; Galloway, J.M.; et al. American Heart Association Guide for Improving Cardiovascular Health at the Community Level, 2013 Update: A Scientific Statement for Public Health Practitioners, Healthcare Providers, and Health Policy Makers. Circulation 2013, 127, 1730–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults. Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) Final Report. Circulation 2002, 106, 3143–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- StataCorp. Stata Statistical Software: Release 18, version 18; StataCorp LLC.: College Station, TX, USA, 2023.
- Li, Y.L.; Lv, J.; Du, Z.P.; Feng, S.; Sheng, J.; Jin, Z.X.; Liu, K.-Y.; Gao, H.; Li, X.-D.; Cao, H.-J.; et al. The levels of phthalate exposure and associations with obesity in an elderly population in China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 201, 110749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Li, G.; Zhao, C.Y.; Na, X.L.; Zhang, Y.B. Association between phthalate exposure and obesity risk: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 102, 104240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, P.M.; Roos, V.; Rönn, M.; Johansson, L.; Ahlström, H.; Kullberg, J.; Lind, L. Serum concentrations of phthalate metabolites are related to abdominal fat distribution two years later in elderly women. Environ. Health 2012, 11, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirillo, T.; Fasano, E.; Esposito, F.; Prete, E.D.; Cocchieri, R.A. Study on the influence of temperature, storage time and packaging type on di-n-butylphthalate and di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate release into packed meals. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2013, 30, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James-Todd, T.M.; Huang, T.; Seely, E.W.; Saxena, A.R. The association between phthalates and metabolic syndrome: The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2001–2010. Environ. Health 2016, 15, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Hanaoka, T.; Yoshimura, M.; Zhang, S.; Wang, P.; Tsukino, H.; Inoue, K.; Nakazawa, H.; Tsugane, S.; Takahashi, K. Decreased Serum Free Testosterone in Workers Exposed to High Levels of Di-n-butyl Phthalate (DBP) and Di-2-ethylhexyl Phthalate (DEHP): A Cross-Sectional Study in China. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 1643–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Sun, J.; Wu, X.; Mao, J.; Han, Q. Percent body fat was negatively correlated with Testosterone levels in male. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, 0294567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaedlich, K.; Gebauer, S.; Hunger, L.; Beier, L.S.; Koch, H.M.; Wabitsch, M.; Fischer, B.; Ernst, J. DEHP deregulates adipokine levels and impairs fatty acid storage in human SGBS-adipocytes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Gu, W.; Zhai, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, C.; Xiao, L.; Chen, D. Phthalate metabolites and sex steroid hormones in relation to obesity in US adults: NHANES 2013–2016. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1340664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Chemicals Agency. Diisobutyl Phthalate (EC No. 201-553-2; CAS No. 84-69-5). ECHA Substance Information. Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.001.412 (accessed on 27 May 2025).

| Characteristic | N = 1124 | MEOHP | MEHHP | ∑DEHP * | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q1 | Q4 | p-Value | Q1 | Q4 | p-Value | Q1 | Q4 | p-Value | ||
| Urinary creatinine concentration (mg/dL) | 154.4 (57.1) | 152.5 (62.4) | 152.0 (54.6) | 0.803 | 150.9 (60.7) | 155.7 (55.9) | 0.481 | 153.4 (62.4) | 153.3 (54.9) | 0.898 |
| Age (years), mean (SD) | 50.7 (3.66) | 50.7 (3.63) | 50.9 (3.74) | 0.541 | 50.6 (3.68) | 50.8 (3.69) | 0.565 | 50.7 (3.68) | 50.7 (3.75) | 0.732 |
| Alcohol (g/day) | 22.5 (21.3) | 21.1 (20.7) | 24.0 (22.7) | 0.081 | 19.9 (19.6) | 24.5 (22.9) | 0.005 | 21.0 (20.5) | 24.0 (22.5) | 0.046 |
| Physical activity (total METs/week) | 35.3 (21.5) | 36.2 (21.5) | 34.3 (21.0) | 0.612 | 35.2 (21.4) | 35.7 (21.5) | 0.971 | 35.9 (21.8) | 35.7 (22.0) | 0.853 |
| Energy intake (kcal/day) | 2945.1 (764.9) | 2850.1 (795.3) | 3011.9 (754.2) | 0.022 | 2862.8 (832.8) | 2980.4 (724.9) | 0.046 | 2855.1 (787.0) | 2976.4 (736.1) | 0.045 |
| Smoking status, n (%) | 0.071 | 0.034 | 0.115 | |||||||
| No smoker | 255 (22.7) | 83 (32.6) | 54 (21.2) | 84 (32.9) | 53 (20.8) | 78 (30.6) | 49 (19.2) | |||
| Former smoker | 487 (43.3) | 110 (22.6) | 123 (25.3) | 105 (21.6) | 129 (26.5) | 108 (22.2) | 130 (26.7) | |||
| Current smoker | 382 (34.0) | 88 (23.0) | 104 (27.2) | 92 (24.1) | 99 (25.9) | 95 (24.9) | 102 (26.7) | |||
| Hypertension | 0.870 | 0.662 | 0.913 | |||||||
| No hypertension | 682 (60.7) | 170 (24.9) | 173 (25.4) | 172 (25.2) | 176 (25.8) | 170 (24.9) | 173 (25.34) | |||
