Understanding Refeeding Syndrome in Critically Ill Patients: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Definition and Background
4. Pathogenesis
5. Clinical Manifestations
6. Diagnosis and Screening
7. Refeeding Syndrome in Critically Ill Patients: General Considerations and Incidence
8. Prognostic Impact of RS in Critically Ill Patients
9. Risk Factors in Critically Ill Patients
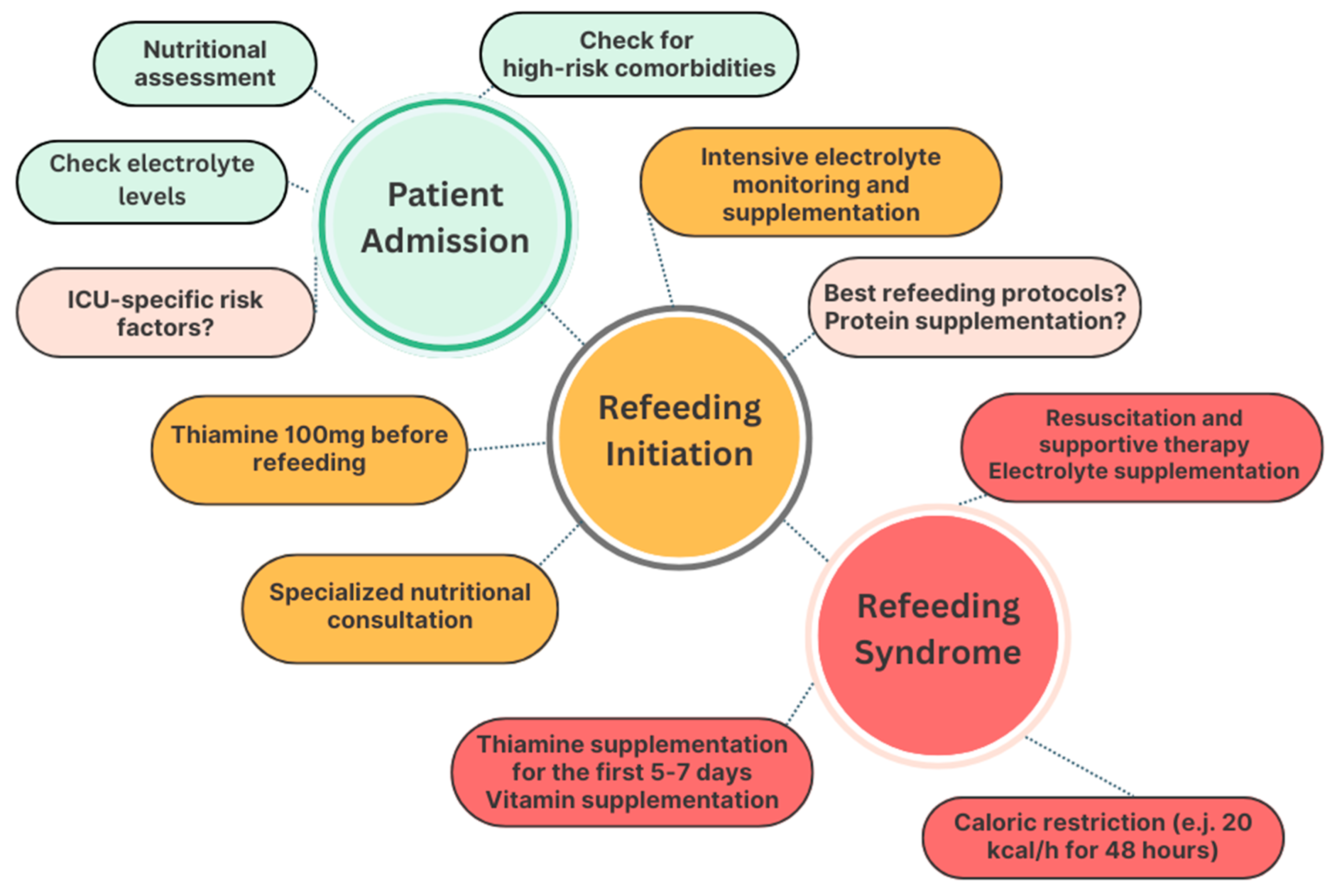
10. Avoidance of RS and Nutritional Management of Refeeding in ICUs
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Da Silva, J.S.V.; Seres, D.S.; Sabino, K.; Adams, S.C.; Berdahl, G.J.; Citty, S.W.; Cober, M.P.; Evans, D.C.; Greaves, J.R.; Gura, K.M.; et al. ASPEN Consensus Recommendations for Refeeding Syndrome. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2020, 35, 178–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponzo, V.; Pellegrini, M.; Cioffi, I.; Scaglione, L.; Bo, S. The Refeeding Syndrome: A Neglected but Potentially Serious Condition for Inpatients. A Narrative Review. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2021, 16, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehanna, H.; Nankivell, P.C.; Moledina, J.; Travis, J. Refeeding Syndrome—Awareness, Prevention and Management. Head Neck Oncol. 2009, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnitker, M.A.; Mattman, P.E.; Bliss, T.L. A Clinical Study of Malnutrition in Japanese Prisoners of War. Ann. Intern. Med. 1951, 35, 69–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, M.R.; Golden, N.H.; Shenker, I.R. Cardiac Arrest and Delirium: Presentations of the Refeeding Syndrome in Severely Malnourished Adolescents with Anorexia Nervosa. J. Adolesc. Health 1998, 22, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraaijenbrink, B.V.C.; Lambers, W.M.; Mathus-Vliegen, E.M.H.; Siegert, C.E.H. Incidence of Refeeding Syndrome in Internal Medicine Patients. Neth. J. Med. 2016, 74, 116–121. [Google Scholar]
- Rinninella, E.; D’Angelo, M.; Borriello, R.; Galasso, T.; Cintoni, M.; Raoul, P.; Impagnatiello, M.; Annicchiarico, B.E.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. Incidence and Impact of Refeeding Syndrome in an Internal Medicine and Gastroenterology Ward of an Italian Tertiary Referral Center: A Prospective Cohort Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buitendag, J.; Variawa, S.; Davids, R.; Ahmed, N. Refeeding Syndrome in Surgical Patients Post Initiation of Artificial Feeding, a Prospective Cohort Study in a Low-Income Country. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2021, 46, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourhassan, M.; Cuvelier, I.; Gehrke, I.; Marburger, C.; Modreker, M.K.; Volkert, D.; Willschrei, H.P.; Wirth, R. Prevalence of Risk Factors for the Refeeding Syndrome in Older Hospitalized Patients. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2018, 22, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Cai, D.; Lai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; He, J.; Zhou, L.; Sun, H. Risk Factors and Outcomes for Refeeding Syndrome in Acute Ischaemic Stroke Patients. Nutr. Diet. 2024, 81, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullam, T.; Hunt, S.L.; Han, M.; Denesia, J.; Chandrashekhar, S.; Jawdat, O.; Piccione, E.; Fernandes, J.A.; Statland, J. Outcomes after Intervention for Enteral Nutrition in Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis in Multidisciplinary Clinics. Muscle Nerve 2024, 70, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Aoki, Y.; Takeshita, E.; Saito, T.; Sugai, K.; Komaki, H.; Nakagawa, E.; Ishiyama, A.; Takanoha, S.; Wada, S.; et al. Hypophosphatemia Is a Common Complication in Severely Disabled Individuals with Neurological Disorders and Is Caused by Infection, Refeeding and Fanconi Syndrome. Brain Dev. 2014, 36, 878–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeja, N.; Grosicki, S. Refeeding Syndrome in Hematological Cancer Patients—Current Approach. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2020, 13, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsello, A.; Trovato, C.M.; Dipasquale, V.; Bolasco, G.; Labriola, F.; Gottrand, F.; Verduci, E.; Diamanti, A.; Romano, C. Refeeding Syndrome in Pediatric Age, An Unknown Disease: A Narrative Review. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2023, 77, e75–e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, C.; Hansen, A.; Levy, P.; Hashim, E. Recognizing Neonatal Refeeding Syndrome and Thiamin Supplementation: A Case Report. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2023, 47, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormack, B.E.; Jiang, Y.; Harding, J.E.; Crowther, C.A.; Bloomfield, F.H.; ProVIDe Trial Group. Neonatal Refeeding Syndrome and Clinical Outcome in Extremely Low-Birth-Weight Babies: Secondary Cohort Analysis From the ProVIDe Trial. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2021, 45, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedli, N.; Stanga, Z.; Sobotka, L.; Culkin, A.; Kondrup, J.; Laviano, A.; Mueller, B.; Schuetz, P. Revisiting the Refeeding Syndrome: Results of a Systematic Review. Nutrition 2017, 35, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netherlands, Committee on Malnutrition; Burger, G.C.E.; Drummond, J.C.; Sandstead, H.R. Malnutrition and Starvation in Western Netherlands: September 1944–July 1945 Pt. 1; General State Printing Office: The Hague, The Netherlands, 1948.
