Targeting Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with Hawthorn Ethanol Extract (HEE): A Comprehensive Examination of Hepatic Lipid Reduction and Gut Microbiota Modulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Hawthorn Ethanol Extract (HEE)
2.2. Animal Experiments
2.3. Pseudo-Germfree Mice (PG) Treated with Antibiotics
2.4. Histopathological Analysis of Animals
2.5. Mouse Serum Indicator Assay
2.6. Quantitative Reverse Transcription–Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR) Analysis
2.7. Gut Microbiota Analysis
2.8. Analysis of Short-Chain Fatty Acids
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
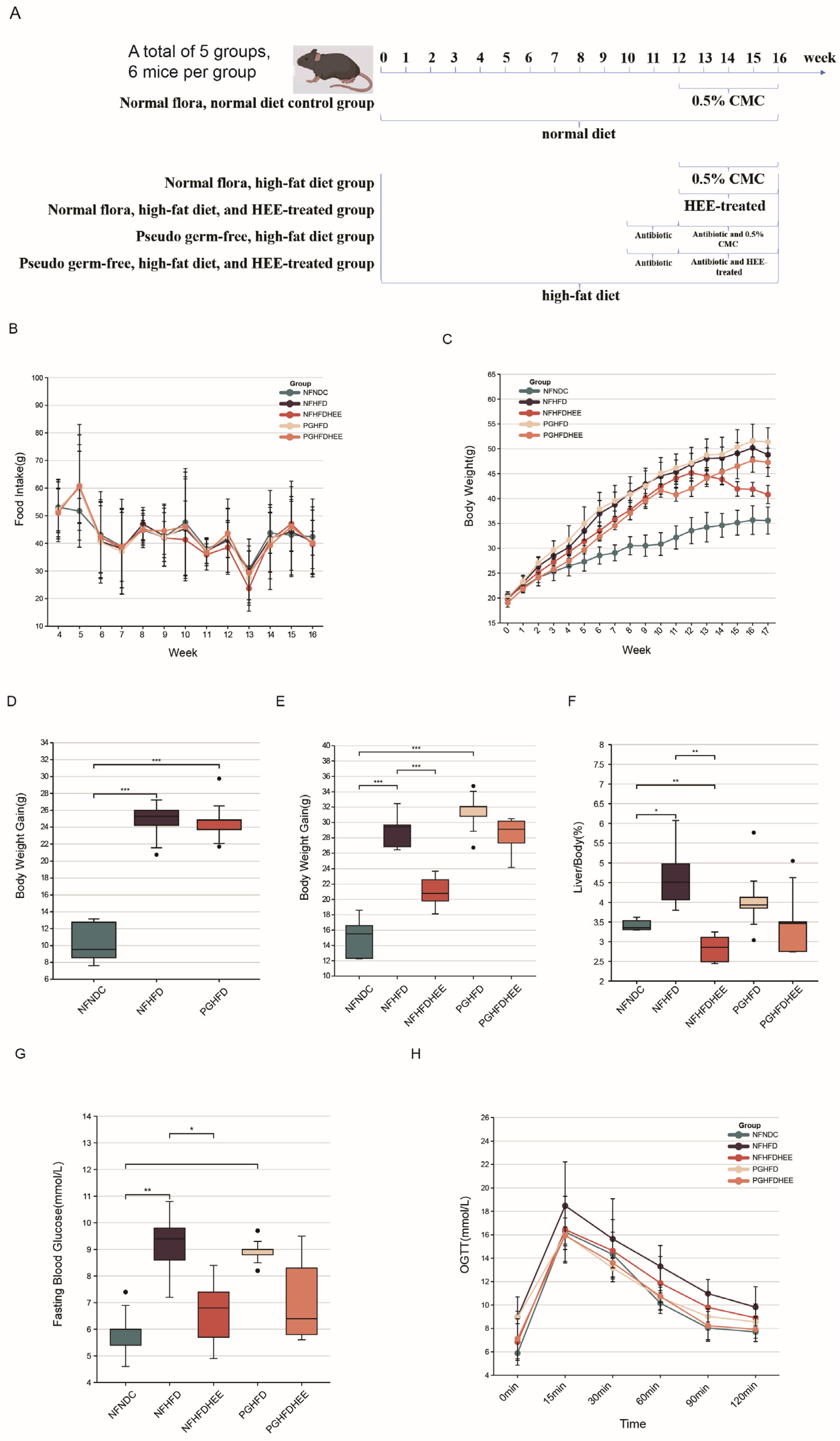
3.1. The Mitigating Effect of HEE on HFD-Induced NAFLD in Mice
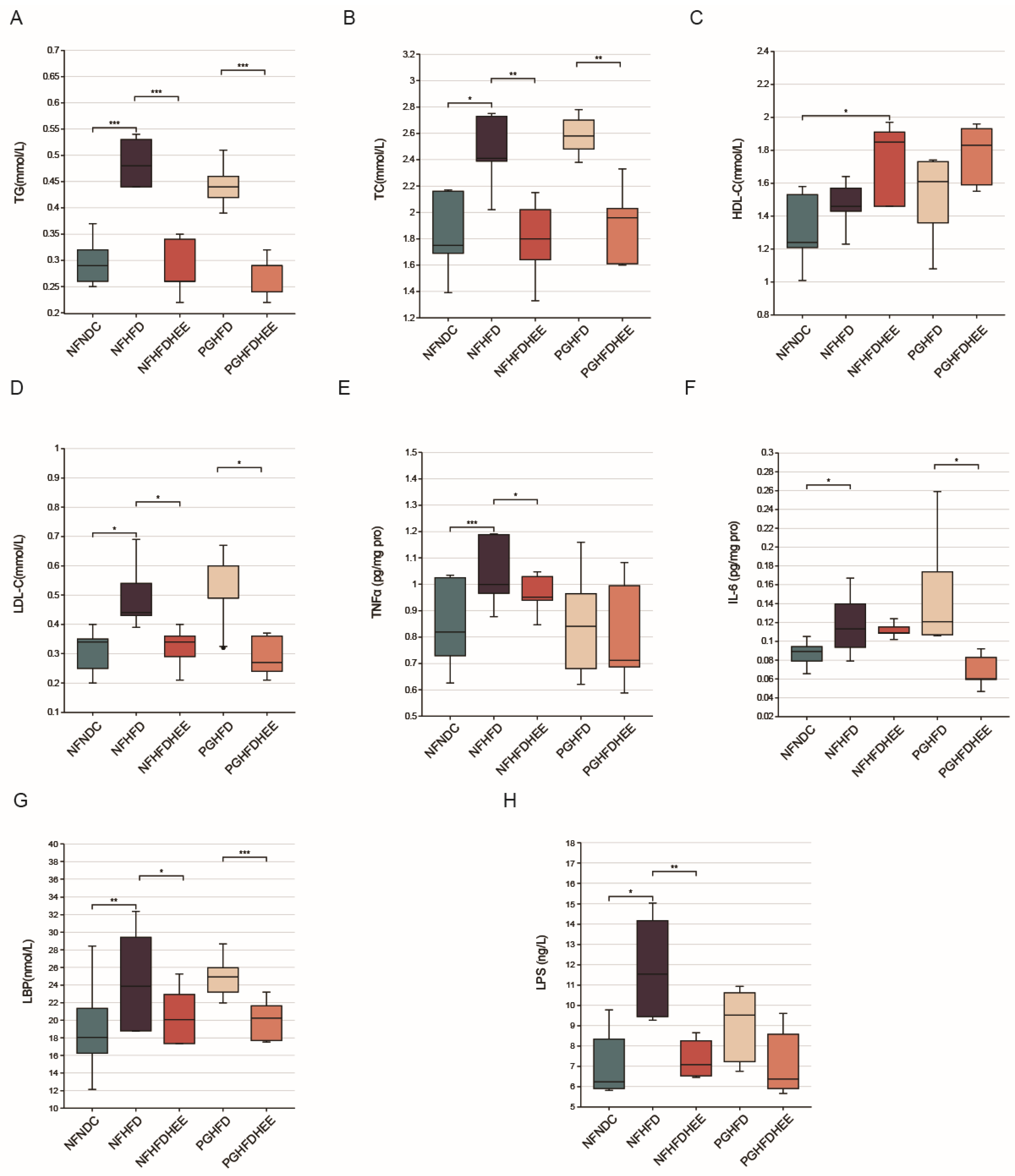
3.2. Modulation of Lipid Profile and Inflammation-Related Cytokines by HEE in HFD Mice
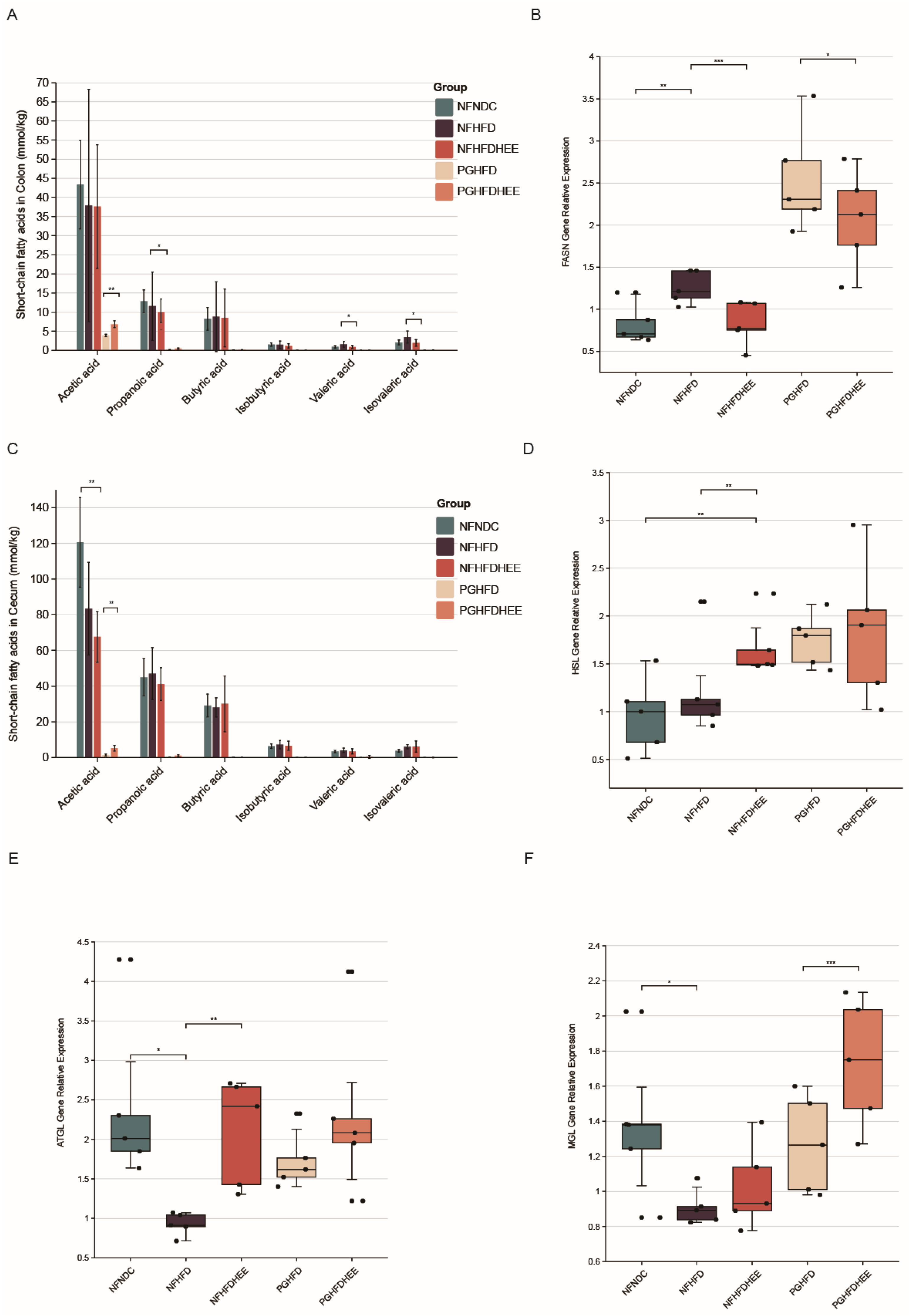
3.3. Effects of HEE on the Expression of Genes Related to Intestinal SCFAs and Hepatic Lipid Metabolism in Mice
3.4. HEE Modulates the Gut Microbiota in HFD Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Friedman, S.L.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Rinella, M.; Sanyal, A.J. Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 908–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Vigliotti, C.; Witjes, J.; Le, P.; Holleboom, A.G.; Verheij, J.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Clément, K. Gut microbiota and human NAFLD: Disentangling microbial signatures from metabolic disorders. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrncir, T.; Hrncirova, L.; Kverka, M.; Hromadka, R.; Machova, V.; Trckova, E.; Kostovcikova, K.; Kralickova, P.; Krejsek, J.; Tlaskalova-Hogenova, H. Gut microbiota and NAFLD: Pathogenetic mechanisms, microbiota signatures, and therapeutic interventions. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Wei, H.; Zhou, Y.; Szeto, C.-H.; Li, C.; Lin, Y.; Coker, O.O.; Lau, H.C.H.; Chan, A.W.; Sung, J.J. High-fat diet promotes colorectal tumorigenesis through modulating gut microbiota and metabolites. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 135–149.