| Hypertension | 442 (39.3) | 111 (25.1) | 108 (24.4) | 109 (24.7) | 105 (23.8) | 111 (25.1) | 108 (24.4) | |||
| Dyslipidaemia | 0.029 | 0.145 | 0.130 | |||||||
| No dyslipidaemia | 390 (34.7) | 86 (22.1) | 110 (28.2) | 94 (24.1) | 107 (27.4) | 87 (22.3) | 108 (27.7) | |||
| Dyslipidaemia | 734 (65.3) | 195 (26.6) | 171 (23.3) | 187 (25.5) | 174 (23.7) | 194 (26.4) | 173 (23.6) | |||
| Diabetes | 0.635 | 0.722 | 0.906 | |||||||
| No diabetes | 1064 (94.7) | 268 (25.2) | 271 (25.5) | 268 (25.2) | 271 (25.5) | 267 (25.1) | 269 (25.3) | |||
| Diabetes | 60 (5.34) | 13 (21.7) | 10 (16.7) | 13 (21.7) | 10 (16.7) | 14 (23.3) | 12 (20.0) | |||
| Work type | 0.007 | 0.018 | 0.001 | |||||||
| Sedentary work (office) | 141 (12.5) | 42 (29.8) | 24 (17.0) | 39 (27.7) | 25 (17.7) | 41 (29.1) | 18 (12.8) | |||
| Manual labour (assembly line) | 983 (87.5) | 239 (24.3) | 257 (26.1) | 242 (24.6) | 256 (26.0) | 240 (24.4) | 263 (26.8) | |||
| Work shift | 0.045 | 0.041 | 0.010 | |||||||
| Rotating: morning–afternoon | 689 (61.3) | 168 (24.4) | 186 (27.0) | 167 (24.2) | 185 (26.9) | 167 (24.2) | 190 (27.6) | |||
| Rotating: morning–afternoon–night | 241 (21.4) | 51 (21.2) | 55 (22.8) | 53 (22.0) | 56 (23.2) | 52 (21.6) | 54 (22.4) | |||
| Central | 96 (8.54) | 31 (32.3) | 17 (17.7) | 27 (28.1) | 17 (17.7) | 31 (32.3) | 13 (13.5) | |||
| Night | 98 (8.72) | 31 (31.6) | 23 (23.5) | 34 (34.7) | 23 (23.5) | 31 (31.6) | 24 (24.5) |
| ∑DEHP * | MEP | MiBP | MnBP | MBzP | MEOHP | MECPP | MEHHP | MCMHP | OH-MiNP | cx-MiDP | OH-MiDP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ∑DEHP | 1.000 | |||||||||||
| MEP | 0.128 | 1.000 | ||||||||||
| MiBP | 0.010 | 0.054 | 1.000 | |||||||||
| MnBP | 0.004 | 0.010 | 0.048 | 1.000 | ||||||||
| MBzP | 0.115 | 0.090 | 0.115 | 0.023 | 1.000 | |||||||
| MEOHP | 0.979 | 0.111 | 0.082 | 0.000 | 0.091 | 1.000 | ||||||
| MECPP | 0.982 | 0.151 | 0.120 | 0.005 | 0.128 | 0.933 | 1.000 | |||||
| MEHHP | 0.996 | 0.118 | 0.096 | 0.004 | 0.114 | 0.973 | 0.970 | 1.000 | ||||
| MCMHP | 0.912 | 0.107 | 0.090 | 0.003 | 0.134 | 0.878 | 0.893 | 0.899 | 1.000 | |||
| OH-MiNP | 0.081 | 0.051 | 0.047 | −0.004 | 0.146 | 0.058 | 0.103 | 0.078 | 0.063 | 1.000 | ||
| cx-MiDP | 0.036 | 0.009 | 0.027 | −0.002 | 0.081 | 0.019 | 0.054 | 0.0300 | 0.046 | 0.219 | 1.000 | |
| OH-MiDP | 0.068 | 0.035 | 0.046 | 0.005 | 0.142 | 0.046 | 0.088 | 0.065 | 0.064 | 0.319 | 0.826 | 1.000 |
