The Differential Modulatory Effects of Potassium Supplementation on Blood Pressure, Vascular Reactivity, Glomerular Filtration Rates, and Oxidative Stress in Different Experimental Hypertensive Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Induction of Hypertension and Blood Pressure Recording
2.3. Isolation of Aortic Rings—Vascular Reactivity Experiments
2.4. Serum Electrolyte, Urea, and Creatinine Analyses
2.5. Serum Malondialdehyde Level Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Potassium Supplementation Differentially Lowered Blood Pressure in Hypertensive Rats
3.2. Potassium Supplementation Reduced the Contractile Response to PE in L-NAME and DOCA-Salt Hypertensive Models
3.3. Potassium Supplementation Did Not Improve ACh Relaxation in L-NAME and DOCA-Salt Hypertensive Models
3.4. Serum Electrolyte, Creatinine, and Urea Levels
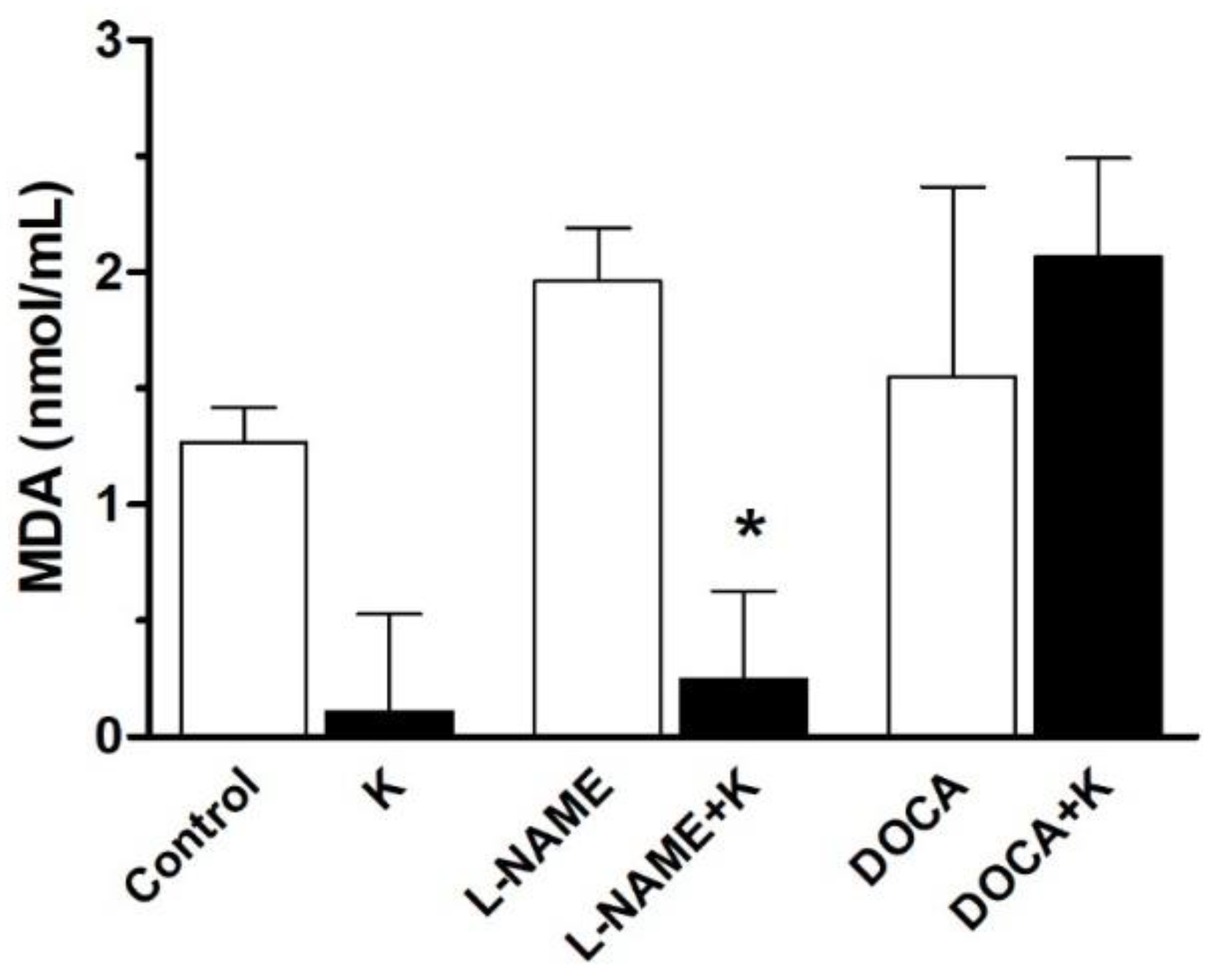
3.5. Serum Malondialdehyde Level
3.6. Body Weight and Glomerular Filtration Rate
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACh | Acetylcholine |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| BP | Blood pressure |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| DBP | Diastolic blood pressure |
| DOCA | Deoxycorticosterone acetate |
| eGFR | Estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| GFR | Glomerular filtration rates |
| HR | Heart rate |
| L-NAME | L-NG-Nitro-arginine methyl ester |
| MAP | Mean arterial blood pressure |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| NOS | Nitric oxide synthase |
| PP | Pulse pressure |
| RBF | Reduced renal blood flow |
| SBP | Systolic blood pressure |
| SEM | Standard error of the mean |
| UNX | Uninephrectomy |
References