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez, K.T.; Enos, R.T.; Bader, J.E.; Sougiannis, A.T.; Carson, M.S.; Chatzistamou, I.; Carson, J.A.; Nagarkatti, P.S.; Nagarkatti, M.; Murphy, E.A. Prolonged high-fat-diet feeding promotes non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and alters gut microbiota in mice. World J. Hepatol. 2019, 11, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.; You, H.J.; Lee, G.; Lee, S.H.; Yoo, T.; Choi, M.; Joo, S.K.; Park, J.H.; Chang, M.S.; Lee, D.H. Interaction effect between NAFLD severity and high carbohydrate diet on gut microbiome alteration and hepatic de novo lipogenesis. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2078612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Zhang, P.; Shen, L.; Niu, L.; Tan, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, L.; Hao, X.; Li, X. Short-chain fatty acids and their association with signalling pathways in inflammation, glucose and lipid metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Piao, X.; Mahfuz, S.; Long, S.; Wang, J. The interaction among gut microbes, the intestinal barrier and short chain fatty acids. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 9, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumpail, B.J.; Li, A.A.; John, N.; Sallam, S.; Shah, N.D.; Kwong, W.; Cholankeril, G.; Kim, D.; Ahmed, A. The therapeutic implications of the gut microbiome and probiotics in patients with NAFLD. Diseases 2019, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, R.Z.; Barbalho, S.M.; Sloan, K.P.; Laurindo, L.F.; Gonzaga, H.F.; Grippa, P.C.; Zutin, T.L.M.; Girio, R.J.; Repetti, C.S.F.; Detregiachi, C.R.P. The effects of probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics in non-alcoholic fat liver disease (NAFLD) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): A systematic review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferolla, S.M.; de Almeida Armiliato, G.N.; Couto, C.A.; Ferrari, T.C.A. Probiotics as a complementary therapeutic approach in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshaghabee, F.M.; Rokana, N.; Panwar, H.; Heller, K.J.; Schrezenmeir, J. Probiotics for dietary management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 1553–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Gu, D.; Peng, J.; Jiang, K.; Li, Z.; Shi, J.; Yang, S.; Li, S.; Fan, X. Ginsenoside Rg1 regulates liver lipid factor metabolism in NAFLD model rats. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 10878–10890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, D.; Xie, Z.; Huang, B.; Zhu, S.; Wang, G.; Zhou, H.; Lin, S.; Lin, Z.; Yang, B. Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide peptide alleviates hepatoteatosis via modulating bile acid metabolism dependent on FXR-SHP/FGF. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 49, 1204–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontes, A.; Ramalho-Santos, J.; Zischka, H.; Azul, A.M. Mushrooms on the plate: Trends towards NAFLD treatment, health improvement and sustainable diets. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 52, e13667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lien, H.-M.; Lin, H.-T.; Huang, S.-H.; Chen, Y.-R.; Huang, C.-L.; Chen, C.-C.; Chyau, C.-C. Protective Effect of Hawthorn Fruit Extract against High Fructose-Induced Oxidative Stress and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Pancreatic β-Cells. Foods 2023, 12, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Zhang, L.; Pan, J.; Shi, H.; Zhang, M.; Li, C. Advances in the study of vascular protective effects and molecular mechanisms of hawthorn (Crataegus anamesa Sarg.) extracts in cardiovascular diseases. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 5870–5890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Liu, H.; Du, X.; Shi, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, S. Hawthorn fruit extract protect against MC-LR-induced hepatotoxicity by attenuating oxidative stress and apoptosis. Environ. Toxicol. 2023, 38, 1239–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhu, S.; Yang, W.; Huang, Q.; Ho, C.-T. The biological fate and bioefficacy of citrus flavonoids: Bioavailability, biotransformation, and delivery systems. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 3307–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, J.; Xie, Y. Improvement strategies for the oral bioavailability of poorly water-soluble flavonoids: An overview. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 570, 118642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, F.; Nakamura, N.; Akao, T.; Hattori, M. Pharmacokinetics of berberine and its main metabolites in conventional and pseudo germ-free rats determined by liquid chromatography/ion trap mass spectrometry. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2006, 34, 2064–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estaki, M.; Jiang, L.; Bokulich, N.A.; McDonald, D.; González, A.; Kosciolek, T.; Martino, C.; Zhu, Q.; Birmingham, A.; Vázquez-Baeza, Y. QIIME 2 enables comprehensive end-to-end analysis of diverse microbiome data and comparative studies with publicly available data. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2020, 70, e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Kong, Q.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Wang, G. A high-fat diet increases gut microbiota biodiversity and energy expenditure due to nutrient difference. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, F.; Duque, A.L.R.F.; Saad, S.M.I.; Sivieri, K. Gut microbiome approaches to treat obesity in humans. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 1081–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, A.; Stephens, J.; Harris, D. Gut microbiota influence in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Gut Pathog. 2021, 13, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crotti, E.; Rizzi, A.; Chouaia, B.; Ricci, I.; Favia, G.; Alma, A.; Sacchi, L.; Bourtzis, K.; Mandrioli, M.; Cherif, A. Acetic acid bacteria, newly emerging symbionts of insects. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 6963–6970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Sheng, L.; Zhong, J.; Tao, X.; Zhu, W.; Ma, J.; Yan, J.; Zhao, A.; Zheng, X.; Wu, G. Desulfovibrio vulgaris, a potent acetic acid-producing bacterium, attenuates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1930874. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, H.C.-H.; Zhang, X.; Ji, F.; Lin, Y.; Liang, W.; Li, Q.; Chen, D.; Fong, W.; Kang, X.; Liu, W. Lactobacillus acidophilus suppresses non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-associated hepatocellular carcinoma through producing valeric acid. eBioMedicine 2024, 100, 104952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Guo, W.