Ergogenic Effects of Combined Caffeine Supplementation and Motivational Music on Anaerobic Performance in Female Handball Players: A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Size Calculation
2.2. Ethics Approval
2.3. Participants
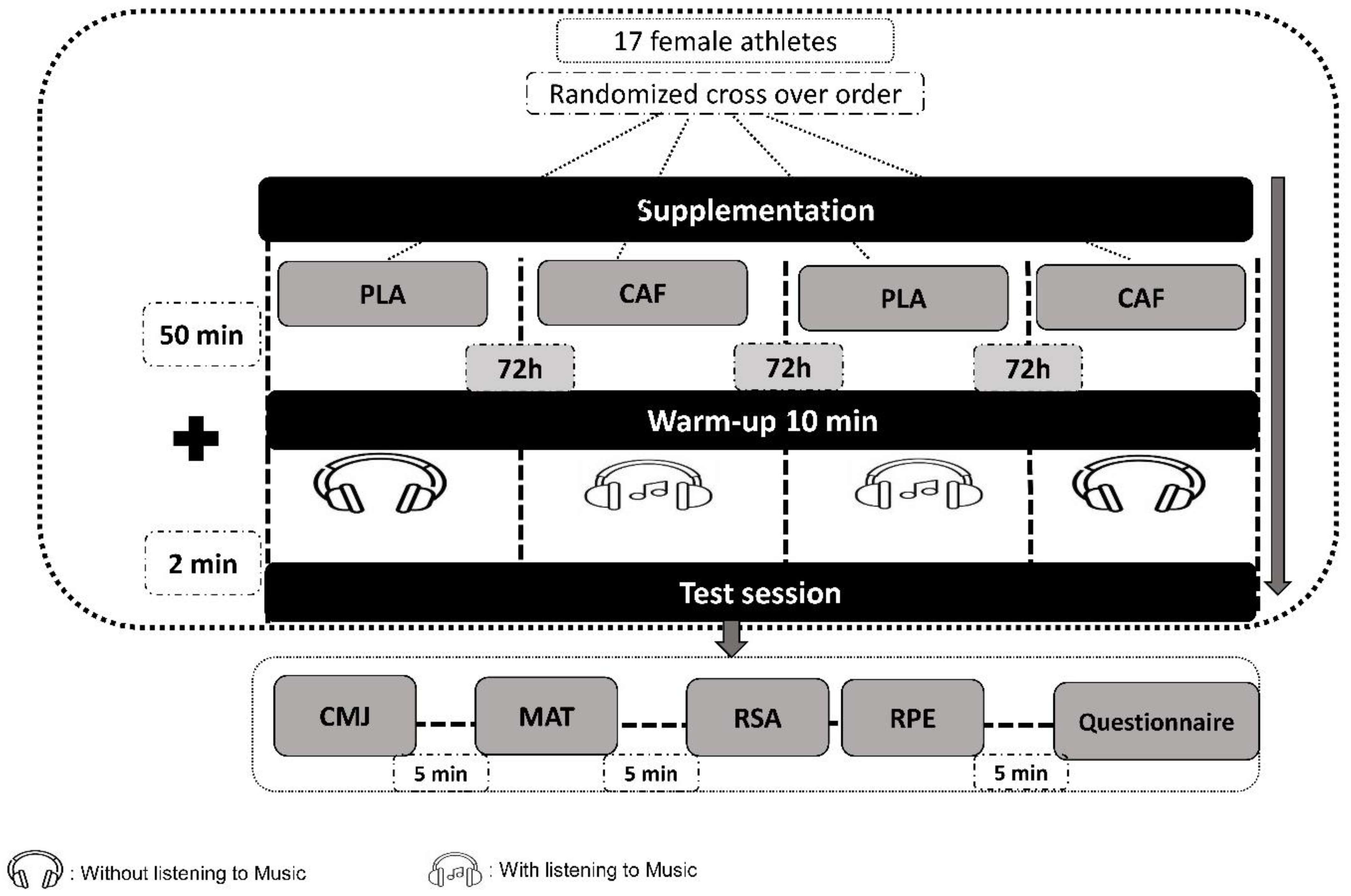
2.4. Experimental Protocol
2.4.1. Warm-Up Protocol
2.4.2. Music Protocol
2.4.3. CAF Administration Protocol
2.4.4. Blinding Protocol
2.4.5. Familiarization Procedure
2.4.6. Standardization and Control Procedures
2.4.7. Assessment of Habitual Consumption and Adverse Effects Related to CAF Intake
2.5. Outcome Measures
2.5.1. Countermovement Jump (CMJ) Test
2.5.2. Modified Agility t-Test (MAT)
2.5.3. Repeated-Sprint Ability Test (RSA Test)
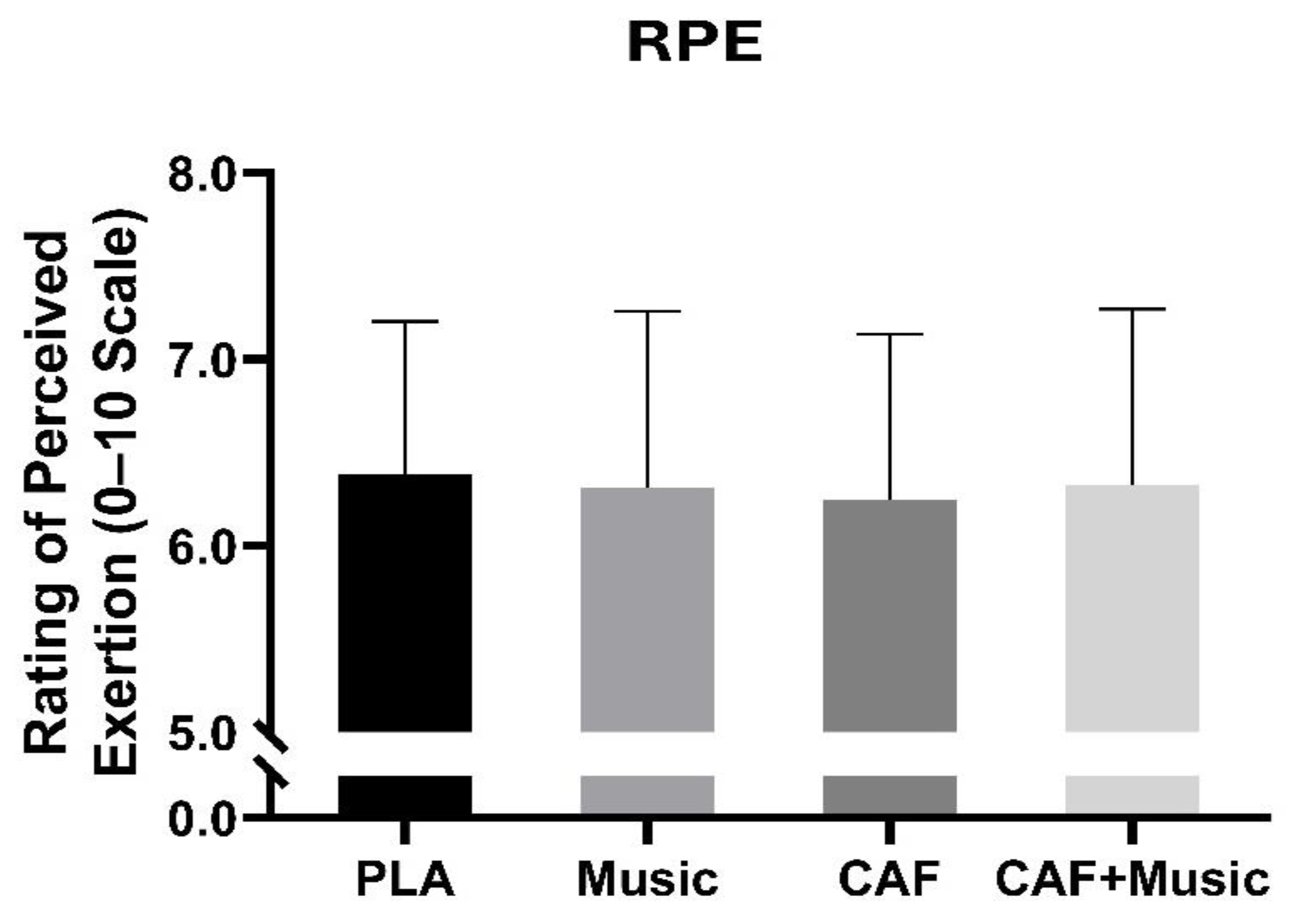
2.5.4. Rating of Perceived Effort (RPE)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. CMJ
3.2. Modified Agility t-Test (MAT)
3.3. RSA
3.4. Rating of Perceived Effort (RPE)
3.5. CAF Side Effects
4. Discussion
4.1. CAF Intake Effects
4.2. Effects of Listening to Music
4.3. Combined Effects of CAF + MUS
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CAF | caffeine |
| CMJ | countermovement jump |
| MAT | modified agility t-test |
| MUS | music (self-selected motivational music) |
| PLA | placebo |
| RSA | repeated-sprint ability |
| RPE | rating of perceived exertion |
| SD | standard deviation |
| ANOVA | analysis of variance |
| PSQI | Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index |
| FFQ | food frequency questionnaire |
| η2p | partial eta squared (effect size measure) |
| dB | decibels |
| BPM | beats per minute |
| BMI | body mass index |
References
- Filip-Stachnik, A.; Spieszny, M.; Stanisz, L.; Krzysztofik, M. Does Caffeine Ingestion Affect the Lower-Body Post-Activation Performance Enhancement in Female Volleyball Players? BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2022, 14, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dergaa, I.; Ben Saad, H.; El Omri, A.; Duque, J.D.P.; Chaabane, M.; Chamari, K. Mental, Physiological and Medical Considerations for Elite Football Players in the Saudi Pro League: A Call for Action. BMJ Open Sport. Exerc. Med. 2023, 9, e001789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, C. Systematic Literature Review on the Immediate Effects of Caffeine on Athletes’ Sports Performance. Preprint 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscatelli, F.; Monda, A.; Messina, A.; Monda, M.; Monda, V.; Villano, I.; De Maria, A.; Nicola, M.; Marsala, G.; De Stefano, M.I.; et al. Evaluation of Orexin-A Salivary Levels and Its Correlation with Attention After Non-Invasive Brain Stimulation in Female Volleyball Players. Sports Med.-Open 2024, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyas, A.J.V.; Khanvilkar, N.P. Role of Sports Psychology in Context to Development of Sports Performance. Int. J. Multidiscip. Res. 2024, 6, 21849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atan, T. Effect of music on anaerobic exercise performance. Biol. Sport 2013, 30, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loizou, G.; Karageorghis, C.I. Effects of Psychological Priming, Video, and Music on Anaerobic Exercise Performance. Scand. Med. Sci. Sports 2015, 25, 909–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLellan, T.M.; Caldwell, J.A.; Lieberman, H.R. A Review of Caffeine’s Effects on Cognitive, Physical and Occupational Performance. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 71, 294–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romdhani, M.; Souissi, N.; Dergaa, I.; Moussa-Chamari, I.; Abene, O.; Chtourou, H.; Sahnoun, Z.; Driss, T.; Chamari, K.; Hammouda, O. The Effect of Experimental Recuperative and Appetitive Post-Lunch Nap Opportunities, With or Without Caffeine, on Mood and Reaction Time in Highly Trained Athletes. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 720493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romdhani, M.; Souissi, N.; Dergaa, I.; Moussa-Chamari, I.; Chaabouni, Y.; Mahdouani, K.; Abene, O.; Driss, T.; Chamari, K.; Hammouda, O. The Effect of Caffeine, Nap Opportunity and Their Combination on Biomarkers of Muscle Damage and Antioxidant Defence during Repeated Sprint Exercise. Biol. Sport 2022, 39, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szerej, K.; Dorobek, W.; Stankiewicz, K.; Świeczkowski-Feiz, J. The Role of Caffeine in Enhancing Physical Performance: From Metabolism to Muscle Function. J. Educ. Health Sport 2024, 59, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.K.; Green, J.M. Caffeine and Anaerobic Performance: Ergogenic Value and Mechanisms of Action. Sports Med. 2009, 39, 813–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima-Silva, A.E.; Cristina-Souza, G.; Silva-Cavalcante, M.D.; Bertuzzi, R.; Bishop, D.J. Caffeine during High-Intensity Whole-Body Exercise: An Integrative Approach beyond the Central Nervous System. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-González, L.M.; Sánchez-Oliver, A.J.; Mata, F.; Jodra, P.; Antonio, J.; Domínguez, R. Acute Caffeine Supplementation in Combat Sports: A Systematic Review. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2018, 15, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Lara, J.; Nieto-Acevedo, R.; Abian-Vicen, J.; Del Coso, J. Can Caffeine Change the Game? Effects of Acute Caffeine Intake on Specific Performance in Intermittent Sports During Competition: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2024, 19, 1180–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Bruton, A.; Marin-Puyalto, J.; Muñiz-Pardos, B.; Matute-Llorente, A.; Del Coso, J.; Gomez-Cabello, A.; Vicente-Rodriguez, G.; Casajus, J.A.; Lozano-Berges, G. Does Acute Caffeine Supplementation Improve Physical Performance in Female Team-Sport Athletes? Evidence from a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinero, J.J.; Lara, B.; Del Coso, J. Effects of Acute Ingestion of Caffeine on Team Sports Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Res. Sports Med. 2019, 27, 238–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bougrine, H.; Cherif, M.; Chtourou, H.; Souissi, N. Can Caffeine Supplementation Reverse the Impact of Time of Day on Cognitive and Short-Term High Intensity Performances in Young Female Handball Players? Chronobiol. Int. 2022, 39, 1144–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougrine, H.; Ammar, A.; Salem, A.; Trabelsi, K.; Jahrami, H.; Chtourou, H.; Souissi, N. Optimizing Short-Term Maximal Exercise Performance: The Superior Efficacy of a 6 Mg/Kg Caffeine Dose over 3 or 9 Mg/Kg in Young Female Team-Sports Athletes. Nutrients 2024, 16, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siquier-Coll, J.; Delgado-García, G.; Soto-Méndez, F.; Liñán-González, A.; García, R.; González-Fernández, F. The Effect of Caffeine Supplementation on Female Volleyball Players’ Performance and Wellness during a Regular Training Week. Nutrients 2023, 16, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Acevedo, R.; García-Sánchez, C.; Bravo-Sánchez, A.; Abián-Vicén, J.; Abián, P.; Portillo, J.; Martínez-Rubio, C.; Lorenzo Calvo, J.; Diaz-Lara, J. Impact of Caffeine Intake on Female Basketball Players’ Performance. Nutrients 2025, 17, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojanović, E.; Stojiljković, N.; Scanlan, A.T.; Dalbo, V.J.; Stanković, R.; Antić, V.; Milanović, Z. Acute Caffeine Supplementation Promotes Small to Moderate Improvements in Performance Tests Indicative of In-Game Success in Professional Female Basketball Players. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 44, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filip-Stachnik, A.; Kaszuba, M.; Dorozynski, B.; Komarek, Z.; Gawel, D.; Del Coso, J.; Klocek, T.; Spieszny, M.; Krzysztofik, M. Acute Effects of Caffeinated Chewing Gum on Volleyball Performance in High-Performance Female Players. J. Hum. Kinet. 2022, 84, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougrine, H.; Ammar, A.; Salem, A.; Trabelsi, K.; Żmijewski, P.; Jahrami, H.; Chtourou, H.; Souissi, N. Effects of Different Caffeine Dosages on Maximal Physical Performance and Potential Side Effects in Low-Consumer Female Athletes: Morning vs. Evening Administration. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougrine, H.; Nasser, N.; Abdessalem, R.; Ammar, A.; Chtourou, H.; Souissi, N. Pre-Exercise Caffeine Intake Attenuates the Negative Effects of Ramadan Fasting on Several Aspects of High-Intensity Short-Term Maximal Performances in Adolescent Female Handball Players. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielgo-Ayuso, J.; Marques-Jiménez, D.; Refoyo, I.; Del Coso, J.; León-Guereño, P.; Calleja-González, J. Effect of Caffeine Supplementation on Sports Performance Based on Differences Between Sexes: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-López, A.; Garriga-Alonso, L.; Montalvo-Alonso, J.J.; Val-Manzano, M.D.; Valades, D.; Vila, H.; Ferragut, C. Sex Differences in the Acute Effect of Caffeine on Repeated Sprint Performance: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2025, 25, e12233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centala, J.; Pogorel, C.; Pummill, S.W.; Malek, M.H. Listening to Fast-Tempo Music Delays the Onset of Neuromuscular Fatigue. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2020, 34, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigliassi, M.; Karageorghis, C.I.; Hoy, G.K.; Layne, G.S. The Way You Make Me Feel: Psychological and Cerebral Responses to Music during Real-Life Physical Activity. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2019, 41, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebabli, N.; Boujabli, M.; Khlifi, M.; Ouerghi, N.; Bouassida, A.; Ben Abderrahman, A.; Van Den Tillaar, R. Effects of 440-Hz vs. 432-Hz Preferred Music Frequencies, during Warm-up, on Intermittent Anaerobic Speed Test Performance in Men and Women Kickboxers: A Double-Blind Crossover Study. PeerJ 2025, 13, e19084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patania, V.M.; Padulo, J.; Iuliano, E.; Ardigò, L.P.; Čular, D.; Miletić, A.; De Giorgio, A. The Psychophysiological Effects of Different Tempo Music on Endurance Versus High-Intensity Performances. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, J.A.; Karageorghis, C.I. Effects of Video, Priming, and Music on Motivation and Self-Efficacy in American Football Players. Int. J. Sports Sci. Coach. 2020, 15, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacon, C.J.; Myers, T.R.; Karageorghis, C.I. Effect of Music-Movement Synchrony on Exercise Oxygen Consumption. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2012, 52, 359–365. [Google Scholar]
- Terry, P.C.; Karageorghis, C.I.; Saha, A.M.; D’Auria, S. Effects of Synchronous Music on Treadmill Running among Elite Triathletes. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2012, 15, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herodek, R.T.; Aleksić Veljković, A.Z.; Živković, M.D.; Ilić, A.Đ.; Uzunović, S.V.; Trajković, N. Effects of Preferred Music on Internal Load in Adult Recreational Athletes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2025, 65, 632–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagini, M.S.; Brown, L.E.; Coburn, J.W.; Judelson, D.A.; Statler, T.A.; Bottaro, M.; Tran, T.T.; Longo, N.A. Effects of Self-Selected Music on Strength, Explosiveness, and Mood. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2012, 26, 1934–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujol, T.J.; Langenfeld, M.E. Influence of Music on Wingate Anaerobic Test Performance. Percept. Mot. Ski. 1999, 88, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Ohkuwa, T.; Itoh, H.; Kitoh, M.; Terasawa, J.; Tsuda, T.; Kitagawa, S.; Sato, Y. Effects of Pre-Exercise Listening to Slow and Fast Rhythm Music on Supramaximal Cycle Performance and Selected Metabolic Variables. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2003, 111, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentouati, E.; Romdhani, M.; Khemila, S.; Chtourou, H.; Souissi, N. The Effects of Listening to Non-Preferred or Self-Selected Music during Short-Term Maximal Exercise at Varied Times of Day. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2023, 130, 539–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotellessa, F.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Trompetto, C.; Marinelli, L.; Mori, L.; Faelli, E.; Schenone, C.; Ceylan, H.İ.; Biz, C.; Ruggieri, P.; et al. Improvement of Motor Task Performance: Effects of Verbal Encouragement and Music—Key Results from a Randomized Crossover Study with Electromyographic Data. Sports 2024, 12, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khemila, S.; Abedelmalek, S.; Romdhani, M.; Souissi, A.; Chtourou, H.; Souissi, N. Listening to Motivational Music during Warming-up Attenuates the Negative Effects of Partial Sleep Deprivation on Cognitive and Short-Term Maximal Performance: Effect of Time of Day. Chronobiol. Int. 2021, 38, 1052–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meglic, C.E.; Orman, C.M.; Rogers, R.R.; Williams, T.D.; Ballmann, C.G. Influence of Warm-Up Music Preference on Anaerobic Exercise Performance in Division I NCAA Female Athletes. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2021, 6, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belkhir, Y.; Rekik, G.; Chtourou, H.; Souissi, N. Listening to Neutral or Self-Selected Motivational Music during Warm-up to Improve Short-Term Maximal Performance in Soccer Players: Effect of Time of Day. Physiol. Behav. 2019, 204, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belkhir, Y.; Rekik, G.; Chtourou, H.; Souissi, N. Does Warming up with Different Music Tempos Affect Physical and Psychological Responses? The Evidence from a Chronobiological Study. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2022, 62, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grgic, J. Caffeine Ingestion Enhances Wingate Performance: A Meta-analysis. Eur. J. Sport. Sci. 2018, 18, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grgic, J.; Varovic, D. Ergogenic Effects of Caffeine on Ballistic (Throwing) Performance: A Meta-Analytical Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grgic, J.; Varovic, D. Moderators of Caffeine’s Effects on Jumping Performance in Females: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Nutr. Assoc. 