Actual Data on Essential Trace Elements in Parkinson’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
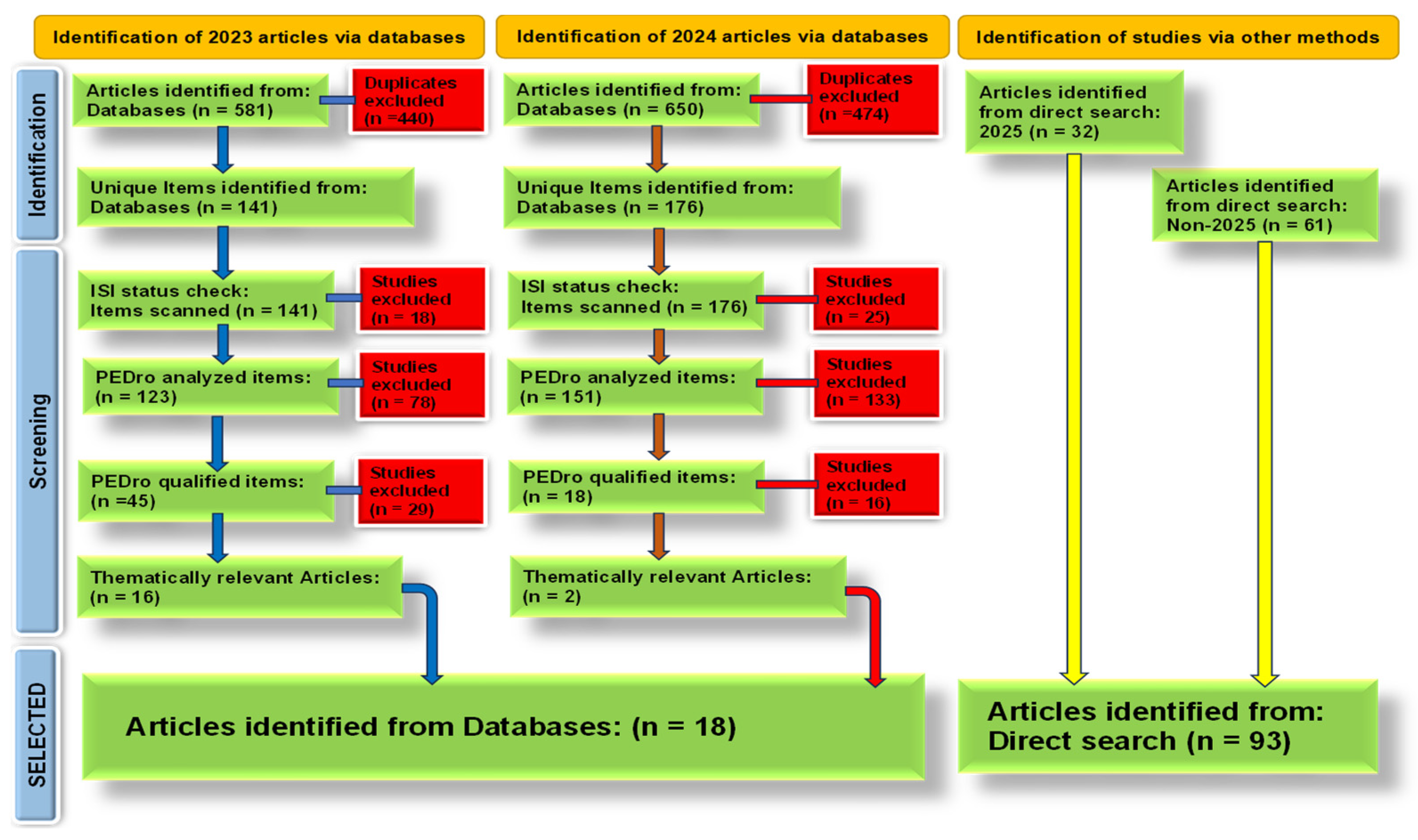
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
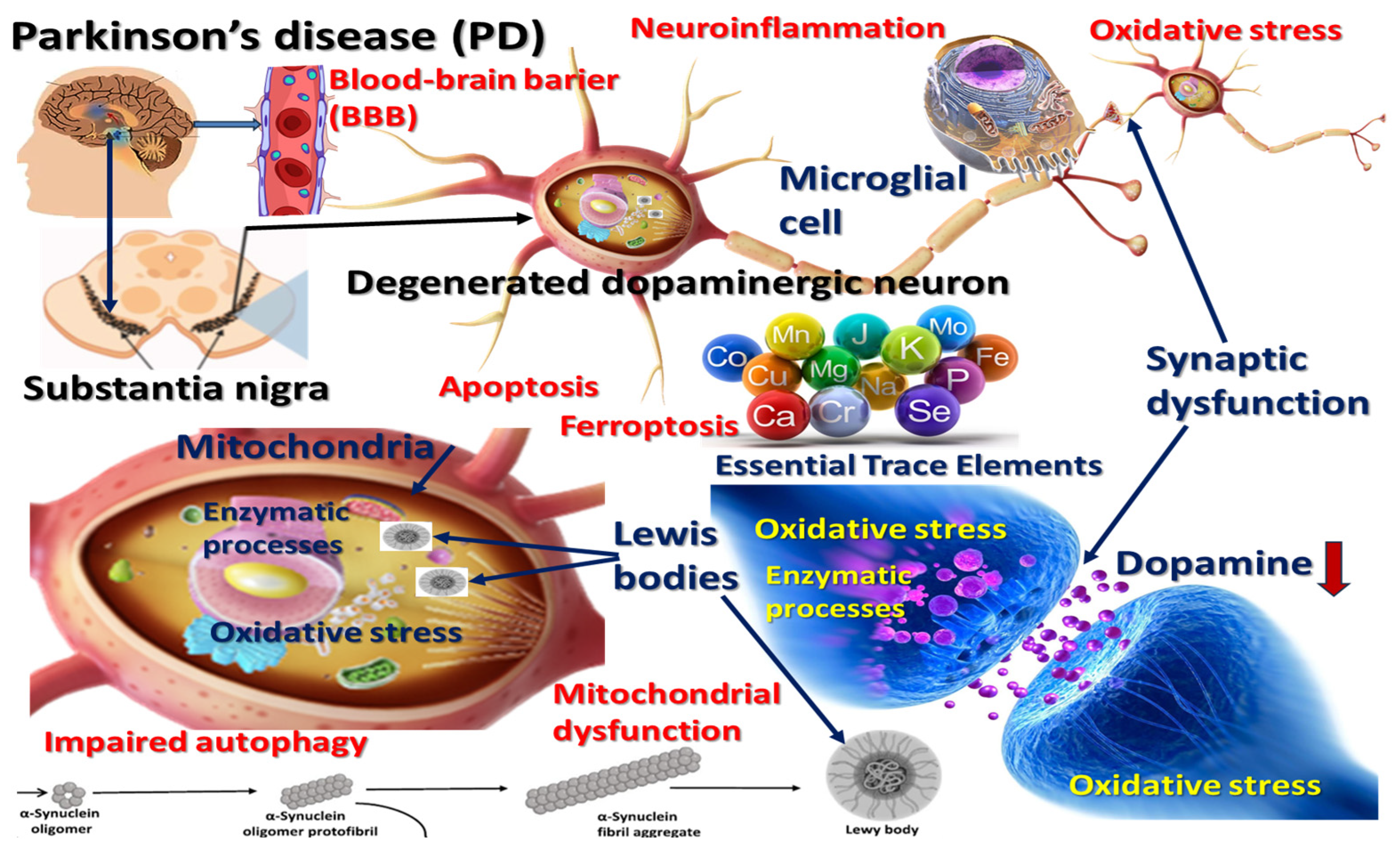
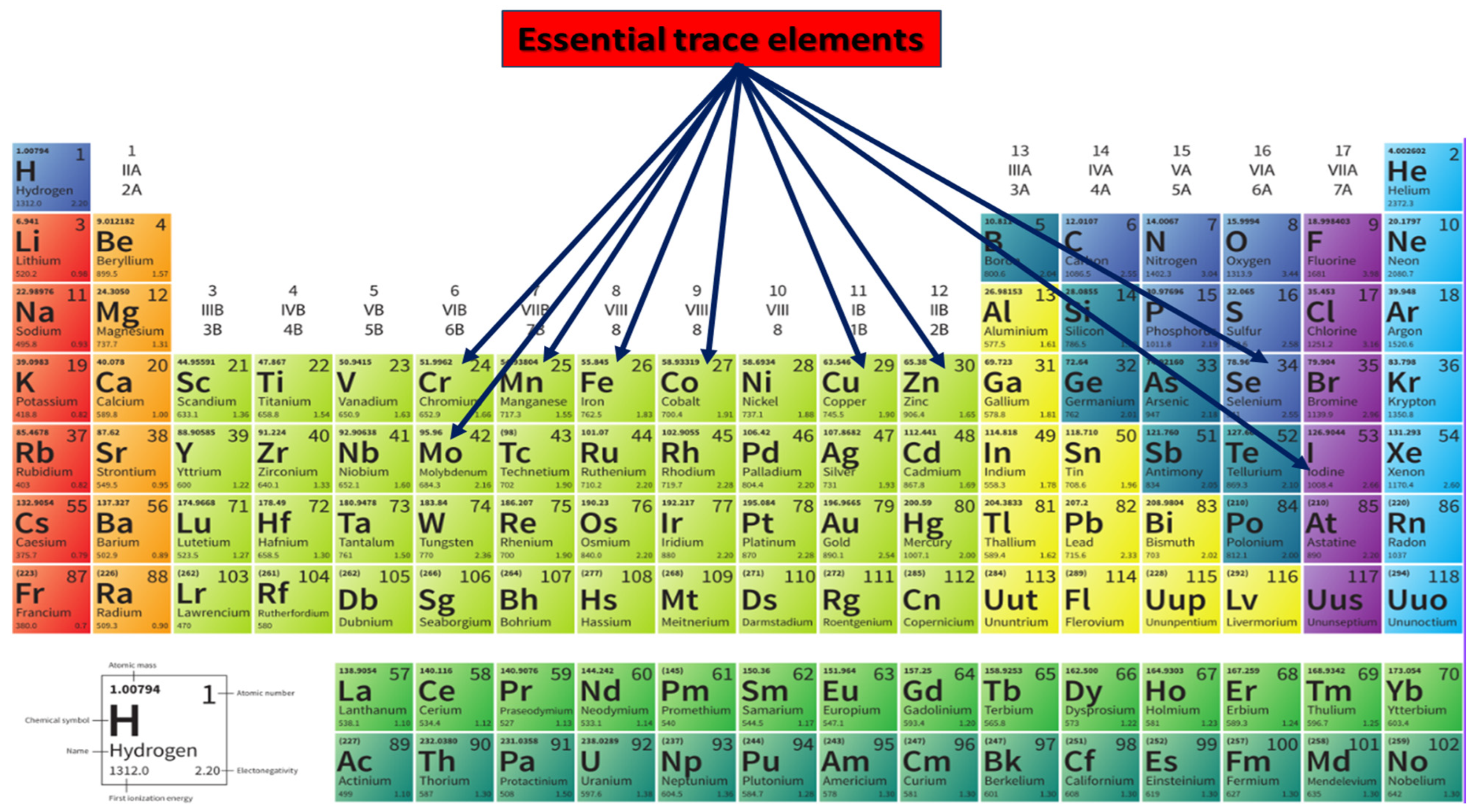
3.1. Trace Elements: Biological Functions and Brain Homeostasis
3.2. Trace-Element Levels Altered in Parkinson’s Disease
3.3. Focused Synthesis of Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms
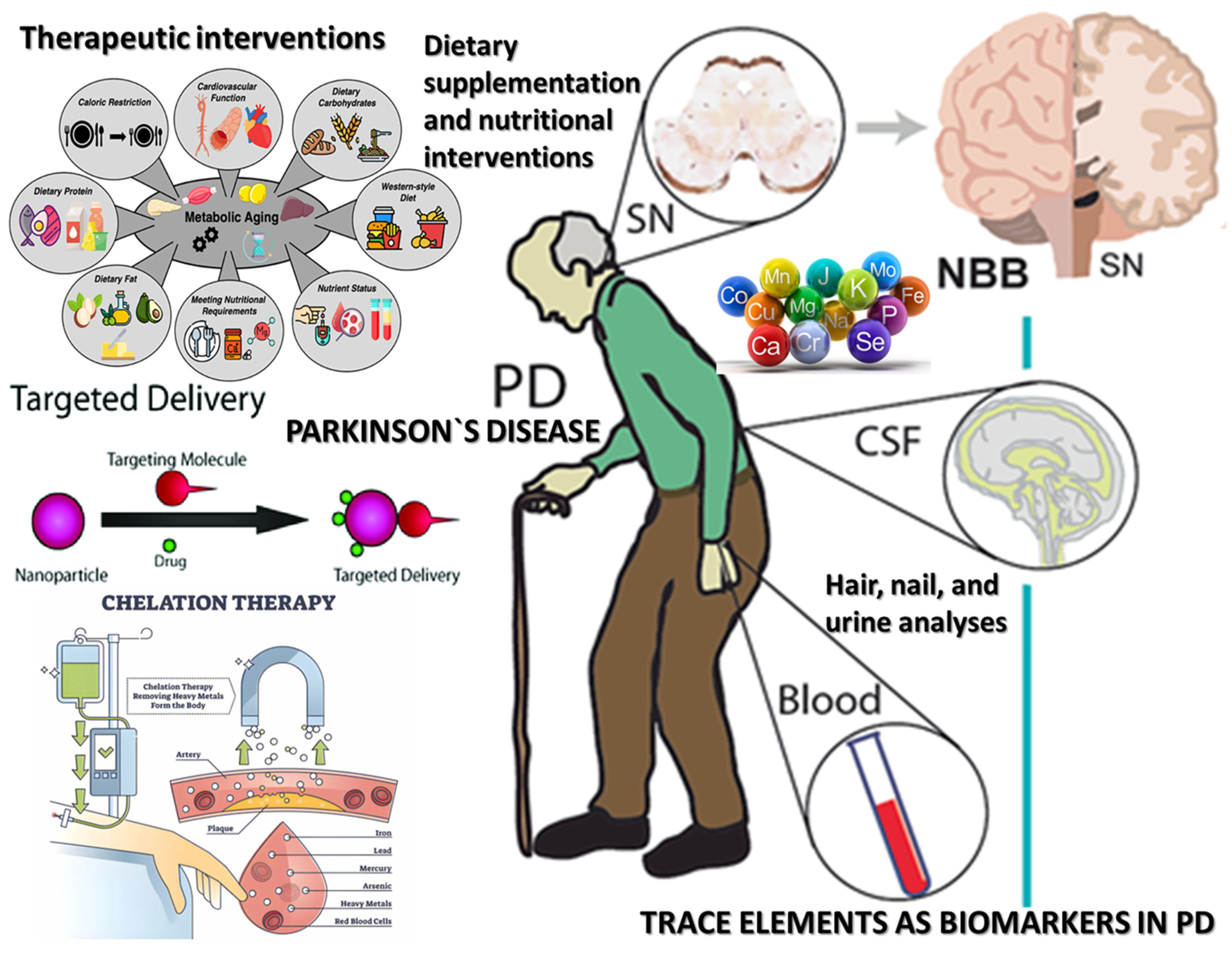
3.4. Trace Elements as Biomarkers in PD
| Trace Element | Biological Tissue | Concentration in PD Patients | Concentration in Controls | Scientific Interpretation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zinc (Zn) | Human body | Lower levels in serum, plasma, and CSF | 2–3 g | The zinc content in the CSF is significantly increased in the brains of PD patients. | [52,59] |
| Zinc (Zn) | Serum | 964 ± 360 µg/L | 1026 ± 323 µg/L | Slight, non-significant decrease in serum Zn; possible systemic redistribution | [31] |
| Zinc (Zn) | Hair | 619.58 ± 262.50 µg/g | 459.30 ± 187.10 µg/g | Systemic redistribution; oxidative shift in hair Zn levels | [87] |
| Zinc (Zn) | Adult human brain | - | 10 µg/g | Post-mortem studies revealed excessive zinc depositions in the substantia nigra | [53,55] |
| Iron (Fe) | Serum | 949 ± 325 µg/L | 1130 ± 428 µg/L | Iron dysregulation is associated with oxidative stress and mitochondrial injury | [31] |
| Iron (Fe) | Hair | 50.98 ± 11.84 µg/g | 72.6 ± 44.8 µg/g | Reduced Fe levels linked to neurodegenerative stress | [87] |
| Copper (Cu) | Serum | 1116 ± 258 µg/L | 1152 ± 282 µg/L | Minor systemic fluctuation; no clear trend; localized brain Cu accumulation | [47] |
| Manganese (Mn) | Serum | 1.27 ± 0.81 µg/L | 2.02 ± 0.50 µg/L | Substantial serum Mn reduction correlating with environmental and mitochondrial impact | [31] |
| Selenium (Se) | Serum | 73.0 ± 18.3 µg/L | 109.8 ± 16.9 µg/L | Se depletion associated with impaired antioxidant defense in PD | [66] |
3.5. Prophylactic and Therapeutic Implications
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tyczyńska, M.; Gędek, M.; Brachet, A.; Stręk, W.; Flieger, J.; Teresiński, G.; Baj, J. Trace Elements in Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia: The Current State of Knowledge. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, S.; Liu, P.; Wang, X.; Li, K. Global, regional and national burden of Parkinson’s disease in people over 55 years of age: A systematic analysis of the global burden of disease study, 1991–2021. BMC Neurol. 2025, 25, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, H.; Dehghani, F.; Ramezan, M.; Gannaban, R.B.; Haque, Z.F.; Rahimi, F.; Abbasi, S.; Shin, A.C. Revisiting the Role of Vitamins and Minerals in Alzheimer’s Disease. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, C.; Onose, G.; Rotariu, M.; Poștaru, M.; Turnea, M.; Galaction, A.I. Role of Microbiota-Derived Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) in Modulating the Gut–Brain Axis: Implications for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease Pathogenesis. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zippenfening, H.A.; Matichescu, M.L.; Raducan, M.R.; Amaricai, E. Postural Analysis in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease and the Importance of Physical Exercise for Postural Correction. Balneo PRM Res. J. 2023, 14, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oancea, C.; Mihai, C.; Gherman, D.; Milicescu, M.; Ancuta, I.; Martin, A.; Bojinca, M.; Stoica, V.; Ciuvica, M.M. Development of a prognostic score for work disability in Romanian patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Disabil. Rehabil. 