Cinnamomum cassia Alleviates Neuropsychiatric Lupus in a Murine Experimental Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Animals and Experimental Protocol
2.2. Behavioral Testing
2.3. Histological Assessment
2.4. Western Blotting
2.5. Immunoprecipitation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cinnamon Supplementation Attenuates Lupus Nephritis
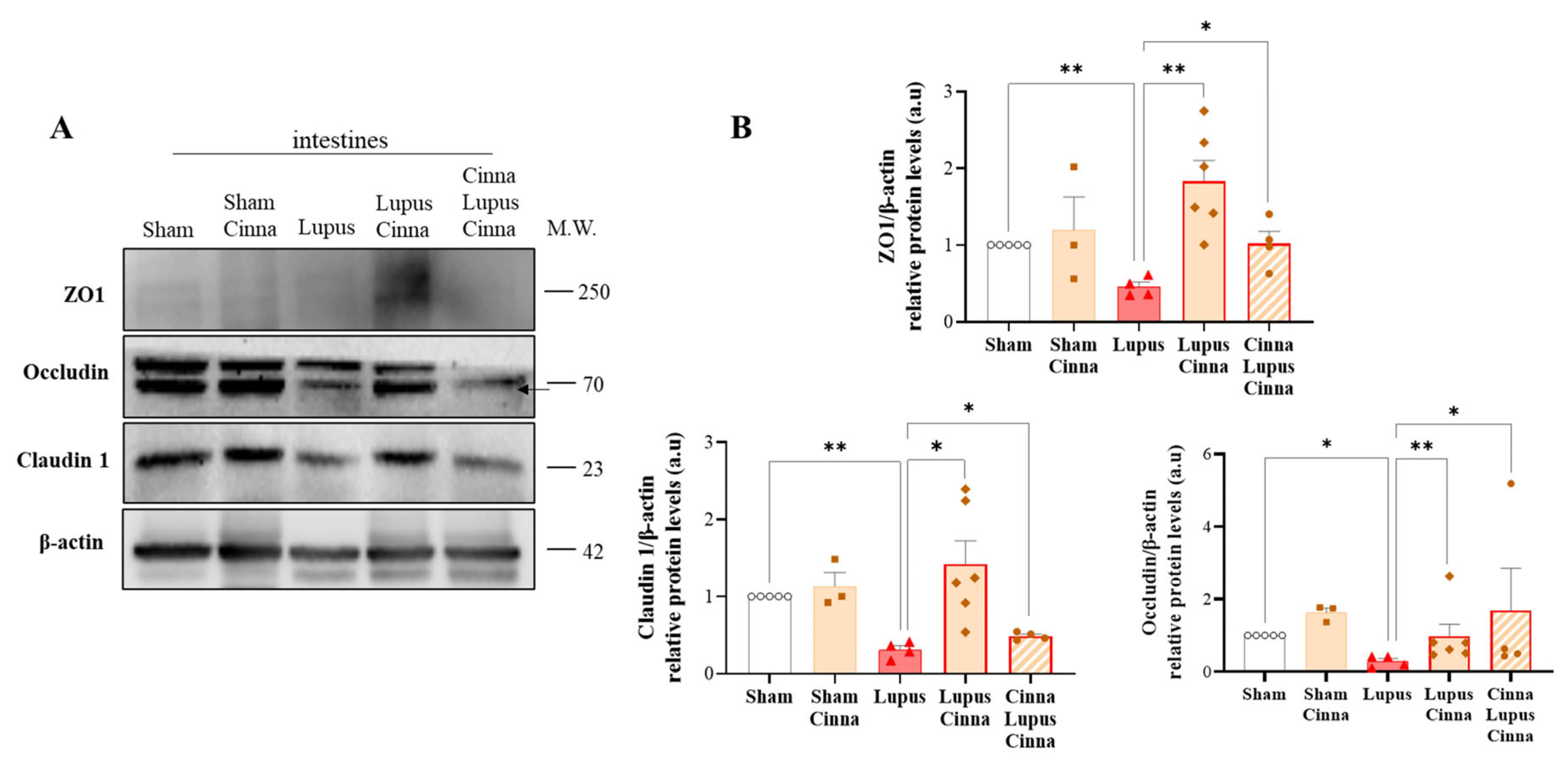
3.2. Cinnamon Supplementation Modulates Intestinal Tight Junction Proteins in Lupus
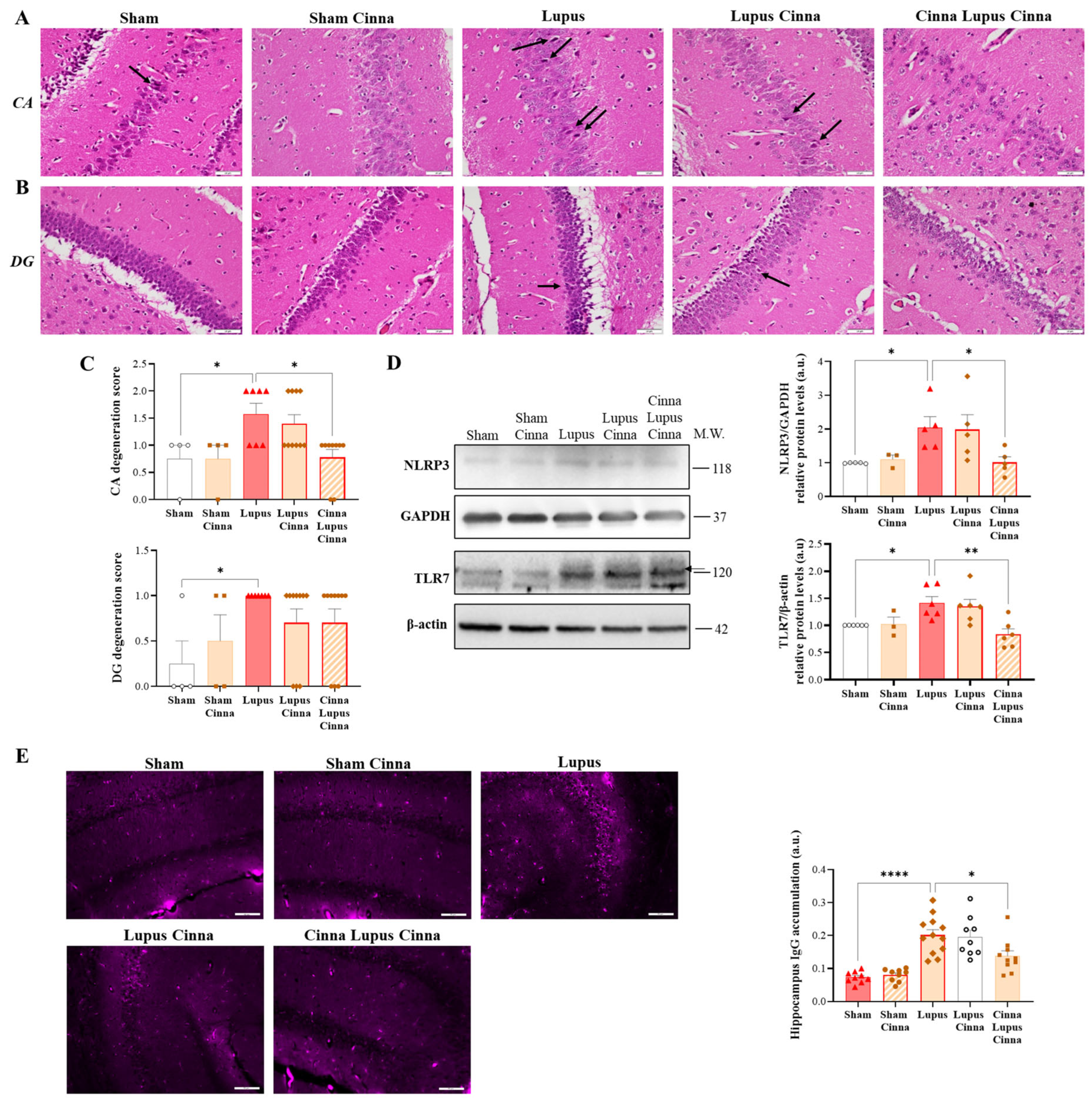
3.3. Cinnamon Ameliorates Brain Histopathology and Inflammatory Markers in Lupus
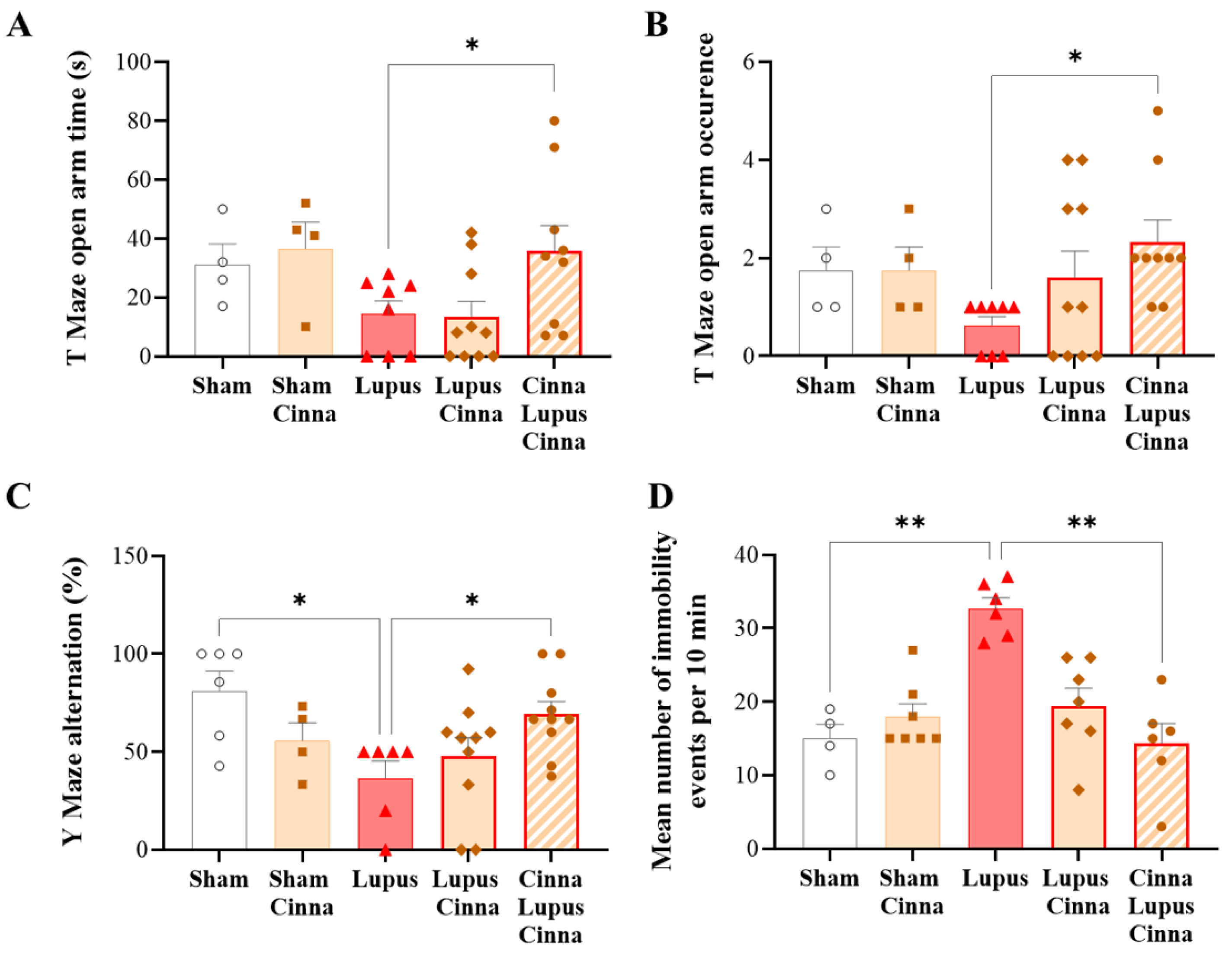
3.4. Cinnamon Improves Behavioral Impairment in Lupus
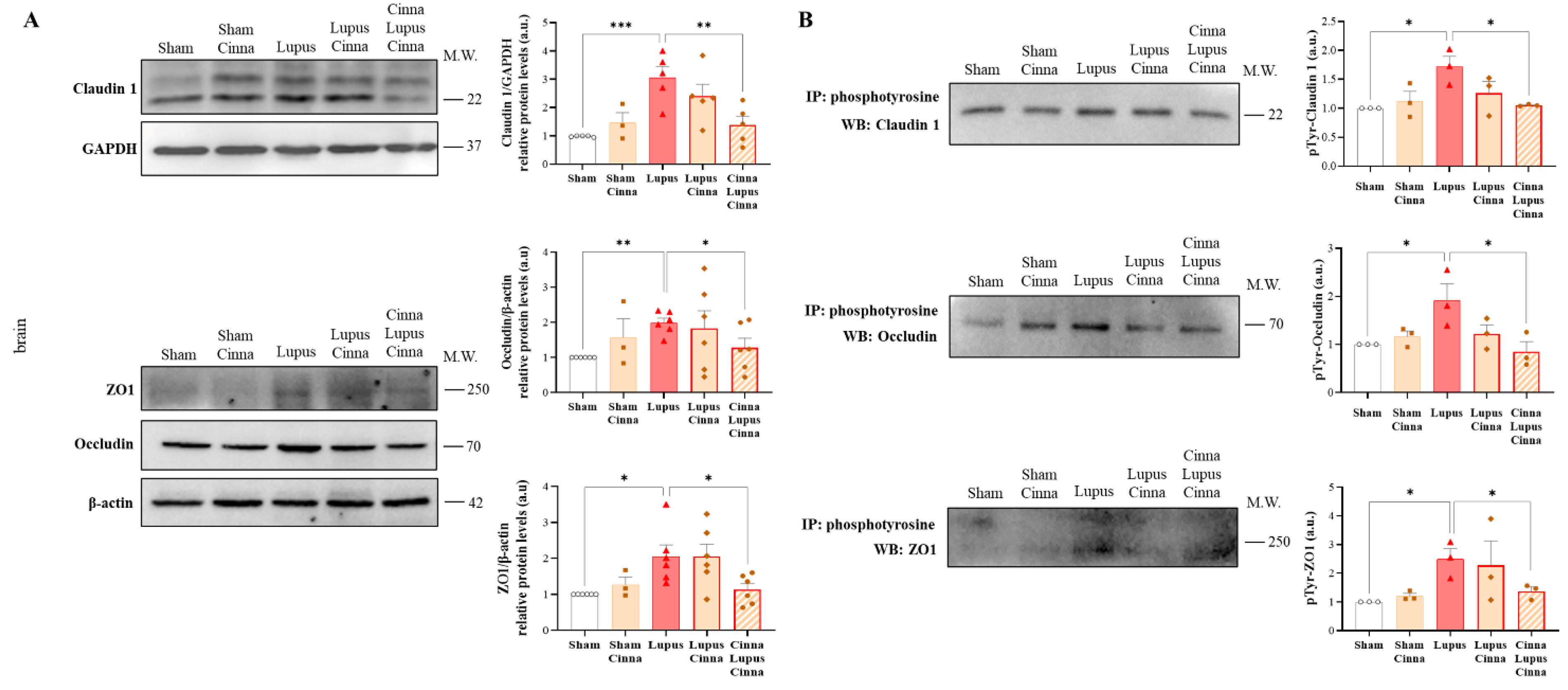
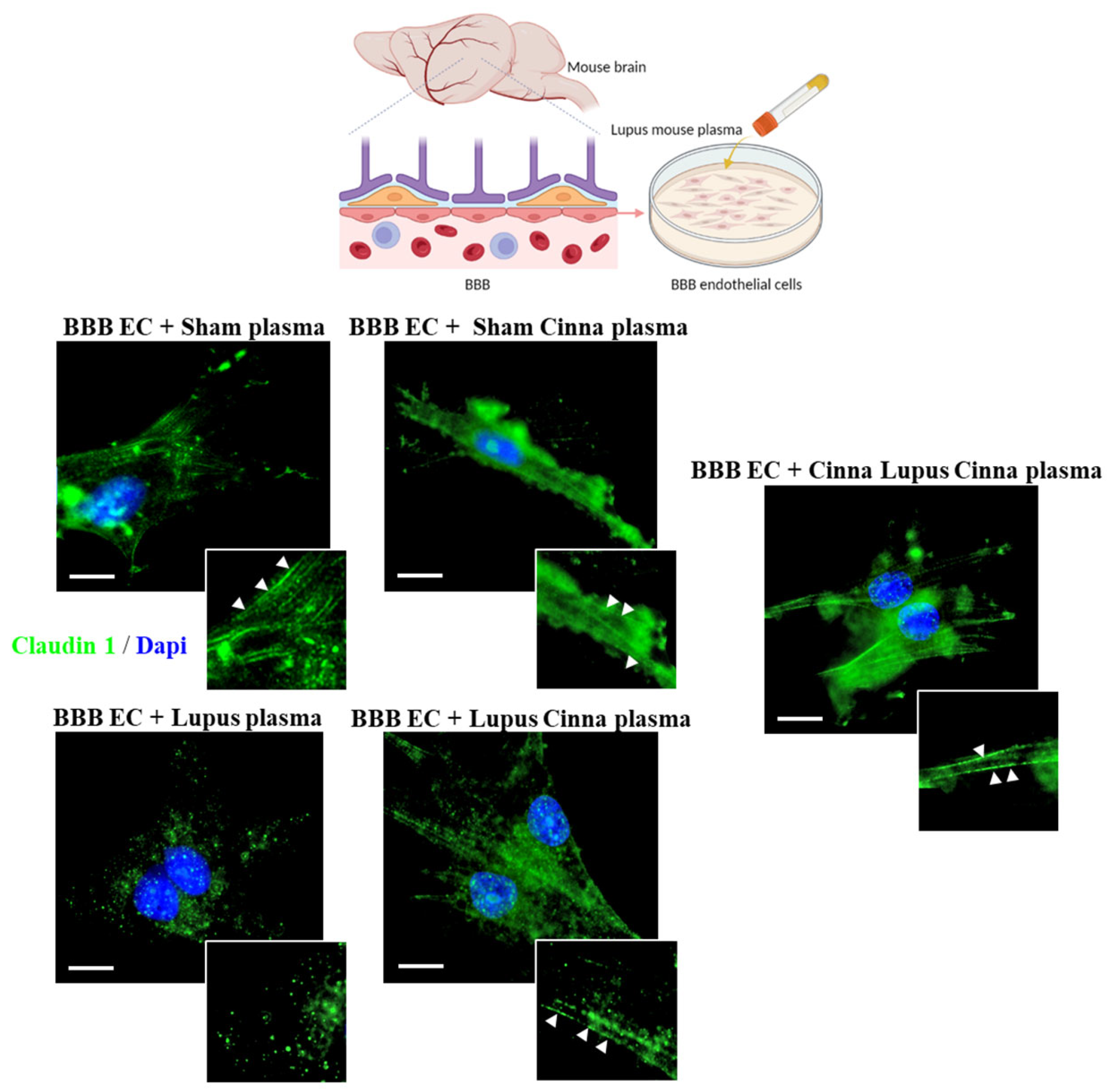
3.5. Cinnamon Modulates Brain Tight Junctions in Lupus
3.6. Cinnamaldehyde Interacts with TLR7
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TJ | Tight junctions |
| BBB | blood brain barrier |
| ZO-1 | Zonula occludens-1 |
| TLR | Toll-like receptors |
| S | Sham |
| L | Lupus |
| LC | Lupus Cinna |
| CLC | Cinna Lupus Cinna |
References
- Kim, J.-W.; Kim, H.-A.; Suh, C.-H.; Jung, J.-Y. Sex Hormones Affect the Pathogenesis and Clinical Characteristics of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 906475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujieda, Y. Diversity of Neuropsychiatric Manifestations in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Immunol. Med. 2020, 43, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertsias, G.K.; Boumpas, D.T. Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Management of Neuropsychiatric SLE Manifestations. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2010, 6, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeltsch-David, H.; Muller, S. Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Cognitive Dysfunction: The MRL-Lpr Mouse Strain as a Model. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokogawa, M.; Takaishi, M.; Nakajima, K.; Kamijima, R.; Fujimoto, C.; Kataoka, S.; Terada, Y.; Sano, S. Epicutaneous Application of Toll-like Receptor 7 Agonists Leads to Systemic Autoimmunity in Wild-Type Mice: A New Model of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 694–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moleón, J.; González-Correa, C.; Miñano, S.; Robles-Vera, I.; de la Visitación, N.; Barranco, A.M.; Gómez-Guzmán, M.; Sánchez, M.; Riesco, P.; Guerra-Hernández, E.; et al. Protective Effect of Microbiota-Derived Short Chain Fatty Acids on Vascular Dysfunction in Mice with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Induced by Toll like Receptor 7 Activation. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 198, 106997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Wang, H.; Lu, L.; Chen, J.; Cheng, Q.; Guo, M.; Hou, Y.; Dou, H. Hippocampal Microglia CD40 Mediates NPSLE Cognitive Dysfunction in Mice. J. Neuroimmunol. 2021, 357, 577620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, A.G.; Gaillard, P.J. Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction and Recovery. J. Neural. Transm. 