2024, 43, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, H.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Lv, Y.; Sun, T.; Yu, L. Effects of Acute Ingestion of Caffeine Capsules on Muscle Strength and Muscle Endurance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda-Babarro, A.; Marqués-Jiménez, D.; Calleja-González, J.; Viribay, A.; León-Guereño, P.; Mielgo-Ayuso, J. Effect of Listening to Music on Wingate Anaerobic Test Performance. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, L.; Yang, H.; Lu, C.; Jiang, L.; Chen, Y. The Effect of Music Tempo on Fatigue Perception at Different Exercise Intensities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delleli, S.; Ouergui, I.; Messaoudi, H.; Ballmann, C.G.; Ardigò, L.P.; Chtourou, H. Effects of Caffeine Consumption Combined with Listening to Music during Warm-up on Taekwondo Physical Performance, Perceived Exertion and Psychological Aspects. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0292498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delleli, S.; Ouergui, I.; Messaoudi, H.; Bridge, C.A.; Ardigò, L.P.; Chtourou, H. Synergetic Effects of a Low Caffeine Dose and Pre-Exercise Music on Psychophysical Performance in Female Taekwondo Athletes. Revista de Artes Marciales Asiáticas 2024, 19, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Diao, P.; Liu, K.; Del Coso, J.; Liu, C. Effects of Caffeine Intake Combined with Self-Selected Music During Warm-Up on Anaerobic Performance: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Crossover Study. Nutrients 2025, 17, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domaszewski, P. Gender Differences in the Frequency of Positive and Negative Effects after Acute Caffeine Consumption. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benton, M.J.; Hutchins, A.M.; Dawes, J.J. Effect of Menstrual Cycle on Resting Metabolism: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNulty, K.L.; Elliott-Sale, K.J.; Dolan, E.; Swinton, P.A.; Ansdell, P.; Goodall, S.; Thomas, K.; Hicks, K.M. The Effects of Menstrual Cycle Phase on Exercise Performance in Eumenorrheic Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2020, 50, 1813–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrosa, M.; Gil-Izquierdo, A.; González-Rodríguez, L.G.; Alférez, M.J.M.; San Juan, A.F.; Sánchez-Gómez, Á.; Calvo-Ayuso, N.; Ramos-Álvarez, J.J.; Fernández-Lázaro, D.; Lopez-Grueso, R.; et al. Nutritional Strategies for Optimizing Health, Sports Performance, and Recovery for Female Athletes and Other Physically Active Women: A Systematic Review. Nutr. Rev. 2024, 83, e1068–e1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, T.W. The Importance of A Priori Sample Size Estimation in Strength and Conditioning Research. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 2323–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.-G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A Flexible Statistical Power Analysis Program for the Social, Behavioral, and Biomedical Sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guelmami, N.; Ben Ezzeddine, L.; Hatem, G.; Trabelsi, O.; Ben Saad, H.; Glenn, J.M.; El Omri, A.; Chalghaf, N.; Taheri, M.; Bouassida, A.; et al. The Ethical Compass: Establishing Ethical Guidelines for Research Practices in Sports Medicine and Exercise Science. Int. J. Sport. Stud. Health 2024, 7, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filip, A.; Wilk, M.; Krzysztofik, M.; Del Coso, J. Inconsistency in the Ergogenic Effect of Caffeine in Athletes Who Regularly Consume Caffeine: Is It Due to the Disparity in the Criteria That Defines Habitual Caffeine Intake? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creinin, M.D.; Keverline, S.; Meyn, L.A. How Regular Is Regular? An Analysis of Menstrual Cycle Regularity. Contraception 2004, 70, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazel, N.; Souissi, A.; Chtourou, H.; Aloui, G.; Souissi, N. The Effect of Music on Short-Term Exercise Performance during the Different Menstrual Cycle Phases in Female Handball Players. Res. Sports Med. 2022, 30, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara, B.; Salinero, J.J.; Giráldez-Costas, V.; Del Coso, J. Similar Ergogenic Effect of Caffeine on Anaerobic Performance in Men and Women Athletes. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 4107–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janse De Jonge, X.A.K. Effects of the Menstrual Cycle on Exercise Performance. Sports Med. 2003, 33, 833–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallarés, J.G.; Fernández-Elías, V.E.; Ortega, J.F.; Muñoz, G.; Muñoz-Guerra, J.; Mora-Rodríguez, R. Neuromuscular Responses to Incremental Caffeine Doses: Performance and Side Effects. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2013, 45, 2184–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballmann, C.G. The Influence of Music Preference on Exercise Responses and Performance: A Review. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2021, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karow, M.C.; Rogers, R.R.; Pederson, J.A.; Williams, T.D.; Marshall, M.R.; Ballmann, C.G. Effects of Preferred and Nonpreferred Warm-Up Music on Exercise Performance. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2020, 127, 912–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karageorghis, C.I.; Priest, D.-L.; Terry, P.C.; Chatzisarantis, N.L.D.; Lane, A.M. Redesign and Initial Validation of an Instrument to Assess the Motivational Qualities of Music in Exercise: The Brunel Music Rating Inventory-2. J. Sports Sci. 2006, 24, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, J.; Hudson, P.; Edwards, B. Effects of Music Tempo upon Submaximal Cycling Performance. Scand. Med. Sci. Sports 2010, 20, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, J.S.; Barrett, L.A.; Chow, J.Y.; Burns, S.F. Effects of Caffeine Supplementation on Performance in Ball Games. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 2453–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suleiman, K.H.; Yates, B.C.; Berger, A.M.; Pozehl, B.; Meza, J. Translating the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index Into Arabic. West. J. Nurs. Res. 2010, 32, 250–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BaHammam, A.S.; Almestehi, W.; Albatli, A.; AlShaya, S. Distribution of Chronotypes in a Large Sample of Young Adult Saudis. Ann. Saudi Med. 2011, 31, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bühler, E.; Bühler, E.; Lachenmeier, D.W.; Winkler, G. Development of a Tool to Assess Caffeine Intake among Teenagers and Young Adults. Ernahr. Umsch. 2014, 61, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dergaa, I.; Fessi, M.S.; Chaabane, M.; Souissi, N.; Hammouda, O. The Effects of Lunar Cycle on the Diurnal Variations of Short-Term Maximal Performance, Mood State, and Perceived Exertion. Chronobiol. Int. 2019, 36, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dergaa, I.; Romdhani, M.; Fessi, M.S.; Ben Saad, H.; Varma, A.; Ben Salem, A.; Gadhavi, B.; Chaabane, M.; Souissi, N.; Hammouda, O. Does Lunar Cycle Affect Biological Parameters in Young Healthy Men? Chronobiol. Int. 2021, 38, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souissi, A.; Dergaa, I.; Chtourou, H.; Ben Saad, H. The Effect of Daytime Ingestion of Melatonin on Thyroid Hormones Responses to Acute Submaximal Exercise in Healthy Active Males: A Pilot Study. Am. J. Mens. Health 2022, 16, 15579883211070383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souissi, M.A.; Gouasmia, C.; Dergaa, I.; Faleh, J.; Trabelsi, O.; Weiss, K.; Rosemann, T.; Dhahbi, W.; Souissi, N.; Knechtle, B. Impact of Evening Blue Light Exposure Timing on Sleep, Motor, and Cognitive Performance in Young Athletes with Intermediate Chronotype. Biol. Sport 2025, 42, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormack, S.J.; Newton, R.U.; McGuigan, M.R.; Doyle, T.L. Reliability of Measures Obtained during Single and Repeated Countermovement Jumps. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2008, 3, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavanaugh, A.A.; Mizuguchi, S.; Sands, W.A.; Ramsey, M.W.; Stone, M.H. Long-Term Changes in Jump Performance and Maximum Strength in a Cohort of National Collegiate Athletic Association Division I Women’s Volleyball Athletes. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2018, 32, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagchi, A.; Raizada, S.; Thapa, R.K.; Stefanica, V.; Ceylan, H.İ. Reliability and Accuracy of Portable Devices for Measuring Countermovement Jump Height in Physically Active Adults: A Comparison of Force Platforms, Contact Mats, and Video-Based Software. Life 2024, 14, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassi, R.H.; Dardouri, W.; Yahmed, M.H.; Gmada, N.; Mahfoudhi, M.E.; Gharbi, Z. Relative and Absolute Reliability of a Modified Agility t-Test and Its Relationship With Vertical Jump and Straight Sprint. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2009, 23, 1644–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhenni, T.; Souissi, A.; Tayech, A.; Yousfi, N.; Mejri, M.A.; Chamari, K.; Souissi, N.; Khlifa, R.; Haddad, M. The Effect of Ramadan Fasting on the Morning–Evening Difference in Team-Handball-Related Short-Term Maximal Physical Performances in Elite Female Team-Handball Players. Chronobiol. Int. 2021, 38, 1488–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, G.A.V. Psychophysical Bases of Perceived Exertion. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1982, 14, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. A Power Primer. Psychol. Bull. 1992, 112, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, W.G. A Scale of Magnitudes for Effect Statistics. New View Stat. 2002, 502, 321. [Google Scholar]
