Effectiveness of Early Versus Late Time-Restricted Eating Combined with Physical Activity in Overweight or Obese Women
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
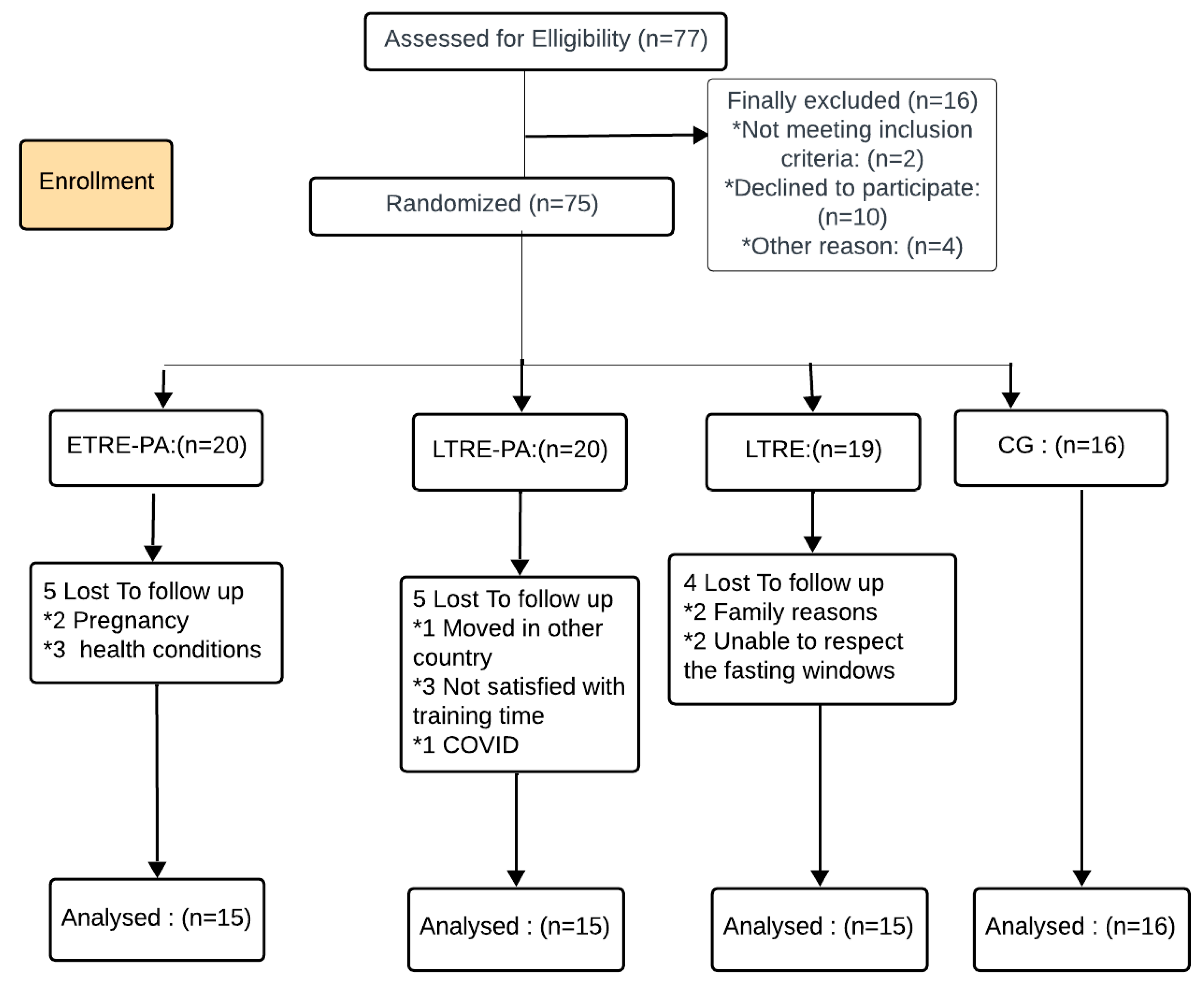
2.1. Participants
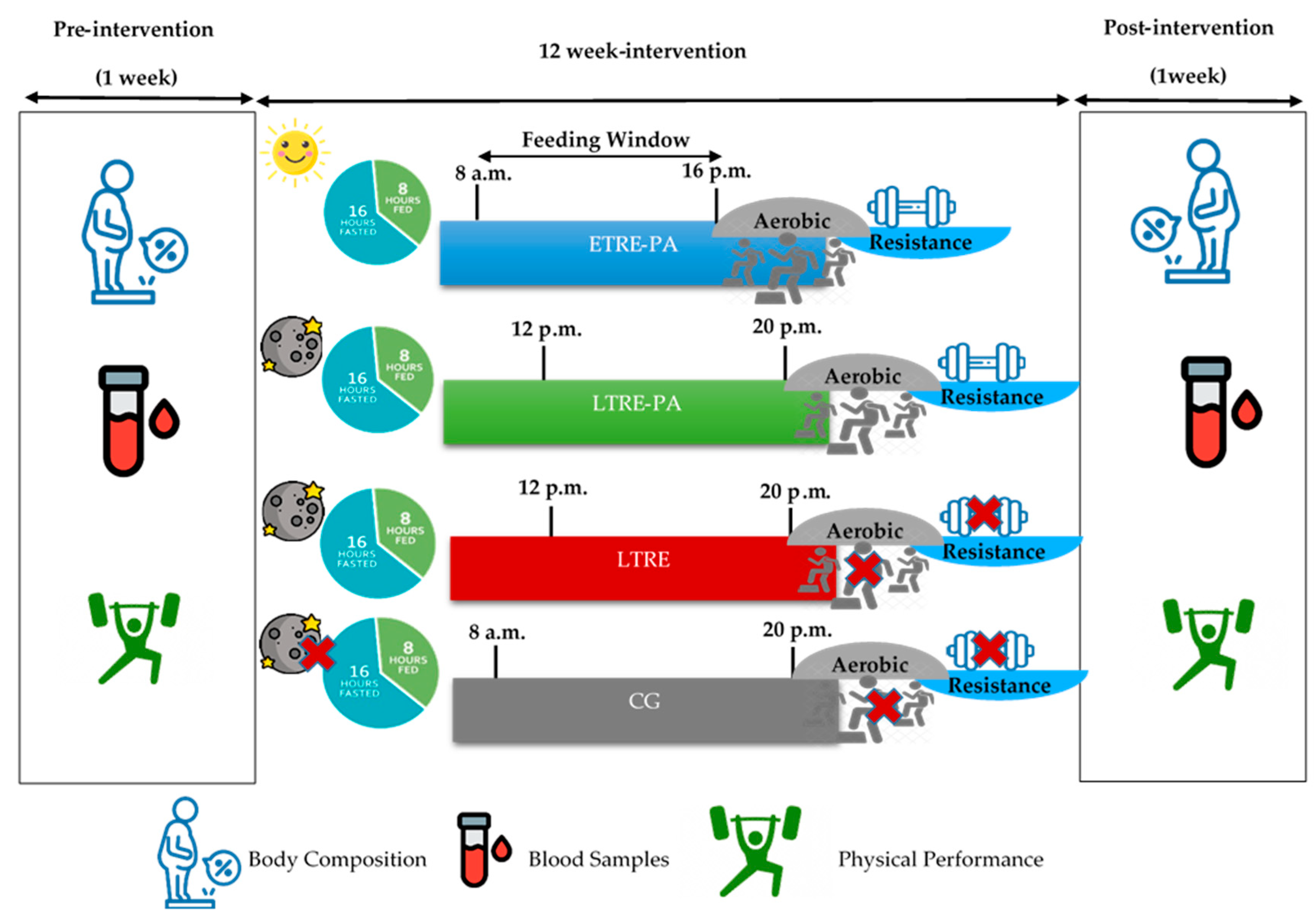
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Training Sessions
2.3.1. Endurance Training
2.3.2. Strength Training
2.4. Outcome Measures
2.5. Blood Samples
2.6. Functional Capacity
2.6.1. Six-Minute Walk Test (6MWT)
2.6.2. Strength Tests
2.6.3. Vertical Jump Test
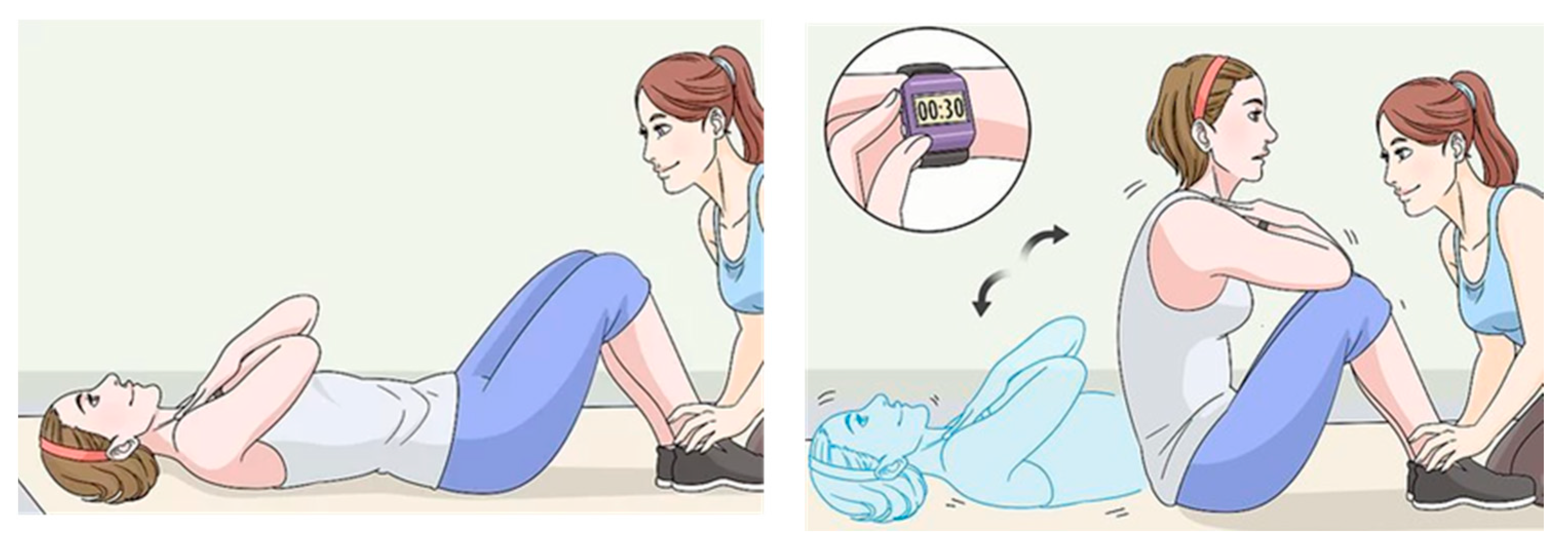
2.6.4. The 30-s Crunch and Squat Tests
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Body Composition
4.2. Metabolic Parameters
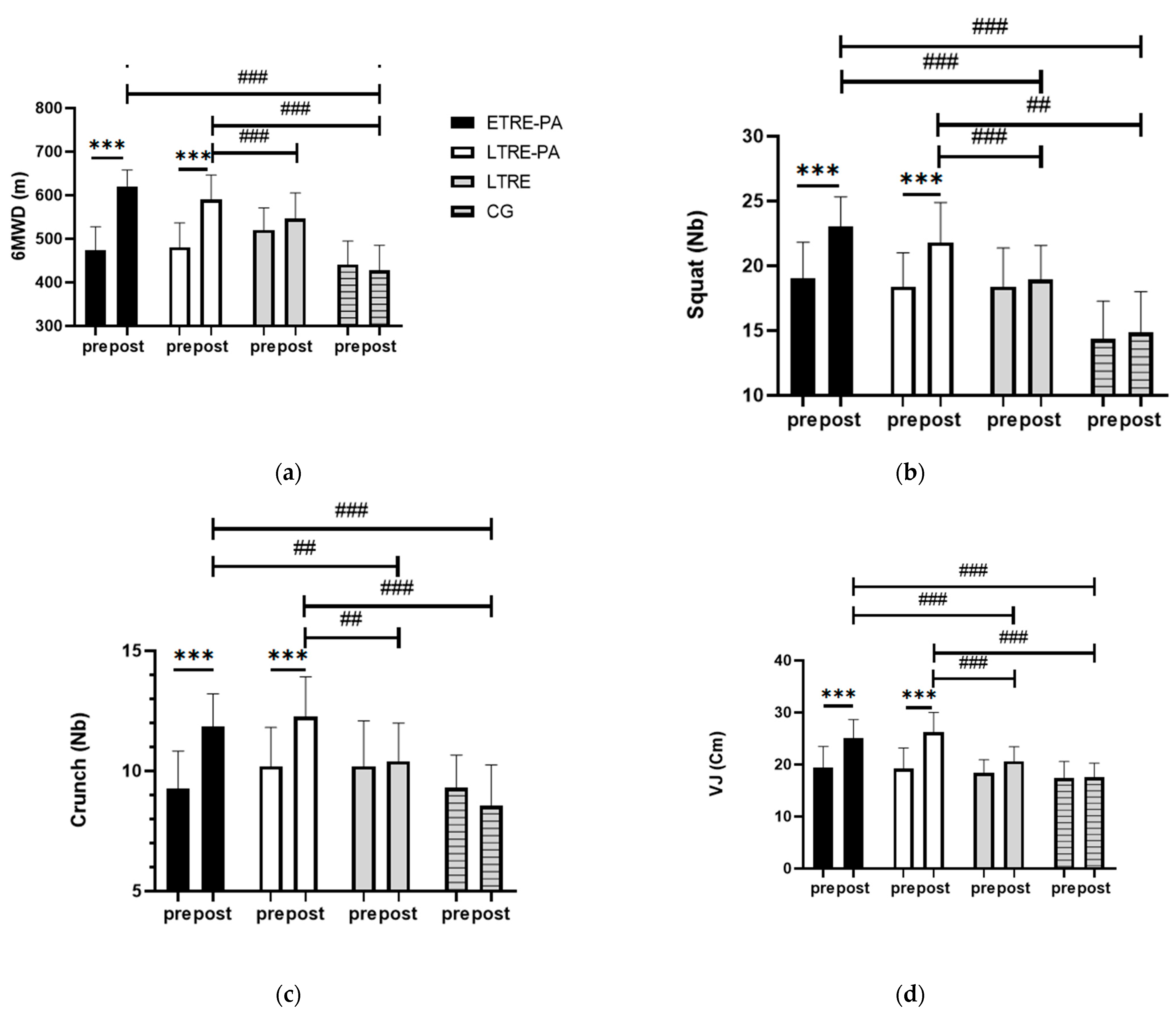
4.3. Functional Capacity
4.3.1. 6MWT
4.3.2. LE and BP 1-RM
4.3.3. Explosiveness and Endurance Strength
5. Discussion
Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Okunogbe, A.; Nugent, R.; Spencer, G.; Powis, J.; Ralston, J.; Wilding, J. Economic Impacts of Overweight and Obesity: Current and Future Estimates for 161 Countries. BMJ Glob. Health 2022, 7, e009773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hales, C.M.; Fryar, C.D.; Carroll, M.D.; Freedman, D.S.; Aoki, Y.; Ogden, C.L. Prevalence of Obesity and Severe Obesity Among Adults: United States, 2017–2018. NCHS Data Brief 2020, 319, 2419–2429. [Google Scholar]
- McDonough, D.; Su, X.; Gao, Z. Health Wearable Devices for Weight and BMI Reduction in Individuals with Overweight/Obesity and Chronic Comorbidities: Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2021, 55, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.D.; Buscemi, J.; Milsom, V.; Malcolm, R.; O’Neil, P.M. Effects on Cardiovascular Risk Factors of Weight Losses Limited to 5-10. Transl. Behav. Med. 2016, 6, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y. Optimal Diet Strategies for Weight Loss and Weight Loss Maintenance. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2021, 30, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesani, A.; Barkhidarian, B.; Jafarzadeh, M.; Akbarzade, Z.; Djafarian, K.; Shab-Bidar, S. Time-Related Meal Patterns and Breakfast Quality in a Sample of Iranian Adults. BMC Nutr. 2023, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamshed, H.; Beyl, R.A.; Della Manna, D.L.; Yang, E.S.; Ravussin, E.; Peterson, C.M. Early Time-Restricted Feeding Improves 24-Hour Glucose Levels and Affects Markers of the Circadian Clock, Aging, and Autophagy in Humans. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, R.A.D.; Szmuchrowski, L.A.; Rosa, J.P.P.; Santos, M.A.P.d.; de Mello, M.T.; Savoi, L.; Porto, Y.F.; de Assis Dias Martins, F., Jr.; Drummond, M.D.M. Intermittent Fasting Promotes Weight Loss without Decreasing Performance in Taekwondo. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, D.L.; Hawley, N.A.; Mohr, A.E.; Hermer, J.; Ofori, E.; Yu, F.; Sears, D.D. Impact of Intermittent Fasting and/or Caloric Restriction on Aging-Related Outcomes in Adults: A Scoping Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2024, 16, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Liu, X.; Bao, L.; Yang, P.; Zhou, H. Health Effects of the Time-Restricted Eating in Adults with Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1079250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, E.A.; Zaman, A.; Sloggett, K.J.; Steinke, S.; Grau, L.; Catenacci, V.A.; Cornier, M.-A.; Rynders, C.A. Early Time-Restricted Eating Compared with Daily Caloric Restriction: A Randomized Trial in Adults with Obesity. Obesity 2022, 30, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Sun, Y.; Ye, Y.; Hu, D.; Zhang, H.; He, Z.; Zhao, H.; Yang, H.; Mao, Y. Randomized Controlled Trial for Time-Restricted Eating in Healthy Volunteers without Obesity. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchison, A.T.; Regmi, P.; Manoogian, E.N.C.; Fleischer, J.G.; Wittert, G.A.; Panda, S.; Heilbronn, L.K. Time-Restricted Feeding Improves Glucose Tolerance in Men at Risk for Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Crossover Trial. Obesity 2019, 27, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazeminasab, F.; Baharlooie, M.; Karimi, B.; Mokhtari, K.; Rosenkranz, S.K.; Santos, H.O. Effects of Intermittent Fasting Combined with Physical Exercise on Cardiometabolic Outcomes: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Studies. Nutr. Rev. 2023, 82, 1726–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albosta, M.; Bakke, J. Intermittent Fasting: Is There a Role in the Treatment of Diabetes? A Review of the Literature and Guide for Primary Care Physicians. Clin. Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, R.F.L.; Muñoz, V.R.; Junqueira, R.L.; de Oliveira, F.; Gaspar, R.C.; Nakandakari, S.C.B.R.; Costa, S.d.O.; Torsoni, M.A.; da Silva, A.S.R.; Cintra, D.E.; et al. Time-Restricted Feeding Combined with Aerobic Exercise Training Can Prevent Weight Gain and Improve Metabolic Disorders in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. J. Physiol. 2022, 600, 797–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petridi, F.; Geurts, J.M.W.; Nyakayiru, J.; Schaafsma, A.; Schaafsma, D.; Meex, R.C.R.; Singh-Povel, C.M. Effects of Early and Late Time-Restricted Feeding on Parameters of Metabolic Health: An Explorative Literature Assessment. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boege, H.L.; Bhatti, M.Z.; St-Onge, M.-P. Circadian Rhythms and Meal Timing: Impact on Energy Balance and Body Weight. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2021, 70, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BaHammam, A.S.; Pirzada, A. Timing Matters: The Interplay between Early Mealtime, Circadian Rhythms, Gene Expression, Circadian Hormones, and Metabolism—A Narrative Review. Clocks Sleep 2023, 5, 507–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, E.F.; Beyl, R.; Early, K.S.; Cefalu, W.T.; Ravussin, E.; Peterson, C.M. Early Time-Restricted Feeding Improves Insulin Sensitivity, Blood Pressure, and Oxidative Stress Even without Weight Loss in Men with Prediabetes. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 1212–1221.