-L.; Li, Q.-Y.; Xu, J.-X.; Cao, Y.-J.; Liu, B.; Yu, X.-D.; Rao, P.-F.; Ni, L.; Lv, X.-C. The protective mechanism of Lactobacillus plantarum FZU3013 against non-alcoholic fatty liver associated with hyperlipidemia in mice fed a high-fat diet. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 3316–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Jiao, T.; Xu, Y.; Li, D.; Si, Q.; Hao, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Bifidobacterium adolescentis and Lactobacillus rhamnosus alleviate non-alcoholic fatty liver disease induced by a high-fat, high-cholesterol diet through modulation of different gut microbiota-dependent pathways. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 6115–6127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.; Huang, J.; Guo, X.; Xia, J.; Hu, M. Romboutsia lituseburensis JCM1404 supplementation ameliorated endothelial function via gut microbiota modulation and lipid metabolisms alterations in obese rats. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2023, 370, fnad016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiri, P.; Hosseini, S.A.; Ghaffari, S.; Tutunchi, H.; Ghaffari, S.; Mosharkesh, E.; Asghari, S.; Roshanravan, N. Role of butyrate, a gut microbiota derived metabolite, in cardiovascular diseases: A comprehensive narrative review. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, B.; Kim, K.H.; Ruan, W.; Kim, H.M.; Jeon, C.O. Lantibiotic-encoding Streptococcus in the human microbiome are underlying risk factors for liver diseases. J. Infect. 2022, 84, e70–e72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Jeon, H.; Na, S.H.; Kwon, H.I.; Selasi, G.N.; Nicholas, A.; Park, T.I.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.C. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia outer membrane vesicles elicit a potent inflammatory response in vitro and in vivo. FEMS Pathog. Dis. 2016, 74, ftw104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.; Zheng, L.; Wei, Y.