2015, 37, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condurache, I.; Filip, G.; Ancuța, P.; Turnea, M.; Rotariu, M.; Ionițe, C. The importance of a multidisciplinary approach to improve the life quality for patients with Parkinson’s disease. Balneo PRM Res. J. 2022, 13, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moos, W.H.; Faller, D.V.; Glavas, I.P.; Kanara, I.; Kodukula, K.; Pernokas, J.; Pernokas, M.; Pinkert, C.A.; Powers, W.R.; Sampani, K. Epilepsy: Mitochondrial connections to the ‘Sacred’ disease. Mitochondrion 2023, 72, 84–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankovic, J.; Tan, E.K. Parkinson’s disease: Etiopathogenesis and treatment. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 91, 795–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrer, N.; Vaknine-Treidel, S.; Zorbaz, T.; Tzur, Y.; Bennett, E.R.; Drori, P.; Suissa, N.; Greenberg, D.S.; Lerner, E.; Soreq, E. Pre-symptomatic Parkinson’s disease blood test quantifying repetitive sequence motifs in transfer RNA fragments. Nat. Aging 2025, 5, 868–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica, S.I.; Bleotu, C.; Ciobanu, V.; Ionescu, A.M.; Albadi, I.; Onose, G.; Munteanu, C. Considerations about Hypoxic Changes in Neuraxis Tissue Injuries and Recovery. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doroszkiewicz, J.; Farhan, J.A.; Mroczko, J.; Winkel, I.; Perkowski, M.; Mroczko, B. Common and Trace Metals in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prashanth, L.; Kattapagari, K.; Chitturi, R.; Baddam, V.R.; Prasad, L. A review on role of essential trace elements in health and disease. J. Dr. NTR Univ. Health Sci. 2015, 4, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeuwenburgh, C.; Heinecke, J.W. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Exercise. Curr. Med. Chem. 2001, 8, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, N.R.; Nandan, D.; Nair, B.G.; Nair, V.A.; Venugopal, P.; Aradhya, R. Oxidative Stress and Redox Imbalance: Common Mechanisms in Cancer Stem Cells and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Cells 2025, 14, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawahara, M.; Kato-Negishi, M.; Tanaka, K.I. Dietary Trace Elements and the Pathogenesis of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, Y.; Liao, W.; Liang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, M.; Guo, Y.; Sin, Q.; Tang, J.; Wang, Z. Environmental pollutants induce NLRP3 inflammasome activation and pyroptosis: Roles and mechanisms in various diseases. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 900, 165851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulos, C.; Yaghi, N.; El Hayeck, R.; Heraoui, G.N.; Fakhoury-Sayegh, N. Nutritional risk factors, microbiota and parkinson’s disease: What is the current evidence? Nutrients 2019, 11, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ren, N.; Cai, Z.; Lin, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, S.; Li, H. Paraquat and MPTP induce neurodegeneration and alteration in the expression profile of microRNAs: The role of transcription factor Nrf2. npj Park. Dis. 2017, 3, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyazı, O.; Korkmaz, D.; Cevher, S.C. Experimental Parkinson models and green chemistry approach. Behav. Brain Res. 2024, 471, 115092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Liu, D.S.; Zhang, Y.B.; Rong, H.; Zhang, X.J. The interaction between alpha-synuclein and mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Biophys. Chem. 2023, 303, 107122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzyzanowski, B.; Mullan, A.F.; Turcano, P.; Camerucci, E.; Bower, J.H.; Savica, R. Air Pollution and Parkinson Disease in a Population-Based Study. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2433602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naliyadhara, N.; Kumar, A.; Kumar Gangwar, S.; Nair Devanarayanan, T.; Hegde, M.; Alqahtani, M.S.; Abbas, M.; Sethi, G.; Kunnumakkara, A. Interplay of dietary antioxidants and gut microbiome in human health: What has been learnt thus far? J. Funct. Foods 2023, 100, 105365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, C.; Galaction, A.I.; Turnea, M.; Blendea, C.D.; Rotariu, M.; Poștaru, M. Redox Homeostasis, Gut Microbiota, and Epigenetics in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Systematic Review. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Shen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, L.; Ma, X.; Song, N.; Xie, J. Homeostasis and metabolism of iron and other metal ions in neurodegenerative diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, J.A.; Musgrove, M.L.; White, S.J.O. Outlining Potential Biomarkers of Exposure and Effect to Critical Minerals: Nutritionally Essential Trace Elements and the Rare Earth Elements. Toxics 2023, 11, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandru, I. The role of sodium in the body stantin. Balneo-Res. J. 2011, 2, 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- Pop, M.S.; Cheregi, D.C.; Onose, G.; Munteanu, C.; Popescu, C.; Rotariu, M.; Turnea, M.-A.; Dogaru, G.; Ionescu, E.V.; Oprea, D.; et al. Exploring the Potential Benefits of Natural Calcium-Rich Mineral Waters for Health and Wellness: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquès, M.; Correig, E.; Capdevila, E.; Gargallo, E.; González, N.; Nadal, M.; Domingo, J.L. Essential and Non-essential Trace Elements in Milks and Plant-Based Drinks. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 4524–4533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellein, K.; Syversen, T.; Steinnes, E.; Nilsen, T.I.L.; Dahl, O.P.; Mitrovic, S.; Duraj, D.; Flaten, T.P. Trace elements in serum from patients with Parkinson’s disease—A prospective case-control study. The Nord-Trøndelag Health Study (HUNT). Brain Res. 2008, 1219, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahhob, Q.R.; Al-Sanaf, A.E.; Mohammed, N.Y.; Abbas, H.J.; Ibrahim, Z.J.; Najim, M.K.; Malik, Z.A.; Budaiwi, Z.K.; Abdul-Jabbar, Z.H.; Kadhamk, M.J. Mineral and trace elements, dietary sources, biological effects, deficiency, and toxicity: A review. Eurasian Chem. Commun. 2023, 5, 536–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues da Silva, R.; Larson, J.; Bothner, B.; DuBois, J.L. Heme and iron limitation in a GI-tract foundation species leads to a reshuffling of the metalloproteome and a shift toward manganese usage. Front. Chem. 2025, 13, 1562189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodirov, S.A. Comparison of Superoxide Dismutase Activity at the Cell, Organ, and Whole-Body Levels. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magro, G.; Laterza, V.; Tosto, F.; Torrente, A. Manganese Neurotoxicity: A Comprehensive Review of Pathophysiology and Inherited and Acquired Disorders. J. Xenobiot. 2025, 15, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetter, V.M.; Demircan, K.; Homann, J.; Chillon, T.S.; Mülleder, M.; Shomroni, O.; Steinhagen-Thiessen, E.; Ralser, M.; Lill, C.M.; Bertram, L. Low blood levels of selenium, selenoprotein P and GPx3 are associated with accelerated biological aging: Results from the Berlin Aging Study II (BASE-II). Clin. Epigenet. 2025, 17, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baj, J.; Flieger, W.; Barbachowska, A.; Kowalska, B.; Flieger, M.; Forma, A.; Karakuła, K.; Tyśkiewicz, K.; Radzikowska, E.; Sitarz, R.; et al. Consequences of Disturbing Manganese Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Hernández, M.I.; Acosta-Saavedra, L.C.; Hernández-Kelly, L.C.; Loaeza-Loaeza, J.; Ortega, A. Microglial Activation in Metal Neurotoxicity: Impact in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Biomed. Res. Int. 2023, 2023, 7389508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmari, A. Blood-Brain Barrier Overview: Structural and Functional Correlation. Neural Plast. 