| Phthalate Metabolites as Continuous ^ | Phthalate Metabolites in Quartiles | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phthalate Metabolites (µg/g Creatinine) | OR (95% CI) for Every 1-ln Increase | p-Value | Q1 OR (95% CI) | Q2 OR (95% CI) | Q3 OR (95% CI) | Q4 OR (95% CI) | p-Test for Linear Trend |
| MEP | |||||||
| Events/n | 317/1084 | 88/272 | 70/270 | 69/272 | 90/270 | ||
| Crude model | 1.02 (0.92, 1.15) | 0.678 | 1 (Ref.) | 0.73 (0.50, 1.06) | 0.71 (0.49, 1.03) | 1.05 (0.73, 1.50) | |
| Adjusted model * | 1.03 (0.91, 1.15) | 0.682 | 1 (Ref.) | 0.70 (0.47, 1.04) | 0.69 (0.46, 1.03) | 1.03 (0.70, 1.51) | |
| MiBP | |||||||
| Events/n | 317/1084 | 98/271 | 77/272 | 79/271 | 63/270 | ||
| Crude model | 0.68 (0.54, 0.86) | 0.001 | 1 (Ref.) | 0.68 (0.49, 1.00) | 0.73 (0.51, 1.04) | 0.54 (0.37, 0.78) | |
| Adjusted model | 0.73 (0.57, 0.93) | 0.010 | 1 (Ref.) | 0.73 (0.49, 1.07) | 0.81 (0.55, 1.19) | 0.55 (0.37, 0.83) | |
| MnBP | |||||||
| Events/n | 317/1084 | 82/269 | 86/70 | 72/273 | 77/272 | ||
| Crude model | 0.89 (0.73, 1.09) | 0.269 | 1 (Ref.) | 1.07 (0.74, 1.53) | 0.82 (0.56, 1.19) | 0.90 (0.62, 1.30) | |
| Adjusted model | 0.92 (0.74, 1.14) | 0.442 | 1 (Ref.) | 1.17 (0.79, 1.73) | 0.84 (0.56, 1.25) | 0.95 (0.64, 1.42) | |
| MBzP | |||||||
| Events/n | 317/1084 | 73/272 | 93/271 | 81/273 | 70/268 | ||
| Crude model | 0.99 (0.84, 1.18) | 0.953 | 1 (Ref.) | 1.42 (0.99, 2.06) | 1.15 (0.79, 1.67) | 0.96 (0.66, 1.41) | |
| Adjusted model | 1.02 (0.85, 1.22) | 0.861 | 1 (Ref.) | 1.53 (1.04, 2.27) | 1.26 (0.84, 1.87) | 0.99 (0.66, 1.49) | |
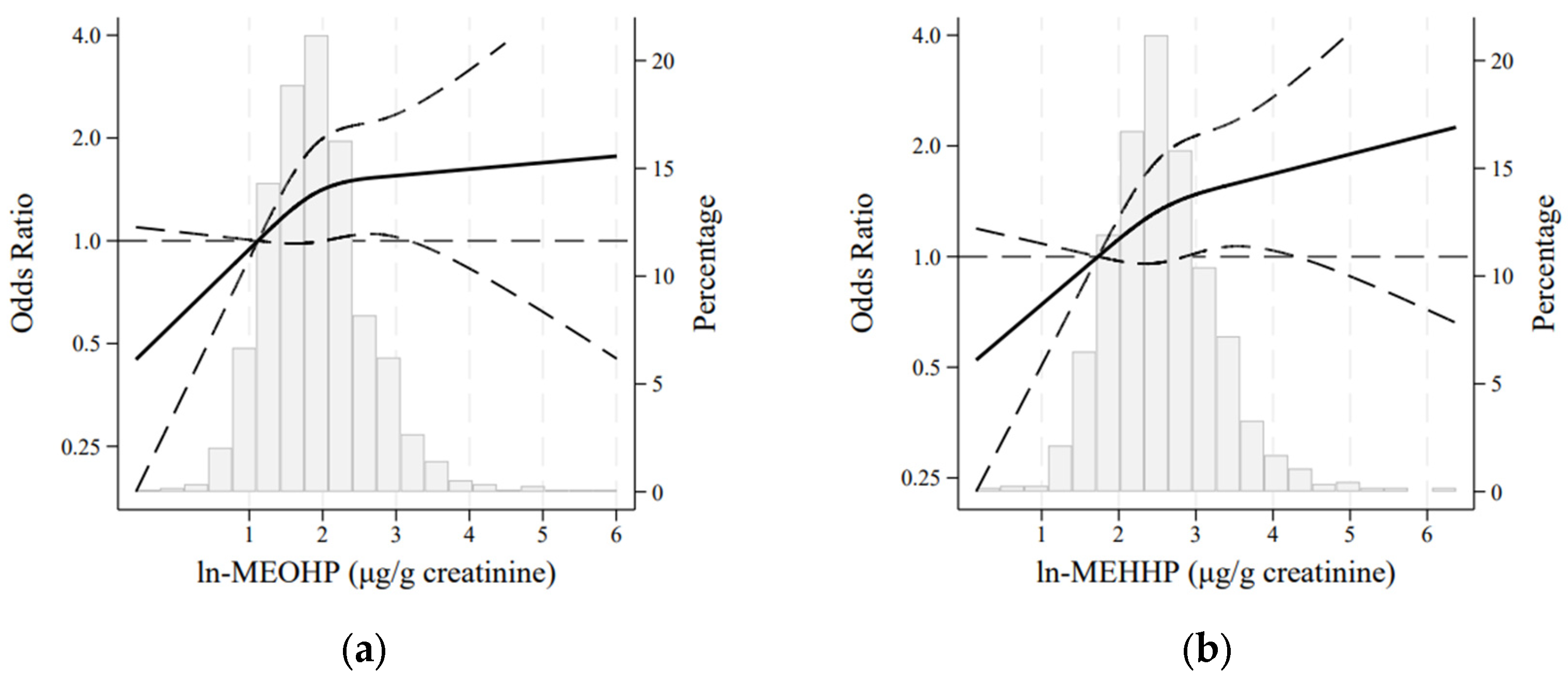
| MEOHP | |||||||
| Events/n | 317/1084 | 65/273 | 99/268 | 72/271 | 81/272 | ||
| Crude model | 1.09 (0.91, 1.31) | 0.342 | 1 (Ref.) | 1.87 (1.29, 2.72) | 1.16 (0.79, 1.71) | 1.36 (0.93, 1.99) | |
| Adjusted model | 1.17 (0.96, 1.42) | 0.119 | 1 (Ref.) | 1.99 (1.33, 2.96) | 1.24 (0.82, 1.88) | 1.53 (1.02, 2.30) | |
| MECPP | |||||||
| Events/n | 317/1084 | 73/274 | 88/270 | 72/268 | 84/272 | ||
| Crude model | 1.11 (0.92, 1.34) | 0.274 | 1 (Ref.) | 1.33 (0.92, 1.93) | 1.01 (0.69, 1.48) | 1.23 (0.85, 1.78) | |
| Adjusted model | 1.14 (0.93, 1.40) | 0.204 | 1 (Ref.) | 1.27 (0.86, 1.88) | 0.97 (0.65, 1.46) | 1.28 (0.86, 1.90) | |
| MEHHP | |||||||
| Events/n | 317/1084 | 70/273 | 87/270 | 78/269 | 82/272 | ||
| Crude model | 1.10 (0.91, 1.31) | 0.324 | 1 (Ref.) | 1.38 (0.95, 2.00) | 1.18 (0.81, 1.73) | 1.25 (0.86, 1.82) | |
| Adjusted model | 1.18 (0.97, 1.43) | 0.096 | 1 (Ref.) | 1.42 (0.95, 2.11) | 1.24 (0.82, 1.86) | 1.43 (0.96, 2.13) | |