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, D.; Yan, S.; Qin, H.; Wang, Q.; Ci, X.; Feng, H. Enterobacter cloacae aggravates metabolic disease by inducing inflammation and lipid accumulation. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 90, 103819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskitalo, A.; Munukka, E.; Toivonen, R.; Hollmén, M.; Kainulainen, H.; Huovinen, P.; Jalkanen, S.; Pekkala, S. Enterobacter cloacae administration induces hepatic damage and subcutaneous fat accumulation in high-fat diet fed mice. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, N.; Bruneau, A.; Zhang, X.; Wang, R.; Wang, J.; Rabot, S.; Gérard, P.; Zhao, L. Endotoxin producers overgrowing in human gut microbiota as the causative agents for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. mBio 2020, 11, e03263-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, T.; Wang, D.; Ding, Y.; Xu, H.; Sun, Y.; Hou, J.; Zhang, Y. Targeting Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with Hawthorn Ethanol Extract (HEE): A Comprehensive Examination of Hepatic Lipid Reduction and Gut Microbiota Modulation. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16091335
Wang T, Wang D, Ding Y, Xu H, Sun Y, Hou J, Zhang Y. Targeting Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with Hawthorn Ethanol Extract (HEE): A Comprehensive Examination of Hepatic Lipid Reduction and Gut Microbiota Modulation. Nutrients. 2024; 16(9):1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16091335
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Tianyu, Dawei Wang, Yinghui Ding, He Xu, Yue Sun, Jumin Hou, and Yanrong Zhang. 2024. "Targeting Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with Hawthorn Ethanol Extract (HEE): A Comprehensive Examination of Hepatic Lipid Reduction and Gut Microbiota Modulation" Nutrients 16, no. 9: 1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16091335
APA StyleWang, T., Wang, D., Ding, Y., Xu, H., Sun, Y., Hou, J., & Zhang, Y. (2024). Targeting Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with Hawthorn Ethanol Extract (HEE): A Comprehensive Examination of Hepatic Lipid Reduction and Gut Microbiota Modulation. Nutrients, 16(9), 1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16091335