- Weinsier, R.L.; Krumdieck, C.L. Death Resulting from Overzealous Total Parenteral Nutrition: The Refeeding Syndrome Revisited. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1981, 34, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignaud, M.; Constantin, J.-M.; Ruivard, M.; Villemeyre-Plane, M.; Futier, E.; Bazin, J.-E.; Annane, D.; AZUREA Group (AnorexieRea Study Group). Refeeding Syndrome Influences Outcome of Anorexia Nervosa Patients in Intensive Care Unit: An Observational Study. Crit. Care 2010, 14, R172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skowrońska, A.; Sójta, K.; Strzelecki, D. Refeeding Syndrome as Treatment Complication of Anorexia Nervosa. Psychiatr. Pol. 2019, 53, 1113–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, A.T.; Rimmer, J. Hypophosphataemia Secondary to Oral Refeeding Syndrome in a Patient with Long-term Alcohol Misuse. Med. J. Aust. 2005, 183, 324–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baars, A.; Timmer, R.; Slee, P.H.T.J. Metabolic disregulation after starting feeding: “refeeding” syndrome: The central role of phosphate. Ned. Tijdschr. Geneeskd. 2002, 146, 906–909. [Google Scholar]
- González Avila, G.; Fajardo Rodríguez, A.; González Figueroa, E. The incidence of the refeeding syndrome in cancer patients who receive artificial nutritional treatment. Nutr. Hosp. 1996, 11, 98–101. [Google Scholar]
- Marinella, M.A. Refeeding Syndrome in Cancer Patients. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2008, 62, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crook, M.A.; Panteli, J.V. The Refeeding Syndrome and Hypophosphataemia in the Elderly. J. Intern. Med. 2005, 257, 397–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doig, G.S.; Simpson, F.; Heighes, P.T.; Bellomo, R.; Chesher, D.; Caterson, I.D.; Reade, M.C.; Harrigan, P.W.J. Restricted versus Continued Standard Caloric Intake during the Management of Refeeding Syndrome in Critically Ill Adults: A Randomised, Parallel-Group, Multicentre, Single-Blind Controlled Trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2015, 3, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olthof, L.E.; Koekkoek, W.A.C.K.; Van Setten, C.; Kars, J.C.N.; Van Blokland, D.; Van Zanten, A.R.H. Impact of Caloric Intake in Critically Ill Patients with, and without, Refeeding Syndrome: A Retrospective Study. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 1609–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marik, P.E.; Bedigian, M.K. Refeeding Hypophosphatemia in Critically Ill Patients in an Intensive Care Unit. A Prospective Study. Arch. Surg. 1996, 131, 1043–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, G.; Nicholls, D. Refeeding Hypophosphatemia in Adolescents with Anorexia Nervosa: A Systematic Review. Nutr. Clin. Pract. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2013, 28, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skipper, A. Refeeding Syndrome or Refeeding Hypophosphatemia: A Systematic Review of Cases. Nutr. Clin. Pract. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2012, 27, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Collaborating Centre for Acute Care (UK). Nutrition Support for Adults: Oral Nutrition Support, Enteral Tube Feeding and Parenteral Nutrition. In National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence: Guidance; National Collaborating Centre for Acute Care (UK): London, UK, 2006; ISBN 978-0-9549760-2-6. [Google Scholar]
- Cioffi, I.; Ponzo, V.; Pellegrini, M.; Evangelista, A.; Bioletto, F.; Ciccone, G.; Pasanisi, F.; Ghigo, E.; Bo, S. The Incidence of the Refeeding Syndrome. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses of Literature. Clin. Nutr. Edinb. Scotl. 2021, 40, 3688–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCray, S.; Walker, S.; Parrish, C.R. Much Ado about Refeeding. Pract. Gastroenterol. 2005, 28, 26–44. [Google Scholar]