| MCMHP | |||||||
| Events/n | 317/1084 | 77/272 | 91/268 | 66/273 | 83/271 | ||
| Crude model | 1.01 (0.82, 1.24) | 0.950 | 1 (Ref.) | 1.30 (0.90, 1.88) | 0.81 (0.55, 1.18) | 1.12 (0.77, 1.62) | |
| Adjusted model | 1.05 (0.84, 1.31) | 0.686 | 1 (Ref.) | 1.44 (0.97, 2.14) | 0.86 (0.57, 1.29) | 1.19 (0.80, 1.77) | |
| ∑DEHP † | |||||||
| Events/n | 317/1084 | 72/274 | 88/269 | 73/268 | 84/273 | ||
| Crude model | 1.10 (0.91, 1.34) | 0.320 | 1 (Ref.) | 1.36 (0.94, 1.98) | 1.05 (0.72, 1.54) | 1.25 (0.86, 1.81) | |
| Adjusted model | 1.16 (0.95, 1.43) | 0.152 | 1 (Ref.) | 1.46 (0.98, 2.16) | 1.04 (0.69, 1.56) | 1.40 (0.94, 2.09) | |
| cx-MiDP | |||||||
| Events/n | 317/1084 | 78/273 | 74/272 | 87/270 | 78/269 | ||
| Crude model | 1.04 (0.87, 1.25) | 0.642 | 1 (Ref.) | 0.93 (0.64, 1.36) | 1.19 (0.82, 1.71) | 1.02 (0.70, 1.48) | |
| Adjusted model | 1.06 (0.87, 1.29) | 0.578 | 1 (Ref.) | 0.94 (0.63, 1.41) | 1.17 (0.79, 1.73) | 1.00 (0.67, 1.49) | |
| OH-MiDP | |||||||
| Events/n | 317/1084 | 73/272 | 83/271 | 80/269 | 81/272 | ||
| Crude model | 1.03 (0.87, 1.22) | 0.722 | 1 (Ref.) | 1.20 (0.83, 1.75) | 1.15 (0.79, 1.68) | 1.16 (0.80, 1.68) | |
| Adjusted model | 1.12 (0.93, 1.35) | 0.224 | 1 (Ref.) | 1.31 (0.88, 1.95) | 1.19 (0.79, 1.77) | 1.36 (0.91, 2.04) | |
| OH-MiNP | |||||||
| Events/n | 317/1084 | 82/273 | 67/269 | 83/269 | 85/273 | ||
| Crude model | 1.08 (0.94, 1.24) | 0.280 | 1 (Ref.) | 0.77 (0.53, 1.13) | 1.04 (0.72, 1.50) | 1.05 (0.73, 1.52) | |
| Adjusted model | 1.10 (0.95, 1.28) | 0.205 | 1 (Ref.) | 0.80 (0.53, 1.20) | 1.06 (0.71, 1.57) | 1.12 (0.76, 1.65) | |
| Phthalate Metabolites as Continuous ^ | Phthalate Metabolites in Quartiles | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phthalate Metabolites (µg/g-Creatinine) | OR (95% CI) for Every 1-ln Increase | p-Value | Q1 OR (95% CI) | Q2 OR (95% CI) | Q3 OR (95% CI) | Q4 OR (95% CI) | p-Test for Linear Trend |
| MEP | |||||||
| Events/n | 246/1124 | 65/281 | 57/281 | 54/281 | 70/281 | ||
| Crude model | 1.06 (0.94, 1.19) | 0.376 | 1 (Ref.) | 0.85 (0.57, 1.26) | 0.79 (0.53, 1.19) | 1.10 (0.75, 1.62) | |
| Adjusted model * | 1.07 (0.95, 1.22) | 0.272 | 1 (Ref.) | 0.86 (0.56, 1.31) | 0.78 (0.51, 1.21) | 1.13 (0.74, 1.70) | |
| MiBP | |||||||
| Events/n | 246/1124 | 73/281 | 62/281 | 59/281 | 52/281 | ||
| Crude model | 0.85 (0.67, 1.08) | 0.178 | 1 (Ref.) | 0.81 (0.55, 1.19) | 0.76 (0.51, 1.12) | 0.65 (0.43, 0.97) | |