- Castro, H.; Raij, L. Potassium in Hypertension and Cardiovascular Disease. Semin. Nephrol. 2013, 33, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippini, T.; Violi, F.; D’Amico, R.; Vinceti, M. The Effect of Potassium Supplementation on Blood Pressure in Hypertensive Subjects: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 230, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCalla, G.; Brown, P.D.; Cole, W.C.; Campbell, C.; Nwokocha, C.R. Cadmium-Induced Hypertension Is Associated with Renal Myosin Light Chain Phosphatase Inhibition via Increased T697 Phosphorylation and P44 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Levels. Hypertens. Res. 2021, 44, 941–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Fang, L.; Xu, J.; Chen, X.; Bai, Y.; Wu, J.; Wu, L.; Zhong, J. The Association of Knowledge, Attitudes and Behaviors Related to Salt with 24-h Urinary Sodium, Potassium Excretion and Hypertensive Status. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, S.B.; Fenton, R.A. K+ and the Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System: New Insights into Their Role in Blood Pressure Control and Hypertension Treatment. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 4451–4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreier, R.; Abdolalizadeh, B.; Asferg, C.L.; Hölmich, L.R.; Buus, N.H.; Forman, J.L.; Andersen, U.B.; Egfjord, M.; Sheykhzade, M.; Jeppesen, J.L. Effect of Increased Potassium Intake on the Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System and Subcutaneous Resistance Arteries: A Randomized Crossover Study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, 1282–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonough, A.A.; Veiras, L.C.; Guevara, C.A.; Ralph, D.L. Cardiovascular Benefits Associated with Higher Dietary K. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 312, E348–E356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunbupha, S.; Apaijit, K.; Potue, P.; Maneesai, P.; Pakdeechote, P. Hesperidin Inhibits L-NAME-Induced Vascular and Renal Alterations in Rats by Suppressing the Renin–Angiotensin System, Transforming Growth Factor-Β1, and Oxidative Stress. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2021, 48, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zatz, R.; Baylis, C. Chronic Nitric Oxide Inhibition Model Six Years On. Hypertension 1998, 32, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaron, K.J.; Sanders, P.W. Role of Dietary Salt and Potassium Intake in Cardiovascular Health and Disease: A Review of the Evidence. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2013, 88, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.J.; MacGregor, G.A. Beneficial Effects of Potassium on Human Health. Physiol. Plant. 2008, 133, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnusson, L.; Sorensen, C.M.; Braunstein, T.H.; Holstein-Rathlou, N.H.; Salomonsson, M. Mechanisms of K + Induced Renal Vasodilation in Normo- and Hypertensive Rats in Vivo. Acta Physiol. 2011, 202, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holécyová, A.; Török, J.; Bernátová, I.; Pechánová, O. Restriction of Nitric Oxide Rather than Elevated Blood Pressure Is Responsible for Alterations of Vascular Responses in Nitric Oxide-Deficient Hypertension. Physiol. Res. 1996, 45, 317–321. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Jia, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Bo, L.; Zhao, X.; Sun, C. Metabonomics Analysis of Kidneys in Rats Administered with Chronic Low-Dose Cadmium by Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2019, 39, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, A.; Chan, V.; Brown, L. The DOCA-Salt Hypertensive Rat as a Model of Cardiovascular Oxidative and Inflammatory Stress. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2010, 6, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczeriszka, M.; Wąsowicz, K. Animal Models of Hypertension: The Status of Nitric Oxide and Oxidative Stress and the Role of the Renal Medulla. Nitric Oxide 2022, 125–126, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benter, I.F.; Canatan, H.; Benboubetra, M.; Yousif, M.H.M.; Akhtar, S. Global Upregulation of Gene Expression Associated with Renal Dysfunction in DOCA-Salt-Induced Hypertensive Rats Occurs via Signaling Cascades Involving Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor: A Microarray Analysis. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2009, 51, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.; Duce, B.; Miric, G.; Sernia, C. Reversal of Cardiac Fibrosis in Deoxycorticosterone Acetate-Salt Hypertensive Rats by Inhibition of the Renin-Angiotensin System. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1999, 10 (Suppl. S1), S143–S148. [Google Scholar]
- Tolvanen, J.P.; Mäkynen, H.; Wu, X.; Hutri-Kähönen, N.; Ruskoaho, H.; Karjala, K.; Pörsti, I. Effects of Calcium and Potassium Supplements on Arterial Tone in Vitro in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 124, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elijovich, F.; Kirabo, A.; Laffer, C.L. Salt Sensitivity of Blood Pressure in Black People: The Need to Sort Out Ancestry Versus Epigenetic Versus Social Determinants of Its Causation. Hypertension 2024, 81, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, J.; Fonseca, J.M.; Ayavire, F.; Salas, F.; Ortiz, M.; Sandoval, J.M.; Benites, J.; Nwokocha, C.R.; Zavala, E.; Paredes, A.; et al. Ascorbate Attenuates Oxidative Stress and Increased Blood Pressure Induced by 2-(4-Hydroxyphenyl) Amino-1,4-Naphthoquinone in Rats. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 8989676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwokocha, C.R.; Gordon, A.; Palacios, J.; Paredes, A.; Cifuentes, F.; Francis, S.; Watson, J.A.; Delgoda, R.; Nwokocha, M.; Alexander-Lindo, R.; et al. Hypotensive and Antihypertensive Effects of an Aqueous Extract from Guinep Fruit (Melicoccus bijugatus Jacq) in Rats. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawa, H.; Ohishi, N.; Yagi, K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 95, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippini, T.; Naska, A.; Kasdagli, M.I.; Torres, D.; Lopes, C.; Carvalho, C.; Moreira, P.; Malavolti, M.; Orsini, N.; Whelton, P.K.; et al. Potassium Intake and Blood Pressure: A Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2020, 9, e015719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Schäfer, S.C.; Haefliger, J.A.; Maillard, M.P.; Alonso, F. Dietary Potassium Supplementation Reduces Chronic Kidney Lesions Independent of Blood Pressure in Deoxycorticosterone-Acetate and High Sodium Chloride-Treated Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Domenighetti, A.A.; Pedrazzini, T.; Burnier, M. Potassium Supplementation Reduces Cardiac and Renal Hypertrophy Independent of Blood Pressure in DOCA/Salt Mice. Hypertension 2005, 46, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zicha, J.; Dobešová, Z.; Behuliak, M.; Kuneš, J.; Vaněčková, I. Preventive Dietary Potassium Supplementation in Young Salt-Sensitive Dahl Rats Attenuates Development of Salt Hypertension by Decreasing Sympathetic Vasoconstriction. Acta Physiol. 2011, 202, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Li, L.L.; Lin, Z.G.; Jiang, Z.C.; Li, H.X.; Zhao, S.G.; Yang, K.B. Blockage of Potassium Channel Inhibits Proliferation of Glioma Cells via Increasing Reactive Oxygen Species. Oncol. Res. 2014, 22, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornas, W.C.; Silva, M.; Tavares, R.; de Lima, W.G.; dos Santos, R.C.; Pedrosa, M.L.; Silva, M.E. Efficacy of the Superoxide Dismutase Mimetic Tempol in Animal Hypertension Models: A Meta-Analysis. J. Hypertens. 