2006, 113, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, A.; Alexander, J.J. Complement and Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity. Mol. Immunol. 2014, 61, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, S.; Gutie Rrez-Díaz, I.; Lo Pez, P.; Suárez, A.; Fernández-Navarro, T.; Sánchez, B.; Margolles, A. Microbiota and Oxidant-Antioxidant Balance in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Nutr. Hosp. 2017, 34, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-P.; Hsu, T.-C.; Hsu, G.-J.; Li, S.-L.; Tzang, B.-S. Cystamine Attenuates the Expressions of NOS- and TLR-Associated Molecules in the Brain of NZB/W F1 Mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 607, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Hölscher, C. GIP Has Neuroprotective Effects in Alzheimer and Parkinson’s Disease Models. Peptides 2020, 125, 170184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Kim, J.Y. Cinnamon Subcritical Water Extract Attenuates Intestinal Inflammation and Enhances Intestinal Tight Junction in a Caco-2 and RAW264.7 Co-Culture Model. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 4350–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Pahan, K. Cinnamon Ameliorates Experimental Allergic Encephalomyelitis in Mice via Regulatory T Cells: Implications for Multiple Sclerosis Therapy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahan, S.; Pahan, K. Can Cinnamon Spice down Autoimmune Diseases? J. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2020, 5, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, H.; An, J. Neuroprotective Effects of Natural Compounds on Neurotoxin-Induced Oxidative Stress and Cell Apoptosis. Nutr. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 1078–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, T.; Sato, H.; Wakamatsu, A.; Ohashi, R.; Ajioka, Y.; Uchiumi, T.; Goto, S.; Narita, I.; Kaneko, Y. Mood Disorder in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Induced by Antiribosomal P Protein Antibodies Associated with Decreased Serum and Brain Tryptophan. J. Immunol. 2021, 206, 1729–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Meng, X.; Zhou, P.; Yin, Z.; Xie, Q.; Zou, H.; Shen, N.; Ye, Z.; Tang, Y. Interferon-α Exacerbates Neuropsychiatric Phenotypes in Lupus-Prone Mice. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraeuter, A.-K.; Guest, P.C.; Sarnyai, Z. The Y-Maze for Assessment of Spatial Working and Reference Memory in Mice. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1916, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maalouly, G.; Hajal, J.; Noujeim, C.; Choueiry, M.; Nassereddine, H.; Smayra, V.; Saliba, Y.; Fares, N. New Insights in Gut-Liver Axis in Wild-Type Murine Imiquimod-Induced Lupus. Lupus 2021, 30, 926–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirén, J.; Pirhonen, J.; Julkunen, I.; Matikainen, S. IFN-Alpha Regulates TLR-Dependent Gene Expression of IFN-Alpha, IFN-Beta, IL-28, and IL-29. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 1932–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.J.; Sohn, K.-C.; Choi, D.-K.; Shi, G.; Hong, D.; Lee, H.-E.; Whang, K.U.; Lee, Y.H.; Im, M.; Lee, Y.; et al. Roles of TLR7 in Activation of NF-κB Signaling of Keratinocytes by Imiquimod. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovelock, D.F.; Liu, W.; Langston, S.E.; Liu, J.; Van Voorhies, K.; Giffin, K.A.; Vetreno, R.P.; Crews, F.T.; Besheer, J. The Toll-like Receptor 7 Agonist Imiquimod Increases Ethanol Self-Administration and Induces Expression of Toll-like Receptor Related Genes. Addict. Biol. 2022, 27, e13176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryanezhad, M.; Abdi, M.; Amini, S.; Hassanzadeh, K.; Valadbeigi, E.; Rahimi, K.; Izadpanah, E.; Moloudi, M.R. Cinnamomum Zeylanicum Extract Has Antidepressant-like Effects by Increasing Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) and Its Receptor in Prefrontal Cortex of Rats. Avicenna J. Phytomed. 2021, 11, 302–313. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Lei, Y.; Wang, R.; Wu, Z.; Wu, G. Cinnamicaldehyde Regulates the Expression of Tight Junction Proteins and Amino Acid Transporters in Intestinal Porcine Epithelial Cells. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 8, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, E.; Hoare, C.; Tanianis-Hughes, J.; Carlson, G.L.; Warhurst, G. Interferon Gamma Induces Translocation of Commensal Escherichia coli across Gut Epithelial Cells via a Lipid Raft-Mediated Process. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 1258–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.T.; Ghosh, C.; Hossain, M.; Linfield, D.; Rezaee, F.; Janigro, D.; Marchi, N.; van Boxel-Dezaire, A.H. IFN-γ, IL-17A, or Zonulin Rapidly Increase the Permeability of the Blood-Brain and Small Intestinal Epithelial Barriers: Relevance for Neuro-Inflammatory Diseases. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 507, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megur, A.; Baltriukienė, D.; Bukelskienė, V.; Burokas, A. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis and Alzheimer’s Disease: Neuroinflammation Is to Blame? Nutrients 2020, 13, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Campbell, M. Tight Junction Modulation at the Blood-Brain Barrier: Current and Future Perspectives. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2020, 1862, 183298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sladojevic, N.; Stamatovic, S.M.; Johnson, A.M.; Choi, J.; Hu, A.; Dithmer, S.; Blasig, I.E.; Keep, R.F.; Andjelkovic, A.V. Claudin-1-Dependent Destabilization of the Blood–Brain Barrier in Chronic Stroke. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 743–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleegal, M.A.; Hom, S.; Borg, L.K.; Davis, T.P. Activation of PKC Modulates Blood-Brain Barrier Endothelial Cell Permeability Changes Induced by Hypoxia and Posthypoxic Reoxygenation. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005, 289, H2012–H2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huppert, J.; Closhen, D.; Croxford, A.; White, R.; Kulig, P.; Pietrowski, E.; Bechmann, I.; Becher, B.; Luhmann, H.J.; Waisman, A.; et al. Cellular Mechanisms of IL-17-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigor, R.R.; Beard, R.S.; Litovka, O.P.; Yuan, S.Y. Interleukin-1β-Induced Barrier Dysfunction Is Signaled through PKC-θ in Human Brain Microvascular Endothelium. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2012, 302, C1513–C1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, K.; Partch, C.L. Analysis of Protein Stability and Ligand Interactions by Thermal Shift Assay. Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. 2015, 79, 28.9.1–28.9.14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maalouly, G.; Saliba, Y.; Hajal, J.; Zein-El-Din, A.; Fakhoury, L.; Najem, R.; Smayra, V.; Nassereddine, H.; Fares, N. Cinnamomum cassia Alleviates Neuropsychiatric Lupus in a Murine Experimental Model. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111820
Maalouly G, Saliba Y, Hajal J, Zein-El-Din A, Fakhoury L, Najem R, Smayra V, Nassereddine H, Fares N. Cinnamomum cassia Alleviates Neuropsychiatric Lupus in a Murine Experimental Model. Nutrients. 2025; 17(11):1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111820
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaalouly, Georges, Youakim Saliba, Joelle Hajal, Anna Zein-El-Din, Luana Fakhoury, Rouaa Najem, Viviane Smayra, Hussein Nassereddine, and Nassim Fares. 2025. "Cinnamomum cassia Alleviates Neuropsychiatric Lupus in a Murine Experimental Model" Nutrients 17, no. 11: 1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111820
APA StyleMaalouly, G., Saliba, Y., Hajal, J., Zein-El-Din, A., Fakhoury, L., Najem, R., Smayra, V., Nassereddine, H., & Fares, N. (2025). Cinnamomum cassia Alleviates Neuropsychiatric Lupus in a Murine Experimental Model. Nutrients, 17(11), 1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111820







