Preoperative Multistrain Probiotic Supplementation Does Not Affect Body Weight Changes or Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Bariatrics: Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Study Protocol
2.4. Probiotic Intervention
2.5. Nutritional Status Assessment
2.6. Metabolic Parameters
2.7. Postoperative Complications
2.8. Statistical Methods
3. Results
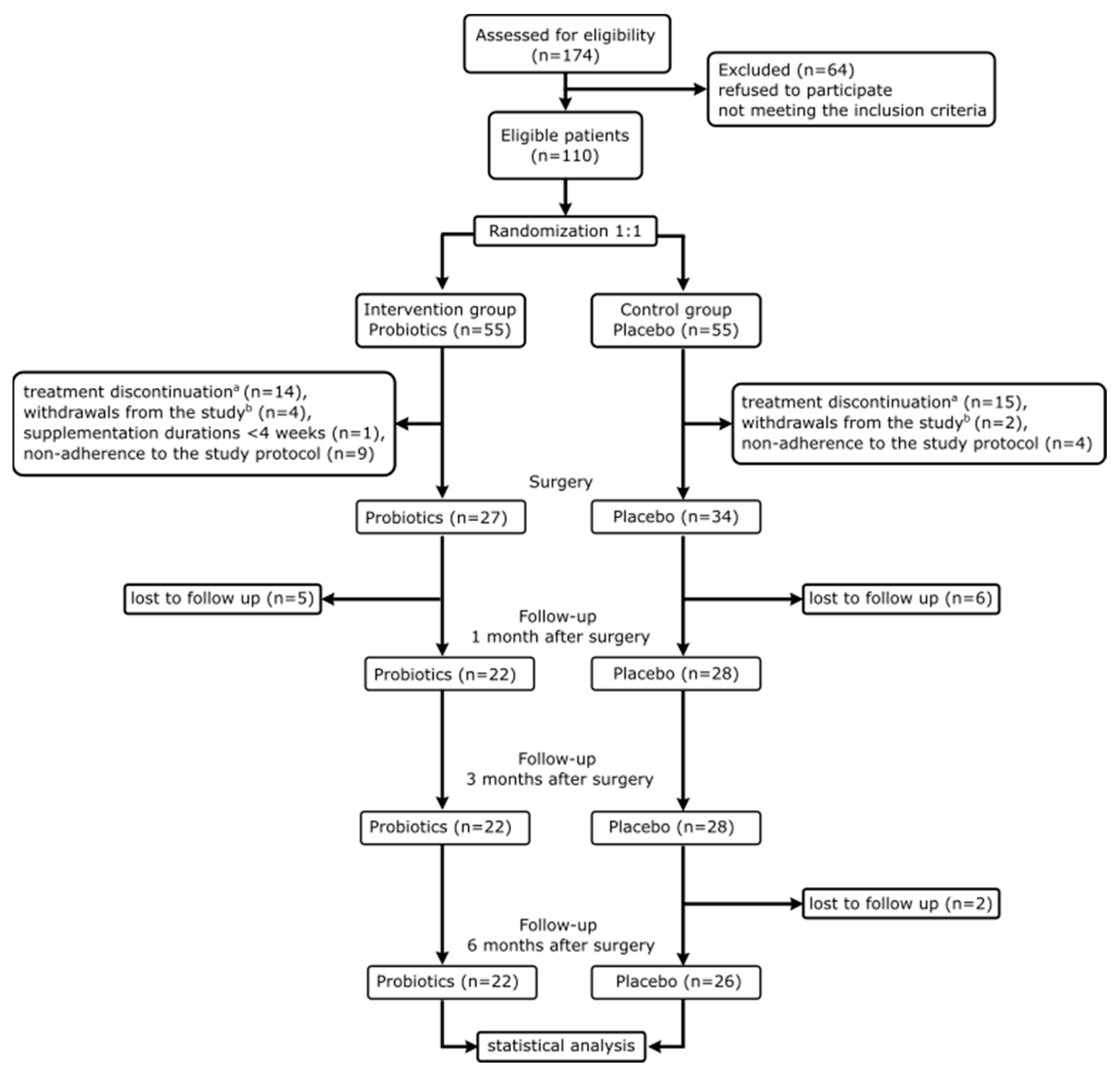
3.1. Flow of Trial Participants and Comparison between Arms
3.2. Primary Outcomes
3.3. Secondary Outcomes
3.3.1. Glycemic Parameters
3.3.2. Lipid Profile
3.3.3. Liver Enzymes
3.3.4. Iron Parameters
3.3.5. Vitamins
3.3.6. Postoperative Complications
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tomé-Castro, X.M.; Rodriguez-Arrastia, M.; Cardona, D.; Rueda-Ruzafa, L.; Molina-Torres, G.; Roman, P. Probiotics as a Therapeutic Strategy in Obesity and Overweight: A Systematic Review. Benef. Microbes 2021, 12, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 1 June 2024).