2015, 33, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamino, H.; Katsushima, M.; Hashimoto, M.; Fujita, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Ikeda, K.; Isomura, N.; Oguri, Y.; Yamamoto, W.; Watanabe, R.; et al. Urinary Sodium-to-Potassium Ratio Associates with Hypertension and Current Disease Activity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Cross-Sectional Study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 23, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bighamian, R.; Hahn, J.O. Relationship between Stroke Volume and Pulse Pressure during Blood Volume Perturbation: A Mathematical Analysis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 459269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Fink, G.D.; Galligan, J.J. Tempol Lowers Blood Pressure and Sympathetic Nerve Activity but Not Vascular O2- in DOCA-Salt Rats. Hypertension 2004, 43, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, C.N.; Ritter, M.L.; Wackman, K.K.; Oliveira, V.; Balapattabi, K.; Grobe, C.C.; Brozoski, D.T.; Reho, J.J.; Nakagawa, P.; Mouradian, G.C.; et al. Cardiometabolic Effects of DOCA-Salt in Male C57BL/6J Mice Are Variably Dependent upon Sodium and Non-Sodium Components of Diet. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2022, 322, R467–R485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Gao, W.; Nguyen, B.V.; Jefferson, J.R.; Liu, Y.; Fan, F.; Roman, R.J. Impaired Renal Hemodynamics and Glomerular Hyperfiltration Contribute to Hypertension-Induced Renal Injury. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2020, 319, F624–F635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwokocha, C.; Palacios, J.; Ojukwu, V.E.; Nna, V.U.; Owu, D.U.; Nwokocha, M.; McGrowder, D.; Orie, N.N. Oxidant-Induced Disruption of Vascular K+ Channel Function: Implications for Diabetic Vasculopathy. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 130, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