2021, 2021, 6564585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.; Kotzur, R.; Richter, F. Blood–brain barrier alterations and their impact on Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis and therapy. Transl. Neurodegener. 2024, 13, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Huang, P.; Wu, Y.; Liu, T.; Shao, N.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J. Engineered Selenium/Human Serum Albumin Nanoparticles for Efficient Targeted Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease via Oral Gavage. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 19961–19980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillemoen, P.K.S.; Bjørke-Monsen, A.L. Ernæringsstatus av vitamin og sporelement. Tidsskr. Nor. Laegeforening 2020, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, R. Neural energy coding patterns of dopaminergic neural microcircuit and its impairment in major depressive disorder: A computational study. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2025, 21, e1012961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura, J.P.; Oliveira, P.J.; Urbano, A.M. Mitochondrial classic metabolism and its often-underappreciated facets. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2025, 1871, 167839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Xu, K.; Ge, J.; Luo, X.; Wu, M.; Wang, N.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q. Targeting Ferroptosis in Parkinson’s Disease: Mechanisms and Emerging Therapeutic Strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapiero, H.; Tew, K.D. Trace elements in human physiology and pathology: Zinc and metallothioneins. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2003, 57, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Cen, Y.; Xiong, L.; Hong, G.; Luo, Y.; Luo, X. Dietary Copper Intake and Risk of Parkinson’s Disease: A Cross-sectional Study. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2024, 202, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, T.A.; Chand, J.; Kandy, A.T.; Antony, S.; Subramanian, G. Unravelling the Proteinopathic Engagement of α-Synuclein, Tau, and Amyloid Beta in Parkinson’s Disease: Mitochondrial Collapse as a Pivotal Driver of Neurodegeneration. Neurochem. Res. 2025, 50, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L. Association between food insecurity and risk of Parkinson’s disease: Insights from NHANES data. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2025, 29, 100464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, H.; Safargar, M.; Găman, M.A.; Akhgarjand, C.; Prabahar, K.; Zarezadeh, H.; Chan, X.Y.; Jamilian, P.; Kord-Varkaneh, H. Association of Higher Intakes of Dietary Zinc with Higher Ferritin or Hemoglobin: A Cross-sectional Study from NHANES (2017–2020). Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoofs, H.; Schmit, J.; Rink, L. Zinc Toxicity: Understanding the Limits. Molecules 2024, 29, 3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.G.; Wu, T.Y.; Zhao, L.X.; Jia, R.J.; Ren, H.; Hou, W.J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Q.; Wang, X.; et al. From zinc homeostasis to disease progression: Unveiling the neurodegenerative puzzle. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 199, 107039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, J.; Ouagazzal, A.M. Synaptic zinc: An emerging player in Parkinson’s disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, A. Postmortem studies in Parkinson’s disease. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2004, 6, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wei, R.; Yong, V.W.; Xue, M. The Important Role of Zinc in Neurological Diseases. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jin, M.; Xie, M.; Yang, Y.; Xue, F.