- Murray, C.J.L.; Aravkin, A.Y.; Zheng, P.; Abbafati, C.; Abbas, K.M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A.; Abdollahi, M.; Abdollahpour, I.; et al. Global Burden of 87 Risk Factors in 204 Countries and Territories, 1990–2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1223–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiggins, T.; Guidozzi, N.; Welbourn, R.; Ahmed, A.R.; Markar, S.R. Association of Bariatric Surgery with All-Cause Mortality and Incidence of Obesity-Related Disease at a Population Level: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.-H.; Yun, K.E.; Kim, J.; Park, E.; Chang, Y.; Ryu, S.; Kim, H.-L.; Kim, H.-N. Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Health among Overweight and Obese Individuals. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zou, R.; Guo, M.; Zheng, H. Characteristics of Gut Microbiota in People with Obesity. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotzampassi, K. Bacteria and Obesity: The Proportion Makes the Difference. Surgery 2013, 3, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, N.R.F.; Zaparolli, M.R.; Cruz, M.R.R.; Schieferdecker, M.E.M.; Campos, A.C.L. Postoperative changes in intestinal microbiota and use of probiotics in roux-en-y gastric bypass and sleeve vertical gastrectomy: An integrative review. ABCD Arq. Bras. Cir. Dig. 2018, 31, e1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Warmbrunn, M.V.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Clément, K. Metabolism and Metabolic Disorders and the Microbiome: The Intestinal Microbiota Associated With Obesity, Lipid Metabolism, and Metabolic Health—Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Strategies. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 573–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.-J.; Li, J.-N.; Nie, Y.-Z. Gut Hormones in Microbiota-Gut-Brain Cross-Talk. Chin. Med. J. 2020, 133, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, C. Modulation of Gut Microbiota and Immune System by Probiotics, Pre-Biotics, and Post-Biotics. Front. Nutr. 2022, 8, 634897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, K.O.; Fries, L.R.; Silva-Zolezzi, I.; Thakkar, S.K.; Iroz, A.; Blanchard, C. Effects of Probiotic Intervention on Markers of Inflammation and Health Outcomes in Women of Reproductive Age and Their Children. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 889040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristofori, F.; Dargenio, V.N.; Dargenio, C.; Miniello, V.L.; Barone, M.; Francavilla, R. Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Effects of Probiotics in Gut Inflammation: A Door to the Body. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 578386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, M.; Darimont, C.; Panahi, S.; Drapeau, V.; Marette, A.; Taylor, V.; Doré, J.; Tremblay, A. Effects of a Diet-Based Weight-Reducing Program with Probiotic Supplementation on Satiety Efficiency, Eating Behaviour Traits, and Psychosocial Behaviours in Obese Individuals. Nutrients 2017, 9, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasama, K.; Mui, W.; Lee, W.J.; Lakdawala, M.; Naitoh, T.; Seki, Y.; Sasaki, A.; Wakabayashi, G.; Sasaki, I.; Kawamura, I.; et al. IFSO-APC Consensus Statements 2011. Obes. Surg. 2012, 22, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannaerts, G.H.H.; Van Mil, S.R.; Stepaniak, P.S.; Dunkelgrün, M.; De Quelerij, M.; Verbrugge, S.J.; Zengerink, H.F.; Biter, L.U. Results of Implementing an Enhanced Recovery After Bariatric Surgery (ERABS) Protocol. Obes. Surg. 2016, 26, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarosz, M.; Rychlik, E.; Stoś, K.; Charzewska, J. Normy Żywienia dla Populacji Polski i ich Zastosowanie; Narodowy Instytut Zdrowia Publicznego—Państwowy Zakład Higieny: Warszawa, Poland, 2020; ISBN 978-83-65870-28-5. [Google Scholar]
- Budzyński, A.; Major, P.; Głuszek, S.; Kaseja, K.; Koszutski, T.; Leśniak, S.; Lewandowski, T.; Lipka, M.; Lisik, W.; Makarewicz, W. Polskie Rekomendacje w Zakresie Chirurgii Bariatrycznej i Metabolicznej. Medycyna Praktyczna. Chirurgia 2017, 13–26. [Google Scholar]
- Deitel, M.; Greenstein, R.J. Recommendations for Reporting Weight Loss. Obes. Surg. 2003, 13, 159–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dindo, D.; Demartines, N.; Clavien, P.-A. Classification of Surgical Complications: A New Proposal With Evaluation in a Cohort of 6336 Patients and Results of a Survey. Ann. Surg. 2004, 240, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, R.; Basson, A.R.; Wearsh, P.; Cominelli, F.; Rodriguez-Palacios, A. Validity of Food Additive Maltodextrin as Placebo and Effects on Human Gut Physiology: Systematic Review of Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 61, 2853–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daghmouri, M.A.; Chaouch, M.A.; Yang, W.; Akremi, S.; Jaoua, H.; Fadhel, K.B.; Gouader, A.; Reissfelder, C.; Elhadedy, H.; Rahbari, N.; et al. Probiotics in Bariatric Surgery Ensure Greater Lipids and Glycemic Profile with No Effect on Anthropometric Measurements and Inflammatory Markers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of RCT. Surg. Open Dig. Adv. 2022, 7, 100061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Kuang, L.; Yang, K.; Xie, J.; Liu, X.; Shen, S.; Li, X.; Wu, S.; Yang, Y.; et al. Effects of Probiotics in Patients with Morbid Obesity Undergoing Bariatric Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Obes. 2023, 47, 1029–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utzschneider, K.M.; Kratz, M.; Damman, C.J.; Hullarg, M. Mechanisms Linking the Gut Microbiome and Glucose Metabolism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 1445–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albillos, A.; De Gottardi, A.; Rescigno, M. The Gut-Liver Axis in Liver Disease: Pathophysiological Basis for Therapy. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 558–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenny, D.J.; Plichta, D.R.; Shungin, D.; Koppel, N.; Hall, A.B.; Fu, B.; Vasan, R.S.; Shaw, S.Y.; Vlamakis, H.; Balskus, E.P.; et al. Cholesterol Metabolism by Uncultured Human Gut Bacteria Influences Host Cholesterol Level. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 28, 245–257.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sargun, A.; Gerner, R.R.; Raffatellu, M.; Nolan, E.M. Harnessing Iron Acquisition Machinery to Target Enterobacteriaceae. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 223, S307–S313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Tang, R.; Wang, J.; Wan, D.; Yin, Y.; Xie, L. Gut Microbiota Bridges the Iron Homeostasis and Host Health. Sci. China Life Sci. 2023, 66, 1952–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, M.; Amaretti, A.; Raimondi, S. Folate Production by Probiotic Bacteria. Nutrients 2011, 3, 118–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherf-Dagan, S.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Zilberman-Schapira, G.; Webb, M.; Buch, A.; Keidar, A.; Raziel, A.; Sakran, N.; Goitein, D.; Goldenberg, N.; et al. Probiotics Administration Following Sleeve Gastrectomy Surgery: A Randomized Double-Blind Trial. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karbaschian, Z.; Mokhtari, Z.; Pazouki, A.; Kabir, A.; Hedayati, M.; Moghadam, S.S.; Mirmiran, P.; Hekmatdoost, A. Probiotic Supplementation in Morbid Obese Patients Undergoing One Anastomosis Gastric Bypass-Mini Gastric Bypass (OAGB-MGB) Surgery: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Clinical Trial. Obes. Surg. 2018, 28, 2874–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, Z.; Karbaschian, Z.; Pazouki, A.; Kabir, A.; Hedayati, M.; Mirmiran, P.; Hekmatdoost, A. The Effects of Probiotic Supplements on Blood Markers of Endotoxin and Lipid Peroxidation in Patients Undergoing Gastric Bypass Surgery; a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Clinical Trial with 13 Months Follow-Up. Obes. Surg. 2019, 29, 1248–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabico, S.; Al-Mashharawi, A.; Al-Daghri, N.M.; Wani, K.; Amer, O.E.; Hussain, D.S.; Ahmed Ansari, M.G.; Masoud, M.S.; Alokail, M.S.; McTernan, P.G. Effects of a 6-Month Multi-Strain Probiotics Supplementation in Endotoxemic, Inflammatory and Cardiometabolic Status of T2DM Patients: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 1561–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szulińska, M.; Łoniewski, I.; Van Hemert, S.; Sobieska, M.; Bogdański, P. Dose-Dependent Effects of Multispecies Probiotic Supplementation on the Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) Level and Cardiometabolic Profile in Obese Postmenopausal Women: A 12-Week Randomized Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2018, 10, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabico, S.; Al-Mashharawi, A.; Al-Daghri, N.M.; Yakout, S.; Alnaami, A.M.; Alokail, M.S.; McTernan, P.G. Effects of a Multi-Strain Probiotic Supplement for 12 