| Adjusted model | 0.91 (0.71, 1.17) | 0.485 | 1 (Ref.) | 0.87 (0.57, 1.31) | 0.85 (0.56, 1.29) | 0.68 (0.44, 1.04) | |
| MnBP | |||||||
| Events/n | 246/1124 | 64/281 | 60/281 | 57/281 | 65/281 | ||
| Crude model | 0.97 (0.79, 1.19) | 0.765 | 1 (Ref.) | 0.92 (0.62, 1.37) | 0.86 (0.58, 1.29) | 1.02 (0.69, 1.51) | |
| Adjusted model | 0.97 (0.78, 1.21) | 0.788 | 1 (Ref.) | 0.95 (0.62, 1.45) | 0.87 (0.57, 1.34) | 1.03 (0.68, 1.58) | |
| MBzP | |||||||
| Events/n | 246/1124 | 62/281 | 61/281 | 58/281 | 65/281 | ||
| Crude model | 1.06 (0.88, 1.26) | 0.557 | 1 (Ref.) | 0.98 (0.66, 1.46) | 0.92 (0.61, 1.38) | 1.06 (0.72, 1.58) | |
| Adjusted model | 1.06 (0.88, 1.29) | 0.523 | 1 (Ref.) | 0.96 (0.63, 1.47) | 0.95 (0.62, 1.46) | 1.03 (0.68, 1.58) | |
| MEOHP | |||||||
| Events/n | 246/1124 | 48/281 | 73/281 | 58/281 | 67/281 | ||
| Crude model | 1.17 (0.96, 1.43) | 0.110 | 1 (Ref.) | 1.70 (1.13, 2.57) | 1.26 (0.83, 1.93) | 1.52 (1.00, 2.30) | |
| Adjusted model | 1.24 (1.00, 1.53) | 0.047 | 1 (Ref.) | 1.79 (1.15, 2.76) | 1.29 (0.82, 2.03) | 1.70 (1.09, 2.64) | |
| MECPP | |||||||
| Events/n | 246/1124 | 53/281 | 64/281 | 57/281 | 72/281 | ||
| Crude model | 1.21 (0.99, 1.48) | 0.066 | 1 (Ref.) | 1.27 (0.84, 1.91) | 1.09 (0.72, 1.66) | 1.48 (0.99, 2.21) | |
| Adjusted model | 1.23 (0.99, 1.53) | 0.062 | 1 (Ref.) | 1.20 (0.78, 1.86) | 1.03 (0.66, 1.60) | 1.51 (0.98, 2.32) | |
| MEHHP | |||||||
| Events/n | 246/1124 | 51/281 | 64/281 | 62/281 | 69/281 | ||
| Crude model | 1.19 (0.98, 1.45) | 0.075 | 1 (Ref.) | 1.33 (0.88, 2.01) | 1.28 (0.84, 1.93) | 1.47 (0.98. 2.21) | |
| Adjusted model | 1.26 (1.03, 1.55) | 0.027 | 1 (Ref.) | 1.32 (0.86, 2.06) | 1.28 (0.82, 1.99) | 1.63 (1.06, 2.52) | |
| MCMHP | |||||||
| Events/n | 246/1124 | 64/281 | 62/281 | 52/281 | 68/281 | ||
| Crude model | 1.01 (0.80, 1.26) | 0.961 | 1 (Ref.) | 0.96 (0.65, 1.43) | 0.77 (0.51, 1.16) | 1.08 (0.73, 1.60) | |
| Adjusted model | 1.08 (0.85, 1.37) | 0.551 | 1 (Ref.) | 1.07 (0.70, 1.64) | 0.84 (0.54, 1.30) | 1.20 (0.79, 1.83) | |
| ∑DEHP † | |||||||
| Events/n | 246/1124 | 52/281 | 62/281 | 64/281 | 68/281 | ||
| Crude model | 1.21 (0.98, 1.48) | 0.071 | 1 (Ref.) | 1.25 (0.83, 1.88) | 1.30 (0.86, 1.96) | 1.41 (0.94, 2.11) | |
| Adjusted model | 1.26 (1.01, 1.58) | 0.038 | 1 (Ref.) | 1.31 (0.85, 2.03) | 1.27 (0.82, 1.96) | 1.54 (0.99, 2.37) | |
| cx-MiDP | |||||||
| Events/n | 246/1124 | 70/281 | 56/281 | 63/281 | 57/281 | ||