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Q. Protective role of antioxidant supplementation for depression and anxiety: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 323, 264–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babić Leko, M.; Langer Horvat, L.; Španić Popovački, E.; Zubčić, K.; Hof, P.R.; Šimić, G. Metals in Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, K.; Khan, H.; Kanojia, N.; Singh, T.G.; Kaur, A.; Kaur, G. Therapeutic Insights on Ferroptosis in Parkinson’s disease. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 930, 175133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambe, T.; Hashimoto, A.; Fujimoto, S. Current understanding of ZIP and ZnT zinc transporters in human health and diseases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 3281–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Liu, T.; Wei, J. Parkinson’s Disease: The Neurodegenerative Enigma Under the “Undercurrent” of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Różaniecka-Zwolińska, K.; Cholewińska, E.; Fotschki, B.; Juśkiewicz, J.; Ognik, K. Manganese deficiency or dietary manganese(III) oxide nanoparticle supplementation: Consequences for hematology, and intestinal and brain immunity in rats. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1528770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Huang, S.; Liu, Y.; Wan, C.; Gu, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, X. Manganese promotes α-synuclein amyloid aggregation through the induction of protein phase transition. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 101469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, S.; Rokad, D.; Malovic, E.; Luo, J.; Harischandra, D.S.; Jin, H.; Anantharam, V.; Kanthasamy, A.; Kanthasamy, A.G. Manganese activates NLRP3 inflammasome signaling and propagates exosomal release of ASC in microglial cells. Sci. Signal 2019, 12, eaat9900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markiv, B.; Expósito, A.; Ruiz-Azcona, L.; Santibáñez, M.; Fernández-Olmo, I. Environmental exposure to manganese and health risk assessment from personal sampling near an industrial source of airborne manganese. Environ. Res. 2023, 224, 115478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, S.; Zhang, M.; Tang, S.; Li, M.; Wu, R.; Wan, S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, H. Effects and Impact of Selenium on Human Health, A Review. Molecules 2025, 30, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salaramoli, S.; Joshaghani, H.R.; Shoeibi, A.; Hashemy, S.I. Selenium and selenoproteins role in Parkinson’s disease: Is there a link between selenoproteins and accumulated alpha-synuclein? J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2024, 81, 127344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyka, P.; Garbo, S.; Fioravanti, R.; Jacob, C.; Hittinger, M.; Handzlik, J.; Kowalski, M.; Nowak, M.; Zieliński, T.; Kaczmarek, M. Selenium-containing compounds: A new hope for innovative treatments in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Drug Discov. Today 2024, 29, 104062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehri, A. Trace elements in human nutrition (II)—An update. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2020, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liuzzi, G.M.; Petraglia, T.; Latronico, T.; Crescenzi, A.; Rossano, R. Antioxidant Compounds from Edible Mushrooms as Potential Candidates for Treating Age-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Kukreti, R.; Saso, L.; Kukreti, S. Oxidative stress: A key modulator in neurodegenerative diseases. Molecules 2019, 24, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyatha, S.; Kim, H.; Lee, D.; Kim, K. Association between Heavy Metal Exposure and Parkinson’s Disease: A Review of the Mechanisms Related to Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Luo, X.; Yin, Y.; Thomas, E.R.; Liu, K.