Weeks in Circulating Endotoxin Levels and Cardiometabolic Profiles of Medication Naïve T2DM Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczmarczyk, M.; Szulińska, M.; Łoniewski, I.; Kręgielska-Narożna, M.; Skonieczna-Żydecka, K.; Kosciolek, T.; Bezshapkin, V.; Bogdański, P. Treatment With Multi-Species Probiotics Changes the Functions, Not the Composition of Gut Microbiota in Postmenopausal Women With Obesity: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 815798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulker, İ.; Yildiran, H. The Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Gut Microbiota in Patients with Obesity: A Review of the Literature. Biosci. Microbiota Food Health 2019, 38, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komorniak, N.; Kaczmarczyk, M.; Łoniewski, I.; Martynova-Van Kley, A.; Nalian, A.; Wroński, M.; Kaseja, K.; Kowalewski, B.; Folwarski, M.; Stachowska, E. Analysis of the Efficacy of Diet and Short-Term Probiotic Intervention on Depressive Symptoms in Patients after Bariatric Surgery: A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo Controlled Pilot Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komorniak, N.; Martynova-Van Kley, A.; Nalian, A.; Wroński, M.; Kaseja, K.; Kowalewski, B.; Kaźmierczak-Siedlecka, K.; Łoniewski, I.; Kaczmarczyk, M.; Podsiadło, K.; et al. Association between Fecal Microbiota, SCFA, Gut Integrity Markers and Depressive Symptoms in Patients Treated in the Past with Bariatric Surgery—The Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Hu, Y.; Tang, J.; Xu, W.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, W. The Implication of Gut Microbiota in Recovery from Gastrointestinal Surgery. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1110787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Zheng, C.; Li, Q.; Xu, T.; Cao, W.; Shi, M.; Huang, F.; Liu, L.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, W.; et al. Preoperative Oral Probiotics Relieve Insulin Resistance and Gut Dysbacteriosis in Patients with Gastric Cancer after Gastrectomy. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 101, 105426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melali, H.; Abdolahi, A.; Sheikhbahaei, E.; Vakili, K.; Mahmoudieh, M.; Keleidari, B.; Shahabi, S. Impact of Probiotics on Gastrointestinal Function and Metabolic Status After Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass: A Double-Blind, Randomized Trial. Obes. Surg. 2024, 34, 2033–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Placebo (n = 26) | Probiotics (n = 22) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (F/M) n | 20/6 | 13/9 | 0.184 |
| Age (years) | 42.2 ± 11.6 | 41 ± 11.2 | 0.701 |
| Duration of supplementation (weeks) | 11.5 ± 1.9 | 11.5 ± 2 | 0.965 † |
| Max weight (kg) | 135.9 ± 21.8 | 138.3 ± 27.1 | 0.733 |
| Weight 6 M PreOP (kg) | 129.2 ± 21.4 | 130.1 ± 31.0 | 0.907 |
| Max BMI (kg/m2) | 45.9 ± 5.0 | 46.2 ± 6.2 | 0.885 |
| BMI 6 M PreOP (kg/m2) | 43.6 ± 4.4 | 43.2 ± 7.1 | 0.825 |