| Crude model | 0.90 (0.73, 1.10) | 0.287 | 1 (Ref.) | 0.75 (0.50, 1.12) | 0.87 (0.59, 1.29) | 0.77 (0.52, 1.14) | |
| Adjusted model | 0.87 (0.70, 1.09) | 0.233 | 1 (Ref.) | 0.76 (0.50, 1.17) | 0.82 (0.54, 1.25) | 0.70 (0.46, 1.08) | |
| OH-MiDP | |||||||
| Events/n | 246/1124 | 59/281 | 59/281 | 64/281 | 64/281 | ||
| Crude model | 1.01 (0.84, 1.22) | 0.892 | 1 (Ref.) | 1.00 (0.67, 1.50) | 1.11 (0.74, 1.66) | 1.11 (0.74, 1.66) | |
| Adjusted model | 1.05 (0.86, 1.28) | 0.649 | 1 (Ref.) | 1.03 (0.67, 1.59) | 1.11 (0.72, 1.69) | 1.15 (0.75, 1.77) | |
| ohminp | |||||||
| Events/n | 246/1124 | 63/281 | 53/281 | 65/281 | 65/281 | ||
| Crude model | 1.10 (0.94, 1.28) | 0.227 | 1 (Ref.) | 0.80 (0.53, 1.21) | 1.04 (0.70, 1.54) | 1.04 (0.70, 1.54) | |
| Adjusted model | 1.10 (0.94, 1.29) | 0.251 | 1 (Ref.) | 0.81 (0.53, 1.25) | 1.02 (0.67, 1.56) | 1.04 (0.68, 1.58) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akritidis, J.; Mérida, D.M.; Torrijo-Belanche, C.; Moreno-Franco, B.; Gimeno-Ruiz, S.; Rey-García, J.; Morales-Suarez-Varela, M.; Guallar-Castillón, P. Phthalate Metabolites and Their Relationship with Abdominal and General Obesity: Evidence from the Aragon Workers’ Health Study (AWHS). Nutrients 2025, 17, 1869. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111869
Akritidis J, Mérida DM, Torrijo-Belanche C, Moreno-Franco B, Gimeno-Ruiz S, Rey-García J, Morales-Suarez-Varela M, Guallar-Castillón P. Phthalate Metabolites and Their Relationship with Abdominal and General Obesity: Evidence from the Aragon Workers’ Health Study (AWHS). Nutrients. 2025; 17(11):1869. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111869
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkritidis, Jordan, Diana María Mérida, Carolina Torrijo-Belanche, Belén Moreno-Franco, Sofía Gimeno-Ruiz, Jimena Rey-García, María Morales-Suarez-Varela, and Pilar Guallar-Castillón. 2025. "Phthalate Metabolites and Their Relationship with Abdominal and General Obesity: Evidence from the Aragon Workers’ Health Study (AWHS)" Nutrients 17, no. 11: 1869. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111869
APA StyleAkritidis, J., Mérida, D. M., Torrijo-Belanche, C., Moreno-Franco, B., Gimeno-Ruiz, S., Rey-García, J., Morales-Suarez-Varela, M., & Guallar-Castillón, P. (2025). Phthalate Metabolites and Their Relationship with Abdominal and General Obesity: Evidence from the Aragon Workers’ Health Study (AWHS). Nutrients, 17(11), 1869. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111869