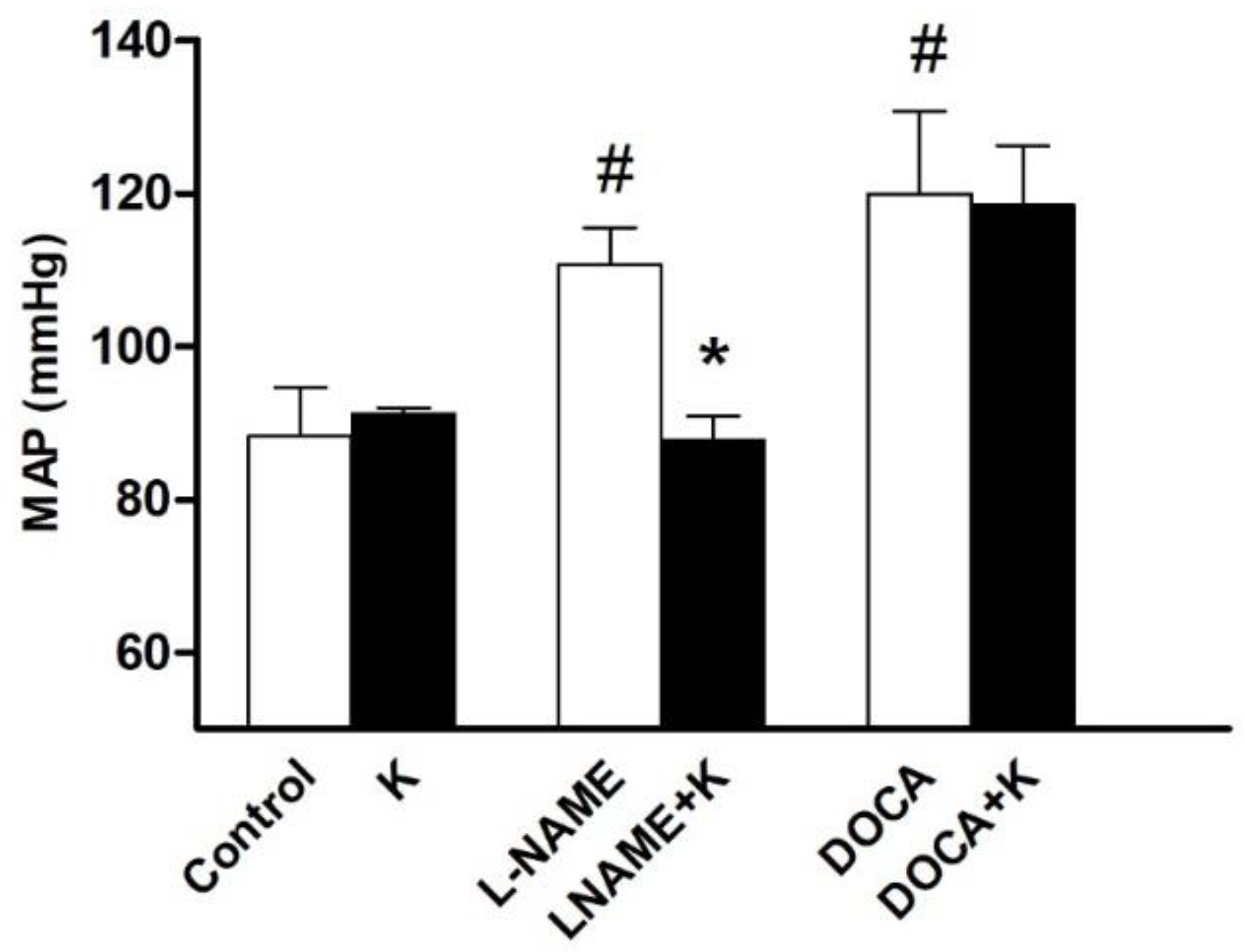
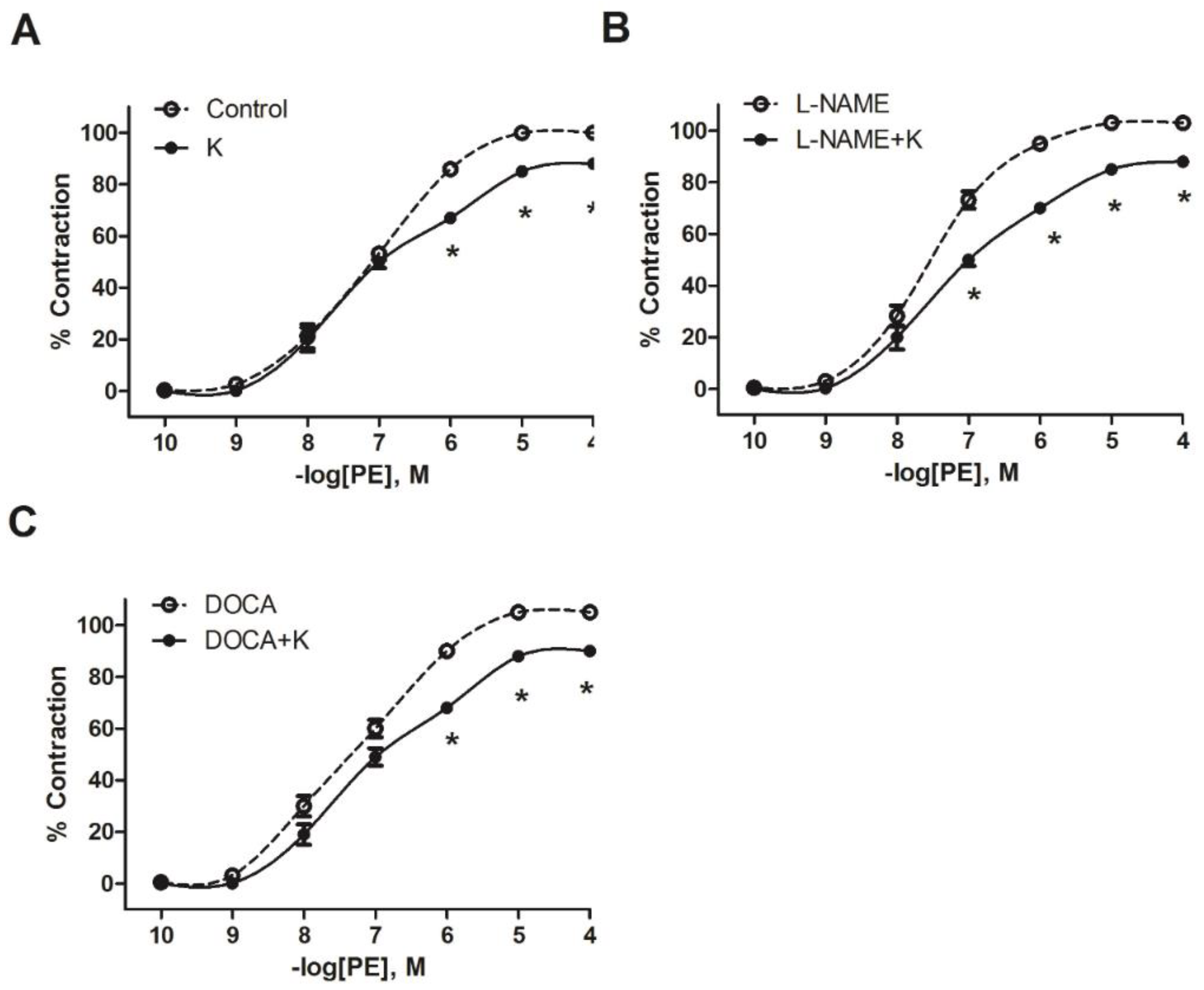

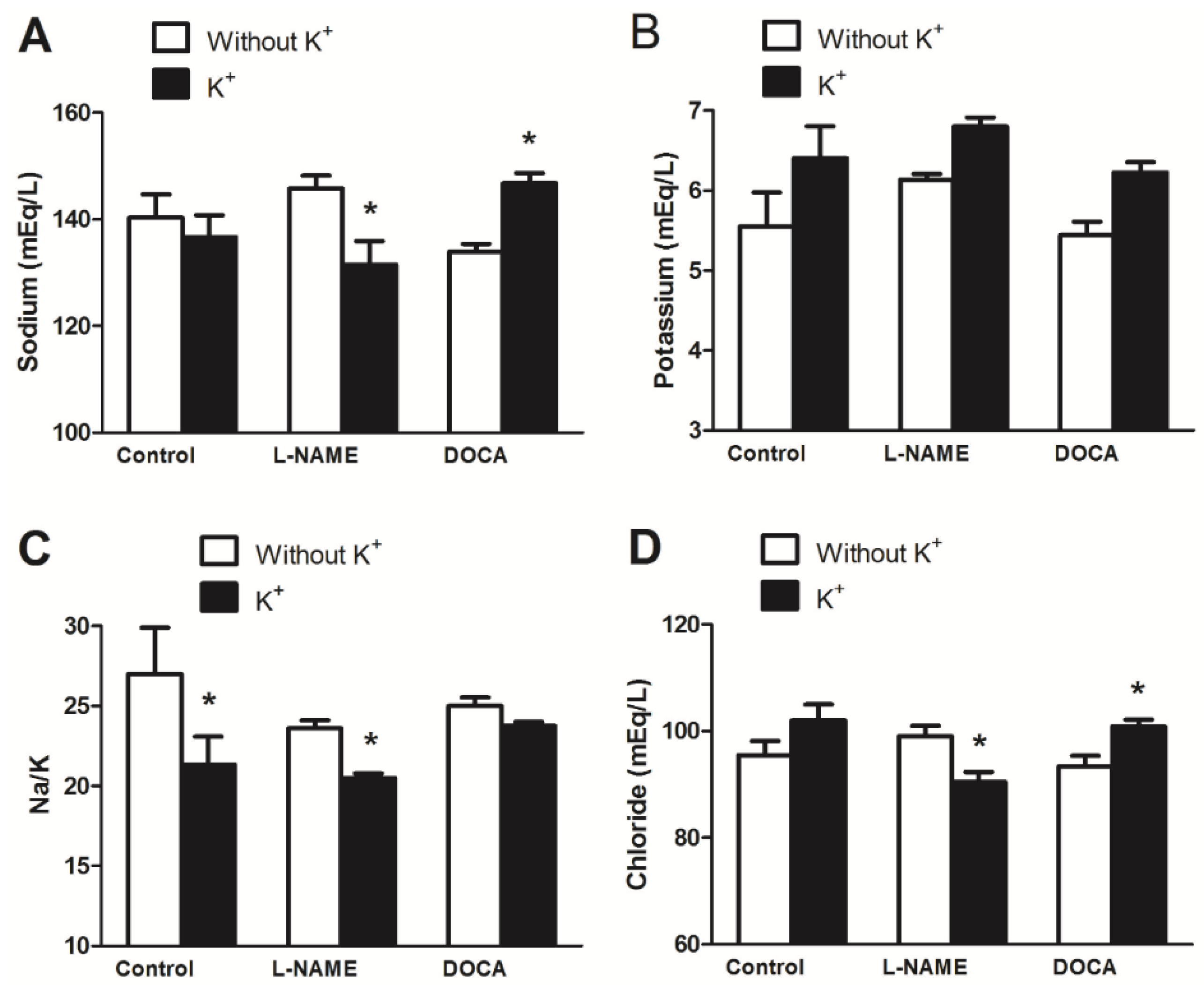
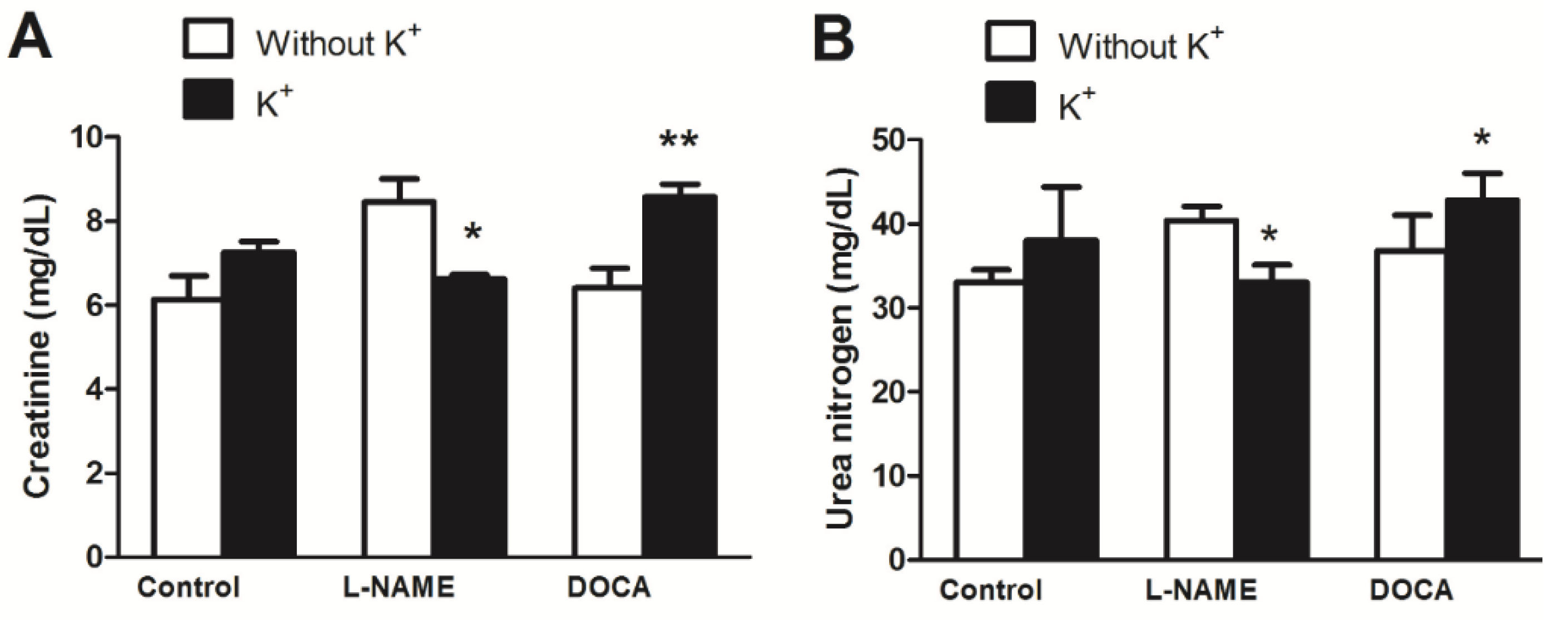
| Parameter | Control | K | L-NAME | L-NAME+K | DOCA | DOCA+K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBP, mmHg/s | 114 ± 7 | 116 ± 3 | 137 ± 5 # | 116 ± 2 * | 135 ± 10 ## | 140 ± 7 |
| DBP, mmHg/s | 76 ± 6 | 78 ± 1 | 98 ± 5 # | 75 ± 4 * | 96 ± 11 # | 104 ± 9 |
| PP, mmHg | 39 ± 1 | 39 ± 3 | 40 ± 1 | 41 ± 1 | 48 ± 1 ### | 36 ± 1 *** |
| Control | K+ | L-NAME | L-NAME+K | DOCA | DOCA+K | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emax. (%) | 98 ± 3 | 82 ± 5 * | 101 ± 2 | 83 ± 4 * | 102 ± 5 | 85 ± 5 * |
| pEC50 (M) | 7.07 ± 0.11 | 7.20 ± 0.19 | 7.48 ± 0.07 | 7.19 ± 0.16 * | 7.19 ± 0.16 | 7.12 ± 0.18 |
| Control | K+ | L-NAME | L-NAME+K | DOCA | DOCA+K | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emax. (%) | 84 ± 1 | 86 ± 3 | 67 ± 2 | 72 ± 2 | 68 ± 3 | 58 ± 1 |
| pEC50 (M) | 6.64 ± 0.03 | 6.91 ± 0.10 * | 6.67 ± 0.09 | 6.69 ± 0.09 | 6.70 ± 0.13 | 6.58 ± 0.05 |
| Parameter | Control | K | L-NAME | L-NAME+K | DOCA | DOCA+K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean initial weight (g) | 281 ± 27 | 250 ± 30 | 210 ± 15 | 240 ± 18 | 279 ± 33 | 230 ± 74 |
| Mean final weight (g) | 409 ± 32 | 377 ± 13 | 304 ± 13 | 324 ± 21 | 381 ± 23 | 357 ± 39 |
| Mean weight change (g) | 128 ± 59 | 127 ± 43 | 94 ± 28 | 84 ± 39 | 102 ± 56 | 127 ± 113 |
| % change | (−)1% | (−)11% | (+)25% |
| Groups | Weight | W0.695 | Creatinine | C−0.660 | Urea | U−0.391 | eGFR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 880 | 409 | 65.34 | 6 | 0.31 | 32 | 0.26 | 4545.03 |
| K+ | 880 | 377 | 61.74 | 7 | 0.28 | 37 | 0.24 | 3665.29 |
| L-NAME | 880 | 304 | 53.16 | 8.5 | 0.24 | 40 | 0.24 | 2693.13 |
| L-NAME + K+ | 880 | 324 | 55.57 | 6.2 | 0.30 | 32 | 0.26 | 3782.85 |