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabel, K.; Hoddy, K.K.; Haggerty, N.; Song, J.; Kroeger, C.M.; Trepanowski, J.F.; Panda, S.; Varady, K.A. Effects of 8-Hour Time Restricted Feeding on Body Weight and Metabolic Disease Risk Factors in Obese Adults: A Pilot Study. Nutr. Healthy Aging 2018, 4, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuppelius, B.; Peters, B.; Ottawa, A.; Pivovarova-Ramich, O. Time Restricted Eating: A Dietary Strategy to Prevent and Treat Metabolic Disturbances. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 683140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maaloul, R.; Ben Dhia, I.; Marzougui, H.; Turki, M.; Kacem, F.H.; Makhlouf, R.; Amar, M.B.; Kallel, C.; Driss, T.; Elleuch, M.H.; et al. Is Moderate-Intensity Interval Training More Tolerable than High-Intensity Interval Training in Adults with Obesity? Biol. Sport. 2023, 40, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batitucci, G.; Faria Junior, E.V.; Nogueira, J.E.; Brandão, C.F.C.; Abud, G.F.; Ortiz, G.U.; Marchini, J.S.; Freitas, E.C. Impact of Intermittent Fasting Combined with High-Intensity Interval Training on Body Composition, Metabolic Biomarkers, and Physical Fitness in Women With Obesity. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 884305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, T.W. The Importance of a Priori Sample Size Estimation in Strength and Conditioning Research. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 2323–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miladi, S.; Hammouda, O.; Ameur, R.; Miladi, S.C.; Feki, W.; Driss, T. Time-Restricted Eating Benefits on Pulmonary Function and Postural Balance in Overweight or Obese Women. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunani, A.; Perna, S.; Soranna, D.; Rondanelli, M.; Zambon, A.; Bertoli, S.; Vinci, C.; Capodaglio, P.; Lukaski, H.; Cancello, R. Body Composition Assessment Using Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA) in a Wide Cohort of Patients Affected with Mild to Severe Obesity. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 3973–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, S. Circadian Physiology of Metabolism. Science 2016, 354, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, C.J.; Yang, J.N.; Scheer, F.A.J.L. The Impact of the Circadian Timing System on Cardiovascular and Metabolic Function. Prog. Brain Res. 2012, 199, 337–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garaulet, M.; Gómez-Abellán, P.; Alburquerque-Béjar, J.J.; Lee, Y.-C.; Ordovás, J.M.; Scheer, F.A.J.L. Timing of Food Intake Predicts Weight Loss Effectiveness. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, J.D.; Ordovás, J.M.; Scheer, F.A.; Turek, F.W. Circadian Rhythms, Metabolism, and Chrononutrition in Rodents and Humans. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beqa Ahmeti, G.; Idrizovic, K.; Elezi, A.; Zenic, N.; Ostojic, L. Endurance Training vs. Circuit Resistance Training: Effects on Lipid Profile and Anthropometric/Body Composition Status in Healthy Young Adult Women. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedewald, W.T.; Levy, R.I.; Fredrickson, D.S. Estimation of the Concentration of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol in Plasma, without Use of the Preparative Ultracentrifuge. Clin. Chem. 1972, 18, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, S.A.F.; Faintuch, J.; Fabris, S.M.; Nampo, F.K.; Luz, C.; Fabio, T.L.; Sitta, I.S.; de Batista Fonseca, I.C. Six-Minute Walk Test: Functional Capacity of Severely Obese before and after Bariatric Surgery. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2009, 5, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, G.; Seelhorst, D.; Snyder, S. Comparison of Metabolic and Heart Rate Responses to Super Slow Vs. Traditional Resistance Training. J. Strength Cond. Res./Natl. Strength. Cond. Assoc. 2003, 17, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macarilla, C.T.; Sautter, N.M.; Robinson, Z.P.; Juber, M.C.; Hickmott, L.M.; Cerminaro, R.M.; Benitez, B.; Carzoli, J.P.; Bazyler, C.D.; Zoeller, R.F.; et al. Accuracy of Predicting One-Repetition Maximum from Submaximal Velocity in The Barbell Back Squat and Bench Press. J. Hum. Kinet. 2022, 82, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crose, A.; Alvear, A.; Singroy, S.; Wang, Q.; Manoogian, E.; Panda, S.; Mashek, D.G.; Chow, L.S. Time-Restricted Eating Improves Quality of Life Measures in Overweight Humans. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Cienfuegos, S.; Ezpeleta, M.; Gabel, K.; Pavlou, V.; Mulas, A.; Chakos, K.; McStay, M.; Wu, J.; Tussing-Humphreys, L.; et al. Time-Restricted Eating Without Calorie Counting for Weight Loss in a Racially Diverse Population. Ann. Intern. Med. 2023, 176, 885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Song, Y. Early Time-Restricted Eating Reduces Weight and Improves Glycemic Response in Young Adults: A Pre-Post Single-Arm Intervention Study. Obes. Facts 2022, 16, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aragon, A.A.; Schoenfeld, B.J. Does Timing Matter? A Narrative Review of Intermittent Fasting Variants and Their Effects on Bodyweight and Body Composition. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yi, P.; Liu, F. The Effect of Early Time-Restricted Eating vs Later Time-Restricted Eating on Weight Loss and Metabolic Health. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 108, 1824–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Nascimento Queiroz, J.; Macedo, R.C.O.; Dos Santos, G.C.; Munhoz, S.V.; Machado, C.L.F.; de Menezes, R.L.; Menzem, E.N.; Moritz, C.E.J.; Pinto, R.S.; Tinsley, G.M.; et al. Cardiometabolic Effects of Early v. Delayed Time-Restricted Eating plus Energetic Restriction in Adults with Overweight and Obesity: An Exploratory Randomised Clinical Trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2022, 129, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamshed, H.; Steger, F.; Bryan, D.; Richman, J.; Warriner, A.; Hanick, C.; Martin, C.; Salvy, S.-J.; Peterson, C. Effectiveness of Early Time-Restricted Eating for Weight Loss, Fat Loss, and Cardiometabolic Health in Adults with Obesity: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2022, 182, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Huang, Y.; Huang, C.; Yang, S.; Wei, X.; Zhang, P.; Guo, D.; Lin, J.; Xu, B.; Li, C.; et al. Calorie Restriction with or without Time-Restricted Eating in Weight Loss. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1495–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagawa, R.; Watanabe, D.; Ito, K.; Ueda, K.; Nakayama, K.; Sanbongi, C.; Miyachi, M. Dose–Response Relationship between Protein Intake and Muscle Mass Increase: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutr. Rev. 2021, 79, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.A.; Zhu, S.; List, E.O.; Duran-Ortiz, S.; Slama, Y.; Berryman, D.E. Musculoskeletal Effects of Altered GH Action. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 867921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakupova, E.I.; Bocharnikov, A.D.; Plotnikov, E.Y. Effects of Ketogenic Diet on Muscle Metabolism in Health and Disease. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, D.A.; Wu, N.; Rohdin-Bibby, L.; Moore, A.H.; Kelly, N.; Liu, Y.E.; Philip, E.; Vittinghoff, E.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Olgin, J.E.; et al. Effects of Time-Restricted Eating on Weight Loss and Other Metabolic Parameters in Women and Men with Overweight and Obesity: The TREAT Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 1491–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, R.E.; Laughlin, G.A.; Sears, D.D.; LaCroix, A.Z.; Marinac, C.; Gallo, L.C.; Hartman, S.J.; Natarajan, L.; Senger, C.M.; Martínez, M.E.; et al. Intermittent Fasting and Human Metabolic Health. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2015, 115, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotarsky, C.J.; Johnson, N.R.; Mahoney, S.J.; Mitchell, S.L.; Schimek, R.L.; Stastny, S.N.; Hackney, K.J. Time-Restricted Eating and Concurrent Exercise Training Reduces Fat Mass and Increases Lean Mass in Overweight and Obese Adults. Physiol. Rep. 2021, 9, e14868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, P.; O’Connor, S.G.; Heckman-Stoddard, B.M.; Sauter, E.R. Time-Restricted Feeding Studies and Possible Human Benefit. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2022, 6, pkac032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasim, I.; Majeed, C.N.; DeBoer, M.D. Intermittent Fasting and Metabolic Health. Nutrients 2022, 14, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Mottillo, E.P. Adipocyte Lipolysis: From Molecular Mechanisms of Regulation to Disease and Therapeutics. Biochem. J. 2020, 477, 985–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Williams, K.J.; Verlande-Ferrero, A.; Chan, A.P.; Su, G.B.; Kershaw, E.E.; Cox, J.E.; Maschek, J.A.; Shapira, S.N.; Christofk, H.R.; et al. Acute Activation of Adipocyte Lipolysis Reveals Dynamic Lipid Remodeling of the Hepatic Lipidome. J. Lipid Res. 2024, 65, 100434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirinzi, V.; Poli, C.; Berteotti, C.; Leone, A. Browning of Adipocytes: A Potential Therapeutic Approach to Obesity. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taetzsch, A.; Roberts, S.B.; Bukhari, A.; Lichtenstein, A.H.; Gilhooly, C.H.; Martin, E.; Krauss, A.J.; Hatch-McChesney, A.; Das, S.K. Eating Timing: Associations with Dietary Intake and Metabolic Health. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2021, 121, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, G.; Souza, M.; Pereira, L. Relationship between Omitting Breakfast and Late Eating with Obesity and Metabolic Disorders: A Review Focusing on Chrononutrition. Arch. Health 2023, 4, 466–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragoo, J.L.; Shapiro, S.A.; Bradsell, H.; Frank, R.M. The Essential Roles of Human Adipose Tissue: Metabolic, Thermoregulatory, Cellular, and Paracrine Effects. J. Cartil. Jt. Preserv. 2021, 1, 100023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.L.; Yadav, P.K.; Yadav, L.K.; Agrawal, K.; Sah, S.K.; Islam, M.N. Association between Obesity and Heart Rate Variability Indices: An Intuition toward Cardiac Autonomic Alteration—A Risk of CVD. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2017, 10, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucidi, P.; Perriello, G.; Porcellati, F.; Pampanelli, S.; Fano, M.; Tura, A.; Bolli, G.; Fanelli, C. Diurnal Cycling of Insulin Sensitivity in Type 2 Diabetes: Evidence for Deviation from Physiology at an Early Stage. Diabetes 2023, 72, 1364–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, P.; Oster, H.; Korf, H.W.; Foster, R.G.; Erren, T.C. Food as a Circadian Time Cue-Evidence from Human Studies. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manoogian, E.N.C.; Chow, L.S.; Taub, P.R.; Laferrère, B.; Panda, S. Time-Restricted Eating for the Prevention and Management of Metabolic Diseases. Endocr. Rev. 2022, 43, 405–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.-N.; Jiang, X.; Tang, W.; Song, P. Influence of Intermittent Fasting on Autophagy in the Liver. Biosci. Trends 2023, 17, 335–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrell, J.M. Circadian Rhythms and Inflammatory Diseases of the Liver and Gut. Liver Res. 2023, 7, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Wan, K.; Miyashita, M.; Ho, R.S.; Zheng, C.; Poon, E.T.; Wong, S.H. The Effect of Time-Restricted Eating Combined with Exercise on Body Composition and Metabolic Health: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Adv. Nutr. 2024, 15, 100262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Real-Hohn, A.; Navegantes, C.; Ramos, K.; Ramos-Filho, D.; Cahuê, F.; Galina, A.; Salerno, V.P. The Synergism of High-Intensity Intermittent Exercise and Every-Other-Day Intermittent Fasting Regimen on Energy Metabolism Adaptations Includes Hexokinase Activity and Mitochondrial Efficiency. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Brandhorst, S.; Shelehchi, M.; Mirzaei, H.; Cheng, C.W.; Budniak, J.; Groshen, S.; Mack, W.J.; Guen, E.; Di Biase, S.; et al. Fasting-Mimicking Diet and Markers/Risk Factors for Aging, Diabetes, Cancer, and Cardiovascular Disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaai8700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, T.; Tinsley, G.; Bianco, A.; Marcolin, G.; Pacelli, Q.F.; Battaglia, G.; Palma, A.; Gentil, P.; Neri, M.; Paoli, A. Effects of Eight Weeks of Time-Restricted Feeding (16/8) on Basal Metabolism, Maximal Strength, Body Composition, Inflammation, and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Resistance-Trained Males. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinsley, G.M.; Moore, M.L.; Graybeal, A.J.; Paoli, A.; Kim, Y.; Gonzales, J.U.; Harry, J.R.; VanDusseldorp, T.A.; Kennedy, D.N.; Cruz, M.R. Time-Restricted Feeding plus Resistance Training in Active Females: A Randomized Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 110, 628–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abaïdia, A.-E.; Daab, W.; Bouzid, M.A. Effects of Ramadan Fasting on Physical Performance: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2020, 50, 1009–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correia, J.M.; Santos, I.; Pezarat-Correia, P.; Silva, A.M.; Mendonca, G.V. Effects of Ramadan and Non-Ramadan Intermittent Fasting on Body Composition: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 625240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Montilla, J.J.; Cuevas-Cervera, M.; Gonzalez-Muñoz, A.; Garcia-Rios, M.C.; Navarro-Ledesma, S. Efficacy of Nutritional Strategies on the Improvement of the Performance and Health of the Athlete: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moro, T.; Tinsley, G.; Longo, G.; Grigoletto, D.; Bianco, A.; Ferraris, C.; Guglielmetti, M.; Veneto, A.; Tagliabue, A.; Marcolin, G.; et al. Time-Restricted Eating Effects on Performance, Immune Function, and Body Composition in Elite Cyclists: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2020, 17, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aird, T.P.; Farquharson, A.J.; Bermingham, K.M.; O’Sulllivan, A.; Drew, J.E.; Carson, B.P. Divergent Serum Metabolomic, Skeletal Muscle Signaling, Transcriptomic, and Performance Adaptations to Fasted versus Whey Protein-Fed Sprint Interval Training. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 321, E802–E820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, A.J.; Langton, H.M.; Mulligan, M.; Egan, B. Effects of 8 Wk of 16:8 Time-Restricted Eating in Male Middle- and Long-Distance Runners. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2021, 53, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.; Ratamess, N.A.; Faigenbaum, A.D.; Bush, J.A.; Beller, N.; Vargas, A.; Fardman, B.; Andriopoulos, T. Effect of Time-Restricted Feeding on Anthropometric, Metabolic, and Fitness Parameters: A Systematic Review. J. Am. Nutr. Assoc. 2022, 41, 810–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinsley, G.M.; Forsse, J.S.; Butler, N.K.; Paoli, A.; Bane, A.A.; La Bounty, P.M.; Morgan, G.B.; Grandjean, P.W. Time-Restricted Feeding in Young Men Performing Resistance Training: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Sport. Sci. 2017, 17, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, J.M.; Santos, I.; Pezarat-Correia, P.; Minderico, C.