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Huang, Z.; Zhao, Y. The interplay of iron, oxidative stress, and α-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease progression. Mol. Med. 2025, 31, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Aguirre, M.; Balzano, T.; Monje, M.H.G.; Esteban-García, N.; Martínez-Fernández, R.; Del Rey, N.L.; Ciorraga, M.; Sánchez-Ferro, A.; Trigo-Damas, I.; Blesa, J.; et al. Nigrostriatal iron accumulation in the progression of Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Park. Dis. 2025, 11, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.T.T.; Peng, T.Y.; Nguyen, T.H.; Bui, T.N.H.; Wang, C.S.; Lee, W.J.; Lin, C.H.; Huang, Y.C.; Chen, Y.L.; Hsu, Y.C.; et al. The crosstalk between copper-induced oxidative stress and cuproptosis: A novel potential anticancer paradigm. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binolfi, A.; Quintanar, L.; Bertoncini, C.W.; Griesinger, C.; Fernández, C.O. Bioinorganic chemistry of copper coordination to alpha-synuclein: Relevance to Parkinson’s disease. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2012, 256, 2188–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Firdous, S.M. Unrevealing the molecular mechanisms of MPTP-induced Parkinson’s in experimental animals. Med. Chem. Res. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, D.H.; Han, S.J.; Son, I. The Multifaceted Role of LRRK2 in Parkinson’s Disease. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.Y.; Yuan, X.L.; Jiang, J.M.; Zhang, P.; Tan, K. Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome in Parkinson’s disease: From molecular mechanism to therapeutic strategy. Exp. Neurol. 2025, 386, 115167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidović, M.; Rikalovic, M.G. Alpha-Synuclein Aggregation Pathway in Parkinson’s Disease: Current Status and Novel Therapeutic Approaches. Cells 2022, 11, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Xiao, X.; Bi, M.; Jiao, Q.; Chen, X.; Yan, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Sun, F. Modulating α-synuclein propagation and decomposition: Implications in Parkinson’s disease therapy. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 98, 102319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, S.; Sato, S.; Yamakado, H.; Takahashi, R.; Hattori, N. Enhanced alpha-synuclein pathology and exacerbated motor dysfunction in alpha-synuclein transgenic mice with autophagy deficiency. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2025, 758, 151514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wen, X.; Jiang, H.; Wang, J.; Song, N.; Xie, J. Interactions between iron and α-synuclein pathology in Parkinson’s disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 141, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, K.; Kaur, P.; Gupta, G.D.; Singh, S. Metals associated neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease: Insight to physiological, pathological mechanisms and management. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 753, 135873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokad, D.; Harischandra, D.S.; Samidurai, M.; Chang, Y.T.; Luo, J.; Lawana, V.; Sarkar, S.; Jin, H.; Anantharam, V.; Kanthasamy, A.G. Manganese Exposure Enhances the Release of Misfolded α-Synuclein via Exosomes by Impairing Endosomal Trafficking and Protein Degradation Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenlla, C.; Lazaro-Hernandez, C.; Fernandez, M.; Perez-Montesino, J.; De Mena, L.; Bargallo, N.; Ezquerra, C.; Martí, L.; Marti, M.J.; Tolosa, Y. Biomarkers of neurodegenerative parkinsonisms: From current clinical to future biological definitions—Literature review and our experience. Neurol. Neurochir. Pol. 2025, 59, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Vestergren, R.; Zhou, Z.; Liang, Y.; Cai, Y. Using hair, nail and urine samples for human exposure assessment of legacy and emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos, A.B.; Kohlmeier, K.A.; Rocha, M.E.; Barreto, G.E.; Barreto, J.A.; de Souza, A.C.A.; de Oliveira, C.F.; Parente, A.; Bezerra, M.F. Hair in Parkinson’s disease patients exhibits differences in Calcium, Iron and Zinc concentrations measured by flame atomic absorption spectrometry—FAAS. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2018, 47, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hao, X.; Yan, J.; Xu, J.; Hu, D.; Ji, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, J. Urine biomarkers discovery by metabolomics and machine learning for Parkinson’s disease diagnoses. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 108230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujral, J.; Gandhi, O.H.; Singh, S.B.; Ahmed, M.; Ayubcha, C.; Werner, T.J.; Mashhoon, J.; Zhuang, H.; Alavi, A.M.; Basu, S. PET, SPECT, and MRI imaging for evaluation of Parkinson’s disease. Am. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2024, 14, 371–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.M.; Wang, Z.Y.; Liang, Y.Y.; Hao, C.W.; Shi, C.H. Digital biomarkers for precision diagnosis and monitoring in Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Digit. Med. 2024, 7, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montvydaitė-Kreivaitienė, O.; Kubilius, R.; Burbulytė, A.; Strašunskas, K.; Klėgėrienė, M. Comparative efficacy of mineral water and mud therapy vs standard rehabilitative interventions: A systematic review of osteoarthritis studies from 2000. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munteanu, C.; Teoibas-Serban, D.; Iordache, L.; Balaurea, M.; Blendea, C.D. Water intake meets the Water from inside the human body—Physiological, cultural, and health perspectives-Synthetic and Systematic literature review. Balneo PRM Res. J. 2021, 12, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoteteu, M.; Munteanu, C.; Ionescu, E.V.; Almășan, R.E. Bioactive substances of the Techirghiol therapeutic mud. Balneo Res. J. 2018, 9, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phokaewvarangkul, O.; Markaki, I.; Moes, H.R.; Petrovic, I.; Schrag, A.; Bhidayasiri, R. Vital nutrition: Enhancing health in advanced Parkinson’s disease with device-aided therapies. J. Neural Transm. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.A.; Anwar, S.; Yunusa, B.M.; Nayik, G.A.; Mousavi Khaneghah, A. The potential of apricot seed and oil as functional food: Composition, biological properties, health benefits & safety. Food Biosci. 2023, 51, 102336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrozek, W.; Socha, J.; Sidorowicz, K.; Skrok, A.; Syrytczyk, A.; Piątkowska-Chmiel, I.; Lis, M.; Kaczor, D.; Kostrzewa, M.; Wolska, A. Pathogenesis and treatment of depression: Role of diet in prevention and therapy. Nutrition 2023, 115, 112143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez, M.T.; Chana-Cuevas, P. New perspectives in iron chelation therapy for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Pharmaceuticals 2018, 11, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Wang, K.; Zhao, X.; Song, B.; Yao, T.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, H.; Lin, J.; Wu, F. Emerging insights into cuproptosis and copper metabolism: Implications for age-related diseases and potential therapeutic strategies. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2024, 16, 1335122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.; Hivare, P.; Solanki, R.; Gupta, S.; Bhatia, D.D. Applications of Bionanomaterials in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Mater. Adv. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Zhang, X.; Du, L.; Ye, M.; Lu, Y.; Xue, J.; Chen, Q.; Li, L.; Zhao, W.; Sun, Y. Molecular imaging nanoprobes for theranostic applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 186, 114320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogra, N.; Jakhmola Mani, R.; Pande Katare, D. Tiny Carriers, Tremendous Hope: Nanomedicine in the Fight against Parkinson’s. J. Dement. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2024, 1, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, M.; Lv, L.; Hu, S.; Qin, L.; Wang, C. Sarcopenia in Parkinson’s disease: From pathogenesis to interventions. Metabolism 2025, 169, 156272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, C.T.; Shiu, Y.L.; Chen, C.A.; Lin, H.Y.; Huang, Y.L.; Lin, C.C. Changes in levels of copper, iron, zinc, and selenium in patients at different stages of chronic kidney disease. Genom. Med. Biomark. Health Sci. 2012, 4, 128–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pan, T.T.; Huang, J.Y.; Wang, X.D.; Chen, D.Z.; Chen, Y.P. Copper’s dual role: Reviewing its impact on liver health and disease. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 152, 114391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra Sekar, P.K.; Thomas, S.M.; Veerabathiran, R. An overview of the role of monoamine oxidase-B in Parkinson’s disease: Implications for neurodegeneration and therapy. Explor. Neuroprot. Ther. 2024, 4, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, A.-H.; Mohamed, W. Nutrigenomics and Trace Elements: Hopes and Hypes for Parkinson’s Treatment. In Trace Elements in Brain Health and Diseases; Springer: Singapore, 2023; pp. 47–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forero-Rodríguez, L.J.; Josephs-Spaulding, J.; Flor, S.; Pinzón, A.; Kaleta, C. Parkinson’s disease and the metal–microbiome–gut–brain axis: A systems toxicology approach. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasilewski, A.; Wasilewska, E.; Serrafi, A. Exploring Diagnostic Markers and Therapeutic Targets in Parkinson’s Disease: A Comprehensive 1H-NMR Metabolomic Analysis—Systematic Review. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2025, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Huang, X.; Geng, X.; Wang, F. Meta-analysis of iron metabolism markers levels of Parkinson’s disease patients determined by fluid and MRI measurements. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2023, 78, 127190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, K.; Liu, M.Y.; Zhong, X.; Wei, M.J. Decreased circulating Zinc levels in Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adani, G.; Filippini, T.; Michalke, B.; Vinceti, M. Selenium and Other Trace Elements in the Etiology of Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Case-Control Studies. Neuroepidemiology 2020, 54, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Popescu, C.; Munteanu, C.; Spînu, A.; Andone, I.; Bistriceanu, R.; Postoiu, R.; Suciu, A.; Giuvara, S.; Vlădulescu-Trandafir, A.-I.; Aurelian, S.M.; et al. Actual Data on Essential Trace Elements in Parkinson’s Disease. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1852. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111852
Popescu C, Munteanu C, Spînu A, Andone I, Bistriceanu R, Postoiu R, Suciu A, Giuvara S, Vlădulescu-Trandafir A-I, Aurelian SM, et al. Actual Data on Essential Trace Elements in Parkinson’s Disease. Nutrients. 2025; 17(11):1852. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111852
Chicago/Turabian StylePopescu, Cristina, Constantin Munteanu, Aura Spînu, Ioana Andone, Roxana Bistriceanu, Ruxandra Postoiu, Andreea Suciu, Sebastian Giuvara, Andreea-Iulia Vlădulescu-Trandafir, Sorina Maria Aurelian, and et al. 2025. "Actual Data on Essential Trace Elements in Parkinson’s Disease" Nutrients 17, no. 11: 1852. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111852
APA StylePopescu, C., Munteanu, C., Spînu, A., Andone, I., Bistriceanu, R., Postoiu, R., Suciu, A., Giuvara, S., Vlădulescu-Trandafir, A.-I., Aurelian, S. M., Pop, N. L., Ciobanu, V., & Onose, G. (2025). Actual Data on Essential Trace Elements in Parkinson’s Disease. Nutrients, 17(11), 1852. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111852