| Type of surgery (LSG/OAGB) | 24/2 | 18/4 | 0.392 ‡ |
| current-smokers n (%) | 7 (26.9) | 1 (4.5) | 0.055 ‡ |
| ever-smokers n (%) | 9 (34.6) | 9 (40.9) | 0.584 |
| DM1 n (%) | 0 | 1 (4.5) | 0.458 ‡ |
| DM2 n (%) | 6 (23.1) | 6 (27.3) | 0.738 |
| HTN n (%) | 14 (53.8) | 12 (54.5) | 0.961 |
| DL n (%) | 17 (65.4) | 15 (68.2) | 0.838 |
| HT n (%) | 9 (34.6) | 7 (31.8) | 0.838 |
| fatty liver n (%) | 21 (80.8) | 19 (86.4) | 0.604 |
| OSAS (%) | 17 (65.4) | 17 (77.3) | 0.367 |
| Impaired fasting glucose n (%) | 9 (34.6) | 11 (0.5) | 0.281 |
| Placebo (n = 26) | Probiotics (n = 22) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vit. D (pg/mL) | 49.9 ± 15.1 | 52.5 ± 15.5 | 0.562 |
| Folic Acid (ng/mL) | 5.8 ± 1.6 | 7.2 ± 2.6 | 0.028 |
| Vit. B12 (pg/mL) | 349.8 ± 93.6 | 349.4 ± 113.6 | 0.99 |
| Iron (ug/dL) | 77.1 ± 30.8 | 82.5 ± 37.9 | 0.59 |
| Insulin (uU/mL) | 20.9 ± 14.9 | 22 ± 18.1 | 0.827 |
| LDH (U/L) | 192.5 ± 41.8 | 196.2 ± 32.7 | 0.738 |
| ALT (U/L) | 37.6 ± 18.3 | 34.7 ± 16.8 | 0.573 |
| AST (U/L) | 24.8 ± 10.9 | 24.2 ± 10.6 | 0.867 |
| GGT (U/L) | 46.4 ± 31.2 | 36.8 ± 18.6 | 0.212 |
| ALP (U/L) | 84.6 ± 26.1 | 75 ± 18.4 | 0.154 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 147.8 ± 67 | 140.5 ± 70.1 | 0.715 |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 43.5 ± 8.6 | 47.1 ± 13.1 | 0.262 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 117.8 ± 39.3 | 115.1 ± 27.8 | 0.787 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 187.7 ± 45.3 | 188.5 ± 34.9 | 0.942 |
| HbA1c% | 5.7 ± 0.7 | 6.1 ± 1.3 | 0.287 |
| HbA1c (mmol/mol) | 39.2 ± 7.2 | 42.7 ± 14.4 | 0.272 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 102.3 ± 16.4 | 112.9 ± 41.3 | 0.238 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 13.8 ± 1.5 | 14.2 ± 1.8 | 0.45 |
| HOMA-IR | 5.6 ± 5.5 | 6.4 ± 6.4 | 0.633 |
| Placebo (n = 26) | Probiotics (n = 22) | Between Subjects Effects (Group) | Within Subjects Effects (Time) | Within Subjects Effects (Time × Group) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (kg) | |||||
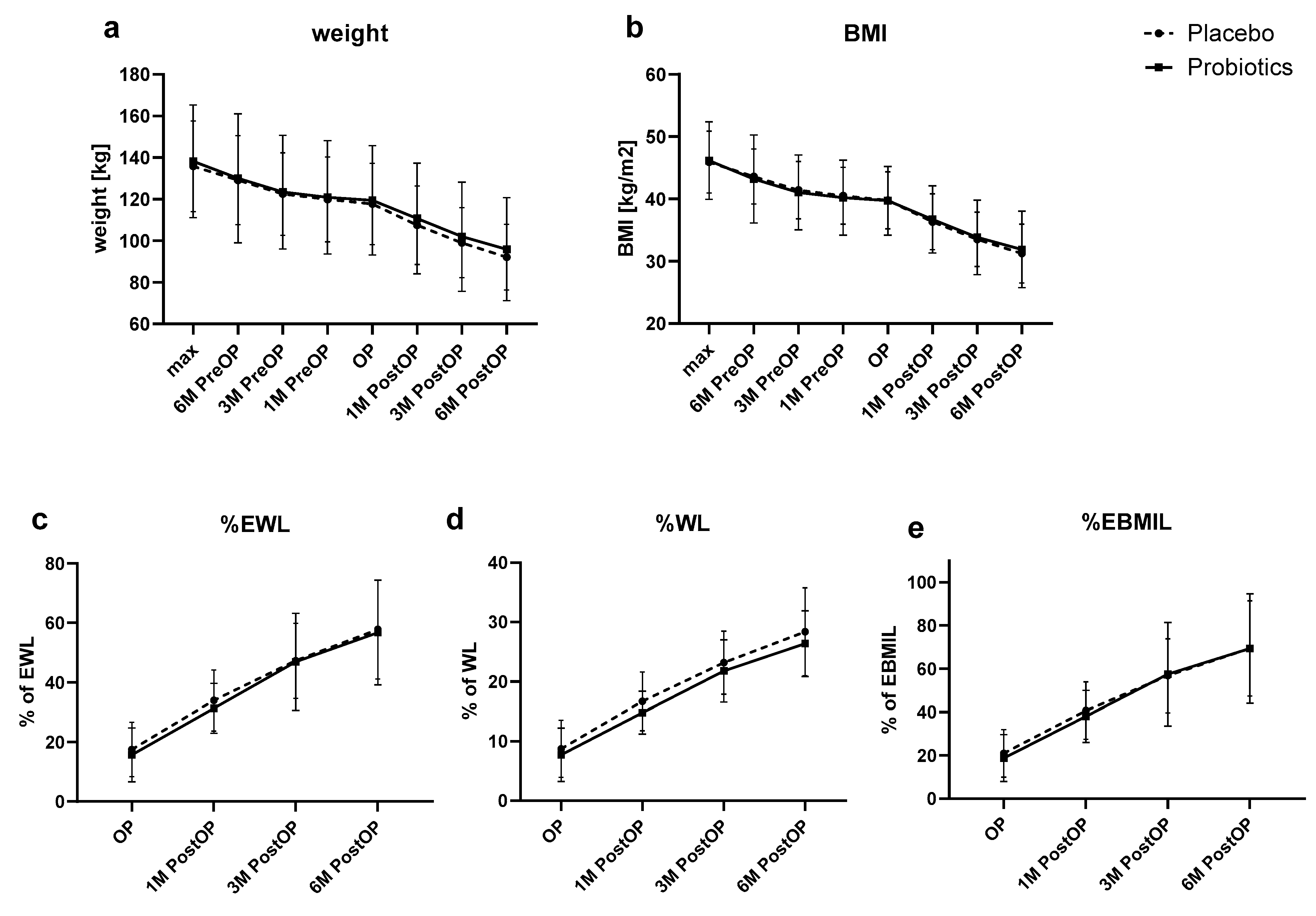
| Max | 135.9 ± 21.8 | 138.3 ± 27.1 | 0.749 | <0.001 | 0.612 |
| 6 M PreOP | 129.2 ± 21.4 | 130.1 ± 31 | |||
| 3 M PreOP–PRO | 122.5 ± 19.8 | 123.4 ± 27.4 | |||
| 1 M PreOP | 119.9 ± 20.4 | 120.9 ± 27.3 | |||
| OP | 117.7 ± 19.5 | 119.5 ± 26.3 | |||
| 1 M PostOP | 107.5 ± 18.9 | 110.8 ± 26.6 | |||
| 3 M PostOP | 99.1 ± 16.9 | 102 ± 26.3 | |||
| 6 M PostOP | 92.1 ± 15.8 | 96 ± 24.7 | |||
| BMI (kg/m2) | |||||
| Max | 45.9 ± 5 | 46.2 ± 6.2 | 0.966 | <0.001 | 0.582 |
| 6 M PreOP | 43.6 ± 4.4 | 43.2 ± 7.1 | |||
| 3 M PreOP–PRO | 41.4 ± 4.6 | 41.1 ± 6 | |||
| 1 M PreOP | 40.5 ± 4.6 | 40.2 ± 6 | |||
| OP | 39.8 ± 4.6 | 39.7 ± 5.5 | |||
| 1 M PostOP | 36.3 ± 4.5 | 36.7 ± 5.4 | |||
| 3 M PostOP | 33.5 ± 4.4 | 33.8 ± 6 | |||
| 6 M PostOP | 31.2 ± 4.7 | 31.9 ± 6.1 | |||
| %WL | |||||
| OP | 8.7 ± 4.8 | 7.7 ± 4.5 | 0.229 | <0.001 | 0.739 |
| 1 M PostOP | 16.7 ± 4.9 | 14.8 ± 3.6 | |||