- Boateng, A.A.; Sriram, K.; Meguid, M.M.; Crook, M. Refeeding Syndrome: Treatment Considerations Based on Collective Analysis of Literature Case Reports. Nutrition 2010, 26, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, M.J.; Melnik, G. The Refeeding Syndrome: An Approach to Understanding Its Complications and Preventing Its Occurrence. Pharmacotherapy 1995, 15, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knochel, J.P. The Pathophysiology and Clinical Characteristics of Severe Hypophosphatemia. Arch. Intern. Med. 1977, 137, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, R.; Kubota, H.; Yugi, K.; Toyoshima, Y.; Komori, Y.; Soga, T.; Kuroda, S. The Selective Control of Glycolysis, Gluconeogenesis and Glycogenesis by Temporal Insulin Patterns. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2013, 9, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geering, K. Functional Roles of Na,K-ATPase Subunits. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2008, 17, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopec, W.; Loubet, B.; Poulsen, H.; Khandelia, H. Molecular Mechanism of Na(+),K(+)-ATPase Malfunction in Mutations Characteristic of Adrenal Hypertension. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-L.; Kuo, E. Mechanism of Hypokalemia in Magnesium Deficiency. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2007, 18, 2649–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persaud-Sharma, D.; Saha, S.; Trippensee, A.W. Refeeding Syndrome. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Helfant, R.H. Hypokalemia and Arrhythmias. Am. J. Med. 1986, 80, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, P.-C.T.; Pham, P.-A.T.; Pham, S.V.; Pham, P.-T.T.; Pham, P.-M.T.; Pham, P.-T.T. Hypomagnesemia: A Clinical Perspective. Int. J. Nephrol. Renov. Dis. 2014, 7, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, L.S.; Hueb, J.C.; Minicucci, M.F.; Azevedo, P.S.; Paiva, S.A.R.; Zornoff, L.A.M. Thiamin Deficiency as a Cause of Reversible Cor Pulmonale. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2008, 91, e7–e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- On behalf of the working group on nutrition and metabolism of the German Geriatric Society (DGG); Janssen, G.; Pourhassan, M.; Lenzen-Großimlinghaus, R.; Jäger, M.; Schäfer, R.; Spamer, C.; Cuvelier, I.; Volkert, D.; Wirth, R. The Refeeding Syndrome Revisited: You Can Only Diagnose What You Know. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 73, 1458–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crook, M.A.; Hally, V.; Panteli, J.V. The Importance of the Refeeding Syndrome. Nutrition 2001, 17, 632–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedli, N.; Stanga, Z.; Culkin, A.; Crook, M.; Laviano, A.; Sobotka, L.; Kressig, R.W.; Kondrup, J.; Mueller, B.; Schuetz, P. Management and Prevention of Refeeding Syndrome in Medical Inpatients: An Evidence-Based and Consensus-Supported Algorithm. Nutrition 2018, 47, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulcini, C.D.; Zettle, S.; Srinath, A. Refeeding Syndrome. Pediatr. Rev. 2016, 37, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rio, A.; Whelan, K.; Goff, L.; Reidlinger, D.P.; Smeeton, N. Occurrence of Refeeding Syndrome in Adults Started on Artificial Nutrition Support: Prospective Cohort Study. BMJ Open 2013, 3, e002173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, N.K.J.; Fowler, R.A.; Bhagwanjee, S.; Rubenfeld, G.D. Critical Care and the Global Burden of Critical Illness in Adults. Lancet 2010, 376, 1339–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casaer, M.P.; Ziegler, T.R. Nutritional Support in Critical Illness and Recovery. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015, 3, 734–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lew, C.C.H.; Yandell, R.; Fraser, R.J.L.; Chua, A.P.; Chong, M.F.F.; Miller, M. Association Between Malnutrition and Clinical Outcomes in the Intensive Care Unit: A Systematic Review. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2017, 41, 744–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, N.M.; Li, J.; Seres, D.; Freedberg, D.E. Assessment of Refeeding Syndrome Definitions and 30-Day Mortality in Critically Ill Adults: A Comparison Study. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2023, 47, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tongyoo, S.; Rawangban, P.; Naorungroj, T. Prevalence, Predictive Factors, and Outcomes of Refeeding Syndrome among Medically Critically Ill Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2025, 40, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, E.; Yeh, D.D.; Quraishi, S.A.; Johnson, E.A.; Kaafarani, H.; Lee, J.; King, D.R.; DeMoya, M.; Fagenholz, P.; Butler, K.; et al. Hypophosphatemia in Enterally Fed Patients in the Surgical Intensive Care Unit. Nutr. Clin. Pract. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2017, 32, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, R.; Huang, H.; Wu, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, D.; Ji, Z.; Lin, Z.; Zang, N.; Pan, S.; Huang, K. Incidence and Outcome of Refeeding Syndrome in Neurocritically Ill Patients. Clin. Nutr. Edinb. Scotl. 2021, 40, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coşkun, R.; Gündoğan, K.; Baldane, S.; Güven, M.; Sungur, M. Refeeding Hypophosphatemia: A Potentially Fatal Danger in the Intensive Care Unit. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 44, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Md Ralib, A.; Mat Nor, M.B. Refeeding Hypophosphataemia after Enteral Nutrition in a Malaysian Intensive Care Unit: Risk Factors and Outcome. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 27, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneeweiss-Gleixner, M.; Haselwanter, P.; Schneeweiss, B.; Zauner, C.; Riedl-Wewalka, M. Hypophosphatemia after Start of Medical Nutrition Therapy Indicates Early Refeeding Syndrome and Increased Electrolyte Requirements in Critically Ill Patients but Has No Impact on Short-Term Survival. Nutrients 2024, 16, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, S.; Egi, M.; Schneider, A.G.; Bellomo, R.; Hart, G.K.; Hegarty, C. Hypophosphatemia in Critically Ill Patients. J. Crit. Care 2013, 28, 536.e9–536.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; Izawa, J.; Wakatake, H.; Saito, H.; Kawabata, C.; Matsushima, S.; Suzuki, A.; Nagatomi, A.; Yoshida, T.; Masui, Y.; et al. Mortality Associated with New Risk Classification of Developing Refeeding Syndrome in Critically Ill Patients: A Cohort Study. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardes, S.; Stello, B.B.; Milanez, D.S.J.; Razzera, E.L.; Silva, F.M. Refeeding Syndrome Risk at ICU Admission Is an Independent Predictor of ICU Readmission but It Is Not Associated with Mortality or Length of Stay in Critically Ill Patients. Intensive Crit. Care Nurs. 2024, 85, 103716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papathanakos, G.; Blot, S.; Koulenti, D. Refeeding Syndrome in the ICU: A Serious Problem Still Lacking an Evidence-Based Approach. Intensive Crit. Care Nurs. 2024, 85, 103771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boot, R.; Koekkoek, K.W.A.C.; van Zanten, A.R.H. Refeeding Syndrome: Relevance for the Critically Ill Patient. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2018, 24, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statlender, L.; Raphaeli, O.; Shochat, T.; Robinson, E.; Hellerman Itzhaki, M.; Bendavid, I.; Fishman, G.; Singer, P.; Kagan, I. Contributing Factors to Hypophosphatemia Development in Critically Ill Ventilated Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.A.; Sabel, A.L.; Gaudiani, J.L.; Mehler, P.S. Predictors of Hypophosphatemia during Refeeding of Patients with Severe Anorexia Nervosa. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2015, 48, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colmenero, M.; Morón, R.; De Dios-Chacón, I.; Fernández-Morales, P.; Mañas-Vera, M.R.; Manzano, F. Incidence of Hypophosphataemia after ICU Admission in Mechanically Ventilated Patients and Its Relationship with Risk Factors for Refeeding Syndrome. Med. Intensiv. Engl. Ed. 2024, 48, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Chen, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhou, M.; Xie, C. Risk Factors for the Development of Refeeding Syndrome in Adults: A Systematic Review. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2025, 40, 76–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Xiao, C.; Chen, L.; Zhang, X.; Kou, Q. Impact of Hypophosphatemia on Outcome of Patients in Intensive Care Unit: A Retrospective Cohort Study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2019, 19, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zhao, X.-L.; Xiong, R.-Q.; Chen, Q.-F.; Wu, Y.-M.; Lin, Z.-Z.; Wang, S.