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Mendonca, G.V. Effects of Time-Restricted Feeding on Supramaximal Exercise Performance and Body Composition: A Randomized and Counterbalanced Crossover Study in Healthy Men. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouhal, H.; Bagheri, R.; Ashtary-Larky, D.; Wong, A.; Triki, R.; Hackney, A.C.; Laher, I.; Abderrahman, A.B. Effects of Ramadan Intermittent Fasting on Inflammatory and Biochemical Biomarkers in Males with Obesity. Physiol. Behav. 2020, 225, 113090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilk, M.; Zajac, A.; Tufano, J.J. The Influence of Movement Tempo During Resistance Training on Muscular Strength and Hypertrophy Responses: A Review. Sports Med. 2021, 51, 1629–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Biomarkers | ETRE-PA | LTRE-PA | LTRE | CG | ANOVA | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre | Post | Pre | Post | Pre | Post | Pre | Post | F(1, 57) | P (Time) | ηp2 (Time) | |
| LDL-c (mmol/L) | 2.75 ± 0.76 | 2.32 ** ± 0.54 | 2.65 ± 0.76 | 2.46 ± 0.95 | 2.38 ± 0.72 | 2.12 ± 0.54 | 3.17 ± 1.08 | 2.39 ± 0.63 | 24.27 | 0.000 | 0.29 |
| TC (mmol/L) | 4.47 ± 0.90 | 3.76 *** ± 0.64 | 4.29 ± 0.96 | 3.98.96 ± 1.38 | 4.13 ± 0.91 | 3.69 ** ± 0.69 | 4.96 ± 1.24 | 3.87 ± 0.85 | 43.07 | 0.000 | 0.43 |
| ALAT (UI/L) | 14.73 ± 10 | 6.38 ** ± 2.14 | 13.60 ± 7.28 | 7.04 * ± 3.34 | 12.66 ± 10.8 | 7.80 ± 2.27 | 19.07 ± 15.66 | 11.31 ± 7.69 | 24.97 | 0.000 | 0.30 |
| ASAT (UI/L) | 18.13 ± 6.45 | 12.53 ± 2.16 | 20.20 ± 14.10 | 12.60 * ± 5.69 | 19.86 ± 10.09 | 15.33 ± 8.98 | 21.31 ± 15.41 | 15.68 ± 7.94 | 12.85 | 0.001 | 0.18 |
| Alkaline Phosphatase (UI/L) | 77.06 ± 34.77 | 79.6 ± 21.56 | 61.60 ± 13.08 | 56.93 ± 16.69 | 79.60 ± 21.56 | 72.00 ± 20.72 | 59.37 ± 14.54 | 45.37 ± 15.51 | 5.62 | 0.02 | 0.09 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miladi, S.; Driss, T.; Ameur, R.; Miladi, S.C.; Miladi, S.J.; Najjar, M.F.; Neffati, F.; Hammouda, O. Effectiveness of Early Versus Late Time-Restricted Eating Combined with Physical Activity in Overweight or Obese Women. Nutrients 2025, 17, 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17010169
Miladi S, Driss T, Ameur R, Miladi SC, Miladi SJ, Najjar MF, Neffati F, Hammouda O. Effectiveness of Early Versus Late Time-Restricted Eating Combined with Physical Activity in Overweight or Obese Women. Nutrients. 2025; 17(1):169. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17010169
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiladi, Sarra, Tarak Driss, Ranya Ameur, Sirine C. Miladi, Samar J. Miladi, Mohamed Fadhel Najjar, Fadoua Neffati, and Omar Hammouda. 2025. "Effectiveness of Early Versus Late Time-Restricted Eating Combined with Physical Activity in Overweight or Obese Women" Nutrients 17, no. 1: 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17010169
APA StyleMiladi, S., Driss, T., Ameur, R., Miladi, S. C., Miladi, S. J., Najjar, M. F., Neffati, F., & Hammouda, O. (2025). Effectiveness of Early Versus Late Time-Restricted Eating Combined with Physical Activity in Overweight or Obese Women. Nutrients, 17(1), 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17010169