| 3 M PostOP | 23.2 ± 5.3 | 21.8 ± 5.2 | |||
| 6 M PostOP | 30.4 ± 11.5 | 26.5 ± 8.8 | |||
| %EWL | |||||
| OP | 17.5 ± 9.1 | 15.7 ± 9.1 | 0.636 | <0.001 | 0.791 |
| 1 M PostOP | 33.9 ± 10.2 | 31.3 ± 8.4 | |||
| 3 M PostOP | 47.3 ± 12.6 | 46.9 ± 16.3 | |||
| 6 M PostOP | 57.8 ± 16.7 | 56.8 ± 17.6 | |||
| %EBMIL | |||||
| OP | 20.9 ± 11 | 18.8 ± 10.8 | 0.803 | <0.001 | 0.7 |
| 1 M PostOP | 40.7 ± 13.3 | 38 ± 12 | |||
| 3 M PostOP | 56.7 ± 17.1 | 57.4 ± 23.9 | |||
| 6 M PostOP | 72.6 ± 34.6 | 62 ± 40.4 | |||
| Baseline | 1 M PostOP | 3 M PostOP | 6 M PostOP | Between Subjects Effects (Group) | Within Subjects Effects (Time) | Within Subjects Effects (Time × Group) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo n = 26 | Probiotics n = 22 | Placebo n = 26 | Probiotics n = 22 | Placebo n = 26 | Probiotics n = 22 | Placebo n = 26 | Probiotics n = 22 | p-Value | p-Value | p-Value | |
| Vit. D (pg/mL) | 49.9 ± 15.1 | 52.5 ± 15.5 | 51.5 ± 12.6 | 58.7 ± 18.5 | 52.4 ± 15.5 | 63.5 ± 18.6 | 57.8 ± 21.3 | 60.1 ± 18.2 | 0.132 | 0.018 | 0.276 |
| Folic Acid (ng/mL) | 5.8 ± 1.6 | 7.2 ± 2.6 | 8.7 ± 3.2 | 8.7 ± 2.9 | 8.9 ± 3.7 | 8.6 ± 3.3 | 11.8 ± 8.3 | 8.8 ± 4.1 | 0.517 | 0.002 | 0.097 |
| Vit. B12 (pg/mL) | 349.8 ± 93.6 | 349.4 ± 113.6 | 483.2 ± 169.8 | 472.3 ± 147.4 | 455.4 ± 202 | 422.1 ± 182.1 | 411 ± 142.6 | 397.6 ± 163.1 | 0.694 | <0.001 | 0.866 |
| Iron (ug/dL) | 77.1 ± 30.8 | 82.5 ± 37.9 | 72.5 ± 20.9 | 72.4 ± 26.1 | 79.2 ± 25.5 | 86.7 ± 32.3 | 85.7 ± 27.1 | 92.8 ± 36.4 | 0.408 | 0.016 | 0.845 |
| Insulin (uU/mL) | 20.9 ± 14.9 | 22 ± 18.1 | 8.5 ± 3.8 | 13.5 ± 9.1 | 7.8 ± 3.4 | 9.3 ± 5.4 | 7.3 ± 2.4 | 9.3 ± 8 | 0.168 | <0.001 | 0.527 |
| LDH (U/L) | 192.5 ± 41.8 | 196.2 ± 32.7 | 179.5 ± 38.1 | 175.7 ± 34.2 | 160.9 ± 46.8 | 176.7 ± 44.6 | 160.7 ± 33.6 | 163.2 ± 36.1 | 0.618 | <0.001 | 0.35 |
| ALT (U/L) | 37.6 ± 18.3 | 34.7 ± 16.8 | 35.6 ± 18.7 | 44 ± 25.5 | 24.1 ± 23.1 | 27.5 ± 14.5 | 17.9 ± 7.4 | 20 ± 8.8 | 0.421 | <0.001 | 0.34 |
| AST (U/L) | 24.8 ± 10.9 | 24.2 ± 10.6 | 21.3 ± 7.5 | 24.9 ± 8.8 | 22.2 ± 24.5 | 25.2 ± 20.7 | 17.7 ± 5.6 | 17.8 ± 6.7 | 0.536 | 0.072 | 0.795 |
| GGT (Ul) | 46.4 ± 31.2 | 36.8 ± 18.6 | 28.3 ± 21.1 | 28.2 ± 15.4 | 25.5 ± 18 | 28.7 ± 32 | 24.5 ± 23.3 | 34.3 ± 54.3 | 0.907 | 0.006 | 0.132 |
| ALP (U/L) | 84.6 ± 26.1 | 75 ± 18.4 | 72.1 ± 22.2 | 69.6 ± 15.9 | 74 ± 24.2 | 77.6 ± 22.7 | 79.7 ± 25.2 | 82.7 ± 25.5 | 0.811 | 0.001 | 0.065 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 147.8 ± 67 | 140.5 ± 70.1 | 111.6 ± 52 | 110.6 ± 29.8 | 105.1 ± 56.1 | 99.2 ± 27.4 | 99.6 ± 41.3 | 99.1 ± 39.9 | 0.756 | <0.001 | 0.901 |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 43.5 ± 8.6 | 47.1 ± 13.1 | 35.8 ± 6.2 | 39.2 ± 8.1 | 40.8 ± 5.6 | 45.3 ± 8.7 | 47.5 ± 6.9 | 51.9 ± 10.3 | 0.061 | <0.001 | 0.906 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 117.8 ± 39.3 | 115.1 ± 27.8 | 109.2 ± 40.3 | 105.6 ± 29 | 112.5 ± 40.4 | 114.5 ± 29.3 | 112.5 ± 34.1 | 117.7 ± 36 | 0.981 | 0.194 | 0.697 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 187.7 ± 45.3 | 188.5 ± 34.9 | 160.7 ± 41.9 | 162.7 ± 34.6 | 168.6 ± 47.9 | 173.3 ± 33.4 | 169.5 ± 43.1 | 182 ± 41 | 0.613 | <0.001 | 0.665 |