-N.; Wu, T.; Pan, S.-Y.; Huang, K.-B. The Performances of SNAQ, GLIM, mNICE, and ASPEN for Identification of Neurocritically Ill Patients at High Risk of Developing Refeeding Syndrome. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koekkoek, W.A.C.; Van Zanten, A.R.H. Is Refeeding Syndrome Relevant for Critically Ill Patients? Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2018, 21, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKnight, C.L.; Newberry, C.; Sarav, M.; Martindale, R.; Hurt, R.; Daley, B. Refeeding Syndrome in the Critically Ill: A Literature Review and Clinician’s Guide. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2019, 21, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, P.; Blaser, A.R.; Berger, M.M.; Calder, P.C.; Casaer, M.; Hiesmayr, M.; Mayer, K.; Montejo-Gonzalez, J.C.; Pichard, C.; Preiser, J.-C.; et al. ESPEN Practical and Partially Revised Guideline: Clinical Nutrition in the Intensive Care Unit. Clin. Nutr. Edinb. Scotl. 2023, 42, 1671–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeki, S.; Culkin, A.; Gabe, S.M.; Nightingale, J.M. Refeeding Hypophosphataemia Is More Common in Enteral than Parenteral Feeding in Adult in Patients. Clin. Nutr. Edinb. Scotl. 2011, 30, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compher, C.; Bingham, A.L.; McCall, M.; Patel, J.; Rice, T.W.; Braunschweig, C.; McKeever, L. Guidelines for the Provision of Nutrition Support Therapy in the Adult Critically Ill Patient: The American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2022, 46, 12–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alencar, L.d.O.; Neto, J.E.F.; Beserra, E.A.; Mendes, J.F.R. Nutritional Therapy in Intensive Care Unit Inpatients at Risk for Refeeding Syndrome: A Systematic Review. Nutrition 2024, 128, 112562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews-Rensch, K.; Capra, S.; Palmer, M. Systematic Review of Energy Initiation Rates and Refeeding Syndrome Outcomes. Nutr. Clin. Pract. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2021, 36, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apiromruck, N.; Kano, H.; Taemkaew, K.; Ingviya, T.; Intusoma, U.; Churuangsuk, C. Association between Energy Delivery from Parenteral Nutrition and Refeeding Syndrome in Hospitalized Adults: A Retrospective Cohort Study. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2024, 48, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahdat Shariatpanahi, Z.; Vahdat Shariatpanahi, M.; Shahbazi, E.; Shahbazi, S. Refeeding Syndrome and Its Related Factors in Critically Ill Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patients: A Prospective Cohort Study. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 830457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slingerland-Boot, R.; Rooijakkers, E.; Koekkoek, K.; van Blokland, D.; Arbous, S.; van Zanten, A. Macronutrient Intake and Outcomes of ICU Patients with Refeeding Hypophosphatemia. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2023, 55, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.J.; Shin, D.B.; Koo, B.K.; Ko, E.S.; Yeo, H.J.; Cho, W.H. The Impact of Multidisciplinary Nutritional Team Involvement on Nutritional Care and Outcomes in a Medical Intensive Care Unit. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 71, 1360–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Hypophosphatemia | Hypokalemia | Hypomagnesemia | Thiamine Deficiency | Fluid Overload |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| muscle weakness tetany paresthesias rhabdomyolysis delirium seizures acute respiratory failure acute heart failure arrhythmias peripheral tissue hypoxia hypotension shock | muscle weakness arrhythmias torsade de pointes hyporeflexia muscle paralysis respiratory depression metabolic alkalosis nausea vomiting constipation | muscle weakness tremors fasciculation tetany ataxia seizures apathy depression nausea vomiting constipation | Wernicke encephalopathy Korsakoff psychosis dry beriberi wet beriberi lactic acidosis | acute heart failure pulmonary edema peripheral edema |
| RS Definition | Diagnostic Criteria |
|---|---|
| Refeeding hypophosphatemia | Various degrees of % phosphate reduction after refeeding or drop below predefined cut-offs [17] |