| DOCA | 880 | 381 | 62.19 | 6 | 0.31 | 35 | 0.25 | 4177.49 |
| DOCA + K+ | 880 | 357 | 59.44 | 8.5 | 0.24 | 38 | 0.24 | 3072.38 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nwokocha, C.R.; Palacios, J.; Reid, M.K.; Nunes, N.J.; Gray, W.; McGrowder, D.; Orie, N.N.; Yakubu, M.A. The Differential Modulatory Effects of Potassium Supplementation on Blood Pressure, Vascular Reactivity, Glomerular Filtration Rates, and Oxidative Stress in Different Experimental Hypertensive Models. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1865. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111865
Nwokocha CR, Palacios J, Reid MK, Nunes NJ, Gray W, McGrowder D, Orie NN, Yakubu MA. The Differential Modulatory Effects of Potassium Supplementation on Blood Pressure, Vascular Reactivity, Glomerular Filtration Rates, and Oxidative Stress in Different Experimental Hypertensive Models. Nutrients. 2025; 17(11):1865. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111865
Chicago/Turabian StyleNwokocha, Chukwuemeka R., Javier Palacios, Melissa Kaydeen Reid, Nikolai Javier Nunes, Wesley Gray, Donovan McGrowder, Nelson N. Orie, and Momoh A. Yakubu. 2025. "The Differential Modulatory Effects of Potassium Supplementation on Blood Pressure, Vascular Reactivity, Glomerular Filtration Rates, and Oxidative Stress in Different Experimental Hypertensive Models" Nutrients 17, no. 11: 1865. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111865
APA StyleNwokocha, C. R., Palacios, J., Reid, M. K., Nunes, N. J., Gray, W., McGrowder, D., Orie, N. N., & Yakubu, M. A. (2025). The Differential Modulatory Effects of Potassium Supplementation on Blood Pressure, Vascular Reactivity, Glomerular Filtration Rates, and Oxidative Stress in Different Experimental Hypertensive Models. Nutrients, 17(11), 1865. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111865