| HbA1c% | 5.7 ± 0.7 | 6.1 ± 1.3 | 5.2 ± 0.5 | 5.4 ± 0.8 | 5.3 ± 0.4 | 5.3 ± 0.7 | 5.3 ± 0.5 | 5.5 ± 1.1 | 0.301 | <0.001 | 0.5 |
| HbA1c (mmol/mol) | 39.2 ± 7.2 | 42.7 ± 14.4 | 33.2 ± 4.8 | 36 ± 9.3 | 34 ± 4.7 | 34.5 ± 8.2 | 34.3 ± 4.9 | 36.3 ± 11.5 | 0.293 | <0.001 | 0.47 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 102.3 ± 16.4 | 112.9 ± 41.3 | 90.8 ± 8.1 | 98.9 ± 13.5 | 87.9 ± 9.1 | 89.2 ± 8.1 | 89.2 ± 11.2 | 90.6 ± 11.9 | 0.098 | <0.001 | 0.341 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 13.8 ± 1.5 | 14.2 ± 1.8 | 13.6 ± 1.2 | 14.1 ± 1.3 | 13.8 ± 1.5 | 14.2 ± 1.2 | 13.7 ± 1.4 | 14.2 ± 1.3 | 0.271 | 0.726 | 0.907 |
| HOMA-IR | 5.6 ± 5.5 | 6.4 ± 6.4 | 2 ± 1 | 3.5 ± 2.7 | 1.7 ± 0.9 | 2.1 ± 1.4 | 1.6 ± 0.6 | 2.2 ± 2.2 | 0.167 | <0.001 | 0.607 |
| Clavien–Dindo Grade | Placebo n (%) | Probiotics n (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| all | 2 (7.7) | 3 (13.6) | 0.649 |
| I | 0 | 1 (4.5) | 0.458 |
| II | 2 (7.7) | 0 | 0.493 |
| IIIa | 0 | 1 (4.5) | 0.458 |
| IIIb | 0 | 1 (4.5) | 0.458 |
| IVa | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| IVb | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| V | 0 | 0 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Potrykus, M.; Czaja-Stolc, S.; Stankiewicz, M.; Szymański, M.; Łoniewski, I.; Kaska, Ł.; Proczko-Stepaniak, M. Preoperative Multistrain Probiotic Supplementation Does Not Affect Body Weight Changes or Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Bariatrics: Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2055. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16132055
Potrykus M, Czaja-Stolc S, Stankiewicz M, Szymański M, Łoniewski I, Kaska Ł, Proczko-Stepaniak M. Preoperative Multistrain Probiotic Supplementation Does Not Affect Body Weight Changes or Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Bariatrics: Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Nutrients. 2024; 16(13):2055. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16132055
Chicago/Turabian StylePotrykus, Marta, Sylwia Czaja-Stolc, Marta Stankiewicz, Michał Szymański, Igor Łoniewski, Łukasz Kaska, and Monika Proczko-Stepaniak. 2024. "Preoperative Multistrain Probiotic Supplementation Does Not Affect Body Weight Changes or Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Bariatrics: Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial" Nutrients 16, no. 13: 2055. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16132055
APA StylePotrykus, M., Czaja-Stolc, S., Stankiewicz, M., Szymański, M., Łoniewski, I., Kaska, Ł., & Proczko-Stepaniak, M. (2024). Preoperative Multistrain Probiotic Supplementation Does Not Affect Body Weight Changes or Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Bariatrics: Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Nutrients, 16(13), 2055. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16132055