| NICE guidelines integrated by Friedli et al. [32,48] | Imminent RS: Decrease in phosphate from baseline >30% or <0.6 mmol/L OR any two other electrolytes decrease below normal range within 72 h after start of nutrition therapy without clinical manifestations Manifest RS: Clinical symptoms of RS associated with the previous phosphate or electrolyte shift within 72 h after start of nutrition therapy |
| King’s College criteria [50] | Severely low electrolyte concentrations (potassium below <2.5 mmol/L, phosphate < 0.32 mmol/L, or magnesium < 0.5 mmol/L) associated with peripheral edema or acute circulatory fluid overload and organ dysfunction including respiratory failure, cardiac failure, and pulmonary oedema |
| ASPEN consensus criteria [1] | Mild RS: A decrease in any one, two, or three of the following: serum phosphorus, potassium, and/or magnesium levels by 10–20% within 5 days of reinitiating or substantially increasing energy provision Moderate RS: A decrease in any one, two, or three of the following: serum phosphorus, potassium, and/or magnesium levels by 20–30% within 5 days of reinitiating or substantially increasing energy provision Severe RS: A decrease in any one, two, or three of the following: serum phosphorus, potassium, and/or magnesium levels by >30% and/or organ dysfunction resulting from a decrease in any of these and/or due to thiamine deficiency within 5 days of reinitiating or substantially increasing energy provision |
| RS Definition | Incidence Rate (%) | Study Design | Population | No. of Patients | Author | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refeeding hypophosphatemia | 34% | Prospective study | Surgical and medical ICU patients | 62 | Marik et al. [29] | 1996 |
| Refeeding hypophosphatemia | 52.1% | Retrospective study | Medical ICU patients | 117 | Coşkun et al. [58] | 2014 |
| Refeeding hypophosphatemia | 39% | Retrospective study | Surgical ICU patients | 213 | Fuentes et al. [56] | 2017 |
| Refeeding hypophosphatemia | 36.8% | Retrospective study | Mechanically ventilated ICU patients | 337 | Olthof et al. [28] | 2018 |
| Refeeding hypophosphatemia | 42.6% | Prospective study | Surgical and medical ICU patients | 109 | Md Ralib et al. [59] | 2018 |
| Refeeding hypophosphatemia | 17.1% | Retrospective study | Neurocritically ill patients | 328 | Xiong et al. [57] | 2020 |
| King’s College criteria—ASPEN criteria | 1.5–12.5% | Prospective study | Surgical ICU patients | 200 | Buitendag et al. [8] | 2021 |
| Eight different definitions including refeeding hypophosphatemia and ASPEN criteria | from 1.5% to 88% | Retrospective study | Medical ICU patients | 2123 | Naik et al. [54] | 2023 |
| Refeeding hypophosphatemia | 47.2% | Prospective study | Medical ICU patients | 195 | Schneeweiss-Gleixner et al. [60] | 2024 |
| NICE criteria and ASPEN criteria | 22.7–27.3% | Retrospective study | Medical ICU patients | 216 | Tongyoo et al. [55] | 2025 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borriello, R.; Esposto, G.; Ainora, M.E.; Podagrosi, G.; Ferrone, G.; Mignini, I.; Galasso, L.; Gasbarrini, A.; Zocco, M.A. Understanding Refeeding Syndrome in Critically Ill Patients: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1866. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111866
Borriello R, Esposto G, Ainora ME, Podagrosi G, Ferrone G, Mignini I, Galasso L, Gasbarrini A, Zocco MA. Understanding Refeeding Syndrome in Critically Ill Patients: A Narrative Review. Nutrients. 2025; 17(11):1866. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111866
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorriello, Raffaele, Giorgio Esposto, Maria Elena Ainora, Giorgio Podagrosi, Giuliano Ferrone, Irene Mignini, Linda Galasso, Antonio Gasbarrini, and Maria Assunta Zocco. 2025. "Understanding Refeeding Syndrome in Critically Ill Patients: A Narrative Review" Nutrients 17, no. 11: 1866. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111866
APA StyleBorriello, R., Esposto, G., Ainora, M. E., Podagrosi, G., Ferrone, G., Mignini, I., Galasso, L., Gasbarrini, A., & Zocco, M. A. (2025). Understanding Refeeding Syndrome in Critically Ill Patients: A Narrative Review. Nutrients, 17(11), 1866. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111866