- Zbinden-Foncea, H.; Rada, I.; Gomez, J.; Kokaly, M.; Stellingwerff, T.; Deldicque, L.; Peñailillo, L. Effects of Caffeine on Countermovement-Jump Performance Variables in Elite Male Volleyball Players. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2018, 13, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, B.I.; Travis, S.K.; Gentles, J.A.; Sato, K.; Lang, H.M.; Bazyler, C.D. The Effects of Caffeine on Jumping Performance and Maximal Strength in Female Collegiate Athletes. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes-Silva, J.P.; Silva Santos, J.F.D.; Branco, B.H.M.; Abad, C.C.C.; Oliveira, L.F.D.; Loturco, I.; Franchini, E. Caffeine Ingestion Increases Estimated Glycolytic Metabolism during Taekwondo Combat Simulation but Does Not Improve Performance or Parasympathetic Reactivation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallis, J.; James, R.S.; Cox, V.M.; Duncan, M.J. Is the Ergogenicity of Caffeine Affected by Increasing Age? The Direct Effect of a Physiological Concentration of Caffeine on the Power Output of Maximally Stimulated EDL and Diaphragm Muscle Isolated from the Mouse. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2017, 21, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, R.; Cordery, P.; Funnell, M.; Mears, S.; James, L.; Watson, P. Chronic Ingestion of a Low Dose of Caffeine Induces Tolerance to the Performance Benefits of Caffeine. J. Sports Sci. 2017, 35, 1920–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bougrine, H.; Salem, A.; Ammar, A.; Souissi, N. Caffeine and Team Ball Performances: A Mini-Review. Tunis. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2023, 1, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabblah, S.; Dixon, D.; Bottoms, L. Sex Differences on the Acute Effects of Caffeine on Maximal Strength and Muscular Endurance. Comp. Exerc. Physiol. 2015, 11, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loy, B.D.; O’Connor, P.J.; Lindheimer, J.B.; Covert, S.F. Caffeine Is Ergogenic for Adenosine A2A Receptor Gene (ADORA2A) T Allele Homozygotes: A Pilot Study. J. Caffeine Res. 2015, 5, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Womack, C.J.; Saunders, M.J.; Bechtel, M.K.; Bolton, D.J.; Martin, M.; Luden, N.D.; Dunham, W.; Hancock, M. The Influence of a CYP1A2 Polymorphism on the Ergogenic Effects of Caffeine. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2012, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grgic, J.; Trexler, E.T.; Lazinica, B.; Pedisic, Z. Effects of Caffeine Intake on Muscle Strength and Power: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2018, 15, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorino, A.J.; Lloyd, L.K.; Crixell, S.H.; Walker, J.L. The Effects of Caffeine on Athletic Agility. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2006, 20, 851–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.M.; Zhao, Z.; Stock, H.S.; Mehl, K.A.; Buggy, J.; Hand, G.A. Central Nervous System Effects of Caffeine and Adenosine on Fatigue. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2003, 284, R399–R404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jebabli, N.; Ouerghi, N.; Bouabid, J.; Bettaib, R. Effect of Caffeine on the Repeated Modified Agility Test from Some Cardiovascular Factors, Blood Glucose and Rating of Perceived Exertion in Young People. Iran. J. Public Health 2017, 46, 755–761. [Google Scholar]
- Lara, B.; Gonzalez-Millán, C.; Salinero, J.J.; Abian-Vicen, J.; Areces, F.; Barbero-Alvarez, J.C.; Muñoz, V.; Portillo, L.J.; Gonzalez-Rave, J.M.; Del Coso, J. Caffeine-Containing Energy Drink Improves Physical Performance in Female Soccer Players. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 1385–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-L.; Cheng, C.-F.; Astorino, T.A.; Lee, C.-J.; Huang, H.-W.; Chang, W.-D. Effects of Carbohydrate Combined with Caffeine on Repeated Sprint Cycling and Agility Performance in Female Athletes. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2014, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, A.; López-Samanes, Á.; Pérez-López, A.; Aguilar-Navarro, M.; Moreno-Heredero, B.; Rivilla-García, J.; González-Frutos, P.; Pino-Ortega, J.; Morencos, E.; Del Coso, J. Effects of Caffeine Ingestion on Physical Performance in Elite Women Handball Players: A Randomized, Controlled Study. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2020, 15, 1406–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buck, C.; Guelfi, K.; Dawson, B.; McNaughton, L.; Wallman, K. Effects of Sodium Phosphate and Caffeine Loading on Repeated-Sprint Ability. J. Sports Sci. 2015, 33, 1971–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves Ribeiro, B.; Pontes Morales, A.; Sampaio-Jorge, F.; Tinoco, F.D.S.; Matos, A.A.D.; Leite, T.C. Acute Effects of Caffeine Intake on Athletic Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Rev. Chil. Nutr. 2017, 44, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzucchi, I.; Felici, F.; Montini, M.; Figura, F.; Sacchetti, M. Caffeine improves neuromuscular function during maximal dynamic exercise. Muscle Nerve 2011, 43, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, G.L.; Park, N.D.; Maresca, R.D.; McKibans, K.I.; Millard-Stafford, M.L. Effect of Caffeine Ingestion on Muscular Strength and Endurance: A Meta-Analysis. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2010, 42, 1375–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, C.; Grgic, J. Caffeine and Exercise: What Next? Sports Med. 2019, 49, 1007–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; O’Donnell, J.; Von Hurst, P.; Foskett, A.; Holland, S.; Starck, C.; Rutherfurd-Markwick, K. Caffeine Ingestion Enhances Perceptual Responses during Intermittent Exercise in Female Team-Game Players. J. Sports Sci. 2016, 34, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.J.; Rushing, B.R.; Sumner, S.J.; Hackney, A.C. Dietary Supplements for Athletic Performance in Women: Beta-Alanine, Caffeine, and Nitrate. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2022, 32, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabir, A.; Hooton, A.; Tallis, J.; Higgins, M.F. The Influence of Caffeine Expectancies on Sport, Exercise, and Cognitive Performance. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, J.C.; Karageorghis, C.I. Moderating Influence of Dominant Attentional Style and Exercise Intensity on Responses to Asynchronous Music. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2013, 35, 625–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dyck, E. Musical Intensity Applied in the Sports and Exercise Domain: An Effective Strategy to Boost Performance? Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliakim, M.; Meckel, Y.; Gotlieb, R.; Nemet, D.; Eliakim, A. Motivational Music and Repeated Sprint Ability in Junior Basketball Players. Acta Kinesiol. Univ. Tartu. 2012, 18, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliakim, M.; Meckel, Y.; Nemet, D.; Eliakim, A. The Effect of Music during Warm-Up on Consecutive Anaerobic Performance in Elite Adolescent Volleyball Players. Int. J. Sports Med. 2006, 28, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarraya, M.; Chtourou, H.; Aloui, A.; Hammouda, O.; Chamari, K.; Chaouachi, A.; Souissi, N. The Effects of Music on High-Intensity Short-Term Exercise in Well Trained Athletes. Asian J. Sports Med. 2012, 3, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebabli, N.; Ben Aabderrahman, A.; Boullosa, D.; Chtourou, H.; Ouerghi, N.; Rhibi, F.; Govindasamy, K.; Saeidi, A.; Clark, C.C.T.; Granacher, U.; et al. Listening to Music during a Repeated Sprint Test Improves Performance and Psychophysiological Responses in Healthy and Physically Active Male Adults. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2023, 15, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasteiro, F.M.; Messias, L.H.D.; Scariot, P.P.M.; Cruz, J.P.; Cetein, R.L.; Gobatto, C.A.; Manchado-Gobatto, F.B. Effects of Preferred Music on Physiological Responses, Perceived Exertion, and Anaerobic Threshold Determination in an Incremental Running Test on Both Sexes. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, S.D.; Karageorghis, C.I. The Effects of Synchronous Music on 400-m Sprint Performance. J. Sports Sci. 2006, 24, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Tao, M.; Gao, J.; Gao, M.; Zhu, H.; He, X. The Difference of Affect Improvement Effect of Music Intervention in Aerobic Exercise at Different Time Periods. Front. Physiol. 2024, 15, 1341351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirizio, G.G.; Nunes, R.S.M.; Vargas, D.A.; Foster, C.; Vieira, E. Time-of-Day Effects on Short-Duration Maximal Exercise Performance. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, P.C.; Karageorghis, C.I.; Curran, M.L.; Martin, O.V.; Parsons-Smith, R.L. Effects of Music in Exercise and Sport: A Meta-Analytic Review. Psychol. Bull. 2020, 146, 91–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chtourou, H.; Chaouachi, A.; Hammouda, O.; Chamari, K.; Souissi, N. Listening to Music Affects Diurnal Variation in Muscle Power Output. Int. J. Sports Med. 2012, 33, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, G.; Wilson, D.; Eubank, M. Effects of Music on Work-Rate Distribution During a Cycling Time Trial. Int. J. Sports Med. 2004, 25, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, W.P. Psychological Components of Effort Sense. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1994, 26, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, M.; Staibano, V.; Franchini, E. Effects of Self-Selected or Randomly Selected Music on Performance and Psychological Responses during a Sprint Interval Training Session. Sci. Sports 2022, 37, 139.e1–139.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, M.; Henrique, N.; Takito, M.; Franchini, E. Effects of Music on Perceptive and Performance Responses during High-Intensity Exercise: A Systematic Review. Sport Sci. Health 2024, 20, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, A.B.; Randell, R.K.; Jeukendrup, A.E. The Metabolic and Performance Effects of Caffeine Compared to Coffee during Endurance Exercise. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, G.L.; Guilherme, J.; Ferreira, L.H.B.; de Souza-Junior, T.P.; Lancha, A.H., Jr. Caffeine and Exercise Performance: Possible Directions for Definitive Findings. Front. Sports Act. Living 2020, 2, 574854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collomp, K.; Ahmaidi, S.; Chatard, J.C.; Audran, M.; Prefaut, C. Benefits of Caffeine Ingestion on Sprint Performance in Trained and Untrained Swimmers. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1992, 64, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, B.; de Oliveira, L.F.; da Silva, R.P.; de Salles Painelli, V.; Gonçalves, L.S.; Yamaguchi, G.; Mutti, T.; Maciel, E.; Roschel, H.; Artioli, G.G. Placebo in Sports Nutrition: A Proof-of-principle Study Involving Caffeine Supplementation. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2017, 27, 1240–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| PLA | MUS | CAF | CAF + MUS | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Questionnaire | Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 1 | Day 2 |
| Muscle soreness | 5.88 | 5.88 | 11.76 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Increased urine output | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5.88 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5.88 |
| Tachycardia | 0 | 0 | 5.88 | 0 | 11.76 | 0 | 5.88 | 0 |
| Anxiety or nervousness | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5.88 | 0 |
| Headache | 5.88 | 5.88 | 0 | 0 | 11.76 | 0 | 11.76 | 0 |
| Gastrointestinal problems | 5.88 | 5.88 | 0 | 11.76 | 11.76 | 5.88 | 5.88 | 5.88 |
| Insomnia | - | 0 | - | 5.88 | - | 0 | - | 11.76 |
| Increased vigor/activeness | 5.88 | 0 | 11.76 | 0 | 5.88 | 0 | 23.52 | 0 |
| Perception of performance improvement | 17.64 | - | 17.64 | - | 17.64 | - | 23.52 | - |
| PLA | MUS | CAF | CAF + MUS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blinding | 11.76 | 23.52 | 23.52 | 17.64 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bougrine, H.; Paillard, T.; Jebabli, N.; Ceylan, H.İ.; Maitre, J.; Dergaa, I.; Stefanica, V.; Abderrahman, A.B. Ergogenic Effects of Combined Caffeine Supplementation and Motivational Music on Anaerobic Performance in Female Handball Players: A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17101613
Bougrine H, Paillard T, Jebabli N, Ceylan Hİ, Maitre J, Dergaa I, Stefanica V, Abderrahman AB. Ergogenic Effects of Combined Caffeine Supplementation and Motivational Music on Anaerobic Performance in Female Handball Players: A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial. Nutrients. 2025; 17(10):1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17101613
Chicago/Turabian StyleBougrine, Houda, Thierry Paillard, Nidhal Jebabli, Halil İbrahim Ceylan, Julien Maitre, Ismail Dergaa, Valentina Stefanica, and Abderraouf Ben Abderrahman. 2025. "Ergogenic Effects of Combined Caffeine Supplementation and Motivational Music on Anaerobic Performance in Female Handball Players: A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial" Nutrients 17, no. 10: 1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17101613
APA StyleBougrine, H., Paillard, T., Jebabli, N., Ceylan, H. İ., Maitre, J., Dergaa, I., Stefanica, V., & Abderrahman, A. B. (2025). Ergogenic Effects of Combined Caffeine Supplementation and Motivational Music on Anaerobic Performance in Female Handball Players: A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial. Nutrients, 17(10), 1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17101613









